Synchronization of Fractional-Order Reaction–Diffusion Neural Networks via ETILC
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Unlike the reference [16], conventional ILC for RDNN which updates controllers at all sampling points, our ETILC adds a sampling-based event-triggering condition only updating when error energy fails to decay, reducing controller updates while ensuring synchronization. ETILC precisely controls the update frequency of ILC inputs through triggering conditions, eliminating the need for additional redundant update operations. In essence, it shares the same design goal as ETC in that both achieve efficient saving of system resources and reduction in energy consumption by decreasing the amount of data transmission and the number of controller updates during the iteration process.
- Different from [23] (ETILC for integer-order systems), our ETILC combines a Lyapunov-like function with the actuator–sensor network and integrates FORDNN’s fractional diffusion terms into an event-triggering condition, adapting to non-local spatial–temporal dynamics.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Fractional-Order Calculus
2.2. Graph Theory
2.3. FORDNN Model
2.4. Synchronization of FORDNN with Iteration
3. Main Result
3.1. Event-Triggering Condition
3.2. Controller Design
3.3. Convergence Analysis
3.3.1. Initial State Fixed FORDNN Model
3.3.2. Initial State Offset FORDNN Model
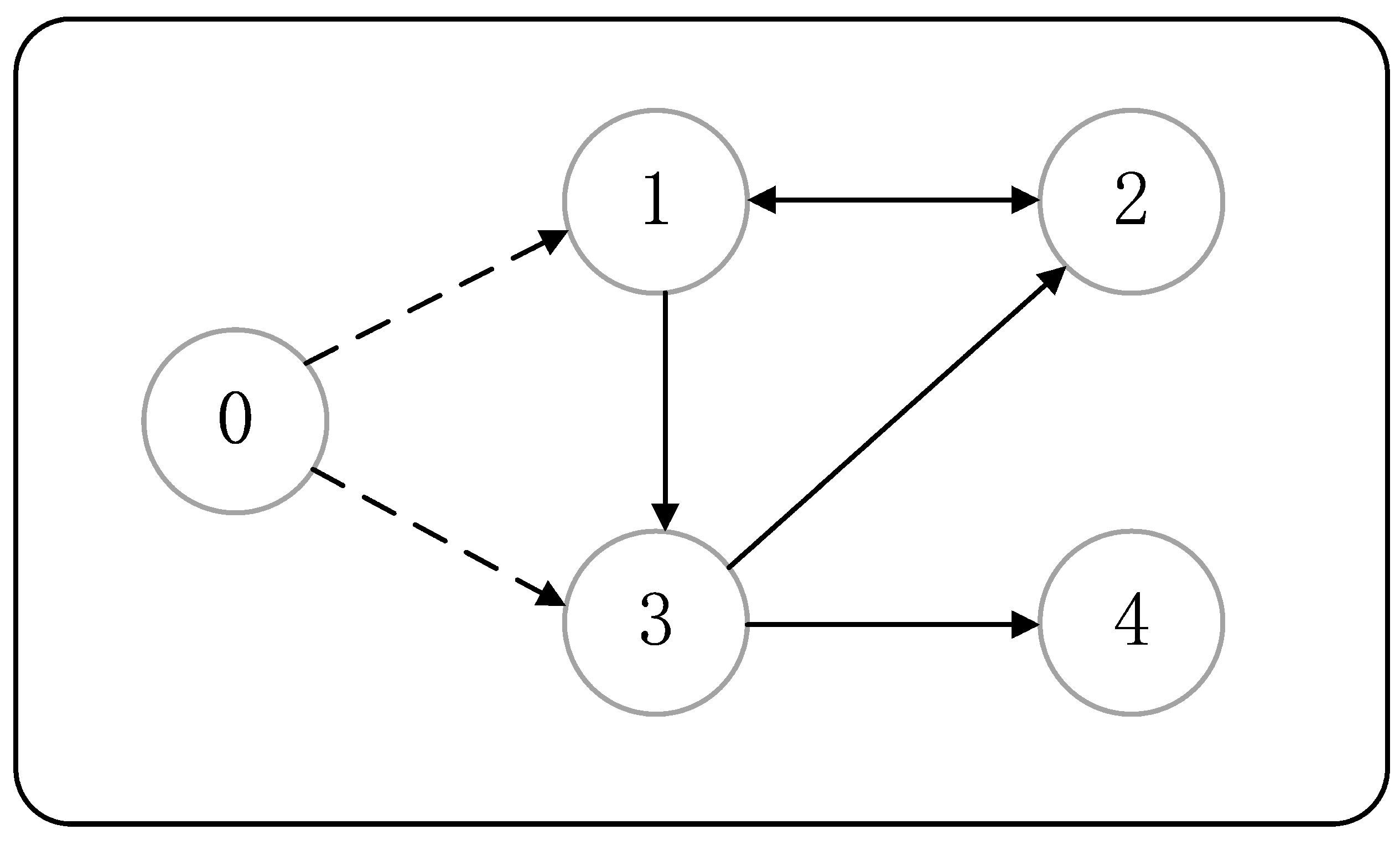
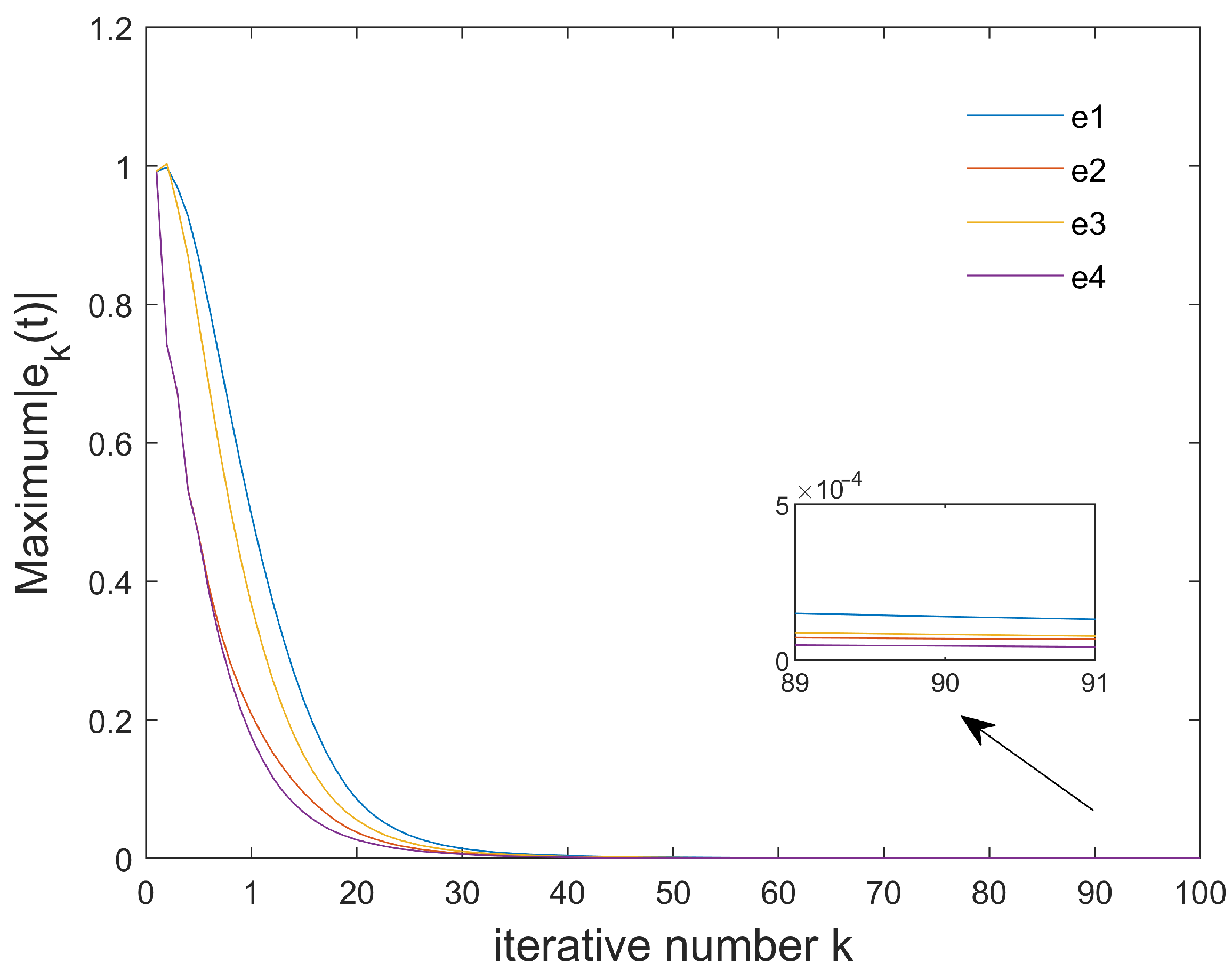
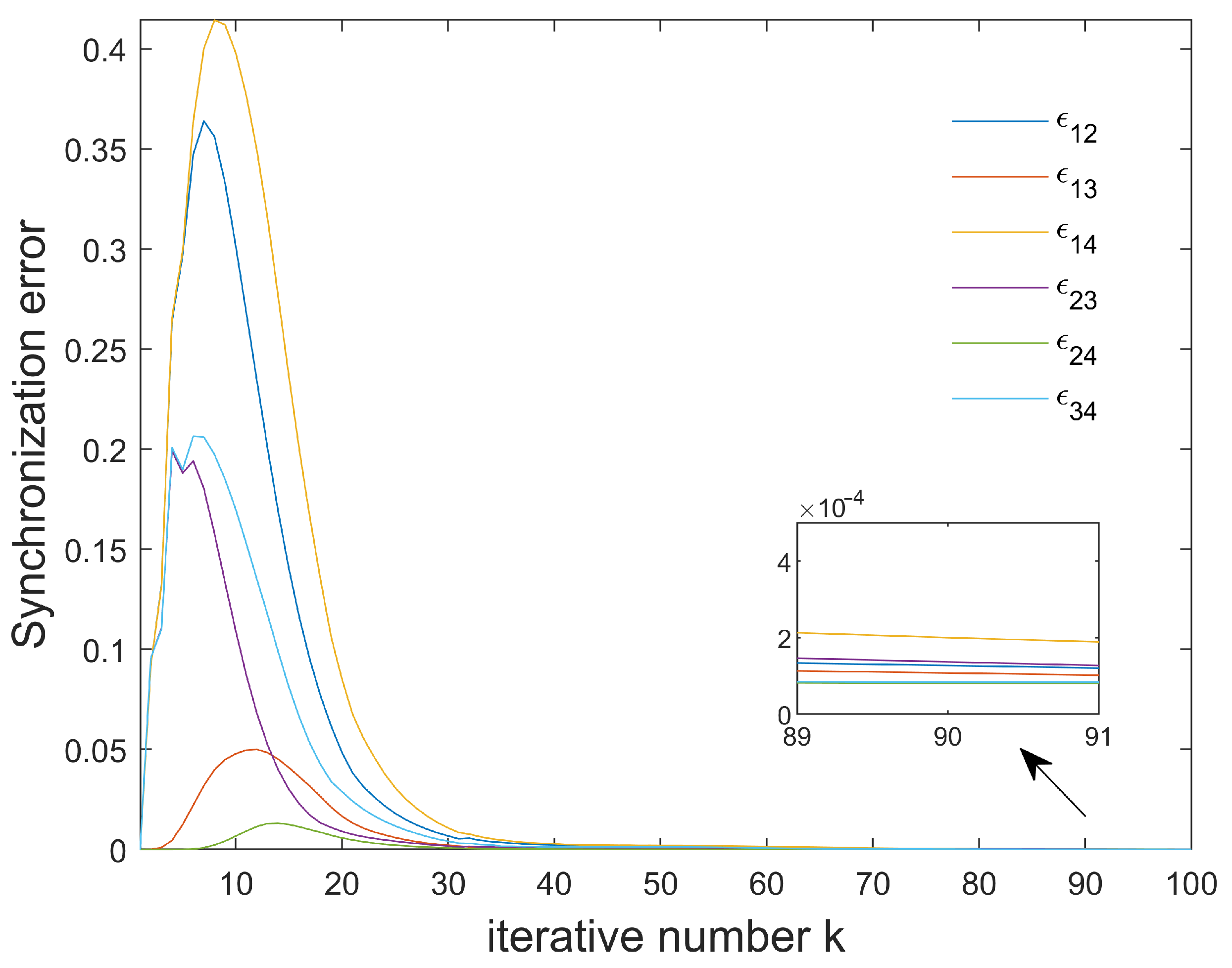
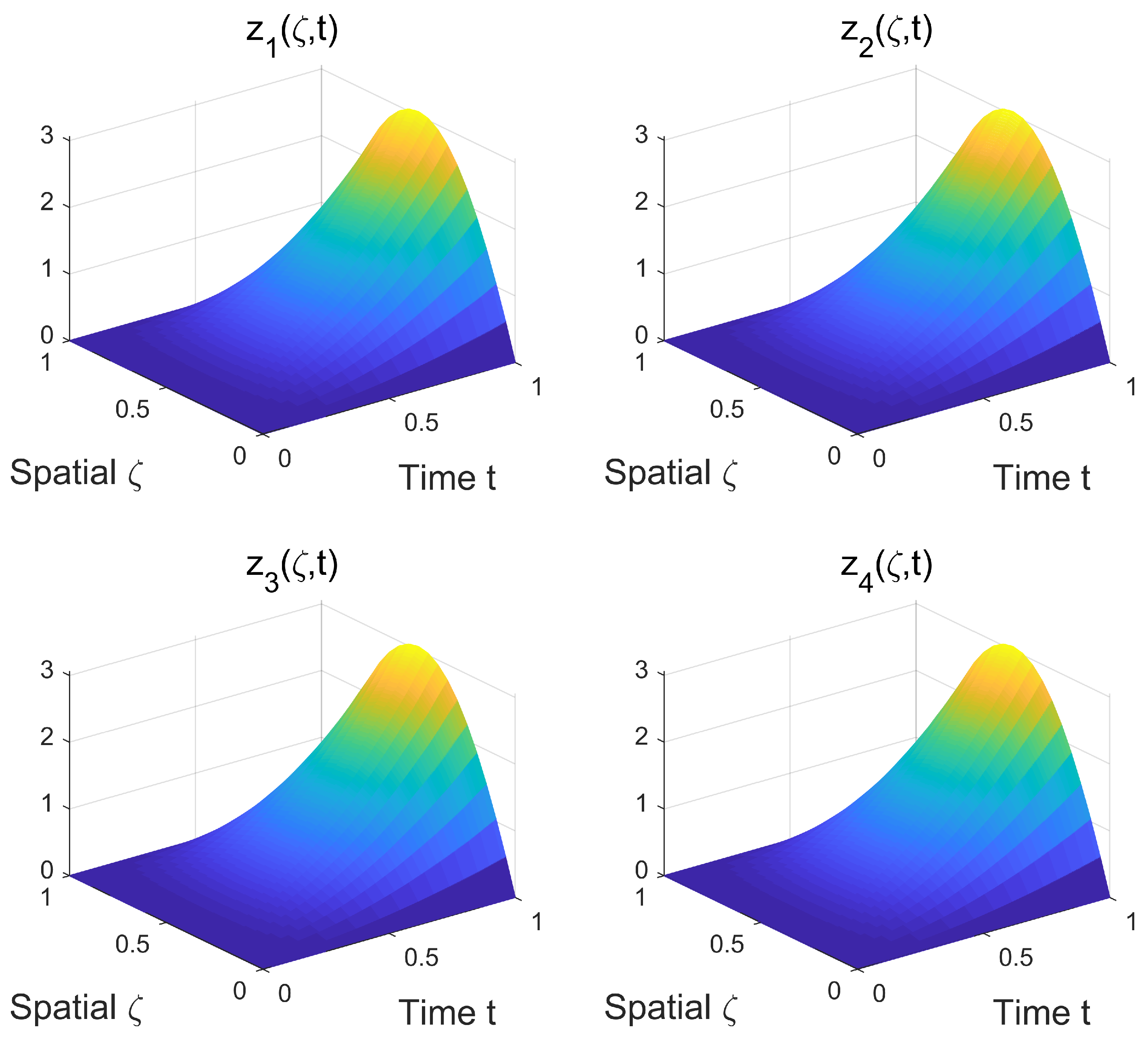
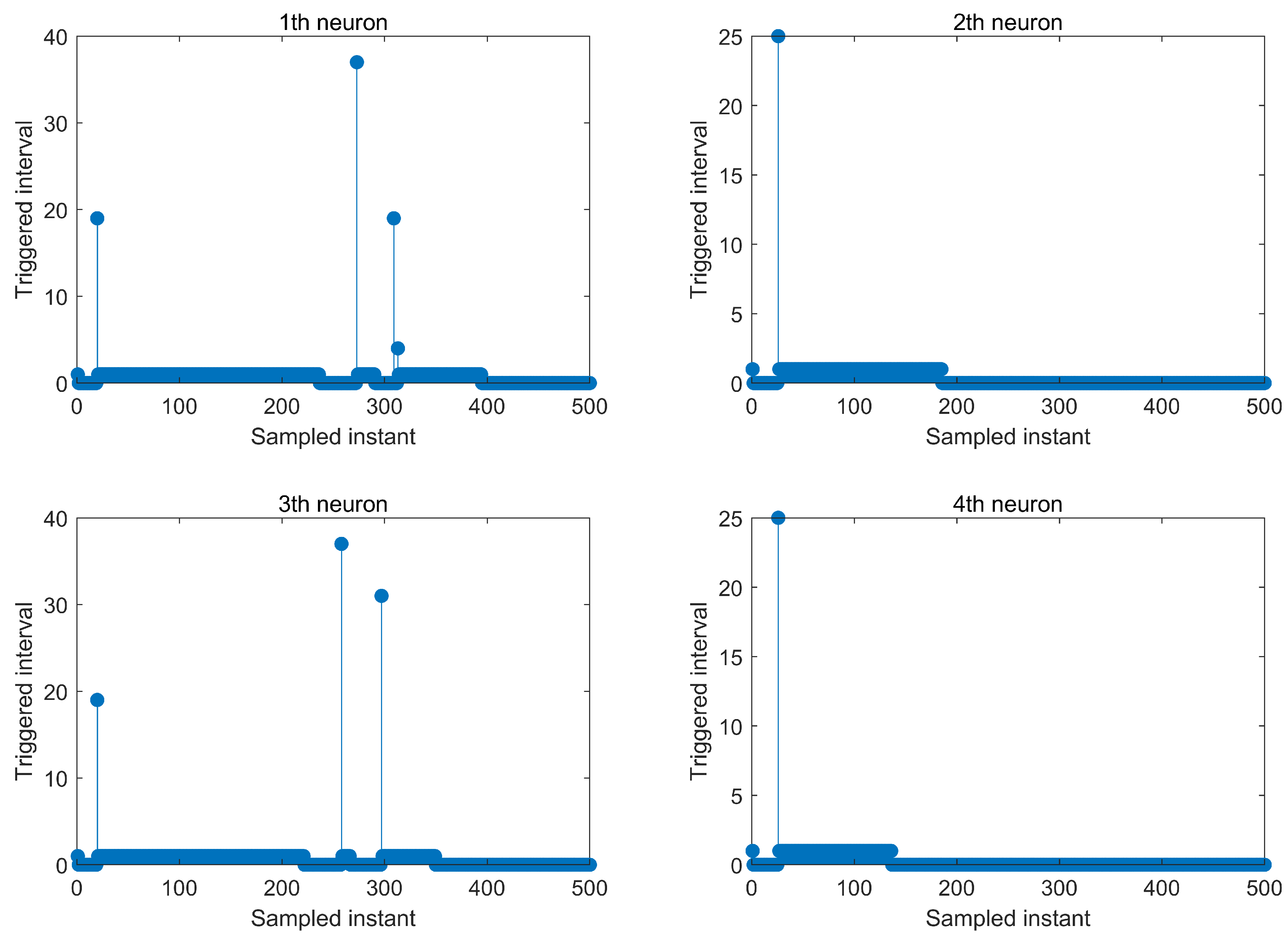
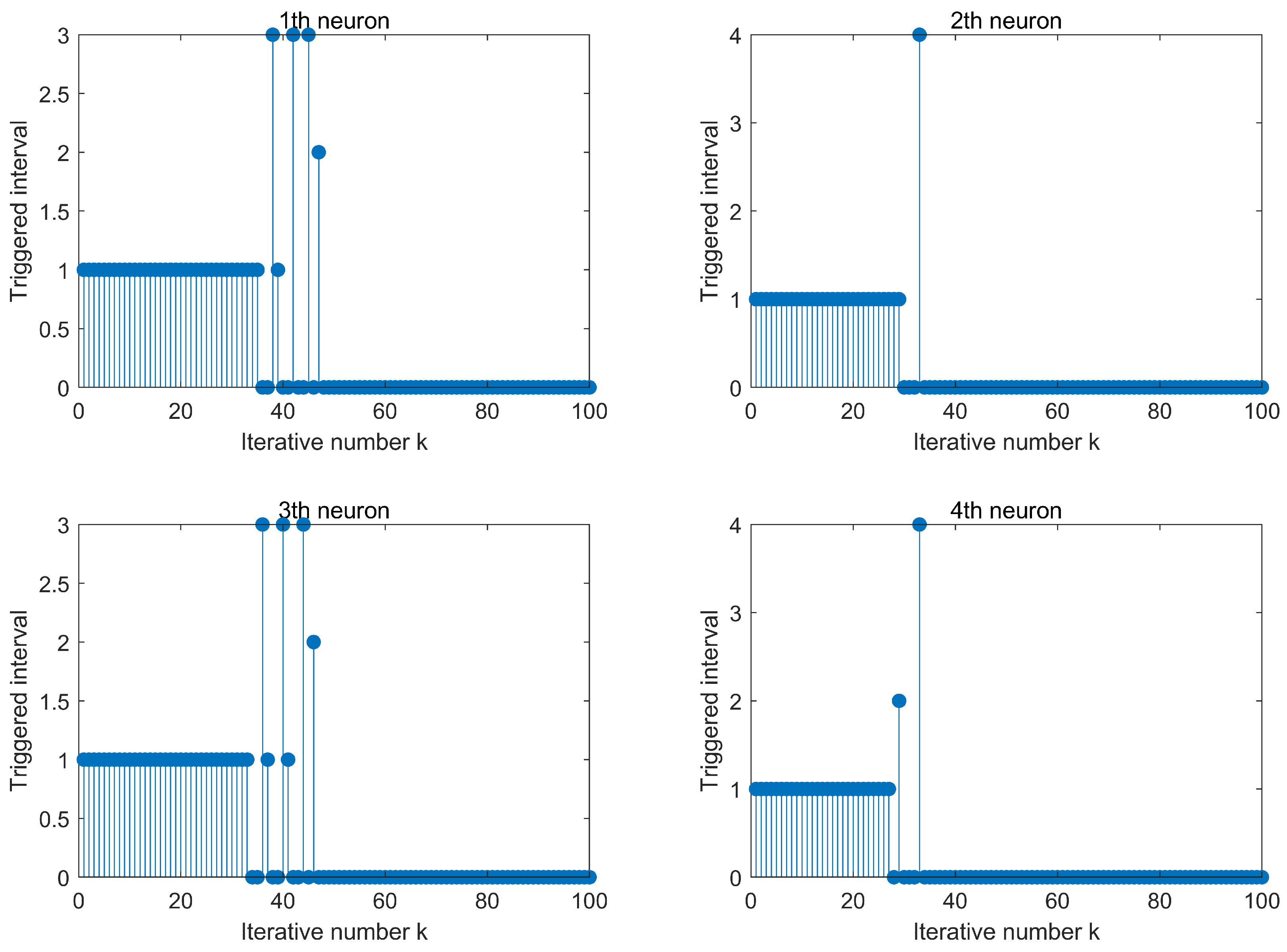
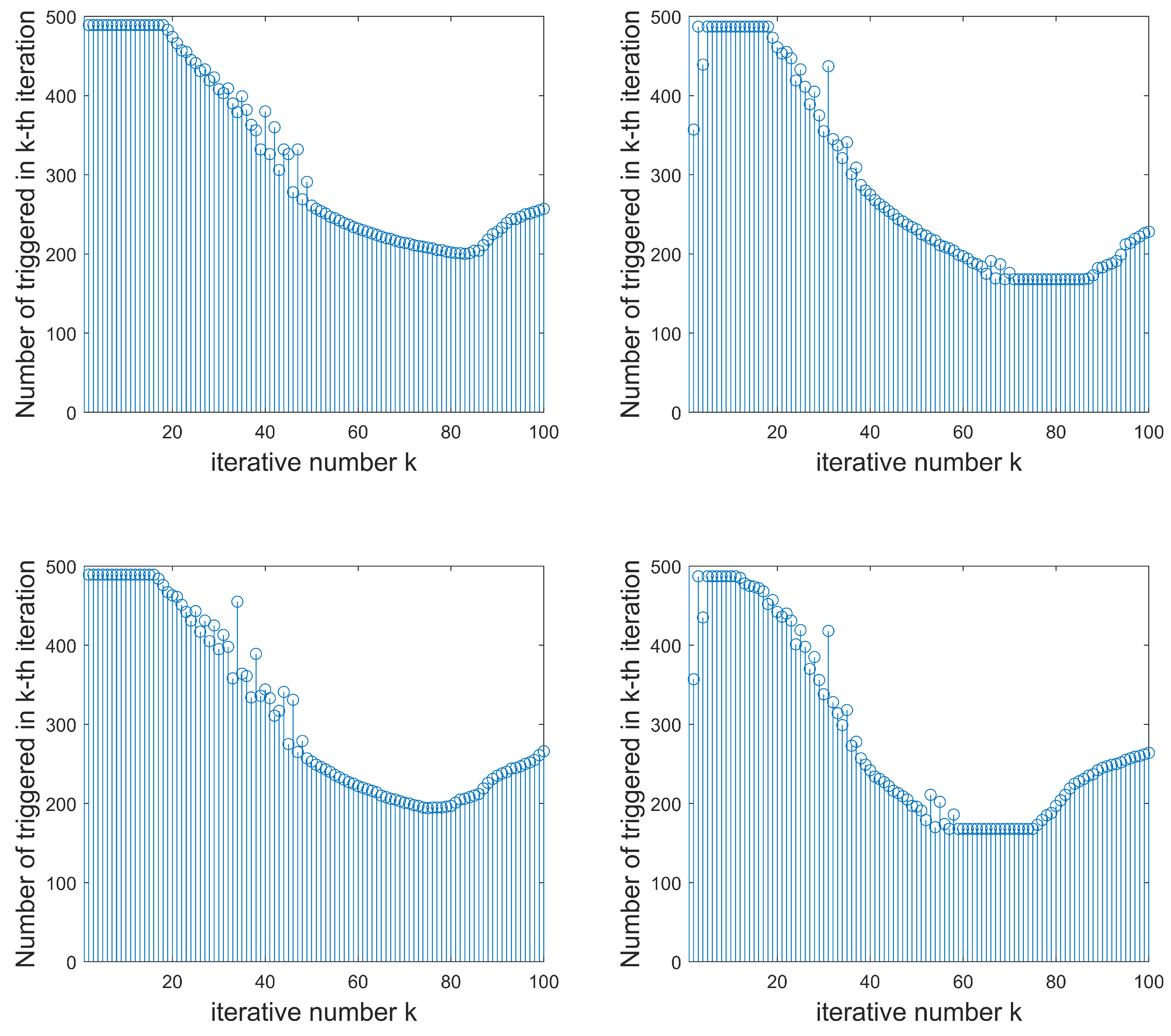
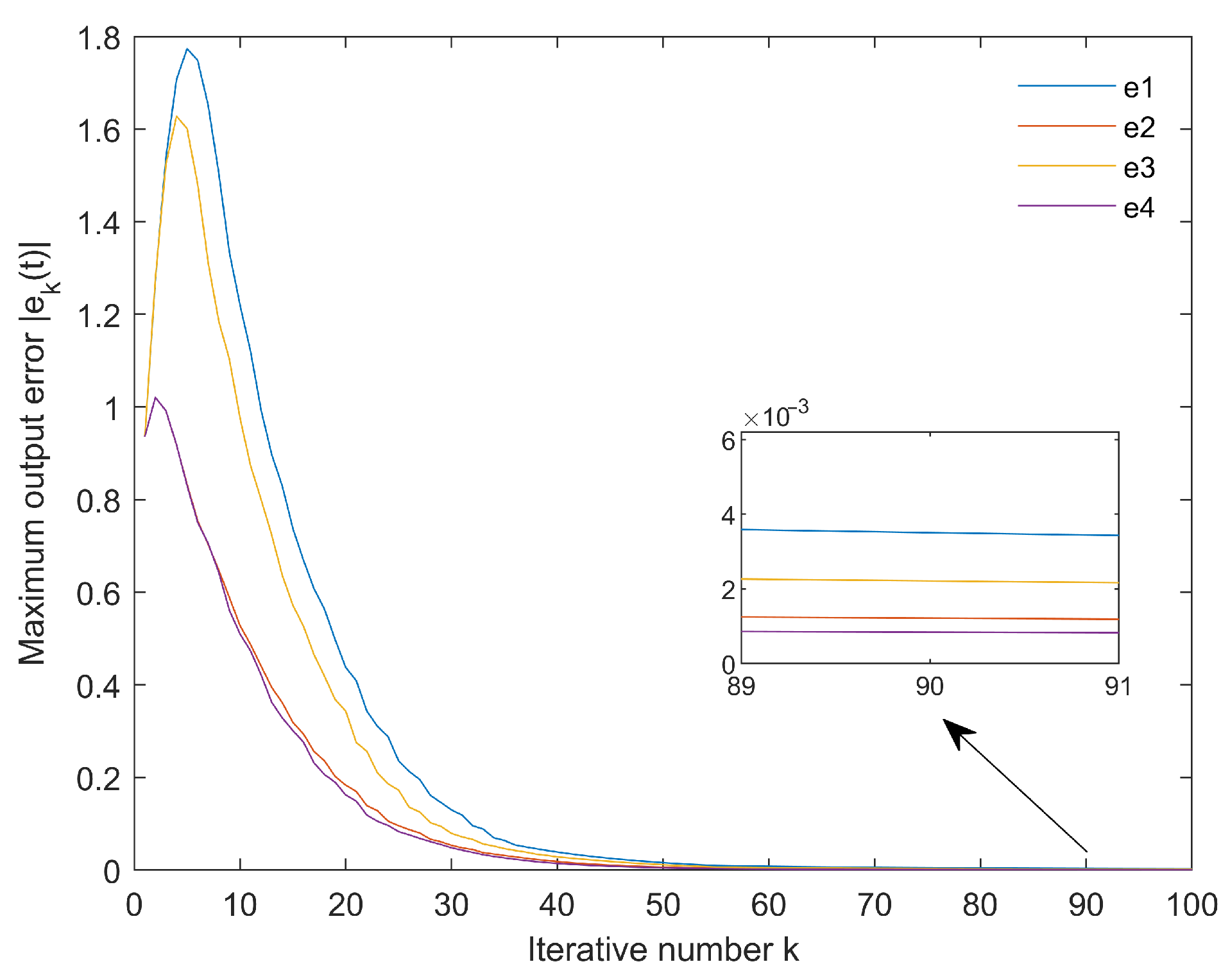
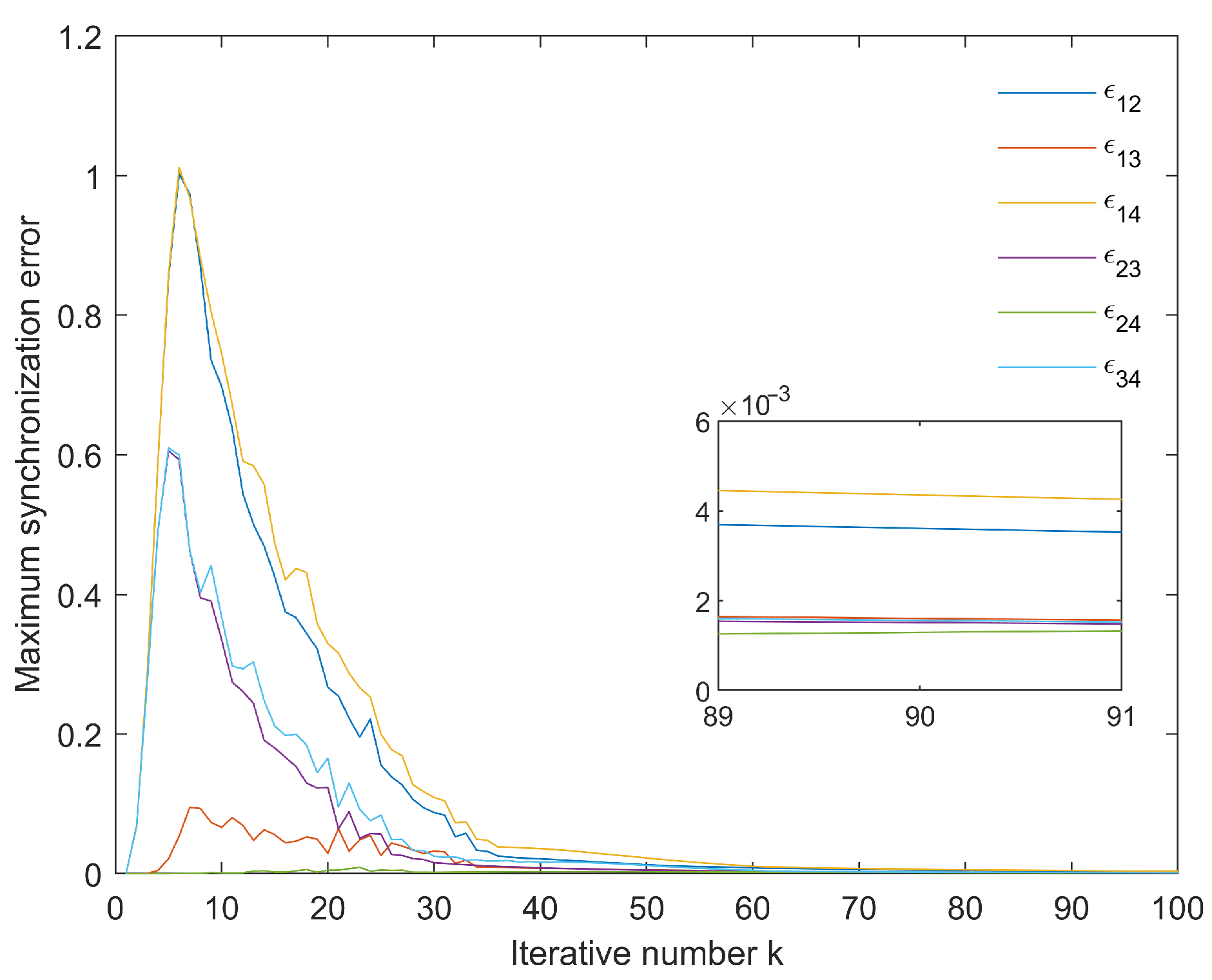
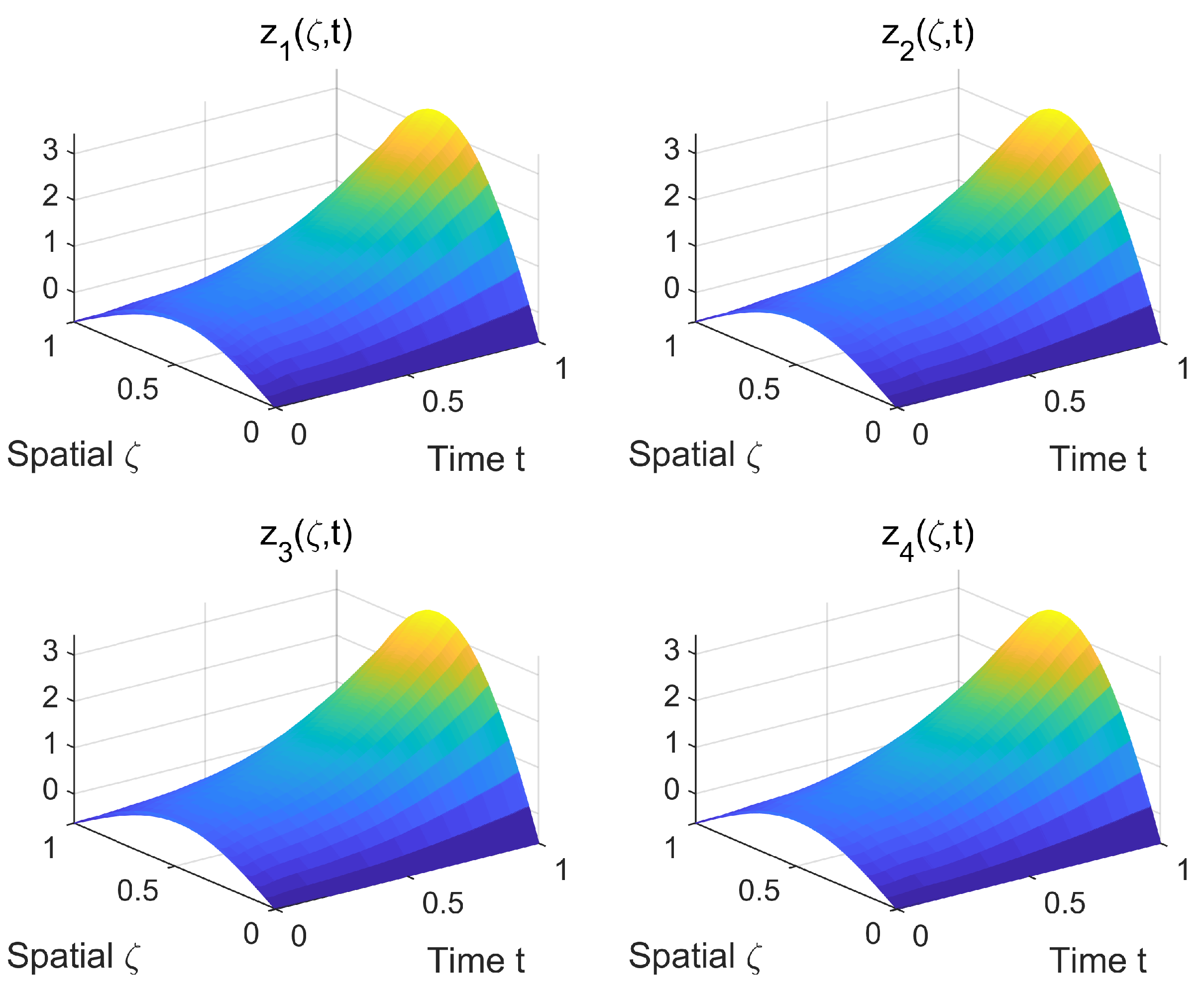
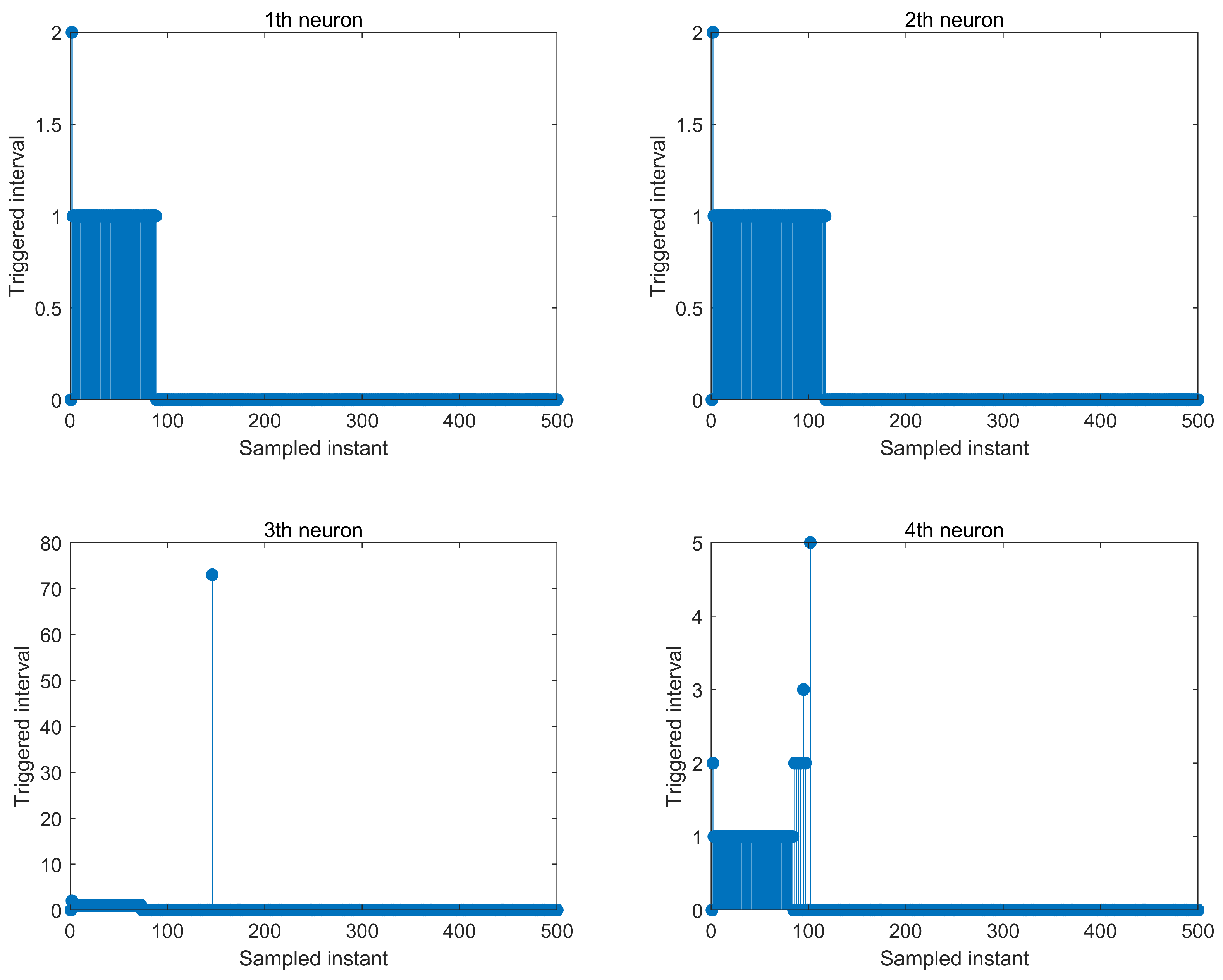
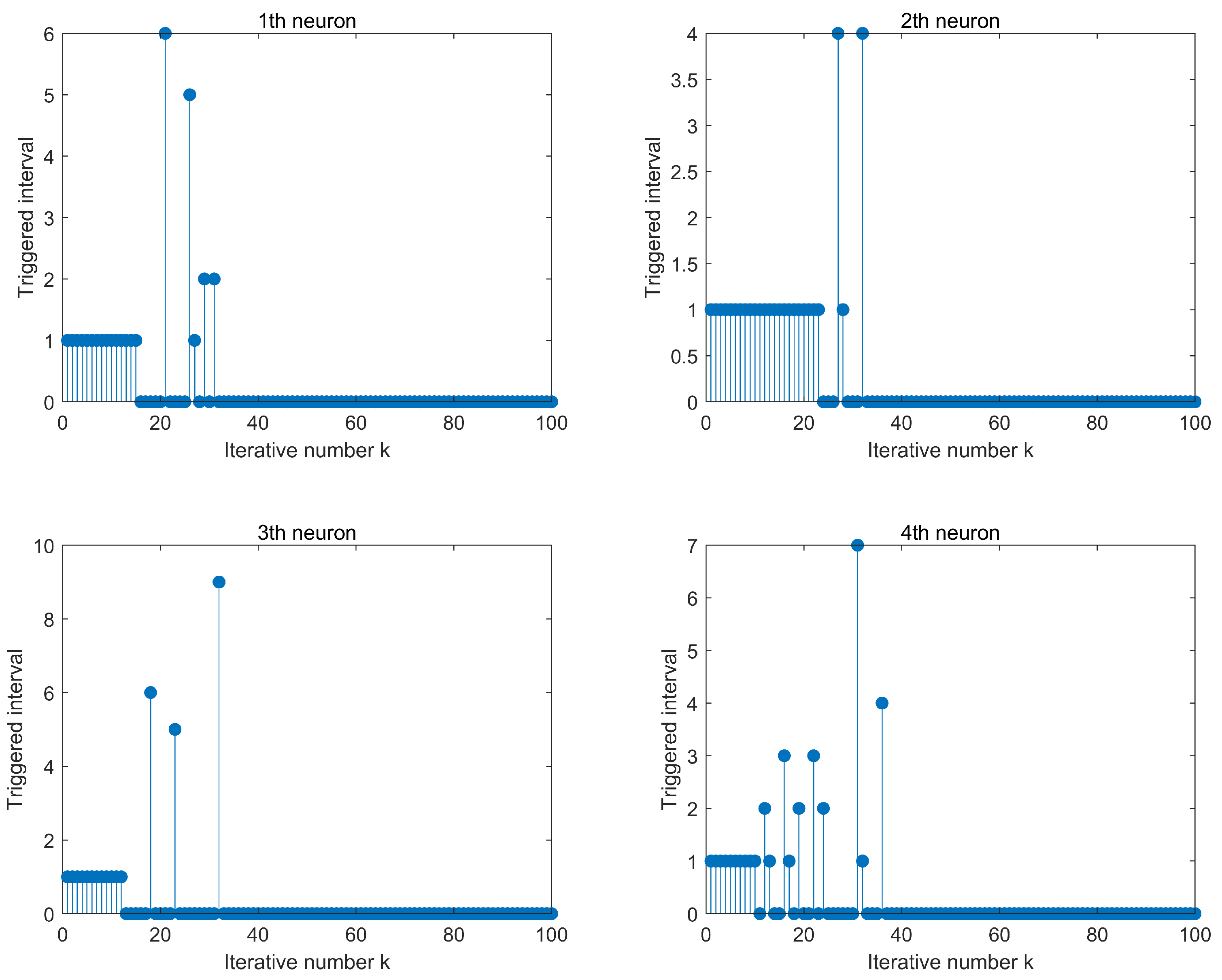
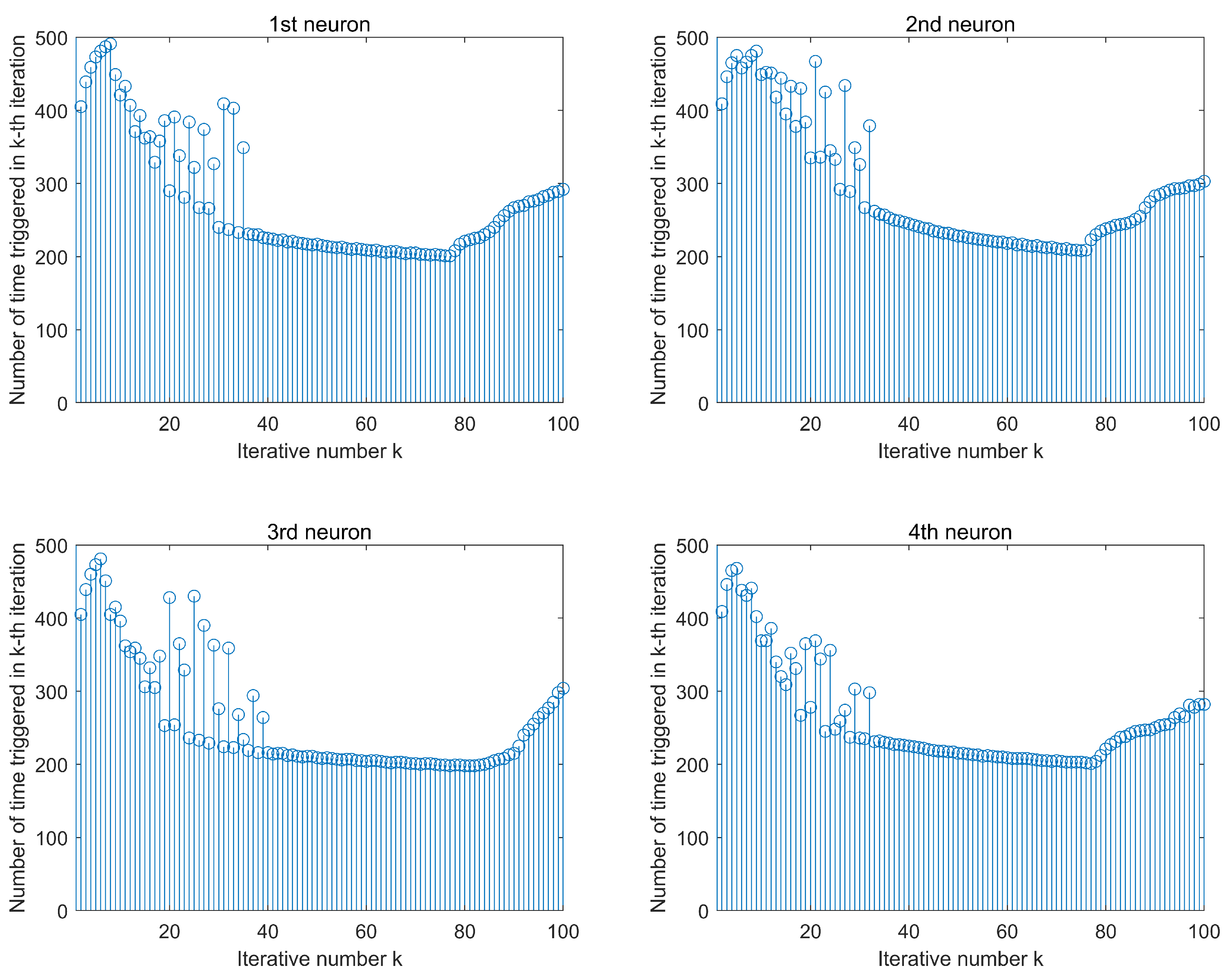
4. Simulations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hopfield, J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Jahan, S.; Nisar, K. Solving fractional bagley- torvik equation by fractional order fibonacci wavelet arising in fluid mechanics. