Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin L1H: High Sensitivity and Specificity of Immunochromatographic Strip Test for Antibody Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant F. gigantica Cathepsin L1H (rFgCathL1H)
2.2. Preparation and Purification of Rabbit anti-rFgCathL1H
2.3. Serum Sample from F. gigantica-Infected Mice and Cattle
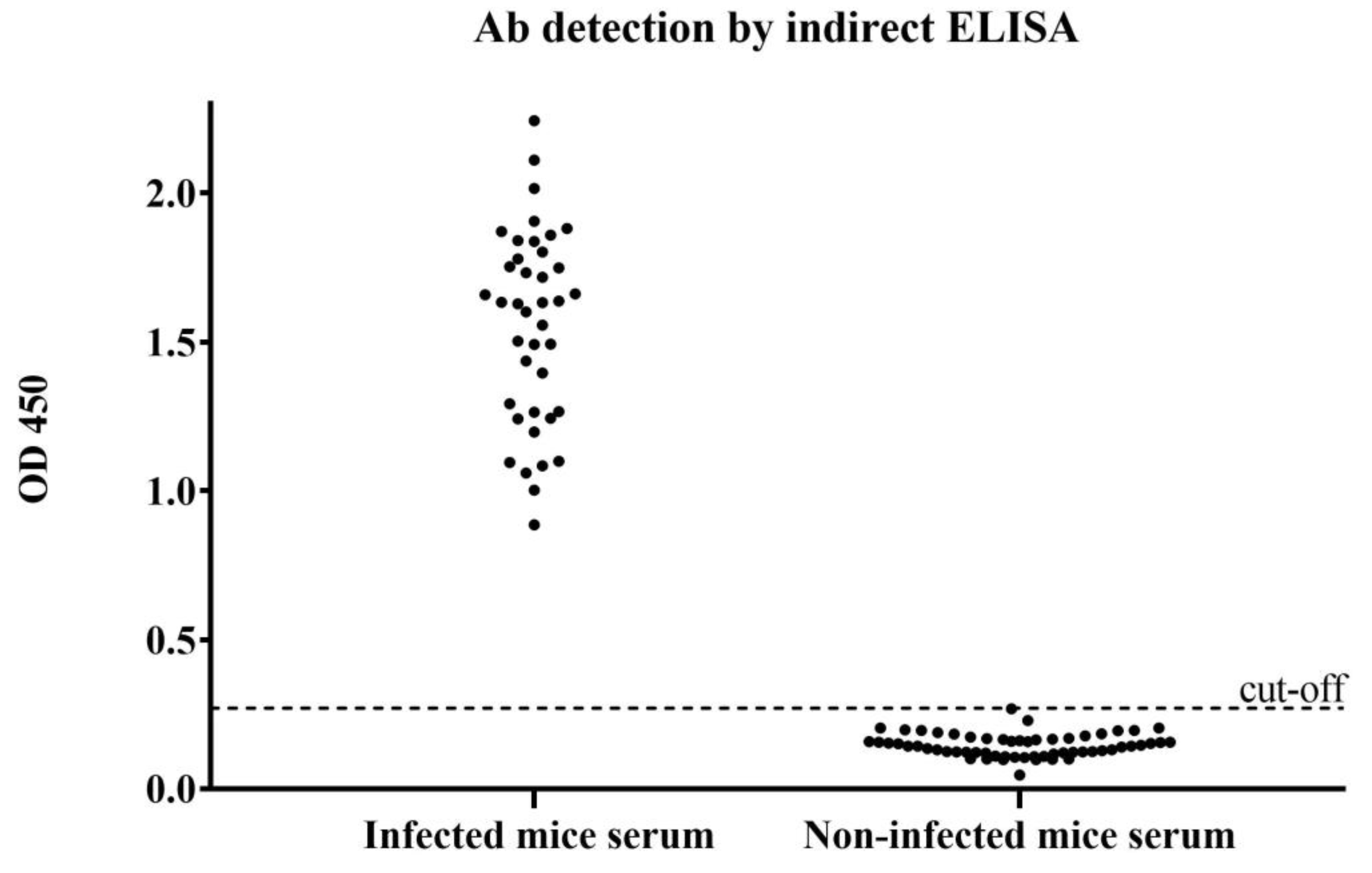
2.4. Detection of the Antibody against FgCathL1H by Indirect ELISA
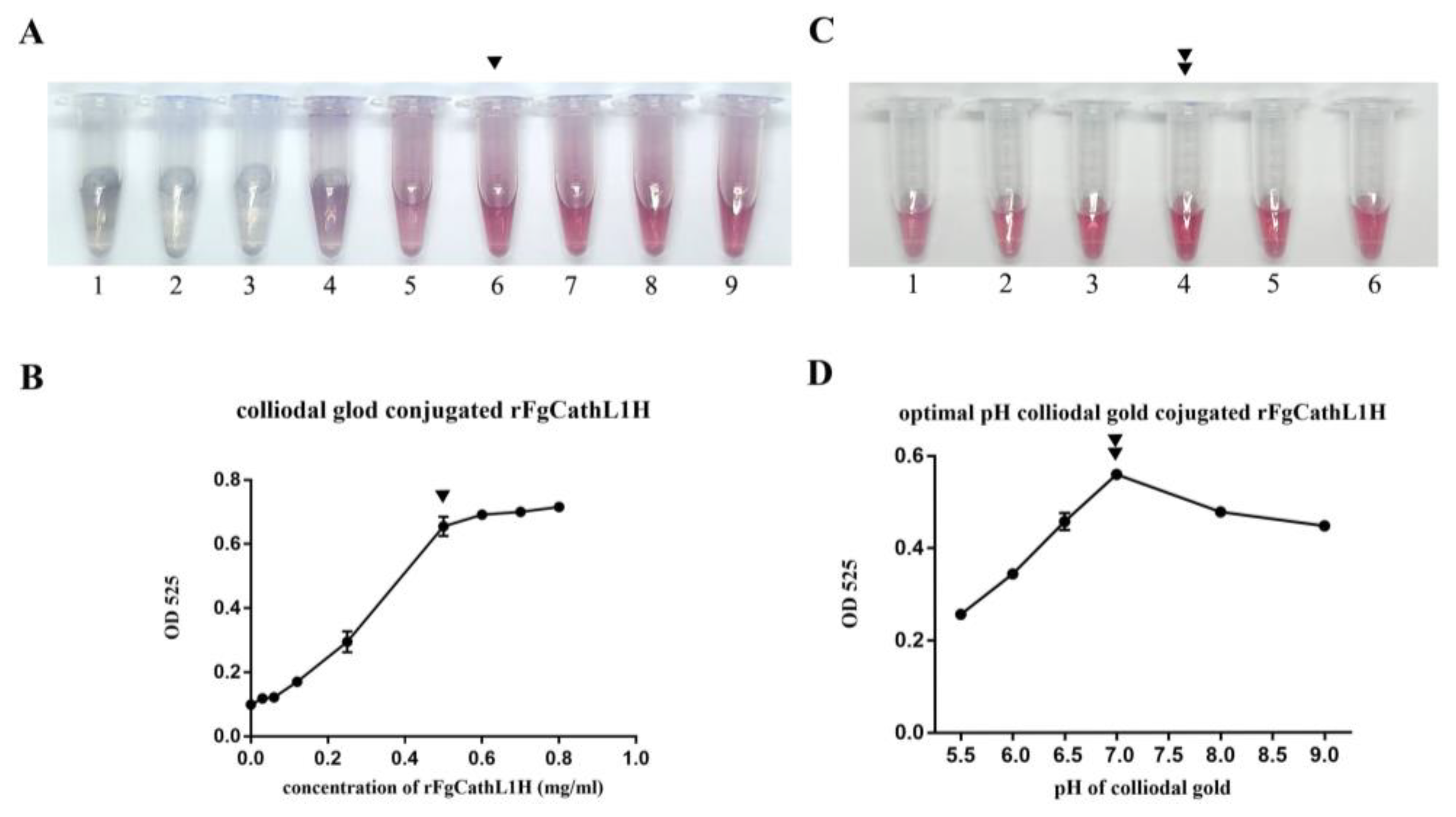
2.5. Optimization Concentration and pH of Colloidal Gold-Conjugated rFgCathL1H
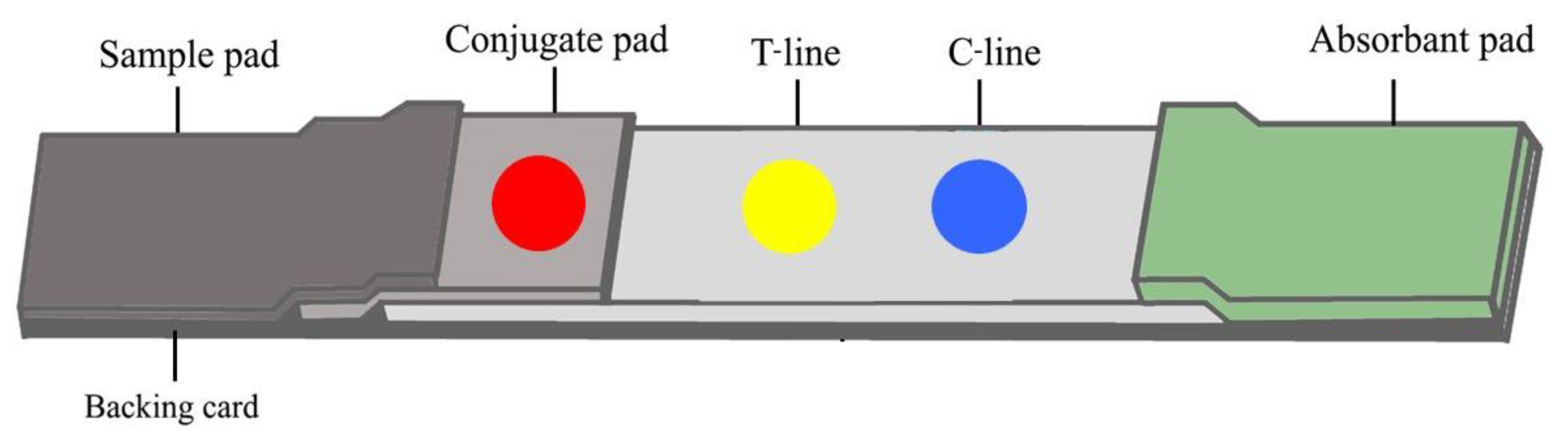
2.6. Preparation of an Immunochromatographic Strip (ICS) Test for Antibody Detection
2.7. Construction and Calculation Result of ICS Test for Antibody Detection
3. Results
3.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Protein FgCathL1H
3.2. Purification of Rabbit anti-rFgCathL1H Serum
3.3. Optimization Concentration and pH of Colloidal Gold-Conjugated rFgCathL1H
3.4. Detection of the Antibody against FgCathL1H by Indirect ELISA
3.5. Development of Rapid Antibody Detection Kits for Fasciolosis
3.6. Immunochromatographic Strip (ICS) Test for Antibody Detection
3.7. Sensitivity and Specificity of ICS Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fascioliasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1154, 71–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caravedo, M.A.; Cabada, M.M. Human Fascioliasis: Current Epidemiological Status and Strategies for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Control. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2020, 11, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Campos, A.; Correia, C.N.; Naranjo-Lucena, A.; Garza-Cuartero, L.; Farries, G.; Browne, J.A.; Mulcahy, G. Fasciola hepatica Infection in Cattle: Analyzing Responses of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) Using a Transcriptomics Approach. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyyu, J.D.; Monrad, J.; Kyvsgaard, N.C.; Kassuku, A.A. Epidemiology of Fasciola gigantica and amphistomes in cattle on traditional, small-scale dairy and large-scale dairy farms in the southern highlands of Tanzania. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2005, 37, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.T.; Gu, Q.Y.; Limpanont, Y.; Song, L.G.; Wu, Z.D.; Okanurak, K.; Lv, Z.Y. Snail-borne parasitic diseases: An update on global epidemiological distribution, transmission interruption and control methods. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.M.; Makundi, A.E.; Namuba, F.V.; Kassuku, A.A.; Keyyu, J.; Hoey, E.M.; Trudgett, A. The distri-bution of Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigatica within southern Tanzania-constraints associated with the intermediate host. Parasitology 2008, 135, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, K.; Valero, M.A.; Peixoto, R.V.; Artigas, P.; Panova, M.; Mas-Coma, S. Distribution of Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica in the endemic area of Guilan, Iran: Relationships between zonal overlap and phenotypic traits. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 31, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, N.; Chaves, A.; Pellegrino, J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in Schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1972, 14, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Tolan, R.W., Jr. Fascioliasis Due to Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica Infection: An Update on This ‘Neglected’ Ne-glected Tropical Disease. Lab. Med. 2011, 42, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.; Khadka, S.; Hamal, R.; Poudyal, S. Human echinostomiasis: A case report. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, S.; Malandrini, J.B.; Pantano, M.L.; Sawicki, M.; Soria, C.C.; Kuo, L.H.; Velasquez, J.N. Fasciola hepatica infection in humans: Overcoming problems for the diagnosis. Acta Parasitol. 2016, 61, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, J.; Duchateau, L.; Claerebout, E.; Williams, D.; Vercruysse, J. Associations between anti-Fasciola hepatica antibody levels in bulk-tank milk samples and production parameters in dairy herds. Prev. Veter. Med. 2007, 78, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkari, B.; Khabisi, S.A. Immunodiagnosis of Human Fascioliasis: An Update of Concepts and Performances of the Serological Assays. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, OE05–OE10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi-Bejestani, M.R.; McGarry, J.W.; Felstead, S.; Ortiz, P.; Akca, A.; Williams, D.J. Development of an antibody detection ELISA for Fasciola hepatica and its evaluation against a commercially available test. Res. Veter. Sci. 2005, 78, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, A.