The Temporal and Spatial Epidemiology Employed in the Elimination of the HIV Epidemic in the Largest Capital of the Brazilian Rainforest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Unit of Analysis
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Variables and Data Source
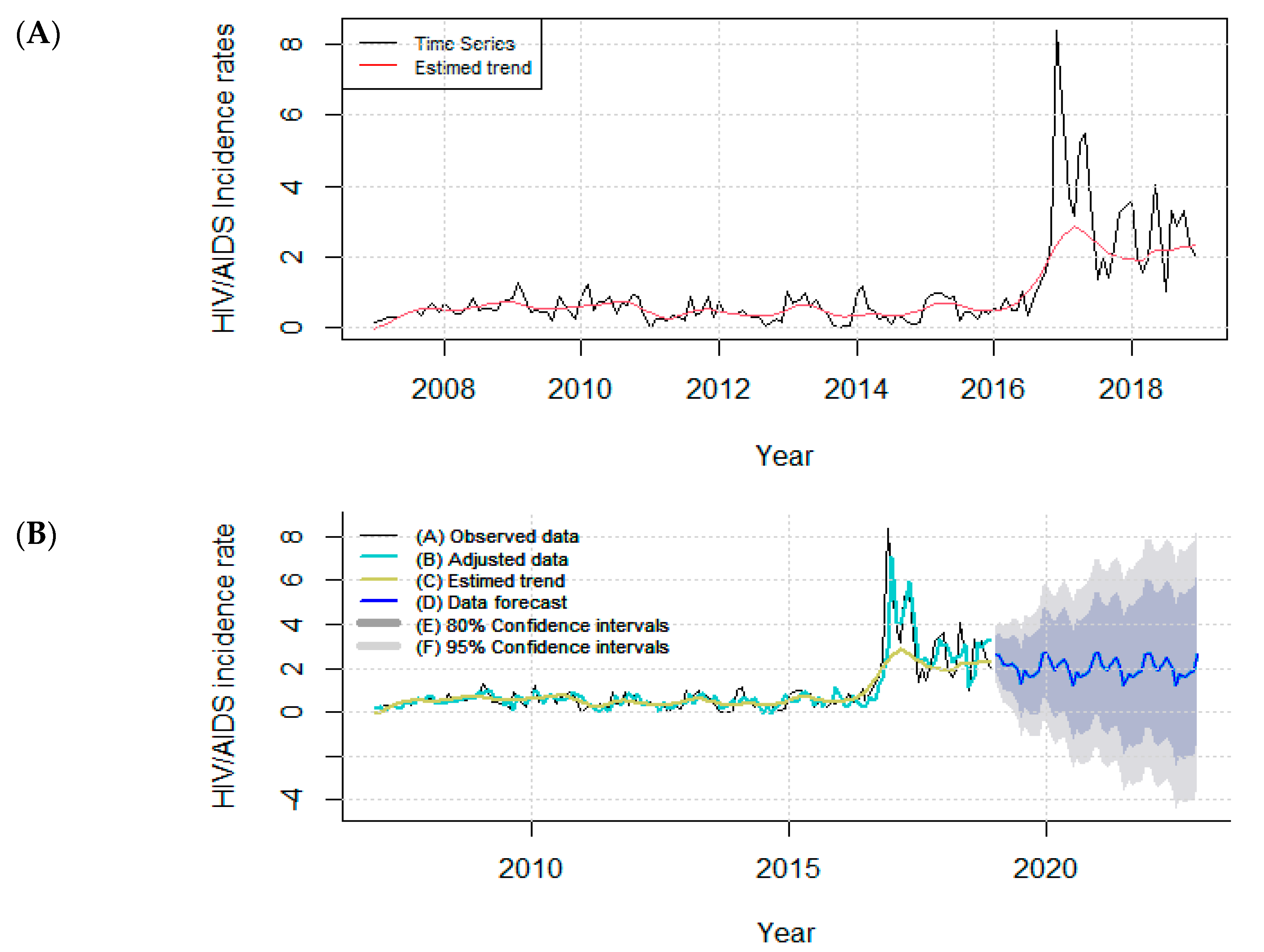
2.4. Time Series Analysis
