The Association Between Syphilis Infection and HIV Acquisition and HIV Disease Progression in Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
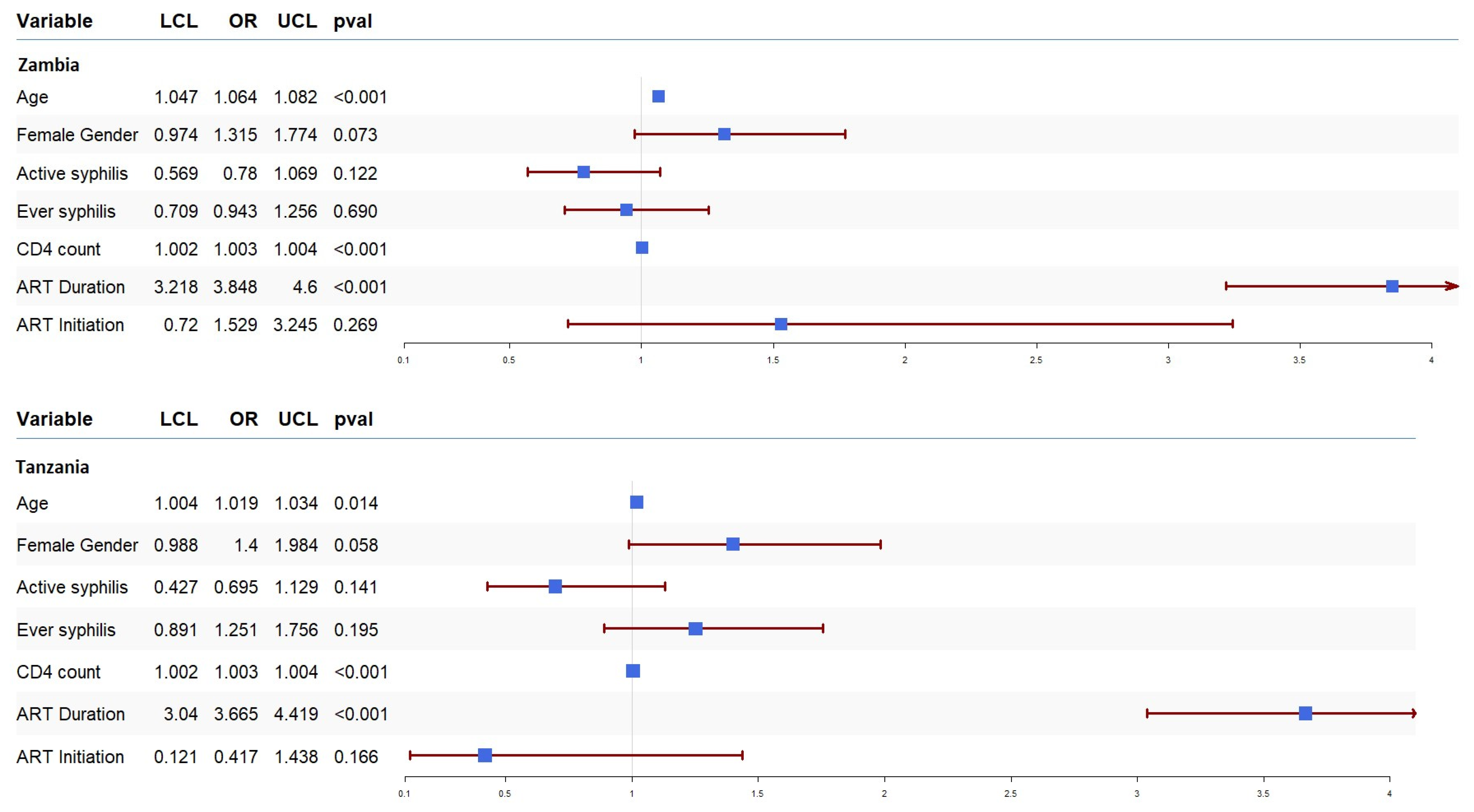
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tudor, M.E.; Al Aboud, A.M.; Leslie, S.W.; Gossman, W. Syphilis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534780/ (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention—Syphilis-Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/syphilis/about/index.html (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Syphilis—Overview. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/syphilis#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Data on Syphilis. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/data-on-syphilis (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Strategic Information. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/stis/strategic-information (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- World Health Organization. Implementing the Global Health Sector Strategies on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2022–2030: Report on Progress and Gaps 2024, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2024. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/378246 (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategy on Sexually Transmitted Infections 2016–2021 Towards Ending STIs. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/246296/WHO-RHR-16.09-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Sun, C.; Yue, X.; Zheng, M.; Fu, G.; Gong, X. Prevalence of syphilis among people living with HIV and its implication for enhanced coinfection monitoring and management in China: A meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1002342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lu, L.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Han, Y.; Lv, W.; Cao, W.; et al. Clinical and immunological characteristics of HIV/syphilis co-infected patients following long-term antiretroviral treatment. Front. Public Health 2024, 11, 1327896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ren, M.; Dashwood, T.; Walmsley, S. The Intersection of HIV and Syphilis: Update on the Key Considerations in Testing and Management. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021, 18, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, M.Y.; Gong, H.Z.; Hu, K.R.; Zheng, H.Y.; Wan, X.; Li, J. Effect of syphilis infection on HIV acquisition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2021, 97, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gilbert, L.; Dear, N.; Esber, A.; Iroezindu, M.; Bahemana, E.; Kibuuka, H.; Owuoth, J.; Maswai, J.; Crowell, T.A.; Polyak, C.S.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with HIV and syphilis co-infection in the African Cohort Study: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Solomon, H.; Moraes, A.N.; Williams, D.B.; Fotso, A.S.; Duong, Y.T.; Ndongmo, C.B.; Voetsch, A.C.; Patel, H.; Lupoli, K.; McAuley, J.B.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of active syphilis and HIV co-Infection among sexually active persons aged 15–59 years in Zambia: Results from the Zambia Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (ZAMPHIA) 2016. