Abstract
Rabies transmitted by sylvatic populations has become an increasing concern in Brazil. A total of 113 participants with a history of contact with sylvatic populations were interviewed in 27 municipalities of Ceará State in northeast Brazil. Questionnaires included questions on knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) regarding sylvatic rabies. Most of the respondents (92%) knew about rabies and confirmed at least one species that transmitted the disease (79.6%). Of these respondents, 69% mentioned monkeys, and 67.2% mentioned dogs. However, 16% of the respondents listed an incorrect species. In general, knowledge on the symptoms and signs and on prevention measures was weak. The majority raised pets (93.8%), most commonly dogs and cats, and, of all the pets, 85.7% were claimed to be vaccinated against rabies. A total of 67.3% reported the appearance of free-living wild animals around their houses, mostly marmosets and wild canids; 18.3% reported that sylvatic populations had attacked animals or humans. Seventy-three percent had raised or still were raising wild animals as pets, mostly capuchin monkeys (79.5%) and marmosets (24.1%). This is the first KAP study on sylvatic rabies in Brazil. The data indicate important knowledge gaps and risk behavior within a high-risk population. There is a need for strengthening and improving sylvatic rabies surveillance and control, combined with the intensification of education and information campaigns.
1. Introduction
Rabies is a neglected tropical disease of major global importance, with thousands of deaths per year worldwide. About 95% of the deaths occur in Africa and Asia. Worldwide, domestic dogs are responsible for transmission in 99% of the cases [1,2].
Similar to most other infectious diseases, low socio-economic strata and rural areas are considered to be at the highest risk [3,4]. In addition to the lack of knowledge regarding the risk of acquiring the disease after exposure, populations in rural areas suffer from limited access to the healthcare system, and financial constraints may hinder travel to the local hospital for post-exposure prophylaxis [4].
The transmission cycle of the rabies virus maintained by dogs and cats can be controlled through effective prophylactic measures [2]. However, the emergence of transmission by sylvatic populations has become an increasing challenge, especially in Brazil [5,6]. In a rural community in the Brazilian State of Amazonas, 57% of the respondents had informal knowledge about rabies, but only 23% had received information from health professionals [7]. In a Pakistani study, all the respondents had heard about the disease and knew about the importance of domestic animals for transmission, especially dogs, which were mentioned by 93% of the respondents [8]. On the other side, only 22% identified cats as putative transmitters [8]. Knowledge regarding the wildlife species involved in the rabies virus transmission was limited in an Indian study where foxes and monkeys were cited as possible transmitters by only about 25% of the participants [9]. In rural Ethiopia, people believed that traditional healers and herbal medicines may cure rabies, indicating the importance of health education in rabies prevention measures, sensitively addressing cultural and gender concerns [10].
We have recently shown that the rabies virus in the State of Ceará in northeast Brazil is transmitted mainly by wild animals [5,6]. The last outbreak of rabies transmitted by dogs in Ceará occurred in 2003 [11]. Of the last six cases of human rabies since 2006, five were transmitted by wild animals [12]. Surveillance and control measures in the state should, therefore, focus on rabies caused by wildlife [12]. However, the population apparently lacked basic knowledge about the disease and the transmission cycle involving sylvatic populations. Thus, knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) were studied among people who had contact with or raised wild mammals as companion animals in the State of Ceará.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Population
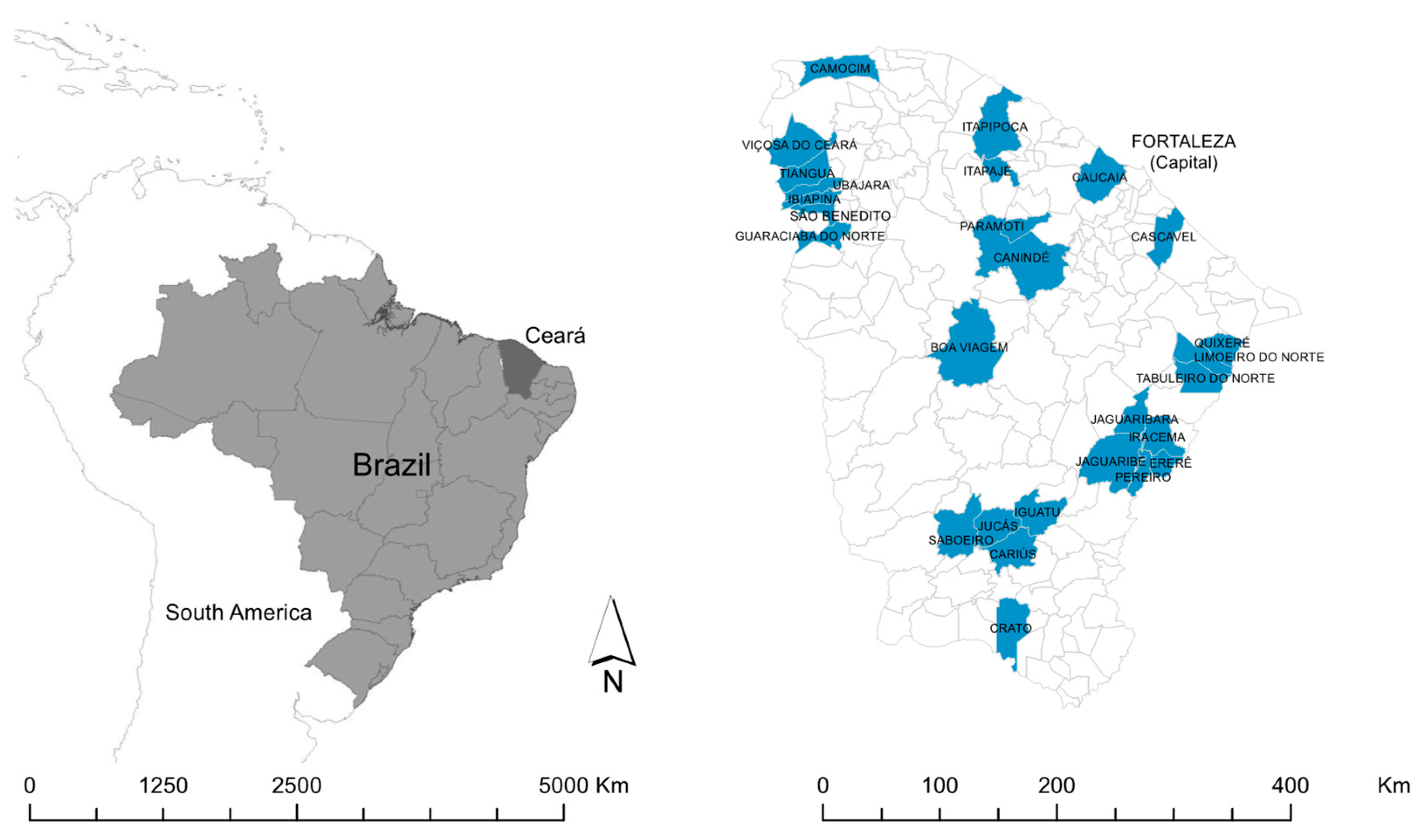
The State of Ceará in the northeast region of Brazil is bordered in the north by the Atlantic Ocean, in the west by the State of Piauí, in the east by the States of Rio Grande do Norte and Paraíba, and in the south by the State of Pernambuco (Figure 1). Ceará has a population of approximately nine million and an area of 149 thousand km2, distributed throughout 184 municipalities [13].
