The Re-Emergence and Emergence of Vector-Borne Rickettsioses in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
Historical Review
2. Re-Emerging Vector-Borne Rickettsioses
2.1. Scrub Typhus
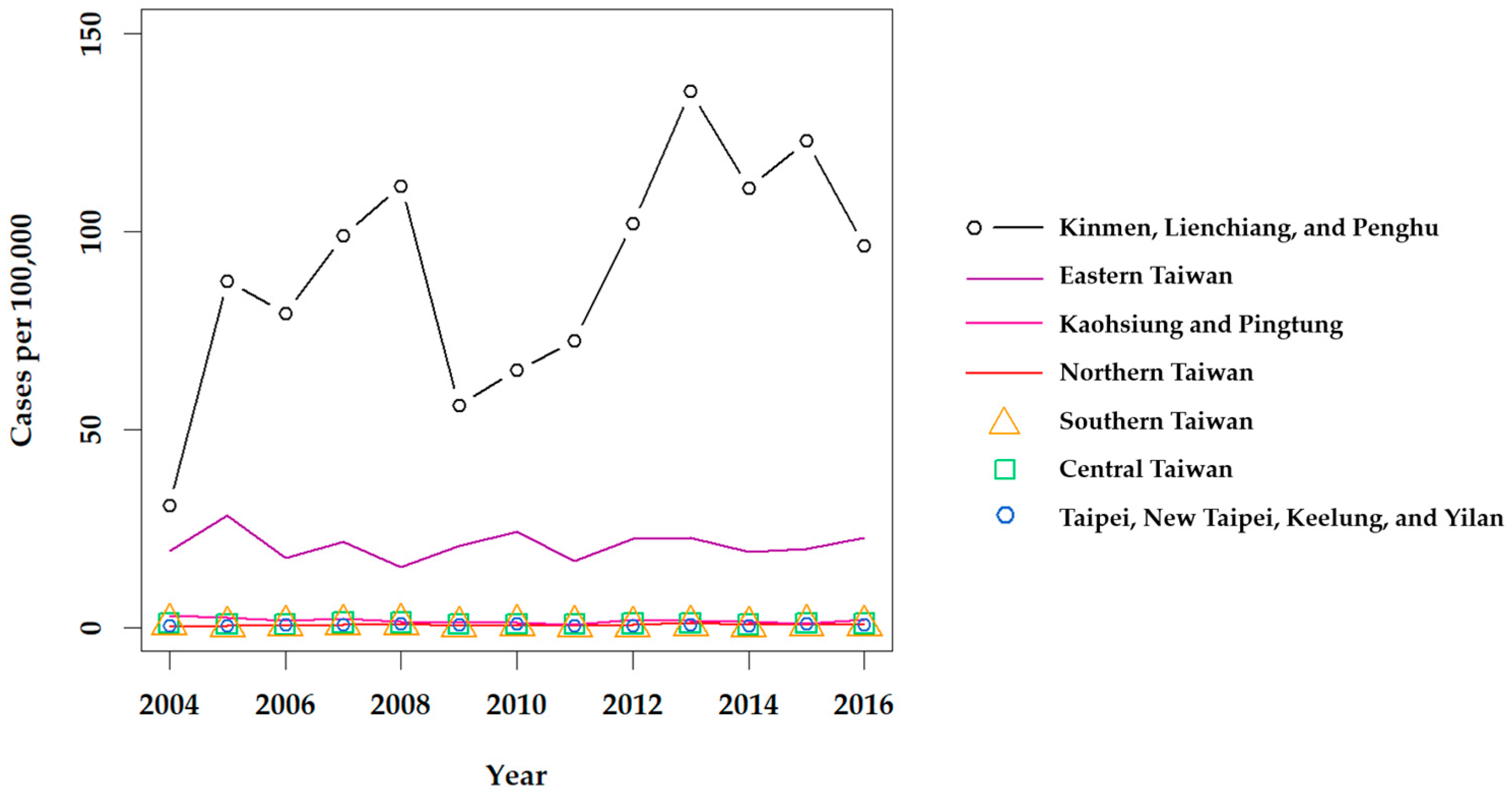
2.1.1. Epidemiology of Scrub Typhus
2.1.2. Clinical Features of Scrub Typhus
2.1.3. Ecology of Scrub Typhus
2.1.4. Genetics of Scrub Typhus
2.2. Murine Typhus
2.2.1. Epidemiology of Murine Typhus
2.2.2. Clinical Features of Murine Typhus
2.2.3. Ecology of Murine Typhus
2.3. Co-Endemic Diseases and Co-Infection
3. Emerging Vector-Borne Rickettsioses
3.1. Spotted Fever Group
Ecology of SFG Rickettsiae
3.2. Rickettsia felis
3.2.1. Clinical Features of R. felis Rickettsiosis
3.2.2. Ecology of R. felis
3.3. Anaplasmataceae
4. Research Gaps and Future Directions
4.1. Scrub Typhus
4.1.1. National Scrub Typhus Genotyping Surveillance
- How do scrub typhus genotypes vary by space and time (i.e., by region and season)?
