Earthquake Insurance in California, USA: What Does Community-Generated Big Data Reveal to Us?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Google Trends: An Overview
2.2. The Method
3. Results and Discussion
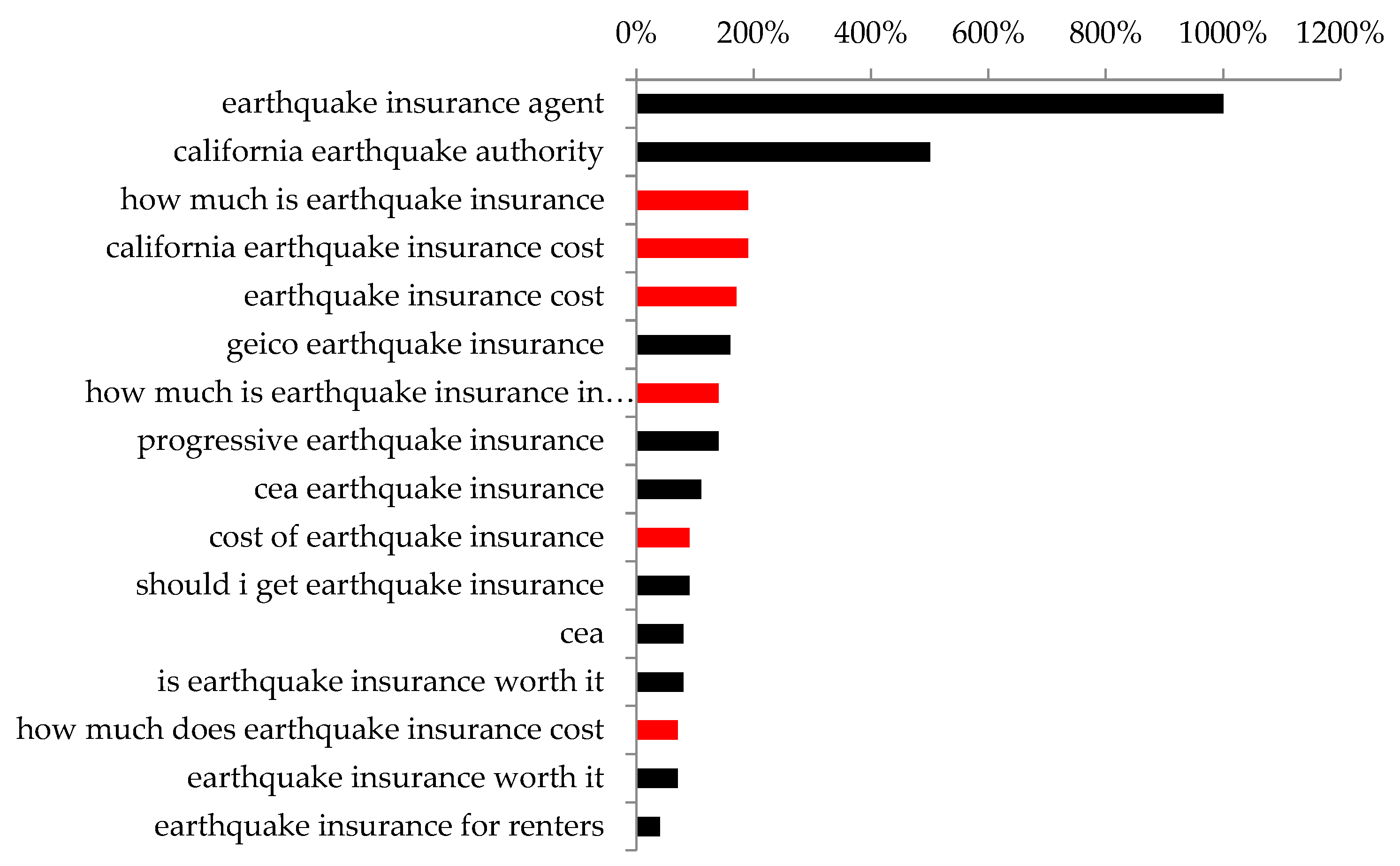
3.1. From the USA to California: A Progressive Zoomed in Analysis
3.2. A closer Analysis: The Earthquakes and Other Natural Hazards as Factors Sparking off Interest
4. Conclusions, Perspectives and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allan, R. Seconds before the big one. Sci. Am. 2011, 304, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellsworth, W.L. Earthquake history, 1769–1989. In The San Andreas Fault System, California; Wallace, R.E., Ed.; Paper 1515; U.S. Geological Survey Professional: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 153–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, R.E. General features. In The San Andreas Fault System, California; Wallace, R.E., Ed.; Paper 1515; U.S. Geological Survey Professional: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gizzi, F.T. Worldwide trends in research on the San Andreas Fault System. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 10893–10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppozada, T.; Branum, D. California earthquake history. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 47, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). A Study of Earthquake Losses in the San Francisco Bay Area—Data and Analysis; A Report Prepared for the Office of Emergency Preparedness; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Gladys, H.C.; Emmet, C. Denial of Disaster; Cameron and Co.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. USGS Earthquake Catalogue. Interactive Map. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/search (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- European Commission. Green Paper on the Insurance of Natural and Man-Made Disasters. 2013. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A52013DC0213 (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- United Nations. Paris Agreement. 