2.5. Spatial Analysis
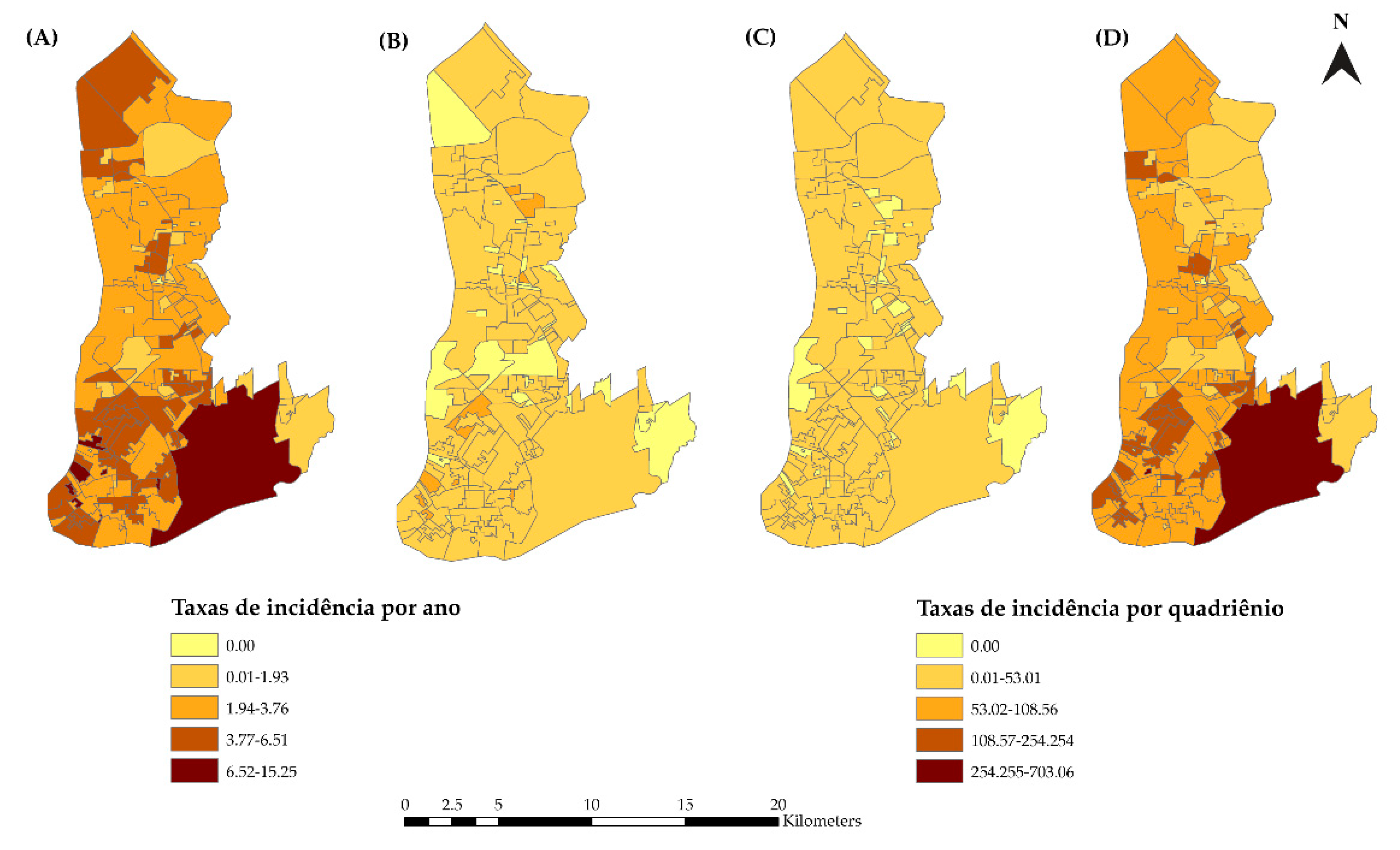
2.5.1. Spatial Distribution of HIV/AIDS Incidence
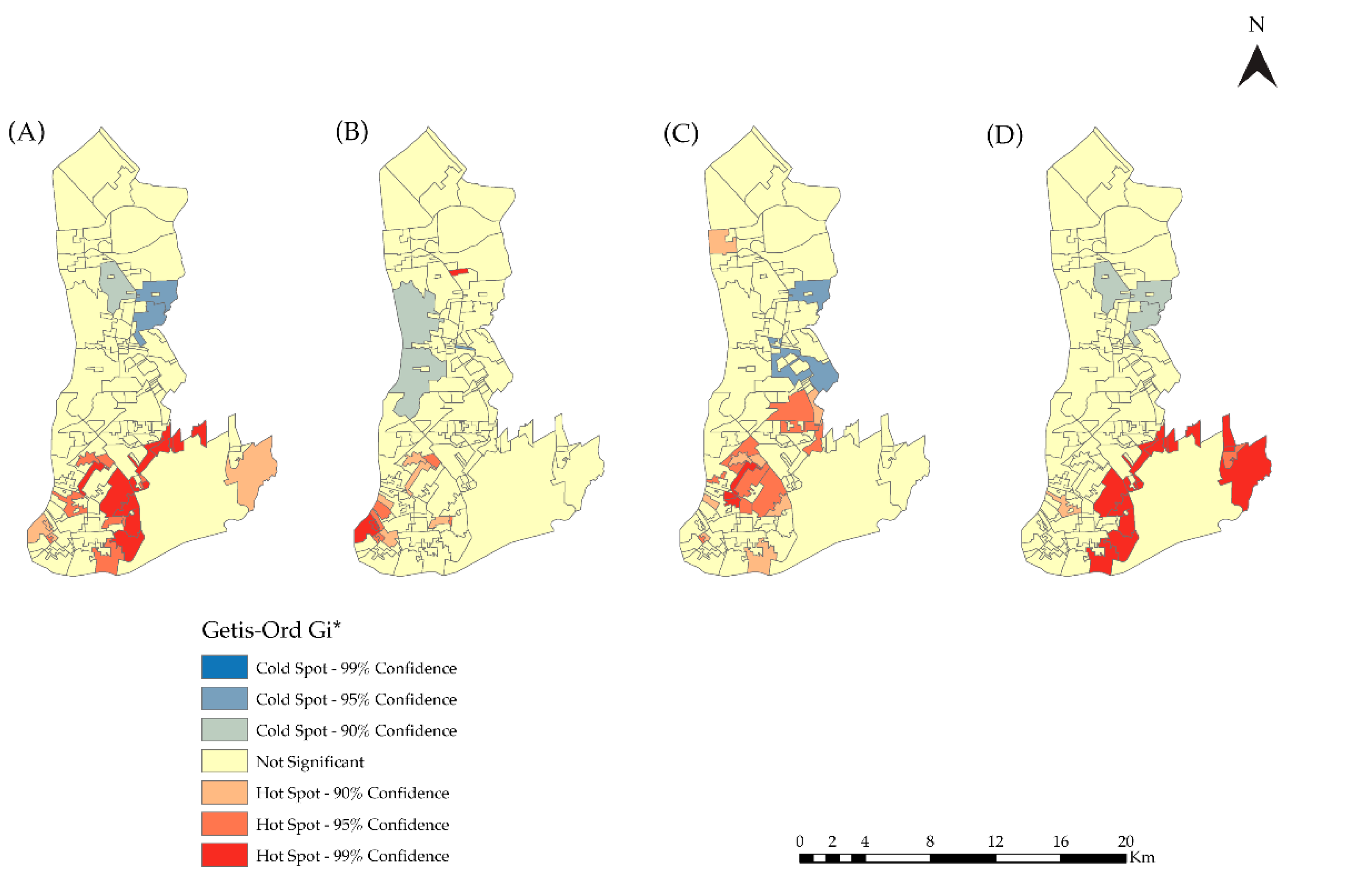
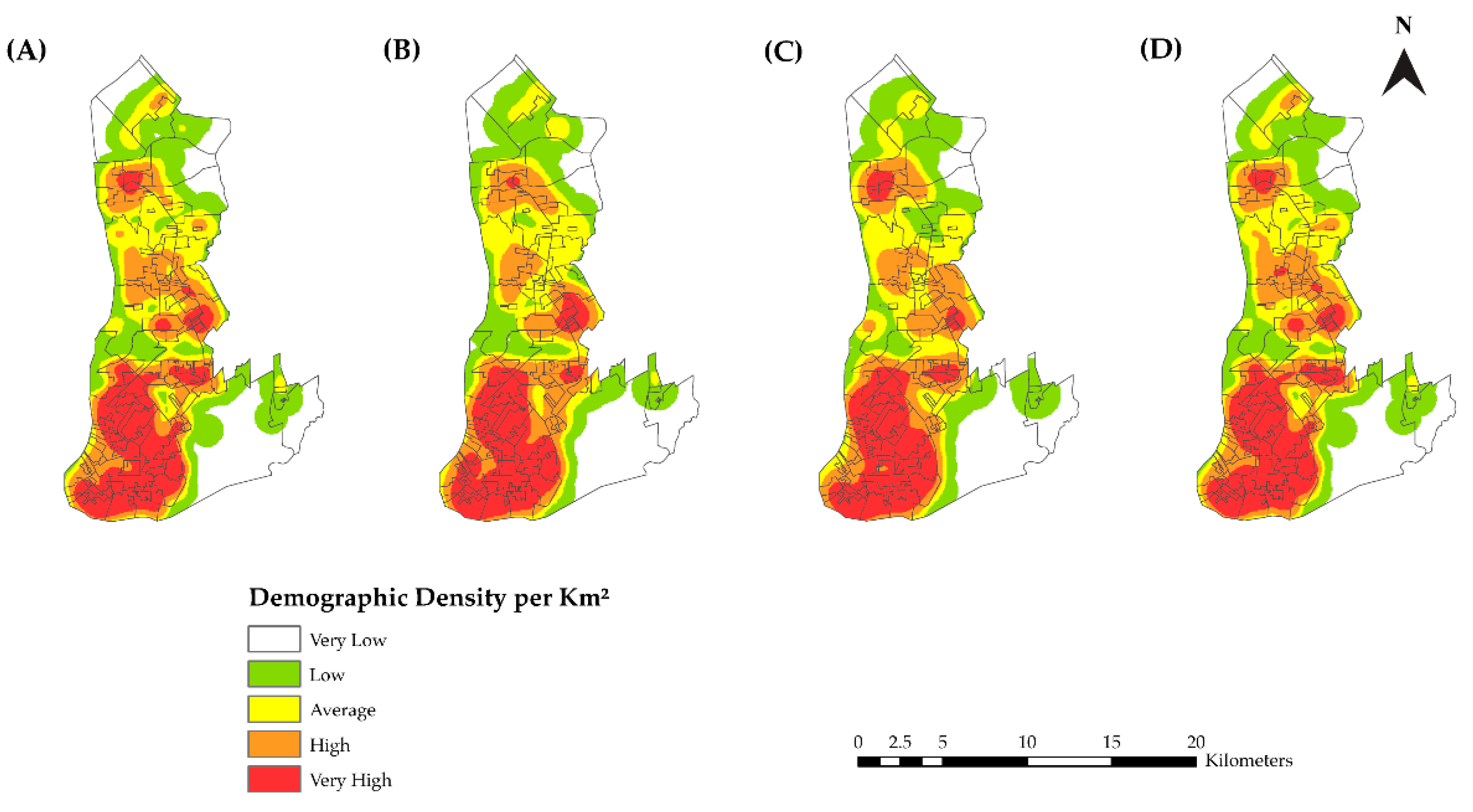
2.5.2. Kernel Density Estimation and Scan Statistics
2.5.3. Spatial Regression Analysis
2.6. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Time Series Analysis
