A Study of Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm: Take Fracmemristor into Swarm Intelligent Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- Section 2 gives some of the mathematical and physical knowledge needed for this paper. Section 2 concentrates on the mathematical principles of fractional memories and how to construct the capacitive scale of v-order chains. There are also several properties contained in the fractional-order memristor.
- (b)
- The formulation of the suggested fractional-order memristive ant colony algorithm (FMCA) is described in Section 3. By designing a fractional-order memristor for each ant to recall the future transfer probability information, a memristive physical system based on fracmemristor is conferred onto the ant. Based on the information placed by the fractional-order memristor (fracmemristor), the non-local characteristic of the fractional order is employed to enable the ant to forecast possibly better probability transfer pathways in the future. We also perform mathematical arguments to ensure that the FMAC converges.
- (c)
- The experimental findings are presented in Section 4. First, we fixed the other parameters of the FMAC and experimentally determined the order range of the fracmemristor. Then, we compared the convergence speed of FMAC with those of ACO, MMAS, and FACA. Finally, we compared the optimal results of several algorithms for the different TSP problems.
2. Background
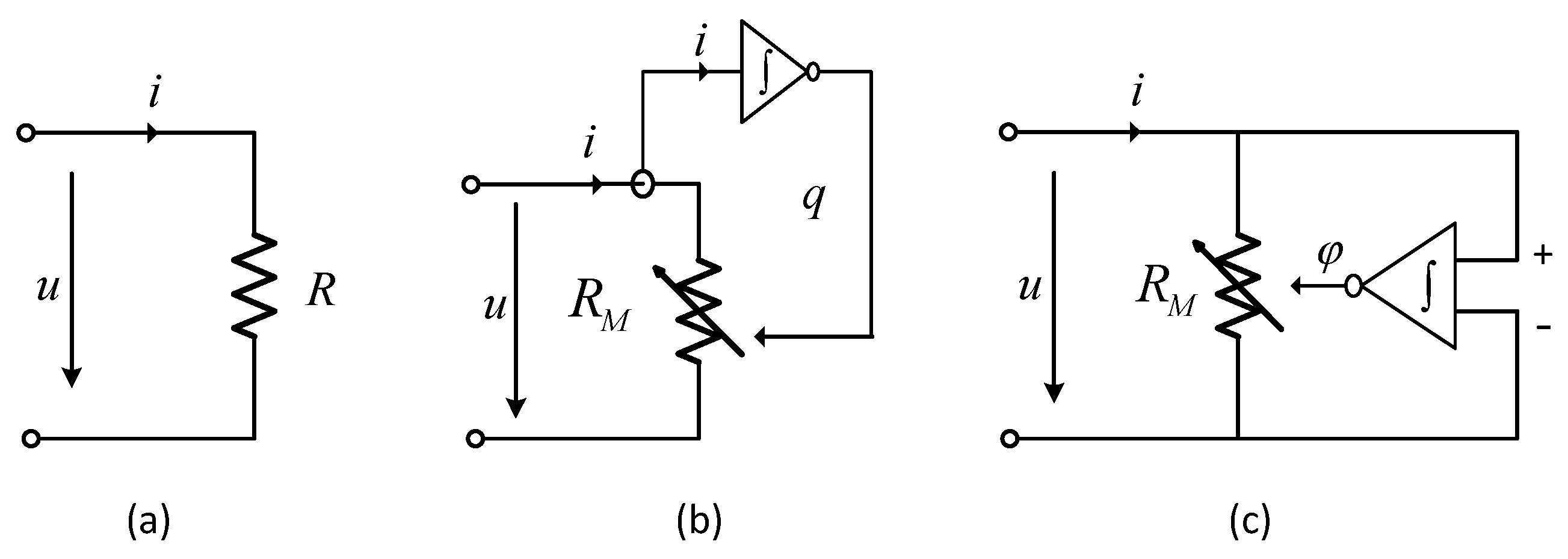
2.1. Memristor
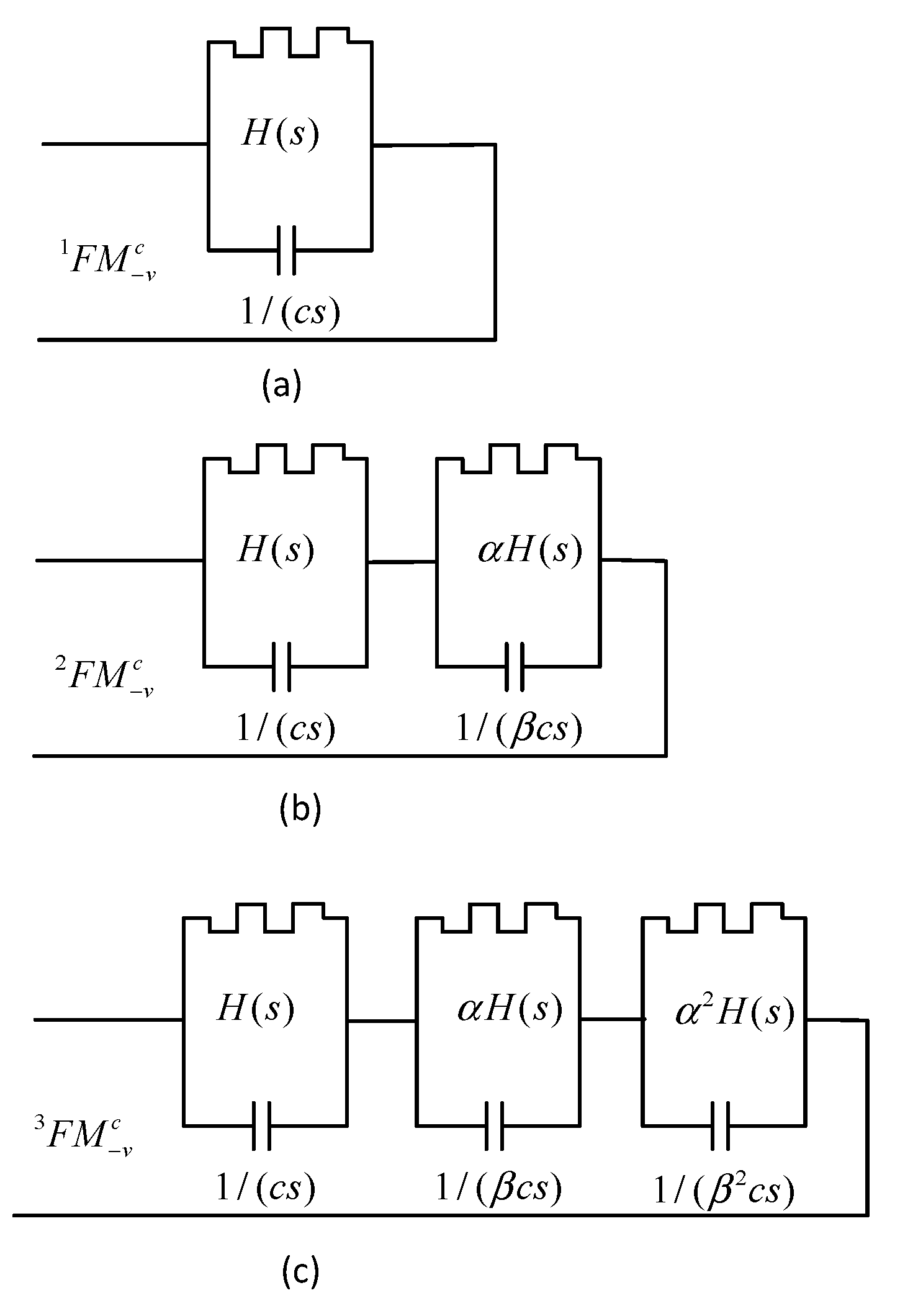
2.2. Fracmemristor
3. Algorithm
3.1. Physical Memristive System of Transition Probability Series in FMAC
3.2. Proposed Iterative Algorithm of the Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm (FMCA)
| Algorithm 1: Proposed Iterative Algorithm of Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm (FMCA) | |
| 1: | Initialization: |
| 2: | Set the number of iterations ; |
| 3: | Initialize ant colony algorithm (ACO) parameters,, , , , , , , , , , , and ; |
| 4: | Place each ant in randomly, ; |
| 5: | for each edge , do |
| 6: | Set ; |
| 7: | Set ; |
| 8 | End |
| 9: | Initialize low-pass filtering fracmemristor (LCSF), |
| 10: | Initialize the parameter of LCSF: |
| 11: | Repeat |
| 12: | for each ant population, number the population from 1 to , |
| 13: | for each ant, number the ant from 1 to , do |
| 14: | Set ; |
| 15: | Repeat |