2015. Available online: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- Zanjani, G. Public Versus Private Underwriting of Catastrophe Risk: Lessons from the California Earthquake Authority. In Risking House and Home: Disasters, Cities, Public Policy; Quigley, J.M., Rosenthal, L.A., Eds.; Berkeley Public Policy Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, D. An Overview of the California Earthquake Authority. Risk Manag. Insur. Rev. 2018, 21, 73–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Aki, K.; Boore, D.; Celebi, M.; Donnellan, A.; Hall, J.; Harris, R.; Hauksson, E.; Heaton, T.; Hough, S.; et al. The magnitude-6.7 Northridge, California, earthquake of 17-January-1994. Science 1994, 66, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- Kunreuther, H.; Roth, R. Paying the Price: The Status and Role of Insurance against Natural Disasters in the United States; Joseph Henry Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffee, D.M.; Russell, T. Behavioral Models of Insurance: The case of the California Earthquake Authority. University of California-Berkeley Working Paper. 2000, pp. 1–43. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.61.4972&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- CEA (California Earthquake Authority). Our Financial Strength. Available online: https://www.earthquakeauthority.com/About-CEA/Financials/CEA-Financial-Strength (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Pothon, A.; Gueguen, P.; Buisine, S.; Bard, P.Y. California earthquake insurance unpopularity: The issue is the price, not the risk perception. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2019, 19, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunreuther, H. Mitigating Disaster Losses through Insurance. J. Risk Uncertai. 1996, 12, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunreuther, H.; Pauly, M. Neglecting Disaster: Why Don’t People Insure against Large Losses? J. Risk Uncertain. 2004, 28, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschky, P.A.; Weck-Hannemann, H. Charity Hazard: A Real Hazard to Natural Disaster Insurance? Environ. Hazards 2007, 7, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, R.; Wagner, G.G. The Political Economy of Natural Disaster Insurance: Lessons from the Failure of a Proposed Compulsory Insurance Scheme in Germany. Eur. Environ. 2007, 17, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunreuther, H.C.; Ginsberg, R.; Miller, L.; Sagi, P.; Slovic, P.; Borkan, B.; Katz, N. Disaster Insurance Protection: Public Policy Lessons; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Slovic, P. Perception of risk. Science 1987, 236, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, R.; Hodgson, M. Earthquake insurance: Mandated disclosure and homeowner response in California. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 1992, 82, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, M.; Seko, M.; Sumita, K. Community rating, cross subsidies and underinsurance: Why so many households in Japan do not purchase earthquake insurance. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2010, 40, 544–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ge, J.; Zhao, J.; Nisar, S. New Consumers’ Perspective in Insuring Earthquakes. In Diversity of Managerial Perspectives from Inside China. Managing the Asian Century; Foo, C., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, F.T.; Porrini, D.; De Masi, F. Building a Natural Hazard Insurance System (NHIS): The Long-lasting Italian Case. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhman, S. Previous Experiences and Risk Perception: The Role of Transference. J. Educ. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2017, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.S.; Paton, D.; Johnston, D.M.; Ronan, K.R.; McClure, J. The role of prior experience in informing and motivating earthquake preparedness. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 22, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfman, N.C.; Cisternas, P.C.; Repetto, P.B.; Castañeda, J.V. Natural disaster preparedness in a multi-hazard environment: Characterizing the sociodemographic profile of those better (worse) prepared. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-W.; Hwang, H.; Chung, J.-B. Factors affecting awareness of preparedness after moderate earthquakes. An analysis of the Pohang earthquake in Korea. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2019, 29, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O. Science knowledge, world views, and information sources in social and cultural contexts: Making sense after a natural disaster. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1999, 36, 187–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.S.; Paton, D.; Johnston, D.M.; Ronan, K.R. Salient beliefs about earthquake hazards and household preparedness. Risk Anal. 2013, 33, 1710–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, H.A.; Mylonakis, E. Google trends: A web-based tool for real-time surveillance of disease outbreaks. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, N.; Han, C.Y. Country-Specific Interests towards Fall Detection from 2004–2021: An Open Access Dataset and Research Questions. Data 2021, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preis, T.; Moat, H.; Stanley, H. Quantifying Trading Behavior in Financial Markets Using Google Trends. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önder, I. Forecasting tourism demand with Google trends: Accuracy comparison of countries versus cities. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 19, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.J.; Wilby, R.L.; Matthews, T.; Murphy, C. The utility of Google Trends as a tool for evaluating flooding in data-scarce places. Area 2022, 54, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, J.; Park, J.; Shao, W.; Song, J.; Kim, J.; Gizzi, F.T.; Porrini, D.; Suh, Y.J. Data-driven modeling reveals the Western dominance of global public interest in earthquakes. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, F.T.; Kam, J.; Porrini, D. Time windows of opportunities to fight earthquake under-insurance: Evidence from Google Trends. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2020, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavragani, A.; Ochoa, G. Google Trends in Infodemiology and Infoveillance: Methodology Framework. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2019, 5, e13439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAQ about Google Trends Data. Available online: https://support.google.com/trends/answer/4365533?hl=en (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- PPIC (Public Police Institute of California). California’s Population. Available online: https://www.ppic.org/publication/californias-population/ (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- USCB United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts. Statistics on Population of California. 2021. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/CA (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- USGS. ANSS Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog (ComCat). Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/data/comcat/ (accessed on 2 April 2022).
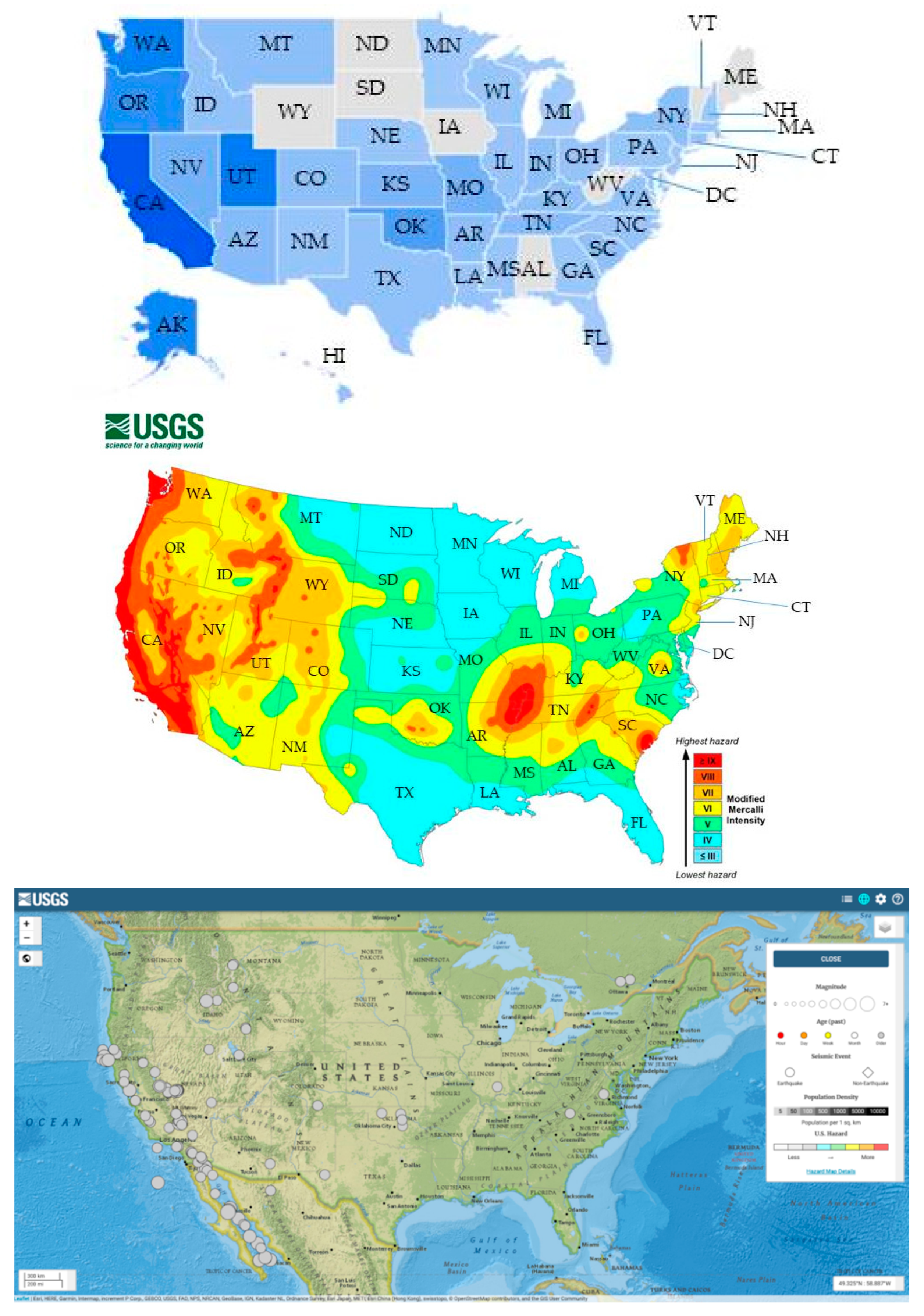
