Abstract
In this paper, we consider the time-fractional two-mode coupled Burgers equation with the Caputo fractional derivative. A modified homotopy perturbation method coupled with Laplace transform (He-Laplace method) is applied to find its approximate analytical solution. The method is to decompose the equation into a series of linear equations, which can be effectively and easily solved by the Laplace transform. The solution process is illustrated step by step, and the results show that the present method is extremely powerful for fractional differential equations.
1. Introduction
The classical Burgers equation, introduced by Bateman [1], is a fundamental model in viscous fluid mechanics. In fact, it is widely used to express different physical phenomenon like shock waves, dispersion in porous media, modelling of gas dynamics, traffic flow and so on [2,3,4,5,6]. The partial differential equations that are first-order in time model the right-moving unidirectional waves in the positive x-direction. A new nonlinear PDE of second-order in time which model both left- and right- going waves are called two-mode equations. Korunsky [7] was the first one to introduce two-mode KdV equation in the scaled form as
where is a field function and represents the height of the water’s free surface above a flat bottom. and are the parameters of nonlinearity, dispersion and phase velocities respectively. This two-mode KdV equation describes the propagation of two different wave modes in the same direction simultaneously, with the same dispersion relation but different parameters of phase velocities, nonlinearity and dispersion. In 2016, Wazwaz [8] used the sense of Korunsky to introduce a new two-mode Burgers equation (TMBE) in the scaled for as
where are as defined earlier.
However, it is very rare that a real life model can be represented by a single partial differential equation, therefore, a couple of partial differential equations are required to provide a complete model. This idea of Korunsky and Wazwaz was further generalized by Jaradat [9], where he introduced a new two-mode coupled Burgers equation (TMCBE) which has the form
It can be observed that if we put in Equation (1) and integrate with respect to the variable t once, we obtain the standard coupled Burgers equation (see [10]).
The study of coupled Burgers equations is very important in the sense that it describes the sedimentation of polydispersive suspension under the effect of gravity [11].
Fractional differential equations involve real or complex order derivatives. They provide more accurate models of the real world problems than the integer order differential equations (for detail [12,13,14,15]). Due to the vast applications of fractional calculus in various disciplines of Science and Engineering, there has been significant growth in its literature in the last few decades. In this paper, we extend the time-derivative in Equation (1) with the fractional derivative. Thus, for , the modified fractional version of Equation (1) obtained is given by the following.
where the fractional derivative may be considered as Caputo fractional derivative as defined in Definition 2 in Section 2. The Equation (2) can be rewritten as
Explicit solutions to the fractional problems involving Burgers equation are rare and possibly non-existent in the literature. Therefore, it is more desirable to look for new techniques to get solutions of fractional differential equations. Methods like Adomian Decomposition Method, Iteration Method, Homotopy Analysis Method, Homotopy Perturbation Method, and Laplace Transform Methods are some of very powerful and useful techniques [16,17,18,19,20,21]. The combination of Laplace Transform and Homotopy Perturbation Method is a new tool which is being used to solve linear and nonlinear fractional differential equations [22].
The paper is organised as follows: Section 2 consists of the definitions and theory required for rest of the paper. In Section 3, we apply Laplace homotopy perturbation method to the considered nonlinear time-fractional model. In Section 4, we discuss a concrete example of main equation and demonstrate the solution graphically. The last section concludes this paper.
2. Definitions and Mathematical Preliminaries
There are various versions of fractional derivatives given by different authors and new definitions have been proposed in recent decades. Here we give the Caputo definition of fractional derivative. Please refer to the books [23,24,25] for the detailed theory of fractional calculus.
Definition 1.
The Riemann-Liouville fractional integral of order ξ for a locally integerable function f of two variables is defined by
and
where Γ denotes the Gamma function.
Definition 2.
The Caputo fractional derivative of order ξ of a m-times continuously differentiable function which is locally integerable function f is defined by
where .
In particular, for , we have
Definition 3.
The Laplace transform of the Caputo fractional derivative is given by
In particular, for , we have
3. Existence and Uniqueness
Let be a bounded interval of real numbers and T be a constant such that . We establish the existence and uniqueness of the solution of the system (3) in this section. Consider the Banach space of real-valued continuous functions defined on (that is, ) with norm given by
If we assume that , , for , then satisfy the Lipschitz condition. For, let and be any two arbitrary functions bounded above, then we have
where is the Lipschitz constant. Similarly, it can be shown that there exist Lipschitz constants and for and respectively. Thus, we note that if and are bounded above, then
where are Lipschitz constants.