| 16: | Take transfer probability series of ant into LCSF |
| 17: | the ant travels from the node to the node; |
| 18: | than set ; |
| 19: | compute all transfer probability in |
| 20: | Until completes travelling all nodes in ; |
| 21: | compute and rank , |
| 22: | return the shortest path ; |
| 23: | end |
| 24: | for the edge in graph, |
| 25: | update pheromone concentration; |
| 26 | then update the transfer probability |
| 27: | end |
| 28: | end |
| 29: | Compute the shortest way of parts of ants; |
| 30: | Update the pheromone concentration on the shortest visited way with ; |
| 31: | Set ; |
| 32: | until the maximum number of cycles is reached; |
| 33: | Compute . |
3.3. Convergence Analysis of FMCA from a Mathematical Point of View
4. Experiment of FMAC in TSP Problem
4.1. Effect of Fractional-Order Coefficients V in FMAC
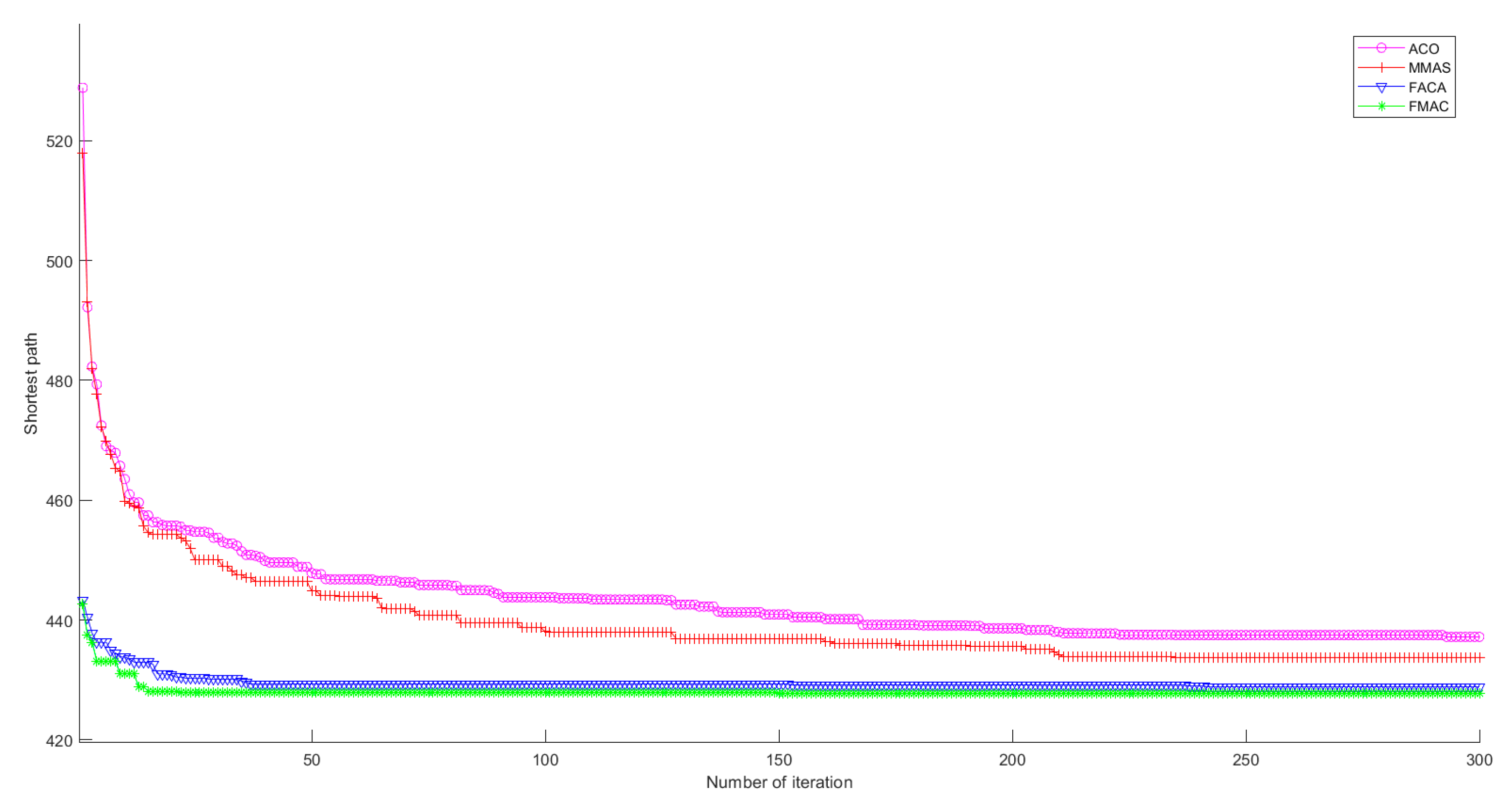
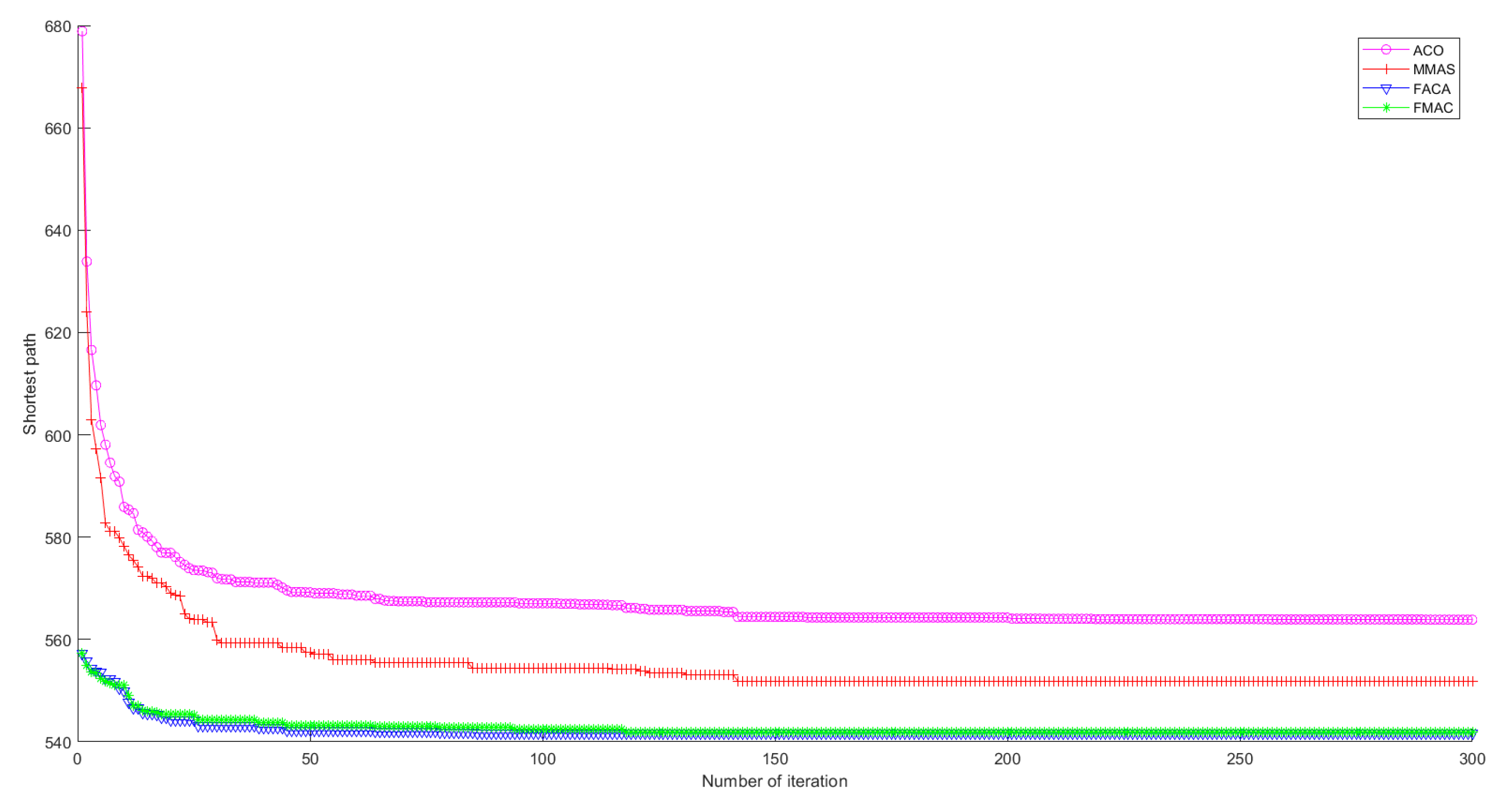
4.2. FMAC Convergence Experiments
4.3. FMAC and Various Improved Ant Colony Algorithms for Comparison
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discusion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorigo, M. Optimization, Learning and Natural Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Caro, G.D. Ant colony optimization: A new meta-heuristic. In Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; Volume 1472, pp. 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Gambardella, L. Ant colony system: A cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniezzo, V.; Colorni, A. The ant system applied to the quadratic assignment problem. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 1999, 11, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V.; Colorni, A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 1996, 26, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzle, T.; Hoos, H. MAX-MIN Ant System and local search for the traveling salesman problem. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 13–16 April 1997; pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Gambardella, L.M. A Study of Some Properties of Ant-Q. In Proceedings of the PPSN Fourth International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, Berlin, Germany, 22–26 September 1996; pp. 656–665. [Google Scholar]