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. Development of a Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Strip for Rapid Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Protein. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ji, R.; Chai, R.; Yuan, N.; Zhang, J.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, C. A novel fluorescence immunochromatographic assay strip for the diagnosis of Schistosomiasis japonica. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grams, R.; Vichasri-Grams, S.; Sobhon, P.; Upatham, E.S.; Viyanant, V. Molecular cloning and characterization of cathepsin L encoding genes from Fasciola gigantica. Parasitol. Int. 2001, 50, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, J.; Brindley, P.J.; Knox, D.; Wolfe, K.H.; Dalton, J.P. Proteinases and associated genes of parasitic helminths. Adv. Parasitol. 1999, 43, 161–266. [Google Scholar]
- Sansri, V.; Changklungmoa, N.; Chaichanasak, P.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. Molecular cloning, characterization and functional analysis of a novel juvenile-specific cathepsin L of Fasciola gigantica. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, L.S.; Tirloni, L.; Pinto, A.F.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates Iii, J.R.; Benavides, U.; Berasain, P. Across intramammalian stages of the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica: A proteomic study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sernandez, V.; Muino, L.; Perteguer, M.J.; Garate, T.; Mezo, M.; Gonzalez-Warleta, M.; Ubeira, F.M. Development and evaluation of a new lateral flow immunoassay for serodiagnosis of human fasciolosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; Sajid, M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Lim, K.C.; Dvorak, J.; Hsieh, I.; McKerrow, J.H. A multienzyme network functions in intestinal protein digestion by a platyhelminth parasite. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39316–39329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, G.J.; Wichers, J.H.; Ferreira, T.M.; Ghati, D.; van Amerongen, A.; Deelder, A.M. Diagnosis of schistosomiasis by reagent strip test for detection of circulating cathodic antigen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5458–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochodo, E.A.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Spek, B.; Reitsma, J.B.; van Lieshout, L.; Polman, K.; Leeflang, M.M. Circulating antigen tests and urine reagent strips for diagnosis of active schistosomiasis in endemic areas. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD009579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.J.; Anderson, B.L.; Litwin, C.M. Rapid immunochromatographic strip test for detection of anti-K39 immunoglobulin G antibodies for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1483–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Liao, D.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, L. Development and application of a colloidal gold test strip for the rapid detection of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wen, T.; Shi, F.J.; Zeng, X.Y.; Jiao, Y.J. Rapid Detection of IgM Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral-Flow Assay. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12550–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Feng, J.; Hong, Y.; Lv, C.; Zhao, D.; Lin, J.; Zhu, C. A novel colloidal gold immunochromatography assay strip for the diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica in domestic animals. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eamsobhana, P.; Tungtrongchitr, A.; Wanachiwanawin, D.; Yong, H.S. Immunochromatographic test for rapid serological diagnosis of human angiostrongyliasis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 73, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, X.R.; Wang, G.X.; Yin, H.; Cai, X.P.; Fu, B.Q.; Zhang, D.L. Development of an immunochromatographic strip for the rapid detection of Toxoplasma gondii circulating antigens. Parasitol. Int. 2011, 60, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Ji, R.; Lin, J.; Zhu, C. Preparation of colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strips for the diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.H.; Yang, Y.T.; Shi, F.; Wang, J.Y.; Steverding, D.; Wang, X. Development of an Immunochromatographic Test for Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis Based on Detection of a Circulating Antigen. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, K.; Wu, Z.; Jin, W.; Wu, W.; Guo, Y.; Di, W. Development of a colloidal gold immunochromato-graphic strip for the rapid detection of antibodies against Fasciola gigantica in buffalo. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1004932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xifeng, W.; Mengfan, Q.; Kai, Z.; Guowu, Z.; Jing, L.; Lixia, W.; Xuepeng, C. Development and evaluation of a colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay based on recombinant protein CatL1D for serodiagnosis of sheep fasciolosis. J. Helminthol. 