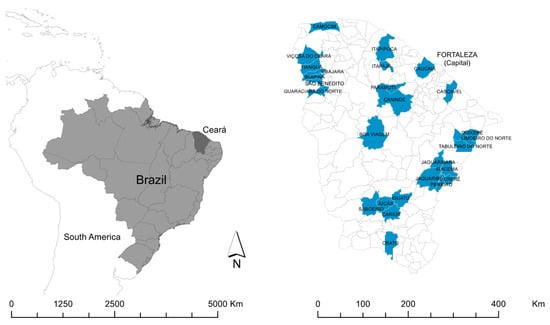
Figure 1.
Location of Ceará State in Brazil, and location of the municipalities included in the study.
In Ceará, rabies virus transmission dynamics have changed during the last few decades, and rabies transmitted by dogs is now controlled. Almost all cases in humans that occurred during the last 18 years were transmitted by wild animals [12].
We performed a KAP study in 27 municipalities dispersed throughout the state (Figure 1). The selection of municipalities was carried out in collaboration with local health professionals (endemic control agents and community health agents) who conducted an active survey of municipalities with records of people with a history of contact with an aggressive wild animal, captive breeding of wild animals and/or interaction of household members with free-living wild animals. These high-risk households were identified in cooperation with community agents. Participants were included and invited for an interview if ≥18 years of age and in the presence of one or both of the following characteristics: the household member has had contact with animals kept in captivity or with free-living animals; history of any aggression by wild mammals.
2.2. Variables and Data Collection
Endemic control agents (agentes de controle de endemias—ACE in Portuguese) and community health agents (agentes comunitários de saúde—ACS in Portuguese) conducted the surveys in their respective municipalities. Participants were interviewed using pre-tested structured questionnaires. The questionnaires consisted of five blocks of closed and open questions. Variables included socio-demographic data, and questions on knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding rabies and its control, with focus on wildlife-mediated transmission (Table 1).

Table 1.
Variables and questions on knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding rabies awareness and prevention, with focus on wildlife rabies, Ceará, Brazil.
We asked for different aspects of knowledge on rabies, risk behaviors, exposures and attitudes and behaviors in relation to capturing and raising wild animals. Feral dogs were included in the group of domestic dogs.
In the first 34 questionnaires applied, the variable regarding the knowledge of people who might have been attacked by mammals was not included. Only after some people mentioned these incidents did we insert this information as a variable.
During the visits, the team was introduced to the family, and the investigator identified the person with most intensive contact with the animals to answer the questionnaire by reading out the questions. If this specific person was less than 18 years old, a parent or guardian was asked to answer the questions. After application of questionnaires, the team in charge conducted education on environmental legislation, risk of zoonotic transmission and animal welfare.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A database was created to consolidate and organize the data using MS Excel 2016 software (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). Analysis was performed using Stata software version 15.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). Categorical variables were presented in absolute and relative frequencies. In the case of numerical variables, measures of central tendency and dispersion were chosen according to normality criteria: mean and standard deviation for normally distributed variables and median and interquartile range for non-normal variables. Answers to open questions were categorized and grouped. Knowledge was stratified according to area of residence (rural/urban).
2.4. Ethical Aspects
The study was approved by the Ethical Review Boards of the Federal University of Ceará (CAAE number—13466719.6.0000.5054) and of the State Health Department (CAAE number—13466719.3001.5051). The municipalities gave their consent for the study. Before application of the questionnaires, the objectives of the study were explained to the participants and that participation would be on a voluntary basis. Informed written consent was obtained. Personal data were kept strictly confidential.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Population
A total of 113 participants were included in the study; there were no refusals to participate in the study. The median number of inhabitants per residence was three (interquartile range: 2–4). Most respondents were females, had elementary school education and resided in rural areas (Table 2).

Table 2.
Characteristics of study participants, Ceará, Brazil, 2019 (n = 113).
3.2. Knowledge
In total, 92% of the respondents—97% in rural areas and 87% in urban areas—said that they had heard of rabies, and that they knew at least one animal species that can transmit the disease (Table 3).

Table 3.
Knowledge about rabies, total and stratified by residential area, Ceará, Brazil (n = 113).
