Lung Involvement in Patients with Leptospirosis in Tropical Australia; Associations, Clinical Course and Implications for Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Ethical Approval
3. Results
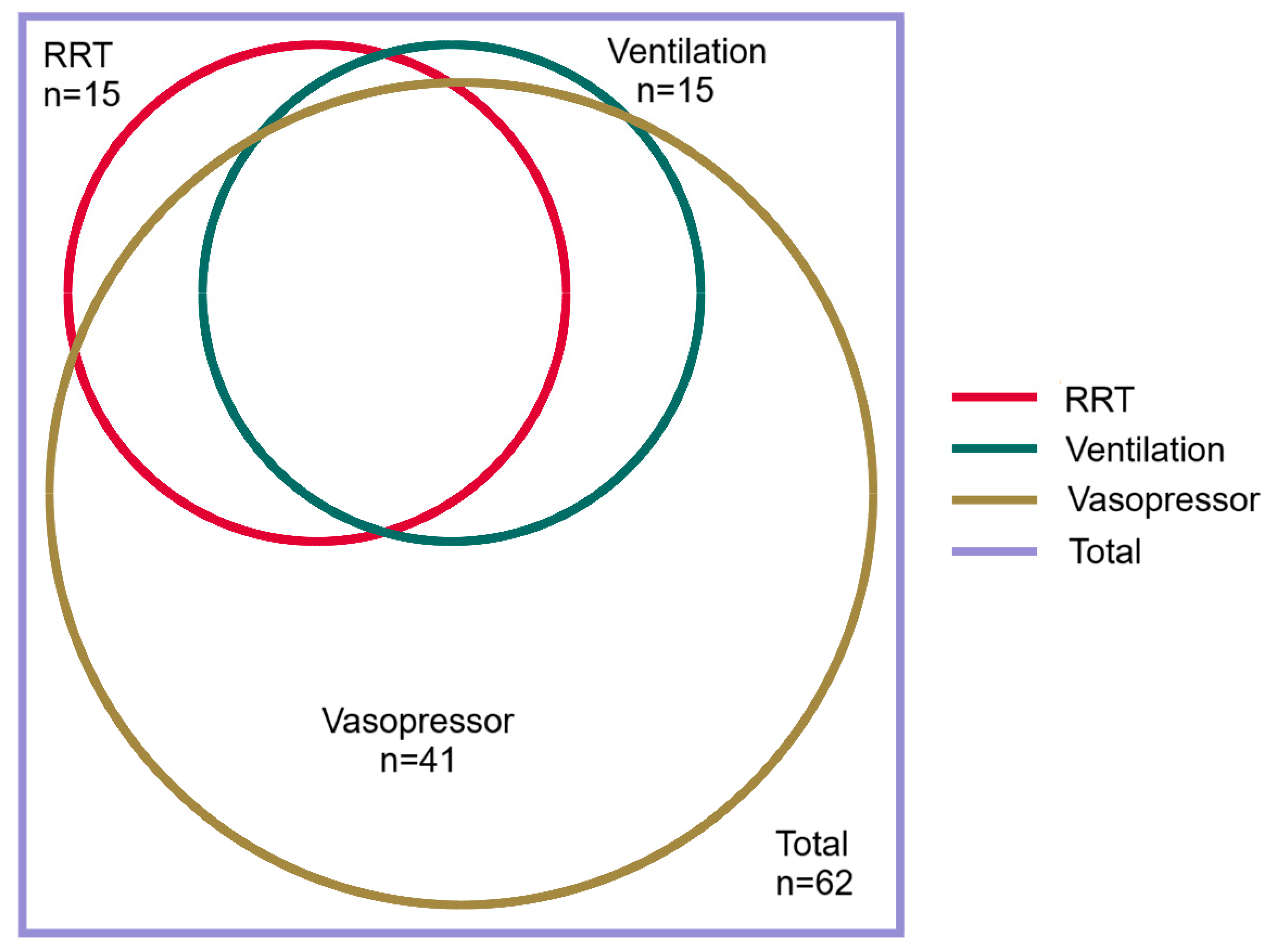
3.1. Lung Involvement
3.2. Pulmonary Haemorrhage
3.3. Clinical Course and Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| DIC | Disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membranous oxygenation |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
References
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, V.; Trivedi, T.H.; Yeolekar, M.E. Epidemic of leptospirosis: An ICU experience. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2004, 52, 619–622. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Zanzi, C.; Dreyfus, A.; Limothai, U.; Foley, W.; Srisawat, N.; Picardeau, M.; Haake, D.A. Leptospirosis—Improving Healthcare Outcomes for a Neglected Tropical Disease. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2025, 12, ofaf035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, J.; Villanueva, S.; Matsui, M. Leptospirosis Pathophysiology: Into the Storm of Cytokines. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, S.; Fernando, N.; Dreyfus, A.; Smith, C.; Rodrigo, C. Leptospirosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Sean, T.C.; Bhavya, K.S.; Sahithya, C.S.; Chan-drasekaran, S.; Palanisamy, R.; Robinson, E.R.; Subbiah, S.K.; Mok, P.L. Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, K.V.; Coburn, J. Leptospira as an emerging pathogen: A review of its biology, pathogenesis and host immune responses. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budiono, E.; Sumardi, R.B.; Riyanto, B.S.; Hisyam, B.; Hartopo, A.B. Pulmonary involvement predicts mortality in severe leptospirosis patients. Acta Med. Indones. 2009, 41, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Spichler, A.S.; Vilaça, P.J.; Athanazio, D.A.; Albuquerque, J.O.; Buzzar, M.; Castro, B.; Seguro, A.; Vinetz, J.M. Predictors of lethality in severe leptospirosis in urban Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, S.; Rodrigo, C.; Haniffa, R. Developing a clinically relevant classification to predict mortality in severe leptospirosis. J. Emerg. Trauma. Shock 2010, 3, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, R.A.Y.; Danguilan, R.A.; Chua, E.; Arakama, M.I.; Ginete-Garcia, J.K.B.; Chavez, J.R. A Scoring Tool to Predict Pulmonary Complications in Severe Leptospirosis with Kidney Failure. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.Z.; Han, S.M.; Edwards, T.; Maung, H.T.; Brett-Major, D.M.; Smith, C.; Lee, N. Antibiotics for treatment of leptospirosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 3, CD014960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, H.P.; Wheeler, A.P.; Bernard, G.R.; Thompson, B.T.; Hayden, D.; deBoisblanc, B.; Connors, A.F., Jr.; Hite, R.D.; Harabin, A.L. Comparison of two fluid-management strategies in acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2564–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Carter, A.; Kennedy, B.J.; Dermedgoglou, A.; Poulgrain, S.S.; Paavola, M.P.; Minto, T.L.; Luc, M.; Hanson, J. Severe leptospirosis in tropical Australia: Optimising intensive care unit management to reduce mortality. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, N.D.; Patankar, A.S. Leptospirosis in Intensive Care Unit. