A New Recombinant Multiepitope Chimeric Protein of Leptospira interrogans Is a Promising Marker for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria and Serum Samples
2.2. Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
2.3. Composition and Design of Multiepitope Chimeric Protein
2.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Chimeric Protein (rChi2)
2.5. Immunoblotting Assay
2.6. ELISA for Detection of Antibody against rChi2
2.7. Immunogenicity of rChi2 in Hamster Model
2.8. Anti-rChi2 Antiserum Reactivity against Different Leptospiral Species
2.9. Ethical Statements
3. Results
3.1. Chimeric Protein Composition and Epitope Conservation among Leptospira spp.
3.2. Expression and Purification of rChi2
3.3. Detection of rChi2-Reactive IgM and IgG Antibodies in Pooled Human Serum Samples
3.4. Reactivity of rChi2 with Individual Human Serum Samples
3.5. rChi2 Is Immunogenic in Hamsters and Elicits Antibodies Capable of Recognizing Pathogenic Leptospira
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, A.R.; Nally, J.E.; Ricaldi, J.N.; Matthias, M.A.; Diaz, M.M.; Lovett, M.A.; Levett, P.N.; Gilman, R.H.; Willig, M.R.; Gotuzzo, E.; et al. Leptospirosis: A zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.L.; Smythe, L.D.; Craig, S.B.; Weinstein, P. Climate change, flooding, urbanisation and leptospirosis: Fuelling the fire? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.B.; Ribeiro, G.; Felzemburgh, R.D.M.; Santana, F.S.; Mohr, S.; Melendez, A.X.T.O.; Queiroz, A.; Santos, A.C.; Ravines, R.R.; Tassinari, W.S.; et al. Impact of Environment and Social Gradient on Leptospira Infection in Urban Slums. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, A.I.; Galvão Reis, M.; Ribeiro Dourado, C.M.; Johnson, W.D.; Riley, L.W. Urban epidemic of severe leptospirosis in Brazil. Salvador Leptospirosis Study Group. Lancet 1999, 354, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faine, S.; Adler, B.; Bolin, C.; Perolat, P. Leptospira and Leptospirosis; MediSci: Melbourne, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, L.H. Leptospirosis. 3. Maintenance, isolation and demonstration of leptospires. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 64, 623–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.G.V.; Vieira, M.L.; Kirchgatter, K.; Alves, I.J.; de Morais, Z.M.