- Taillard, E.D. FANT: Fast Ant System; Technical Report; Istituto Dalle Molle Di Studi Sull Intelligenza Artificiale: Lugano, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Roux, O.; Fonlupt, C.; Talbi, E.G.; Robilliard, D. ANTabu—Enhanced Version; Technical Report LIL-99-01; Laboratoire d’Informatique du Littorral, Université du Littoral: Calais, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kaji, T. Approach by ant tabu agents for Traveling Salesman Problem. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, e-Systems and e-Man for Cybernetics in Cyberspace (Cat. No. 01CH37236), Tucson, AZ, USA, 7–10 October 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullnheimer, B.; Kotsis, G.; Strauß, C. Parallelization Strategies for the Ant System. In High Performance Algorithms and Software in Nonlinear Optimization. Applied Optimization; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniezzo, V.; Carbonaro, A. An ANTS heuristic for the frequency assignment problem. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2000, 16, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, G.; Sinclair, M. Ant colony optimisation for virtual-wavelength-path routing and wavelength allocation. In Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; Volume 3, p. 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, I.; Matsui, S. Improving the performance of ACO algorithms by adaptive control of candidate set. In Proceedings of the 2003 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, CEC’03, Canberra, ACT, Australia, 8–12 December 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, I.; Matsui, S. Boosting ACO with a Preprocessing Step. In Applications of Evolutionary Computing; Cagnoni, S., Gottlieb, J., Hart, E., Middendorf, M., Raidl, G.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G. Ant colony optimization algorithm with random perturbation behavior to the problem of optimal unit commitment with probabilistic spinning reserve determination. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2004, 69, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Memristor-The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O.; Kang, S.M. Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ventra, M.; Pershin, Y.V.; Chua, L.O. Circuit Elements With Memory: Memristors, Memcapacitors, and Meminductors. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sah, M.P.; Yang, C.; Cho, S.; Chua, L.O. Memristor Emulator for Memristor Circuit Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2012, 59, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Sah, M.P.; Kim, H.; Chua, L.O. Three Fingerprints of Memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 3008–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.; Rakkiyappan, R.; Cao, J. Finite-time synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based neural networks with time delays. Neural Netw. 2016, 73, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, P. On the periodic dynamics of memristor-based neural networks with time-varying delays. Inf. Sci. 2014, 279, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkare, S.; Panwar, N.; Kumbhare, P.; Das, B.; Ganguly, U. PCMO-Based RRAM and NPN Bipolar Selector as Synapse for Energy Efficient STDP. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Lorival, J.-E.; Marc, F.; Cabaret, T.; Jousselme, B.; Derycke, V.; Klein, J.-O.; Maneux, C. Multiscaled Simulation Methodology for Neuro-Inspired Circuits Demonstrated with an Organic Memristor. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 2017, 4, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, K.B.; Spanier, J. The Fractional Calculus: Integrations and Differentiations of Arbitrary Order; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, Some Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, L. Image Enhancement Based on Rough Set and Fractional Order Differentiator. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Ren, J.; Gui, Q. Adaptive Fractional Image Enhancement Algorithm Based on Rough Set and Particle Swarm Optimization. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Yan, H.; He, H. Multi-focus image fusion based on fractional-order derivative and intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2020, 21, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.-X.; Zhang, X. Injected Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via L1 Decomposition Model and Guided Filtering. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2022, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, X. Adaptive fractional multi-scale edge-preserving decomposition and saliency detection fusion algorithm. ISA Trans. 2020, 107, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeller, R.C. Applications of the Fractional Calculus to the Theory of Viscoelastinode. J. Appl. Mech. 1984, 51, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossikhin, Y.A.; Shitikova, M.V. Applications of Fractional Calculus to Dynamic Problems of Linear and Nonlinear Heredi-Tary Mechanics of Solids. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1997, 50, 15–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsafty, A.H.; Hamed, E.M.; Fouda, M.E.; Said, L.A.; Madian, A.H.; Radwan, A.G. Study of fractional flux-controlled memristor emulator connections. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), Thessaloniki, Greece, 7–9 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Si, G.; Diao, L.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y. Generalized modeling of the fractional-order memcapacitor and its character analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 59, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.G.; Moaddy, K.; Hashim, I. Amplitude Modulation and Synchronization of Fractional-Order Memristor-Based Chua’s Circuit. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 2013, 758676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.A.; Said, L.A.; Radwan, A.G.; Soliman, A.M. General fractional order mem-elements mutators. Microelectron. J. 2019, 90, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafagna, D.; Grassi, G. On the simplest fractional-order memristor-based chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 70, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.-F. Measurement Units and Physical Dimensions of Fractance-Part I: Position of Purely Ideal Fractor in Chua’s Axiomatic Circuit Element System and Fractional-Order Reactance of Fractor in Its Natural Implementation. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 3379–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.-F. Measurement Units and Physical Dimensions of Fractance-Part II: Fractional-Order Measurement Units and Physical Dimensions of Fractance and Rules for Fractors in Series and Parallel. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 3398–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.-F.; Yuan, X.; Yu, B. Analog Circuit Implementation of Fractional-Order Memristor: Arbitrary-Order Lattice Scaling Fracmemristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-Y.; Pu, Y.-F.; Liu, B.; Yu, B.; Zhou, J.-L. A mathematical analysis: From memristor to fracmemristor. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 060204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.