- Do clinical manifestations vary by scrub typhus genotype (e.g., signs and symptoms)?
4.1.2. Antibiotic-Resistant Scrub Typhus
4.1.3. Investigation of Migratory Birds
4.2. Murine Typhus
4.3. Emerging Vector-Borne Rickettsioses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dumler, J.S.; Barbet, A.F.; Bekker, C.P.; Dasch, G.A.; Palmer, G.H.; Ray, S.C.; Rikihisa, Y.; Rurangirwa, F.R. Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: Unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‘HGE agent’ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 2145–2165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr. The ecology of chigger-borne rickettsiosis (scrub typhus). J. Med. Entomol. 1974, 11, 237–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.A.; Sacci, J.B., Jr.; Schriefer, M.E.; Endris, R.G.; Azad, A.F. Molecular identification of rickettsia-like microorganisms associated with colonized cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis). Insect Mol. Biol. 1994, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Blanton, L.S.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae as emerging infectious agents. Clin. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, J.J.; Beier, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Ammerman, N.C.; Shallom, J.M.; Purkayastha, A.; Sobral, B.S.; Azad, A.F. Plasmids and rickettsial evolution: Insight from Rickettsia felis. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioterrorism Agents/Diseases. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6v8JGX5t6 (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Centers for Disease Control (Taiwan). 2017 Centers for Disease Control Annual Report; Centers for Disease Control, Ministry of Health and Welfare, R.O.C. (Taiwan): Taipei City, Taiwan, 2017.
- Hatori, J. On the concordance of eruptive lymphadenitis fever in Formosa with tsutsugamushi disease. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 1916, 11, 415–449. [Google Scholar]
- Morishita, K. Distribution of tsutsugamushi disease in Formosa and its outbreaks. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1934, 33, 549–551. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, T. Development of medical science in Formosa. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1951, 50, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Hatori, J. A report of investigation on eruptive lymphadenitis fever in Formosa (I). J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1915, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, K. A story on the study tour to Formosa. J. Chiba. Med. Assoc. 1930, 8, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi, C. Studies on the unknown fever of the Pescadores. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1932, 31, 1412. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamiya, C.; Honda, S. Observations on the tsutsugamushi disease of the Pescadores. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1933, 32, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.H.; Chiang, T.L. The effect of universal health insurance on health care utilization in Taiwan. Results from a natural experiment. JAMA 1997, 278, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.H.; Lu, H.Y.; Tsai, J.J.; Yu, S.K.; Huang, J.H.; Shu, P.Y. Human case of Rickettsia felis infection, Taiwan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1970–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.H.; Chang, L.L.; Lin, J.N.; Tsai, K.H.; Hung, Y.C.; Kuo, L.L.; Lin, H.H.; Chen, Y.H. Human spotted fever group rickettsioses are underappreciated in southern Taiwan, particularly for the species closely-related to Rickettsia felis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Naval Medical Research Unit No. 2, Phnom Penh. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6uk4ZZpxi (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Cooper, W.C.; Chen, W.F.; Lien, J.C.; Hsu, S.H. Scrub typhus in the Pescadores Islands: An epidemiologic and clinical study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.C.; Lin, W.P.; Chao, P.S.; Kuo, N.T.; Chen, C.M. Clinical observations of scrub typhus on Penghu (the Pescadores Islands). Trop. Geogr. Med. 1975, 27, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bourgeois, A.L.; Olson, J.G.; Ho, C.M.; Fang, R.C.; Van Peenen, P.F. Epidemiological and serological study of scrub typhus among Chinese military in the Pescadores Islands of Taiwan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1977, 71, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.G.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Fang, R.C. Population indices of chiggers (Leptotrombidium deliense) and incidence of scrub typhus in Chinese military personnel, Pescadores Islands of Taiwan, 1976–1977. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1982, 76, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, J.