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Romero, E.C.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. OmpL1 is an Extracellular Matrix- and Plasminogen-Interacting Protein of Leptospira spp. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 3679–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimanote, P.; Wongdeethai, N.; Jieanampunkul, P.; Samonkiert, S.; Leepiyasakulchai, C.; Kalambaheti, T.; Prachayasittikul, V. Recombinant ligA for leptospirosis diagnosis and ligA among the Leptospira spp. clinical isolates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 72, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalayon, P.; Chanket, P.; Boonchawalit, T.; Chattanadee, S.; Srimanote, P.; Kalambaheti, T. Leptospirosis serodiagnosis by ELISA based on recombinant outer membrane protein. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 105, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.R.; Longhi, M.T.; de Morais, Z.M.; Romero, E.C.; Blanco, R.M.; Kirchgatter, K.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Nascimento, A.L. Evaluation of Leptospiral Recombinant Antigens MPL17 and MPL21 for Serological Diagnosis of Leptospirosis by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Artiushin, S.C.; Velineni, S.; Vedhagiri, K.; Vijayachari, P.; Timoney, J.F. Surface-associated Hsp60 chaperonin of Leptospira interrogans serovar Autumnalis N2 strain as an immunoreactive protein. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 30, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitashoji, E.; Koizumi, N.; Lacuesta, T.L.V.; Usuda, D.; Ribo, M.R.; Tria, E.S.; Go, W.S.; Kojiro, M.; Parry, C.M.; Dimaano, E.M.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Recombinant Immunoglobulin-like Protein A-Based IgM ELISA for the Early Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in the Philippines. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Vijayachari, P.; Sugunan, A.P.; Sharma, S.; Sehgal, S.C. Leptospiral proteins expressed during acute & convalescent phases of human leptospirosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 120, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, L.G.; Teixeira, A.F.; Filho, A.F.; Souza, G.O.