Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Treponema pallidum and Haemophilus ducreyi in Yaws-Like Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. T. pallidum and H. ducreyi Multiplex qPCR Assay
2.4. T. pallidum and H. ducreyi RPA (TPHD-RPA) Assay
2.4.1. Molecular Standard
2.4.2. TPHD-RPA Primers and Probes
2.4.3. TPHD-RPA Assay
2.4.4. Analytical Singleplex RPA Assay Sensitivity and Specificity
2.4.5. Clinical Performance of TPHD-RPA Assay
2.4.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
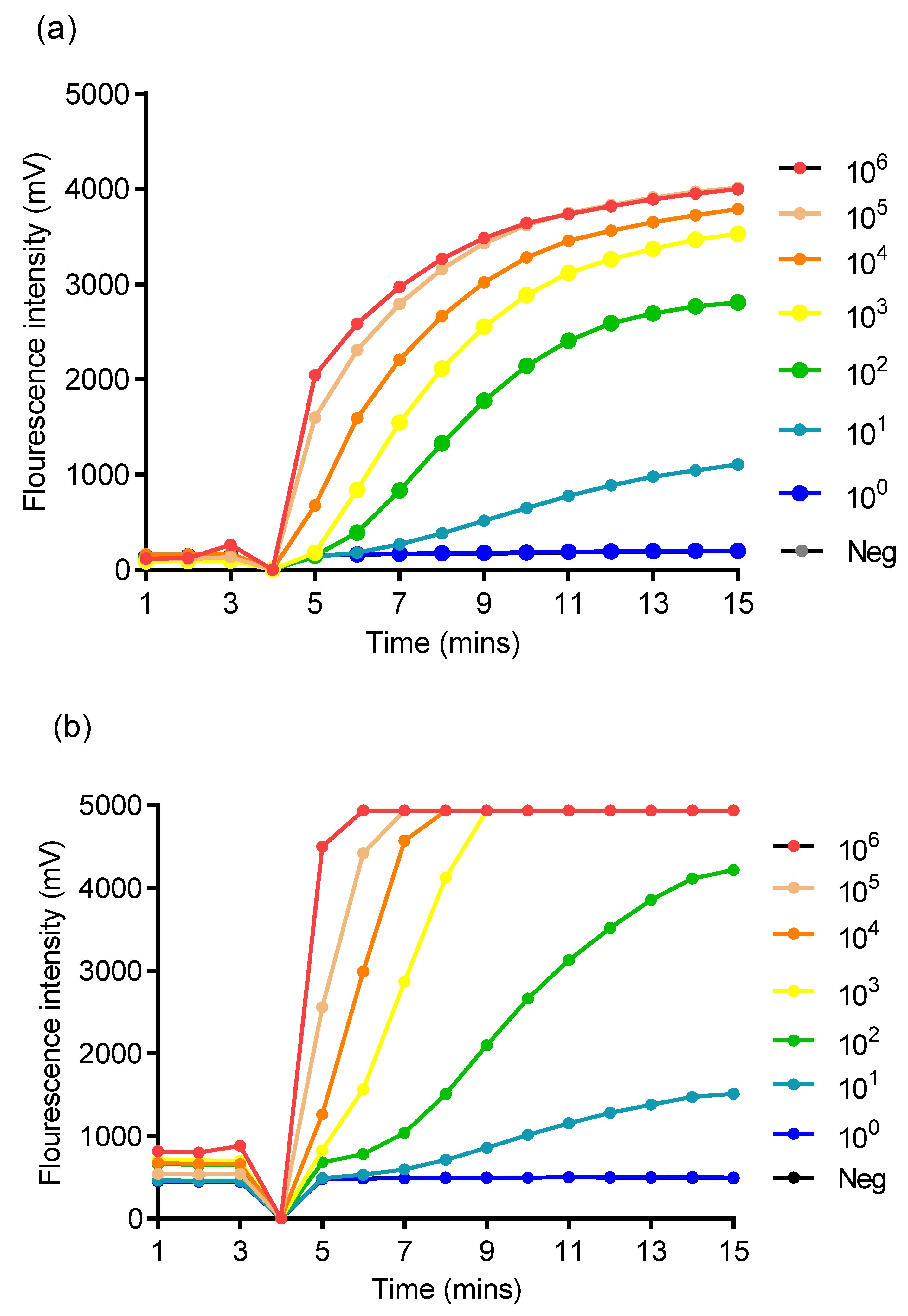