- USGS. Seismic Hazard Map Showing the Intensity of Potential Earthquake Ground Shaking That Has a 2% Change of Occurring in 50 Years. 2016. Available online: https://d9-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/s3fs-public/thumbnails/image/GroundShaking.jpg (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Field, E.H.; Biasi, G.P.; Bird, P.; Dawson, T.E.; Felzer, K.R.; Jackson, D.D.; Johnson, K.M.; Jordan, T.H.; Madden, C.; Michael, A.J.; et al. Long-Term Time-Dependent Probabilities for the Third Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast (UCERF3). Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2015, 105, 511–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X. Feeling is believing? Evidence from earthquake shaking experience and insurance demand. J. Risk Insur. 2019, 87, 351–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
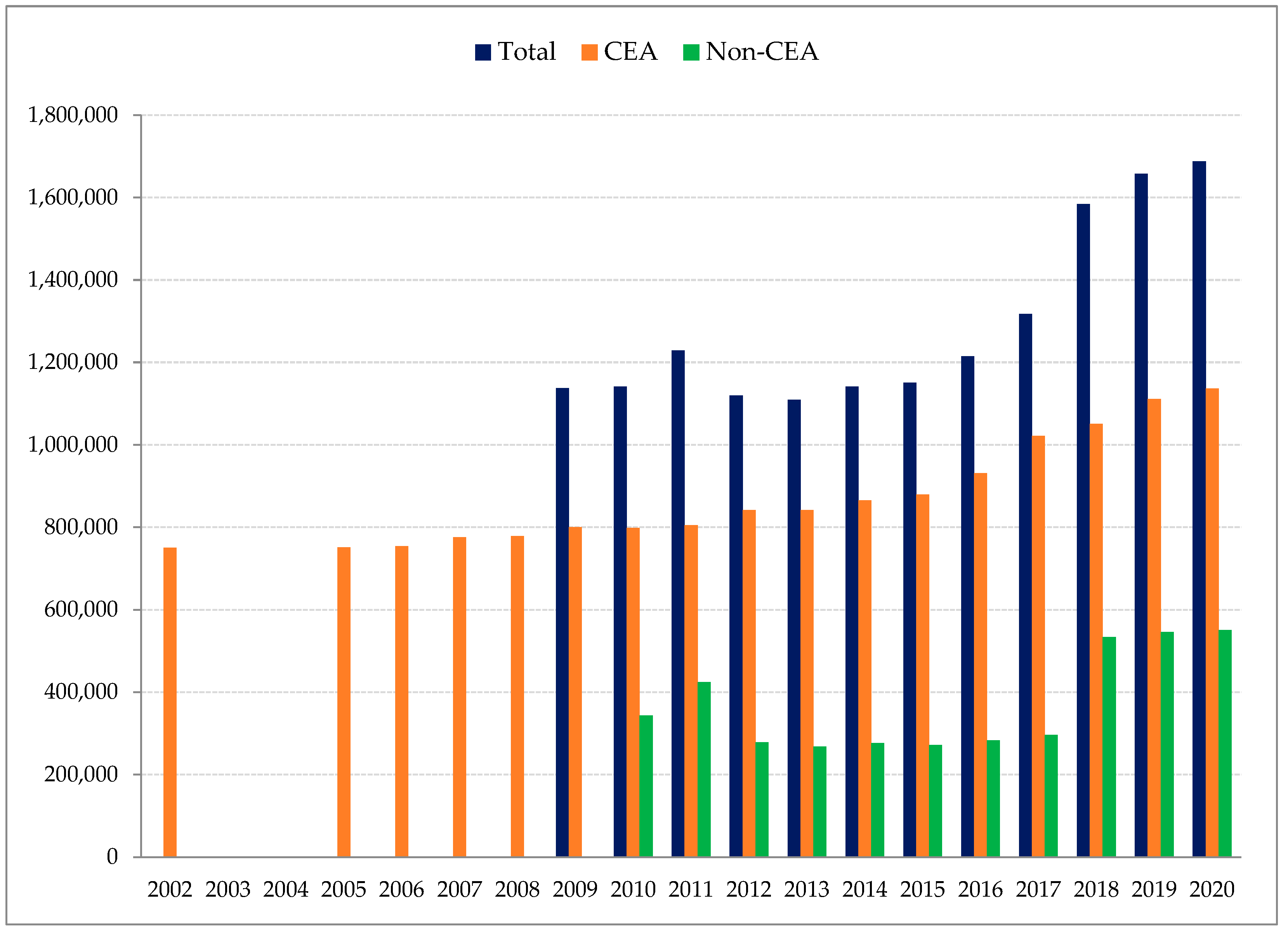
- CEA, California Earthquake Authority. Annual Legislative Reports, Years 2009–2020. Available online: https://www.earthquakeauthority.com/About-CEA/Annual-Legislative-Report (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- CEA, California Earthquake Authority. Audited Financial Statements. Years 2002, 2005–2008. Available online: https://www.earthquakeauthority.com/About-CEA/Financials/Financial-Statements (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Craig, R.K. Harvey, Irma, and the NFIP. Did the 2017 Hurricane Season Matter to Flood Insurance Reauthorization? (23 February 2018). University of Arkansas at Little Rock Law Review, Forthcoming, University of Utah College of Law Research Paper No. 249. 2018. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3129088 (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- NOAA. Costliest U.S. Tropical Cyclones Tables Updated. 2018. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/news/UpdatedCostliest.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- House Hearing, Assessing Fema’s Readiness for Future Disasters. Hearing before the Committee on Homeland Security on Homeland Security House of Representatives One Hundred Sixteenth Congress First Session. 2019. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CHRG-116hhrg38302/html/CHRG-116hhrg38302.htm (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- PRC (Pew Research Center). Demographic and Economic Profiles of Hispanics by State and County. 2014. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/hispanic/states/state/ca (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Breakwell, G.M. The Psychology of Risk; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, J.; Henrich, L.; Johnston, D.; Doyle, E.E. Are two earthquakes better than one? How earthquakes in two different regions affect risk judgments and preparation in three locations. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 16, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, D.; Smith, L.; Johnston, D. When good intentions turn bad: Promoting natural hazard preparedness. Aust. J. Emerg. Manag. 2005, 20, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
