Prognostic Indicators for the Early Prediction of Severe Dengue Infection: A Retrospective Study in a University Hospital in Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Patient Recruitment and Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Dengue and Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever (DHF); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. Dengue Report; Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health: Nonthaburi, Thailand, 2022.
- Carlos, C.C.; Oishi, K.; Cinco, M.T.; Mapua, C.A.; Inoue, S.; Cruz, D.J.; Pancho, M.A.; Tanig, C.Z.; Matias, R.R.; Morita, K.; et al. Comparison of clinical features and hematologic abnormalities between dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever among children in the Philippines. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeraja, M.; Lakshmi, V.; Teja, V.D.; Umabala, P.; Subbalakshmi, M.V. Serodiagnosis of dengue virus infection in patients presenting to a tertiary care hospital. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 24, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, L.; Nurfitri, E. Pediatric logistic organ dysfunction score as a predictive tool of dengue shock syndrome outcomes. Paediatr. lndones. 2012, 52, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, B.E.; Koraka, P.; Osterhaus, A.D. Dengue virus pathogenesis: An integrated view. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Report of the Scientific Working Group Meeting on Dengue; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Chang, K.; Lu, P.L.; Ko, W.C.; Tsai, J.J.; Tsai, W.H.; Chen, C.D.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, T.C.; Hsieh, H.C.; Pan, C.Y.; et al. Dengue fever scoring system: New strategy for the early detection of acute dengue virus infection in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2009, 108, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwarto, S.; Nainggolan, L.; Sinto, R.; Effendi, B.; Ibrahim, E.; Suryamin, M.; Sasmono, R.T. Dengue score: A proposed diagnostic predictor for pleural effusion and/or ascites in adults with dengue infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marois, I.; Forfait, C.; Inizan, C.; Klement-Frutos, E.; Valiame, A.; Aubert, D.; Gourinat, A.C.; Laumond, S.; Barsac, E.; Grangeon, J.P.; et al. Development of a bedside score to predict dengue severity. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwan, A.; Gustawan, I.; Gunawijaya, E.; Soetjiningsih, S.; Ariawati, K.; Hartawan, I. Implementation of Dengue Recurrent Shock Prediction Score in pediatric dengue shock syndrome. Paediatr. Indones. 2021, 60, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever: Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- World Health Organization. Dengue Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Lee, I.K.; Liu, J.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.H. Development of a simple clinical risk score for early prediction of severe dengue in adult patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, K.M.; Khalid, B.; Ching, S.M.; Chee, H.Y. Meta-analysis of dengue severity during infection by different dengue virus serotypes in primary and secondary infections. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongpan, S.; Wisitwong, A.; Tawichasri, C.; Patumanond, J.; Namwongprom, S. Development of dengue infection severity score. ISRN Pediatr. 2013, 2013, 845876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangkawibha, N.; Rojanasuphot, S.; Ahandrik, S.; Viriyapongse, S.; Jatanasen, S.; Salitul, V.; Phanthumachinda, B.; Halstead, S.B. Risk factors in dengue shock syndrome: A prospective epidemiologic study in Rayong, Thailand. I. The 1980 outbreak. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1984, 120, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, D.S.; Nisalak, A.; Johnson, D.E.; Scott, R.M. A prospective study of dengue infections in Bangkok. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 38, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, S.; Aung, M.M.; Shwe, T.N.; Aye, M.; Zaw, A.; Aye, K.; Aye, K.M.; Aaskov, J. Risk factors in dengue shock syndrome. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiner, D.L.; Cairney, J. What’s under the ROC? An introduction to receiver operating characteristics curves. Can. J. Psychiatry 2007, 52, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Brouste, Y.; Najioullah, F.; Hochedez, P.; Hatchuel, Y.; Moravie, V.; Kaidomar, S.; Besnier, F.; Abel, S.; Rosine, J.; et al. Predictors of severe manifestations in a cohort of adult dengue patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rivera, E.J.; Rigau-Pérez, J.G. Dengue severity in the elderly in Puerto Rico. Pan. Am. J. Public Health 2003, 13, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, N.T.; Thao, N.T.H.; Ha, T.T.N.; Lan, N.T.P.; Nga, P.T.T.; Thuy, T.T.; Tuan, H.M.; Nga, C.T.P.; Tuong, V.V.; Dat, T.V.; et al. Development of clinical decision rules to predict recurrent shock in dengue. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucunawangsih, F.K.; Dewi, B.E.; Sungono, V.; Lugito, N.P.H.; Sutrisna, B.; Pohan, H.T.; Syahrurachman, A.; Widodo, D.; Ronoatmodjo, S.; Sudaryo, M.K.; et al. Scoring model to predict dengue infection in the early phase of illness in primary health care centre. Arch. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Ho, T.N.; Nguyen, V.V.C.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ha, M.T.; Ta, V.T.; Nguyen, L.D.H.; Phan, L.; Han, K.Q.; Duong, T.H.K.; et al. An evidence-based algorithm for early prognosis of severe dengue in the outpatient setting. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, A.; Pathak, D.; Gupta, N.; Simalti, A.; Gupta, D.; Gupta, S.; Chugh, P. Early predictors of mortality in children with severe dengue fever: A prospective study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantracheewathorn, T.; Tantracheewathorn, S. Risk factors of dengue shock syndrome in children. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2007, 90, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Chacko, B.; Subramanian, G. Clinical, laboratory and radiological parameters in children with dengue fever and predictive factors for dengue shock syndrome. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2008, 54, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deen, J.L.; Harris, E.; Wills, B.; Balmaseda, A.; Hammond, S.N.; Rocha, C.; Dung, N.M.; Hung, N.T.; Hien, T.T.; Farrar, J.J. The WHO dengue classification and case definitions: Time for a reassessment. Lancet 2006, 368, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Lum, L.C.; Kroeger, A. Classifying dengue: A review of the difficulties in using the WHO case classification for dengue haemorrhagic fever. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 1238–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaruk, P.; Srisuphanunt, M. Meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of dengue risk score for dengue virus infection. Thail. Sci. Technol. J. 2019, 27, 512–525. [Google Scholar]
