Prediction of Mortality by Clinical Laboratory Parameters in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Study Search
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Screening and Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
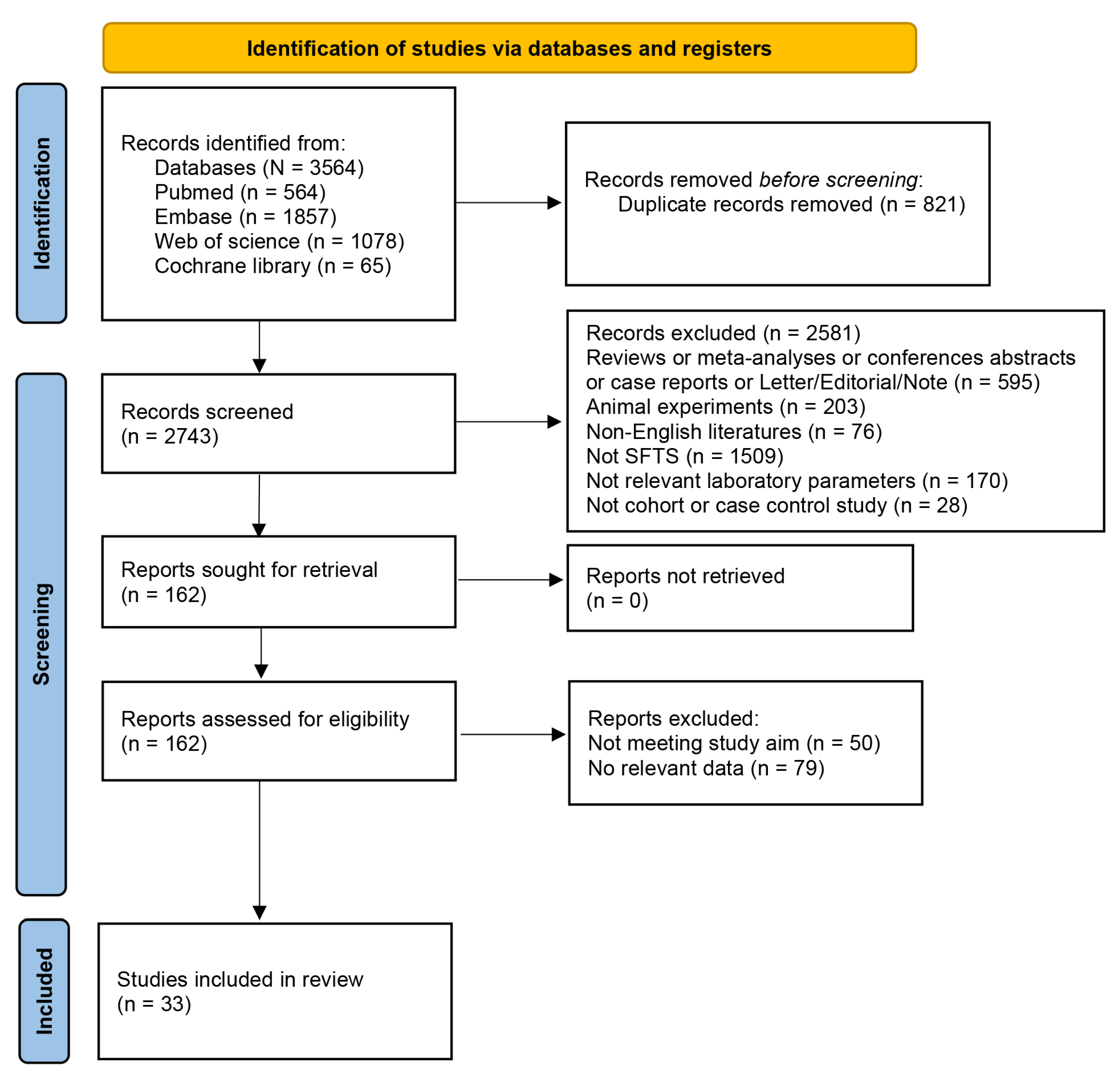
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics and Quality
3.3. Meta-Analyses
3.3.1. Association of Viral Load with SFTS Mortality
3.3.2. Association of Blood Routine Indicators with SFTS Mortality
3.3.3. Association of Coagulation Indicators with SFTS Mortality
3.3.4. Association of Liver Function Indicators with SFTS Mortality
3.3.5. Association of Kidney Function Indicators with SFTS Mortality
3.3.6. Association of Myocardial Function Indicators with SFTS Mortality
3.3.7. Association of Other Laboratory Parameters with SFTS Mortality
3.4. Subgroup Analyses
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis and Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, H.; Shen, S.; Chen, L.; Fan, Z.; Wen, Q.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; La, B.; et al. Global epidemiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in human and animals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2024, 48, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Song, S.W.; Bae, S.G.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Lee, C.; Jeong, S.; Kim, M.; Sa, W.; et al. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in Ticks and SFTS Incidence in Humans, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2292–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Shimojima, M.; Fukushi, S.; Tani, H.; Fukuma, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Singh, H.; Suda, Y.; Shirabe, K.; Toda, S.; et al. Phylogenetic and Geographic Relationships of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in China, South Korea, and Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, D.; Dai, K.; Zhao, G.P.; Li, X.L.; Shi, W.Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Fang, L.Q. Mapping the global potential transmission hotspots for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome by machine learning methods. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.C.; Yun, Y.; Van An, L.; Kim, S.H.; Thao, N.T.P.; Man, P.K.C.; Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Cho, N.H.; Lee, K.H. Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohaib, A.; Zhang, J.; Saqib, M.; Athar, M.A.; Hussain, M.H.; Chen, J.; Sial, A.U.; Tayyab, M.H.; Batool, M.; Khan, S.; et al. Serologic Evidence of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Related Viruses in Pakistan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, A.M.; Nguyen, Y.T.H.; Kim, Y.; Ha, N.Y.; Kang, J.G.; Kim, H.; San, B.; Kyaw, O.; Htike, W.W.; Choi, D.O.; et al. Genotypic Heterogeneity of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Scrub Typhus Patients and Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Co-infection, Myanmar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1878–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansilapin, C.; Tangwangvivat, R.; Hoffmann, C.S.; Chailek, C.; Lekcharoen, P.; Thippamom, N.; Petcharat, S.; Taweethavonsawat, P.; Wacharapluesadee, S.; Buathong, R.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in Thailand: Using a one health approach to respond to novel zoonosis and its implications in clinical practice. One Health Outlook 2024, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoensakulchai, S.; Matsuno, K.; Nakayama, E.E.; Shioda, T.; Imad, H.A. Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2025, 112, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, H.; Sun, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Yao, M.; Yuan, G. Analysis of the laboratory indexes and risk factors in 189 cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Medicine 2020, 99, e18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lu, Q.B.; Yao, W.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.A.; Cui, N.; Yuan, C.; Yang, T.; Peng, X.F.; Lv, S.M.; et al. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of favipiravir in treating patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. eBioMedicine 2021, 72, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.M.; Lei, X.Y.; Yu, X.J. Meta-analysis of the clinical and laboratory parameters of SFTS patients in China. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Ge, Z.; Cui, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Tian, D. Clinical manifestations of death with severe fever and thrombocytopenia syndrome: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3960–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dualis, H.; Zefong, A.C.; Joo, L.K.; Dadar Singh, N.K.; Syed Abdul Rahim, S.S.; Avoi, R.; Jeffree, M.S.; Hassan, M.R.; Ibrahim, M.Y.; Omar, A. Factors and outcomes in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS): A systematic review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 67, 102501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, B.; Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, J.; Wu, C. Risk factors associated with fatality of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89119–89129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Wei, X.; Yuan, H.; Xu, X.; Liang, H.; Wen, H. Clinical laboratory parameters and fatality of Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xue, X.