Factors Associated with Hepatitis B and C Co-Infection among HIV-Infected Patients in Singapore, 2006–2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Statistical Methods
2.3. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soriano, V.; Barreiro, P.; Nuñez, M. Management of Chronic Hepatitis B and C in HIV-Coinfected Patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Crane, M.; Audsley, J.; Avihingsanon, A.; Sasadeusz, J.; Lewin, S.R. HIV-Hepatitis B Virus Coinfection: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. AIDS 2017, 31, 2035–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchoff, J.; Tran, O.C.; Chen, L.; Bornschlegel, K.; Drobnik, A.; Kersanske, L.; Fuld, J. Impact of Hepatitis B on Mortality and Specific Causes of Death in Adults with and without HIV Co-Infection in NYC, 2000-2011. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbhandari, R.; Jun, T.; Khalili, H.; Chung, R.T.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. HBV/HIV Coinfection Is Associated with Poorer Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with HBV or HIV. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroth, L.; Pol, S.; Miailhes, P.; Lacombe, K.; Lopes, A.; Fillion, A.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Borsa-Lebas, F.; Salmon, D.; Rosenthal, E.; et al. Therapeutic Management and Evolution of Chronic Hepatitis B: Does HIV Still Have an Impact? The EPIB 2012 Study. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNAIDS. Miles To Go: Closing Gaps Breaking Barriers Righting Injustices. 2018. Available online: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/miles-to-go_en.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- WHO Hepatitis B Fact Sheets. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Ang, L.W.; Tey, S.H.; Cutter, J.; James, L.; Goh, K.T. Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among children and adolescents in Singapore, 2008–2010. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, L.W.; Cutter, J.; James, L.; Goh, K.T. Seroepidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Adults in Singapore: A 12-Year Review. Vaccine 2013, 32, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.; Ang, L.W.; Cutter, J.; James, L.; Goh, K.T. Evaluation on the effectiveness of the national childhood immunisation programme in Singapore, 1982-2007. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2010, 39, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Alter, M.J. Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis and HIV Co-Infection. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, L.; Easterbrook, P.; Gower, E.; McDonald, B.; Sabin, K.; McGowan, C.; Yanny, I.; Razavi, H.; Vickerman, P. Prevalence and Burden of HCV Co-Infection in People Living with HIV: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.G. Time for Action on Viral Hepatitis. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2016, 45, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Update on the HIV/AIDS situation in Singapore 2017 (June 2018), MOH Resources & Statistics. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/infectious-disease-statistics/hiv-stats/update-on-the-hiv-aids-situation-in-singapore-2017-(june-2018) (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Lim, R.B.; Tan, M.T.; Young, B.; Lee, C.C.; Leo, Y.S.; Chua, A.; Ng, O.T. Risk factors and time-trends of cytomegalovirus (CMV), syphilis, toxoplasmosis and viral hepatitis infection and seroprevalence in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected patients. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2013, 42, 667–673. [Google Scholar]
- Hyams, K.C. Risks of chronicity following acute hepatitis B virus infection: a review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 20, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattovich, G.; Bortolotti, F.; Donato, F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Chemello, L.; Benvegnù, L. Natural history of hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, J.T.; Diepolder, H.M.; Zachoval, R.; Gruener, N.H.; Jung, M.C.; Ulsenheimer, A.; Schraut, W.W.; Schirren, C.A.; Waechtler, M.; Backmund, M.; et al. Acute hepatitis C: High rate of both spontaneous and treatment-induced viral clearance. Gastroenterology 2003, 358, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradling, P.R.; Richardson, J.T.; Buchacz, K.; Moorman, A.C.; Brooks, J.T. Prevalence of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Patients in the HIV Outpatient Study, 1996-2007. J. Viral. Hepat. 2010, 17, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askari, A.; Hakimi, H.; Nasiri Ahmadabadi, B.; Hassanshahi, G.; Kazemi Arababadi, M. Prevalence of Hepatitis B Co-Infection among HIV Positive Patients: Narrative Review Article. Iran. J. Public Health 2014, 43, 705–712. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wong, W.-W.; Law, M.G.; Kiertiburanakul, S.; Yunihastuti, E.; Merati, T.P.; Lim, P.L.; Chaiwarith, R.; Phanuphak, P.; Lee, M.P.; et al. Hepatitis B and C Co-Infection in HIV Patients from the TREAT Asia HIV Observational Database: Analysis of Risk Factors and Survival. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, A.; Khan, A.H.; Sulaiman, S.A.S.; Soo, C.T.; Khan, K. HBV and HIV Co-Infection: Prevalence and Clinical Outcomes in Tertiary Care Hospital Malaysia. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, T.; Lusida, M.I. Viral Hepatitis and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Co-Infections in Asia. World J. Virol. 2015, 4, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinello, M.; Amin, J.; Matthews, G.V.; Dore, G.J. Prevalence and Disease Burden of HCV Coinfection in HIV Cohorts in the Asia Pacific Region: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AIDS Rev. 2016, 18, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Huy, B.V.; Vernavong, K.; Kính, N.V. HBV and HCV Coinfection among HIV/AIDS Patients in the National Hospital of Tropical Diseases, Vietnam. AIDS Res. Treat. 