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luetkemeyer, A.F.; Donnell, D.; Dombrowski, J.C.; Cohen, S.; Grabow, C.; Brown, C.E.; Malinski, C.; Perkins, R.; Nasser, M.; Lopez, C.; et al. Postexposure Doxycycline to Prevent Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Molina, J.M.; Charreau, I.; Chidiac, C.; Pialoux, G.; Cua, E.; Delaugerre, C.; Capitant, C.; Rojas-Castro, D.; Fonsart, J.; Bercot, B.; et al. Post-exposure prophylaxis with doxycycline to prevent sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men: An open-label randomised substudy of the ANRS IPERGAY trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Gao, S.; Li, X.Z.; Martcheva, M. Modeling Syphilis and HIV Coinfection: A Case Study in the USA. Bull. Math. Biol. 2023, 85, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mussa, A.; Jarolimova, J.; Ryan, R.; Wynn, A.; Ashour, D.; Bassett, I.V.; Philpotts, L.L.; Freyne, B.; Morroni, C.; Dugdale, C.M. Syphilis Prevalence Among People Living With and Without HIV in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2024, 51, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, L.; Pan, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J.; Luo, M.; Cheng, W.; Chai, C. Current syphilis infection in virally suppressed people living with HIV: A cross-sectional study in eastern China. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1366795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roth, J.A.; Franzeck, F.C.; Balakrishna, S.; Lautenschlager, S.; Thurnheer, M.C.; Trellu, L.T.; Cavassini, M.; Vernazza, P.; Bernasconi, E.; Braun, D.; et al. Repeated Syphilis Episodes in HIV-Infected Men Who Have Sex With Men: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study on Risk Factors and the Potential Role of Syphilis Immunity. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billock, R.M.; Samoff, E.; Lund, J.L.; Pence, B.W.; Powers, K.A. HIV Viral Suppression and Pre-exposure Prophylaxis in HIV and Syphilis Contact Tracing Networks: An Analysis of Disease Surveillance and Prescription Claims Data. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2021, 88, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zetola, N.M.; Klausner, J.D. Syphilis and HIV Infection: An Update. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchacz, K.; Patel, P.; Taylor, M.; Kerndt, P.R.; Byers, R.H.; Holmberg, S.D.; Klausner, J.D. Syphilis increases HIV viral load and decreases CD4 cell counts in HIV-infected patients with new syphilis infections. AIDS 2004, 18, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment (PHIA) Project. Available online: https://phia.icap.columbia.edu/ (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Tanzania Commission for AIDS (TACAIDS); Zanzibar AIDS Commission (ZAC). Tanzania HIV Impact Survey (THIS) 2016–2017: Final Report. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. December 2018. Available online: https://phia.icap.columbia.edu/tanzania-final-report/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Ministry of Health, Zambia. Zambia Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment (ZAMPHIA) 2016: Final Report. Lusaka, Ministry of Health. February 2019. Available online: https://phia.icap.columbia.edu/zambia-final-report/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- PHIA Data Use Manual. Available online: https://phia-data.icap.columbia.edu/storage/Country/28-09-2021-22-01-17-615390ad6a147.