Multi-Scale Damage Evolution of Soil-Rock Mixtures Under Freeze–Thaw Cycles: Revealed by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Testing and Fractal Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
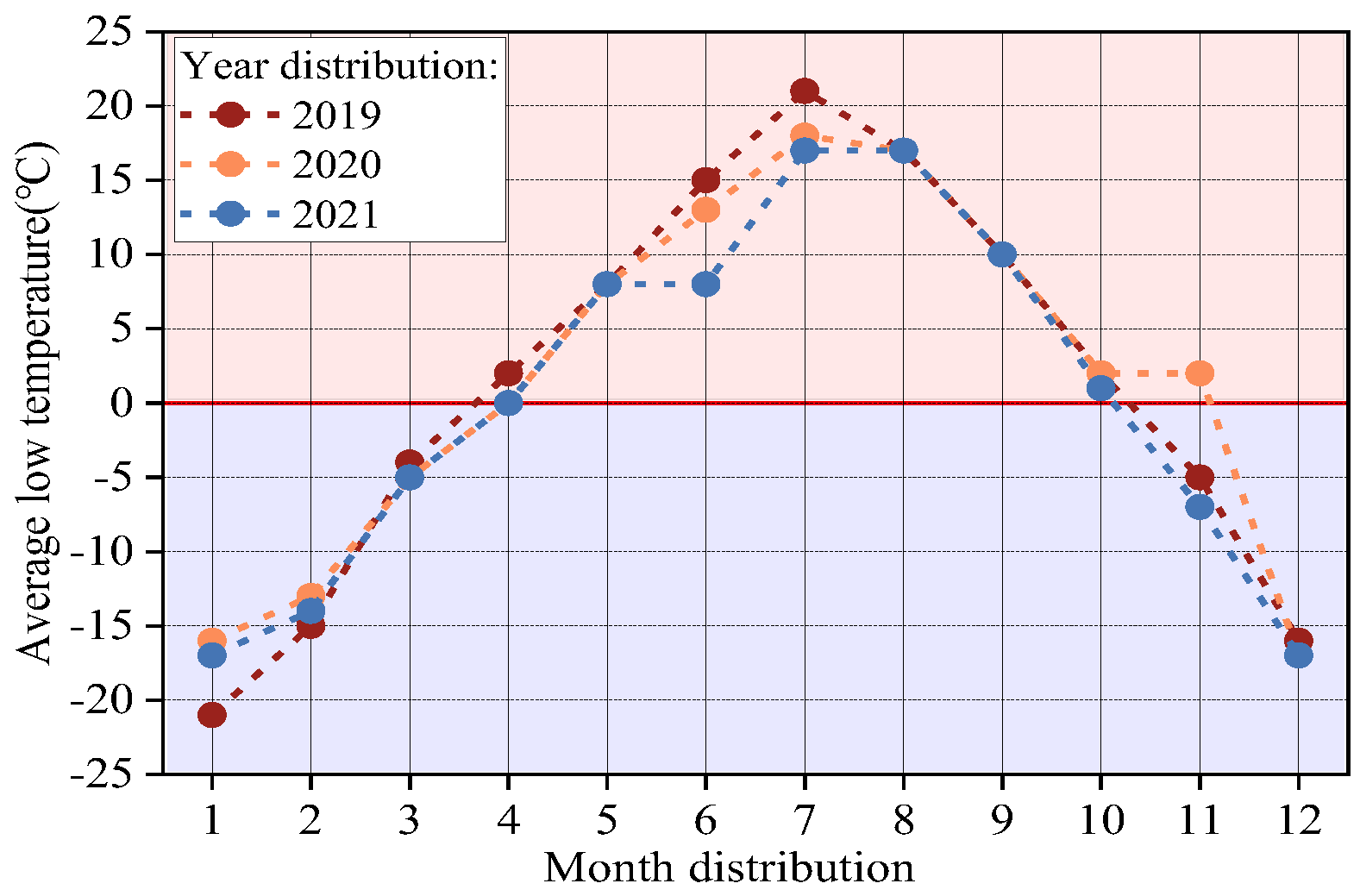
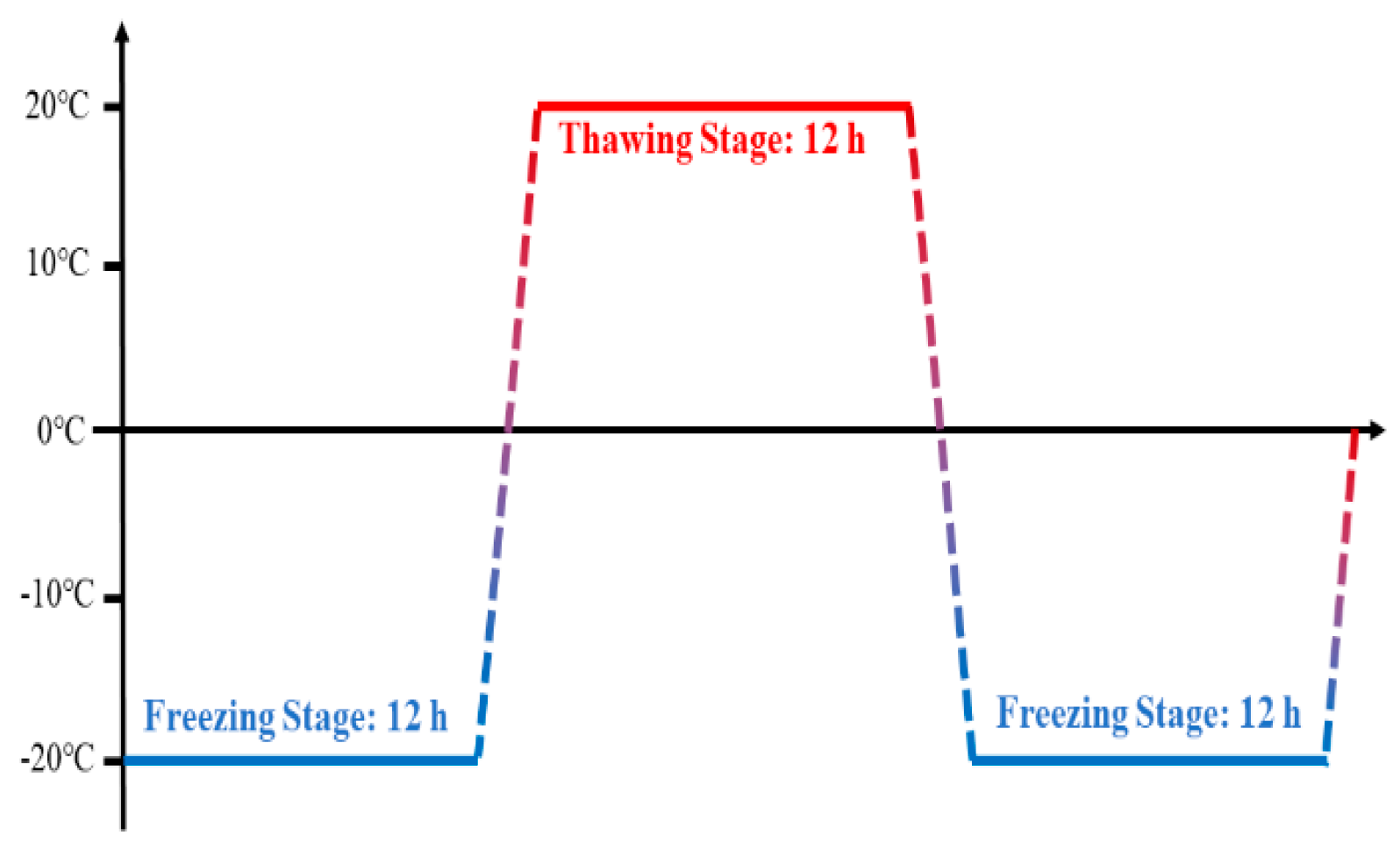
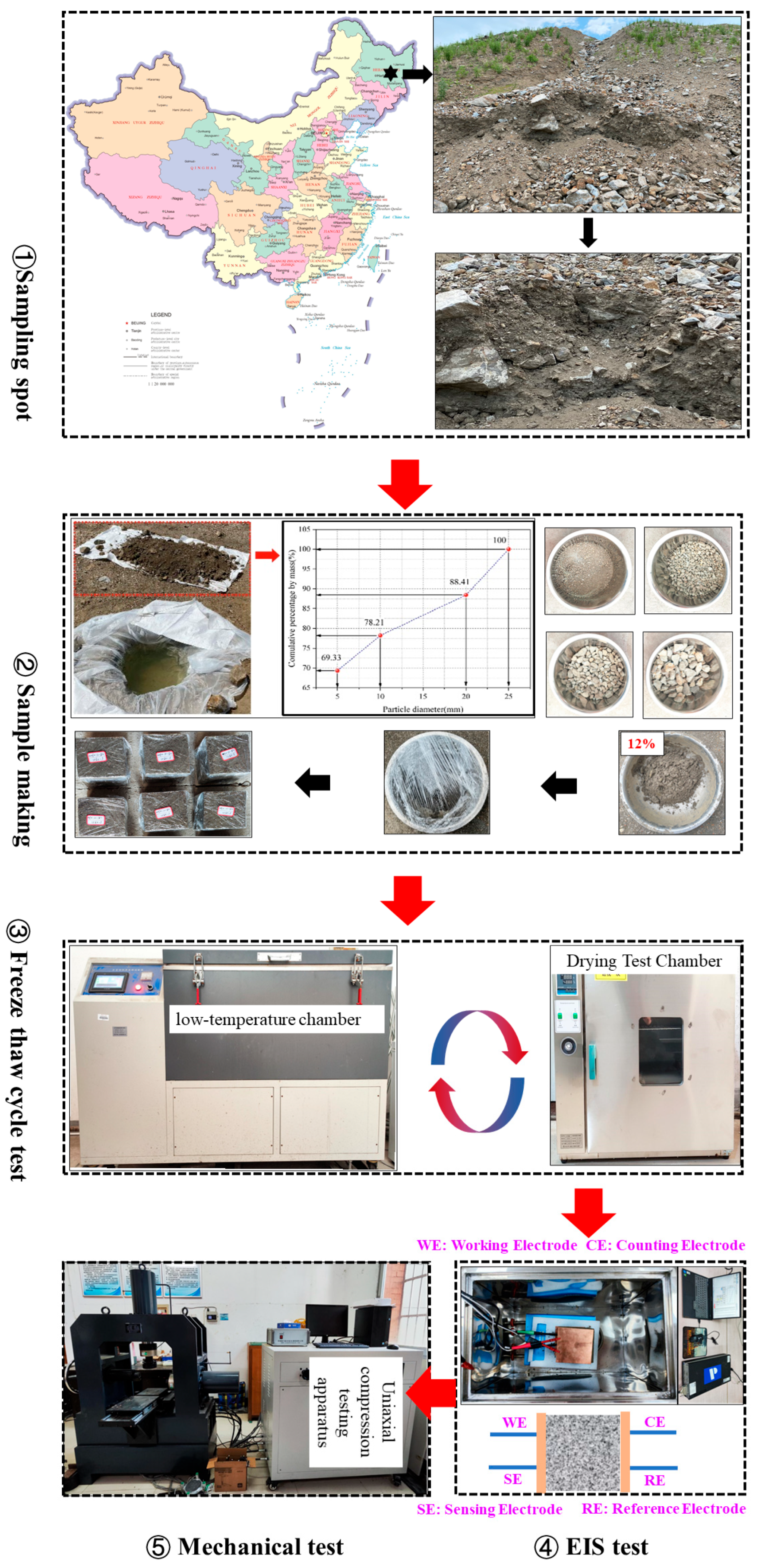
2.1. Sample Preparation and Experimental Testing
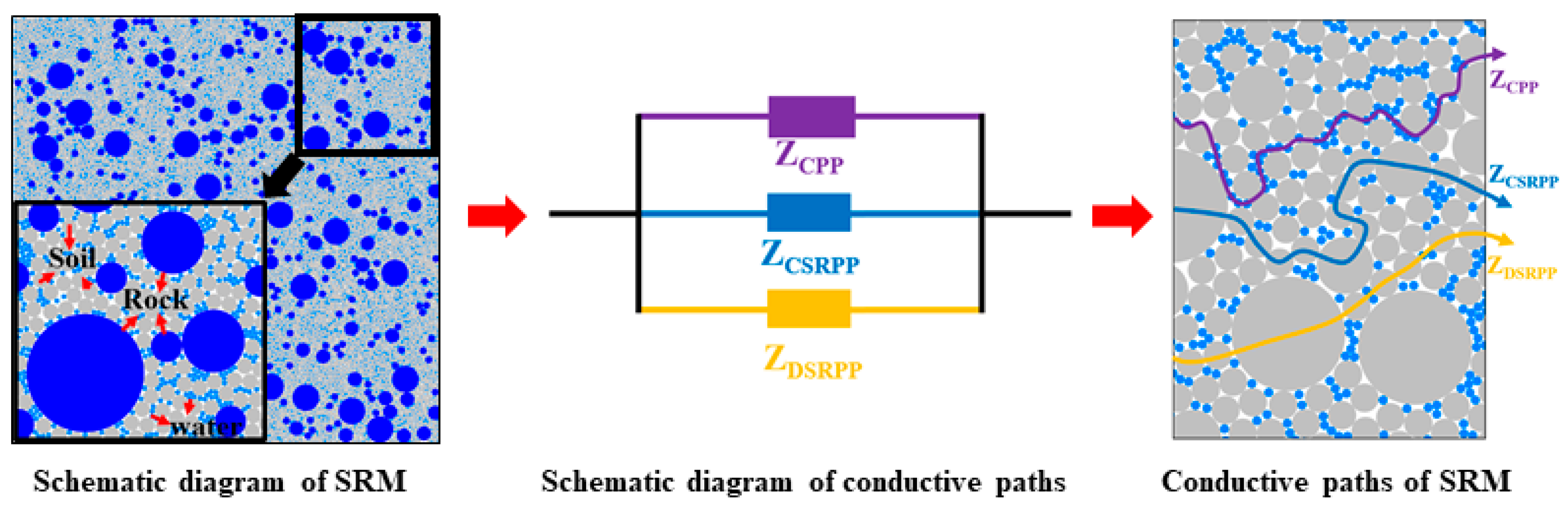
2.2. Equivalent Circuit Modeling
2.3. Calculation of Fractal Dimension for Contact Surfaces of Soil-Rock Agglomerates
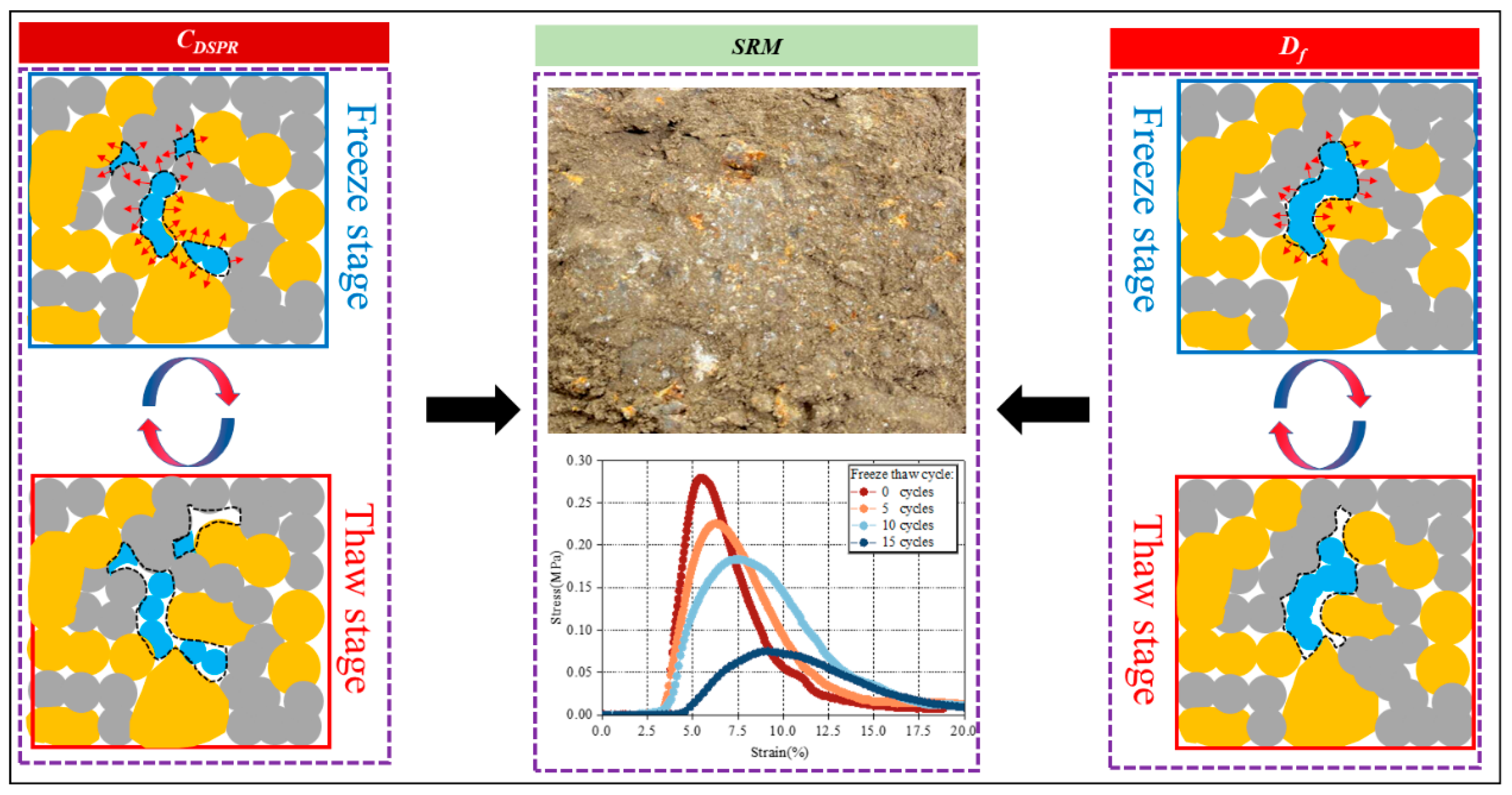
3. Results Analysis
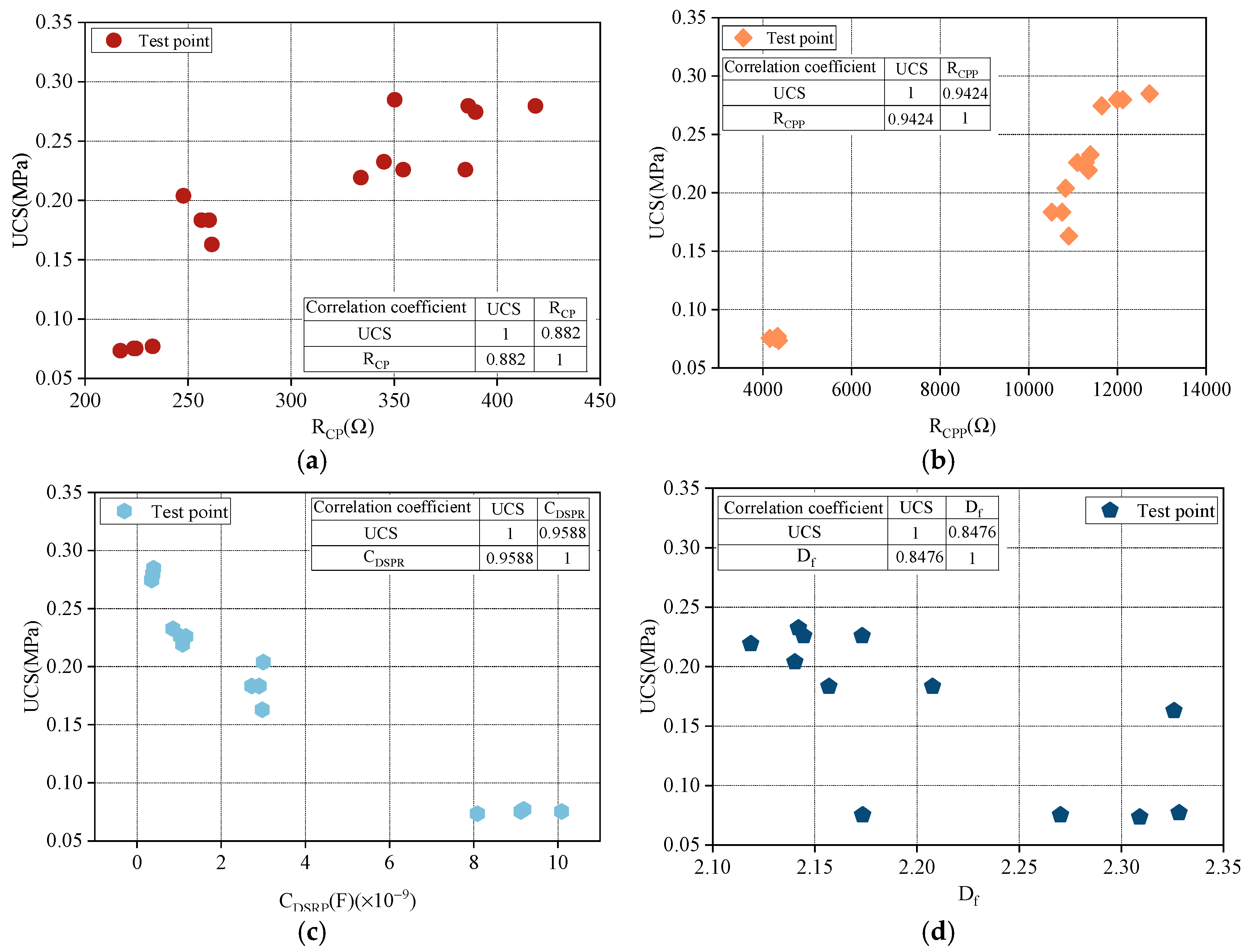
3.1. Evolution Patterns of Characteristic Parameters in Equivalent Models of Different Conductive Pathways Under F–T Cycles
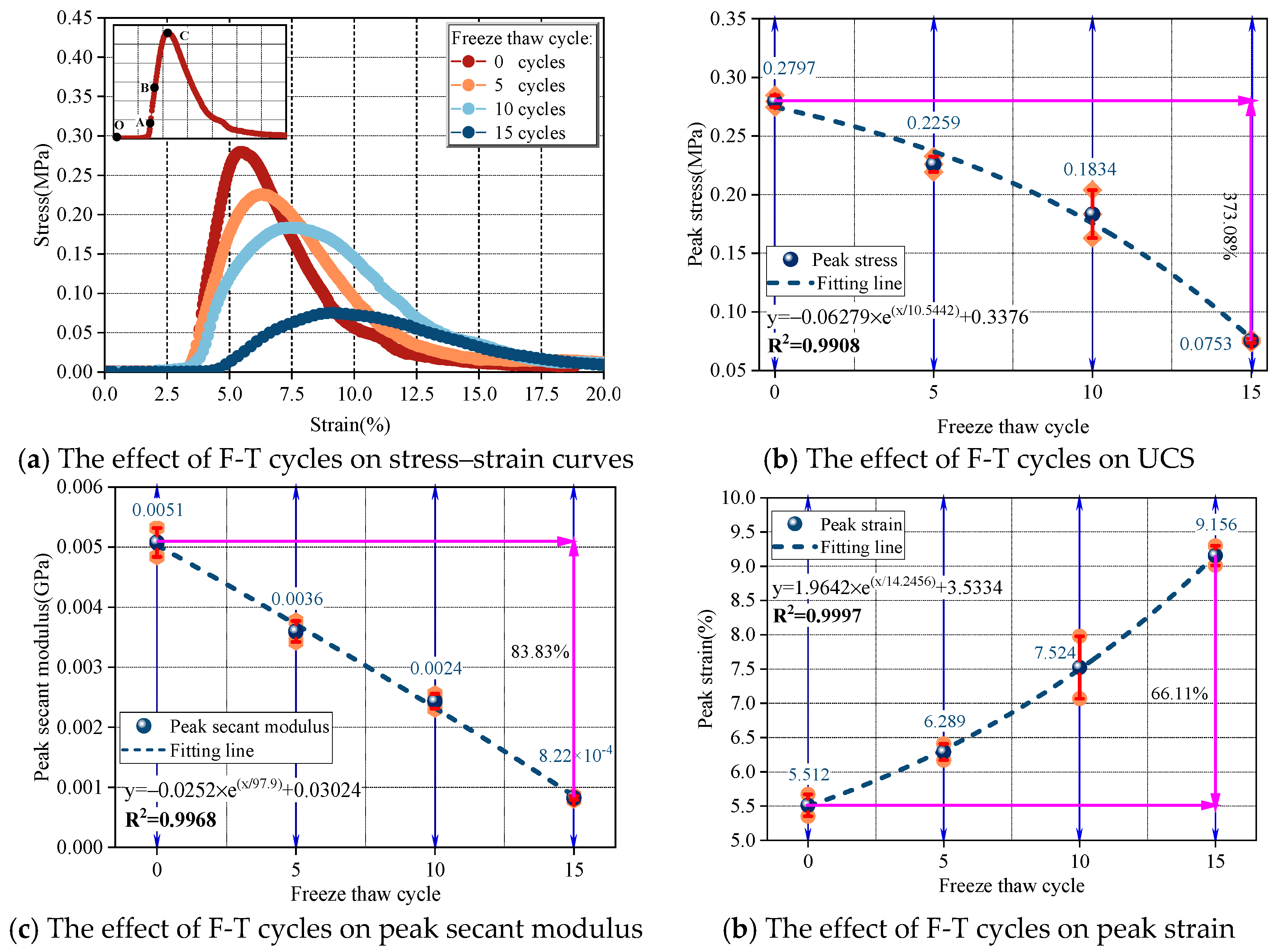
3.2. Evolution of Uniaxial Mechanical Properties of SRM Under F–T Cycles
4. Discussion
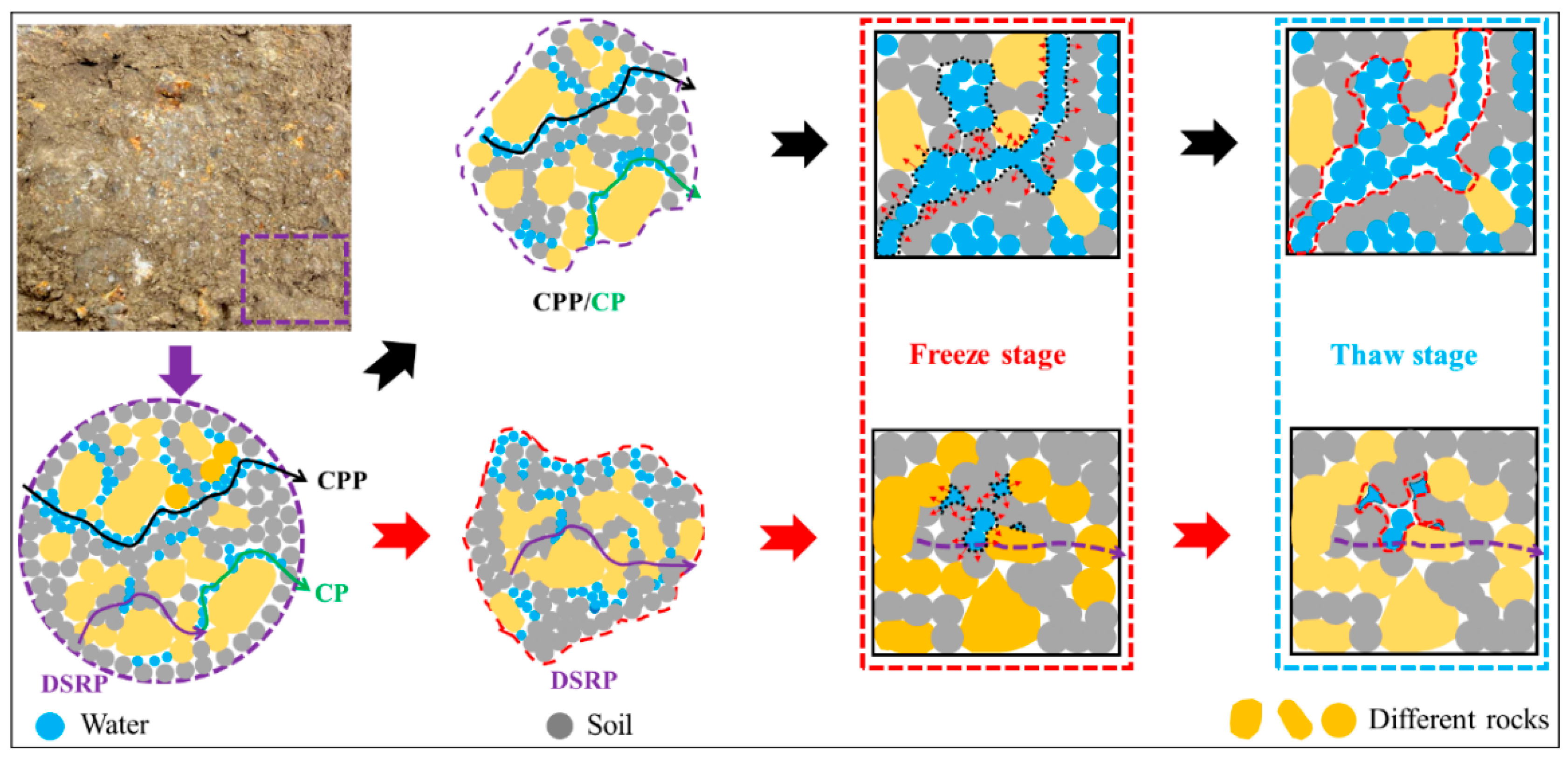
4.1. Mechanism of F–T Cycle Effects on the Microstructure of SRM
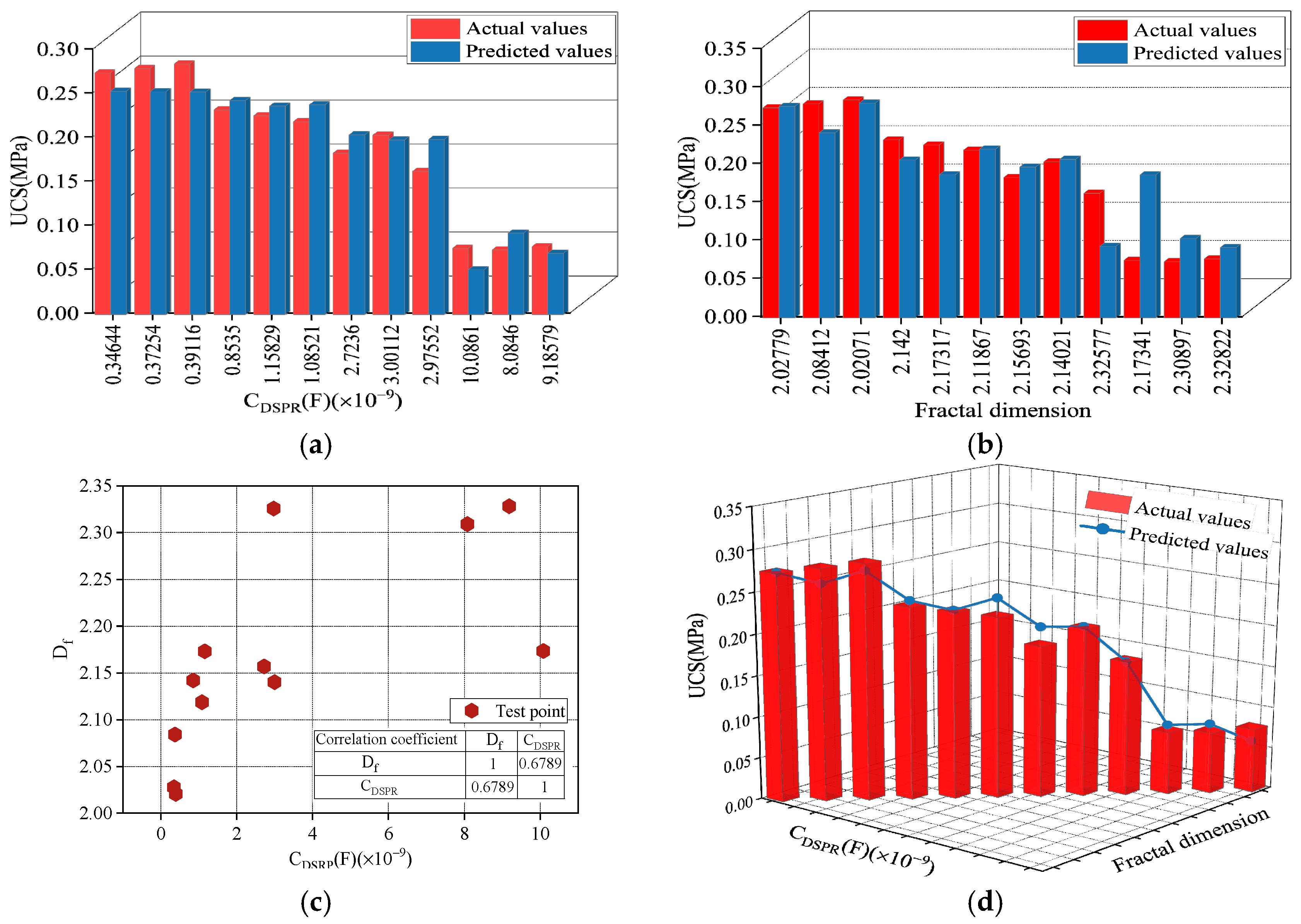
4.2. Predicting Model for Freeze–Thaw UCS of SRM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SRM | Soil–Rock mixtures |
| F–T cycles | freeze–thaw cycles |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| UCS | Uniaxial compression strength |
| CP | Continuous pore water path of DSRPP |
| CPP | Continuous pore water conductive path |
| DSRPP | Discontinuous soil–rock–pore water conductive path |
| DSRP | Discontinuous soil-rock conductive path |
| RCP | The resistance of CP |
| RCPP | The resistance of CPP |