- Halstead, S.B.; Udomsakdi, S.; Singharaj, P.; Nisalak, A. Dengue chikungunya virus infection in man in Thailand, 1962–1964. 3. Clinical, epidemiologic, and virologic observations on disease in non-indigenous white persons. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1969, 18, 984–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, O.; Lauschke, A.; Frank, C.; Shu, P.Y.; Niedrig, M.; Huang, J.H.; Stark, K.; Jelinek, T. Dengue antibody prevalence in German travelers. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivbalan, S.; Anandnathan, K.; Balasubramanian, S.; Datta, M.; Amalraj, E. Predictors of spontaneous bleeding in Dengue. Indian J. Pediatr. 2004, 71, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, L.; Schreiber, M.; Low, J.G.; Ong, A.; Tolfvenstam, T.; Lai, Y.L.; Ng, L.C.; Leo, Y.S.; Thi Puong, L.; Vasudevan, S.G.; et al. Decision tree algorithms predict the diagnosis and outcome of dengue fever in the early phase of illness. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.; Demmler-Harrison, G.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Steinbach, W.J.; Hotez, P.J. Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmannitya, S. Clinical spectrum and management of dengue haemorrhagic fever. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1987, 18, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flamand, C.; Fritzell, C.; Prince, C.; Abboud, P.; Ardillon, V.; Carvalho, L.; Demar, M.; Boukhari, R.; Papaix-Puech, M.; Elenga, N.; et al. Epidemiological assessment of the severity of dengue epidemics in French Guiana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, J.; Douglass, K.; Gidwani, S.; Khatri, U.; Gaballa, D.; Pousson, A.; Mangla, N.; Smith, J. Seasonal dengue surge: Providers⬨tm) perceptions about the impact of dengue on patient volume, staffing and use of point of care testing in Indian emergency departments. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
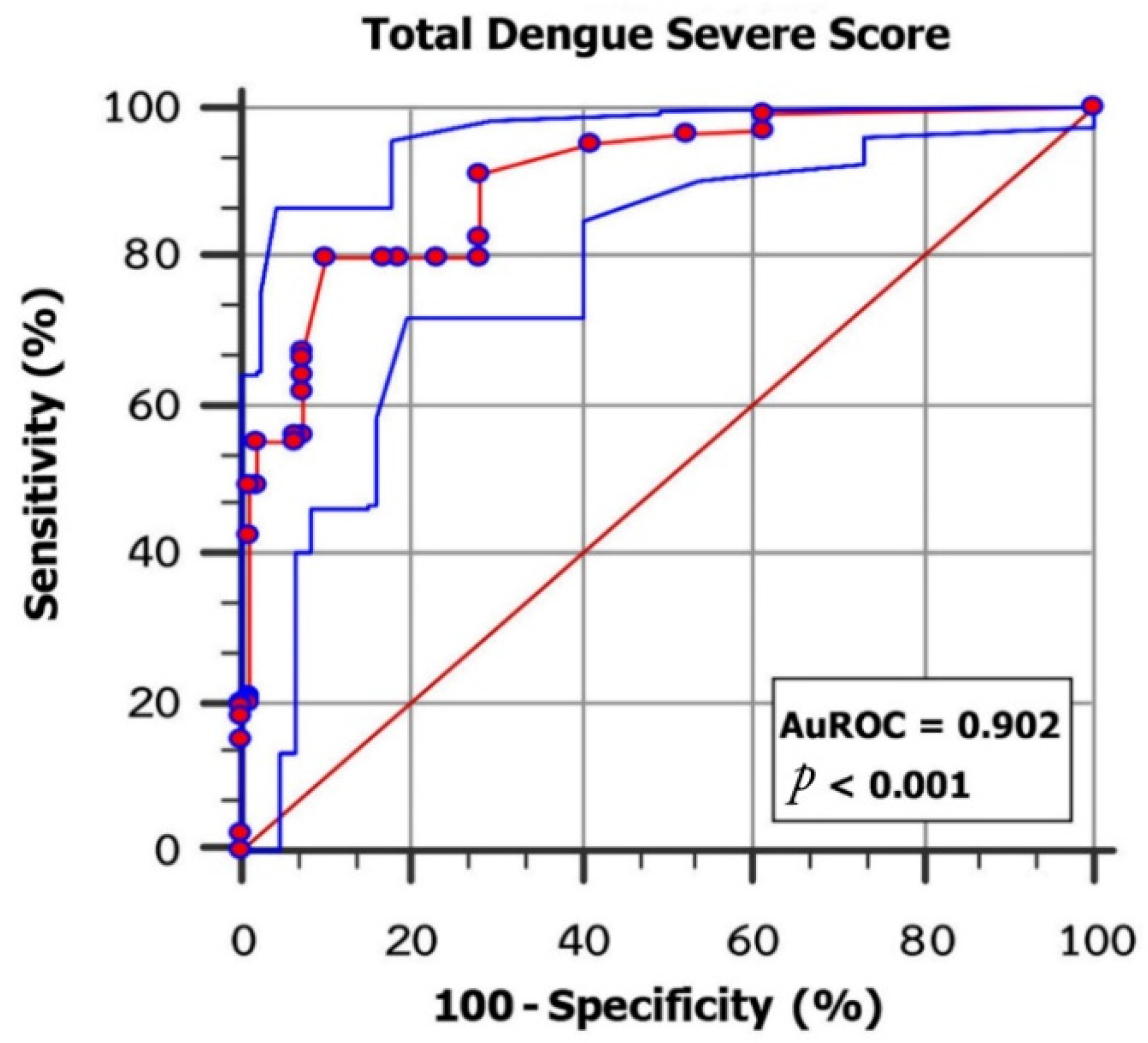
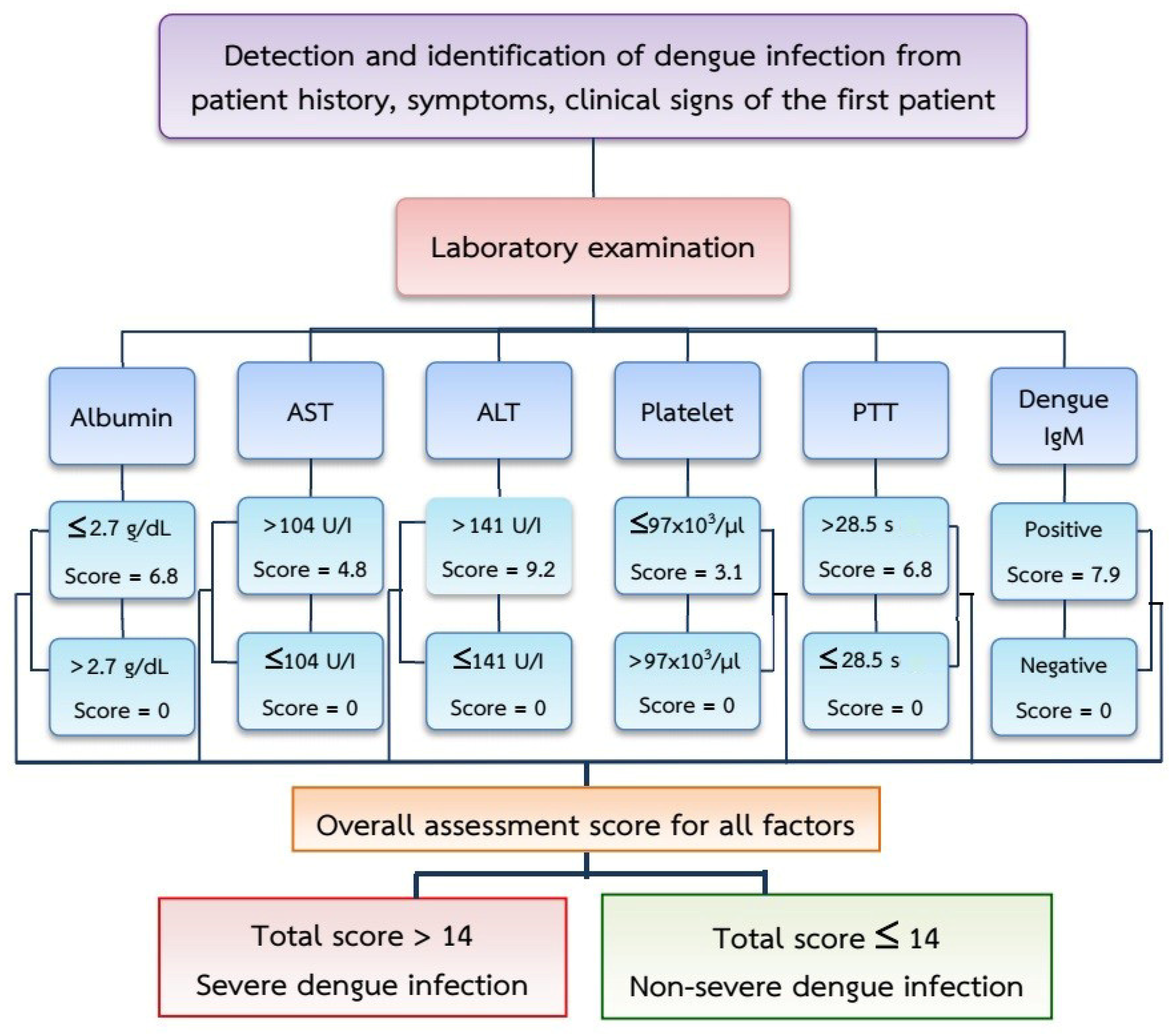
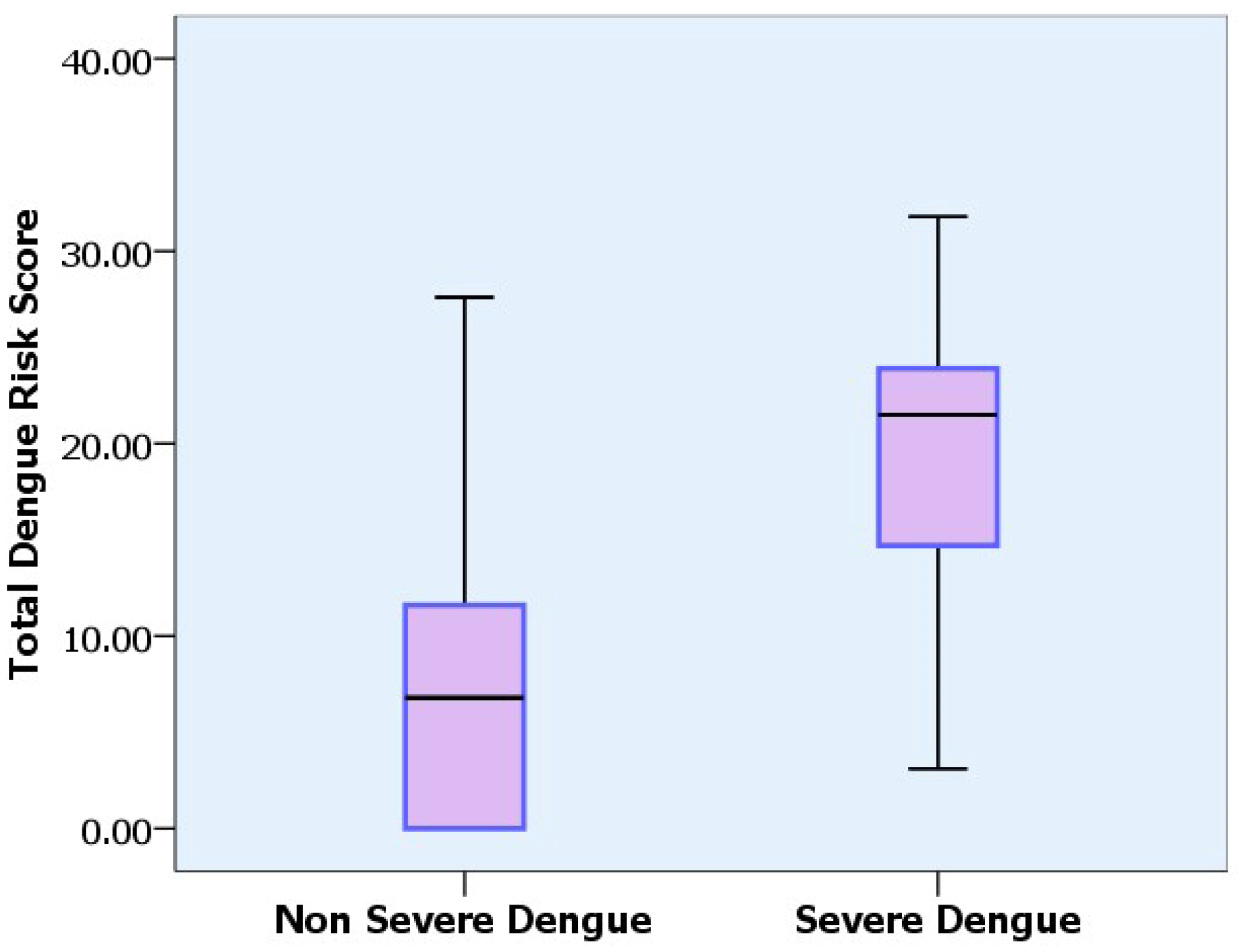
| Parameter: (Predictors) | Category | n | Odds Ratio (OR) * | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | Coefficient * | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin (g/dl) | ≤2.7 | 43 | 6.438 | 2.23–18.56 | <0.001 | 0.683 | 0 |
| >2.7 | 259 | 6.8 | |||||