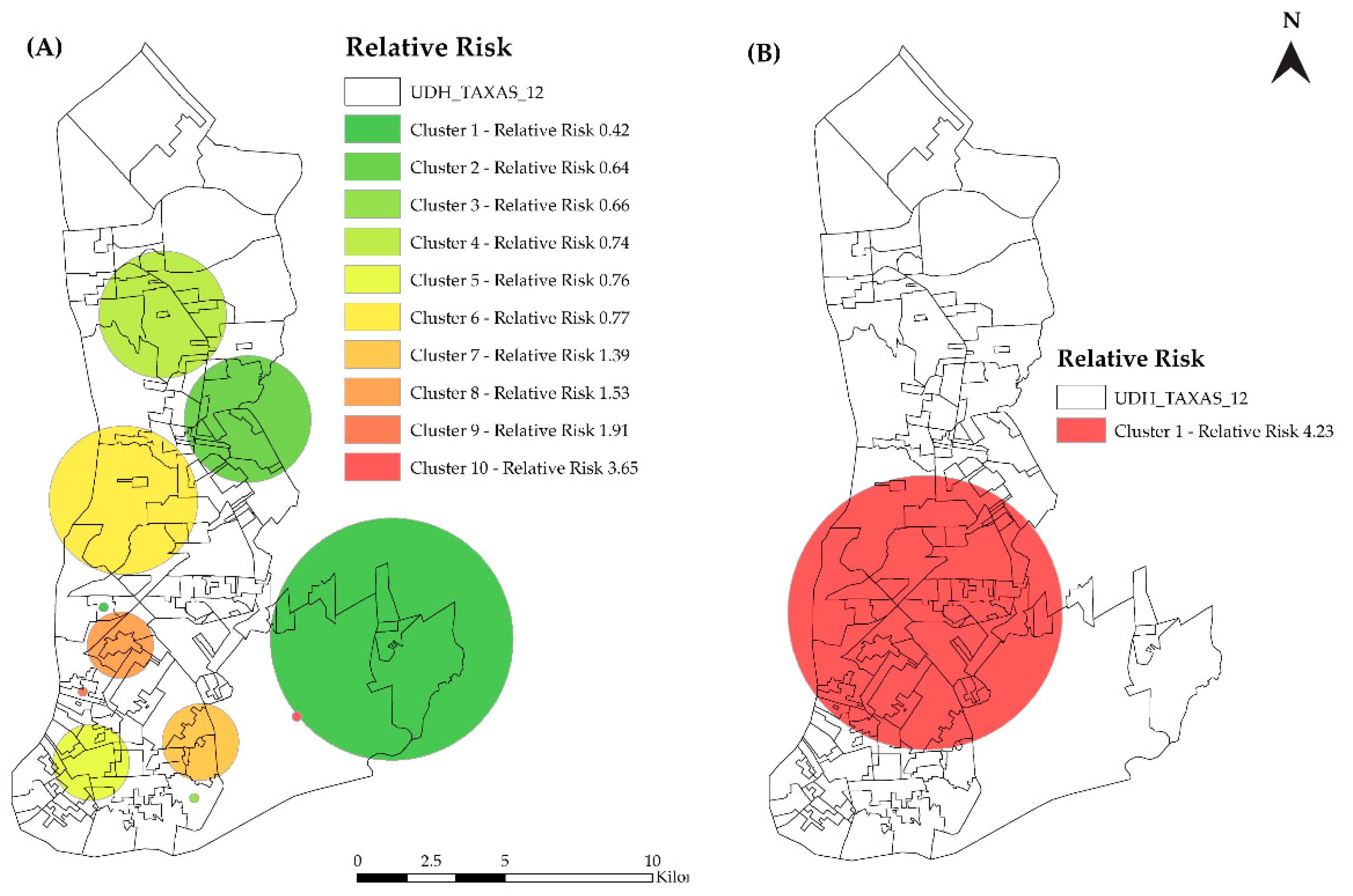
3.2. Spatial Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS. UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic Shows that 2020 Targets Will not Be Met because of Deeply Unequal Success; COVID-19 Risks Blowing HIV Progress Way off Course. 2020. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/pressreleaseandstatementarchive/2020/july/20200706_global-aids-report (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Pan American Health Organization. New Cases of HIV Infection Increased by More than 20% in Latin America in the Last Decade. 2020. Available online: https://www.paho.org/pt/noticias/30-11-2020-novos-casos-infeccao-por-hiv-aumentaram-mais-20-na-america-latina-na-ultima (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Ministry of Health of Brazil; Secretariat of Health Surveillance; Department of Chronic Conditions Diseases and Sexually Transmitted Infections. Epidemiological Report HIV/AIDS 2020; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2020; 68p.