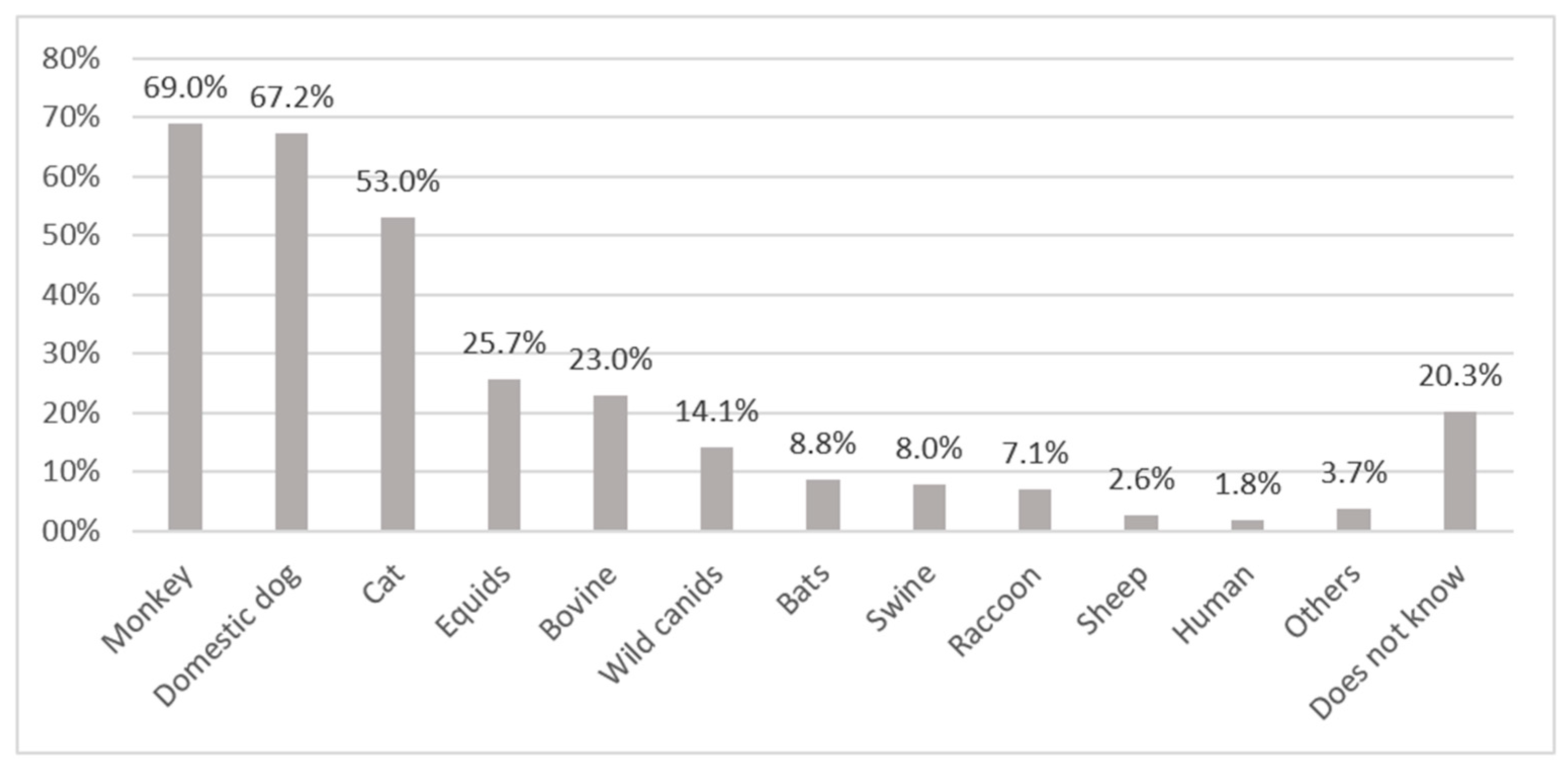
In general, knowledge of the animal species that may transmit rabies was low. Of the 80% who reported knowing the transmission species, 16% reported incorrect species. About 67–69% mentioned correctly domestic dogs and monkeys, and 53% cats, while about 20% were not able to respond to this question (Figure 2). As domestic dogs also roam freely around in the communities, the respondents did not differentiate between feral and domestic dogs.
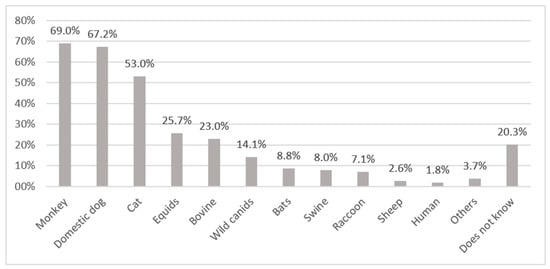
Figure 2.
Animals or categories of animals reported by respondents to be rabies virus transmitting animals. Others: snake (0.9%), parrot (0.9%), jaguar (0.9%), goat (0.9%), opossum (0.1%).
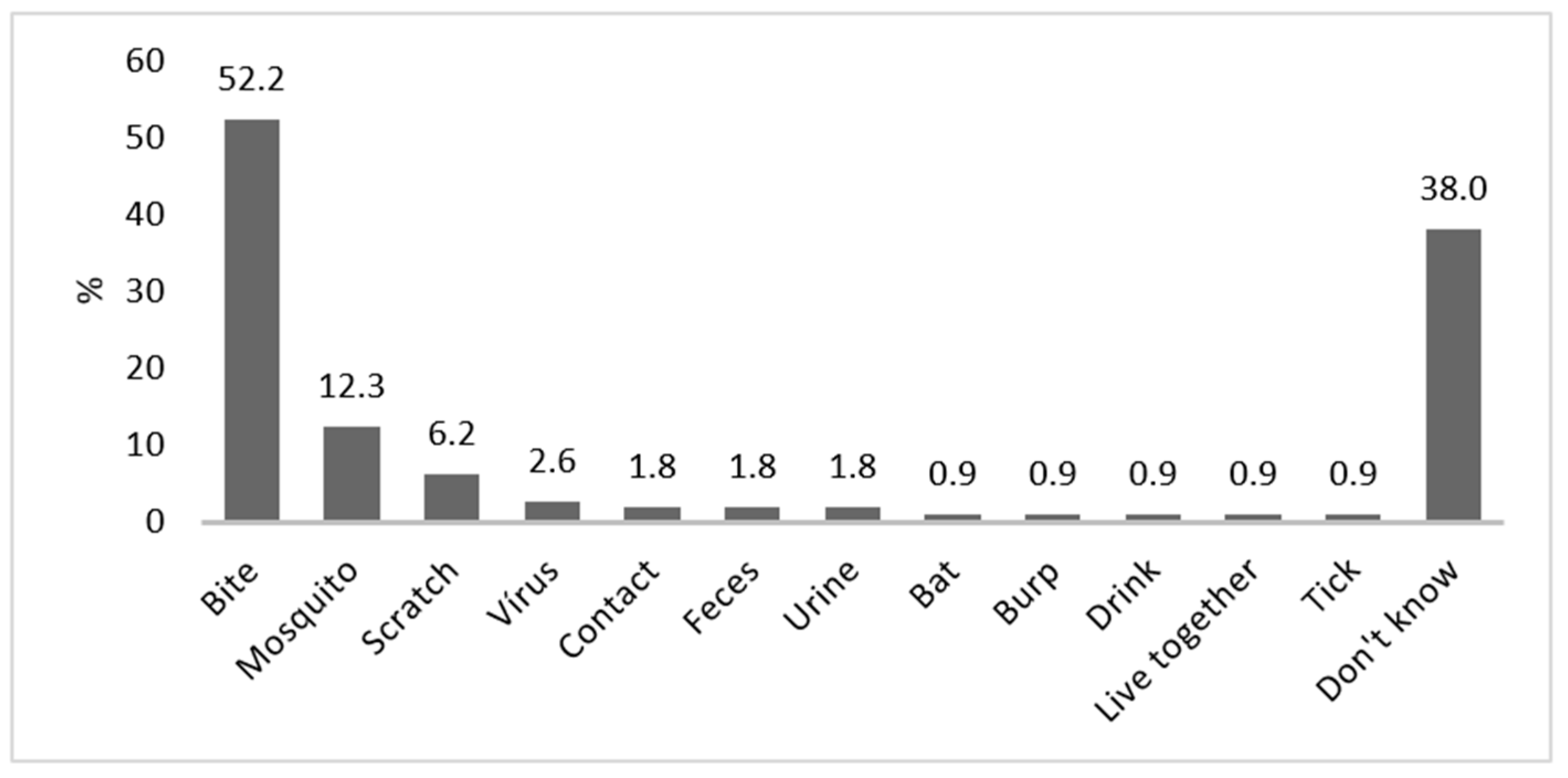
Knowledge on the mode of transmission was weak, and 38% did not know the mode of transmission at all. About 52% mentioned correctly animal bites and 6% scratches, but 12% believed that mosquitoes would transmit rabies. Other incorrect modes of transmission cited by respondents included transmission by urine and feces (Figure 3).
