Abstract
Sequential minimal optimization (SMO) method is an algorithm for solving optimization problems arising from the training process of support vector machines (SVM). The SMO algorithm is mainly used to solve the optimization problem of the objective function of SVM, and it can have high accuracy. However, its optimization accuracy can be improved. Fractional order calculus is an extension of integer order calculus, which can more accurately describe the actual system and get more accurate results. In this paper, the fractional order sequential minimal optimization (FOSMO) method is proposed based on the SMO method and fractional order calculus for classification. Firstly, an objective function is expressed by a fractional order function using the FOSMO method. The representation and meaning of fractional order terms in the objective function are studied. Then the fractional derivative of Lagrange multipliers is obtained according to fractional order calculus. Lastly, the objective function is optimized based on fractional order Lagrange multipliers, and then some experiments are carried out on the linear and nonlinear classification cases. Some experiments are carried out on two-classification and multi-classification situations, and experimental results show that the FOSMO method can obtain better accuracy than the normal SMO method.
1. Introduction
The sequential minimal optimization (SMO) algorithm is used to solve the optimization problem of the objective function of support vector machines (SVM). The SVM method was proposed in 1995 by Vapnik, the leader of AT&T Bell Labs [1], and the SVM method is a classification technique. It has been continually researched and used since its introduction because of its efficiency in solving small sample, nonlinear, and high-dimensional pattern recognition problems. The SVM method would transform the final problem into solving a convex quadratic programming problem with a globally optimal solution. However, the data in practice are often large in size and complex in dimensionality. This can lead to problems such as long machine computing time, excessive memory consumption, and low accuracy. In order to solve these issues, extensive research has been done. The SMO method is an algorithm for solving optimization problems arising from the training process of SVM. The SMO method was proposed by John Platt of Microsoft Research in 1998 [2], and it is widely used in the training process of SVM now. Previously available SVM training methods had to use complex methods and required expensive third-party secondary planning tools. The SMO algorithm can better avoid these problems. The SMO method is developed from the decomposition algorithm [3], and it decomposes a large problem into several sub-problems with only two variables, and then the sub-problems would be solved firstly. The SMO algorithm solves not only the problem of uncertainty in the multi-sample classification solution but also the problem of relatively long operation time [4].
The SMO algorithm has been applied in various fields. For quantum-classical hybrid algorithms, a sequential minimal optimization method was proposed in [5], and it converges faster. The optimization problem of the parameterized quantum circuits is divided into solvable sub-problems, and the efficiency was proved. A sequential minimal optimization regression approach for local pier scour depth estimation was proposed in [6]. The comparison results showed that the method could get higher prediction performance than other methods. The SMO method was used during a parallel FPGA implementation of the training phase of SVM [7], and it could enable the resolution of a complex convex optimization problem through simple steps. The SMO implementation was also highly parallel. Human activity detection has been carried out by employing the time efficiency and optimality of SMO method to train SVM [8], and the accuracy was higher than other methods. The SMO method was also used to analyze data and reveal rules and patterns in the process of data mining [9], and it could improve the accuracy of the anomaly detection rate. The results showed that the SMO method enhanced the rate of positive detection besides reducing the rate of false alarms and achieving a high accuracy at the same time. The advance SMO method was used in a modern automated approach to improve efficiency and decrease the difficulty of lung tumor diagnosis [10]. An overall performance accuracy of 0.962 was obtained. A model based on the sequential minimal optimization algorithm was developed for predicting the range of the prices for each medicine [11], and the results demonstrated that the model derived by the SMO algorithm provided good performance at an accuracy of approximately 92.62%, with high sensitivity and precision. A novel hybrid model of a sequential minimal optimization and support vector machine was proposed for an accurate landslide susceptibility mapping [12], and results of the study showed that the model had the highest performance for landslide susceptibility mapping. In [13], the sequential minimal optimization was used to classify diabetic retinopathy. An enhanced algorithm based on the knowledge of a context ontology methodology for sequential minimal optimization was suggested in [14], and the experimental analysis demonstrated that the method improved by 2% of accuracy when compared to semantic ontology. A parallel-hybrid algorithm that combines SVM, sequential minimal optimization with stochastic gradient descent methods was proposed to optimize the calculation of the weight