- de Holanda, E.R.; Galvão, M.T.G.; Pedrosa, N.L.; Paiva, S.D.S.; De Almeida, R.L.F. Spatial analysis of infection by the human immunodeficiency virus among pregnant women1. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2015, 23, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daw, M.A.; Daw, A.M.; Sifennasr, N.E.M.; Draha, A.M.; Daw, A.A.; Daw, A.A.; Ahmed, M.O.; Mokhtar, E.S.; El-Bouzedi, A.H.; Daw, I.M.; et al. Spatiotemporal analysis and epidemiological characterization of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in Libya within a twenty five year period: 1993–2017. AIDS Res. Ther. 2019, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falavina, L.P.; Lentsck, M.H.; Mathias, T.A.D.F. Tendência e distribuição espacial de doenças infecciosas em gestantes no estado do Paraná-Brasil. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2019, 27, e3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Guo, W.; Tang, W.; Mahapatra, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Ding, Z.; Cai, C.; Cui, Y.; Sun, J. Spatial Analysis of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Epidemic among Men Who Have Sex with Men in China, 2006–2015. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, H.; Ramjee, G. Spatial clustering of “measured” and “unmeasured” risk factors for HIV infections in hyper-endemic communities in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: Results from geoadditive models. AIDS Care 2015, 27, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, T.; Feng, Y.B.; Li, M.; Chen, F.F.; Li, Y.G.; Jin, S.S.; Bu, K.; Wang, L. Characteristics of the HIV/AIDS Epidemic in Women Aged 15–49 Years from 2005 to 2012 in China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.C.P.; De Almeida, A.S.; Braga, J.U.; O’Dwyer, G.; Junior, P.C.A.; Daumas, R.P.; Lino, V.T.S.; Andrade, M.K.D.N.; Monteiro, D.L.M.; Barros, M.B.D.L. Spatial dynamics of AIDS incidence in the elderly in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997–2011. Cad. Saúde Pública. 2015, 31, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, X.; Mao, S.; Shi, N.; Hui, X. The spatial distribution pattern of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome in China. Geospat. Health 2016, 11, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Callander, D.; DiClemente, R.; Trinh-Shevrin, C.; Thorpe, L.E.; Duncan, D.T. Location of Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Services Across New York City Neighborhoods: Do Neighborhood Socio-demographic Characteristics and HIV Incidence Matter? AIDS Behav. 2019, 23, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Dai, J.; Luo, H.; Yang, C.; Dong, L.; Jin, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, L.; et al. Spatial clusters of HIV-1 genotypes in a recently infected population in Yunnan, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Dai, J.; Luo, H.; Yang, C.; Dong, L.; Jin, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, L.; et al. Demographic characteristics and spatial clusters of recent HIV-1 infections among newly diagnosed HIV-1 cases in Yunnan, China, 2015. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelaw, Y.A.; Magalhães, R.J.S.; Assefa, Y.; Williams, G. Spatial clustering and socio-demographic determinants of HIV infection in Ethiopia, 2015–2017. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 82, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramjee, G.; Sartorius, B.; Morris, N.; Wand, H.; Reddy, T.; Yssel, J.D.; Tanser, F. A decade of sustained geographic spread of HIV infections among women in Durban, South Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merzouki, A.; Styles, A.; Estill, J.; Orel, E.; Baranczuk, Z.; Petrie, K.; Keiser, O. Identifying groups of people with similar sociobehavioural characteristics in Malawi to inform HIV interventions: A latent class analysis. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2020, 23, e25615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. 2010 Census. 2010. Available online: https://ww2.ibge.gov.br/home/ (accessed on 9 May 2019).