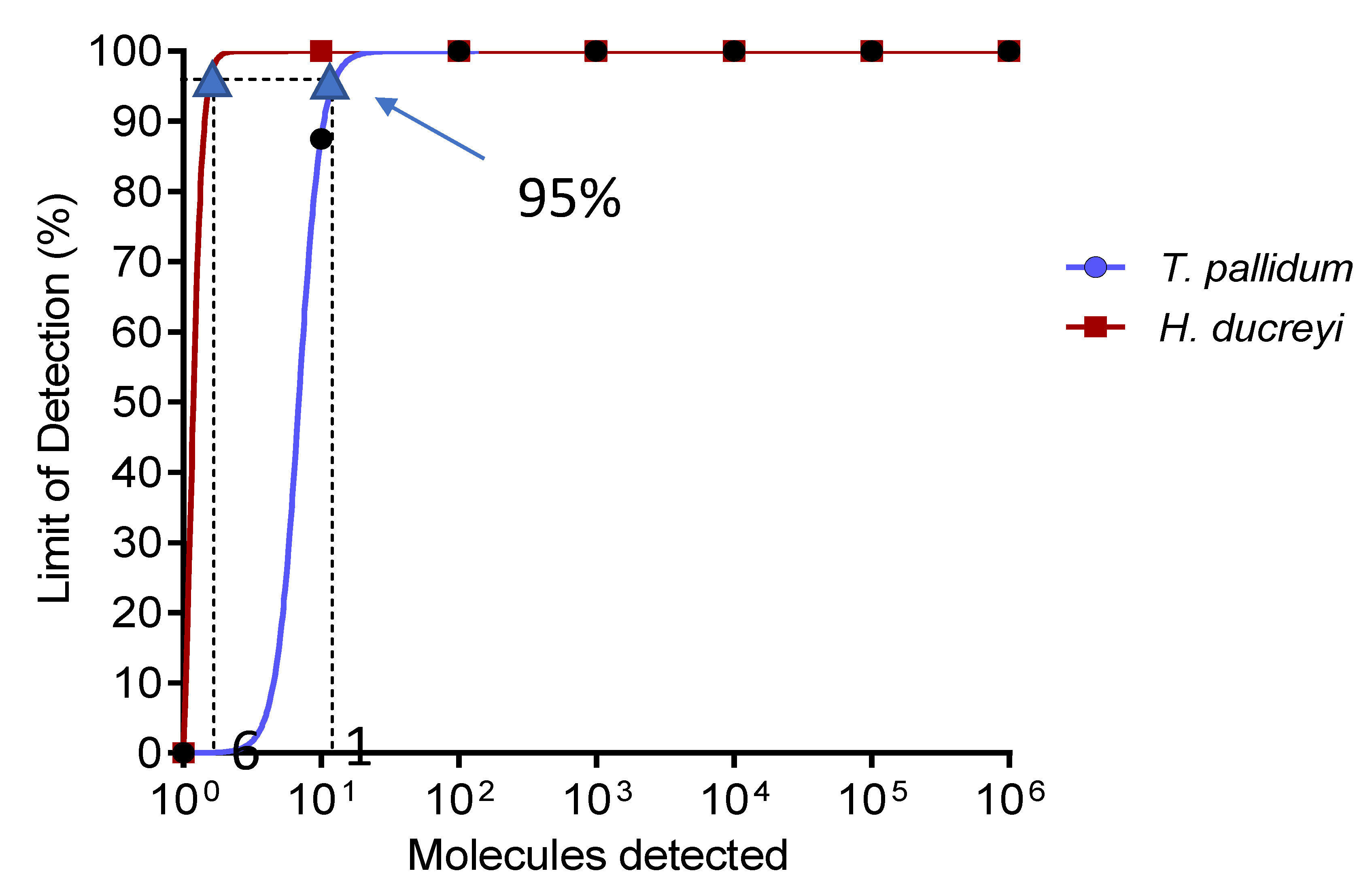
3.1. Analytical Sensitivity of Singleplex RPA Assay and Specificity of TPHD-RPA Assay
3.2. Clinical Performance of TPHD-RPA Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitjà, O.; Asiedu, K.; Mabey, D. Yaws. Lancet 2013, 381, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.; Solomon, A.W.; Mabey, D.C. Endemic treponemal diseases. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Fact Sheet on Yaws 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs316/en/ (accessed on 8 November 2017).