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Heinemann, M.B.; Romero, E.C.; Nascimento, A.L. Immune response and protective profile elicited by a multi-epitope chimeric protein derived from Leptospira interrogans. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 57, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AiHua, S.U.N.; Yuan, W.A.N.G.; Peng, D.U.; Shengling, W.U.; Jie, Y.A.N. A sensitive and specific IgM-ELISA for the serological diagnosis of human leptospirosis using a rLipL32/1-LipL21-OmpL1/2 fusion protein. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 291–299. [Google Scholar]
- Malmström, J.; Beck, M.; Schmidt, A.; Lange, V.; Deutsch, E.W.; Aebersold, R. Proteome-wide cellular protein concentrations of the human pathogen Leptospira interrogans. Nature 2009, 460, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, E.J.; Fernandes, L.G.; Sivasankaran, S.K.; Bayles, D.O.; Alt, D.P.; Lippolis, J.D.; Nally, J.E. Some like it hot, some like it cold; proteome comparison of Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo strains propagated at different temperatures. J. Proteom. 2022, 262, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.; Gunasekaran, D.; Rex, D.; Sikha, T.; Phukan, H.; Kiran, K.; Pinto, S.; Prasad, T.; Madanan, M. Extracellular Proteome Analysis Shows the Abundance of Histidine Kinase Sensor Protein, DNA Helicase, Putative Lipoprotein Containing Peptidase M75 Domain and Peptidase C39 Domain Protein in Leptospira interrogans Grown in EMJH Medium. Pathogens 2021, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghi, A.; Pappalardo, E.; Hester, S.; Thomas, B.; Pretre, G.; Picardeau, M. Pathogenic Leptospira interrogans Exoproteins Are Primarily Involved in Heterotrophic Processes. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.-B.; Zhuang, X.-R.; Huang, L.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.-L.; Ding, X.-L.; Chang, Y.-F.; et al. Comparative subproteome analysis of three representative Leptospira interrogans vaccine strains reveals cross-reactive antigens and novel virulence determinants. J. Proteom. 2015, 112, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.B.; Teixeira, A.F.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Overcoming problems to produce the recombinant protein LipL21 of Leptospira interrogans. 2022. Submitted to publication.