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 25, S134–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengren, P.; Johnston, L.; Ismail, I.; Smith, S.; Hanson, J. The Characteristics of Patients that Develop Severe Leptospirosis: A Scoping Review. Preprints 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularatne, S.A.; Budagoda, B.D.; de Alwis, V.K.; Wickramasinghe, W.M.; Bandara, J.M.; Pathirage, L.P.; Gamlath, G.R.; Wijethunga, T.J.; Jayalath, W.A.; Jayasinghe, C.; et al. High efficacy of bolus methylprednisolone in severe leptospirosis: A descriptive study in Sri Lanka. Postgrad. Med. J. 2011, 87, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, C.; Lakshitha de Silva, N.; Goonaratne, R.; Samarasekara, K.; Wijesinghe, I.; Parththipan, B.; Rajapakse, S. High dose corticosteroids in severe leptospirosis: A systematic review. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.V.; Vasava, A.H.; Bhatia, L.C.; Patel, T.C.; Patel, N.K.; Patel, N.T. Plasma exchange with immunosuppression in pulmonary alveolar haemorrhage due to leptospirosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 131, 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseka, C.L.; Dahanayake, N.J.; Mihiran, D.J.D.; Wijesinghe, K.M.; Liyanage, L.N.; Wickramasuriya, H.S.; Wijayaratne, G.B.; Sanjaya, K.; Bodinayake, C.K. Pulmonary haemorrhage as a frequent cause of death among patients with severe complicated Leptospirosis in Southern Sri Lanka. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, L.; Singh, G.; Townsend, D.; Nagendran, J.; Sligl, W. Extracorporeal Life Support for Severe Leptospirosis: Case Series and Narrative Review. J. Assoc. Med. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Can. 2024, 9, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, J.; Shan, X.; Zhou, B. Advances in the study of nebulized tranexamic acid for pulmonary hemorrhage. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2025, 81, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System. Available online: https://nindss.health.gov.au/pbi-dashboard/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Smith, S.; Kennedy, B.J.; Dermedgoglou, A.; Poulgrain, S.S.; Paavola, M.P.; Minto, T.L.; Luc, M.; Liu, Y.H.; Hanson, J. A simple score to predict severe leptospirosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, H.; Rosengren, P.; Kinneally, T.; Prideaux, L.; Smith, S.; Hanson, J. Presentation and Clinical Course of Leptospirosis in a Referral Hospital in Far North Queensland, Tropical Australia. Pathogens 2025, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairhead, L.J.; Smith, S.; Sim, B.Z.; Stewart, A.G.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Binotto, E.; Law, M.; Hanson, J. The seasonality of infections in tropical Far North Queensland, Australia: A 21-year retrospective evaluation of the seasonal patterns of six endemic pathogens. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2022, 2, e0000506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Statistics for Australian Locations. Summary Statistics Cairns Aero. Available online: https://www.bom.gov.au/climate/averages/tables/cw_031011.shtml (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Leptospirosis—Laboratory Case Definition. Available online: https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/leptospirosis-laboratory-case-definition?language=en (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Leptospirosis Reference Laboratory. Accreditations, Certifications and Terms of Reference. Available online: https://www.health.qld.gov.au/public-health/forensic-and-scientific-services/testing-analysis/disease-investigation-and-analysis/leptospirosis-reference-laboratory/laboratory-accreditation-and-certification (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.W.; Wheeler, A.P.; Bernard, G.R.; Hayden, D.L.