Stability and Optimal Control of a Fractional SEQIR Epidemic Model with Saturated Incidence Rate
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Population supplement rate | |
| Infection rate of the susceptible | |
| Proportion of the susceptible vaccinated | |
| Natural mortality | |
| Government control rate | |
| Infection conversion rate of exposed population | |
| Recovery rate of infected people | |
| Case fatality rate of the infected | |
| Infection conversion rate of the isolated | |
| Removal rate of the the isolated |
2. Preliminaries
- (i)
- If for any , then is a non-decreasing function;
- (ii)
- If for any , then is a non-increasing function.
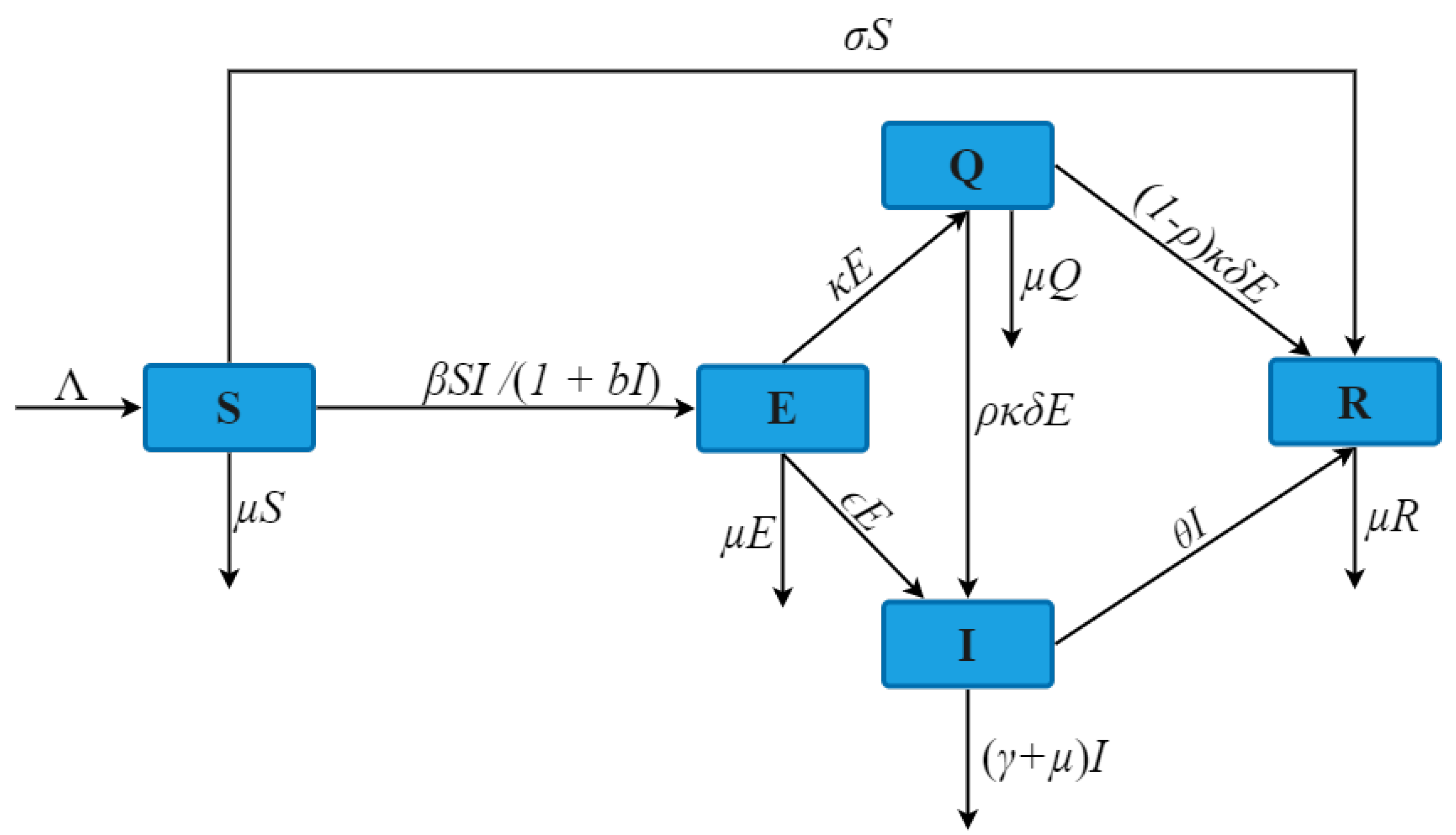
3. Stability Analysis of the Model
3.1. Basic Reproduction Number
3.2. Stability of Equilibrium Point
4. Stochastic Stability Analysis around the Endemic Equilibrium
5. Fractional-Order Optimal Control
- (i)
- The set of controls and corresponding state variables is nonempty;
- (ii)
- V is convex and closed;
- (iii)
- The right side of the system (35) is bounded by a linear function with the control and state variables;
- (iv)
- The integrand of the objective functionis convex on the set V;
- (v)
- There exist constants and such that the integrand satisfies
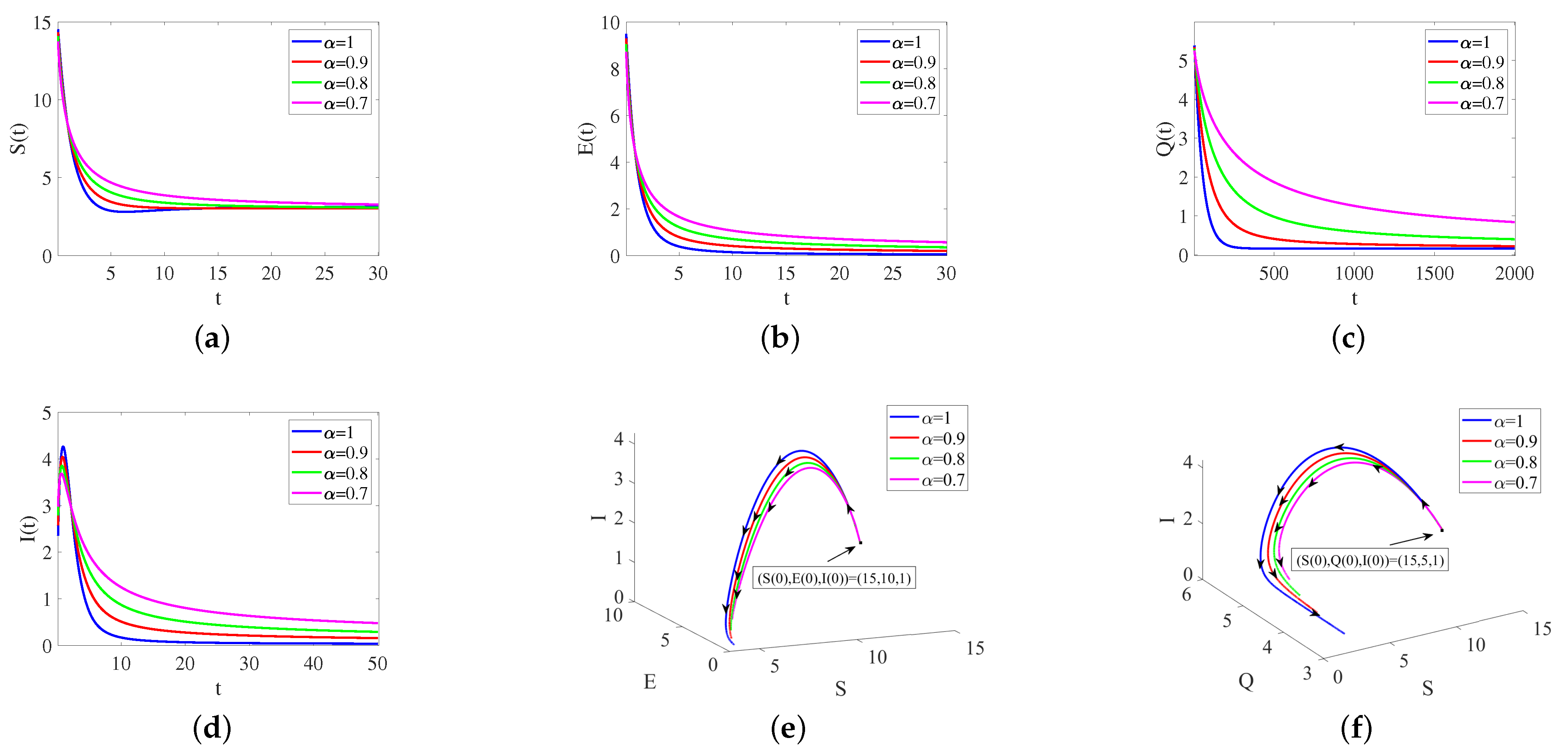
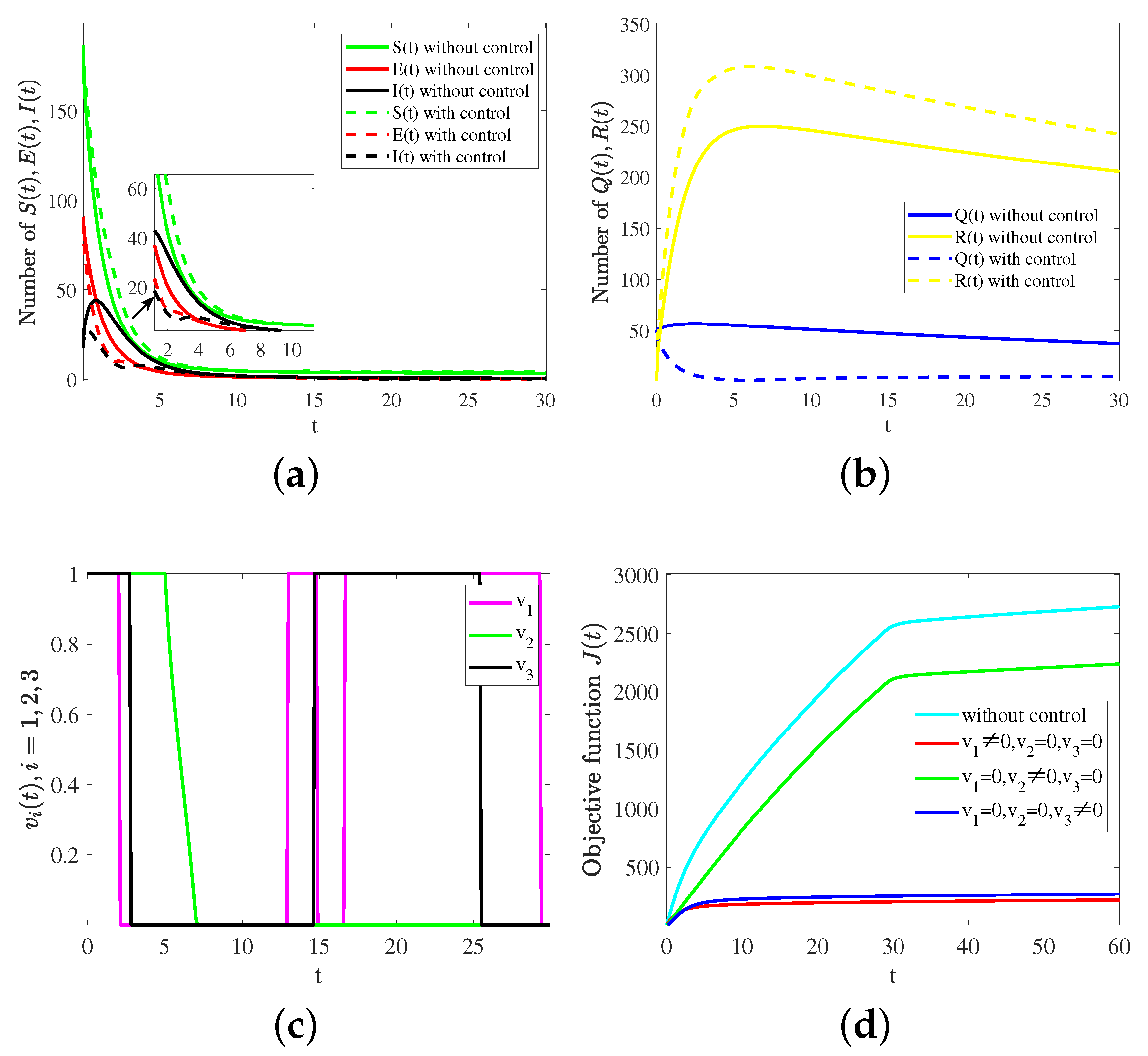
6. Simulation and Sensitivity Analysis
6.1. Numerical Analysis without Control Strategy
6.2. Numerical Analysis with Control Strategy
6.3. Sensitivity Analysis
7. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part I. Nature 1979, 280, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, J.Z. Analysis of an SIR model with bilinear incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 2390–2402. [Google Scholar]
- De-León, C.V. On the global stability of SIS, SIR and SIRS epidemic models with standard incidence. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2011, 12, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.X.; Liu, S.; Wang, H. Backward bifurcation of an epidemic model with standard incidence rate and treatment rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2008, 9, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.K.; Mondal, P.K. Global dynamics and bifurcation in a delayed SIR epidemic model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2011, 12, 2058–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, H.M. Analysis of a saturation incidence SVEIRS epidemic model with pulse and two time delays. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 214, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Teng, Z. Global asymptotic stability of a delayed SEIRS epidemic model with saturation incidence. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2008, 37, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M.; Anderson, R.M. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part II. Nature 1979, 280, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, V.; Serio, G. A generalization of the Kermack–Mckendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 1978, 42, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Q. Bifurcation analysis of an SIS epidemic model with saturated incidence rate and saturated treatment function. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 226, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Xue, D.; Pan, F. Dynamic analysis and optimal control for a fractional-order delayed SIR epidemic model with saturated treatment. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 2022, 137, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.H.; Li, C.P.; Lu, J.H. Stability analysis of linear fractional differential system with multiple time delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 2007, 48, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbas, A.A.; Srivastava, H.M.; Trujillo, J.J. Theory and Application of Fractional Differential Equations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 204. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Petráš, I.; Terpák, J. Fractional calculus as a simple tool for modeling and analysis of long memory process in industry. Mathematics 2019, 7, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.H. Short memory principle and a predictor-corrector approach for fractional differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 206, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Wu, H.Q.; Gao, J.D. Exponential synchronization for variable-order fractional discontinuous complex dynamical networks with short memory via impulsive control. Neural. Netw. 2022, 148, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnathambi, R.; Rihan, F.A. Stability of fractional-order prey-predator system with time-delay and Monod-Haldane functional response. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 92, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Zhao, W.C. Stability and bifurcation control analysis of a delayed fractional-order eco-epidemiological system. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 2022, 137, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, H. Applications of Fractional Calculus in Physics; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, Y.; Islam, S. Complex dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with saturated incidence rate and treatment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 493, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, I. Fractional-Order Nonlinear Systems: Modeling, Analysis and Simulation; Springer Science Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Odibat, Z.M.; Shawagfeh, N.T. Generalized Taylor’s formula. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 86, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S. Electric Conductance of Biological Systems; Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1933; Volume 1, pp. 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedian, M.; Khalighi, M.; Azimi-Tafreshi, N.; Jafari, G.R.; Ausloos, M. Memory effects on epidemic evolution: The susceptible-infected-recovered epidemic model. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 022409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. A study on eco-epidemiological model with fractional operators. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2022, 156, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.; Brito da Cruz, A.M.C.; Martins, N.; Monteiro, M.T.T. An epidemiological MSEIR model described by the Caputo fractional derivative. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2018, 7, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Mahata, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Roy, B.; Salimi, M.; Ahmadian, A. Study of fractional order SEIR epidemic model and effect of vaccination on the spread of COVID-19. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2022, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameena, I.; Baleanuc, D.; Ali, H.M. An efficient algorithm for solving the fractional optimal control of SIRV epidemic model with a combination of vaccination and treatment. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2020, 137, 109892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabti, A.; Ghanbari, B. Global stability analysis of a fractional SVEIR epidemic model. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2021, 44, 8577–8597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, M.; Ledesma-Araujo, A.; Gordillo, L.; Marín, J.F. Mutation and SARS-CoV-2 strain competition under vaccination in a modified SIR model. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2023, 166, 112964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.N.; Mbalawata, I.S.; Mirau, S.S.; Masandawa, L. Mathematical modeling of vaccination as a control measure of stress to fight COVID-19 infections. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2023, 166, 112920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislavsky, A.A. Memory effects and macroscopic manifestation of randomness. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Y. Stability and asymptotic properties of the SEQIR epidemic model. Appl. Math. Lett. 2023, 141, 108604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Jana, S.; Nandi, S.K.; Khatua, A.; Adak, S.; Kar, T.K. A model based study on the dynamics of COVID-19: Prediction and control. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2020, 136, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diethelm, K. Monotonicity of functions and sign changes of their caputo derivatives. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2016, 19, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Y.L.; Teng, Z. Dynamical analysis of a fractional-order predator-prey model incorporating a prey refuge. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 54, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Podlubny, I. Stability of fractional-order nonlinear dynamic systems: Lyapunov direct method and generalized mittag-leffer stability. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 59, 1810–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Driessche, P.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahrouz, A.; Omari, L.; Kiouach, D. Global analysis ofa deterministic and stochastic non-linear SIRS epidemic model. Nonlinear Anal-Model. 2011, 16, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Majee, S.; Jana, S.; Das, D.K.; Kar, T.K. Global dynamics of a fractional-order HFMD model incorporating optimal treatment and stochastic stability. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2022, 161, 112291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanas’ev, V.N.; Kolmanowskii, V.B.; Nosov, V.R. Mathematical Theory of Control Systems Design; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Li, X. A note on global stability of an SEI epidemic model with acute and chronic stages. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 196, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Chen, D.; Feng, H.; Zhu, H.; Lv, H. Digital twins in unmanned aerial vehicles for rapid medical resource delivery in epidemics. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 25106–25114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Peng, Z.; Hu, J. On model identification based optimal control and it’s applications to multi-agent learning and control. Mathematics 2023, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, R.; Khan, Y.; Islam, S. A mathematical analysis of Pine Wilt disease with variable population size and optimal control strategies. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2018, 108, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L.; Hu, R.; Yang, B. Endoscope image mosaic based on pyramid ORB. Biomed. Signal Proces. 2022, 71, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Hu, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Improved feature point pair purification algorithm based on SIFT during endoscope image stitching. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 840594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. 