costs in [15]. The performance of the proposed method was better than the classical SMO method. Suspended sediment load modeling through advanced computational algorithms was of major importance and a challenging topic for developing highly accurate hydrological models. A sequential minimal optimization method was applied for suspended sediment load modeling in [16]. Water sources pollution is a great environmental problem that negatively affects life. The SMO method was applied to water quality parameters of the Akkopru stream located in the province of Van [17]. Autism spectrum disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder caused by several nervous system problems that change the function of the brain. It is either congenital or occurs in the early years of life. The SMO method was used in [18] and the results could be useful. A timely prediction with accuracy about crop yield could be valuable for greater food production and maintainability of sustainable agricultural growth. The SMO method was used for wheat production in [19], and the results would be helpful for agriculture. The SMO algorithm was proposed to minimize the cost function in [20], which decoupled the constraint of the mutual collisions in each iteration to save the planning time and experiment results showed that the method had good performance in obstacle-rich environments and was efficient for a large number of UAVs. The smallest possible sub-problem at each step was optimized by the SMO method in [21] and it could be used as an efficient local solver within a global optimization strategy. The extensive computational experiments and results showed that the algorithm was a valuable alternative to the state-of-the-art algorithms for standard quadratic optimization problems. The SMO method was used in [22] for optimizing SVM, and the SMO-optimized models showed better performance than non-optimized models. The SMO of SVM was an effective method to deal with classification and regression problems [23]. A generalized SMO-type algorithm framework with a simple iterative format and easy implementation was provided. The numerical results showed that the algorithm was significantly shorter than that of the other plain algorithms. A generalized framework of accelerating the stochastic sub-gradient descent was proposed in [24] for a variety of SVM, and experimental results on a variety of datasets and learning applications confirmed that the method can speed up the SMO method.
The SMO algorithm is based on integer order calculus. The above studies are based on the integer order SMO algorithm. If the integer order SMO algorithm can extend to the fractional order SMO algorithm, better results should be obtained, as fractional order calculus is an extension of integer order calculus, which can describe the real system more accurately and obtain more precise results [25]. The traditional calculus should be extended to better describe and study such phenomena. The SMO algorithm is extended to the fractional order sequential minimum optimization algorithm in this paper. The major innovations of the article are presented below.
- According to the fractional order calculus, the fractional derivative of Lagrange multiplier is obtained.
- The fractional expression of the objective function can be obtained; with further calculations, updated value calculation expressions can be obtained.
- A fractional order sequential minimum optimization method is proposed for classification.
- A large number of experiments are performed. There are linearly divisible cases and nonlinear cases, and there are binary cases and multi-categorical examples. The experimental results show that the fractional order sequential minimum optimization algorithm is better than the traditional SMO method.
The remainder of the article is structured in the following way. In Section 2, fractional order calculus has been introduced for further research. In Section 3, the fractional order sequential minimum optimization method for classification is deduced in detail. Section 4 verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method through some experiments. There are linearly divisible cases and nonlinear cases, and there are binary cases and multi-categorical examples. Finally, our conclusions are derived in Section 5.
2. Fractional Order Calculus
The nature of the real world is fractional order, and many phenomena in nature cannot be accurately described by the traditional integer order calculus equations. The essence of fractional order calculus is arbitrary order. The order of fractional calculus can be a real number, and it also can be a complex number. The operator of fractional order calculus may be written by [26], where letters a and t express the lower limit and the upper limit separately, and denotes the order.
There are three commonly used fractional order calculus definitions. They are fractional order calculus GL definition, fractional order calculus RL definition, and fractional order calculus Caputo definition [27].
The fractional order calculus GL definition is defined as follows:
where expresses a binomial coefficient, and the j denotes a natural number.
The fractional order calculus RL definition is defined as follows:
where , and Γ represents Gamma function and its definition is , where the real part of z is greater than 0. Gamma function is the most commonly used function in fractional order calculus.
The fractional order calculus Caputo definition is defined as follows:
where . In some conditions, these three fractional order calculus definitions are harmonized [28].