2014, 2014, 581021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Liu, F.L.; Yao, Z.H.; Duo, L.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.T. Comparison of HIV-, HBV-, HCV- and Co-Infection Prevalence between Chinese and Burmese Intravenous Drug Users of the China-Myanmar Border Region. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.T.; Doraisingham, S.; Tan, K.L.; Oon, C.J.; Ho, M.L.; Chen, A.J.; Chan, S.H. The Hepatitis B Immunization Programme in Singapore. Bull. World Health Organ. 1989, 67, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E. Tackling Subutex Abuse in Singapore. Singap. Med. J. 2006, 47, 919–921. [Google Scholar]
- Overview of Singapore’s Drug Situation in 2017, Central Narcotics Bureau. Available online: https://www.cnb.gov.sg/docs/default-source/drug-situation-report-documents/cnb-annual-stats-release-for-2017_12-jun.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Soh, B.Y.-M.; Kumar, R.; Ekstrom, V.S.-M.; Lin, C.Y.-H.; Thangaraju, S.D.; Tan, H.H.; Chan, K.P.; Choong, L.H.L.; Teo, D.; Chow, W.C. Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection and the IL28B Genotype Polymorphism among Blood Donors and High-Risk Populations. Singap. Med. J. 2018, 60, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, E.; Estes, C.; Blach, S.; Razavi-Shearer, K.; Razavi, H. Global Epidemiology and Genotype Distribution of the Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S45–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents Living with HIV. Department of Health and Human Services. Available online: http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Peters, L.; Klein, M.B. Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus in HIV-Infected Patients. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2015, 10, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, E.; Heimer, R. HIV Prevalence among Intravenous Drug Users: Model-based Estimates from New Haven’s Legal Needle Exchange. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1992, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Berg, C.; Smit, C.; Van Brussel, G.; Coutinho, R.; Prins, M. Full Participation in Harm Reduction Programmes Is Associated with Decreased Risk for Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Hepatitis C Virus: Evidence from the Amsterdam Cohort Studies among Drug Users. Addiction 2007, 102, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, H.; Jarlais, D.C.; Friedman, S.R.; Purchase, D.; Alter, M.J. Reduced Risk of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C among Injection Drug Users in the Tacoma Syringe Exchange Program. Am. J. Public Health 1995, 85, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.S.J.; Azman, A.; Samsurijan, M.S.; Badaruddin, R.F.R.; Vadevelu, K.; Yahaya, M.H.; Latiff, A.R.A. Implementation Dilemmas of the Needle Syringe Exchange Programme (NSEP): Between the Law and Prevention. Pac. Sci. Rev. B Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2016, 2, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lim, S.G.; Lee, G.H. Pathway to Hepatitis Elimination and Control. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2018, 47, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| HIV Mono-Infected | Co-Infected with HBV Only | Co-Infected with HCV Only | Co-Infected with both HBV and HCV | p Value † | All | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| All | 2644 (100.0) | 220 (100.0) | 185 (100.0) | 16 (100.0) | 3065 (100.0) | ||
| Age group (years) at HIV diagnosis | 0.004 | ||||||
| 10–19 | 48 (1.8) | 1 (0.5) | 7 (3.8) | 0 (0.0) | 56 (1.8) | ||
| 20–29 | 578 (21.9) | 23 (10.5) | 39 (21.1) | 5 (31.3) | 645 (21.0) | ||
| 30–39 | 718 (27.2) | 72 (32.7) | 59 (31.9) | 5 (31.3) | 854 (27.9) | ||
| 40–49 | 654 (24.7) | 60 (27.3) | 40 (21.6) | 4 (25.0) | 758 (24.7) | ||
| 50–59 | 454 (17.2) | 42 (19.1) | 34 (18.4) | 0 (0.0) | 530 (17.3) | ||
| 60–69 | 149 (5.6) | 19 (8.6) | 6 (3.2) | 2 (12.5) | 176 (5.7) | ||
| 70+ | 43 (1.6) | 3 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 46 (1.5) | ||
| Gender | 0.032 | ||||||
| Female | 177 (6.7) | 5 (2.3) | 7 (3.8) | 1 (6.3) | 190 (6.2) | ||
| Male | 2467 (93.3) | 215 (97.7) | 178 (96.2) | 15 (93.8) | 2875 (93.8) | ||
| Ethnic Group | <0.0005 | ||||||
| Chinese | 2014 (76.2) | 187 (85.0) | 117 (63.2) | 11 (68.8) | 2329 (76.0) | ||
| Malay | 400 (15.1) | 22 (10.0) | 56 (30.3) | 5 (31.3) | 483 (15.8) | ||
| Indian | 138 (5.2) | 2 (0.9) | 4 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 144 (4.7) | ||
| Others | 92 (3.5) | 9 (4.1) | 8 (4.3) | 0 (0.0) | 109 (3.6) | ||
| Marital Status | 0.622 | ||||||
| Never married | 1431 (54.1) | 116 (52.7) | 96 (51.9) | 10 (62.5) | 1653 (53.9) | ||
| Married | 591 (22.4) | 48 (21.8) | 32 (17.3) | 3 (18.8) | 674 (22.0) | ||
| Separated/Divorced/Widowed | 265 (10.0) | 26 (11.8) | 25 (13.5) | 1 (6.3) | 317 (10.3) | ||
| Unknown | 357 (13.5) | 30 (13.6) | 32 (17.3) | 2 (12.5) | 421 (13.7) | ||
| Mode of HIV transmission | <0.0005 | ||||||
| Homosexual | 1009 (38.2) | 79 (35.9) | 65 (35.1) | 8 (50.0) | 1161 (37.9) | ||
| Heterosexual | 1197 (45.3) | 99 (45.0) | 35 (18.9) | 3 (18.8) | 1334 (43.5) | ||
| Bisexual | 306 (11.6) | 25 (11.4) | 24 (13.0) | 3 (18.8) | 358 (11.7) | ||
| IDU | 4 (0.2) | 3 (1.4) | 8 (4.3) | 1 (6.3) | 16 (0.5) | ||
| IDU and sexual | 53 (2.0) | 5 (2.3) | 48 (25.9) | 1 (6.3) | 107 (3.5) | ||
| Others | 13 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 15 (0.5) | ||
| Unknown | 62 (2.3) | 8 (3.6) | 4 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 74 (2.4) | ||
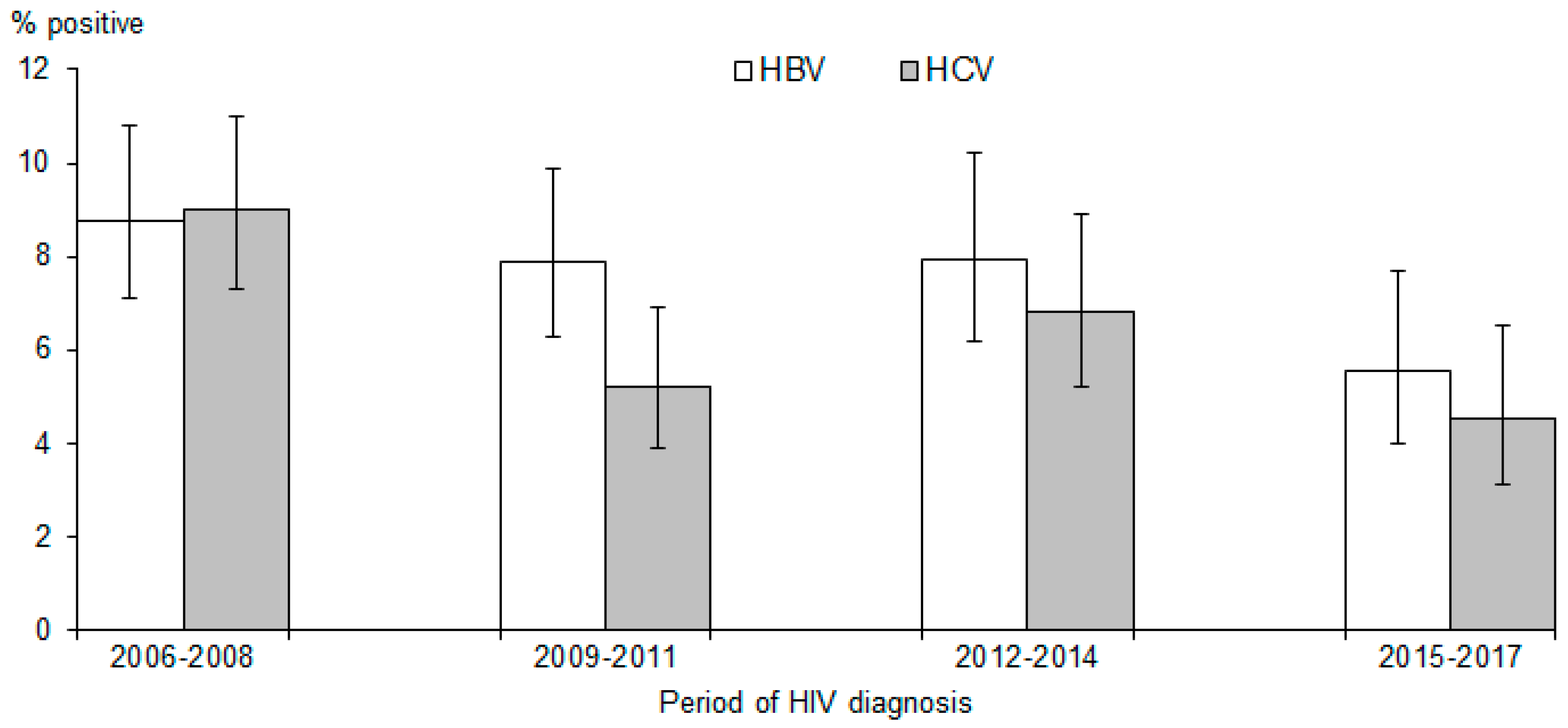
| Period of HIV diagnosis | 0.011 | ||||||
| 2006-2008 | 748 (28.3) | 72 (32.7) | 74 (40.0) | 7 (43.8) | 901 (29.4) | ||
| 2009-2011 | 755 (28.6) | 63 (28.6) | 40 (21.6) | 5 (31.3) | 863 (28.2) | ||
| 2012-2014 | 605 (22.9) | 53 (24.1) | 45 (24.3) | 3 (18.8) | 706 (23.0) | ||