- Gruber, A.; Zingales, B. Alternative method to remove antibacterial antibodies from antisera used for screening of expression libraries. Biotechniques 1995, 19, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Maneewatch, S.; Adisakwattana, P.; Chaisri, U.; Saengjaruk, P.; Srimanote, P.; Thanongsaksrikul, J.; Sakolvaree, Y.; Poungpan, P.; Chaicumpa, W. Therapeutic epitopes of Leptospira LipL32 protein and their characteristics. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2014, 27, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turner, L.H. Leptospirosis. II. Serology. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 62, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapna, K.; Ashaiba, A.; Kumar, T.R.; Shashidhar, V.; Arun, A.B.; Prasad, K.S. Evaluation of anti-LipL32 carbon nanotube immunofluorescence probe (carbo-lip) and comparison with MAT, IgM ELISA, IgM spot test and culture for early detection of leptospirosis at local hospital. J. Microbiol. Methods 2022, 195, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhylkibayev, A.; Akishev, Z.; Khassenov, B.; Sarina, N.; Ramankulov, Y.; Mukanov, K.; Eskendirova, S. Obtaining and characterization of a recombinant LipL32 protein for detection of leptospirosis. Trop. Biomed. 2018, 35, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Vedhagiri, K.; Velineni, S.; Timoney, J.F.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Vijayachari, P.; Narayanan, R.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Detection of LipL32-specific IgM by ELISA in sera of patients with a clinical diagnosis of leptospirosis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2013, 107, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anita, K.; Premlatha, M.M.; Kanagavel, M.; Mercy, C.S.A.; Raja, V.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Evaluation of combined B cell specific N-terminal immunogenic domains of LipL21 for diagnosis of leptospirosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Vijayachari, P.; Sharma, S.; Sugunan, A.P.; Selvin, J.; Sehgal, S.C. Serodiagnosis of severe leptospirosis: Evaluation of ELISA based on the recombinant OmpL1 or LipL41 antigens of Leptospira interrogans serovar autumnalis. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2008, 102, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, B.; Bahaman, A.R.; Zakaria, Z.; Bejo, S.K.; Mutalib, A.R.; Bande, F.; Suleiman, N. Antigenic potential of a recombinant polyvalent DNA vaccine against pathogenic leptospiral infection. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 124, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.L.; Rizzi, C.; da Cunha, C.E.P.; Dorneles, J.; Neto, A.C.P.S.; Amaral, M.G.; Hartwig, D.D.; Dellagostin, O.A. Recombinant BCG strains expressing chimeric proteins derived from Leptospira protect hamsters against leptospirosis. Vaccine 2019, 37, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettin, E.B.; Dorneles, J.; Hecktheuer, A.S.; Madruga, A.B.; Neto, A.C.P.S.; McBride, A.J.A.; Oliveira, T.L.; Grassmann, A.A.; Dellagostin, O.A. TonB-dependent receptor epitopes expressed in M. bovis BCG induced significant protection in the hamster model of leptospirosis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 106, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorneles, J.; Madruga, A.B.; Neto, A.C.P.S.; Rizzi, C.; Bettin, B.; Hecktheuer, A.S.; de Castro, C.C.; Fernandes, C.G.; Oliveira, T.L.; Dellagostin, O.A. Protection against leptospirosis conferred by Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressing antigens from Leptospira interrogans. Vaccine 2020, 38, 8136–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Lata, S.; Shankar, U.N.; Akif, M. Immunoinformatics-Based Designing of a Multi-Epitope Chimeric Vaccine From Multi-Domain Outer Surface Antigens of Leptospira. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 735373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Shiraz, M.; Akif, M. Multiepitope-based vaccine design by exploring antigenic potential among leptospiral lipoproteins using comprehensive immunoinformatics and structure-based approaches. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, J.M.; Siqueira, G.H.; de Souza, G.O.; Heinemann, M.B.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Chapola, E.G.B.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Characterization of two new putative adhesins of Leptospira interrogans. Microbiology 2017, 163, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.R.; Fernandes, L.G.; de Souza, G.O.