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Lin, H.M. Field observation of the bionomics of Leptotrombidium deliensis, the vector of scrub typhus in the Pescadores. Acta Med. Biol. 1967, 15, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gale, J.L.; Irving, G.S.; Wang, H.C.; Lien, J.C.; Chen, W.F.; Cross, J.H. Scrub-typhus in eastern Taiwan. 1970. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1974, 23, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.G.; Scheer, E.J. Correlation of scrub typhus incidence with temperature in the Pescadores Islands of Taiwan. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1978, 72, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.G. Forecasting the onset of a scrub typhus epidemic in the Pescadores Islands of Taiwan using daily maximum temperatures. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1979, 31, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.G.; Bourgeois, A.L. Changing risk of scrub typhus in relation to socioeconomic development in the Pescadores Islands of Taiwan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1979, 109, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.G.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Fang, R.C.; Coolbaugh, J.C.; Dennis, D.T. Prevention of scrub typhus. Prophylactic administration of doxycycline in a randomized double blind trial. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1980, 29, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.Y.; Tsai, K.H.; Yu, S.K.; Cheng, C.H.; Yang, J.S.; Su, C.L.; Hu, H.C.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, J.H.; Shu, P.Y. Phylogenetic analysis of 56-kDa type-specific antigen gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates in Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Ko, W.C.; Lee, H.L.; Chen, H.Y. Clinical manifestations and complications of rickettsiosis in southern Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2002, 101, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Wang, P.H.; Tseng, S.J.; Ko, C.F.; Teng, H.J. Epidemiology of scrub typhus in eastern Taiwan, 2000–2004. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 59, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System. Available online: https://nidss.cdc.gov.tw/en/ (accessed on 1 October 2017).
- Taiwan MOI Open Data, County Map (TWD97). Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6ulHQaQr6 (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- 2010 Population and Housing Census. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6ulK9WkV4 (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Tsai, P.J.; Yeh, H.C. Scrub typhus islands in the Taiwan area and the association between scrub typhus disease and forest land use and farmer population density: Geographically weighted regression. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Wu, P.C.; Lung, S.C.; Su, H.J. Effects of extreme precipitation to the distribution of infectious diseases in Taiwan, 1994–2008. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonell, A.; Lubell, Y.; Newton, P.N.; Crump, J.A.; Paris, D.H. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Huang, J.L.; Ko, C.Y.; Lee, P.F.; Wang, H.C. Spatial analysis of scrub typhus infection and its association with environmental and socioeconomic factors in Taiwan. Acta Trop. 2011, 120, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsay, R.W.; Chang, F.Y. Serious complications in scrub typhus. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 1998, 31, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, T.H.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, D.S.; Kao, J.H. Milder clinical manifestation of scrub typhus in Kinmen, Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2013, 112, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jim, W.T.; Chiu, N.C.; Chan, W.T.; Ho, C.S.; Chang, J.H.; Huang, S.Y.; Wu, S. Clinical manifestations, laboratory findings and complications of pediatric scrub typhus in eastern Taiwan. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2009, 50, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Liu, J.W. Coinfection with leptospirosis and scrub typhus in Taiwanese patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Liu, S.F.; Liu, J.W.; Chung, Y.H.; Su, M.C.; Lin, M.C. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in scrub typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.M.; Won, K.J.; Park, C.Y.; Yu, K.D.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, T.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.K.; Song, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Distribution of eschars on the body of scrub typhus patients: A prospective study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Hagiwara, T.; Kishimoto, T.; Shiga, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Furuya, Y.; Kaiho, I.; Ito, T.; Nemoto, H.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Scrub typhus in Japan: Epidemiology and clinical features of cases reported in 1998. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamiya, C. The tsutsugamushi disease of the Pescadores, as determined by Weil-Felix reaction, and its relationship with spotted fever. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1933, 32, 1808. [Google Scholar]