| 2015-2017 | 536 (20.3) | 32 (14.5) | 26 (14.1) | 1 (6.3) | 595 (19.4) | ||
| AIDS-defining illnesses/opportunistic infections within one year of HIV diagnosis | 0.113 | ||||||
| No | 1396 (52.8) | 98 (44.5) | 92 (49.7) | 8 (50.0) | 1594 (52.0) | ||
| Yes | 1248 (47.2) | 122 (55.5) | 93 (50.3) | 8 (50.0) | 1471 (48.0) | ||
| Ever on ART | 0.620 | ||||||
| Yes | 2522 (95.4) | 208 (94.5) | 182 (98.4) | 16 (100.0) | 2928 (95.5) | ||
| No | 122 (4.6) | 12 (5.5) | 3 (1.6) | 0 (0.0) | 137 (4.5) | ||
| Ever used recreational or illicit drugs * | <0.0005 | ||||||
| No | 542 (20.5) | 34 (15.5) | 33 (17.8) | 0 (0.0) | 609 (19.9) | ||
| Yes | 251 (9.5) | 27 (12.3) | 61 (33.0) | 6 (37.5) | 345 (11.3) | ||
| Unknown | 1851 (70.0) | 159 (72.3) | 91 (49.2) | 10 (62.5) | 2111 (68.9) | ||
| Time first tested positive for HBV/HCV | <0.0005 | ||||||
| Before HIV diagnosis | |||||||
| 1–12 months | 7 (3.2) | 5 (2.7) | 4 (25.0) | ||||
| <1 month | 23 (10.5) | 11 (5.9) | 2 (12.5) | ||||
| From HIV diagnosis ** | |||||||
| <1 month | 103 (46.8) | 45 (24.3) | 4 (25.0) | ||||
| 1–3 months | 53 (24.1) | 34 (18.4) | 3 (18.8) | ||||
| 4–6 months | 7 (3.2) | 4 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | ||||
| 7–12 months | 3 (1.4) | 9 (4.9) | 0 (0.0) | ||||
| 13–24 months | 5 (2.3) | 13 (7.0) | 2 (12.5) | ||||
| 25–48 months | 10 (4.5) | 18 (9.7) | 1 (6.3) | ||||
| >48 months | 9 (4.1) | 46 (24.9) | 0 (0.0) | ||||
| HIV Mono-Infected | Co-Infected with HBV Only | Co-Infected with HCV Only | Co-Infected with both HBV and HCV | p Value † | All | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||||
| CD4 (cells/mm3); n (%) | 2514 (100.0) | 208 (100.0) | 166 (100.0) | 16 (100.0) | 0.049 | 2904 (100.0) | ||
| >350 | 758 (30.2) | 48 (23.1) | 56 (33.7) | 5 (31.3) | 867 (29.9) | |||
| 201–350 | 598 (23.8) | 43 (20.7) | 44 (26.5) | 2 (12.5) | 687 (23.7) | |||
| ≤200 | 1158 (46.1) | 117 (56.3) | 66 (39.8) | 9 (56.3) | 1350 (46.5) | |||
| Median CD4 [IQR] | 230 [53–392] | 143 [33–332] | 278 [115–424] | 169 [22–393] | 225 [53–390] | |||
| HIV viral load (copies/mL); n (%) | 1689 (100.0) | 141 (100.0) | 112 (100.0) | 12 (100.0) | 0.212 | 1954 (100.0) | ||
| ≤200 | 1618 (95.8) | 135 (95.7) | 107 (95.5) | 10 (83.3) | 1870 (95.7) | |||
| >200 | 71 (4.2) | 6 (4.3) | 5 (4.5) | 2 (16.7) | 84 (4.3) | |||
| Median viral load in 1000 s [IQR] | 83 [19–306] | 176 [33–559] | 83 [23–283] | 74 [1–758] | 87 [19–321] | |||
| AST (U/liter); n (%) | 2021 (100.0) | 179 (100.0) | 125 (100.0) | 12 (100.0) | <0.005 | 2337 (100.0) | ||
| ≤48 | 1787 (88.4) | 132 (73.7) | 101 (80.8) | 8 (66.7) | 2028 (86.8) | |||
| >48 | 234 (11.6) | 47 (26.3) | 24 (19.2) | 4 (33.3) | 309 (13.2) | |||
| Median AST (U/liter) [IQR] | 26 [21–35] | 32 [27–49] | 28 [23–38] | 35 [29–99] | 27 [22–36] | |||
| ALT (U/liter); n (%) | 2143 (100.0) | 187 (100.0) | 135 (100.0) | 12 (100.0) | <0.005 | 2477 (100.0) | ||
| ≤55 | 1917 (89.5) | 147 (78.6) | 112 (83.0) | 8 (66.7) | 2184 (88.2) | |||