Fractional order systems based on fractional order calculus have demonstrated superior performance in various industries. The electric circuit model based on fractional order Caputo calculus can handle a wide range of fractional order dynamics in electrical circuits [29]. The effectiveness of the model had been illustrated by graphical representation with simulation. Fractional order derivative operators can impact memory effects on population dynamics in computer viruses [30]. The results highlight the memory effect associated with fractional order derivatives, where past states and behaviors continue to influence the system. The ability to capture these memory effects through fractional calculus can be considered a benefit. Fractional order calculus was modeled for hyperthermia therapy of cancerous tumor sitting [31]. The experiments derived excellent agreement during a hyperthermia treatment of different kinds of tumors. The fractional order approach investigated the system of tsunami wave propagation along an oceanic coastline [32]. The numerical simulations verified the effectiveness. A fractional order Caputo model was established for the COVID-19 pandemic [33]. Relevant statistical data verified the effectiveness of the model for depicting the COVID-19 pandemic. Fractional derivative operators were used for the core loss prediction [34]. The results showed the accuracy of significant frequency bandwidths. Fractional derivatives were used to modify a Duffing system [35]. The results show that the fractional elements clearly modify the system dynamics and significantly increase the system energy efficiency. Fractional order calculus can extend the capabilities of integer order calculus in accurately describing actual systems. Then the fractional order sequential minimum optimization algorithm is proposed for more precise classification tasks.
3. Methods
The sequential minimal optimization algorithm can train SVM for classification and tasks [36]. The sequential minimal optimization with pinball loss was developed to reduce the impact of measurement error [37]. Simulation results demonstrated that the method had high accuracy, robustness, and computational efficiency in bulk power grids. When the data are big, there will be some problems, such as long machine computing time and excessive memory consumption.
The sequential minimal optimization algorithm is based on integer order calculus. The nature of the real world is fractional order systems. Traditional calculus can be expanded to fractional order calculus. The sequential minimal optimization algorithm would be expanded to the fractional order sequence minimum optimization algorithm.
3.1. Fractional Order Expressions
In order to get better results, the objective function, classification criterion, and decision function all should be expressed accurately. Firstly, fractional order expressions would be deduced based on fractional order calculus.
For the function x, the integer order derivative of the function is
Replacing the integer number n with an arbitrary number μ, while p is also defined as an arbitrary number. Let z = μ, and the integral form of the Gamma function can be expressed as
It can be expressed in its limiting form as
Then for an arbitrary μ and a non-natural number p, there is
Based on Equation (7), the following expression can be obtained
And then
These are fractional order derivatives. The fractional derivative of Lagrange multiplier is obtained by this fractional order derivative.
3.2. Fractional Order SMO
The fractional order objective function will better describe the system problems for more accurate results, and then the fractional order objective function would work. The optimal value of the objective function and the constraints are reduced
where is a constant, and denotes the Lagrange multiplier. These Lagrange multipliers can be fractional order Lagrange multipliers. They can contribute to better-describing problems and
Here, are the old Lagrange multipliers, and denote the updated Lagrange multipliers. The optimal value of the objective function and the constraints are the same as the integer order function.
When , there are
When , there are
Let denote the difference between the predicted value and the true value . Then the expression can be obtained
Multiplying at each side of expression , we can get
where . Then it can be , and the objective function of the sub-problem is converted to a problem containing only . At this point, the objective function is
And then
Then the objective function ψ can be derived by order.
Substituting the above formula and simplifying, we can get
where . When , there is
Then
Due to the restriction, the updation of is
For , there is
By computing, the offset b satisfies the following condition
where
From the above derivation, the optimal solution of the objective function can be obtained, and then the optimal values can be deduced. So, the hyperplane and decision function can be determined. The key differences between the traditional SMO method and the FOSMO method are fractional order expressions, because there is an additional parameter: the fractional order. When the fractional order is 1, that is the traditional SMO method.
3.3. FOSMO Classification Algorithm
In this paper, the fractional order sequential minimum optimization method for classification is proposed, and the steps can be summarized as follows:
S1: simplifying optimization problems in support vector machines, and simplification result is an objective function containing two items of Lagrange multiplier and ;
S2: obtaining fractional derivatives of and respectively, according to the fractional order calculus definition;
S3: substituting the fractional derivative of the and into the optimization problems in support vector machines to obtain fractional order expression of the objective function; with further calculations, obtaining updated value calculation expressions of , , and obtaining the values of and using heuristic algorithm;
S4: updating the offset b of hyperplane function according to the values of and ;
S5: processing the data and determining the classification according to the decision function.
Then some experiments are performed on the fractional order sequential minimum optimization method. There are linearly divisible cases and nonlinear cases, and there are binary cases and multi-categorical examples.
4. Experiments
The sequential minimal optimization method is the best algorithm for training SVM, and it can obtain better results than other classification methods. The sequential minimal optimization-support vector machine hybrid classifier was the best compared to artificial neural networks, simple logistic, K-nearest neighbor, decision tree, and random forest [18]. The comparison results between traditional integer order sequential minimum optimization algorithm and fractional order sequential minimum optimization algorithm could be illustrated in experiments in this section.