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Heinemann, M.B.; Romero, E.C.; Nascimento, A.L. Multifunctional and Redundant Roles of Leptospira interrogans Proteins in Bacterial-Adhesion and fibrin clotting inhibition. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, R.F.; Romero, E.C.; Fernandes, L.G.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; de Morais, Z.M.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Novel Leptospira interrogans protein Lsa32 is expressed during infection and binds laminin and plasminogen. Microbiology 2015, 161, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G.L. The lipoprotein LipL32, an enigma of leptospiral biology. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seixas, F.K.; da Silva, F.; Hartwig, D.D.; Cerqueira, G.; Amaral, M.; Fagundes, M.Q.; Dossa, R.G.; Dellagostin, O.A. Recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressing the LipL32 antigen of Leptospira interrogans protects hamsters from challenge. Vaccine 2007, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, D.S.D.; Cullen, P.A.; Lo, M.; Srikram, A.; Sermswan, R.W.; Adler, B. Recombinant LipL32 and LigA from Leptospira are unable to stimulate protective immunity against leptospirosis in the hamster model. Vaccine 2011, 29, 3413–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Rathinam, S.R.; Priya, C.G.; Muthukkaruppan, V.R.; Stevenson, B.; Timoney, J.F. LruA and LruB Antibodies in Sera of Humans with Leptospiral Uveitis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courrol, D.D.S.; Silva, C.C.F.D.; Prado, L.G.; Chura-Chambi, R.M.; Morganti, L.; De Souza, G.O.; Heinemann, M.B.; Isaac, L.; Conte, F.P.; Barbosa, A.S.; et al. Leptolysin, a Leptospira secreted metalloprotease of the pappalysin family with broad-spectrum activity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 1231, 966370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Murphy, A.M.; Locarnini, S.A.; Faine, S. Detection of specific anti-leptospiral immunoglobulins M and G in human serum by solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 11, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernukha, Y.G.; Shishkina, Z.S.; Baryshev, P.M.; Kokovin, I.L. The