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/I) | >104 | 181 | 6.129 | 3.65–10.28 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0 |
| ≤104 | 121 | 4.8 | |||||
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/I) | >141 | 99 | 5.133 | 2.74–9.63 | <0.001 | 0.683 | 9.2 |
| ≤141 | 203 | 0 | |||||
| Platelet count (103/µL) | ≤97 | 190 | 1.882 | 1.16–3.06 | 0.010 | 0.999 | 3.1 |
| >97 | 112 | 0 | |||||
| Partial Thromboplastin Time (s) | >28.5 | 113 | 7.09 | 4.00–12.59 | <0.001 | 1.883 | 6.8 |
| ≤28.5 | 189 | 0 | |||||
| Dengue IgM | YES | 90 | 2.407 | 1.43–4.07 | 0.001 | 1.146 | 7.9 |
| NO | 212 | 0 |
| Parameter | Non-Severe n = 107 | Severe n = 195 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | (n, %) | 44 | (41.1) | 92 | (47.2) | 0.321 |
| Female | (n, %) | 63 | (58.9) | 103 | (52.8) | |
| Age (Year) | Mean ± SD | 21.81 ± 18.14 | 26.67 ± 16.55 | 0.019 | ||
| <5 | (n, %) | 12 | (11.2) | 13 | (6.7) | 0.001 |
| 5–10 | (n, %) | 18 | (16.8) | 18 | (9.2) | |
| 11–20 | (n, %) | 37 | (34.6) | 52 | (26.7) | |
| 21–30 | (n, %) | 17 | (15.9) | 44 | (22.6) | |
| 31–40 | (n, %) | 10 | (9.3) | 28 | (14.4) | |
| >40 | (n, %) | 13 | (12.1) | 40 | (20.5) | |
| Clinical Profile | ||||||
| Day of Illness | Mean ± SD | 3.49 ± 1.56 | 3.87 ± 1.5 | 0.038 | ||
| Rash | (n, %) | 23 | (21.50) | 42 | (21.5) | 0.993 |
| Headache | (n, %) | 17 | (15.90) | 34 | (17.4) | 0.732 |
| Cough | (n, %) | 3 | (2.80) | 3 | (1.5) | 0.453 |
| Vomiting | (n, %) | 27 | (25.2) | 58 | (29.7) | 0.400 |
| Abdominal Pain | (n, %) | 7 | (6.50) | 26 | (13.3) | 0.048 |
| Anorexia | (n, %) | 6 | (5.60) | 29 | (14.9) | 0.007 |
| Melena | (n, %) | 13 | (12.10) | 27 | (13.8) | 0.679 |
| Hemodynamic | Mean ± SD | |||||
| Systolic Blood Pressure: SBP | (mmHg) | 113.84 ± 16.75 | 113.83 ± 12.64 | 0.996 | ||
| Diastolic Blood Pressure: DBP | (mmHg) | 89.32 ± 15.47 | 88.59 ± 14.87 | 0.689 | ||
| Pulse Pressure: PP | (mmHg) | 24.52 ± 19.17 | 25.24 ± 19.48 | 0.758 | ||
| Hematological | Mean ± SD | |||||
| Hematocrit | % | 38.19 ± 5.74 | 41.28 ± 6.24 | <0.001 | ||
| Hemoglobin | g/dL | 6.81 ± 7.12 | 7.51 ± 5.36 | 0.337 | ||
| White Blood Cell Count | 103/μL | 4.39 ± 2.5 | 5.05 ± 2.88 | 0.045 | ||
| Neutrophil | % | 48.32 ± 20.9 | 41.29 ± 17.8 | 0.004 | ||
| Lymphocyte | % | 36.87 ± 19.17 | 39.1 ± 14.4 | 0.295 | ||
| Atypical Lymphocyte | % | 5.38 ± 6.99 | 11.18 ± 8.58 | <0.001 | ||