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Ware, L.B. Comparison of the SpO2/FIO2 ratio and the PaO2/FIO2 ratio in patients with acute lung injury or ARDS. Chest 2007, 132, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.J.; Dalston, M.O.; Carvalho, J.E.; Setúbal, S.; Oliveira, J.M.; Pereira, M.M. Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of the severe pulmonary form of leptospirosis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2002, 35, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, E.D.; Costa, E.; Sacramento, E.; Caymmi, A.L.; Neto, C.A.; Barreto Lopes, M.; Lopes, A.A. Chest radiograph abnormalities in patients hospitalized with leptospirosis in the city of Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 5, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanomkiat, W.; Poonsawat, P. Pulmonary radiographic findings in 118 leptospirosis patients. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2005, 36, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchiori, E.; Lourenço, S.; Setúbal, S.; Zanetti, G.; Gasparetto, T.D.; Hochhegger, B. Clinical and imaging manifestations of hemorrhagic pulmonary leptospirosis: A state-of-the-art review. Lung 2011, 189, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Mauad, T.; Bethlem, E.P.; Carvalho, C.R. Pathology and pathophysiology of pulmonary manifestations in leptospirosis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemo, A.C.; Duarte, M.I.; Alves, V.A.; Takakura, C.F.; Santos, R.T.; Nicodemo, E.L. Lung lesions in human leptospirosis: Microscopic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural features related to thrombocytopenia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arean, V.M. The pathologic anatomy and pathogenesis of fatal human leptospirosis (Weil’s disease). Am. J. Pathol. 1962, 40, 393–423. [Google Scholar]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Mauad, T.; Bethlem, E.P.; Carvalho, C.R. Leptospiral pneumonias. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2007, 13, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemo, A.C.; Duarte-Neto, A.N. Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Hemorrhagic Syndrome in Human Leptospirosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 1970–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammakumpee, K.; Silpapojakul, K.; Borrirak, B. Leptospirosis and its pulmonary complications. Respirology 2005, 10, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiana, S.; Mikulski, M.; Becam, J.; Lacassin, F.; Lefèvre, P.; Gourinat, A.C.; Goarant, C.; D’Ortenzio, E. Risk factors and predictors of severe leptospirosis in New Caledonia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, L.; Rodrigues, A.C., Jr.; Sanches, T.R.; Souza, R.B.; Seguro, A.C. Leptospirosis leads to dysregulation of sodium transporters in the kidney and lung. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F586–F592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, E.R.; Ganoza, C.A.; Campos, K.; Ricaldi, J.N.; Torres, S.; Silva, H.; Céspedes, M.J.; Matthias, M.A.; Swancutt, M.A.; López Liñán, R.; et al. Clinical spectrum of pulmonary involvement in leptospirosis in a region of endemicity, with quantification of leptospiral burden. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotto, P.C.; Nascimento, C.M.; Eluf-Neto, J.; Marotto, M.S.; Andrade, L.; Sztajnbok, J.; Seguro, A.C. Acute lung injury in leptospirosis: Clinical and laboratory features, outcome, and factors associated with mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Gulati, A. Pulmonary manifestations of leptospirosis. Lung India 2012, 29, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioachimescu, O.C.; Stoller, J.K. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: Diagnosing it and finding the cause. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2008, 75, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaghy, M.; Rees, A.J. Cigarette smoking and lung haemorrhage in glomerulonephritis caused by autoantibodies to glomerular basement membrane. Lancet 1983, 2, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Drug Strategy Household Survey 2022–2023; Australian Institute of Health Welfare: Canberra, Australia, 2025.
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkader, R.C.; Daher, E.F.; Camargo, E.D.; Spinosa, C.; da Silva, M.V. Leptospirosis severity may be associated with the intensity of humoral immune response. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. S. Paulo 2002, 44, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, V.V.; Nagar, V.S.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Bhalgat, P.S.; Juvale, N.I. Pulmonary leptospirosis: An excellent response to bolus methylprednisolone. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luks, A.M.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; Hirschmann, J.V. Leptospirosis presenting as diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: Case report and literature review. Chest 2003, 123, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwattayakul, K.; Kaewtasi, S.; Chueasuwanchai, S.; Hoontrakul, S.; Chareonwat, S.; Suttinont, C.; Phimda, K.; Chierakul, W.; Silpasakorn, S.; Suputtamongkol, Y. An open randomized controlled trial of desmopressin and pulse dexamethasone as adjunct therapy in patients with pulmonary involvement associated with severe leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Corticosteroid Treatment for Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagshaw, R.J.; Stewart, A.G.A.; Smith, S.; Carter, A.W.; Hanson, J. The Characteristics and Clinical Course of Patients with Scrub Typhus and Queensland Tick Typhus Infection Requiring Intensive Care Unit Admission: A 23-year Case Series from Queensland, Tropical Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.; Smith, S.; Stewart, J.; Hanson, J. Acute Q Fever Patients Requiring Intensive Care Unit Support in Tropical Australia, 2015–2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2025, 31, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izurieta, R.; Galwankar, S.; Clem, A. Leptospirosis: The “mysterious” mimic. J. Emerg. Trauma. Shock 2008, 1, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, F.; Riphagen-Dalhuisen, J.; Wijers, N.; Hak, E.; Van der Sande, M.A.; Morroy, G.; Schneeberger, P.M.; Schimmer, B.; Notermans, D.W.; Van der Hoek, W. Antibiotic therapy for acute Q fever in The Netherlands in 2007 and 2008 and its relation to hospitalization. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, H.M.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bradley, K.K.; Dahlgren, F.S.; Drexler, N.A.; Dumler, J.S.; Folk, S.M.; Kato, C.Y.; Lash, R.R.; Levin, M.L.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Tickborne Rickettsial Diseases: Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Other Spotted Fever Group Rickettsioses, Ehrlichioses, and Anaplasmosis—United States. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2016, 65, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavey, R.; Stewart, A.G.A.; Bagshaw, R.; Smith, S.; Vincent, S.; Hanson, J. Respiratory manifestations of rickettsial disease in tropical Australia; Clinical course and implications for patient management. Acta Trop. 2025, 266, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.P.; Lam, S.W.; Mohanty, S.; Alam, S.; Pattnaik, R.; Mahanta, K.C.; Hasan, M.U.; Charunwatthana, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Day, N.P.; et al. Fluid resuscitation of adults with severe falciparum malaria: Effects on Acid-base status, renal function, and extravascular lung water. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.D.; Semler, M.W.; Rice, T.W. Fluid Management in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naorungroj, T.; Prajantasen, U.; Sanla-Ead, T.; Viarasilpa, T.; Tongyoo, S. Restrictive fluid management with early de-escalation versus usual care in critically ill patients (reduce trial): A feasibility randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care 2025, 29, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A.; Looareesuwan, S.; Warrell, M.J.; Kasemsarn, P.; Intaraprasert, R.; Bunnag, D.; Harinasuta, T. Dexamethasone proves deleterious in cerebral malaria. A double-blind trial in 100 comatose patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 306, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedel, W.L.; Nora, D.G.; Salluh, J.I.; Lisboa, T.; Póvoa, P. Corticosteroids for severe influenza pneumonia: A critical appraisal. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 5, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losonczy, L.I.; Papali, A.; Kivlehan, S.; Calvello Hynes, E.J.; Calderon, G.; Laytin, A.; Moll, V.; Al Hazmi, A.; Alsabri, M.; Aryal, D.; et al. White Paper on Early Critical Care Services in Low Resource Settings. Ann. Glob. Health 2021, 87, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.J.; Dunser, M.W.; Dondorp, A.M.; Adhikari, N.K.; Iyer, S.; Kwizera, A.; Lubell, Y.; Papali, A.; Pisani, L.; Riviello, B.D.; et al. Current challenges in the management of sepsis in ICUs in resource-poor settings and suggestions for the future. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, A.R.; Ansdell, V.E.; Effler, P.V.; Middleton, C.R.; Sasaki, D.M. Assessment of the clinical presentation and treatment of 353 cases of laboratory-confirmed leptospirosis in Hawaii, 1974–1998. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, S.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Holmes, K.; Fresh, J.W.; Watten, R.H. Sporadic anicteric leptospirosis in South Vietnam. A study in 150 patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 1973, 79, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevejo, R.T.; Rigau-Pérez, J.G.; Ashford, D.A.; McClure, E.M.; Jarquín-González, C.; Amador, J.J.; de los Reyes, J.O.; Gonzalez, A.; Zaki, S.R.; Shieh, W.J.; et al. Epidemic leptospirosis associated with pulmonary hemorrhage-Nicaragua, 1995. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seijo, A.; Coto, H.; San Juan, J.; Videla, J.; Deodato, B.; Cernigoi, B.; Messina, O.G.; Collia, O.; de Bassadoni, D.; Schtirbu, R.; et al. Lethal leptospiral pulmonary hemorrhage: An emerging disease in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 1004–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayachari, P.; Sugunan, A.P.; Sharma, S.; Roy, S.