Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem?
Abstract
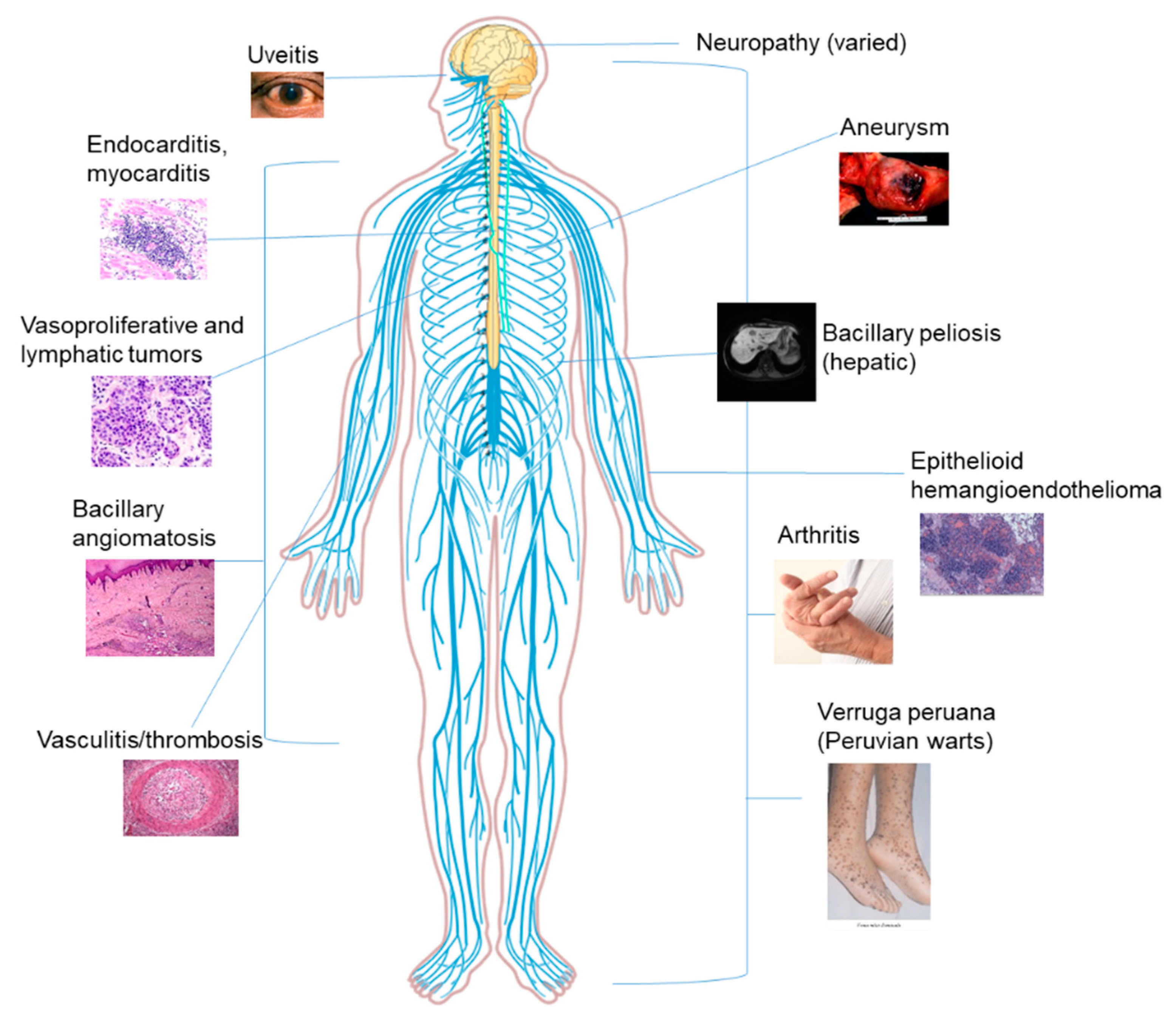
1. Introduction
2. Bartonella in Domestic Animals and the Potential for Transmission
2.1. Cats
2.2. Dogs
2.3. Other Domestic Animals
3. Vectors for Bartonella Species
3.1. Fleas and Lice
3.2. Arachnids (Spiders and Ticks)
4. Bartonella in the Wild (Reservoirs)
4.1. Rodents
4.2. Bats
5. Bartonella as a Coinfection in Humans
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angelakis, E.; Raoult, D. Pathogenicity and treatment of bartonella infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Williams, C.; Wey, A.C.; Henn, J.B.; Maggi, R.; Carrasco, S.; Mazet, J.; Boulouis, H.J.; Maillard, R.; et al. Bartonella endocarditis: A pathology shared by animal reservoirsand patients. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1166, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannino, F.; Salucci, S.; Di Provvido, A.; Paolini, A.; Ruggieri, E. Bartonella infections in humans dogs and cats. Vet. Ital. 2018, 54, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonellosis, one health and all creatures great and small. Vet. Dermatol. 2017, 28, 96-e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Tekaya, H.; Gorvel, J.P.; Dehio, C. Bartonella and Brucella—Weapons and strategies for stealth attack. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a010231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Greenberg, R.; Maggi, R.G.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Lewis, A.; Bradley, J.M. Bartonella henselae bloodstream infection in a boy with pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome. J. Cent. Nervous Syst. Dis. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeropoulos, D.; Asproudis, I.; Stefaniotou, M.; Moschos, M.M.; Mentis, A.; Malamos, K.; Kalogeropoulos, C. Bartonella henselae- and quintana-associated uveitis: A case series and approach of a potentially severe disease with a broad spectrum of ocular manifestations. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Schweickert, L.A.; Maggi, R.G.; Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M.; Woods, C.W. Hallucinations, sensory neuropathy, and peripheral visual deficits in a young woman infected with bartonella koehlerae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3415–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurfield, A.N.; Boulouis, H.J.; Chomel, B.B.; Heller, R.; Kasten, R.W.; Yamamoto, K.; Piemont, Y. Coinfection with bartonella clarridgeiae and bartonella henselae and with different bartonella henselae strains in domestic cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2120–2123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Ericson, M.; Maggi, R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Vasculitis, cerebral infarction and persistent bartonella henselae infection in a child. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabra, D.; Yeh, S.; Shantha, J.G. Ocular manifestations of bartonellosis. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 29, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L.C.; Pincerato, K.; Yoshimura, A.A.; Andrade, F.E.M.; Barros, A. Cat scratch disease presenting as axillary lymphadenopathy and a palpable benign mammary nodule mimicking a carcinoma. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 2018, 51, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaki, S.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Papaspirou, P.; Lazaris, D. Cat-scratch disease presenting as a solitary tumour in the breast: Report of three cases. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reproduct. Biol. 2003, 106, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povoski, S.P.; Spigos, D.G.; Marsh, W.L. An unusual case of cat-scratch disease from bartonella quintana mimicking inflammatory breast cancer in a 50-year-old woman. Breast J. 2003, 9, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbacher, M.E.; Klotz, S.; Klotz, J.; Pinnas, J.L. Bartonella henselae and the potential for arthropod vector-borne transmission. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guru, P.K.; Agarwal, A.; Fritz, A. A miraculous recovery: Bartonella henselae infection following a red ant bite. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouls, L.M.; Van De Pol, I.; Rijpkema, S.G.T.; Schot, C.S. Detection and identification of ehrlichia, borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, and bartonella species in dutch ixodes ricinus ticks. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarelli, P.E.; Maggi, R.G.; Hopkins, S.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Trull, C.L.; Bradley, J.M.; Hegarty, B.C.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella henselae infection in a family experiencing neurological and neurocognitive abnormalities after woodlouse hunter spider bites. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leulmi, H.; Bitam, I.; Berenger, J.M.; Lepidi, H.; Rolain, J.M.; Almeras, L.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Competence of cimex lectularius bed bugs for the transmission of bartonella quintana, the agent of trench fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003789. [Google Scholar]
- Kordick, D.L.; Wilson, K.H.; Sexton, D.J.; Hadfield, T.L.; Berkhoff, H.A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Prolonged bartonella bacteremia in cats associated with cat-scratch disease patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 3245–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Droz, S.; Chi, B.; Horn, E.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Whitney, A.M.; Brenner, D.J. Bartonella koehlerae sp. Nov., isolated from cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Margileth, A.M.; Baehren, D.F. Chest-wall abscess due to cat-scratch disease (csd) in an adult with antibodies to bartonella clarridgeiae: Case report and review of the thoracopulmonary manifestations of CSD. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avidor, B.; Graidy, M.; Efrat, G.; Leibowitz, C.; Shapira, G.; Schattner, A.; Zimhony, O.; Giladi, M. Bartonella koehlerae, a new cat-associated agent of culture-negative human endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Lantos, P.M.; Woods, C.W.; Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M. Bartonella vinsonii subsp. Berkhoffii and bartonella henselae bacteremia in a father and daughter with neurological disease. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Stuckey, M.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Henn, J.B.; Koehler, J.E.; Chang, C.C. Experimental infection of cats with afipia felis and various bartonella species or subspecies. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.; Chi, B.; Yamamoto, K.; Roberts-Wilson, J.; Gurfield, A.N.; Abbott, R.C.; Pedersen, N.C.; Koehler, J.E. Experimental transmission of bartonella henselae by the cat flea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, R.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Koehler, J.E.; Pedersen, N.C. Experimental and natural infection with bartonella henselae in domestic cats. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1997, 20, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskouizadeh, K.; Zahraei-Salehi, T.; Aledavood, S. Detection of bartonella henselae in domestic cats’ saliva. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2010, 2, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Sigmon, B.; Nicholson, W.L. Isolation of bartonella quintana from a woman and a cat following putative bite transmission. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, Y.; Ballhorn, W.; Kempf, V.A.J. Molecular detection of bartonella henselae in 11 ixodes ricinus ticks extracted from a single cat. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Maggi, R.G.; Diniz, P.P.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Molecular and serological diagnosis of bartonella infection in 61 dogs from the United States. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Soto, F.; Sepúlveda, M.; Bittencourt, P.; Benevenute, J.L.; Ikeda, P.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii and B. henselae in dogs. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1202–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, E.