2019, 94, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, K.-H.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Huang, J.-C.; Tien, D.-C. The Effect of NaCl/pH on Colloidal Nanogold Produced by Pulsed Spark Discharge. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 612324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Indirect ELISA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| ICS Test | Positive | 39 | 0 |
| Negative | 1 | 60 | |
| Total | 40 | 60 | |
| Method | ICS Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Cattle serum | Positive | 11 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 10 | |
| Total | 11 | 10 | |
| Diagnostic Valves | Ab Detection by ICS Test |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | 97.50 |
| Specificity (%) | 99.99 |
| Positive predictive value (%) | 99.99 |
| Negative predictive value (%) | 98.36 |
| Accuracy (%) | 99.00 |
| False-positive rate (%) | 0.00 |
| False-negative rate (%) | 2.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suksomboon, P.; Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N. Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin L1H: High Sensitivity and Specificity of Immunochromatographic Strip Test for Antibody Detection. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8030164
Suksomboon P, Kueakhai P, Changklungmoa N. Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin L1H: High Sensitivity and Specificity of Immunochromatographic Strip Test for Antibody Detection. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(3):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8030164
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuksomboon, Phawiya, Pornanan Kueakhai, and Narin Changklungmoa. 2023. "Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin L1H: High Sensitivity and Specificity of Immunochromatographic Strip Test for Antibody Detection" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 3: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8030164
APA StyleSuksomboon, P., Kueakhai, P., & Changklungmoa, N. (2023). Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin L1H: High Sensitivity and Specificity of Immunochromatographic Strip Test for Antibody Detection. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(3), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8030164