3.1. Existence of the Solution
Using the definition of integral operator (1), we construct the following iterative formula for the system (4)
Let the differences between successive terms be given by and , then we have
Now, we consider
Let , then
Therefore, exists and is smooth. Similarly, it can be shown that exists and is smooth.
3.2. Uniqueness
Let and are two solutions, then
that is
If we assume that , then
Similarly, we can prove the uniqueness of .
Hence, system (3) has a unique solution.
4. Solution of Two Mode Coupled Burgers Equations
We consider the nonlinear coupled fractional partial differential Equation (3) and apply Laplace Homotopy Perturbation Method [19,26,27,28]. Now, applying Laplace transform in Equation (3) with respect to the variable t and using the Laplace transform of Caputo fractional derivative, we get
where , . We construct the homotopy for the Equation (6) as follows.
Now comparing the corresponding powers of h in (10), we get the following homotopies.
and so on. In fact, we can rewrite the above system of equations as
for
Now applying the inverse laplace transform in each of the above equations, we obtain and so on.
5. Convergence Analysis
We discuss the convergence of the solution of given problem in the following theorem.
Theorem 1.
Proof.
Let and be the sequence of partial sums of the series and respectively. For all , we have
So that
which implies
Now, implies that , then
Since, is bounded, we get
Thus the sequence is Cauchy in the Banach space and hence convergent. Similarly, we can show that the sequence is convergent. Hence, that the infinite series and converge to and respectively. □
6. An Illustrative Example
We consider the nonlinear coupled fractional partial differential Equation (3) along with the initial conditions given as
Now solving the system (3) by Laplace Homotopy Perturbation Method, we have
Taking inverse Laplace transform of above equations, we get
Next, we have
Taking inverse Laplace transform, we get
Thus, we can find the rest of the terms in a similar manner.
Hence, the approximate solution is given by and .
As we can see that the evaluation of the terms becomes cumbersome, we further simplify the fractional two-mode coupled burgers equations by taking
with initial conditions
Applying LHPM, we have
and so on. Now we apply inverse Laplace transform in each of the above equations to get the as follows,
and so on. Thus, the approximate solution is given by
Following the similar arguments give us
We note that the approximate solutions and both tend to as which is the exact solution of the standard coupled burgers equation.
The graphical representation of an approximate solutions for different values of are given in Figure 1. Furthermore, the comparison of Figure 1 and Figure 2 shows that the approximate solutions calculated by LHPM is very close to the exact solution as is very close to 1 because both graphs are similar.
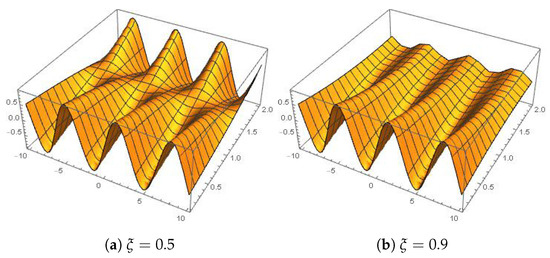
Figure 1.
Approximate solutions for and .
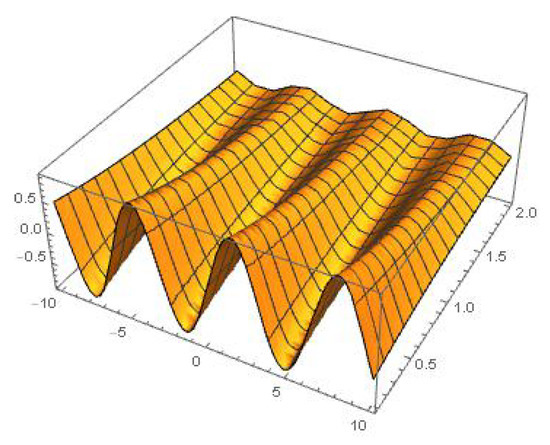
Figure 2.