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqhtani, M.; Owolabi, K.; Saad, K. Efficient numerical techniques for computing the riesz fractional-order reaction-diffusion models arising in biology. Chaos Solitions Fractals 2022, 161, 112394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Aouiti, C.; Liu, Z. Bifurcation caused by delay in a fractional-order coupled oremonator model in chemistry. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2022, 88, 371–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Upadhyay, R.K. Diverse neuronal responses of a fractional-order Izhikevich model: Journey from chattering to fast spiking. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 91, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrama, T.R.; Gade, P.M. Fractional-order neuronal maps: Dynamics, control and stability analysis. Pramana 2024, 98, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, F.; Wils, S.; De Schutter, E.; Augustine, G.J. Anomalous diffusion in Purkinje cell dendrites caused by spines. Neuron 2006, 52, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M. Novel intermittent pinning control beyond the semigroup framework for fractional-order delayed inertial memristive neural networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2026, 202, 117568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, H.; Hu, C. Exponential synchronization of fractional-order reaction-diffusion coupled neural networks with hybrid delay-dependent impulses. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 3167–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Ali, M.; Karthikeyan, R. Adaptive strategies and its application in the mittag-leffler synchronization of delayed fractional-order complex-valued reaction-diffusion neural networks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 3294–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamova, I.; Stamov, G. Mittag-leffler synchronization of fractional neural networks with time-varying delays and reaction-diffusion terms using impulsive and linear controllers. Neural Netw. 2017, 96, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, B. Pinning synchronization of spatial diffusion coupled reaction-diffusion neural networks with and without multiple time-varying delays. Neurocomputing 2017, 227, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, W.; Tang, Z. Quasi-synchronization of heterogeneous neural networks with hybrid time delays via sampled-data saturating impulsive control. Chaos Solitions Fractals 2024, 182, 114788. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xing, K.; Li, J. Adaptive synchronization of delayed reaction-diffusion fcnns via learning control approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 28, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, F.; Li, W. Exponential synchronization of fractional-order multilayer coupled neural networks with reaction-diffusion terms via intermittent control. Neural Netw. 2021, 33, 16019–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y. Iterative learning control-based tracking synchronization for linearly coupled reaction-diffusion neural networks with time delay and iteration-varying switching topology. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 3822–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Masayoshi, T. Neural-network-based iterative learning control for multiple tasks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4178–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Huang, X.; Meng, B. Neural network-based iterative learning control for trajectory tracking of unknown SISO nonlinear systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 232, 120863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Event-triggered bipartite synchronization of coupled multi-order fractional neural networks. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 255, 109733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, T. Synchronization of switched neural networks with communication delays via the event-triggered control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 2334–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, J.; Kashkynbaye, A.; Cai, S. Adaptive dynamic event-triggered cluster synchronization in an array of coupled neural networks subject to cyber-attacks. Neurocomputing 2022, 511, 380–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Lin, N. Event-triggered learning consensus of networked heterogeneous nonlinear agents with switching topologies. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 385, 3803–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Chi, R.; Huang, B.; Hou, Z. Event-triggered nonlinear iterative learning control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 5118–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Chi, R.; Huang, B. Event-triggered ILC for optimal consensus