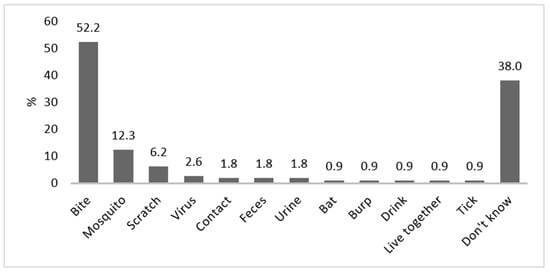
Figure 3.
Modes of transmission for rabies, as reported by respondents (bites, scratches and bats were considered as correct answers). Contact means touching and/or feeding the animals; live together means that animals are leashed or kept in cages on the property.
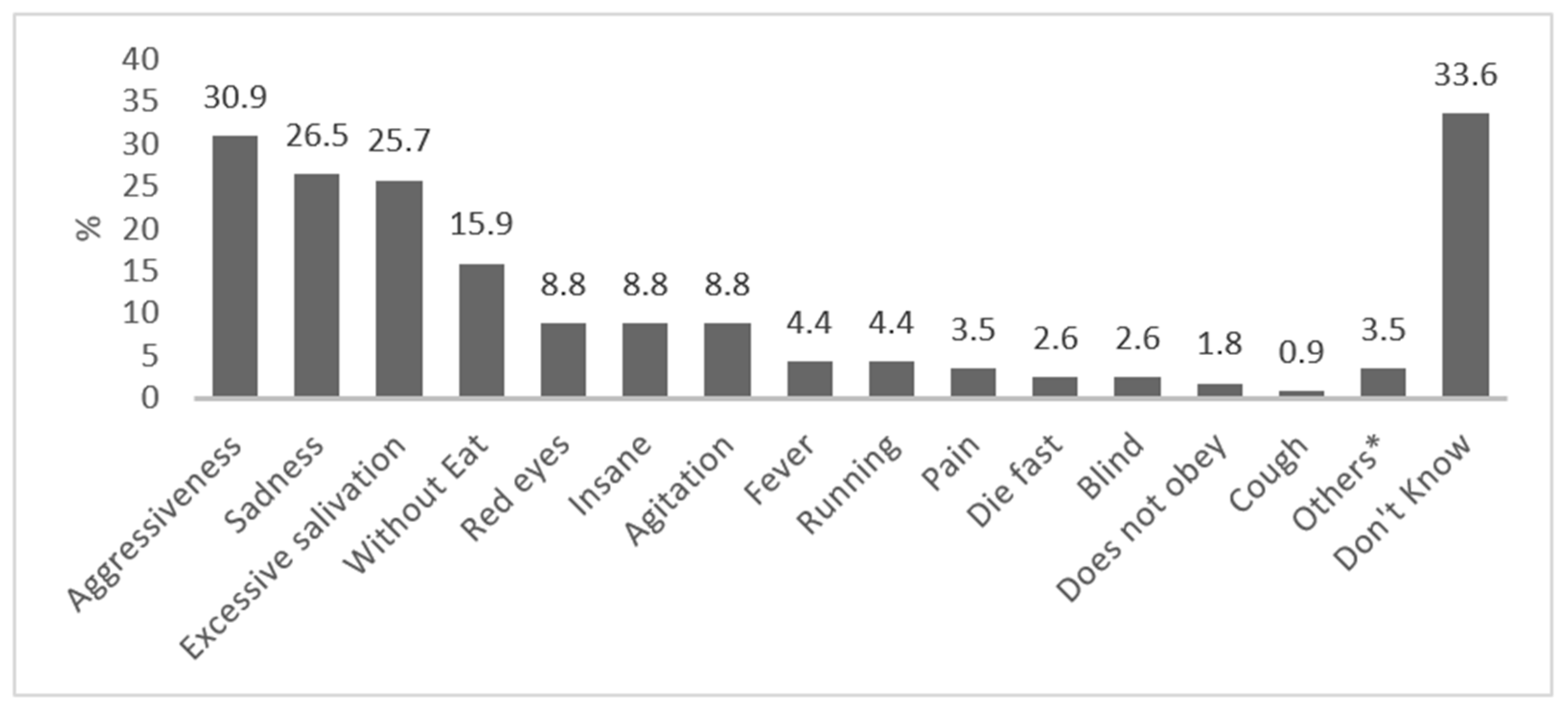
The symptoms/clinical signs cited by the respondents are presented in Figure 4. Three common symptoms and signs—aggressiveness, salivation and anorexia—were among the topmost mentioned responses.
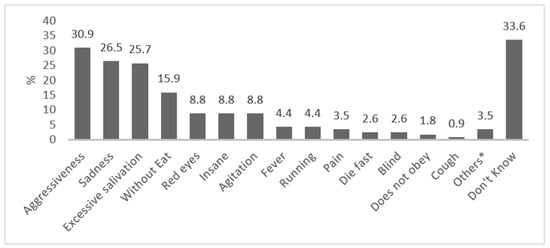
Figure 4.
Symptoms of rabies, as reported by respondents. * Others: barking (0.9%), not drinking sufficiently (0.9%), stiff tail (0.9%), quivering (0.9%).