- Hatori, J. Report of the investigation on exanthematous bubonic fever in Formosa (III). J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1916, 170, 963–990. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, L.Y.; Jeon, M.; Choi, S.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, C.S.; Rhee, K.S. Relative bradycardia in scrub typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 1316–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, N.P.J.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus and other tropical rickettsioses. In Infectious Diseases, 4th ed.; Cohen, J., Powderly, W.G., Opal, S.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1091–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.; Lee, N.Y.; Ko, W.C.; Lin, W.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, J.J.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Lu, P.L. Characteristics of scrub typhus, murine typhus, and Q fever among elderly patients: Prolonged prothrombin time as a predictor for severity. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Lee, P.L.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, H.C. Surveillance of potential hosts and vectors of scrub typhus in Taiwan. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.H.; Huang, I.T.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Chen, L.K. New genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi isolated from humans in eastern Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.; Chen, Y.H.; Lee, N.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, J.J.; Lu, P.L.; Chen, T.C.; Hsieh, H.C.; Lin, W.R.; et al. Murine typhus in southern Taiwan during 1992–2009. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.M.; Lin, C.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Tsai, K.H.; Wu, W.J.; Huang, C.G.; Chang, C.C. Identification of Rickettsia felis in fleas but not ticks on stray cats and dogs and the evidence of Rickettsia rhipicephali only in adult stage of Rhipicephalus sanguineus and Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 34, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.H.; Lu, H.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Wang, P.J.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, C.G.; Wu, W.J.; Shu, P.Y. Rickettsia felis in cat fleas in Taiwan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.H.; Huang, C.G.; Fang, C.T.; Shu, P.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Wu, W.J. Prevalence of Rickettsia felis and the first identification of Bartonella henselae Fizz/CAL-1 in cat fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) from Taiwan. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.R.; Tsai, H.P.; Tsui, P.Y.; Weng, M.H.; Kuo, M.D.; Lin, H.C.; Chen, K.C.; Ji, D.D.; Chu, D.M.; Liu, W.T. Genetic typing, based on the 56-kilodalton type-specific antigen gene, of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains isolated from chiggers collected from wild-caught rodents in Taiwan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3398–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, C.L. The potential effect of exotic Pacific rats Rattus exulans on vectors of scrub typhus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Huang, J.L.; Shu, P.Y.; Lee, P.L.; Kelt, D.A.; Wang, H.C. Cascading effect of economic globalization on human risks of scrub typhus and tick-borne rickettsial diseases. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.R.; Tsai, H.P.; Weng, M.H.; Lin, H.C.; Chen, K.C.; Kuo, M.D.; Tsui, P.Y.; Hung, Y.W.; Hsu, H.L.; Liu, W.T. Field assessment of Orientia tsutsugamushi infection in small mammals and its association with the occurrence of human scrub typhus in Taiwan. Acta Trop. 2014, 131, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Huang, J.L.; Lin, T.E.; Wang, H.C. Detection of Rickettsia spp. and host and habitat associations of fleas (Siphonaptera) in eastern Taiwan. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Shu, P.Y.; Mu, J.J.; Lee, P.L.; Wu, Y.W.; Chung, C.K.; Wang, H.C. Widespread Rickettsia spp. infections in ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea) in Taiwan. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, P.Y.; Tsai, K.H.; Weng, M.H.; Hung, Y.W.; Liu, Y.T.; Hu, K.Y.; Lien, J.C.; Lin, P.R.; Shaio, M.F.; Wang, H.C.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of spotted fever group rickettsiae in Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.H.