Exact solution.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we have solved time-fractional two-mode coupled Burgers equations using Laplace homotopy perturbation method. An illustrative example has been solved with initial conditions. It has been shown by a well-known example that the given method is very efficient and reliable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.G.; Formal analysis, R.S., P.G. and A.A.; Investigation, R.S., P.G. and J.-H.H.; Methodology, J.-H.H. and A.A.; Software, R.S.; Supervision, J.-H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
There is no data used in the paper.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to reviewers for improvement in the paper. This work was supported by Taif University Researcher Supporting Project number (TURSP- 2020/326), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present paper.
References
- Bateman, H. Some recent researches on the motion of fluids. Mon. Weather Rev. 1915, 43, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, J.M. A Mathematical Model Illustrating the Theory of Turbulence. In Advances in Applied Mechanics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1948; Volume 1, pp. 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momani, S. Non-perturbative analytical solutions of the space-and time-fractional Burgers equations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2006, 28, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawashdeh, M.S. A reliable method for the space-time fractional Burgers and time-fractional Cahn-Allen equations via the FRDTM. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 2017, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, K.M.; Al-Sharif, E.H.F. Analytical study for time and time-space fractional Burgers’ equation. Adv. Differ. Equa. 2017, 2017, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, N. Burgers equation with a fractional derivative, hereditary effects on nonlinear acoustic waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 225, 631–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, S.V. Soliton solutions for a second-order KdV equation. Phys. Lett. 1994, 185, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazwaz, A.M. A two-mode Burgers equation of weak shock waves in a fluid: Multiple kink solutions and other exact solutions. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2016, 3, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, H.M. Two-mode coupled Burgers equation:Multiple-kink solutions and other exact solutions. Alex. Eng. J. 2017, 57, 2151–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, T.A.; Yavuz, M.; Bulut, H.; Baskonus, H.M. Investigation of the fractional coupled viscous Burgers’ equation involving Mittag-Leffler kernel. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 527, 121126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esipov, S.E. Coupled Burgers equations: A model of polydispersive sedimentation. Phys. Rev. 1995, 52, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkahtani, B.S.T.; Alkahtani, J.O.; Dubey, R.S.; Goswami, P. The solution of modified fractional Bergman’s minimal blood glucose-insulin model. Entropy 2017, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaurasia, V.B.L.; Dubey, R.S. Analytical solution for the differential equation containing generalized fractional derivative operators and Mittag-Leffler-type function. Int. Sch. Res. Not. Isrn Appl. Math. 2011, 2011, 682381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, R.S.; Goswami, P. Analytical Solution of the Nonlinear Diffusion Equation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrahili, M.; Dubey, R.S.; Shafay, A. Inclusion of Fading Memory to Banister Model of Changes In Physical Condition Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. 2020, 13, 881–888. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; An, H.-L. Numerical solutions of coupled Burgers equations with time- and space-fractional derivatives. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 200, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeleze, A.A.; Kilicman, A.; Taib, B.M. Note on the Convergence Analysis of Homotopy Perturbation Method for Fractional Partial Differential Equations. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 803902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouch, Z.; Yavuz, M.; Özdemir, N. Numerical solutions and synchronization of a variable-order fractional chaotic system. Math. Model. Numer. Simul. Appl. (MMNSA) 2021, 1, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- JHe, H. Homotopy perturbation technique. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1999, 178, 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, S.; Khalid, A.; Sultana, S.; Hammouch, Z.; Shah, R.; Alsharif, A.M. A novel analytical view of time-fractional Korteweg-De Vries equations via a new integral transform. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripacharasakullert, P.; Sawangtong, W.; Sawangtong, P. An Approximate Analytical Solution of the Fractional Multi-Dimensional Burgers Equation by the Homotopy Perturbation Method. Adv. Differ. Equations 2019, 2019, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H. Numerical Solution of Time-Fractional Klein–Gordon Equation by Using the Decomposition Methods. Asme-J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 11, 041015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.S.; Ross, B. An Introdution to the Fractional Calculus and Fractional Differential Equations; J. Willey & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kilbas, A.A.; Srivastava, H.M.; Trujillo, J.J. Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations; Elsevier North-Holland Science Publishers: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 204. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.H. Perturbation Methods: Basic and Beyond; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.H. Application of Homotopy Perturbation Method to Nonlinear Wave Equations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2005, 26, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; El-Dib, Y.O. The enhanced homotopy perturbation method for axial vibration of strings. Facta Univ. Mech. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).