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Sehgal, S.C. Leptospirosis in the Andaman Islands, India. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinetz, J.M. Leptospirosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 14, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smythe, L.; Dohnt, M.; Norris, M.; Symonds, M.; Scott, J. Review of leptospirosis notifications in Queensland 1985 to 1996. Commun. Dis. Intell. 1997, 21, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Hanson, J. Improving the mortality of severe leptospirosis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitre, T.; Drover, K.; Chaudhuri, D.; Zeraaktkar, D.; Menon, K.; Gershengorn, H.B.; Jayaprakash, N.; Spencer-Segal, J.L.; Pastores, S.M.; Nei, A.M.; et al. Corticosteroids in Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Systematic Review, Pairwise, and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Explor. 2024, 6, e1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dequin, P.F.; Meziani, F.; Quenot, J.P.; Kamel, T.; Ricard, J.D.; Badie, J.; Reignier, J.; Heming, N.; Plantefève, G.; Souweine, B.; et al. Hydrocortisone in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charya, A.V.; Holden, V.K.; Pickering, E.M. Management of life-threatening hemoptysis in the ICU. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 5139–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raykar, N.P.; Makin, J.; Khajanchi, M.; Olayo, B.; Munoz Valencia, A.; Roy, N.; Ottolino, P.; Zinco, A.; MacLeod, J.; Yazer, M.; et al. Assessing the global burden of hemorrhage: The global blood supply, deficits, and potential solutions. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211054995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotto, P.C.; Ko, A.I.; Murta-Nascimento, C.; Seguro, A.C.; Prado, R.R.; Barbosa, M.C.; Cleto, S.A.; Eluf-Neto, J. Early identification of leptospirosis-associated pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome by use of a validated prediction model. J. Infect. 2010, 60, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | All n = 109 | No Lung Involvement a n = 47 | Lung Involvement a n = 62 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) b | 38 (24–56) | 33 (21–53) | 42 (26–62) | 0.07 |
| Child (age < 16 years) | 6 (6) | 3 (6) | 3 (5) | 1.0 |
| Male sex | 93 (85) | 39 (83) | 54 (87) | 0.55 |
| Rural or remote residence c | 87 (80) | 36 (77) | 51 (81) | 0.47 |
| Wet season presentation | 65 (60) | 28 (60) | 37 (60) | 0.99 |
| Leptospirosis in initial differential diagnosis | 70 (64) | 32 (68) | 38 (61) | 0.46 |
| Duration of symptoms prior to antibiotic therapy (days) b | 4 (3–5) | 3 (2–5) | 5 (4–6) | 0.001 |
| Any comorbidity d | 13 (12) | 6 (13) | 7 (11) | 1.0 |
| Diabetes mellitus d | 2 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1.0 |
| Cardiac failure d | 3 (3) | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | 0.58 |
| Ischaemic heart disease d | 2 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1.0 |
| Chronic kidney disease d | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Chronic lung disease d | 5 (5) | 2 (4) | 3 (5) | 1.0 |
| Liver disease d | 5 (5) | 3 (6) | 2 (3) | 0.65 |
| Malignancy d | 2 (2) | 0 | 2 (3) | 0.51 |
| Autoimmune disease d | 0 | - | - | - |
| Immunosuppressed d | 0 | - | - | - |
| Hazardous Alcohol use d | 29 (27) | 13 (28) | 16 (26) | 0.83 |
| Current smoker d | 40 (37) | 14 (30) | 26 (42) | 0.19 |
