Analysis of the Specific Expression Profile of Immune Cells in Infants and Young Children Infected with RSV and Construction of a Disease Prediction Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
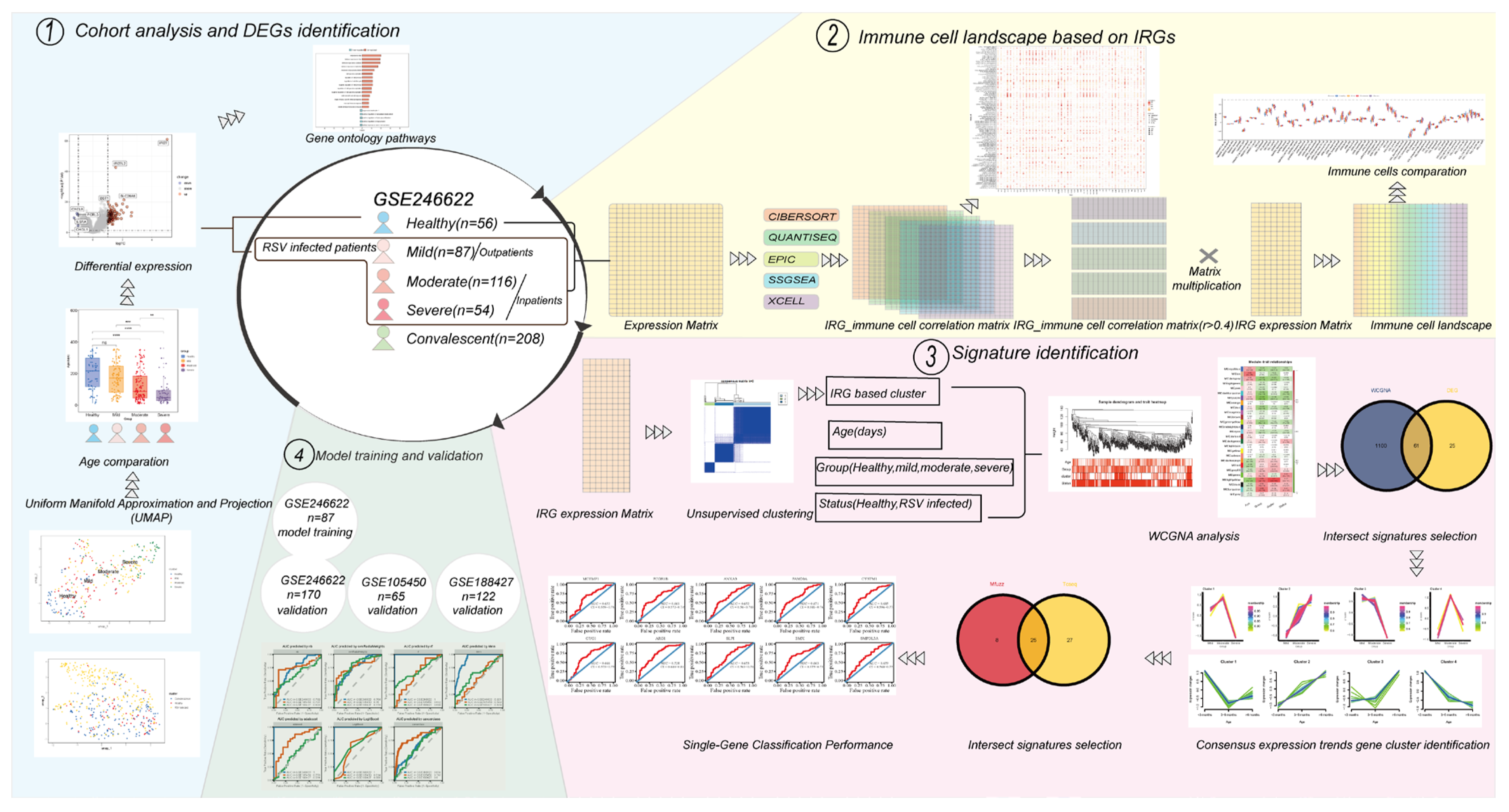
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Immune Cell-Related Genes (IRGs)
2.2. Analysis of RSV-Infected Cohorts
2.3. Immune Cell Landscape
2.4. Clustering
2.5. Weighted Correlation Network Analysis (WGCNA) [19]
2.6. Signatures Identification
2.7. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) and Predictive Model Construction
3. Results
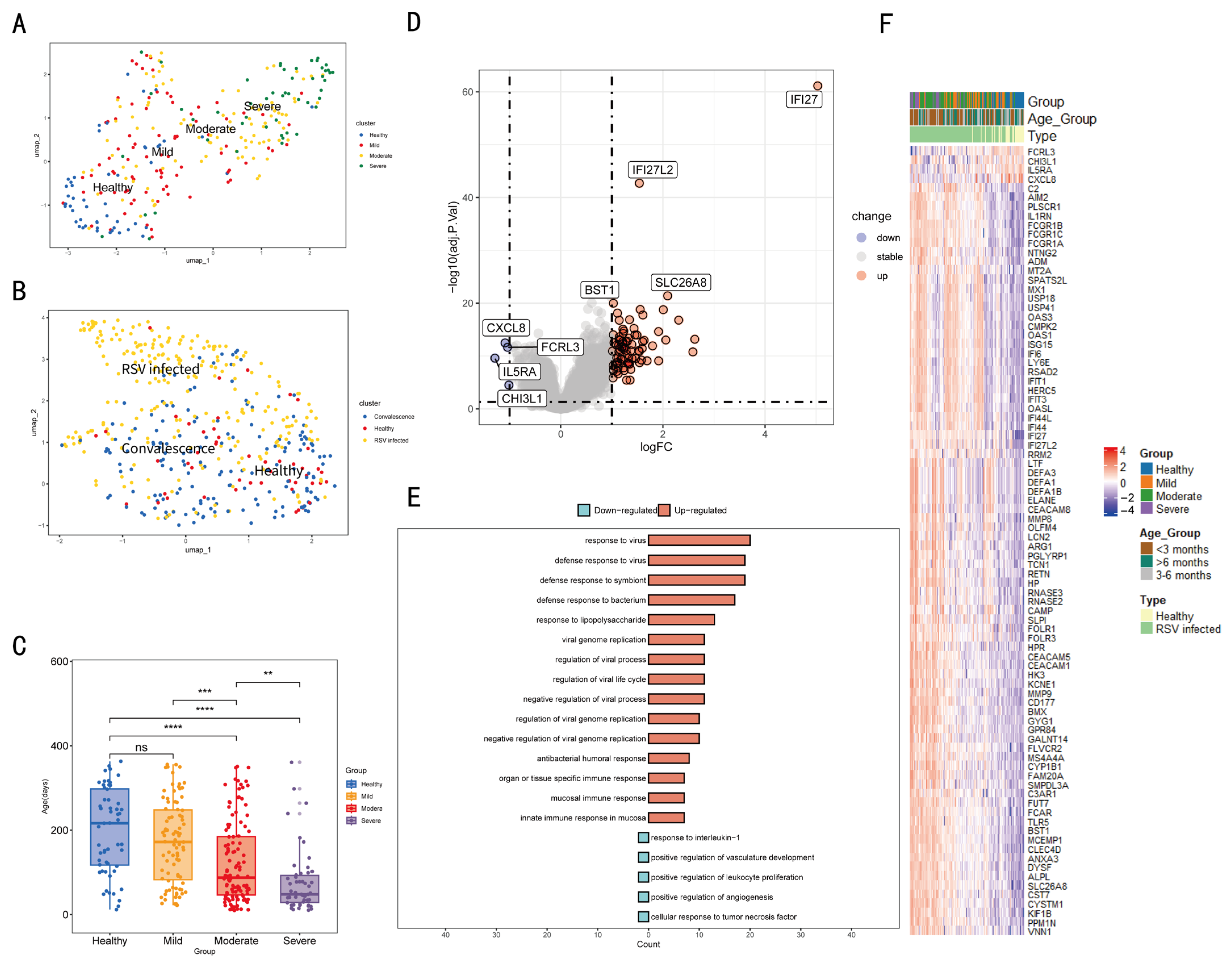
3.1. Gene Expression Was Different Among Individuals with Different Infection Status and Severity
3.2. Immune Cell-Related Genes Exhibit the Close Correlation Between the Severity of Symptoms in RSV-Infected Individuals and Immune Cells
3.3. Clustering and Annotation of Immune Cell-Related Gene Expression
3.4. Co-Expressed Genes Related to Age, Group (Severity of Infection), Cluster, and Status (Infection Status)
3.5. TCseq and Mfuzz Were Used to Analyze the Co-Expressed Gene Module
3.6. Ten Genes That Could Distinguish the Severity of RSV Infection Were Screened
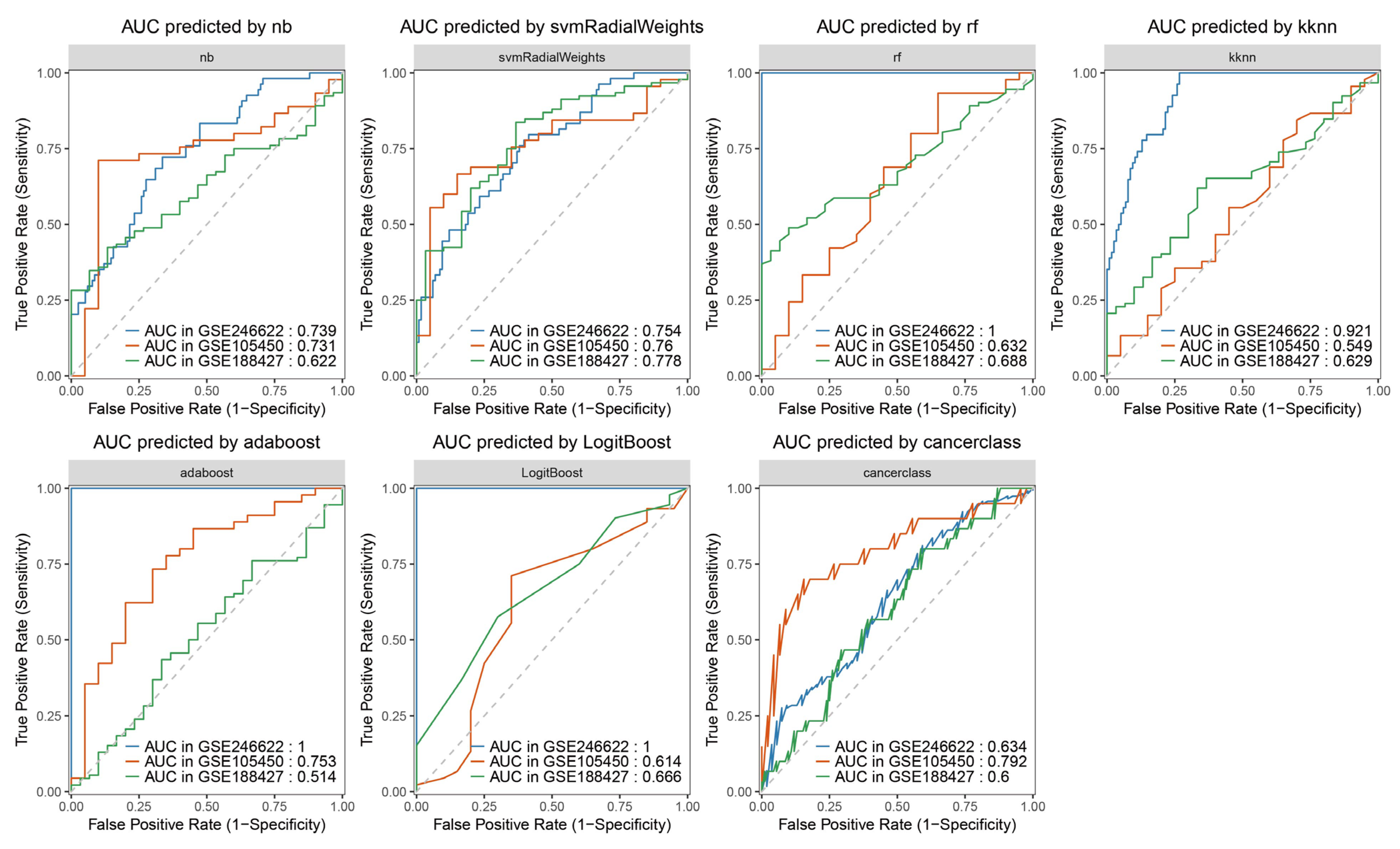
3.7. Constructing Machine Learning Algorithm Models
4. Discussion
4.1. MCEMP1 and CYSTM1
4.2. FCGR1B
4.3. ANXA3 and GYG1
4.4. FAM20A and ARG1
4.5. SLPI
4.6. BMX
4.7. SMPDL3A
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mejias, A.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, R.; Oliva, S.; Peeples, M.E.; Ramilo, O. The journey to a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Weinberg, G.A.; Iwane, M.K.; Blumkin, A.K.; Edwards, K.M.; Staat, M.A.; Auinger, P.; Griffin, M.R.; Poehling, K.A.; Erdman, D.; et al. The burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection in young children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichinger, K.M.; Kosanovich, J.L.; Lipp, M.; Empey, K.M.; Petrovsky, N. Strategies for active and passive pediatric RSV immunization. Ther. Adv. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 9, 2515135520981516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, T.R.; Crabtree, J.; Rein-Weston, A.; Blimkie, D.; Thommai, F.; Wang, X.Y.; Lavoie, P.M.; Furlong, J.; Fortuno, E.S., 3rd; Hajjar, A.M.; et al. Neonatal innate TLR-mediated responses are distinct from those of adults. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7150–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiela, S.J.; Koru-Sengul, T.; Adkins, B. Murine neonatal recent thymic emigrants are phenotypically and functionally distinct from adult recent thymic emigrants. Blood 2009, 113, 5635–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, S.B. Vaccine-Associated Enhanced Viral Disease: Implications for Viral Vaccine Development. BioDrugs 2021, 35, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckwardt, T.J.; Morabito, K.M.; Graham, B.S. Determinants of early life immune responses to RSV infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 16, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, L.; Sagfors, A.M.; Openshaw, P.J.; Culley, F.J. Immunity to RSV in Early-Life. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, N.; Oner, D.; Abraham, Y.; McGinley, J.; Drysdale, S.B.; Wildenbeest, J.G.; Crabbe, M.; Vanhoof, G.; Thys, K.; Thwaites, R.S.; et al. Single-cell immune profiling reveals markers of emergency myelopoiesis that distinguish severe from mild respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, S.; Velazquez, V.M.; Ye, F.; Mertz, S.; Acero-Bedoya, S.; Smith, B.; Bunsow, E.; Garcia-Maurino, C.; Oliva, S.; Cohen, D.M.; et al. Immune profiles provide insights into respiratory syncytial virus disease severity in young children. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw0268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justicia-Grande, A.J.; Pardo-Seco, J.; Cebey-Lopez, M.; Vilanova-Trillo, L.; Gomez-Carballa, A.; Rivero-Calle, I.; Puente-Puig, M.; Curros-Novo, C.; Gomez-Rial, J.; Salas, A.; et al. Development and Validation of a New Clinical Scale for Infants with Acute Respiratory Infection: The ReSVinet Scale. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racle, J.; de Jonge, K.; Baumgaertner, P.; Speiser, D.E.; Gfeller, D. Simultaneous enumeration of cancer and immune cell types from bulk tumor gene expression data. eLife 2017, 6, e26476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotello, F.; Mayer, C.; Plattner, C.; Laschober, G.; Rieder, D.; Hackl, H.; Krogsdam, A.; Loncova, Z.; Posch, W.; Wilflingseder, D.; et al. Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq data. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Hu, Z.; Butte, A.J. xCell: Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4, Article17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Futschik, M.E. Mfuzz: A software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2007, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Adegboro, A.A.; Fasoranti, D.O.; Dai, L.; Pan, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Mime: A flexible machine-learning framework to construct and visualize models for clinical characteristics prediction and feature selection. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, D.K.; Holman, R.C.; Newman, R.D.; Liu, L.L.; Stout, J.W.; Anderson, L.J. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980–1996. JAMA 1999, 282, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Teng, M.N.; Collins, P.L.; Prince, G.A.; Exner, M.; Regele, H.; Lirman, D.D.; Rabold, R.; Hoffman, S.J.; Karp, C.L.; et al. A role for immune complexes in enhanced respiratory syncytial virus disease. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieren, D.K.J.; Boer, M.C.; de Wit, J. The adaptive immune system in early life: The shift makes it count. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1031924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen, S.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, R.; Diaz, A.; Oliva Rodriguez-Pastor, S.; Ramilo, O.; Mejias, A. Infant Immune Response to Respiratory Viral Infections. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2019, 39, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, M.T.; Peebles, R.S., Jr. Mechanisms of respiratory syncytial virus modulation of airway immune responses. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, E.; Tuckerman, J.; Licciardi, P.V.; Wurzel, D. Respiratory syncytial virus, recurrent wheeze and asthma: A narrative review of pathophysiology, prevention and future directions. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2022, 58, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, S.L. The development of respiratory inflammation in children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2006, 7, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restori, K.H.; Srinivasa, B.T.; Ward, B.J.; Fixman, E.D. Neonatal Immunity, Respiratory Virus Infections, and the Development of Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.; Heinonen, S.; Hasrat, R.; Bunsow, E.; Smith, B.; Suarez-Arrabal, M.C.; Chaussabel, D.; Cohen, D.M.; Sanders, E.A.; Ramilo, O.; et al. Nasopharyngeal Microbiota, Host Transcriptome, and Disease Severity in Children with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, N.; Hou, P.; Fan, R.; Liu, S. Integrated Bioinformatics Exploration and Preliminary Clinical Verification for the Identification of Crucial Biomarkers in Severe Cases of COVID-19. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venancio, T.M.; Aravind, L. CYSTM, a novel cysteine-rich transmembrane module with a role in stress tolerance across eukaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; An, X.X.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.L.; Wu, S.J.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, C.L.; Fang, X.M. Analysis and validation of diagnostic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration characteristics in pediatric sepsis by integrating bioinformatics and machine learning. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lowrie, D.B.; Fan, X.Y. Probe Signal Values in mRNA Arrays Imply an Excessive Involvement of Neutrophil FCGR1 in Tuberculosis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Identification of hub genes and pathogenesis in Kawasaki disease based on bioinformatics analysis. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2024, 67, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y. FAM20A: A potential diagnostic biomarker for lung squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1424197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, S.; Barouni, R.M.; Fabbi, M.; Cuozzo, J.; Fracasso, G.; Adamo, A.; Ugel, S.; Trovato, R.; De Sanctis, F.; Giacca, M.; et al. Neutralization of NET-associated human ARG1 enhances cancer immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, R.; Barisione, G.; Mastracci, L.; Grossi, F.; Orengo, A.M.; Costa, R.; Truini, M.; Fabbi, M.; Ferrini, S.; Barbieri, O. IL-8 induces exocytosis of arginase 1 by neutrophil polymorphonuclears in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywa, T.M.; Sosnowska, A.; Matryba, P.; Rydzynska, Z.; Jasinski, M.; Nowis, D.; Golab, J. Myeloid Cell-Derived Arginase in Cancer Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, P.J.; McElvaney, N.G.; Greene, C.M. SLPI and inflammatory lung disease in females. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, S.; Liao, J.; Qin, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Lan, L.; Hu, W.; et al. BMX deletion mitigates neuroinflammation induced by retinal ischemia/reperfusion through modulation of the AKT/ERK/STAT3 signaling cascade. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, D.; Power, M.A.; Smith, S.I.; Li, C.L. Predominant expression of murine Bmx tyrosine kinase in the granulo-monocytic lineage. Blood 1997, 90, 4332–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, F.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Ji, H.; et al. A novel BMX variant promotes tumor cell growth and migration in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33405–33415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traini, M.; Quinn, C.M.; Sandoval, C.; Johansson, E.; Schroder, K.; Kockx, M.; Meikle, P.J.; Jessup, W.; Kritharides, L. Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase acid-like 3A (SMPDL3A) is a novel nucleotide phosphodiesterase regulated by cholesterol in human macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32895–32913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Chung, H. SMPDL3A links cholesterol metabolism to the cGAS-STING pathway. Immunity 2023, 56, 2459–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ren, K.; Sun, H.; Ren, T.; Ma, K.; Chen, J. Analysis of the Specific Expression Profile of Immune Cells in Infants and Young Children Infected with RSV and Construction of a Disease Prediction Model. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2026, 11, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010010
Ren K, Sun H, Ren T, Ma K, Chen J. Analysis of the Specific Expression Profile of Immune Cells in Infants and Young Children Infected with RSV and Construction of a Disease Prediction Model. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2026; 11(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Kai, Honggang Sun, Tian Ren, Kailun Ma, and Jizheng Chen. 2026. "Analysis of the Specific Expression Profile of Immune Cells in Infants and Young Children Infected with RSV and Construction of a Disease Prediction Model" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 11, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010010
APA StyleRen, K., Sun, H., Ren, T., Ma, K., & Chen, J. (2026). Analysis of the Specific Expression Profile of Immune Cells in Infants and Young Children Infected with RSV and Construction of a Disease Prediction Model. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 11(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010010