| CDSRP | The double parallel-plate capacitance of DSRP |
| Df | Fractal dimension |
References
- Xu, W.J.; Hu, R.L.; Tan, R.J. Some geomechanical properties of soil–rock mixtures in the Hutiao Gorge area, China. Geotechnique 2007, 57, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Tang, L.; Wang, P.; Zheng, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Jin, L.; Yu, Y.; Duan, X. A creep model for soil-rock mixture considering the effect of rock contents and freeze-thaw cycles. Eng. Geol. 2024, 333, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Deng, H.; Zhao, B.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, S. A study of uniaxial compressive strength degradation model of soil-rock mixtures under freeze-thaw deterioration based on equivalent model characteristics of conductive paths. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 437, 136975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pu, H.; Xue, K.; Xu, J.; Ni, H. Mechanical Response and Damage Characteristics of Frozen–Thawed Sandstone Across Various Temperature Ranges Under Impact Loads. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tan, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y. Analysis of damage characteristics for skarn subjected to freeze-thaw cycles based on fractal theory. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Shan, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. A Binary Medium Constitutive Model for Frozen Solidified Saline Soil in Cold Regions and Its Fractal Characteristics Analysis. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kaunda, R.B.; Zhou, K. Experimental investigations on the effects of ambient freeze-thaw cycling on dynamic properties and rock pore structure deterioration of sandstone. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Liu, W.; Deng, H. NMR research on deterioration characteristics of microscopic structure of sandstones in freeze–thaw cycles. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2997–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Shi, W. Strength deterioration model of saturated sandstone under freeze-thaw cycles. Rock Soil Mech. 2019, 40, 926–932. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Zhou, K.; Gao, F.; Xu, C.; Li, J. A new damage constitutive model for frozen-thawed sandstone under triaxial conditions: Considering the characteristics of pre-peak compaction and post-peak residual strength. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2024, 33, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Gao, F.; Zhou, K.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic tensile mechanical properties of water-saturated and frozen sandstone after freeze-thaw fatigue damage treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 9323–9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Gao, F.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Yang, C. Pore Structure Evolution Characteristics and Damage Mechanism of Sandstone Subjected to Freeze–Thaw Cycle Treatment: Insights from Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Testing and Fractal Theory. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Xu, Q.; Hu, R.L. Study on the shear strength of soil–rock mixture by large scale direct shear test. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.J.; Zhang, H.Y. Meso and macroscale mechanical behaviors of soil–rock mixtures. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 3765–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Jia, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C. Granular discrete element simulation of the evolution characteristics of the shear band in soil–rock mixture based on particle rotation analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Han, W.; Xiong, Y.; Qian, J. Effects of moisture and stone content on the shear strength characteristics of soil-rock mixture. Materials 2023, 16, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Hu, R.; Oyediran, I.A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Geomechanical characterization of Zhangmu soil-rock mixture deposit. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2014, 32, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.H.; Liu, J.-J.; Luo, H.; Yang, M.-H. Experimental studies of shear strength characteristics and influencing factors of soil-rock aggregate mixture. Rock Soil Mech. 2017, 38, 965–972. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.Z.; Xu, W.J.; Wei, C.F.; Meng, Q.S. Influence of water content and shear rate on the mechanical behavior of soil-rock mixtures. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, B. Macro–meso freeze–thaw damage mechanism of soil–rock mixtures with different rock contents. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, F.; Yang, H.; Gao, W.; Miao, L. Orthogonal experimental study of soil–rock mixtures under the freeze–thaw cycle environment. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1376–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xing, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, H. Damage mechanism of soil-rock mixture after freeze-thaw cycles. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2019, 26, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, G.; Luo, T.; Jin, L.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, G. Mechanism of shear strength deterioration of soil-rock mixture after freeze–thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 200, 103585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Jin, L.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Sun, Q.; Wu, D.; Li, G. Mechanism of strength degradation of frozen soil–rock mixture under temperature rise-induced particle ice film ablation. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2023, 34, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Jin, L.; Yang, G. Shear properties and pore structure characteristics of soil–rock mixture under freeze–thaw cycles. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 3233–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z.; Qiu, P.; Yu, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Jia, H. Exploring strength deterioration mechanism of soil-rock mixture based on pore structure characteristics under freeze–thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 217, 104040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G. Equivalent circuit model for AC electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Bai, X.