-F.; Wang, J. Fractional-order global optimal backpropagation machine trained by an improved fractional-order steepest descent method. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2020, 21, 809–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couceiro, M.; Sivasundaram, S. Novel fractional order particle swarm optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 283, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.-F.; Siarry, P.; Zhu, W.-Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, N. Fractional-Order Ant Colony Algorithm: A Fractional Long Term Memory Based Cooperative Learning Approach. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 69, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSPLIB. Standard Test Set for TSP Problem of Universität Heidelberg. Available online: http://comopt.ifi.uni-heidelberg.de/software/TSPLIB95 (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Gülcü, Ş.; Mahi, M.; Baykan, Ö.K.; Kodaz, H. A parallel cooperative hybrid method based on ant colony optimization and 3-Opt algorithm for solving traveling salesman problem. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 5 | |
| 0.1 | |
| 0.2 | |
| 1.7 |
| −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| −0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.6563 | 0.6016 | 0.5640 | 0.5358 | 0.5134 | 0.4951 |
| −0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.375 | 0.3125 | 0.2734 | 0.2461 | 0.2256 | 0.2095 |
| −0.25 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.1563 | 0.1172 | 0.0952 | 0.0809 | 0.0708 | 0.0632 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.25 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.0938 | 0.0547 | 0.0376 | 0.0282 | 0.0223 | 0.0183 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 0.0625 | 0.0391 | 0.0273 | 0.0205 | 0.0161 |
| 0.75 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.0938 | 0.0391 | 0.0220 | 0.0143 | 0.0101 | 0.0076 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Minimum Solution | Maximum Solution | Average Solution | Root Mean Square Error | Relative Error (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.75 | 21,282 | 22,064 | 21,673.7 | 450.83 | 1.85 |
| −0.5 | 21,282 | 21,976 | 21,550.3 | 327.16 | 1.37 |
| −0.25 | 21,282 | 21,518 | 21,483.7 | 136.19 | 0.39 |
| 0.0 | 21,282 | 21,926 | 21,582.4 | 373.54 | 1.48 |
| 0.25 | 21,282 | 21,926 | 21,571.6 | 346.77 | 1.23 |
| 0.5 | 21,282 | 21,873 | 21,490.4 | 201.86 | 0.51 |