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, J.H.; Lu, H.Y.; Su, C.L.; Shu, P.Y. Isolation and identification of a novel spotted fever group rickettsia, strain IG-1, from Ixodes granulatus ticks collected on Orchid Island (Lanyu), Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Huang, C.L.; Wang, H.C. Identification of potential hosts and vectors of scrub typhus and tick-borne spotted fever group rickettsiae in eastern Taiwan. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.H.; Chang, S.F.; Yen, T.Y.; Shih, W.L.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, H.C.; Yu, X.J.; Wen, T.H.; Wu, W.J.; Shu, P.Y. Prevalence of antibodies against Ehrlichia spp. and Orientia tsutsugamushi in small mammals around harbors in Taiwan. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.H.; Chiang, P.F.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, K.Y.; Lin, M.C.; Wu, H.S. Prevalence of ectoparasites and the seroepidemiology of murine typhus in murine-like animals at international ports in Taiwan, 2004–2011. Taiwan Epidemiol. Bull. 2012, 28, 320–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.C.; Shu, P.Y.; Mu, J.J.; Wang, H.C. High prevalence of Rickettsia spp. infections in small mammals in Taiwan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, A.; Ohashi, N.; Urakami, H.; Miyamura, S. Classification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in a new genus, Orientia gen. nov., as Orientia tsutsugamushi comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzard, L.; Fuller, A.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Richards, A.L.; Aukkanit, N.; Nguyen, C.; Jiang, J.; Fenwick, S.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; Fuerst, P.A.; Ching, W.M.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: The geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48 (Suppl. 3), S203–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Ha, N.Y.; Min, C.K.; Kim, H.I.; Yen, N.T.; Lee, K.H.; Oh, I.; Kang, J.S.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Diversification of Orientia tsutsugamushi genotypes by intragenic recombination and their potential expansion in endemic areas. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Wardrop, N.; Chang, C.T.; Wang, H.C.; Atkinson, P.M. Significance of major international seaports in the distribution of murine typhus in Taiwan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005430. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, E.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia and rickettsia-like organisms. In Infectious Diseases, 4th ed.; Cohen, J., Powderly, W.G., Opal, S.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1666–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L. The ecology of murine typhus-a critical review. Trop. Dis. Bull. 1978, 75, 237–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremeeva, M.; Dasch, G. Other Rickettsia species. In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 5th ed.; Long, S.S., Prober, C.G., Fischer, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 957–966. [Google Scholar]
- Day, N.P. Leptospirosis. In Infectious Diseases, 4th ed.; Cohen, J., Powderly, W.G., Opal, S.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1102–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.H.; Sun, W.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, J.N.; Liao, M.H.; Liu, S.S.; Chang, T.Y.; Tsai, K.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, H.H.; et al. The epidemiology and characteristics of Q fever and co-infections with scrub typhus, murine typhus or leptospirosis in Taiwan: A nationwide database study. Zoonoses Public Health 2016, 64, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Socolovschi, C.; Labruna, M.B.; Mediannikov, O.; Kernif, T.; Abdad, M.Y.; Stenos, J.; Bitam, I.; Fournier, P.E.; et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: A geographic approach. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 657–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padgett, K.A.; Bonilla, D.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Glaser, C.; Lane, R.S.; Porse, C.C.; Castro, M.B.; Messenger, S.; Espinosa, A.; Hacker, J.; et al. The eco-epidemiology of Pacific Coast tick fever in California. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Armstrong, M.; Graves, S.; Hajkowicz, K. Rickettsia australis and Queensland tick typhus: A rickettsial spotted fever group infection in Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.E.; Dumler, J.S.; Greub, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Raoult, D. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new Rickettsia isolates and description of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5456–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Yao, C.T.; Shih, H.C.; Chung, L.H.; Liao, H.C.; Hsu, Y.C.; Wang, H.C. Tick-borne pathogens in ticks collected from birds in Taiwan. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanton, L.S.; Walker, D.H. Flea-borne rickettsioses and rickettsiae. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelakis, E.; Mediannikov, O.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia felis: The complex journey of an emergent human pathogen. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.R.; Schmidtmann, E.T.; Azad, A.F. Infection of colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis (bouché), with a rickettsia-like microorganism. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 43, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis, an emerging flea-borne rickettsiosis. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Osorio, C.E.; Zavala-Velazquez, J.E.; Arias Leon, J.J.; Zavala-Castro, J.E. Rickettsia felis as emergent global threat for humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, K.E.; Macaluso, K.R. Ecology of Rickettsia felis: A review. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, A.N.; Fogarty, C.; Krueger, L.; Macaluso, K.R.; Odhiambo, A.; Nguyen, K.; Farris, C.M.; Luce-Fedrow, A.; Bennett, S.; Jiang, J.; et al. Rickettsial infections among Ctenocephalides felis and host animals during a flea-borne rickettsioses outbreak in Orange County, California. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.J.; Yin, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chiang, Y.C.; Chang, C.D.; Liao, M.H.; Chiang, C.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Lin, S.C. Identification of the causative agents of Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in dogs in Taiwan by nested PCR, indirect immunofluorescent-antibody assay, and sequence analysis of the 16s rRNA gene. Taiwan Vet. J. 2006, 32, 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.J.; Sun, H.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Huang, H.P. Prevalence and risk factors of canine ticks and tick-borne diseases in Taipei, Taiwan. J. Vet. Clin. Sci. 2009, 2, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-L. Serological survey of equine piroplasmosis, equine granulocytic anaplasmosis, and equine Lyme disease in Taiwan. Taiwan Vet. J. 2010, 36, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa, Y.; Tsai, Y.L.; Chang, C.C.; Hsu, T.H.; Chou, C.C. The prevalence of Anaplasma platys and a potential novel Anaplasma species exceed that of Ehrlichia canis in asymptomatic dogs and Rhipicephalus sanguineus in Taiwan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzawa, T.; Uchishima, Y.; Fukui, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Pan, M.J.; Kadosaka, T.; Takada, N. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Anaplasma bovis in small wild mammals from Taichung and Kinmen Island, Taiwan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 67, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.H.; Lien, J.C.; Tsai, H.P.; Lin, P.R.; Guo, M.D.; Liu, W.T. Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection in rodent ticks-Kinmen, 2009. Taiwan Epidemiol. Bull. 2010, 26, 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, M.H.; Tsai, H.P.; Lin, P.R.; Kuo, C.C.; Guo, M.D.; Liu, W.T. Investigation of Ehrlichia chaffeensis infections in rodents in Kinmen area, 2012. Taiwan Epidemiol. Bull. 2014, 30, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.H. Scrub typhus—scientific neglect, ever-widening impact. NEJM 2016, 375, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, G.; Chouriyagune, C.; Ruangweerayud, R.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Jongsakul, K.; Teja-Isavadharm, P.; Bhodhidatta, D.; Corcoran, K.D.; Dasch, G.A.; et al. Scrub typhus infections poorly responsive to antibiotics in northern Thailand. Lancet 1996, 348, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanskul, P.; Linthicum, K.J.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Mungviriya, S.; Ratanatham, S.; Suwanabun, N.; Sattabongkot, J.; Watt, G. A new ecology for scrub typhus associated with a focus of antibiotic resistance in rice farmers in Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, G.; Kantipong, P.; Jongsakul, K.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D. Azithromycin activities against Orientia tsutsugamushi strains isolated in cases of scrub typhus in northern Thailand. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2817–2818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watt, G.; Kantipong, P.; Jongsakul, K.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Strickman, D. Doxycycline and rifampicin for mild scrub-typhus infections in northern Thailand: A randomised trial. Lancet 2000, 356, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D. Characterization of mutations in the rpoB gene in naturally rifampin-resistant Rickettsia species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.H.; Huang, C.K.; Weng, H.C.; Chung, H.C.; Liang, S.H.; Lin, J.N.; Lin, C.W.