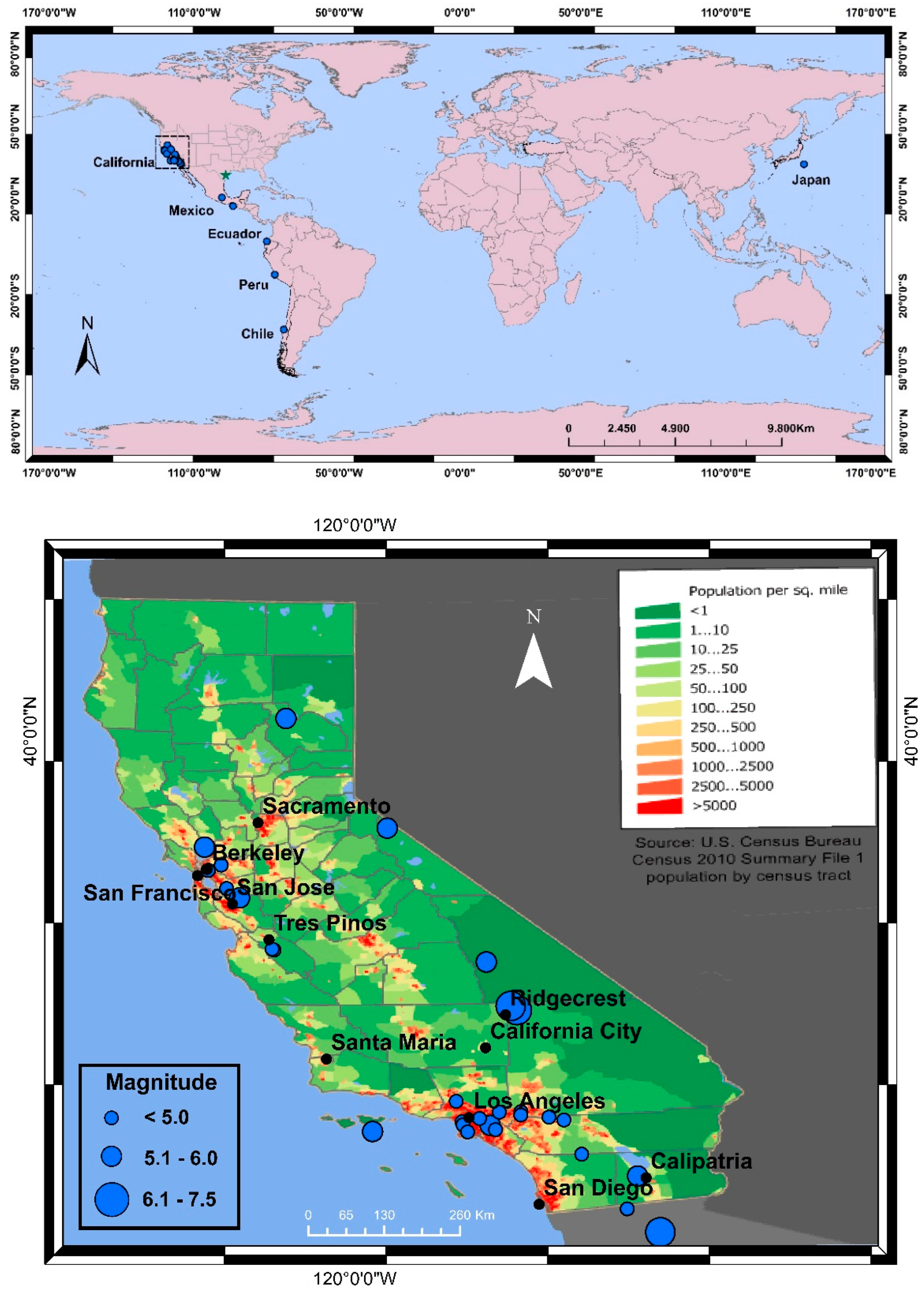
- USGS. M 7.1—2019 Ridgecrest Earthquake Sequence, Impact Summary. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/ci38457511/impact (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- USGS. Community Internet Intensity Map for M 4.5-1km SSE of Pleasant Hill, CA. Map Processed 5 November 2021. 2021. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/nc73291880/dyfi/intensity (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Marti, M.; Stauffacher, M.; Matthes, J.; Wiemer, S. Communicating earthquake preparedness: The influence of induced mood, perceived risk, and gain or loss frames on homeowners’ attitudes toward general precautionary measures for earthquakes. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindell, M.K.; Perry, R.W. Household adjustment to earthquake hazard: A review of research. Env. Behav. 2000, 32, 461–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X. Risk Awareness and Adverse Selection in Catastrophe Insurance: Evidence from California’s Residential Earthquake Insurance Market. J. Risk Uncertain. 2020, 61, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colón-Morales, C.M.; Giang, W.; Alvarado, M. Informed Decision-making for Health Insurance Enrollment: Survey Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2021, 5, e27477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU. Study on Consumers’ Decision Making in Insurance Services: A Behavioural Economics Perspective. Final Report. Specific Contract—No. 2014 85 08. Implementing Framework Contract—EAHC/2011/CP/01/LE. Prepared by London Economics, Ipsos and VVA Europe. Available online: https://european-union.europa.eu/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).




| Period | Years | Total Days | Total RSV | Days RSV = 0 | % Days RSV = 0 | % Days RSV > 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole | 2004–2021 | 6574 | 13,490 | 5040 | 77 | 23 |
| I | 2004–2009 | 2191 | 2267 | 2023 | 92 | 8 |
| II | 2010–2015 | 2191 | 3849 | 1718 | 78 | 22 |
| III | 2016–2021 | 2192 | 7373 | 1299 | 59 | 41 |