| >55 | 226 (10.5) | 40 (21.4) | 23 (17.0) | 4 (33.3) | 293 (11.8) | |||
| Median ALT (U/liter) [IQR] | 24 [18–35] | 30 [24–52] | 25 [17–39] | 36 [28–82] | 24 [18–36] | |||
| % Co-Infected with HBV | Univariable Model | Multivariable Model ** | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | (95% CI) | p Value | aOR | (95% CI) | p Value | |||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||||||
| 10–29 | 4.1 | 1.00 | Referent | 1.00 | Referent | |||
| 30–49 | 8.7 | 2.22 | (1.47, 3.35) | <0.0005 | 2.24 | (1.49, 3.39) | <0.0005 | |
| 50–69 | 8.9 | 2.27 | (1.44, 3.57) | <0.0005 | 2.33 | (1.48, 3.67) | <0.0005 | |
| 70+ | 6.5 | 1.62 | (0.47, 5.52) | 0.443 | 1.77 | (0.52, 6.06) | 0.364 | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female | 3.2 | 1.00 | Referent | 1.00 | Referent | |||
| Male | 8.0 | 2.67 | (1.17, 6.08) | 0.020 | 2.84 | (1.24, 6.51) | 0.014 | |
| Ethnic group | 0.012 | |||||||
| Chinese | 8.5 | 2.04 | (1.10, 3.81) | 0.024 | ||||
| Malay | 5.6 | 1.30 | (0.64, 2.67) | 0.471 | ||||
| Indian and others | 4.3 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Marital status | 0.953 | |||||||
| Single | 7.6 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Married | 7.6 | 0.99 | (0.71, 1.39) | 0.963 | ||||
| Divorced/Separated/Widowed | 8.5 | 1.13 | (0.73, 1.74) | 0.586 | ||||
| Unknown | 7.6 | 1.00 | (0.67, 1.49) | 0.988 | ||||
| Mode of HIV transmission | 0.067 | 0.047 | ||||||
| Sexual | 7.6 | 1.00 | Referent | 1.00 | Referent | |||
| IDU | 25.0 | 4.05 | (1.29, 12.66) | 0.016 | 4.50 | (1.41, 14.38) | 0.011 | |
| Sexual and IDU | 5.6 | 0.72 | (0.31, 1.66) | 0.444 | 0.69 | (0.30, 1.59) | 0.378 | |
| Others and unknown | 10.1 | 1.37 | (0.68, 2.76) | 0.384 | 1.35 | (0.67, 2.74) | 0.404 | |
| Period of HIV diagnosis | 0.148 | |||||||
| 2006–2008 | 8.8 | 1.64 | (1.08, 2.49) | 0.022 | ||||
| 2009–2011 | 7.9 | 1.46 | (0.95, 2.24) | 0.086 | ||||
| 2012–2014 | 7.9 | 1.47 | (0.94, 2.29) | 0.091 | ||||
| 2015–2017 | 5.5 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| AIDS-defining illnesses/opportunistic infections within one year of HIV diagnosis | ||||||||
| No | 6.6 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Yes | 8.8 | 1.36 | (1.04, 1.78) | 0.024 | ||||
| Ever used recreational or illicit drugs * | 0.057 | |||||||
| No | 5.6 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Yes | 9.6 | 1.79 | (1.09, 2.94) | 0.022 | ||||
| Unknown | 8.0 | 1.47 | (1.01, 2.15) | 0.046 | ||||
| % Co-Infected with HCV | Univariable Model | Multivariable Model ** | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | (95% CI) | p Value | aOR | (95% CI) | p Value | |||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 0.800 | |||||||
| 10–29 | 7.3 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| 30–49 | 6.7 | 0.92 | (0.65, 1.29) | 0.615 | ||||
| 50–69 | 5.9 | 0.81 | (0.53, 1.23) | 0.317 | ||||
| 70+ | 0.0 | - | - | - | - | |||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female | 4.2 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Male | 6.7 | 1.64 | (0.79, 3.37) | 0.181 | ||||
