Artemether and Praziquantel: Origin, Mode of Action, Impact, and Suggested Application for Effective Control of Human Schistosomiasis
Abstract
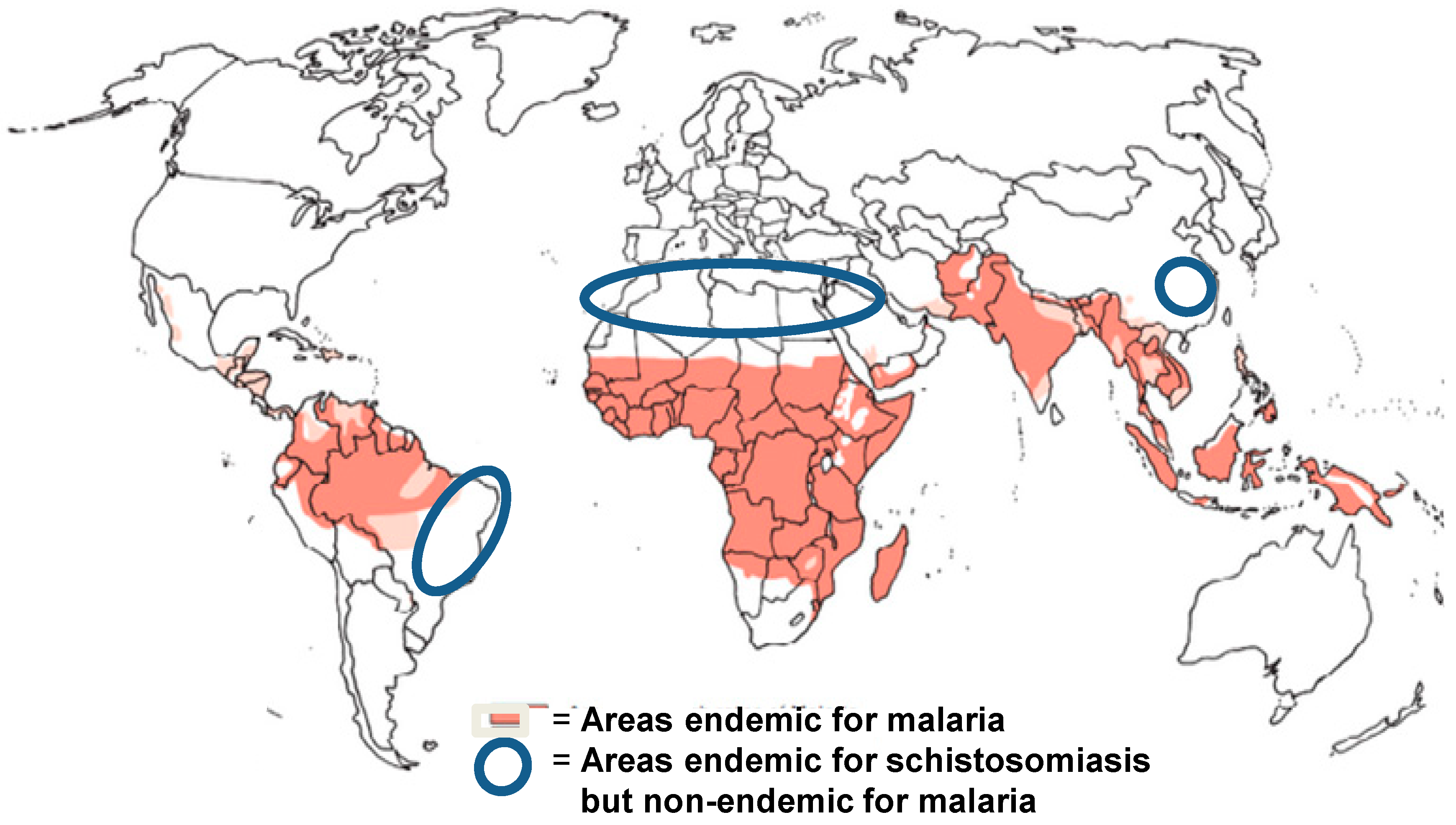
1. Background
2. Pharmacological Aspects
2.1. The Artemisinins
2.2. Praziquantel
2.3. Combination Treatment
3. Drug Resistance
3.1. Artemether
3.2. Praziquantel
4. Trials and Community-based Studies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/NTD_RoadMap_2012_Fullversion.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2018).