- Municipal Health Secretary of Belém. Municipal Health Plan (MHP) 2018–2021; Municipal Health Secretary: Belém, Brazil, 2017; 108p. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Development Programme. Atlas of Human Development of Brazil. 2013. Available online: https://atlasbrasil.org.br/2013/ (accessed on 25 August 2019).
- Institute for Applied Economic Research. Atlas of Social Vulnerability in Brazilian Municipalities. 2015. Available online: https://ivs.ipea.gov.br/images/publicacoes/Ivs/publicacao_atlas_ivs.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2019).
- Bailey, T.C.; Gatrell, A.C. Interactive Spatial Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Belém. Belém Urban Mobility Plan; Belem City Hall: Belém, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 5th ed.; Wiley: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; OText: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, K.J.; Greenland, S.; Lash, T.L. Modern Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health of Brazil; Secretariat of Health Surveillance. Oswaldo Cruz Foundation Introduction to Spatial Statistics for Public Health; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2007.
- Fusco, A.P.B.; Arcêncio, R.A.; Yamamura, M.; Palha, P.F.; dos Reis, A.A.; Alecrim, T.F.D.A.; Protti, S.T. Spatial distribution of tuberculosis in a municipality in the interior of São Paulo, 2008–2013. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2017, 25, e2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kulldorff, M.; Nagarwalla, N. Spatial disease clusters: Detection and inference. Stat. Med. 1995, 14, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.B.; Cellegari-Jacques, S.M. Measures of association in epidemiological studies: Relative risk and odds ratio. J. Pediatr. 1998, 74, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- De Assis, I.S.; Arcoverde, M.; Ramos, A.C.V.; Alves, L.S.; Berra, T.Z.; Arroyo, L.H.; De Queiroz, A.A.R.; Dos Santos, D.T.; Belchior, A.D.S.; Alves, J.D.; et al. Social determinants, their relationship with leprosy risk and temporal trends in a tri-border region in Latin America. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS. China Focuses on Strengthening HIV Prevention. 2017. Available online: https://unaids.org.br/2017/11/china-se-concentra-no-fortalecimento-da-prevencao-do-hiv/ (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Ordinance No. 77, of 12 January 2012. Provides for Rapid Tests, in Primary Care, for the Detection of HIV and Syphilis, as well as Rapid Tests for Other Diseases, within the Scope of Prenatal Care for Pregnant Women and Their Sexual Partners; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2012.
- Leon, C.; Koosed, T.; Philibert, B.; Raposo, C.; Benzaken, A.S. HIV/AIDS health services in Manaus, Brazil: Patient perception of quality and its influence on adherence to antiretroviral treatment. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.R.; De Oliveira, S.S.; Pereira, I.R.B.D.O.; Dos Santos, W.N.; Fernandes, S.F.; Da Silva, R.A.R. Construct validation: Coping with HIV/AIDS in Primary Health Care. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2019, 72, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, M.S.; Raniere, J.C.; Paes, C.J.O.; Gonçalves, L.H.T.; Cunha, C.L.F.; Ferreira, G.R.O.N.; Botelho, E.P. The association between knowledge about HIV and risk factors in young Amazon people. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2020, 73, e20190453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.J.M.; Pol, A.P.; Abad, A.S. Using the R-MAPE index as a resistant measure of forecast accuracy. Psicothema 2013, 25, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyoni, S.P.; Nyoni, T. Adults newly infected with HIV in Zimbabwe: A box-jenkins ARIMA approach. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 7, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchi, E.M.; Grangeiro, A.; Ferraz, D.; Pinheiro, T.F.; Alencar, T.; Ferguson, L.; Estevam, D.L.; Munhoz, R. From evidence to action: Challenges for the Brazilian National Health System to offer HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to the most vulnerable people. Cad. Saúde Pública. 2018, 34, e00206617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Ministry of Health Records Increases in HIV Cases in 2016; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, December 2017.