| Ethnic group | <0.0005 | 0.020 | ||||||
| Chinese | 5.5 | 1.17 | (0.64, 2.14) | 0.616 | 1.38 | (0.72, 2.62) | 0.330 | |
| Malay | 12.6 | 2.90 | (1.53, 5.50) | 0.001 | 2.19 | (1.10, 4.34) | 0.026 | |
| Indian and others | 4.7 | 1.00 | Referent | 1.00 | Referent | |||
| Marital status | 0.169 | |||||||
| Single | 6.4 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Married | 5.2 | 0.80 | (0.54, 1.18) | 0.264 | ||||
| Divorced/Separated/Widowed | 8.2 | 1.30 | (0.83, 2.04) | 0.244 | ||||
| Unknown | 8.1 | 1.28 | (0.86, 1.92) | 0.226 | ||||
| Mode of HIV transmission | <0.0005 | <0.0005 | ||||||
| Sexual | 4.8 | 1.00 | Referent | 1.00 | Referent | |||
| IDU | 56.3 | 25.30 | (9.28, 68.93) | <0.0005 | 19.15 | (6.74, 54.38) | <0.0005 | |
| Sexual and IDU | 45.8 | 16.62 | (10.95, 25.22) | <0.0005 | 15.01 | (9.69, 23.25) | <0.0005 | |
| Others and unknown | 5.6 | 1.17 | (0.47, 2.93) | 0.736 | 1.10 | (0.44, 2.76) | 0.845 | |
| Period of HIV diagnosis | 0.002 | 0.004 | ||||||
| 2006–2008 | 9.0 | 2.08 | (1.33, 3.25) | 0.001 | 2.00 | (1.25, 3.21) | 0.004 | |
| 2009–2011 | 5.2 | 1.16 | (0.71, 1.89) | 0.558 | 1.06 | (0.63, 1.77) | 0.831 | |
| 2012–2014 | 6.8 | 1.53 | (0.95, 2.49) | 0.083 | 1.51 | (0.91, 2.52) | 0.111 | |
| 2015–2017 | 4.5 | 1.00 | Referent | 1.00 | Referent | |||
| AIDS-defining illnesses/opportunistic infections within one year of HIV diagnosis | ||||||||
| No | 6.3 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Yes | 6.9 | 1.10 | (0.83, 1.47) | 0.508 | ||||
| Ever used recreational or illicit drugs * | <0.0005 | |||||||
| No | 5.4 | 1.00 | Referent | |||||
| Yes | 19.4 | 4.21 | (2.71, 6.54) | <0.0005 | ||||
| Unknown | 4.8 | 0.88 | (0.59, 1.31) | 0.524 | ||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choy, C.Y.; Ang, L.W.; Ng, O.T.; Leo, Y.S.; Wong, C.S. Factors Associated with Hepatitis B and C Co-Infection among HIV-Infected Patients in Singapore, 2006–2017. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020087
Choy CY, Ang LW, Ng OT, Leo YS, Wong CS. Factors Associated with Hepatitis B and C Co-Infection among HIV-Infected Patients in Singapore, 2006–2017. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2019; 4(2):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020087
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoy, Chiaw Yee, Li Wei Ang, Oon Tek Ng, Yee Sin Leo, and Chen Seong Wong. 2019. "Factors Associated with Hepatitis B and C Co-Infection among HIV-Infected Patients in Singapore, 2006–2017" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 4, no. 2: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020087
APA StyleChoy, C. Y., Ang, L. W., Ng, O. T., Leo, Y. S., & Wong, C. S. (2019). Factors Associated with Hepatitis B and C Co-Infection among HIV-Infected Patients in Singapore, 2006–2017. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(2), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020087