- WHO. Schistosomiasis Fact Sheet of 20 February 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schistosomiasis (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- Hotez, P.J.; Asojo, O.A.; Adesina, A.M. Nigeria: “Ground Zero” for the high prevalence neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.; El Morshedy, H. Efficacy of two praziquantel treatments among primary school children in an area of high Schistosoma mansoni endemicity, Nile Delta, Egypt. Parasitology 2011, 138, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoby, T.; Galal, N.; Fenwick, A.; Barakat, R.; El-Hawey, A.; Nooman, Z.; Habib, M.; Abdel-Wahab, F.; Gabr, N.S.; Hammam, H.M.; et al. The epidemiology of schistosomiasis in Egypt: Summary findings in nine governorates. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryseels, B. Schistosomiasis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, S.; de Vlas, S.J.; Stelma, F.; Vereecken, K.; Gryseels, B.; Polman, K. The contribution of water contact behavior to the high Schistosoma mansoni Infection rates observed in the Senegal River Basin. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Wegner, D.H. Multicentre trials of praziquantel in human schistosomiasis: Design and techniques. Bull. World Health Organ. 1979, 57, 767–771. [Google Scholar]
- Colley, D.G.; Bustinduy, A.L.; Secor, W.E.; King, C.H. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 2014, 383, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.N.; Bergquist, R.; Leonardo, L.; Yang, G.J.; Yang, K.; Sudomo, M.; Olveda, R. Schistosomiasis japonica control and research needs. Adv. Parasitol. 2010, 72, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H. Parasites and poverty: The case of schistosomiasis. Acta Trop. 2010, 113, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, S.I.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulkader, R.S.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abebo, T.A.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1260–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Bergquist, R.; Li, S.Z.; Zhou, X.N. “Farewell to the God of Plague”: The Importance of Political Commitment Towards the Elimination of Schistosomiasis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The development of the antimalarial drugs with new type of chemical structure–qinghaosu and dihydroqinghaosu. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Publ. Health 2004, 35, 250–251. [Google Scholar]
- Faurant, C. From bark to weed: The history of artemisinin. Parasite 2011, 18, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.H.; Su, X. Artemisinin: Discovery from the Chinese herbal garden. Cell 2011, 146, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klayman, D.L. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): An antimalarial drug from China. Science 1985, 228, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, B. A present from Chairman Mao. Welcome News Supplement 6: Research Directions in Malaria. Wellcome Trust 2002, 25 Suppl. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.L. How Chinese scientists discovered qinghaosu (artemisinin) and developed its derivatives? What are the future perspectives? Med. Trop. Rev. Corps Sante Colonial 1998, 58, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, M.T.; Saify, Z.S.; Sultana, N.; Ahmad, I.; Saeed-Ul-Hassan, S.; Tariq, I.; Khanum, M. Malaria and artemisinin derivatives: An updated review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1879–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. Artemisinin-A Gift from Traditional Chinese Medicine to the World (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 10210–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambo, E.; Khater, E.I.; Chen, J.H.; Bergquist, R.; Zhou, X.N. Nobel prize for the artemisinin and ivermectin discoveries: A great boost towards elimination of the global infectious diseases of poverty. Infec. Dis. Poverty 2015, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.J.; Fu, L.F.; Shao, P.P.; Wu, F.Z.; Fan, C.Z.; Shu, H.; Ren, C.X.; Sheng, X.L. Experimental studies on antischistosomal activity of qinghaosu. Chin. Med. J. 1980, 60, 422–425. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.H.; Sun, J. Schistosoma hemozoin and its possible roles. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagola, S.; Stephens, P.W.; Bohle, D.S.; Kosar, A.D.; Madsen, S.K. The structure of malaria pigment beta-haematin. Nature 2000, 404, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homewood, C.A.; Jewsbury, J.M. Comparison of malarial and schistosome pigment. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1972, 66, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, B.; Robert, A. Heme as trigger and target for trioxane-containing antimalarial drugs. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Charman, W.N.; Chiu, F.C.; Prankerd, R.J.; Dong, Y.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Charman, S.A. Relationship between antimalarial activity and heme alkylation for spiro- and dispiro-1,2,4-trioxolane antimalarials. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.H.; Keiser, J.; Chollet, J.; Utzinger, J.; Dong, Y.; Endriss, Y.