2D/3D multimode medical image registration based on normalized cross-correlation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göllmann, L.; Kern, D.; Maurer, H. Optimal control problems with delays in state and control variables subject to mixed control-state constraints. Optim. Control Appl. Meth. 2009, 30, 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, W.H.; Rishel, R.W. Deterministic and Stochastic Optimal Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Lu, T. Dynamic analysis and optimal control of a fractional order model for hand-foot-mouth disease. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 64, 565–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, D.L. Differential Equations: Classical to Controlled; Mathematics in Science and Engineering; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Baskonus, H.M.; Bulut, H. On the numerical solutions of some fractional ordinary differential equations by fractional Adams-Bashforth-Moulton method. Open Math. 2015, 13, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K.; Kar, T.K. Global dynamics of a tuberculosis model with sensitivity of the smear microscopy. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2021, 146, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remark 1 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | [1 0.9 0.8 0.7] |
| Remark 2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | [1 0.9 0.8 0.7] |
| Remark 3 | 2 | [0 0.3 0.6 0.9] | [0 0.3 0.6 0.9] | 0.95 |
| Remark 4 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 1 |
| Remark 5 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.95 |
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity index value | +0.7839 | +0.8276 | −0.6674 | −0.1750 | −0.1707 |
| Parameters | |||||
| Sensitivity index value | +0.1224 | −0.5220 | −0.06522 | +0.1363 | +0.1664 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, D.; Li, Q.; Zhao, W. Stability and Optimal Control of a Fractional SEQIR Epidemic Model with Saturated Incidence Rate. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7070533
Sun D, Li Q, Zhao W. Stability and Optimal Control of a Fractional SEQIR Epidemic Model with Saturated Incidence Rate. Fractal and Fractional. 2023; 7(7):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7070533
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Deguo, Qing Li, and Wencai Zhao. 2023. "Stability and Optimal Control of a Fractional SEQIR Epidemic Model with Saturated Incidence Rate" Fractal and Fractional 7, no. 7: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7070533
APA StyleSun, D., Li, Q., & Zhao, W. (2023). Stability and Optimal Control of a Fractional SEQIR Epidemic Model with Saturated Incidence Rate. Fractal and Fractional, 7(7), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7070533