- Ministry of Health of Brazil; Secretariat of Health Surveillance; Department of Chronic Conditions Diseases and Sexually Transmitted Infections. Epidemiological Report HIV/AIDS 2017; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2017; 64p.
- Ministry of Health of Brazil; Secretariat of Health Surveillance; Department of Chronic Conditions Diseases and Sexually Transmitted Infections. Epidemiological Report HIV/AIDS 2018; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; 72p.
- Ministry of Health of Brazil; Secretariat of Health Surveillance; Department of Chronic Conditions Diseases and Sexually Transmitted Infections. Epidemiological Report HIV/AIDS 2019; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2019; 72p.
- Vieira, D.C.D.M.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Rodrigues, J.C. Mapeamento e análise de desigualdades socioespaciais: Abordagem interpretativa a partir da cidade de Belém, Pará. Geosaberes 2018, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.T.N.; Silva, S.P.C.; Fernandes, F.E.C.V.; Santana, L.D.; Silva, T.I.M. Epidemiological profile of HIV/AIDS cases registered in a Specialized Outpatient Service. Rev. Gest. Saúde 2019, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Test | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Kolmogorov–Smirnov | <0.001 |
| F | 0.712 |
| Box–Pierce | 0.808 |
| Model STL + ARIMA (2,1,2) | |
| RMSE | 0.64 |
| MAE | 0.35 |
| MAPE | 83.48 |
| Incidence Rate | Observed General G | Z-Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2007–2018 | 0.041 | 3.464 | 0.000 |
| 2007–2010 | 0.036 | 0.642 | 0.524 |
| 2011–2014 | 0.046 | 4.157 | 0.008 |
| 2015–2018 | 0.043 | 3.404 | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, B.R.L.; Rodrigues, T.B.; Gomes, D.; Arcêncio, R.A.; Gir, E.; Ferreira, G.R.O.N.; Polaro, S.H.I.; Botelho, E.P. The Temporal and Spatial Epidemiology Employed in the Elimination of the HIV Epidemic in the Largest Capital of the Brazilian Rainforest. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090225
Dias BRL, Rodrigues TB, Gomes D, Arcêncio RA, Gir E, Ferreira GRON, Polaro SHI, Botelho EP. The Temporal and Spatial Epidemiology Employed in the Elimination of the HIV Epidemic in the Largest Capital of the Brazilian Rainforest. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(9):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090225
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Bruna Rafaela Leite, Taymara Barbosa Rodrigues, Dulce Gomes, Ricardo Alexandre Arcêncio, Elucir Gir, Glenda Roberta Oliveira Naiff Ferreira, Sandra Helena Isse Polaro, and Eliã Pinheiro Botelho. 2022. "The Temporal and Spatial Epidemiology Employed in the Elimination of the HIV Epidemic in the Largest Capital of the Brazilian Rainforest" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 9: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090225
APA StyleDias, B. R. L., Rodrigues, T. B., Gomes, D., Arcêncio, R. A., Gir, E., Ferreira, G. R. O. N., Polaro, S. H. I., & Botelho, E. P. (2022). The Temporal and Spatial Epidemiology Employed in the Elimination of the HIV Epidemic in the Largest Capital of the Brazilian Rainforest. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(9), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090225