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Tanner, M. In vitro and in vivo activities of synthetic trioxolanes against major human schistosome species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradines, V.; Portela, J.; Boissier, J.; Cosledan, F.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. Trioxaquine PA1259 alkylates heme in the blood-feeding parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2403–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Kamaraj, S.; Bulbule, V.J.; Chiu, F.C.; Chollet, J.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Hein, C.D.; Papastogiannidis, P.; Morizzi, J.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship of the Antimalarial Ozonide Artefenomel (OZ439). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2654–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Xiao, S.H. Effect of ozonide OZ418 against Schistosoma japonicum harbored in mice. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Dong, H.F.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Q.P.; Jiang, M.S. Efficacy of praziquantel and artemisinin derivatives for the treatment and prevention of human schistosomiasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, D.; Goswami, A.; Saikia, P.P.; Barua, N.C.; Rao, P.G. Artemisinin and its derivatives: A novel class of anti-malarial and anti-cancer agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.H.; Mei, J.Y.; Jiao, P.Y. Schistosoma japonicum-infected hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) used as a model in experimental chemotherapy with praziquantel, artemether, and OZ compounds. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Chollet, J.; Utzinger, J.; Matile, H.; Mei, J.; Tanner, M. Artemether administered together with haemin damages schistosomes in vitro. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 95, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.H.; You, J.Q.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Experimental studies on early treatment of schistosomal infection with artemether. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Publ. Health 1995, 26, 306–318. [Google Scholar]
- Djimde, A.; Lefevre, G. Understanding the pharmacokinetics of Coartem. Malar. J. 2009, 8 (Suppl. 1), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.D.; Zarowiecki, M.; Marchant, J.S. Ca2+ channels and praziquantel: A view from the free world. Parasitol. Int. 2013, 62, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Binggui, S.; Chollet, J.; Tanner, M. Tegumental changes in 21-day-old Schistosoma mansoni harboured in mice treated with artemether. Acta Trop. 2000, 75, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupit, P.M.; Cunningham, C. What is the mechanism of action of praziquantel and how might resistance strike? Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bais, S.; Greenberg, R.M. TRP channels as potential targets for antischistosomals. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2018, 8, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.X.; Liu, G.J.; Zhang, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Ni, J.; Wei, J.F.; Zhou, L.K.; Duan, X.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. Systematic review of benefits and harms of artemisinin-type compounds for preventing schistosomiasis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2003, 83, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shuhua, X.; Chollet, J.; Weiss, N.A.; Bergquist, R.N.; Tanner, M. Preventive effect of artemether in experimental animals infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitol. Int. 2000, 49, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabah, A.A.; Fletcher, C.; Webbe, G.; Doenhoff, M.J. Schistosoma mansoni: Chemotherapy of infections of different ages. Exp. Parasitol. 1986, 61, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnert, R.; Andrews, P. Praziquantel, a new board-spectrum antischistosomal agent. Zeitschrift fur Parasitenkunde 1977, 52, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.H.; Yue, W.J.; Yang, Y.Q.; You, J.Q. Susceptibility of Schistosoma japonicum to different developmental stages to praziquantel. Chin. Med. J. 1987, 100, 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.X. New insight into praziquantel against various developmental stages of schistosomes. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, S.; Pica-Mattoccia, L.; William, S.; El-Lakkani, N.; Cioli, D. Effect of praziquantel on the immature stages of Schistosoma haematobium. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.U.; Utzinger, J.; Shen, B.G.; Tanner, M.; Chollet, J. Ultrastructural alterations of adult Schistosoma haematobium harbored in mice following artemether administration. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 2006, 24, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Shu-Hua, X.; Utzinger, J.; Chollet, J.; Tanner, M. Effect of artemether administered alone or in combination with praziquantel to mice infected with Plasmodium berghei or Schistosoma mansoni or both. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Q&A on artemisinin resistance. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/malaria/media/artemisinin_resistance_qa/en/ (accessed on 11 November 2018).
