Diagnosis of Murine Typhus by Serology in Peninsular Malaysia: A Case Report Where Rickettsial Illnesses, Leptospirosis and Dengue Co-Circulate
Abstract
1. Introduction
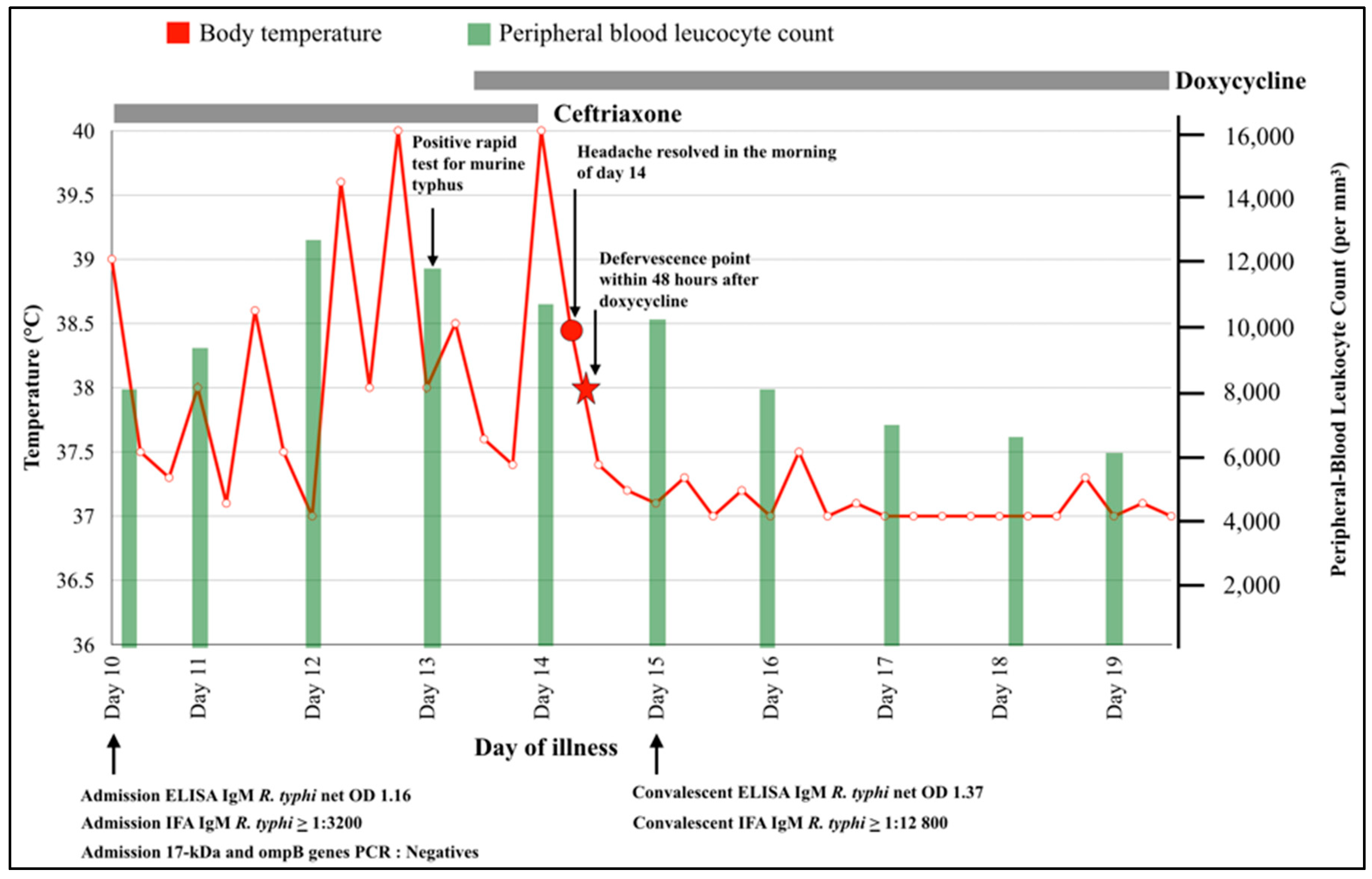
2. Case Report
Ethics Statement
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paris, D.H.; Dumler, J.S. State of the art of diagnosis of rickettsial diseases: The use of blood specimens for diagnosis of scrub typhus, spotted fever group rickettsiosis, and murine typhus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, D.H.; Shelite, T.R.; Day, N.P.; Walker, D.H. Unresolved problems related to scrub typhus: A seriously neglected life-threatening disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, S.T.; Rohani, M.Y. The use of the indirect immunoperoxidase test for the serodiagnosis of rickettsial diseases in Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health. 2002, 33, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phetsouvanh, R.; Thojaikong, T.; Phoumin, P.; Sibounheuang, B.; Phommasone, K.; Chansamouth, V.; Lee, S.J.; Newton, P.N.; Blacksell, S.D. Inter- and intra-operator variability in the reading of indirect immunofluorescence assays for the serological diagnosis of scrub typhus and murine typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.M.; Cho, Y.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Shim, S.K. Usefulness of eschar PCR for diagnosis of scrub typhus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, H.W.; Hossain, M.; Leopold, S.; Anantatat, T.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Sinha, I.; Plewes, K.; Maude, R.J.; Chowdhury, M.H.; Paul, S.; et al. Rickettsial Illnesses as Important Causes of Febrile Illness in Chittagong. Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theunissen, C.; Cnops, L.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Huits, R.; Bottieau, E. Acute-phase diagnosis of murine and scrub typhus in Belgian travelers by polymerase chain reaction: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malheiro, L.; Ceia, F.; Alves, J.; Carvalho, A.C.; Sobrinho-Simoes, J.; Sousa, R.; Sarmento, A.; Santos, L. Severe interstitial pneumonia due to murine typhus in a patient returning from Bali. IDCases 2017, 9, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, J.; Margolin, J.; Coleman, N.E.; Demmler-Harrison, G.; Lam, F.; Shah, M.D. A Severe Case of Murine Typhus Presenting With Anemia and Severe Thrombocytopenia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 40, e185–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, N.; Nakamura-Uchiyama, F.; Kobayashi, K.; Takasaki, T.; Ogasawara, Y.; Ando, S.; Iwabuchi, S.; Ohnishi, K. Severe murine typhus with shock and acute respiratory failure in a Japanese traveler after returning from Thailand. J. Travel. Med. 2013, 20, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, S.; Rattanavong, S.; Lee, S.J.; Panyanivong, P.; Craig, S.B.; Tulsiani, S.M.; Blacksell, S.D.; Dance, D.A.B.; Dubot-Pérès, A.; Sengduangphachanh, A.; et al. Orientia, rickettsia, and leptospira pathogens as causes of CNS infections in Laos: A prospective study. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e104–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.E.; Thi, M.; Alkhateb, R.; Agarwal, A.; Sharkey, F.E.; Dayton, C.; Anstead, G.M. Case Report: Fulminant Murine Typhus Presenting with Status Epilepticus and Multi-Organ Failure: An Autopsy Case and a Review of the Neurologic Presentations of Murine Typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, P.N.; Keolouangkhot, V.; Lee, S.J.; Choumlivong, K.; Sisouphone, S.; Vongsouvath, M.; Mayxay, M.; Chansamouth, V.; Davong, V.; Phommasone, K.; et al. A Prospective, Open-Label, Randomized Trial of Doxycycline Versus Azithromycin for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Murine Typhus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Human Leptospirosis: Guidance for Diagnosis, Surveillance and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, D.H.; Blacksell, S.D.; Nawtaisong, P.; Jenjaroen, K.; Teeraratkul, A.; Chierakul, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Kantipong, P.; Day, N.P.J. Diagnostic accuracy of a loop-mediated isothermal PCR assay for detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi during acute Scrub Typhus infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keysary, A.; Strenger, C. Use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques with cross-reacting human sera in diagnosis of murine typhus and spotted fever. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1034–1035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Civen, R.; Ngo, V. Murine typhus: An unrecognized suburban vectorborne disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, Z.; Kallumadanda, S.; Wang, F.; Hemmige, V.; Musher, D. Acute Febrile Illness and Complications Due to Murine Typhus, Texas, USA1,2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayxay, M.; Castonguay-Vanier, J.; Chansamouth, V.; Dubot-Peres, A.; Paris, D.H.; Phetsouvanh, R.; Tangkhabuanbutra, J.; Douangdala, P.; Inthalath, S.; Souvannasing, P.; et al. Causes of non-malarial fever in Laos: A prospective study. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e46–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Jarman, R.G.; Bailey, M.S.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Jenjaroen, K.; Gibbons, R.V.; Paris, D.H.; Premaratna, R.; De Silva, H.J.; Lalloo, D.G.; et al. Evaluation of six commercial point-of-care tests for diagnosis of acute dengue infections: The need for combining NS1 antigen and IgM/IgG antibody detection to achieve acceptable levels of accuracy. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Lim, C.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Jintaworn, S.; Kantipong, P.; Richards, A.L.; Paris Daniel, H.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Day, N.P.J. Optimal Cutoff and Accuracy of an IgM Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Diagnosis of Acute Scrub Typhus in Northern Thailand: An Alternative Reference Method to the IgM Immunofluorescence Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; Chan, C.T.; Paxton, H.; Thompson, K.; Howard, R.; Dasch, G.A. Comparative evaluation of a commercial enzyme immunoassay for the detection of human antibody to Rickettsia typhi. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1995, 2, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clements, M.L.; Dumler, J.S.; Fiset, P.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr.; Snyder, M.J.; Levine, M.M. Serodiagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever: Comparison of IgM and IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and indirect fluorescent antibody test. J. Infect. Dis. 1983, 148, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phommasone, K.; Paris, D.H.; Anantatat, T.; Castonguay-Vanier, J.; Keomany, S.; Souvannasing, P.; Blacksell, S.D.; Mayxay, M.; Newton, P.N. Concurrent Infection with murine typhus and scrub typhus in southern Laos—The mixed and the unmixed. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phimda, K.; Hoontrakul, S.; Suttinont, C.; Chareonwat, S.; Losuwanaluk, K.; Chueasuwanchai, S.; Chierakul, W.; Suwancharoen, D.; Silpasakorn, S.; Saisongkorh, W.; et al. Doxycycline versus azithromycin for treatment of leptospirosis and scrub typhus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3259–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.E.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M.J. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Milton, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuhana, Y.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Sujariyakul, P.; Sonthayanon, P.; Chotivanich, K.; Paris, D.H.; Pukrittayakamee, S.; Blacksell, S.D.; Hanboonkunupakarn, B. Diagnosis of Murine Typhus by Serology in Peninsular Malaysia: A Case Report Where Rickettsial Illnesses, Leptospirosis and Dengue Co-Circulate. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4010023
Yuhana Y, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, Sujariyakul P, Sonthayanon P, Chotivanich K, Paris DH, Pukrittayakamee S, Blacksell SD, Hanboonkunupakarn B. Diagnosis of Murine Typhus by Serology in Peninsular Malaysia: A Case Report Where Rickettsial Illnesses, Leptospirosis and Dengue Co-Circulate. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2019; 4(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuhana, Yazli, Ampai Tanganuchitcharnchai, Pimpan Sujariyakul, Piengchan Sonthayanon, Kesinee Chotivanich, Daniel H. Paris, Sasithon Pukrittayakamee, Stuart D. Blacksell, and Borimas Hanboonkunupakarn. 2019. "Diagnosis of Murine Typhus by Serology in Peninsular Malaysia: A Case Report Where Rickettsial Illnesses, Leptospirosis and Dengue Co-Circulate" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 4, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4010023
APA StyleYuhana, Y., Tanganuchitcharnchai, A., Sujariyakul, P., Sonthayanon, P., Chotivanich, K., Paris, D. H., Pukrittayakamee, S., Blacksell, S. D., & Hanboonkunupakarn, B. (2019). Diagnosis of Murine Typhus by Serology in Peninsular Malaysia: A Case Report Where Rickettsial Illnesses, Leptospirosis and Dengue Co-Circulate. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4010023