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Farahani, M.; Killian, R.; Reid, G.A.; Musuka, G.; Mugurungi, O.; Kirungi, W.; Nuwagaba-Biribonwoha, H.; El-Sadr, W.M.; Justman, J. Prevalence of syphilis among adults and adolescents in five sub-Saharan African countries: Findings from Population-based HIV Impact Assessment surveys. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e1413–e1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachathep, K.; Radin, E.; Hladik, W.; Hakim, A.; Saito, S.; Burnett, J.; Brown, K.; Phillip, N.; Jonnalagadda, S.; Low, A.; et al. Population-Based HIV Impact Assessments Survey Methods, Response, and Quality in Zimbabwe, Malawi, and Zambia. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2021, 87 (Suppl. S1), S6–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ho, D.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric Preprocessing for Parametric Causal Inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Haule, A.; Msemwa, B.; Mgaya, E.; Masikini, P.; Kalluvya, S. Prevalence of syphilis, neurosyphilis and associated factors in a cross-sectional analysis of HIV infected patients attending Bugando Medical Centre, Mwanza, Tanzania. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mboowa, G.; Inda, D.A. Seroprevalence of syphilis among human immunodeficiency virus positive individuals attending immune suppressed syndrome clinic at international hospital Kampala, Uganda. Int. STD Res. Rev. 2015, 3, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katamba, C.; Chungu, T.; Lusale, C. HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B coinfections in Mkushi, Zambia: A cross-sectional study. F1000Research 2019, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruangtragool, L.; Silver, R.; Machiha, A.; Gwanzura, L.; Hakim, A.; Lupoli, K.; Musuka, G.; Patel, H.; Mugurungi, O.; Tippett Barr, B.A.; et al. Factors associated with active syphilis among men and women aged 15 years and older in the Zimbabwe Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (2015–2016). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan, L.; Yu, A.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Ma, P. Consequences of HIV/Syphilis Co-Infection on HIV Viral Load and Immune Response to Antiretroviral Therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chan, P.; Tang, T.H.C.; Kwong, R.T.S.; Chan, L.; Chan, H.S.Y.; Lam, K.W.; Ting, W.M.; Yung, S.K.; Lam, E.C.T.; Chu, M.Y.; et al. Effects of syphilis infection among HIV-1-positive individuals on suppressive antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Res. Ther. 2022, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Zambia (n = 21,280) | Tanzania (n = 32,635) | |
|---|---|---|
| Variable | N (%) | N (%) |
| Age | 29 (IQR: 21–39) | 31 (IQR: 22–45) |
| Female gender | 12,109 (56.9%) | 18,172 (55.7%) |
| Male | 9171 (43.1%) | 14,463 (44.3%) |
| Active syphilis | ||
| Yes | 591 (2.8%) | 328 (1%) |
| No | 18,566 (87.2%) | 32,306 (99%) |
| Ever syphilis | ||
| Yes | 1361 (6.4%) | 2026 (6.2%) |
| No | 17,796 (83.6%) | 30,608 (93.8%) |
| HIV acquired | 2467 (11.6%) | 1895 (5.8%) |
| Viral load suppressed | 1465 (6.9%) | 994 (3%) |