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z. A model based on meta-analysis to evaluate poor prognosis of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1307960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Robertson, J.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Systematic Reviews: Beyond the Basics, Oxford, UK, 3–5 July 2000; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Tufanaru, C.; Munn, Z.; Stephenson, M.; Aromataris, E. Fixed or random effects meta-analysis? Common methodological issues in systematic reviews of effectiveness. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Ma, A.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Xu, C.; Han, B.; Xu, Y.; Tang, L. Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Serum Albumin Ratio Predicts Fatal Outcomes in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 111, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Song, X.; Bo, J. A nomogram to predict mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Tian, S. High CRP/PNI levels predict an unfavorable prognosis in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A propensity score matching study. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zou, S.; Wei, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Peng, J. Kinetics and Prognostic Significance of Laboratory Markers in Patients With Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: Insight From a Comprehensive Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 229, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Tang, G.; Wei, W.; Liu, W.; Hou, H. The clinical and immunological characteristics in fatal severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) infection. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 248, 109262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, J.R.; Kim, M.; Oh, H.; Heo, S.T. Epidemiologic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome at Tertiary Hospital in Jeju for 10 years. Infect. Chemother. 2023, 55, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, L.; Peng, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; Ji, W.; Ge, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Increased cTnI Predicts Early Death in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia: A Multicenter Study in North China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 2579–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C. Novel nomograms to predict risk and prognosis in hospitalized patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1321490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, S.; Fan, L.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; et al. The Association Between Elevated Myocardial Injury-Related Biomarker (TnI) and Increased Mortality in Patients With Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ni, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, C.; He, F. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with 28-day mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, Z.; Ren, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; et al. Eosinophils and basophils in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients: Risk factors for predicting the prognosis on admission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, W.; Ma, R.; Han, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, Z.; Ren, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, A.; et al. High levels of C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR) are associated with a poor prognosis in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in early stage. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5375–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Zhou, W.; Lin, L.; Ge, Z.; Lai, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Activated partial thromboplastin time predicts mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A multicenter study in north China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Lin, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. High C-reactive protein to lymphocyte ratio predicts mortality outcomes of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A multicenter study in China. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cao, K.; Shen, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, M.; Yu, W. Clinical Characteristics and Immune Status of Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viral Immunol. 2022, 35, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, Z. Risk Factors and Clinical Characteristics of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2020, 13, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wan, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, L.