at specified data points of heterogeneous networked agents with switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 8951–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Dai, X.; Zhou, R. Sampling-based event-triggered iterative learning control in nonlinear hyperbolic distributed parameter systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Sun, X.; Man, J. Synchronization of fractional-order spatiotemproal complex-valued neural networks in finite-time interval and its application. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 8207–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Academie Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte-Mermoud, M.; Aguila-Camacho, N.; Gallegos, J. Using general quadratic Lyapunov function to prove Lyapunov uniform stability for fractional order systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 22, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Gao, J.; Ding, Y. A generalized gronwall inequality and its application to a fractional differential equation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2007, 328, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Cui, B.; Wu, W. Event-driven observer-based control for distributed parameter systems using mobile sensor and actuator. Comput. Math. Appl. 2016, 72, 2854–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, S. Synchronization of Fractional-Order Reaction–Diffusion Neural Networks via ETILC. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120764
Dai X, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, Tian S. Synchronization of Fractional-Order Reaction–Diffusion Neural Networks via ETILC. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(12):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120764
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Xisheng, Yehui Liu, Yanxue Wang, Jianxiang Zhang, and Senping Tian. 2025. "Synchronization of Fractional-Order Reaction–Diffusion Neural Networks via ETILC" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 12: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120764
APA StyleDai, X., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., & Tian, S. (2025). Synchronization of Fractional-Order Reaction–Diffusion Neural Networks via ETILC. Fractal and Fractional, 9(12), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120764