-H. Interpretation of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) circuit model for soils. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 4318–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, R.; Wang, L.; Zou, Z.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Z.; Lu, S. An analytical model for anchor-mortar interface bonding based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 105196. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Chen, L. Study on the characteristics of the soil-rock mixture structure based on the high-frequency extremum of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 4135–4141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Gao, Q. Study on pore characteristics of soil-rock mixture resistance similarity based on the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 41, 120–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Gao, Q. Structural characteristics of soil-rock mixtures based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Catena 2021, 207, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, E.S. The Strength and Deformation Properties of Melange. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Medley, E.W. The Engineering Characterization of Melanges and Similar Block-in-Matrix Rocks (Bimrocks). Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. Model development and experimental verification for permeability coefficient of soil–rock mixture. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04016106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Geotechnical Test Method Standard. 2019. Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/zc/wjk/art/2019/art_17339_241309.html (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Waller, A.M.; Hampton, A.N.S.; Compton, R.G. An alternating current impedance study of polypyrrole/poly (vinyl chloride) composites. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1989, 85, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-viand, A.; Mahjani, M.G.; Jafarian, M. Determination of fractal rough surface of polypyrrole film: AFM and electrochemical analysis. Synth. Met. 2014, 191, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Main Parameters | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Start Frequency (Hz) | 10,00,000 |
| End Frequency (Hz) | 0.01 |
| Data Quality | 3 |
| Current Range (mA) | 2 |
| Voltage Range (V) | +/−6 |
| Electrometer Mode | Differential |
| Regression Parameters | Regression Coefficient | p | F | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.260942484 | 8.86 × 10−11 (**) | 8.74689 × 10−7 (**) | 0.9193 | |
| CDSPR | −20,825,862.1 | 8.75 × 10−7 (**) |
| Regression Parameters | Regression Coefficient | p | F | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.520750596 | 0.000398 (**) | 0.001047 (**) | 0.6749 | |
| −0.61370175 | 0.001047 (**) |