| Zambia | Tanzania | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HIV Positive (n = 2467, 12.9%) | HIV Negative (n = 16,648, 87.1%) | p-Value | HIV Positive (n = 1895, 5.8%) | HIV Negative (n = 30,740, 94.2%) | p-Value |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Age | 38 (IQR: 30–45) | 27 (IQR: 20–38) | <0.001 | 39 (IQR: 30–47) | 30 (IQR: 21–44) | <0.001 |
| Female gender | 1688 (68.4%) | 9285 (55.8%) | <0.001 | 1297 (68.4%) | 16,875 (54.9%) | <0.001 |
| Active syphilis | ||||||
| Yes | 225 (9.1%) | 366 (2.2%) | <0.001 | 76 (4%) | 252 (0.8%) | <0.001 |
| No | 2242 (90.9%) | 16281 (97.8%) | 1819 (96%) | 30,487 (99.2%) | ||
| Ever syphilis | ||||||
| Yes | 406 (16.4%) | 955 (5.7%) | <0.001 | 271 (14.3%) | 1755 (5.7%) | <0.001 |
| No | 2061 (83.6%) | 15,692 (94.3%) | 1624 (85.7%) | 28,984 (94.3%) | ||
| Zambia | Tanzania | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HIV Suppressed (n = 487, 61.5%) | HIV Not Suppressed (n = 305, 38.5%) | p-Value | HIV Suppressed (n = 299, 55.1%) | HIV Not Suppressed (n = 243, 44.8%) | p-Value |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Age | 40 (IQR: 32–46) | 32 (IQR: 28–42) | <0.001 | 43 (IQR: 36–52) | 40 (IQR: 32–49) | <0.001 |
| CD4 count | 475 (IQR: 344–635) | 333 (IQR:207–492.5) | <0.001 | 483.5 (IQR: 346.8–655) | 328 (IQR: 191–485) | <0.001 |
| Female gender | 332 (68.2%) | 189 (62%) | 0.07 | 196 (65.5%) | 140 (57.6%) | 0.06 |
| Active syphilis | ||||||
| Yes | 127 (26.1%) | 95 (31.1%) | 0.1235 | 36 (12.0%) | 40 (16.5%) | 0.171 |
| No | 360 (73.9%) | 210 (68.9%) | 263 (88%) | 203 (83.5%) | ||
| Ever syphilis | ||||||
| Yes | 242 (49.7%) | 156 (51.1%) | 0.7153 | 157 (52.5%) | 114 (46.9%) | 0.2266 |
| No | 245 (50.3%) | 149 (48.9%) | 142 (47.5%) | 129 (53.1%) | ||
| ART status | 457 (93.8%) | 33 (10.8%) | <0.001 | 265 (88.6%) | 33 (13.6%) | <0.001 |
| ART initiation | 343 (70.4%) | 34 (11.1%) | 0.29 | 169 (56.5%) | 27 (11.1%) | 0.219 |
| ART duration | ||||||
| Not on ART | 69 (14.2%) | 264 (86.5%) | <0.001 | 33 (11.0%) | 199 (81.9%) | <0.001 |
| On ART < 12 months | 66 (13.5%) | 10 (3.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| On ART 12–23 months | 56 (11.5%) | 4 (1.3%) | 27 (9%) | 5 (2%) | ||
| On ART 24 months or more | 279 (57.3%) | 26 (8.5%) | 186 (62.2%) | 25 (10.3%) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandla, S.; Nakka, R.; Khan, R.A.; Salboukh, F.; Ghebremichael, M. The Association Between Syphilis Infection and HIV Acquisition and HIV Disease Progression in Sub-Saharan Africa. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10030065
Gandla S, Nakka R, Khan RA, Salboukh F, Ghebremichael M. The Association Between Syphilis Infection and HIV Acquisition and HIV Disease Progression in Sub-Saharan Africa. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandla, Sindhuri, Raja Nakka, Ruhul Ali Khan, Fatemeh Salboukh, and Musie Ghebremichael. 2025. "The Association Between Syphilis Infection and HIV Acquisition and HIV Disease Progression in Sub-Saharan Africa" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10030065
APA StyleGandla, S., Nakka, R., Khan, R. A., Salboukh, F., & Ghebremichael, M. (2025). The Association Between Syphilis Infection and HIV Acquisition and HIV Disease Progression in Sub-Saharan Africa. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10030065