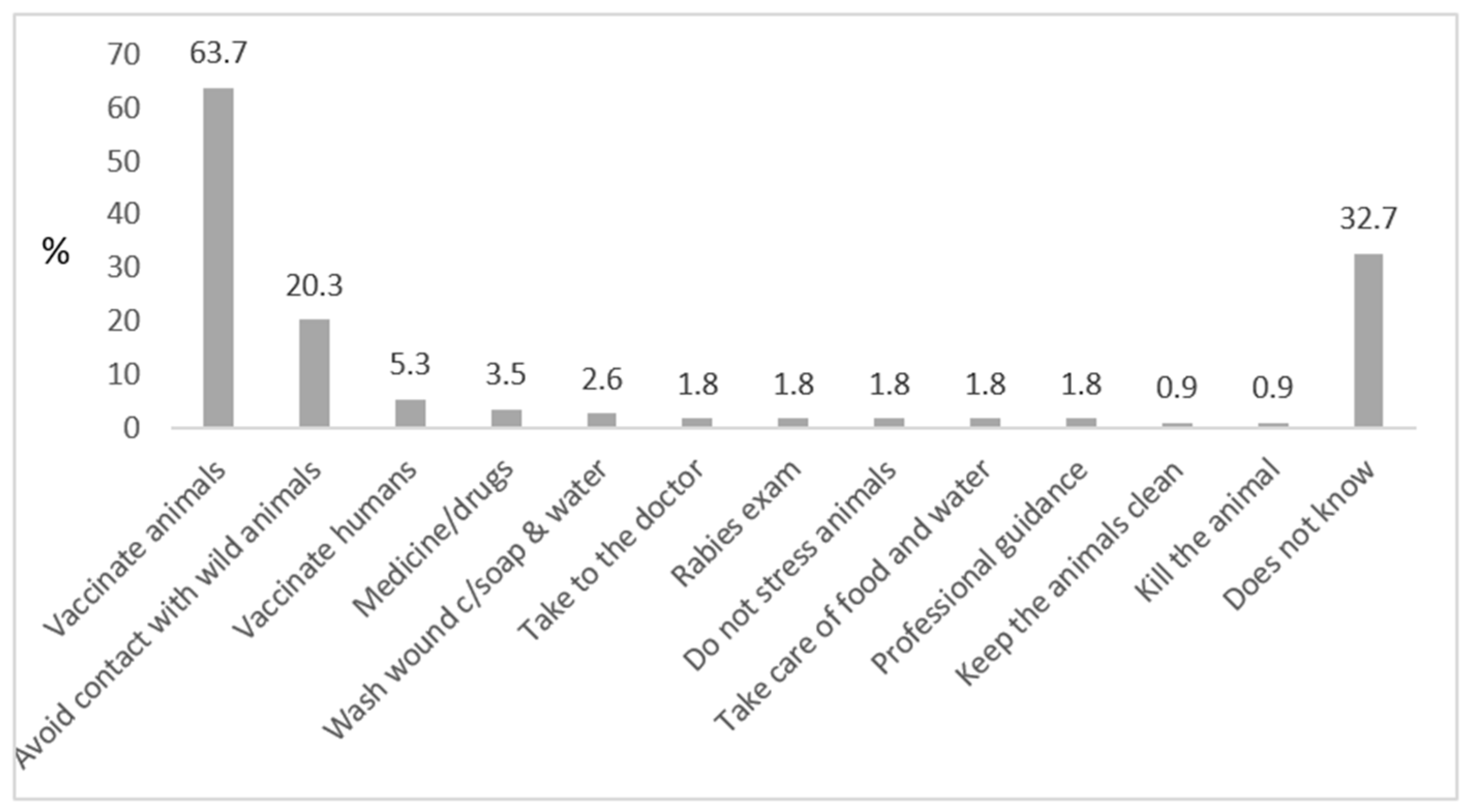
Almost 64% answered animal vaccination as a form of prevention, followed by 20% who stated avoidance of contact with wild animals. Other answers that are not adequate measures of rabies prevention included: medication, not stressing the animals and taking care of the animals’ food, water and hygiene (Figure 5).
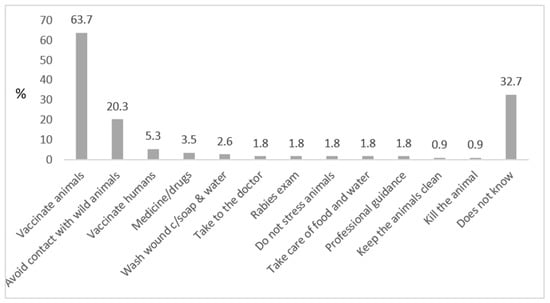
Figure 5.
Knowledge on prevention of rabies, as reported by respondents (vaccination of animals and avoiding contact with wild animals were considered as correct answers). Killing the animal was considered an incorrect answer; after an act of aggression, domestic animals (esp. dogs) should be observed for a defined period at a safe place (without the possibility of contact to other animals or to humans).
3.3. Attitudes and Practices
Almost all the families kept domestic animals, mainly dogs and cats. Most of them had vaccinated their companion animals (dogs and cats), but much less often their production animals, such as pigs, cattle and sheep (Table 4).

Table 4.
Presence of domestic animals in the households and vaccination status, Ceará, Brazil, 2021 (n = 113).
Most families reported that free-living wild animals appeared on their properties, mostly marmosets and wild canids (Cerdocyon thous), and that these animals had contact with their domestic animals, especially marmosets with dogs and cats, and wild canids with humans and monkeys (Figure 6).
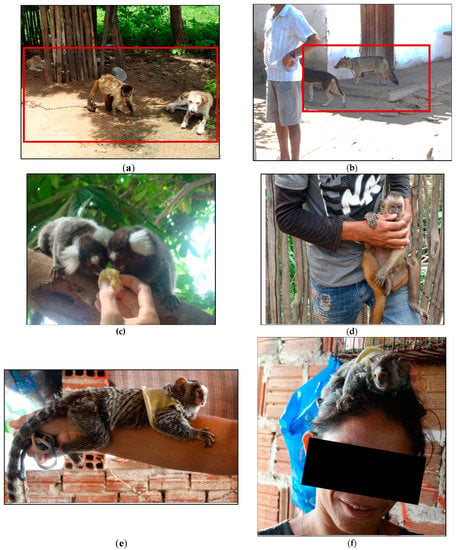
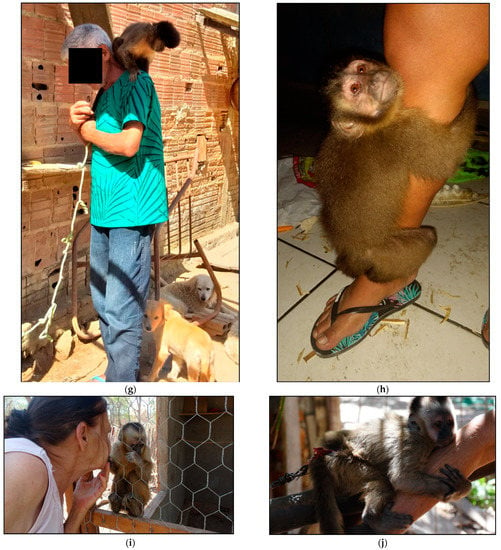


Figure 6.