| Period | Years | Spearman (1) | Pearson (1) | Spearman (2) | Pearson (2) | Spearman (3) | Pearson (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 2004–2009 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| II | 2010–2015 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| III | 2016–2021 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.12 | 0.35 |
| RSV Range | Level of Attention |
|---|---|
| 1–25 | Low (L) |
| 26–50 | Moderate (M) |
| 51–75 | High (H) |
| 76–100 | Very High (VH) |
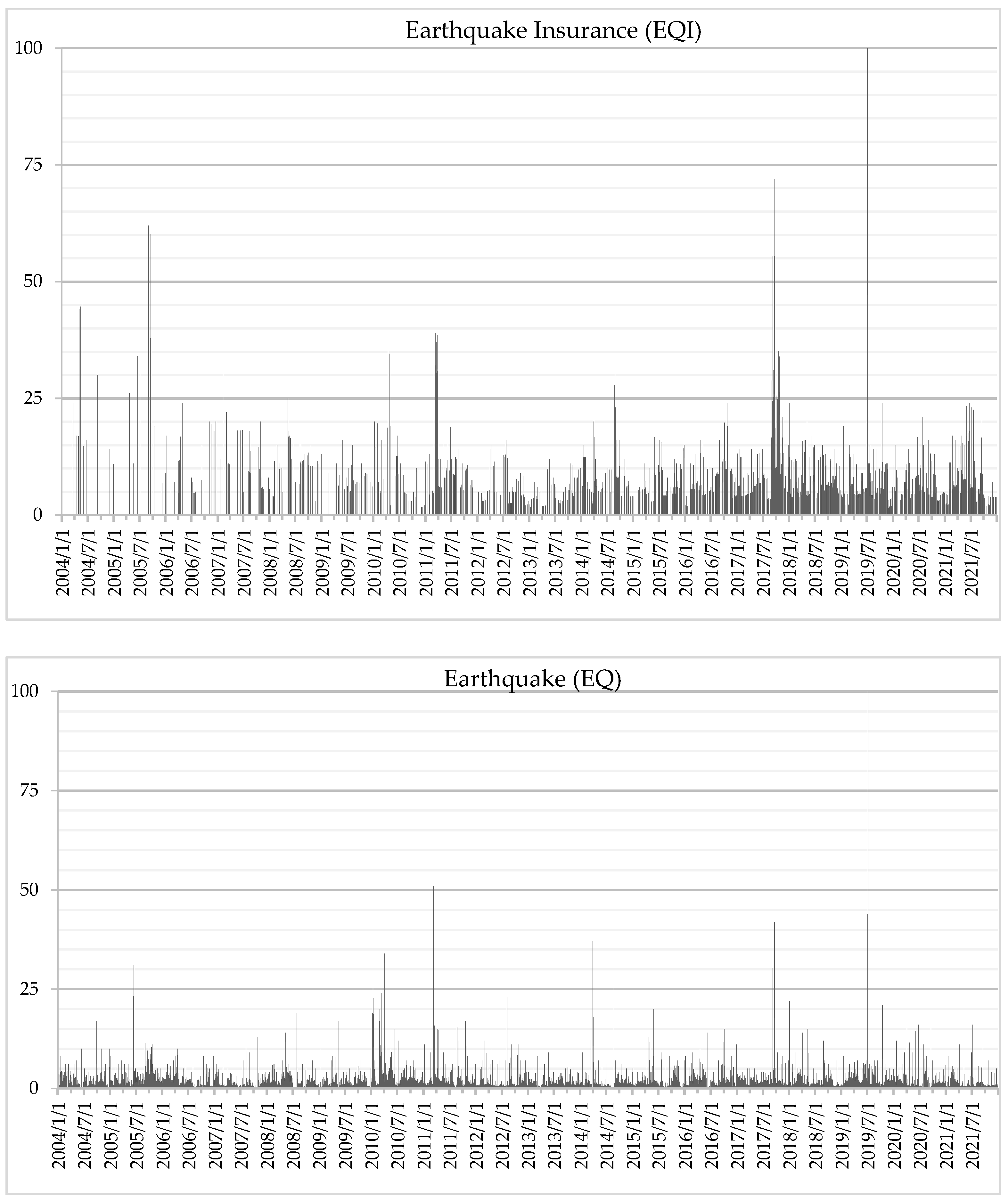
| Period | Event Date | Triggering Event | Epicentral/ Affected Area | Magnitude/ Category | Period of Interest (days) | Days RSV = 0 | RSV (min, max, mean) | Level of Interest in the Highest RSV Day | Level of Interest of the Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 16 June 2005 | EQ | 4 km NE of Yucaipa, CA | 4.9 | 1 | 0 | 34,34,34 | M | M |
| I | 2 September 2005 | EQ | 13 km WNW of Calipatria, CA | 5.1 | 2 | 0 | 34,62,48 | H | M |
| I | 15 August 2007 | EQ | 41 km SW of San Vicente de Cañete, Peru | 8.0 | 1 | 0 | 18,18,18 | L | L |
| I | 31 October 2007 | EQ | 6 km NNE of East Foothills, CA | 5.5 | 2 | 0 | 6,20,13 | L | L |
| II | 27 February 2010 | EQ | 36 km WNW of Quirihue, Chile | 8.8 | 3 | 0 | 7,16,10 | L | L |
| II | 4 April 2010 5–7 April | EQ | 12 km SW of Delta, B.C., MX; Eqs close to Ocotillo | 7.2 5.0 (max) | 2 | 0 | 18,19,18 | L | L |
| II | 11 March 2011 | EQ | 2011 Great Tohoku Earthquake, Japan | 9.1 | 17 | 6 | 0,39,21 | M | L |
| II | 20,21 October 2011 | EQ | 2 km,1 km SE of Berkeley, California | 4.0 3.8 | 6 | 0 | 10,11,13 | L | L |
| II | 24 May 2013 | EQ | 2 km NNE of Canyondam, CA | 5.7 | 2 | 0 | 10,12,11 | L | L |
| II | 15 January 2014 | EQ | 5 km NNE of Fontana, CA | 4.4 | 4 | 0 | 6,15,10 | L | L |
| II | 29 March 2014 | EQ | 2 km NW of Brea, CA | 5.1 | 5 | 0 | 12,22,17 | L | L |
| II | 24 August 2014 | EQ | South Napa, CA | 6.0 | 8 | 1 | 0,32,18 | M | L |
| III | 21 July 2015 25 July, 2015 | EQ | 3 km of Freemont, CA 1 km of Fonfata, CA | 4.0 3.8 | 4 | 0 | 8,15,10 | L | L |
| III | 16 April 2016 | EQ | 27 km SSE of Muisne, Ecuador | 7.8 | 6 | 1 | 0,16,9 | L | L |
| III | 25–31 August 2017 | HUR | Hurricane Harvey (TX-LA) | 4 | 8 | 0 | 10,29,21 | M | L-M |
| III | 8 September 2017 | EQ | near the coast of Chiapas, Mexico | 8.2 | 8 | 0 | 8,55,26 | H | M |
| III | 19 September 2017 | EQ | 1 km S of Matzaco, Mexico | 7.1 | 7 | 0 | 11,72,39 | H | M |