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Tian, D.; Wen, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. A nomogram to predict mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome at the early stage-A multicenter study in China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Z. A nomogram including admission serum glycated albumin/albumin ratio to predict mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, L.H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, D.W.; Wang, W.J.; Xu, A.M.; Qi, Y.J. Blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio is a novel predictor of fatal outcome for patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Sun, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zou, G.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. A new model for predicting the outcome and effectiveness of drug therapy in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A multicenter Chinese study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Cao, C.; Dong, W.; Hu, J.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hua, T.; Yang, M. Development and validation of a clinical and laboratory-based nomogram to predict mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Xiong, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, D.; Peng, C.; Zheng, X. A simple and practical score model for predicting the mortality of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. Medicine 2016, 95, e5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, A.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, M. A Newly Established Severity Scoring System in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 242, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y. Risk Factors for Death in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 109, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xiao, L.; Shi, D.; Cui, D.; Du, T.; Zheng, Y. Establishment and validation of a prognostic nomogram for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A retrospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Jia, B.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, X.; et al. Association of gastrointestinal symptoms with mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Jia, B.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, X.; et al. Association of liver function and prognosis in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Jia, B.; Tian, B.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, X.; et al. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 4895–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Shu, Z.; Wu, W.; Cai, H.; Shi, Y. Prediction of Prognosis in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 78, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, W.; Li, A.; Deng, L.; Xiong, Y. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of acute kidney injury in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1236091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Jiao, F.; Du, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, M.; Li, A.; Deng, L.; Xiong, Y. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: Prevalence, characteristics, and impact on prognosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Lin, X.; Zheng, C.; Tang, S.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Dai, Z.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Z. Establishment and validation of a clinical risk scoring model to predict fatal risk in SFTS hospitalized patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kang, L.; He, L.; Sheng, N.; Qin, J.; Ma, S.; Xu, H.; Hu, L.; Zou, G.; et al. NLR, A Convenient Early-Warning Biomarker of Fatal Outcome in Patients With Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 907888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.N.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Seo, J.W.; Kim, D.Y.; Yun, N.R.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, C.M.; Jung, S.I.; Kim, U.J.; et al. Viral Load as a Factor Affecting the Fatality of Patients Suffering from Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viruses 2022, 14, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; Huang, D.; Sai, L. Analysis of risk factors associated with fatal outcome among severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients from 2015 to 2019 in Shandong, China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Hu, K.; Yi, Z.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Xu, B.; Huang, X. Changes in peripheral blood cytokines in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4704–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; He, Y.W.; Dai, Y.A.; Xiong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, D.J.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Luo, X.L.; Cheng, Y.L.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel Bunyavirus in China: Pathogenesis and correlates of fatal outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Ge, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Tian, D.; et al. The predictive effect of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) on the risk of death in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS): A multi-center study in China. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.K.; Lu, Q.B.; Chen, W.W.; Xu, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.F.; Du, J.; Li, H.; Yao, K.; Zhai, D.; et al. Arginine deficiency is involved in thrombocytopenia and immunosuppression in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liang, M.; Ning, J.; Gu, W.; Jiang, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; et al. Pathogenesis of emerging severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in C57/BL6 mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10053–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bibi, A.; Xu, Y.; Li, T. The AST/ALT Ratio (De Ritis Ratio) Represents an Unfavorable Prognosis in Patients in Early-Stage SFTS: An Observational Cohort Study. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 725642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.K.; Yang, Z.D.; Du, J.; Xing, B.; Cui, N.; Zhang, P.H.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.A.; Lu, Q.B.; Liu, W. Endothelial activation and dysfunction in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Huang, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Overview of the immunological mechanism underlying severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.S.; Jin, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Ra, S.H.; Kim, T.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, M.C.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.; Cha, H.H.; et al. Viral and Immunologic Factors Associated with Fatal Outcome of Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Korea. Viruses 2021, 13, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.D.; Hu, J.G.; Lu, Q.B.; Guo, C.T.; Cui, N.; Peng, W.; Wang, L.Y.; Qin, S.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, P.H.; et al. The prospective evaluation of viral loads in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 78, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, P. Predictive Value of the Platelet-to-Albumin Ratio (PAR) on the Risk of Death at Admission in Patients Suffering from Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5647–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zou, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, X.; Jiang, F.; Yu, H. Score risk model for predicting severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome mortality. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, Q.B.; Cui, N.; Li, H.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Z.D.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. Case-fatality ratio and effectiveness of ribavirin therapy among hospitalized patients in china who had severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.P.; Liang, M.F.; Ye, J.B.; Liu, Q.H.; Xiong, C.H.; Long, B.; Lin, W.B.; Cui, N.; Zou, Z.Q.; Song, Y.L.; et al. Prognostic value of clinical and immunological markers in acute phase of SFTS virus infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O870–O878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prkno, A.; Wacker, C.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Schlattmann, P. Procalcitonin-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients with severe sepsis and septic shock—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; Chou, R.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author and Year | Study Type | Study Design | Country | Study Sites | Hospital Level | N (M/F) | Fatal Number | Non-Fatal Number | Mean Age (Years) | Laboratory Parameters | NOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cao et al., 2024 [21] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Two | Tertiary | 217 (92/125) | 60 | 157 | 64.0 | LYM MONO PLT ALB ALP ALT GGT BUN CK CRP PCT PT | High |
| Fang et al., 2024 [22] | Retrospective | Case control study | China | One | Tertiary | 394 (189/205) | 92 | 302 | 65.68 ± 10.14 | PLT ALT AST CK CK-MB LDH BUN Cr PT APTT TT DD FIB | High |
| Guo et al., 2024 [23] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 610 (352/258) | 81 | 529 | 61.47 | CK-MB PT | High |
| Hou et al., 2024 [24] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 93 (38/55) | 37 | 56 | 63.94 ± 2.63 | APTT LDH PLT ALB PCT TT DD | High |
| Huang et al., 2023 [25] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 47 (28/19) | 23 | 24 | 62.61 ± 5.03 | LDH PCT APTT TT | High |
| Kim et al., 2023 [26] | Retrospective | Cohort study | Republic of Korea | One | Tertiary | 91 (53/38) | 10 | 81 | 60.86 ± 15.01 | APTT | High |
| Li et al., 2024 [27] | Prospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Secondary/Tertiary | 686 (330/356) | 87 | 599 | 65.99 ± 2.41 | AST LDH CK CK-MB | High |
| Li et al., 2023 [28] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 200 (94/106) | 35 | 165 | 70.76 ± 3.11 | WBC NEU LYM MONO PLT ALT APTT AST CRP CK CK-MB GGT LDH BUN PCT PT Cr UA DD ALB Viral load | High |
| Liang et al., 2024 [29] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 580 (242/338) | 111 | 469 | 60.98 ± 2.44 | PLT Viral load Cr | High |
| Liu et al., 2022 [30] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 182 (88/94) | 24 | 158 | 59.64 ± 12.74 | NEU LYM NLR WBC | High |