Examples of contact of wild animals with domestic animals and the population: (a) monkey living in the same environment as domestic dogs and cats; (b) domestic dog (Canis familiaris) and domesticated wild canid (Cerdocyon thous) living in the same environment; (c) human contact with marmosets in backyard; (d) human contact with monkey in backyard; (e,f) human contact with marmoset. (g–j) nail monkey breeders in contact with the animals.
The animals appeared frequently in the backyards and on a daily basis (Figure 6, Table 5). The respondents also reported that animals, mostly monkeys (Sapajus libidinosus), marmosets (Callithrix jacchus) and wild canids (C. thous), had attacked domestic dogs and humans (Table 5).

Table 5.
Presence of free-living wild animals on respondents’ properties and contacts between wild and domestic animals, Ceará, Brazil, 2019 (n = 113). Domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) include both owned dogs and feral dogs.
About 73% said they had raised or currently raised wild animals as pets. These were mostly capuchin monkeys and marmosets. More than half stated that there had been aggressions to domestic animals and humans, with the majority of aggressions by capuchin monkeys and marmosets to humans (Figure 7), and about 62% of the humans attacked did not receive any anti-rabies post-exposure prophylaxis (Table 6).
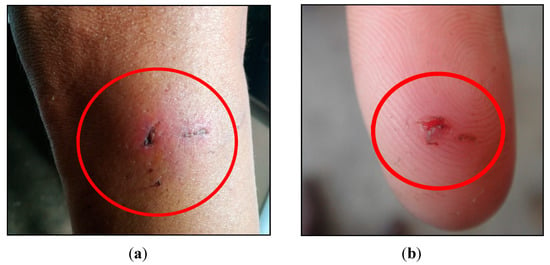
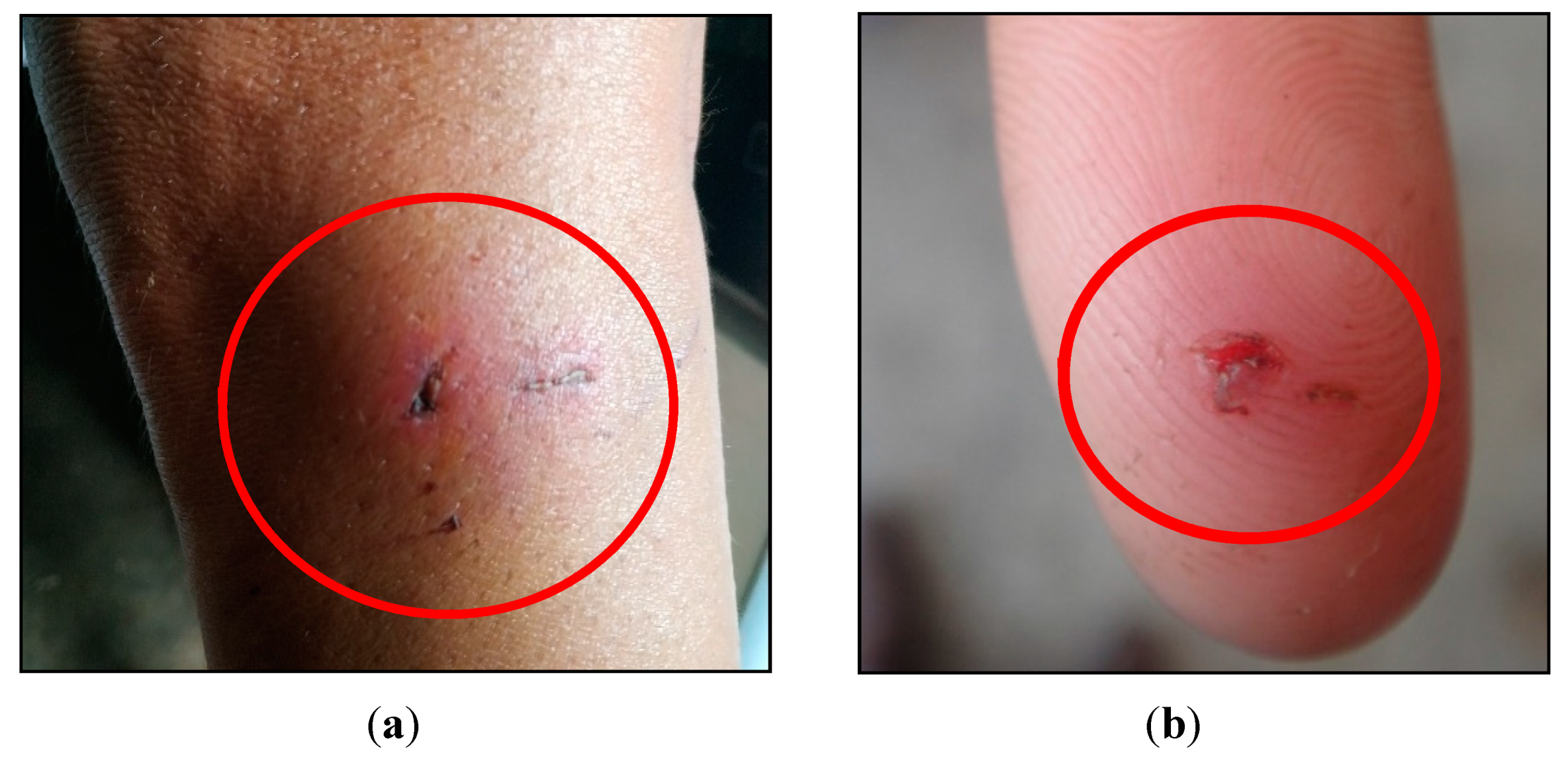
Figure 7.
Examples of aggressions by wild animals to humans: (a) bite by a capuchin monkey at the leg of a person; (b) marmoset aggression on the index finger of a person.

Table 6.
Wild animals kept as companion animals, aggression and the type of contact between humans and animals on the respondents’ properties, Ceará, Brazil, 2019 (n = 113).
After environmental education performed within the realm of data collection, 70% of the families that had animals in captivity decided to voluntarily surrender the animals to the competent bodies for rehabilitation and subsequent release into their natural habitats. Most of these were capuchin monkeys and marmosets.
4. Discussion
This is the first KAP study on sylvatic rabies in Brazil. Our data indicate some general knowledge about rabies and virus transmission in the studied high-risk population, but also incomplete knowledge, especially on the clinical signs of rabies in domestic and wild animals, preventive rabies management for animals and on the species that are important transmitters.