- Tilley, L.; Straimer, J.; Gnadig, N.F.; Ralph, S.A.; Fidock, D.A. Artemisinin Action and Resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergquist, R.; Utzinger, J.; Keiser, J. Controlling schistosomiasis with praziquantel: How much longer without a viable alternative? Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioli, D.; Valle, C.; Angelucci, F.; Miele, A.E. Will new antischistosomal drugs finally emerge? Trends Parasitol. 2008, 24, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfy, W.M.; Hishmat, M.G.; El Nashar, A.S.; Abu El Einin, H.M. Evaluation of a method for induction of praziquantel resistance in Schistosoma mansoni. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, F.F.; Coelho, P.M.; Araujo, N.; Kusel, J.R.; Katz, N.; Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Mattos, A.C. Schistosoma mansoni: A method for inducing resistance to praziquantel using infected Biomphalaria glabrata snails. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Metwally, A.; Farghaly, A.; Bruce, J.; Tao, L.F.; Bennett, J.L. Characterization of isolates of Schistosoma mansoni from Egyptian villagers that tolerate high doses of praziquantel. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 55, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, P.G.; Doenhoff, M.J. Drug-resistant schistosomiasis: Resistance to praziquantel and oxamniquine induced in Schistosoma mansoni in mice is drug specific. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hug. 1994, 51, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, I.N.; Sanchez, M.C.; Mkoji, G.M.; Agola, L.E.; Runo, S.M.; Cupit, P.M.; Cunningham, C. Praziquantel sensitivity of Kenyan Schistosoma mansoni isolates and the generation of a laboratory strain with reduced susceptibility to the drug. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2014, 4, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melman, S.D.; Steinauer, M.L.; Cunningham, C.; Kubatko, L.S.; Mwangi, I.N.; Wynn, N.B.; Mutuku, M.W.; Karanja, D.M.; Colley, D.G.; Black, C.L.; et al. Reduced susceptibility to praziquantel among naturally occurring Kenyan isolates of Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Botros, S.; Metwally, A.; William, S.; Farghally, A.; Tao, L.F.; Day, T.A.; Bennett, J.L. Resistance to praziquantel: Direct evidence from Schistosoma mansoni isolated from Egyptian villagers. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.; Munoz, J.; Gascon, J.; Valls, M.E.; Corachan, M. Failure of standard treatment with praziquantel in two returned travelers with Schistosoma haematobium infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.M.; Thiengo, R.; Conceicao, M.J.; Rey, L.; Lenzi, H.L.; Pereira Filho, E.; Ribeiro, P.C. Therapeutic failure of praziquantel in the treatment of Schistosoma haematobium infection in Brazilians returning from Africa. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2005, 100, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.M.; Pereira Filho, E.; Thiengo, R.; Ribeiro, P.C.; Conceicao, M.J.; Panasco, M.; Lenzi, H.L. Schistosomiasis haematobia: Histopathological course determined by cystoscopy in a patient in whom praziquantel treatment failed. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2008, 50, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.S.; Li, H.J.; Dai, J.R.; Wang, W.; Qu, G.L.; Tao, Y.H.; Xing, Y.T.; Li, Y.Z.; Qian, K.; Wei, J.Y. Studies on resistance of Schistosoma to praziquantel XIII resistance of Schistosoma japonicum to praziquantel is experimentally induced in laboratory. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2011, 23, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Liang, Y.S.; Dai, J.R.; Wang, W.; Qu, G.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Xing, Y.T.; Tao, Y.H.; Qian, K.; Jia, Y.; et al. Studies on resistance of Schistosoma to praziquantel XIV experimental comparison of susceptibility to praziquantel between PZQ-resistant isolates and PZQ-susceptible isolates of Schistosoma japonicum in stages of adult worms, miracidia and cercariae. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2011, 23, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Q.; You-Sheng, L.; Wei, W.; Guo-Li, Q.; Hong-Jun, L.; Zhen-Kun, Y.; Zheng-Yang, Z.; Yuntian, X.; Jian-Rong, D. Studies on resistance of Schistosoma to praziquantel XVII Biological characteristics of praziquantel-resistant isolates of Schistosoma japonicum in mice. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2017, 29, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Timson, D.J. The mechanism of action of praziquantel: Six hypotheses. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Seventh Meeting of the Working Group on Monitoring of Neglected Tropical Diseases Drug Effi Cacy. Geneva, 26–27 February 2018. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/273620/WHO-CDS-NTD-PCT-2018.06-eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 3 November 2018).