| Platelet Count | 103/μL | 154.65 ± 53.43 | 47.85 ± 28.39 | <0.001 | ||
| Prothrombin Time: PT | s | 13.68 ± 1.76 | 14.47 ± 3.09 | 0.050 | ||
| International Normalized Ratio: INR | 1.38 ± 1.69 | 1.19 ± 0.32 | 0.246 | |||
| Partial Thromboplastin Time: PTT | s | 36.72 ± 14.92 | 41.93 ± 22.54 | 0.016 | ||
| Biochemical | Mean ± SD | |||||
| Total Protein: TP | g/dL | 6.77 ± 0.84 | 6.51 ± 0.86 | 0.014 | ||
| Albumin: Alb | g/dL | 3.29 ± 0.42 | 3.14 ± 0.51 | 0.007 | ||
| TP/Alb Ratio | 2.06 ± 0.19 | 2.10 ± 0.28 | 0.110 | |||
| Aspartate Aminotransferase: AST | U/I | 136.48 ± 139.57 | 405.57 ± 1456 | 0.058 | ||
| Alanine Aminotransferase: ALT | U/I | 93.7 ± 86.84 | 222.07 ± 384.68 | 0.001 | ||
| Immunological | Positive | |||||
| Nonstructural Protein 1: NS1 Ag | (n, %) | 71 | (66.4) | 128 | (65.6) | 0.901 |
| Dengue IgM | (n, %) | 24 | (22.4) | 66 | (33.8) | 0.032 |
| Dengue IgG | (n, %) | 26 | (24.3) | 85 | (43.6) | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srisuphanunt, M.; Puttaruk, P.; Kooltheat, N.; Katzenmeier, G.; Wilairatana, P. Prognostic Indicators for the Early Prediction of Severe Dengue Infection: A Retrospective Study in a University Hospital in Thailand. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080162
Srisuphanunt M, Puttaruk P, Kooltheat N, Katzenmeier G, Wilairatana P. Prognostic Indicators for the Early Prediction of Severe Dengue Infection: A Retrospective Study in a University Hospital in Thailand. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(8):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080162
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrisuphanunt, Mayuna, Palakorn Puttaruk, Nateelak Kooltheat, Gerd Katzenmeier, and Polrat Wilairatana. 2022. "Prognostic Indicators for the Early Prediction of Severe Dengue Infection: A Retrospective Study in a University Hospital in Thailand" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 8: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080162
APA StyleSrisuphanunt, M., Puttaruk, P., Kooltheat, N., Katzenmeier, G., & Wilairatana, P. (2022). Prognostic Indicators for the Early Prediction of Severe Dengue Infection: A Retrospective Study in a University Hospital in Thailand. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(8), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080162