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, H.H. Clinical characteristics of acute Q fever, scrub typhus, and murine typhus with delayed defervescence despite doxycycline treatment. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.M.; Chao, C.C.; Lei, H.; Li, B.; Tsai, S.; Hung, G.C.; Ching, W.M.; Lo, S.C. Intraspecies comparative genomics of three strains of Orientia tsutsugamushi with different antibiotic sensitivity. Genom. Data 2017, 12, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Otsuru, M.; Fujii, T.; Toma, H.; Sato, Y. Surveys on vector mites of tsutsugamushi disease in Taiwan and the Ryukyu Islands. Med. Entomol. Zool. 1990, 41, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.Y.; Kim, G.; Cho, N.H. Epidemiological trends of scrub typhus: Global incidence and vector distribution. In Rickettsiales: Biology, Molecular Biology, Epidemiology, and Vaccine Development; Thomas, S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, A.F.; Radulovic, S.; Higgins, J.A.; Noden, B.H.; Troyer, J.M. Flea-borne rickettsioses: Ecologic considerations. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Ortiz, D.; Torres-Castro, M.; Koyoc-Cardena, E.; Lopez, K.; Panti-May, A.; Rodriguez-Vivas, I.; Puc, A.; Dzul, K.; Zavala-Castro, J.; Medina-Barreiro, A.; et al. Molecular evidence of Rickettsia typhi infection in dogs from a rural community in Yucatan, Mexico. Biomedica 2016, 36, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nogueras, M.M.; Pons, I.; Ortuno, A.; Miret, J.; Pla, J.; Castella, J.; Segura, F. Molecular detection of Rickettsia typhi in cats and fleas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noden, B.H.; Davidson, S.; Smith, J.L.; Williams, F. First detection of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis in fleas collected from client-owned companion animals in the southern Great Plains. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, P.; Conti, L. One health and emerging infectious diseases: Clinical perspectives. In One Health: The Human-Animal-Environment Interfaces in Emerging Infectious Diseases; Mackenzie, J.S., Jeggo, M., Daszak, P., Richt, J.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri-Chhetri, R.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, C.C.; Shih, H.C.; Liao, H.C.; Sun, C.M.; Khatri-Chhetri, N.; Wu, H.Y.; Pei, K.J. Surveillance of ticks and associated pathogens in free-ranging Formosan pangolins (Manis pentadactyla pentadactyla). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Lee, C.C.; Tsang, C.L.; Chung, Y.T. Detection and characterization of four novel genotypes of Ehrlichia canis from dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 146, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Scrub Typhus Group | Typhus Group | Spotted Fever Group | Transitional Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O. tsutsugamushi | R. typhi | Rickettsia spp. | R. felis | ||
| NNDSS, Taiwan CDC | notifiable | non-notifiable | |||
| humans | Lu, 2010 1,2,3 [29] Yang, 2012 1,2,3 [52] | Chang, 2012 1 [53] | Lai, 2014 1 [17] | Tsai, 2008 1,2 [16] Lai, 2014 1 [17] | |
| arthropod ectoparasites | domestic animals | Hsu, 2011 2 [54] | Tsai, 2009 2,3 [55] Hsu, 2011 2 [54] Tsai, 2011 2 [56] | ||
| Small mammals | Lin, 2011 2 [57] Kuo, 2011 2 [58] Kuo, 2012 2 [59] Lin, 2014 2 [60] Kuo, 2015 2 [51] | Kuo, 2012 2 [61] Kuo, 2015 2 [62] | Tsui, 2007 1,2,3 [63] Tsai, 2008 1,2,3,* [64] Kuo, 2012 2 [59] Kuo, 2012 2 [61] Kuo, 2015 2 [62] | Tsui, 2007 1,2,3 [63] Kuo, 2012 2 [61] Kuo, 2015 2 [62] | |
| small mammals | Kuo, 2011 1 [65] Lin, 2014 1,2 [60] Kuo, 2015 1 [51] Tsai, 2016 1 [66] | Chien, 2012 1 [67] Kuo, 2012 1 [61] Kuo, 2015 1,2 [68] | Kuo, 2011 1 [65] Kuo, 2012 1 [61] Kuo, 2015 1,2 [68] | Kuo, 2015 1,2 [68] | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minahan, N.T.; Chao, C.-C.; Tsai, K.-H. The Re-Emergence and Emergence of Vector-Borne Rickettsioses in Taiwan. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3010001
Minahan NT, Chao C-C, Tsai K-H. The Re-Emergence and Emergence of Vector-Borne Rickettsioses in Taiwan. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2018; 3(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinahan, Nicholas T., Chien-Chung Chao, and Kun-Hsien Tsai. 2018. "The Re-Emergence and Emergence of Vector-Borne Rickettsioses in Taiwan" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 3, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3010001
APA StyleMinahan, N. T., Chao, C.-C., & Tsai, K.-H. (2018). The Re-Emergence and Emergence of Vector-Borne Rickettsioses in Taiwan. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 3(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3010001