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Singhasivanon, O.U.; Namekata, D.Y.; Kasten, R.W.; Kass, P.H.; Cortes-Vecino, J.A.; Gennari, S.M.; Rajapakse, R.P.; Huong, L.T.; et al. Bartonella infection in urban and rural dogs from the tropics: Brazil, Colombia, Sri Lanka and Vietnam. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Fernandez, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Solano-Gallego, L. Bartonella infections in cats and dogs including zoonotic aspects. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, P.P.; Morton, B.A.; Tngrian, M.; Kachani, M.; Barrón, E.A.; Gavidia, C.M.; Gilman, R.H.; Angulo, N.P.; Brenner, E.C.; Lerner, R.; et al. Infection of domestic dogs in peru by zoonotic bartonella species: A cross-sectional prevalence study of 219 asymptomatic dogs. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Blann, K.R.; Stebbins, M.E.; Muñana, K.R.; Davidson, M.G.; Jackson, H.A.; Willard, M.D. Clinicopathological abnormalities and treatment response in 24 dogs seroreactive to bartonella vinsonii (berkhoffii) antigens. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2004, 40, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedenberg, S.G.; Balakrishnan, N.; Guillaumin, J.; Cooper, E.S.; Lewis, K.; Russell, D.S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Splenic vasculitis, thrombosis, and infarction in a febrile dog infected with bartonella henselae. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2015, 25, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ereqat, S.; Nasereddin, A.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Abdelkader, A.; Al-Jawabreh, A.; Zaid, T.; Azmi, K.; Abdeen, Z. Molecular evidence of bartonella species in ixodid ticks and domestic animals in palestine. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Chomel, B.B.; Chuang, S.-T.; Tsai, K.-H.; Wu, W.-J.; Huang, C.-G.; Yu, J.-C.; Sung, M.-H.; Kass, P.H.; et al. Bartonella infection in shelter cats and dogs and their ectoparasites. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.W.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella DNA in dog saliva. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1948–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.L.; Maggi, R.; Shuler, J.; Alward, A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Detection of bartonella henselae in the blood of 2 adult horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmero, J.; Pusterla, N.; Cherry, N.A.; Kasten, R.W.; Mapes, S.; Boulouis, H.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Chomel, B.B. Experimental infection of horses with bartonella henselae and bartonella bovis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, N.A.; Jones, S.L.; Maggi, R.G.; Davis, J.L.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella spp. Infection in healthy and sick horses and foals from the southeastern United States. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, R.; Cohen, L.; Morick, D.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Harrus, S.; Gottlieb, Y. Identification of different bartonella species in the cattle tail louse (haematopinus quadripertusus) and in cattle blood. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5477–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Heller, R.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Ueno, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Bleich, V.C.; Pierce, B.M.; Gonzales, B.J.; et al. Bartonella spp. Isolated from wild and domestic ruminants in north America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolain, J.M.; Rousset, E.; La Scola, B.; Duquesnel, R.; Raoult, D. Bartonella schoenbuchensis isolated from the blood of a French cow. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, R.; Riegel, P.; Barrat, F.; Bouillin, C.; Thibault, D.; Gandoin, C.; Halos, L.; Demanche, C.; Alliot, A.; Guillot, J.; et al. Bartonella chomelii sp. nov., isolated from French domestic cattle (bos taurus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoy, M.; Bai, Y.; Enscore, R.; Rizzo, M.R.; Bender, S.; Popov, V.; Albayrak, L.; Fofanov, Y.; Chomel, B. Bartonella melophagi in blood of domestic sheep (ovis aries) and sheep keds (melophagus ovinus) from the southwestern US: Cultures, genetic characterization, and ecological connections. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 190, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, R.G.; Kosoy, M.; Mintzer, M.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Isolation of candidatus bartonella melophagi from human blood. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, R.; Kubina, M.; Mariet, P.; Riegel, P.; Delacour, G.; Dehio, C.; Lamarque, F.; Kasten, R.; Boulouis, H.J.; Monteil, H.; et al. Bartonella alsatica sp. nov., a new bartonella species isolated from the blood of wild rabbits. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt 1, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Roblot, F.; Rolain, J.M.; Besnier, J.M.; Loulergue, J.; Bastides, F.; Choutet, P. First isolation of bartonella alsatica from a valve of a patient with endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanclaude, D.; Godmer, P.; Leveiller, D.; Pouedras, P.; Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M. Bartonella alsatica endocarditis in a French patient in close contact with rabbits. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15 (Suppl. 2), 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelakis, E.; Lepidi, H.; Canel, A.; Rispal, P.; Perraudeau, F.; Barre, I.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D. Human case of bartonella alsatica lymphadenitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernif, T.; Parola, P.; Ricci, J.C.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M. Molecular detection of bartonella alsatica in rabbit fleas, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 2013–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G.Z.; Sun, Z.Z.; Bai, J.Y.; Jiang, B.G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.G.; Yang, H.; Tian, G.; et al. Transmission and maintenance cycle of bartonella quintana among rhesus macaques, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Kabeya, H.; Yoshino, A.; Sekine, W.; Suzuki, K.; Tamate, H.B.; Yamazaki, S.; Chomel, B.B.; Maruyama, S. Japanese macaques (macaca fuscata) as natural reservoir of bartonella quintana. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2168–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, G.; Li, D.; Song, X.; Birtles, R.J.; Zhao, F. Bartonella quintana infections in captive monkeys, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bai, J.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Zeng, L.; Shi, Y.-S.; Qiu, Z.-L.; Ye, H.-H.; Zhang, X.-F.; Lu, Q.-B.; Kosoy, M.; et al. Genetic diversity of bartonella quintana in macaques suggests zoonotic origin of trench fever. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernif, T.; Leulmi, H.; Socolovschi, C.; Berenger, J.M.; Lepidi, H.; Bitam, I.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Acquisition and excretion of bartonella quintana by the cat flea, ctenocephalides felis felis. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; Lawrence, A.; Reichel, M.P. Cat fleas (ctenocephalides felis) carrying rickettsia felis and bartonella species in Hong Kong. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasereddin, A.; Risheq, A.; Harrus, S.; Azmi, K.; Ereqat, S.; Baneth, G.; Salant, H.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Abdeen, Z. Bartonella species in fleas from palestinian territories: Prevalence and genetic diversity. J. Vector Ecol. J. Soc. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nziza, J.; Tumushime, J.C.; Cranfield, M.; Ntwari, A.E.; Modry, D.; Mudakikwa, A.; Gilardi, K.; Slapeta, J. Fleas from domestic dogs and rodents in rwanda carry rickettsia asembonensis and bartonella tribocorum. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2019, 33, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangthong, K.; Promsthaporn, S.; Leepitakrat, S.; Schuster, A.L.; McCardle, P.W.; Kosoy, M.; Takhampunya, R. The distribution and diversity of bartonella species in rodents and their ectoparasites across Thailand. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeter, S.A.; Gundi, V.A.; Rood, M.P.; Kosoy, M.Y. Molecular detection and identification of bartonella species in xenopsylla cheopis fleas (siphonaptera: Pulicidae) collected from rattus norvegicus rats in Los Angeles, California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7850–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, A.; Altet, L.; Chirife, A.D.; Proboste, T.; Millan, J. Drivers of bartonella infection in micromammals and their fleas in a mediterranean peri-urban area. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bown, K.J.; Bennet, M.; Begon, M. Flea-borne bartonella grahamii and bartonella taylorii in bank voles. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstead, G.M. The centenary of the discovery of trench fever, an emerging infectious disease of World War 1. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e164–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini-Martinez, A.A.; Marquez, A.C.; Bravo-Estupinan, D.M.; Calixto, O.J.; Lopez-Castillo, C.A.; Botero-Garcia, C.A.; Hidalgo, M.; Cuervo, C. Bartonella quintana and typhus group rickettsiae exposure among homeless persons, Bogota, Colombia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louni, M.; Mana, N.; Bitam, I.; Dahmani, M.; Parola, P.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. Body lice of homeless people reveal the presence of several emerging bacterial pathogens in northern Algeria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drali, R.; Sangare, A.K.; Boutellis, A.; Angelakis, E.; Veracx, A.; Socolovschi, C.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D. Bartonella quintana in body lice from scalp hair of homeless persons, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, D.L.; Cole-Porse, C.; Kjemtrup, A.; Osikowicz, L.; Kosoy, M. Risk factors for human lice and bartonellosis among the homeless, San Francisco, California, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghidey, F.Y.; Igbinosa, O.; Mills, K.; Lai, L.; Woods, C.; Ruiz, M.E.; Fishbein, D.; Sampath, R.; Lowery, R.; Wortmann, G. Case series of bartonella quintana blood culture-negative endocarditis in Washington, DC. JMM Case Rep. 2016, 3, e005049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.A.; Spach, D.H.; Kippen, D.A.; Sugg, N.K.; Regnery, R.L.; Sayers, M.H.; Stamm, W.E. Seroprevalence to bartonella quintana among patients at a community clinic in downtown Seattle. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.E.; Minnick, M.F.; Lepidi, H.; Salvo, E.; Raoult, D. Experimental model of human body louse infection using green fluorescent protein-expressing bartonella quintana. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Drali, R.; Shako, J.C.; Davoust, B.; Diatta, G.; Raoult, D. A new clade of african body and head lice infected by bartonella quintana and yersinia pestis-democratic Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Previte, D.J.; Yoon, K.S.; Murenzi, E.; Koehler, J.E.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Lee, S.H.; Clark, J.M. Comparison of the proliferation and excretion of bartonella quintana between body and head lice following oral challenge. Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeter, S.A.; Diniz, P.P.; Battisti, J.M.; Munderloh, U.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Levy, M.G. Infection and replication of bartonella species within a tick cell line. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 49, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Hayashidani, H.; Pusterla, N.; Kasten, R.W.; Madigan, J.E.; Chomel, B.B. Investigation of bartonella infection in ixodid ticks from California. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 25, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkiewicz, E.C.; Hemmerich, C.; Rusch, D.B.; Fuqua, C.; Clay, K. Concordance of bacterial communities of two tick species and blood of their shared rodent host. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2566–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, R.G.; Toliver, M.; Richardson, T.; Mather, T.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Regional prevalences of borrelia burgdorferi, borrelia bissettiae, and bartonella henselae in ixodes affinis, ixodes pacificus and ixodes scapularis in the USA. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayol, C.; Jaaskelainen, A.; Koskela, E.; Kyrolainen, S.; Mappes, T.; Siukkola, A.; Kallio, E.R. Sympatric ixodes-tick species: Pattern of distribution and pathogen transmission within wild rodent populations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, A.; Reiter, M.; Schotta, A.M.; Stockinger, H.; Stanek, G. Detection of bartonella spp. In ixodes ricinus ticks and bartonella seroprevalence in human populations. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, Y.; O’Rourke, F.; Kempf, V.A.J. Bartonella spp.—A chance to establish one health concepts in veterinary and human medicine. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotte, V.; Bonnet, S.; Le Rhun, D.; Le Naour, E.; Chauvin, A.; Boulouis, H.J.; Lecuelle, B.; Lilin, T.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Transmission of bartonella henselae by ixodes ricinus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.; Cote, M.; Le Rhun, D.; Lecuelle, B.; Levin, M.L.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.I. Vector competence of the tick ixodes ricinus for transmission of bartonella birtlesii. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himsworth, C.G.; Parsons, K.L.; Jardine, C.; Patrick, D.M. Rats, cities, people, and pathogens: A systematic review and narrative synthesis of literature regarding the ecology of rat-associated zoonoses in urban centers. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (Larchmont N.Y.) 2013, 13, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.M.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Rubio, A.V.; Graham, C.B.; Montenieri, J.A.; Osikowicz, L.M.; Bai, Y.; Acosta-Gutierrez, R.; Avila-Flores, R.; Gage, K.L.; et al. Molecular survey of bartonella species and yersinia pestis in rodent fleas (siphonaptera) from Chihuahua, Mexico. J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayman, D.T.; McDonald, K.D.; Kosoy, M.Y. Evolutionary history of rat-borne bartonella: The importance of commensal rats in the dissemination of bacterial infections globally. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daly, J.S.; Worthington, M.G.; Brenner, D.J.; Moss, C.W.; Hollis, D.G.; Weyant, R.S.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Weaver, R.E.; Daneshvar, M.I.; O’Connor, S.P. Rochalimaea elizabethae sp. nov. Isolated from a patient with endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 872–881. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, J.A.; Flynn, C.; Regnery, R.L.; Vlahov, D.; Childs, J.E. Antibodies to bartonella species in inner-city intravenous drug users in Baltimore, MD. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996, 156, 2491–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castle, K.T.; Kosoy, M.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Phelan, L.; Bai, Y.; Gage, K.L.; Leepitakrat, W.; Monkanna, T.; Khlaimanee, N.; Chandranoi, K.; et al. Prevalence and diversity of bartonella in rodents of northern Thailand: A comparison with bartonella in rodents from southern China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosoy, M.; Bai, Y.; Sheff, K.; Morway, C.; Baggett, H.; Maloney, S.A.; Boonmar, S.; Bhengsri, S.; Dowell, S.F.; Sitdhirasdr, A.; et al. Identification of bartonella infections in febrile human patients from Thailand and their potential animal reservoirs. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Morway, C.; Sheff, K.W.; Bai, Y.; Colborn, J.; Chalcraft, L.; Dowell, S.F.; Peruski, L.F.; Maloney, S.A.; Baggett, H.; et al. Bartonella tamiae sp. Nov., a newly recognized pathogen isolated from three human patients from Thailand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabeya, H.; Colborn, J.M.; Bai, Y.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Richardson, J.H.; Maruyama, S.; Kosoy, M.Y. Detection of bartonella tamiae DNA in ectoparasites from rodents in thailand and their sequence similarity with bacterial cultures from Thai patients. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (Larchmont N.Y.) 2010, 10, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandelaki, G.; Malania, L.; Bai, Y.; Chakvetadze, N.; Katsitadze, G.; Imnadze, P.; Nelson, C.; Harrus, S.; Kosoy, M. Human lymphadenopathy caused by ratborne bartonella, tbilisi, Georgia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malania, L.; Bai, Y.; Osikowicz, L.M.; Tsertsvadze, N.; Katsitadze, G.; Imnadze, P.; Kosoy, M. Prevalence and diversity of bartonella species in rodents from Georgia (caucasus). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, J.E.; Knobel, D.L.; Agwanda, B.; Bai, Y.; Breiman, R.F.; Cleaveland, S.; Njenga, M.K.; Kosoy, M. Prevalence and diversity of small mammal-associated bartonella species in rural and urban Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Osinubi, M.O.V.; Osikowicz, L.; McKee, C.; Vora, N.M.; Rizzo, M.R.; Recuenco, S.; Davis, L.; Niezgoda, M.; Ehimiyein, A.M.; et al. Human exposure to novel bartonella species from contact with fruit bats. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushadze, L.; Bai, Y.; Osikowicz, L.; McKee, C.; Sidamonidze, K.; Putkaradze, D.; Imnadze, P.; Kandaurov, A.; Kuzmin, I.; Kosoy, M. Prevalence, diversity, and host associations of bartonella strains in bats from Georgia (caucasus). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.Y.; Tsigrelis, C.; Baddour, L.M.; Lepidi, H.; Rolain, J.M.; Patel, R.; Raoult, D. Candidatus bartonella mayotimonensis and endocarditis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veikkolainen, V.; Vesterinen, E.J.; Lilley, T.M.; Pulliainen, A.T. Bats as reservoir hosts of human bacterial pathogen, bartonella mayotimonensis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckey, M.J.; Boulouis, H.J.; Cliquet, F.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Servat, A.; Arechiga-Ceballos, N.; Echevarria, J.E.; Chomel, B.B. Potentially zoonotic bartonella in bats from France and Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, P.; Seki, M.C.; Carrasco, A.O.T.; Rudiak, L.V.; Miranda, J.M.D.; Goncalves, S.M.M.; Hoppe, E.G.L.; Albuquerque, A.C.A.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; Passos, C.E.; et al. Evidence and molecular characterization of bartonella spp. And hemoplasmas in neotropical bats in Brazil. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2038–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuttin, G.L.; De Salvo, M.N.; La Rosa, I.; Dohmen, F.E.G. Neorickettsia risticii, rickettsia sp. And bartonella sp. In tadarida brasiliensis bats from Buenos Aires, Argentina. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 52, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, C.D.; Kosoy, M.Y.; Bai, Y.; Osikowicz, L.M.; Franka, R.; Gilbert, A.T.; Boonmar, S.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Peruski, L.F. Diversity and phylogenetic relationships among bartonella strains from Thai bats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandor, A.D.; Foldvari, M.; Krawczyk, A.I.; Sprong, H.; Corduneanu, A.; Barti, L.; Gorfol, T.; Estok, P.; Kovats, D.; Szekeres, S.; et al. Eco-epidemiology of novel bartonella genotypes from parasitic flies of insectivorous bats. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskaluk, A.E.; Stuckey, M.J.; Jaffe, D.A.; Kasten, R.W.; Aguilar-Setien, A.; Olave-Leyva, J.I.; Galvez-Romero, G.; Obregon-Morales, C.; Salas-Rojas, M.; Garcia-Flores, M.M.; et al. Molecular detection of bartonella species in blood-feeding bat flies from mexico. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (Larchmont N.Y.) 2018, 18, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguina, C.; Garcia, P.J.; Gotuzzo, E.; Cordero, L.; Spach, D.H. Bartonellosis (carrion’s disease) in the modern era. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Caso, W.; Mazulis, F.; Weilg, C.; Aguilar-Luis, M.A.; Sandoval, I.; Correa-Nunez, G.; Li, D.; Song, X.; Liu, Q.; Del Valle-Mendoza, J. Co-infection with bartonella bacilliformis and mycobacterium spp. In a coastal region of Peru. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galfsky, D.; Krol, N.; Pfeffer, M.; Obiegala, A. Long-term trends of tick-borne pathogens in regard to small mammal and tick populations from Saxony, Germany. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noden, B.H.; Tshavuka, F.I.; van der Colf, B.E.; Chipare, I.; Wilkinson, R. Exposure and risk factors to coxiella burnetii, spotted fever group and typhus group rickettsiae, and bartonella henselae among volunteer blood donors in Namibia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, M.; Raoult, D. Q fever. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 518–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewska-Badora, J.; Moniuszko, A.; Zukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Zwolinski, J.; Piatek, J.; Pancewicz, S. Serological survey in persons occupationally exposed to tick-borne pathogens in cases of co-infections with borrelia burgdorferi, anaplasma phagocytophilum, bartonella spp. And babesia microti. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2012, 19, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holden, K.; Boothby, J.T.; Kasten, R.W.; Chomel, B.B. Co-detection of bartonella henselae, borrelia burgdorferi, and anaplasma phagocytophilum in ixodes pacificus ticks from California, USA. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (Larchmont N.Y.) 2006, 6, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskow, E.; Rao, R.V.; Mordechai, E. Concurrent infection of the central nervous system by borrelia burgdorferi and bartonella henselae: Evidence for a novel tick-borne disease complex. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.; Cote, M.; Paul, R.E.; Bonnet, S. Questing ticks in suburban forest are infected by at least six tick-borne pathogens. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (Larchmont N.Y.) 2011, 11, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mietze, A.; Strube, C.; Beyerbach, M.; Schnieder, T.; Goethe, R. Occurrence of bartonella henselae and borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato co-infections in ticks collected from humans in Germany. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytykiewicz, H.; Karbowiak, G.; Werszko, J.; Czerniewicz, P.; Sprawka, I.; Mitrus, J. Molecular screening for bartonella henselae and borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato co-existence within ixodes ricinus populations in central and eastern parts of Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2012, 19, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, K.; Merilainen, L.; Franz, O.; Pirttinen, H.; Quevedo-Diaz, M.; Croucher, S.; Gilbert, L. Evaluating polymicrobial immune responses in patients suffering from tick-borne diseases. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bartonella Species | Host (s) | Vector(s) |
|---|---|---|
| B. henselae | Cat, human, dogs, horses | Fleas, lice, ticks, spiders |
| B. quintana | Humans, macaques, cats, dogs | Human body lice, fleas, bed bugs |
| B. bacilliformis | Humans | Sandflies, fleas |
| B. koehlerae | Cats, dogs, humans | Fleas |
| B. vinsonii ssp. berkhoffi | Dogs, horses, foxes, humans | Fleas, ticks |
| B. bovis | Cattle, cats, dogs, human | Biting flies, ticks |
| B. clarridgeiae | Cats, dogs | Fleas, ticks |
| B. rattimassiliensis | Rats | Fleas |
| B. tamiae | Rats, humans | Mites |
| B. tribocorum | Rats | Fleas |
| B. rousetii | Bats | Bat flies |
| B. schoenbuchensis | Cattle | Biting flies, ticks |
| B. chomelii | Cattle | Biting flies, ticks |
| B. doshiae | Rats, humans | Fleas |
| B. grahamii | Mice, humans | Fleas |
| B. birtlesii | Mice | Fleas |
| B. mayotimonensis | Bats, humans | Bat flies, fleas, ticks |
| B. elizabethae | Rats, humans, dogs | Fleas |
| B. washoensis | Dogs, humans | Fleas, ticks |
| B. rochalimae | Dogs, humans | Fleas, ticks |
| B. vinsonii ssp. arupensis | Dogs, humans | Fleas, ticks |
| B.melophagi | Sheep, humans | Sheep keds |
| B. alsatica | Rabbits, humans | Fleas, ticks |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheslock, M.A.; Embers, M.E. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020069
Cheslock MA, Embers ME. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2019; 4(2):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020069
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheslock, Mercedes A., and Monica E. Embers. 2019. "Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem?" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 4, no. 2: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020069
APA StyleCheslock, M. A., & Embers, M. E. (2019). Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(2), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4020069