dynamics of IgM- and IgG-antibodies in leptospiral infection in man. Zent. Bakteriol Orig A 1976, 236, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, G.; Alquiza, L.M.; Padre, L.P.; Tuazon, M.L.; Laughlin, L.W. The Rapid Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: A Prospective Comparison of the Dot Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and the Genus-Specific Microscopic Agglutination Test at Different Stages of Illness. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 157, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.V.; Camargo, E.D.; Batista, L.; Vaz, A.J.; Brandão, A.P.; Nakamura, P.M.; Negrão, J.M. Behaviour of specific IgM, IgG and IgA class antibodies in human leptospirosis during the acute phase of the disease and during convalescence. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 98, 268–272. [Google Scholar]
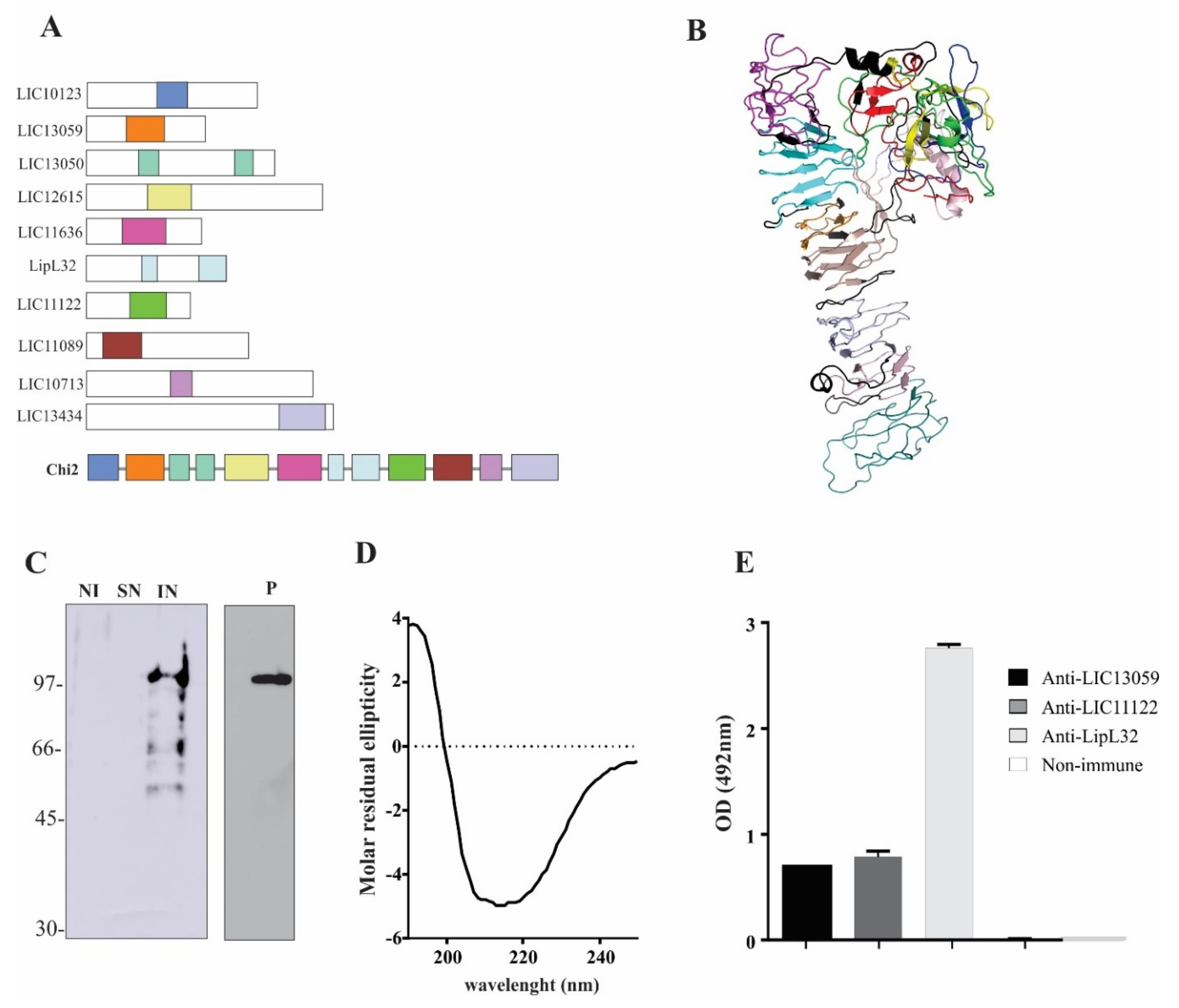
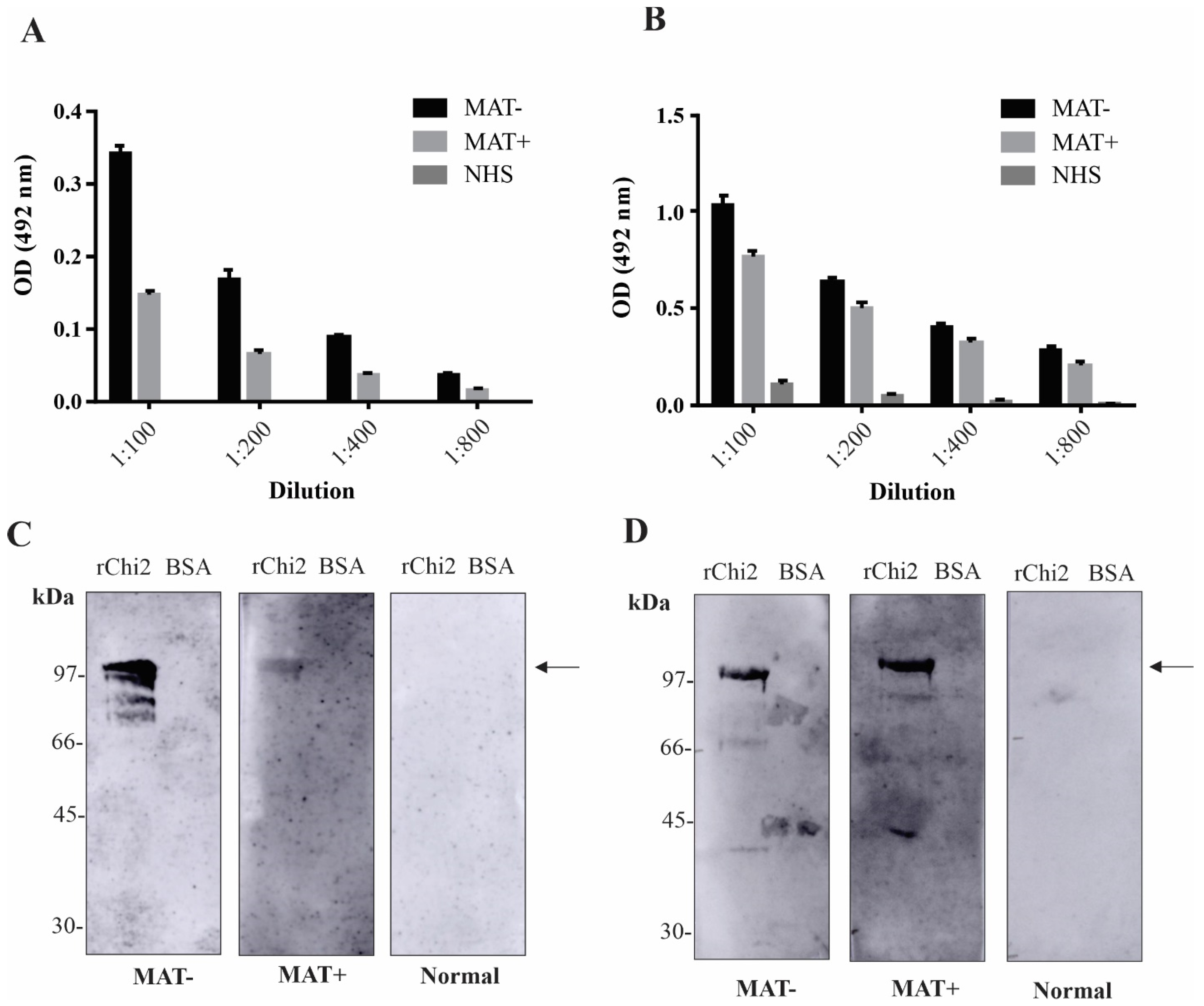
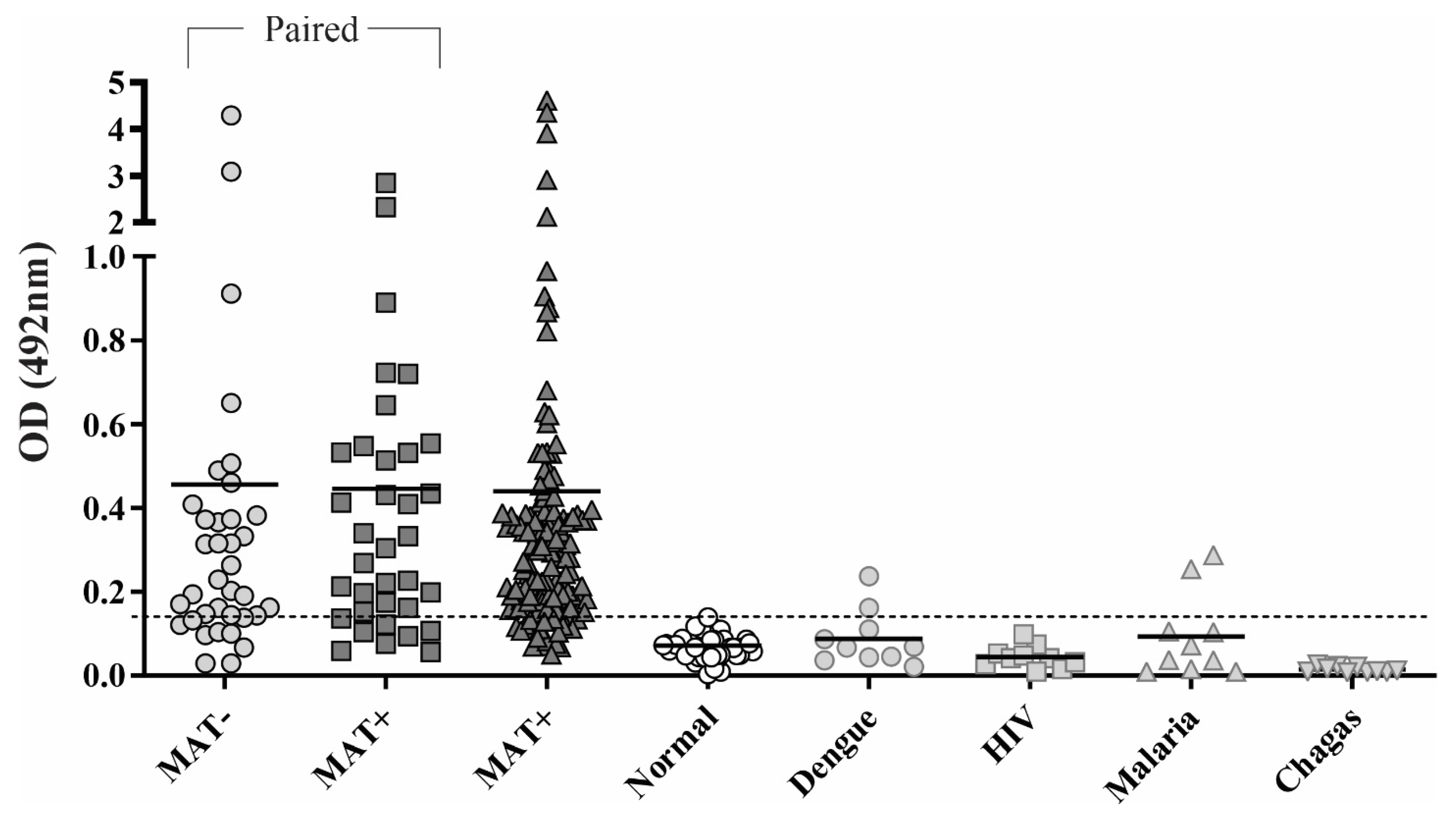
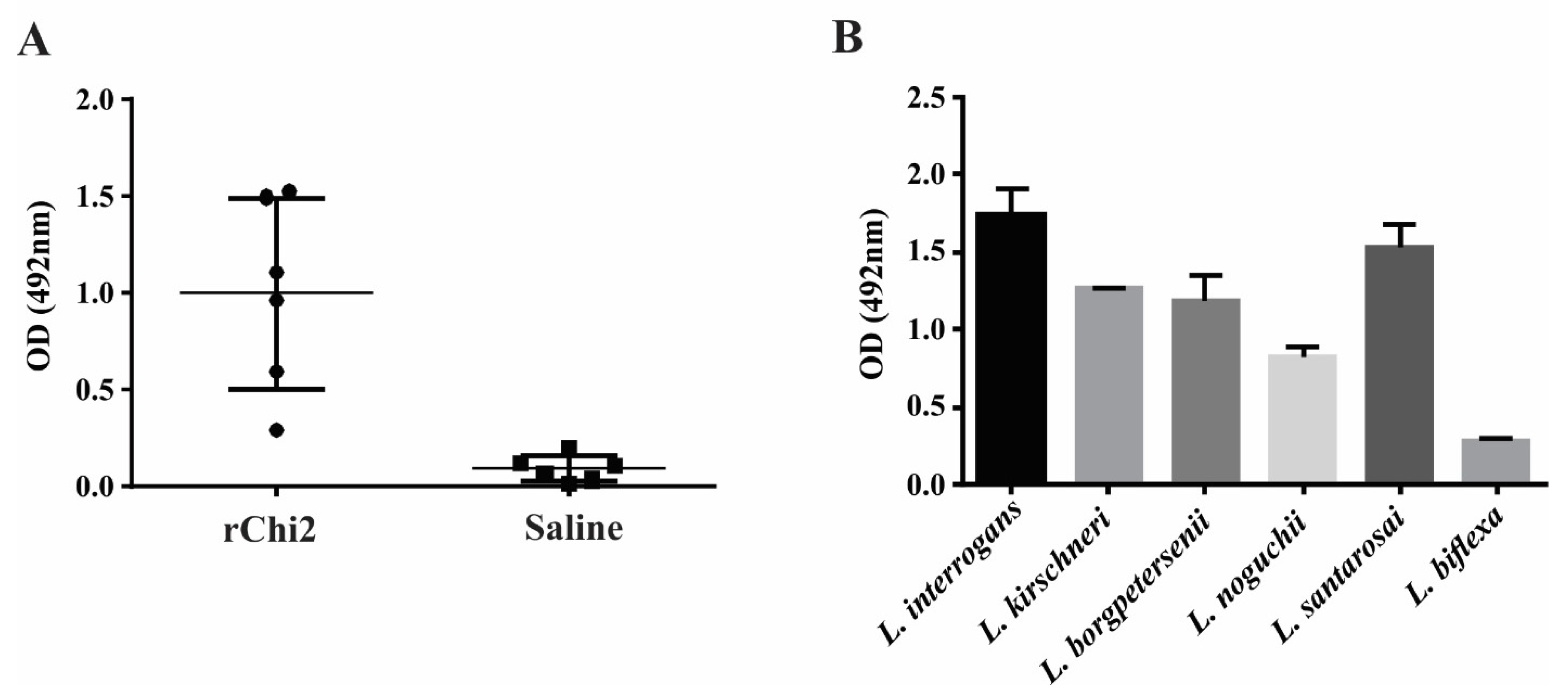
| Protein | Conserved | Selected | Predicted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain a | Region | Epitopes b | |
| LIC10123 | FecR | 132–191 | 3 |
| (91–201) | |||
| LIC13059 | - | 76–150 | 3 |
| LIC13050 | Big | 100–140/287–324 | 2/2 |
| (67–164)/(250–343) | |||
| LIC12615 | DUF3383 | 120–205 | 4 |
| (270–458) | |||
| LIC11636 | AIM24 | 70–155 | 5 |
| (3–206) | |||
| LipL32 | LipL32 | 108–138/220–272 | 2 * |
| (47–243) | |||
| LIC11122 | FecR | 84–155 | 3 |
| (53–155) | |||
| LIC11089 | - | 30–105 | 5 |
| LIC10713 | Peptidase_M75 | 161–203 | 2 |
| (58–351) | |||
| LIC13434 | Peptidase_M43 | 374–464 | 4 |
| (318–466) |
| 10123 | 13059 | 13050 | 12615 | 11636 | LipL32 | 11122 | 11089 | 10713 | 13434 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. interrogans serovar Copenhageni | 100 | 100 | 100/100 | 100 | 100 | 100/100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| L. kirschneri Cynopteri | 100 | 96 | 100/97 | 94 | 100 | 100/100 | 100 | 99 | 98 | 99 |
| L. noguchii Panama | 100 | 96 | 100/97 | 94 | 95 | 100/100 | 94 | 92 | 86 | 98 |
| L. alstoni Pingchang | 93 | 91 | 98/97 | 76 | 98 | 97/98 | 90 | 83 | 85 | 92 |