4.1. Linear Case
Here, data are from the data_test2.mat, and this is a randomly generated dataset containing 80 data with labels, of which 40 are positive cases with label +1 and 40 are negative cases with label −1. The maximum iteration number is set to 50 and the error value is 0.01, and the initial value of b is 0. The original data are shown in Figure 1 and the red circles are the negative cases with label −1 and the green squares are the positive cases with label +1.
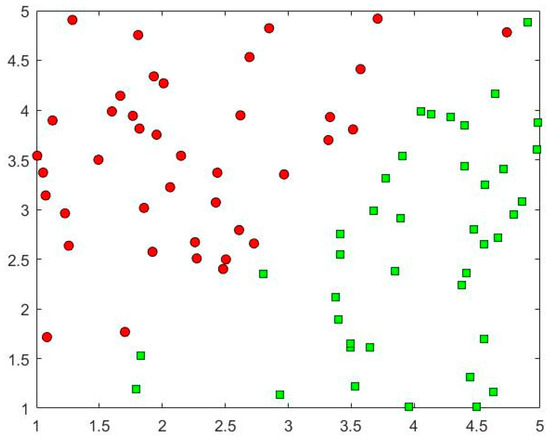
Figure 1.
The original diagram of data_test2. The red circles are the negative cases with label −1 and the green squares are the positive cases with label +1.
Applying the fractional order SMO on these data, the data classification results are shown in Table 1. Using MATLAB 2017, the relaxation variable influence factor C is 0.8.

Table 1.
Classification table of linearly separable when impact factor C is 0.8.
As shown in Table 1, when the order is 1, the number of correct classifications is 75 and the number of incorrect classifications is 5, and the correct classification rate is 93.75%. When the order is 1.4, the number of correct classifications is 76 and the number of incorrect classifications is 4, and the correct classification rate is 95%. It can be seen that the FOSMO method demonstrates better classification accuracy than the traditional SMO on linear classification cases. However, the result is not significant. The classification effects for when the order is 1 and 1.4, respectively, are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
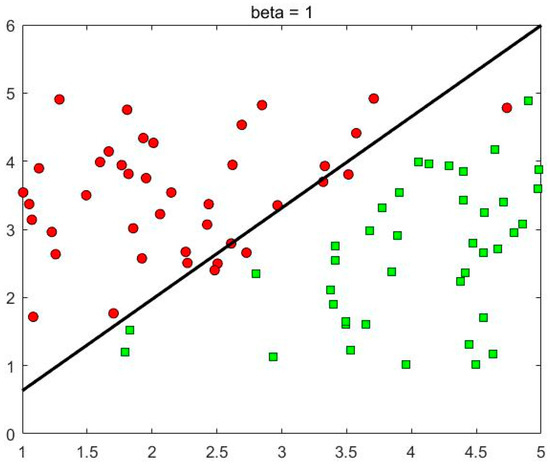
Figure 2.
Classification diagram when the derivative order is 1. The red circles are the negative cases with label −1 and the green squares are the positive cases with label +1.
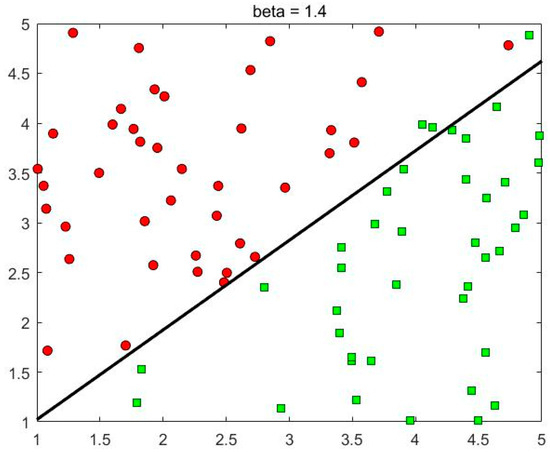
Figure 3.
Classification diagram when the derivative order is 1.4. The red circles are the negative cases with label −1 and the green squares are the positive cases with label +1.
Comparing the integer order SMO algorithm with the fractional order SMO algorithm, it can be found that the most significant change is the update method of . Because the value range of is larger in the fractional order SMO algorithm, the accuracy of the fractional order SMO algorithm is higher than that of the SMO algorithm.