| Regression Parameters | Regression Coefficient | p | F | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.75759538 | 0.000112 (**) | 8.34657 × 10−8 (**) | 0.9733 | |
| CDSPR | −16,158,088 | 3.51 × 10−6 (**) | ||
| −0.2364532 | 0.002097 (**) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.; Wang, L.; Tian, G.; Deng, H. Multi-Scale Damage Evolution of Soil-Rock Mixtures Under Freeze–Thaw Cycles: Revealed by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Testing and Fractal Theory. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9100624
Deng J, Wang L, Tian G, Deng H. Multi-Scale Damage Evolution of Soil-Rock Mixtures Under Freeze–Thaw Cycles: Revealed by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Testing and Fractal Theory. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(10):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9100624
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Junren, Lei Wang, Guanglin Tian, and Hongwei Deng. 2025. "Multi-Scale Damage Evolution of Soil-Rock Mixtures Under Freeze–Thaw Cycles: Revealed by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Testing and Fractal Theory" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 10: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9100624
APA StyleDeng, J., Wang, L., Tian, G., & Deng, H. (2025). Multi-Scale Damage Evolution of Soil-Rock Mixtures Under Freeze–Thaw Cycles: Revealed by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Testing and Fractal Theory. Fractal and Fractional, 9(10), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9100624