| L. weilii Ranarum | 92 | 89 | 98/97 | 76 | 98 | 97/98 | 88 | 82 | 78 | 90 |
| L. alexanderi Manhao | 95 | 91 | 100/97 | ND | 93 | 97/96 | 89 | 84 | 82 | 92 |
| L. borgpetersenii Hardjo-bovis | 93 | 89 | 100/97 | ND | 90 | 100/100 | 86 | 77 | 81 | 93 |
| L. santarosai Shermani | 93 | 88 | 100/100 | 40 | 90 | 100/100 | 89 | 78 | 81 | 92 |
| L. kmetyi Malaysia | 97 | 41 (c = 30) | 100/95 | 80 | 95 | 97/96 | 90 | 69 | 70 | 88 |
| L. fainei Hurstbridge | 69 | 39 | 63/57 | 38 | 74 | 90/75 | 62 | 43 | 52 | 56 |
| L. broomii Hurstbridge | 69 | 0 | 60/62 | 44 | 75 | 85/73 | 62 | 37 | 48 | 56 |
| L. wolffi Khorat | 66 | 37 (c = 46) | 70/65 | ND | 75 | 90/70 | 62 | ND | 43 | 56 |
| L. liceraciae Varillal | 65 | 0 | 64/60 | ND | 71 | 90/64 | 57 | 31 | 46 | 56 |
| L. inadai Lyme | 69 | 39 | 60/60 | 44 (c = 045) | 74 | 86/73 | 62 | 40 | 48 | 57 |
| L. biflexa Patoc | 50 | 0 | 63/51 | ND | ND | ND/ND | 40 | ND | ND | 50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, L.G.V.; Avelar, K.E.S.; Romero, E.C.; Heinemann, M.B.; Kirchgatter, K.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. A New Recombinant Multiepitope Chimeric Protein of Leptospira interrogans Is a Promising Marker for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7110362
Fernandes LGV, Avelar KES, Romero EC, Heinemann MB, Kirchgatter K, Nascimento ALTO. A New Recombinant Multiepitope Chimeric Protein of Leptospira interrogans Is a Promising Marker for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(11):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7110362
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Luis G. V., Kátia E. S. Avelar, Eliete C. Romero, Marcos B. Heinemann, Karin Kirchgatter, and Ana L. T. O. Nascimento. 2022. "A New Recombinant Multiepitope Chimeric Protein of Leptospira interrogans Is a Promising Marker for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 11: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7110362
APA StyleFernandes, L. G. V., Avelar, K. E. S., Romero, E. C., Heinemann, M. B., Kirchgatter, K., & Nascimento, A. L. T. O. (2022). A New Recombinant Multiepitope Chimeric Protein of Leptospira interrogans Is a Promising Marker for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(11), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7110362