The results are a matter of concern since we have recently shown that, in Ceará State, rabies virus transmission dynamics have undergone important changes, with a shift from dog-mediated transmission to transmission by sylvatic populations [5,6]. In fact, previous studies from Ceará indicated that insufficient knowledge of populations living in high-risk areas was related to inadequate prevention measures after aggression by wild animals [6,12]. From 1990 to 2016, 19 cases of human rabies transmitted by marmosets were reported in Brazil, with the highest numbers of cases in Ceará and Piauí States [14]. Consequently, sylvatic rabies has been the focus of the rabies control programs, including information and education campaigns emphasizing the risk of wild animals transmitting rabies virus to humans.
In Brazil, keeping wild animals is prohibited by law, but about ¾ of the interviewed families in our study had raised wild animals as companion animals (mainly capuchin monkeys), and also the vast majority kept domestic animals (mostly dogs and cats) that interacted with sylvatic populations (in the wild and in captivity). On the other hand, domestic animals usually live intensively close to their owners, favoring the occurrence of aggressions. Thus, there is an increased risk of rabies virus transmission between wild animals, domestic animals and, consequently, humans. Most families were not fully aware about the legislation and the health risk of keeping wild animals and handed over their wild animals to the respective authorities after being informed about the rabies virus transmission risk. This indicates a high effectiveness of the focused information and education campaigns.
The common coexistence of domestic and wild animals as evidenced in this study and the circulation of rabies virus variants maintained and transmitted by wild animals (marmosets and wild canids) in the region further strengthen the importance of anti-rabies vaccinations of dogs and cats. Increased human/animal and domestic animal/wild animal interaction may also have been caused by the human invasion into former sylvatic areas, agricultural intensification and loss of natural habitats.
In the last five years, a large number of rabies virus-infected bats were identified in urban areas in Ceará [5]. Of the 21 registered human rabies cases in Brazil from 2016 to 2019, three (14.3%) were due to exposure by domestic cats, with the involvement of the variant of the hematophagous bat Desmodus rotundus [15]. This spillover from wild to domestic animals is of major concern considering the risk of unvaccinated domestic animals—only 50% of cats are vaccinated—coming into contact with these species. A spillover has been observed in Brazil since 2016, with the isolation of a virus variant from hematophagous bats and wild canids in domestic dogs and cats [16,17].
In contrast to other settings, such as in Kigali (Rwanda), where only 21% had vaccinated their dogs [18], a relatively high number of companion animals (especially dogs) have been vaccinated in Ceará State as a result of intensive campaigns for many years, but the production animals have been vaccinated to a much lesser extent. In several countries, mainly in Europe and North America, wild animals, such as foxes, have been vaccinated using vaccine-containing baits within the realm of eliminating wildlife-mediated rabies [19,20]. Although a study evidenced the production of antibodies against rabies after the use of a NIL-2 cell culture vaccine applied to marmosets (C. jacchus) in Ceará State [21], the practice of vaccinating wild animals is not yet recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. In Brazil, vaccination of wild animals is not available as a control strategy, and additional laboratory and field studies are needed to assess if this approach is feasible within the northeast Brazilian setting.
Our study revealed that more than 30% of the people attacked by wild animals had not received any type of post-exposure prophylaxis, possibly because they were unaware of the transmission risk and the importance of post-exposure prophylaxis. A recent study has evidenced that all six human rabies cases that occurred during the last years in Ceará State in the period 2004–2021 were related to sylvatic rabies viral strains (five infections transmitted by wild animals, one by a domestic dog), and that only one patient had presented at a primary healthcare center before the onset of symptoms or clinical signs [12]. Another study from Fortaleza, the capital of Ceará State, evidenced that more than half of the people who kept marmosets as pets had been attacked by them at least once, and that about ¾ of these did not seek any health care center for receiving post-exposure prophylaxis; 58% did not know about the risk of transmission from the attack [22]. In general, respondents in rural areas had better knowledge on rabies virus transmission, symptoms, treatment and prevention than those residing in urban areas.
The situation is similar in other countries and settings. For example, in Pakistan, only 40% sought medical attendance after a dog bite [8]. Similar to our results, several studies from different settings in Grenada, Pakistan, Ghana and Ethiopia evidenced that rabies was known by the majority but that knowledge on transmission was insufficient, with only 40–60% mentioning animal bites as the principal way of transmission [8,18,23,24,25,26]. Only two respondents in our study knew about the importance of washing the wound with soap and water after a bite; a similar finding was reported in the Rwandan study [18]. All this evidence shows clearly that, in addition to the focus on wildlife-mediated rabies, information and education campaigns should consider insufficient knowledge of the population on transmission, immediate prevention measures and the importance of seeking healthcare after aggression by any animal (domestic or wild). In addition, access to the health system is an important factor and may have impacted the likelihood to seek healthcare in these different settings.
The One Health approach has been considered to be highly effective in controlling zoonotic diseases at the community level [27]. Within this realm, the Ceará State rabies control program has applied an integrated approach to rabies prevention and control, emphasizing environmental education, wild animal husbandry, legislation, zoonosis risk and animal welfare [13]. A multidisciplinary team has been assigned to address the different pillars of the control program. This team includes, for example, veterinarians, nurses, pharmacists, community health agents and information and education specialists [12]. These professionals are vaccinated, and their rabies-specific antibodies are assessed annually.
Our study is subject to limitations, such as the difficulty in identifying the families that had wild animals in captivity because most of them were afraid of being denounced and punished by environmental authorities. Given this context, the participants were included in collaboration with local community health agents and not recruited at random. As this purposive sampling procedure has been applied to include respondents of a specific high-risk group, the population is not representative of the general population. However, this study was not meant to include a representative sample of the state’s population but to draw a picture of the knowledge, attitudes and practices of populations at a high risk for acquiring rabies, with a focus on sylvatic populations. Another difficulty was the access to the homes of families that lived in rural areas where the largest number of families were registered, and the interruption of the visits due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, the interpretation of the results regarding the external validity should be undertaken with care.