From Table 1, it can be found that the classification correct rate does not exceed the integer order from the order of 0.1 to 0.9. Only when the fractional order is greater than 1, good results will be obtained. To verify this, the relaxation variable factor C is taken to be 0.5. The results for when C is 0.5 are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Classification table when impact factor C is 0.5.
It can be seen from Table 2 that the classification effect is better than integer order when the order is 0.3, 0.4, 0.8, and 0.9. When the order is 1, there are 73 correct classifications and 7 incorrect classifications, and the correct classification rate is 91.25%. When the order is 0.4, there are 78 correct classifications and 2 incorrect classifications, and the correct classification rate is 97.5%. The correct classification rate is 6.25% higher than order 1. So, it is obvious that the classification effect of order 0.4 is better than that order 1. From the above results, it can be seen that good results can be obtained from order 0.1 to 0.9. Combined with the above analysis, it also can be seen that the classification correctness results will vary due to different orders, but there will always be fractional orders with better classification results than integer orders.
For the nonlinear cases, the conclusion also holds true.
4.2. Data_Test1
Here, the nonlinear case is from data_test1.mat, and the data_test1.mat contains 200 test samples, and 100 are positive cases with label +1 and 100 are negative cases with label −1. In order to verify the high accuracy of the fractional order SMO, examples are carried out by MATLAB 2017.
The test results for when C is 0.5, b is 0, tolKKT is 0.01, maxIter is 80, and sigma is 0.9 are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Classification table of non-linearly when the impact factor C is 0.5.
As can be seen from Table 3, the integer order SMO has the best result compared to the others when the order is 1. Then the order can be further refined between 0.95 order and 1.05 order. On the basis of the original parameters, the experimental results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Classification table when the impact factor C is 0.5.
Table 4 shows that when the order is 0.96 and 1.03, the classification results are better than the integer order. When the order is 1, the number of correct classifications is 192, and the number of incorrect classifications is 8, and the correct classification rate is 96%. When the order is 0.96, the number of correct classifications is 193, and the number of incorrect classifications is 7, and the correct classification rate is 96.5%. It can be seen that the fractional order SMO can still achieve better classification accuracy than the integer order SMO method on nonlinear classification cases.
4.3. Sonar Data
This example is performed on 60-dimensional sonar data. The sonar data are used to determine whether the target is rock (R) or mine (M) by obtaining signals based on different aspect degrees. The sonar data are a binary dataset with 208 data in total, including 111 mine labels and 97 rock labels. Now the better predicted result is about 88%. Here, the sonar data are classified by the fractional order SMO algorithm.
Firstly, the sonar labels are processed by defining the R label as 1 and the M label as −1. Secondly, the data are normalized before classification, and although the data values are all between 0 and 1, the maximum and minimum differences are nearly 100 times. Finally, parameters are set. The relaxation variable C is 2, the initial value of offset b is 0, the maximum tolerance tolKKT is 0.01, the maximum number of iterations maxIter is 80, and sigma is 1.5 in the Gaussian kernel function. The classification results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Classification table of Sonar data.
It can be seen from Table 5 that the correct classification rate is 95.67% when the order is 1.1. When the order is 1.3, the correct classification rate is 94.23%. For the integer order 1st order SMO, the correct classification rate is 78.85%. The comparison shows that the classification effect of fractional order SMO is better than the integer order SMO method.
4.4. Multiclassification Case
For the multi-classification case, the fractional order sequential minimum optimization classification algorithm will be adapted by the one-to-one algorithm. For fractional order one-to-one multi-classification algorithms, the main idea is to use the one-to-one algorithm to call the fractional order sequential minimum optimization algorithm in binary classification.
Let the training sample set T with K categories. The process is as follows:
S1: All different kinds of sample sets are combined two by two, and it is possible to obtain a total of k(k − 1)/2 different kinds of combinations;
S2: The sample points in the different class combinations are formed into a training set T(i, j);
S3: Invoke the binary classification and solve P judgment functions separately: . If , then the sample point X belongs to class i and the class i gets one vote. Otherwise, the sample point X belongs to class j and class j gets one vote.
S4: The votes number will be counted respectively based on the P judgment functions. The category with the most votes is the final judgment category.