| III | 13 November 2017 | EQ | 18 km SSE of Tres Pinos, CA | 4.6 | 3 | 0 | 6,11,11 | L | L |
| III | 4 Jan 2018 | EQ | 2 km SE of Berkley, CA | 4.4 | 2 | 0 | 12,24,18 | L | L |
| III | 5 April 2018 | EQ | 29 km SW of S. Cruz Is, CA | 5.3 | 3 | 0 | 7,16,12 | L | L |
| III | 8 May 2018 | EQ | 11 km N of Cabazon, CA | 4.5 | 2 | 0 | 20,20,20 | L | L |
| III | 29 August 2018 | EQ | 4 km N of La Verne, CA | 4.4 | 2 | 0 | 12,12,12 | L | L |
| III | 4 July 2019 6 July 2019 | EQ | Ridgecrest Earthquake Sequence, CA | 6.4 7.1 | 8 | 0 | 20,100,43 | VH | M |
| III | 15 October 2019 | EQ | Tres Pinos, CA Pleasant Hill, CA | 4.7 4.5 | 4 | 0 | 9,24,14 | L | L |
| III | 4 April 2020 | EQ | 17 km ESE of Anza, CA | 4.9 | 2 | 0 | 5,11,8 | L | L |
| III | 22 April 2020 | EQ | 1 km S of View park-Wind. Hills, CA | 3.7 | 2 | 0 | 14,14,14 | L | L |
| III | 24 June 2020 | EQ | 18 km SSE of Lone Pine, CA | 5.8 | 3 | 0 | 17,17,17 | L | L |
| III | 30 July 2020 | EQ | 1 km SE of Sylmar, CA | 4.2 | 2 | 0 | 11,21,16 | L | L |
| III | 3 August 2020 | EQ | 3 km SW of Yorba Linda, CA | 3.5 | 4 | 0 | 5,15,10 | L | L |
| III | 19 September 2020 | EQ | 3 km WSW of South El Monte, CA | 4.5 | 7 | 0 | 4,13,7 | L | L |
| III | 5 April 2021 | EQ | 2 km E of Lennox, CA | 4.0 | 5 | 0 | 5,15,8 | L | L |
| III | 8 July 2021 | EQ | Antelope Valley, CA | 6.0 | 2 | 0 | 6,23,14 | L | L |
| III | 18 September 2021 | EQ | 2 km E of Carson, CA | 4.3 | 4 | 0 | 4,24,11 | L | L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gizzi, F.T.; Potenza, M.R. Earthquake Insurance in California, USA: What Does Community-Generated Big Data Reveal to Us? Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020060
Gizzi FT, Potenza MR. Earthquake Insurance in California, USA: What Does Community-Generated Big Data Reveal to Us? Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2022; 6(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleGizzi, Fabrizio Terenzio, and Maria Rosaria Potenza. 2022. "Earthquake Insurance in California, USA: What Does Community-Generated Big Data Reveal to Us?" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 6, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020060
APA StyleGizzi, F. T., & Potenza, M. R. (2022). Earthquake Insurance in California, USA: What Does Community-Generated Big Data Reveal to Us? Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 6(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020060