In conclusion, our study shows that there are important knowledge gaps within a high-risk population with contact to sylvatic populations, with inadequate practices regarding keeping wild animals and measures taken after animal aggressions. There is a need for strengthening and improving the sylvatic rabies surveillance and information and education programs to improve knowledge regarding virus transmission and preventive measures. Health education in high-risk communities should focus on sylvatic rabies, vaccination of domestic and farm animals and post-exposure prophylaxis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.F.H.D., C.H.A. and J.H.; methodology, N.F.H.D., P.P.L.B., D.B.A., S.R.F., P.C.R., W.F.d.O., C.H.A. and J.H.; formal analysis, N.F.H.D., P.P.L.B. and J.H.; field investigation, N.F.H.D., D.B.A., S.R.F., R.W.P.N., W.F.d.O. and R.H.V.; writing—original draft preparation, N.F.H.D., P.P.L.B., P.C.R., C.H.A. and J.H.; writing—review and editing, all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the Federal University of Ceará (CAAE number: 13466719.6.000.5054) and of the State Health Department (CAAE number: 13466719.3001.5051).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the state and municipal health secretariats, especially the community health agents (CHAs) and the endemic disease control agents (ECAs) who contributed so much to this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pantha, S.; Subedi, D.; Poudel, U.; Subedi, S.; Kaphle, K.; Dhakal, S. Review of rabies in Nepal. One Health 2020, 10, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Expert Consultation on Rabies: Third Report; WHO Technical Report Series 1012; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, B.N.; Patel, D.; Lacouture, M.E. Epidemiology and Burden of Disease. In Dermatologic Principles and Practice in Oncology; Lacouture, M.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, K.; Coudeville, L.; Lembo, T.; Sambo, M.; Kieffer, A.; Attlan, M.; Barrat, J.; Blanton, J.D.; Briggs, D.J.; Cleaveland, S.; et al. Estimating the global burden of endemic canine rabies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, N.F.H.; Alencar, C.H.; Cavalcante, K.K.D.S.; Correia, F.G.S.; Romijn, P.C.; Araujo, D.B.; Favoretto, S.R.; Heukelbach, J. Increased detection of rabies virus in bats in Ceará State (Northeast Brazil) after implementation of a passive surveillance programme. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, N.F.H.; Pires Neto, R.J.; Viana, V.F.; Feijão, L.X.; AbreuIva, K.G.; Melo, M.L.A.; Sousa, A.Q.; Alencar, C.H.; Heukelbach, J. Epidemiologia da raiva humana no estado do Ceará, 1970 a 2019. Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde 2021, 30, e2020354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.J.C.; Fernandes, M.E.F. Rabies: Knowledge and practices regarding rabies in rural communities of the Brazilian Amazon basin. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ayaz, R.; Mehtab, A.; Naz, K.; Haider, W.; Gondal, M.A.; Umer, M.; Afzal, M.I.; Shah, N.A.; Afzal, M.S.; et al. Knowledge, attitude & practices (KAPs) regarding rabies endemicity among the community members, Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2019, 200, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.S.; Choudhary, S.K. Knowledge, attitude, behavior and practice study on dog-bites and its management in the context of prevention of rabies in a rural community of Gujarat. Indian J. Community Med. 2005, 30, 81–83. Available online: https://www.ijcm.org.in/text.asp?2005/30/3/81/42854 (accessed on 13 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Kabeta, T.; Deresa, B.; Tigre, W.; Ward, M.P.; Mor, S.M. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of animal bite victims attending an Anti-rabies Health Center in Jimma Town, Ethiopia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoretto, S.R.; de Mattos, C.C.; de Morais, N.B.; Carrieri, M.L.; Rolim, B.N.; Silva, L.M.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Durigon, E.L.; de Mattos, C.A. Rabies virus maintained by dogs in humans and terrestrial wildlife, Ceará State, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1978–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, N.F.H.; Alencar, C.H.; Pires Neto, R.J.; Moreno, J.O.; Melo, I.M.L.A.; Duarte, B.H.; Heukelbach, J. Integration of human rabies surveillance and preventive measures in the State of Ceará, Northeast Brazil. One Health Implement. Res. 2021, 1, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Estatística e Geografia. Censo Demográfico 2010; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2017.
- Kotait, I.; Oliveira, R.N.; Carrieri, M.L.; Castilho, J.G.; Macedo, C.I.; Pereira, P.M.C.; Boere, V.; Montebello, L.; Rupprecht, C.E. Non-human primates as a reservoir for rabies virus in Brazil. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, N.F.H.; Pires Neto, R.D.J.; Viana, V.F.; Feijão, L.X.; Alencar, C.H.; Heukelbach, J. Clinical aspects of human rabies in the state of Ceará, Brazil: An overview of 63 cases. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, e01042021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministério da Saúde. Raiva: O Que é, Causas, Sintomas, Tratamento, Diagnóstico e Prevenção; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brasil, 2021. Available online: http://www.saude.gov.br/saude-de-a-z/raiva/#epidemiologia (accessed on 4 July 2021).
- Kotait, I.; Carrieri, M.L.; Carnieli Júnior, P.; Castilho, J.G.; Oliveira, R.N.; Macedo, C.I.; Ferreira, K.C.S.; Achkar, S.M. Reservatórios silvestres do vírus da raiva: Um desafio para a saúde pública. BEPA. Bol. Epidemiol. Paul. 2007, 4, 2–8. Available online: http://periodicos.ses.sp.bvs.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1806-42722007000400001&lng=pt&tlng=pt (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Ntampaka, P.; Nyaga, P.N.; Niragire, F.; Gathumbi, J.K.; Tukei, M. Knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding rabies and its control among dog owners in Kigali city, Rwanda. PLoS ONE 2019, 20, e0210044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.T.; Freuling, C.M. Rabies control in Europe: An overview of past, current and future strategies. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2018, 37, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, D.; Algeo, T.P.; Nelson, K.M.; Chipman, R.B.; Donovan, D.; Blanton, J.D.; Niezgoda, M.; Rupprecht, C.E. Oral rabies vaccination in North America: Opportunities, complexities and challenges. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.C.; Oliveira, A.N.; Romijn, P.C.; Kimura, L.M. Resposta imune produzida por vacinas anti-rábicas em sagüis (Callithrix sp). Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 1999, 32, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aguiar, T.D.F.; Costa, E.C.; Rolim, B.N.; Romijn, P.C.; Morais, N.B.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Risco de transmissão do vírus da raiva oriundo de sagui (Callithrix jacchus), domiciliado e semidomiciliado, para o homem na região metropolitana de Fortaleza, estado do Ceará. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2011, 44, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasgow, L.; Worme, A.; Keku, E.; Forde, M. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding rabies in Grenada. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuni, B.; Tarkang, E.; Manu, E.; Amu, H.; Ayanore, M.A.; Aku, F.Y.; Ziema, S.A.; Bosoka, S.A.; Adjuik, M.; Kweku, M. Dog Owners’ knowledge about rabies and other factors that influence canine anti-rabies vaccination in the Upper East Region of Ghana. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihon, A.; Meresa, D.; Tesfaw, A. Rabies: Knowledge, Attitude and Practices in and Around South Gondar, North West Ethiopia. Diseases 2020, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinchen, S.; Tenzin, T.; Hall, D.; van der Meer, F.; Sharma, B.; Dukpa, K.; Cork, S.C. A community-based knowledge, attitude, and practice survey on rabies among cattle owners in selected areas of Bhutan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heukelbach, J. One Health & Implementation Research: Improving health for all. One Health Implement. Res. 2021, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).