The data are normalized first prior to multiple classifications. The specific role of normalization is to generalize the statistical distribution of the uniform sample. Normalization between 0 and 1 is the statistical probability distribution and normalization between −1 and +1 is the statistical coordinate distribution. If there are two variables uniformly distributed and x1 is in the range of 100,000 to 200,000, the x2 is between 1 and 2. It is obvious that x2 is difficult to display if they are in the same coordinate system and these points of x2 will be ignored for classification. In order to make these points not be ignored, normalization should be done.
For the classical Iris data, the FOSMO classification algorithm is applied for debugging, asing the random function to disrupt the order of the data. The labels of the data are also disrupted accordingly. The FOSMO binary classification algorithm is called using a one-to-one approach. To verify the improvement of fractional order in accuracy, the Gaussian radial basis kernel function is used to test the classification of the classical Iris data and the experimental data are obtained from UCI. Firstly, normalization is used for the data and then randomly disordered order and the corresponding labels were also disordered. To ensure the accuracy of the data, each order was run five times, and then the value with the most occurrences was taken. The classification results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Multi-classification table of Iris data.
It can be seen from Table 6 that the accuracy is 95.33% when the order is 0.8. When the order is 0.9, the accuracy is also 95.33%. For the integer order 1st order SMO, the accuracy is 94.67%. The comparison results show that the FOSMO is better than the integer order SMO method.
5. Conclusions
The SMO algorithm is one of the main algorithmic theories in SVM. In this paper, the FOSMO classification algorithm is proposed for classification by combining fractional order calculus with the SMO algorithm. The fractional order Lagrange multiplier is deduced by fractional order calculus. Fractional order objective function with fractional order Lagrange multipliers can describe the real systems more accurately and there is a specific parameter: the fractional order. The classification accuracy is determined by the fractional order. It is a challenge to determine the optimal fractional order when implementing the FOSMO method in practical applications. Through the experimental results, we can find that the FOSMO algorithm can always obtain a higher accuracy result than the traditional SMO method for both linear and nonlinear cases. It can be concluded that the FOSMO algorithm has a higher accuracy than the integer order SMO algorithm for practical systems. Owing to fractional order calculus, the FOSMO method would also be fit for more complex and sophisticated systems in the field of machine learning and classification.
The advantage of the FOSMO algorithm is that it can obtain higher accuracy. However, there are difficulties with it. The optimal fractional order is not easy to determine. This optimal fractional order is also the main sensitive parameter that has an impact on the optimization performance. The future research directions would be the optimal fractional order in complex fractional order systems. It is also an important topic in the theory of fractional order systems. The FOSMO algorithm would be a small step to a fractional order machine learning system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z. and L.D.; methodology, C.Z. and L.D.; software, C.Z. and L.D.; investigation, C.Z.; resources, C.Z. and L.D.; data curation, C.Z. and L.D.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.Z. and L.D.; visualization, C.Z. and Y.H.; supervision, C.Z. and Y.H.; project administration, C.Z.; funding acquisition, C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 61862062 and 61104035.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J.C. Sequential Minimal Optimization: A Fast Algorithm for Training Support Vector Machines. In Advances in Kernel Methods-Support Vector Learning; Microsoft: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 212–223. [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin, R.M. Everything Old is New Again: A Fresh Look at Historical Approaches in Machine Learning; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.J.; Keerthi, S.S.; Ong, C.J.; Uvaraj, P.; Fu, X.J.; Lee, H.P. Developing parallel sequential minimal optimization for fast training support vector machine. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.M.; Fujii, K.; Todo, S. Sequential minimal optimization for quantum-classical hybrid algorithms. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 2, 043158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayadelen, C.; Altay, G.; Onal, S.; Onal, Y. Sequential minimal optimization for local scour around bridge piers. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2022, 40, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, D.H.; Torquato, M.F.; Fernandes, M.A. A parallel implementation of sequential minimal optimization on FPGA. Microprocess Microsyst. 2019, 69, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, G.; Khan, A.U.; Siddiqi, A.; Khan, M.U.G. Human activity recognition using mixture of heterogeneous features and sequential minimal optimization. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2019, 10, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadal, S.; Mokhtar, R.; Abdelhaq, M.; Alsaqour, R.; Ali, E.S.; Saeed, R. Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection Using K-Mean Array and Sequential Minimal Optimization. Electronics 2022, 11, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.V.; Jawhar, S.J. Automatic segmentation and classification of lung tumour using advance sequential minimal optimisation techniques. IET Image Process 2020, 14, 3355–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentrakan, A.; Yang, C.C.; Wong, W.K. How Well Does a Sequential Minimal Optimization Model Perform in Predicting Medicine Prices for Procurement System? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Prakash, I.; Chen, W.; Ly, H.-B.; Ho, L.S.; Omidvar, E.; Tran, V.P.; Bui, D.T. A Novel Intelligence Approach of a Sequential Minimal Optimization-Based Support Vector Machine for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, L.K.; Padinjappurathu, S.G.; Kadry, S.; Damaševičius, R. Detection of diabetic retinopathy using a fusion of textural and ridgelet features of retinal images and sequential minimal optimization classifier. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sornalakshmi, M.; Balamurali, S.; Venkatesulu, M.; Krishnan, M.N.; Ramasamy, L.K.; Kadry, S.; Manogaran, G.; Hsu, C.-H.; Muthu, B.A. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Hybrid method for mining rules based on enhanced Apriori algorithm with sequential minimal optimization in healthcare industry. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 10597–10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, G.; Acı, Ç.İ. SVM-SMO-SGD: A hybrid-parallel support vector machine algorithm using sequential minimal optimization with stochastic gradient descent. Parallel Comput. 2022, 113, 102955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.J.S.; Meshram, S.G.; Khosravi, K.; Moatamed, A. Suspended Sediment Modeling Using Sequential Minimal Optimization Regression and Isotonic Regression Algorithms Integrated with an Iterative Classifier Optimizer. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2022, 179, 3751–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldemir, A. Water quality modelling using combination of support vector regression with sequential minimal optimization for Akkopru stream in van, Turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Yücelbaş, Ş.; Yücelbaş, C. Autism spectrum disorder detection using sequential minimal optimization-support vector machine hybrid classifier according to history of jaundice and family autism in children. Concurr. Comput. Pr. Exp. 2022, 34, e6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Hussain, I. Prediction of Wheat Production Using Machine Learning Algorithms in northern areas of Pakistan. Telecommun. Policy 2022, 46, 102370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X. Multi-UAV trajectory planning using gradient-based sequence minimal optimization. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 137, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisori, R.; Lapucci, M.; Sciandrone, M. A study on sequential minimal optimization methods for standard quadratic problems. Q. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 20, 685–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lee, T.-Y. Incorporating support vector machine with sequential minimal optimization to identify anticancer peptides. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, X.; Li, S. A fast conjugate functional gain sequential minimal optimization training algorithm for LS-SVM model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 35, 6095–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Shan, Y.Y.; Quan, X.; Zheng, G.S. Accelerating Sequential Minimal Optimization via Stochastic Subgradient Descent. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, M.; Huang, Y. Formal Verification of Fractional-Order PID Control Systems Using High-er-Order Logic. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubng, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Technical University of Kosice: Košice, Slovak Repubic, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Lu, T. Fractional System Analysis and Design; National Defence Industry Press: Arlington, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, C.; Guan, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Ye, S. Formalization of Consistency of Fractional Calculus in HOL4. Comput. Sci. 2016, 43, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Shah, K.; Jahan, S.; Abdeljawad, T. An efficient method for the fractional electric circuits based on Fibonacci wavelet. Results Phys. 2023, 52, 106753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, İ.; Hussain, A.; Kanwal, T. Investigating the impact of memory effects on computer virus population dynamics: A fractal–fractional approach with numerical analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 174, 113845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmazoglu, M. Hyperthermia therapy of cancerous tumor sitting in breast via analytical fractional model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 164, 107271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfwzan, W.; Yao, S.-W.; Allehiany, F.; Ahmad, S.; Saifullah, S.; Inc, M. Analysis of fractional non-linear tsunami shallow-water mathematical model with singular and non singular kernels. Results Phys. 2023, 52, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yu, Y.; Ren, G.; Sun, Y.; Si, X. Stability analysis and optimal control of a fractional-order generalized SEIR model for the COVID-19 pandemic. Appl. Math. Comput. 2023, 457, 128210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharne, B.; Sebald, G. Fractional derivatives for the core losses prediction: State of the art and beyond. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 563, 169961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysak, A.; Sedlmayr, M. Damping efficiency of the Duffing system with additional fractional terms. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 111, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, S.; Liu, S. Fast Support Vector Machine Training Via Three-term Conjugate-link SMO Algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 139, 109478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kou, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Li, F. Transient stability assessment in bulk power grids using sequential minimal optimization based support vector machine with pinball loss. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).