- King, C.H. The evolving schistosomiasis agenda 2007-2017-Why we are moving beyond morbidity control toward elimination of transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorshedy, H.; Tanner, M.; Bergquist, R.N.; Sharaf, S.; Barakat, R. Prophylactic effect of artemether on human schistosomiasis mansoni among Egyptian children: A randomized controlled trial. Acta Trop. 2016, 158, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorshedy, H.; Bergquist, R.; El-Ela, N.E.; Eassa, S.M.; Elsakka, E.E.; Barakat, R. Can human schistosomiasis mansoni control be sustained in high-risk transmission foci in Egypt? Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang-Etoh, P.C.; Ejezie, G.C.; Useh, M.F.; Inyang-Etoh, E.C. Efficacy of a combination of praziquantel and artesunate in the treatment of urinary schistosomiasis in Nigeria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.Y.; McManus, D.P.; Gray, D.J.; Balen, J.; Luo, X.S.; He, Y.K.; Ellis, M.; Williams, G.M.; Li, Y.S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of safety and efficacy of combined praziquantel and artemether treatment for acute schistosomiasis japonica in China. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J.; Gnaka, H.N.; Yapi, A.; N’Guessan, N.A.; Kigbafori, S.D.; Lengeler, C.; Chollet, J.; Shuhua, X.; Tanner, M. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oral artemether for the prevention of patent Schistosoma haematobium infections. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzinger, J.; N’Goran, E.K.; N’Dri, A.; Lengeler, C.; Xiao, S.; Tanner, M. Oral artemether for prevention of Schistosoma mansoni infection: Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2000, 355, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez del Villar, L.; Burguillo, F.J.; Lopez-Aban, J.; Muro, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of artemisinin based therapies for the treatment and prevention of schistosomiasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, R.; El Morshedy, H.; Farghaly, A. Neglected Tropical Diseases—Middle East and North Africa; McDowell, M.A., Rafati, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, R.M. Epidemiology of Schistosomiasis in Egypt: Travel through Time: Review. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.; Farghaly, A.; El Morshedy, H.; Hassan, M.; Miller de, W. Impact of National Schistosomiasis Control Program in Kafr El-Sheikh governorate, Nile Delta, Egypt: An independent evaluation. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 1998, 73, 737–753. [Google Scholar]
- Haggag, A.A.; Rabiee, A.; Abd Elaziz, K.M.; Gabrielli, A.F.; Abdel Hay, R.; Ramzy, R.M.R. Mapping of Schistosoma mansoni in the Nile Delta, Egypt: Assessment of the prevalence by the circulating cathodic antigen urine assay. Acta Trop. 2017, 167, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.; Elmorshedy, H. Annual report of the project entitled: “Establishment and monitoring of cohort school children in Kafer El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt, in preparation for schistosomiasis vaccine candidate testing when appropriate”. Vaccine Development Project (SVDP); Funded by USAID& Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population (EMHP), 1996-2001. Unpublished work.
- Doenhoff, M.J.; Cioli, D.; Utzinger, J. Praziquantel: Mechanisms of action, resistance and new derivatives for schistosomiasis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, A.; Jourdan, P. Schistosomiasis elimination by 2020 or 2030? Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulibaly, J.T.; N’Gbesso, Y.K.; Knopp, S.; N’Guessan, N.A.; Silue, K.D.; van Dam, G.J.; N’Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J. Accuracy of urine circulating cathodic antigen test for the diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni in preschool-aged children before and after treatment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Q.; Jing, X.; Feng, T.; Lv, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.L.; Chao, L.V.; Bergquist, R.; Li, S.Z.; Zhou, X.N. Field evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) platform for the detection of Schistosoma japonicum infection in Oncomelania hupensis snails. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, R.; Yang, G.J.; Knopp, S.; Utzinger, J.; Tanner, M. Surveillance and response: Tools and approaches for the elimination stage of neglected tropical diseases. Acta Trop. 2015, 141, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogongo, P.; Kariuki, T.M.; Wilson, R.A. Diagnosis of schistosomiasis mansoni: An evaluation of existing methods and research towards single worm pair detection. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corstjens, P.L.; De Dood, C.J.; Kornelis, D.; Fat, E.M.; Wilson, R.A.; Kariuki, T.M.; Nyakundi, R.K.; Loverde, P.T.; Abrams, W.R.; Tanke, H.J.; et al. Tools for diagnosis, monitoring and screening of Schistosoma infections utilizing lateral-flow based assays and upconverting phosphor labels. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1841–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, R. Good things are worth waiting for. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, D.G.; Andros, T.S.; Campbell, C.H., Jr. Schistosomiasis is more prevalent than previously thought: What does it mean for public health goals, policies, strategies, guidelines and intervention programs? Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergquist, R.; Elmorshedy, H. Artemether and Praziquantel: Origin, Mode of Action, Impact, and Suggested Application for Effective Control of Human Schistosomiasis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3040125
Bergquist R, Elmorshedy H. Artemether and Praziquantel: Origin, Mode of Action, Impact, and Suggested Application for Effective Control of Human Schistosomiasis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2018; 3(4):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3040125
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergquist, Robert, and Hala Elmorshedy. 2018. "Artemether and Praziquantel: Origin, Mode of Action, Impact, and Suggested Application for Effective Control of Human Schistosomiasis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 3, no. 4: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3040125
APA StyleBergquist, R., & Elmorshedy, H. (2018). Artemether and Praziquantel: Origin, Mode of Action, Impact, and Suggested Application for Effective Control of Human Schistosomiasis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 3(4), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3040125