- Mitjà, O.; Marks, M.; Konan, D.J.P.; Ayelo, G.; Gonzalez-Beiras, C.; Boua, B.; Houinei, W.; Kobara, Y.; Tabah, E.N.; Nsiire, A.; et al. Global epidemiology of yaws: A systematic review. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e324–e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Eradication of yaws—The Morges Strategy. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2012, 87, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Mitjà, O.; Houinei, W.; Moses, P.; Kapa, A.; Paru, R.; Hays, R.; Lukehart, S.; Godornes, C.; Bieb, S.V.; Grice, T.; et al. Mass Treatment with Single-Dose Azithromycin for Yaws. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.; Mitjà, O.; Vestergaard, L.S.; Pillay, A.; Knauf, S.; Chen, C.; Bassat, Q.; Martin, D.L.; Fegan, D.; Taleo, F.; et al. Challenges and key research questions for yaws eradication. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 3099, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitjà, O.; Lukehart, S.A.; Pokowas, G.; Moses, P.; Kapa, A.; Godornes, C.; Robson, J.; Cherian, S.; Houinei, W.; Kazadi, W.; et al. Haemophilus ducreyi as a cause of skin ulcers in children from a yaws-endemic area of Papua New Guinea: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.; Chi, K.H.; Vahi, V.; Pillay, A.; Sokana, O.; Pavluck, A.; Mabey, D.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Solomon, A.W. Haemophilus ducreyi associated with skin ulcers among children, Solomon Islands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1705–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.; Goncalves, A.; Vahi, V.; Sokana, O.; Puiahi, E.; Zhang, Z.; Dalipanda, T.; Bottomley, C.; Mabey, D.; Solomon, A.W. Evaluation of a Rapid Diagnostic Test for Yaws Infection in a Community Surveillance Setting. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.H.; Danavall, D.; Taleo, F.; Pillay, A.; Ye, T.; Nachamkin, E.; Kool, J.L.; Fegan, D.; Asiedu, K.; Vestergaard, L.S.; et al. Molecular differentiation of treponema pallidum subspecies in skin ulceration clinically suspected as yaws in vanuatu using real-time multiplex PCR and serological methods. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahil, S.; Goyal, K. Rapid molecular diagnosis of chronic skin ulcers. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Becherer, L.; Bakheit, M.; Frischmann, S.; Stinco, S.; Borst, N.; Zengerle, R.; Von Stetten, F. Simplified Real-Time Multiplex Detection of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Using Novel Mediator Displacement Probes with Universal Reporters. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4741–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becherer, L.; Knauf, S.; Marks, M.; Lueert, S.; Frischmann, S.; Borst, N.; Von Stetten, F.; Bieb, S.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; Asiedu, K.; et al. Multiplex mediator displacement loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of treponema pallidum and haemophilus ducreyi. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basing, L.A.W.; Simpson, S.V.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; Linnes, J.C. A Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for the Detection of Treponema pallidum subsp. pertenue. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA Detection using Recombination Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for Diagnostic Applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, D.; Ghosh, P.; Khan, M.A.A.; Hossain, F.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Matlashewski, G.; Kroeger, A.; Olliaro, P.; Abd El Wahed, A. Mobile Suitcase Laboratory for Rapid Detection of Leishmania donovani using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Wahed, A.; Patel, P.; Faye, O.; Thaloengsok, S.; Heidenreich, D.; Matangkasombut, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, K.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Sall, A.A.; Hufert, F.T.; et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid diagnostics of dengue infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.; Faye, O.; Faye, O.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Patel, P.; Batejat, C.; Manugerra, J.C.; Adjami, A.; Niedrig, M.; Hufert, F.T.; et al. Development of Mobile Laboratory for Viral Hemorrhagic Fever Detection in Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, M.; Ahor, H.S.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Agbavor, B.; Sarpong, F.N.; Laing, K.; Wansbrough-Jones, M.; Phillips, R.O. Rapid detection of mycobacterium ulcerans with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Peng, D.; Ye, W.; Chai, L.; Qi, J.; Yu, Z.; Ruan, L.; Sun, M. Determination of plasmid copy number reveals the total plasmid DNA amount is greater than the chromosomal DNA amount in Bacillus thuringiensis YBT-1520. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, D.S.; Lehman, D.A.; Lillis, L.; Peterson, D.; Singhal, M.; Armes, N.; Parker, M.; Piepenburg, O.; Overbaugh, J. Rapid detection of HIV-1 proviral DNA for early infant diagnosis using recombinase polymerase amplification. MBio 2013, 4, e00135-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Gonzalez, A.; Saldarriaga, O.A.; Tartaglino, L.; Gacek, R.; Temple, E.; Sparks, H.; Melby, P.C.; Travi, B.L. A Novel Molecular Test to Diagnose Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis at the Point of Care. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrman, B.; Richards-Kortum, R. Inhibition of Recombinase Polymerase Amplification by Background DNA: A lateral Flow-Based Method for Enriching Target DNA. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratna, G.; Manamperi, A.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Wickremasinge, R.; Gunawardena, K.; Yapa, B.; Pathirana, N.; Pathirana, H.; de Silva, N.; Sooriyaarachchi, M.; et al. Evaluation of rapid extraction and isothermal amplification techniques for the detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from skin lesions of suspected cases at the point of need in Sri Lanka. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.; Roller, M.; Alslim, L.M.A.; Böhlken-fascher, S.; Fechner, K.; Czerny, C.; Ahmed Abd El, W. Development of Rapid Extraction Method of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis DNA from Bovine Stool Samples. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Sequence | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|
| TP_RPA_FP3 | GTAACACTAATGTCGAGACTGAAAAGGAGTGC | 144 bp |
| TP_RPA_RP2 | GAATGATGAGACGCTCACACTTGTTATGC | |
| TP_RPA_P1 | GTATCTGCATCTGCTGTGCAGGATCCGGCA (BHQ2-dT) (X-dSpacer) (ROX-dT)GTCCAAGCTGTCATG-PH | |
| Hd_RPA_FP3 | TACTCAGGCAACGGATACCCAACATGCA | 169 bp |
| Hd_RPA_RP1 | GAGGTAAATCAGGCTGTTACAGGTCATTTA | |
| Hd_RPA_P1 | TACGCCTAAATCGTTAACTGCGGGATTAGG (BHQ2-dT) (X-dSpacer) (FAM-dT)AGATGGCCATGGTAG-PH |
| Target Organism | Samples Category | Sensitivity % | Specificity % | PPV % | NPV % | N | TPHD-RPA | qPCR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (95% CI) | (95% CI) | (95% CI) | (95% CI) | pos | neg | ||||
| T. pallidum | All samples | 94 | 100 | 100 | 97 | 49 | pos | 16 | 0 |
| (73−100) | (89−100) | (81−100) | (85−100) | neg | 1 | 32 | |||
| Samples containing a single organism | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 42 | pos | 10 | 0 | |
| (72−100) | (89−100) | (72−100) | (89−100) | neg | 0 | 32 | |||
| Samples containing both pathogens | 86 | 100 | 100 | 97 | 39 | pos | 6 | 0 | |
| (49−100) | (89−100) | (61−100) | (84−100) | neg | 1 | 32 | |||
| H. ducreyi | All samples | 95 | 100 | 100 | 97 | 49 | pos | 20 | 0 |
| (77−100) | (88−100) | (84−100) | (83−100) | neg | 1 | 28 | |||
| Samples containing a single organism | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 42 | pos | 14 | 0 | |
| (78−100) | (88−100) | (78−100) | (88−100) | neg | 0 | 28 | |||
| Samples containing both pathogens | 86 | 100 | 100 | 97 | 39 | pos | 6 | 0 | |
| (49−100) | (89−100) | (61−100) | (85−100) | neg | 1 | 32 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frimpong, M.; Simpson, S.V.; Ahor, H.S.; Agbanyo, A.; Gyabaah, S.; Agbavor, B.; Amanor, I.B.; Addo, K.K.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Kissenkötter, J.; et al. Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Treponema pallidum and Haemophilus ducreyi in Yaws-Like Lesions. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5040157
Frimpong M, Simpson SV, Ahor HS, Agbanyo A, Gyabaah S, Agbavor B, Amanor IB, Addo KK, Böhlken-Fascher S, Kissenkötter J, et al. Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Treponema pallidum and Haemophilus ducreyi in Yaws-Like Lesions. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(4):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5040157
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrimpong, Michael, Shirley Victoria Simpson, Hubert Senanu Ahor, Abigail Agbanyo, Solomon Gyabaah, Bernadette Agbavor, Ivy Brago Amanor, Kennedy Kwasi Addo, Susanne Böhlken-Fascher, Jonas Kissenkötter, and et al. 2020. "Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Treponema pallidum and Haemophilus ducreyi in Yaws-Like Lesions" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 4: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5040157
APA StyleFrimpong, M., Simpson, S. V., Ahor, H. S., Agbanyo, A., Gyabaah, S., Agbavor, B., Amanor, I. B., Addo, K. K., Böhlken-Fascher, S., Kissenkötter, J., Wahed, A. A. E., & Phillips, R. O. (2020). Multiplex Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Treponema pallidum and Haemophilus ducreyi in Yaws-Like Lesions. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(4), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5040157