| Liu et al., 2022 [31] | Retrospective | Case control study | China | One | Tertiary | 194 (101/93) | 23 | 171 | 62.39 ± 11.85 | AST | High |
| Liu et al., 2022 [32] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 155 (77/78) | 22 | 133 | 61.98 ± 11.70 | ALB ALP ALT APTT AST Cr CRP GGT Hb LDH LYM LYM% MONO NEU NEU% PCT PLT PT RBC TBIL TT WBC | High |
| Peng et al., 2024 [33] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Secondary/Tertiary | 541 (275/266) | 60 | 481 | 62.02 ± 2.46 | Cr APTT AST | High |
| Qian et al., 2023 [34] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Secondary/Tertiary | 882 (428/454) | 157 | 725 | 63.99 ± 2.35 | CK APTT AST | High |
| Wang et al., 2022 [35] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Two | Tertiary | 122 (64/58) | 20 | 102 | 61.66 ± 13.02 | APTT | High |
| Wang et al., 2020 [36] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 51 (27/24) | 16 | 35 | 57.52 ± 12.37 | WBC NEU LYM Hb PLT ALT AST CK LDH BUN Cr PT APTT FIB | High |
| Wang et al., 2019 [37] | Prospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Secondary/Tertiary | 429 (228/201) | 69 | 360 | 60.8 ± 12.1 | WBC NEU NEU% LYM LYM% MONO RBC Hb PLT LDH CK-MB BUN Cr PT APTT ALT ALB | High |
| Wang et al., 2024 [38] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 214 (95/119) | 57 | 157 | 67.9 ± 10.6 | LYM% NEU | High |
| Wang et al., 2024 [39] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Two | Tertiary | 437 (190/247) | 101 | 336 | NA | WBC NEU LYM MONO PLT RBC Hb CRP PCT ALT GGT TBIL ALB ALP BUN Cr PT APTT TT | High |
| Wei et al., 2022 [53] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Two | Tertiary | 228 (107/121) | 51 | 177 | 62.96 ± 3.02 | NLR BUN NEU LYM PLT ALP ALB | High |
| Xia et al., 2023 [40] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Tertiary | 161 (63/98) | 26 | 135 | 64.22 ± 3.23 | WBC PLT ALT CK Hb Viral load | High |
| Xiao et al., 2024 [41] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 372 (166/206) | 79 | 293 | 66.93 ± 2.56 | Viral load PT | High |
| Xiong et al., 2016 [42] | Retrospective | Cohort Study | China | One | Tertiary | 179 (71/108) | 34 | 145 | 58.08 ± 11.86 | Viral load PLT NEU% LYM% ALT AST GGT Cr LDH CK TT APTT | High |
| Yang et al., 2017 [43] | Retrospective | Cohort Study | China | One | Tertiary | 123 (62/61) | 31 | 92 | 59.50 ± 11.52 | WBC PLT Cr K+ LDH APTT CK ALB | High |
| Yang et al., 2023 [44] | Retrospective | Cohort Study | China | One | Tertiary | 109 (50/59) | 27 | 82 | 67.64 ± 3.75 | LYM ALB PLT DD | High |
| Yang et al., 2024 [45] | Retrospective | Case control study | China | One | Tertiary | 292 (150/142) | 72 | 220 | 67.84 ± 2.45 | DD | High |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [46] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Tertiary | 304 (155/149) | 70 | 234 | 61.95 ± 3.14 | WBC PLT ALT LDH ALB Cr PT | High |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [48] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | Multi | Tertiary | 292 (150/142) | 69 | 223 | 61.45 ± 3.27 | WBC RBC Hb PLT ALT GGT Cr BUN TBIL PT APTT | High |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [47] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 291 (151/140) | 65 | 226 | 62.92 ± 3.33 | WBC PLT ALT ALP GGT TBIL Cr PT | High |
| Zhang et al., 2025 [49] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 101 (55/46) | 17 | 84 | 65.25 ± 10.67 | NEU% LYM% NLR PLT AST BUN LDH TT APTT | High |
| Zhang et al., 2023 [50] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 208 (110/98) | 37 | 171 | 65 ± 8 | WBC NEU NEU% LYM LYM% Hb PLT ALT AST TBIL ALB ALP GGT LDH BUN K+ CK-MB PT APTT TT FIB DD CRP PCT Viral load | High |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [51] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 290 (147/143) | 50 | 240 | 64.34 ± 7.21 | Cr | High |
| Zhong et al., 2024 [52] | Retrospective | Cohort study | China | One | Tertiary | 427 (189/238) | 86 | 341 | 66.93 ± 2.44 | LYM MONO NEU PLT ALB UA K+ ALT AST LDH TT PT APTT FIB Cr Viral load CK | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Ding, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Ma, X. Prediction of Mortality by Clinical Laboratory Parameters in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070193
Yan S, Ding X, Gao Q, Zhao L, Li C, Sun Z, Ma X. Prediction of Mortality by Clinical Laboratory Parameters in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(7):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070193
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shicui, Xuebin Ding, Qiao Gao, Lili Zhao, Cong Li, Zhenlu Sun, and Xuejun Ma. 2025. "Prediction of Mortality by Clinical Laboratory Parameters in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 7: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070193
APA StyleYan, S., Ding, X., Gao, Q., Zhao, L., Li, C., Sun, Z., & Ma, X. (2025). Prediction of Mortality by Clinical Laboratory Parameters in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(7), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070193