| 0.75 | 21,282 | 21,508 | 21,301.5 | 54.12 | 0.13 |
| 1 | 21,282 | 21,703 | 21,432.7 | 97.16 | 0.32 |
| Optimization Algorithms | Best Solution | Average Solution | Time Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | |||
| ACO [2] | 7542 | 7657.2 | 43.24 |
| MMAS [6] | 7542 | 7596.3 | 56.48 |
| PACO-3opt [49] | 7542 | 7542 | NA |
| FACA [47] | 7542 | 7542 | 119.57 |
| FMAC (ours) | 7542 | 7542 | 75.17 |
| (b) | |||
| ACO [2] | 437 | 443.5 | 57.84 |
| MMAS [6] | 431 | 436.1 | 75.34 |
| PACO-3opt [49] | 426 | 426.3 | NA |
| FACA [47] | 426 | 427.4 | 156.77 |
| FMAC (ours) | 426 | 426.8 | 92.38 |
| (c) | |||
| ACO [2] | 544 | 563.6 | 129.04 |
| MMAS [6] | 537 | 552.9 | 167.58 |
| PACO-3opt [49] | 538 | 539.85 | NA |
| FACA [47] | 538 | 541.0 | 354.22 |
| FMAC (ours) | 538 | 541.3 | 186.18 |
| (d) | |||
| ACO [2] | 648 | 662.1 | 274.62 |
| MMAS [6] | 634 | 651.3 | 358.81 |
| PACO-3opt [49] | 629 | 630.5 | NA |
| FACA [47] | 629 | 630.6 | 758.10 |
| FMAC (ours) | 629 | 630.39 | 489.37 |
| (e) | |||
| ACO [2] | 1212 | 1216.7 | 300.71 |
| MMAS [6] | 1212 | 1214.5 | 383.83 |
| PACO-3opt [49] | 1213 | 1217.1 | NA |
| FACA [47] | 1211 | 1213.0 | 758.17 |
| FMAC (ours) | 1212 | 1214.1 | 512.09 |
| (f) | |||
| ACO [2] | 678 | 686.3 | 119.76 |
| MMAS [6] | 675 | 682.6 | 155.10 |
| PACO-3opt [49] | 676 | 677.85 | NA |
| FACA [47] | 675 | 680.1 | 323.82 |
| FMAC (ours) | 675 | 679.2 | 219.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, W.; Pu, Y. A Study of Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm: Take Fracmemristor into Swarm Intelligent Algorithm. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7030211
Zhu W, Pu Y. A Study of Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm: Take Fracmemristor into Swarm Intelligent Algorithm. Fractal and Fractional. 2023; 7(3):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7030211
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Wuyang, and Yifei Pu. 2023. "A Study of Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm: Take Fracmemristor into Swarm Intelligent Algorithm" Fractal and Fractional 7, no. 3: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7030211
APA StyleZhu, W., & Pu, Y. (2023). A Study of Fractional-Order Memristive Ant Colony Algorithm: Take Fracmemristor into Swarm Intelligent Algorithm. Fractal and Fractional, 7(3), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7030211