| PCR positive e | 88/98 (90) | 33/40 (83) | 55/58 (95) | 0.09 |
| Culture positive e | 30/47 (63) | 15/21 (71) | 14/26 (54) | 0.25 |
| Either PCR or culture positive e | 92/101 (91) | 35/41 (85) | 57/60 (95) | 0.15 |
| Serovar Zanoni e | 24/62 (39) | 7/29 (24) | 17/33 (52) | 0.04 |
| Serovar Australis e | 12/62 (19) | 5/29 (17) | 7/33 (21) | 1.0 |
| Variable | All n = 109 | No Lung Involvement a n = 47 | Lung Involvement a n = 62 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjective symptoms | ||||
| Headache | 79 (72) | 36 (77) | 43 (69) | 0.40 |
| Fevers | 104 (95) | 46 (98) | 58 (94) | 0.39 |
| Rigors | 40 (37) | 16 (34) | 24 (39) | 0.62 |
| Confusion | 8 (7) | 2 (4) | 6 (10) | 0.46 |
| Fatigue | 43 (39) | 16 (34) | 27 (44) | 0.32 |
| Abdominal pain | 42 (39) | 19 (40) | 23 (37) | 0.72 |
| Myalgia | 82 (75) | 35 (74) | 47 (76) | 0.87 |
| Arthralgia | 46 (42) | 21 (45) | 25 (40) | 0.65 |
| Diarrhoea | 39 (36) | 13 (28) | 26 (42) | 0.12 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 73 (67) | 33 (70) | 40 (65) | 0.53 |
| Chest pain | 9 (8) | 3 (6) | 6 (10) | 0.73 |
| Dyspnoea | 16 (15) | 5 (11) | 11 (18) | 0.30 |
| Cough | 32 (29) | 9 (19) | 23 (37) | 0.04 |
| URTI symptoms | 15 (14) | 7 (15) | 8 (13) | 0.79 |
| Haemoptysis | 12 (11) | 0 | 12 (19) | 0.001 |
| Abnormal bleeding or bruising | 11 (10) | 4 (9) | 7 (11) | 0.75 |
| Objective examination findings | ||||
| Hepatomegaly | 11 (10) | 3 (6) | 8 (13) | 0.35 |
| Splenomegaly | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Lymphadenopathy | 6 (6) | 1 (2) | 5 (8) | 0.23 |
| Conjunctival suffusion | 22 (20) | 9 (19) | 13 (21) | 1.0 |
| Skin rash | 19 (17) | 8 (17) | 11 (18) | 1.0 |
| Abnormal chest auscultation | 44 (40) | 10 (21) | 34 (55) | <0.001 |
| Vital signs at presentation | ||||
| Oliguria b | 42 (39) | 12 (26) | 30 (48) | 0.02 |
| Temperature ° Celsius c | 37.1 (36.8–37.6) | 37.2 (36.8–37.8) | 37.1 (36.8–37.6) | 0.62 |
| Supplemental oxygen given | 23 (21) | 3 (6) | 20 (32) | 0.001 |
| SpO2/FiO2 | 462 (450–471) | 467 (457–471) | 462 (296–467) | 0.008 |
| Respiratory rate | 20 (18–24) | 20 (18–24) | 20 (18–25) | 0.54 |
| Heart rate | 99 (80–115) | 97 (78–107) | 104 (83–116) | 0.24 |
| Systolic blood pressure c,d | 111 (100–124) | 111 (99–124) | 111 (104–124) | 0.40 |
| Vasopressors administered e | 42 (39) | 11 (23) | 31 (50) | 0.005 |
| Impaired consciousness | 6 (6) | 0 | 6 (10) | 0.04 |
| Disease severity score | ||||
| SPiRO score c,f | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–1) | 2 (1–2) | 0.001 |
| All n = 109 n (%) | ICU Admission n = 56 Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | Pulmonary Haemorrhage n = 26 Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | Mechanical Ventilation n = 15 Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multilobar changes | 50 (46) | 2.59 (1.19–5.54) | 0.02 | 26.31 (5.78–119.71) | <0.001 | 22.56 (2.84–178.92) | <0.001 |
| Alveolar changes | 54 (50) | 5.81 (2.55–13.27) | <0.001 | 21.20 (4.68–96.01) | <0.001 | 18.9 (2.39–149.71) | 0.005 |
| Only interstitial changes | 8 (7) | 0.29 (0.06–1.51) | 0.14 | 0.43 (0.05–3.79) | 0.45 | 0.89 (0.10–7.78) | 0.91 |
| No imaging changes | 47 (43) | 0.24 (0.11–0.54) | 0.001 | 0.03 (0.00–0.25) | 0.001 | - a | - a |
| All n = 109 | No Lung Involvement n = 47 | Lung Involvement n = 62 | p | No Pulmonary Haemorrhage n = 83 | Pulmonary Haemorrhage n = 26 | p | No Mechanical Ventilation n = 94 | Mechanical Ventilation n = 15 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to antibiotics (days) a | 4 (3–5) | 3 (2–5) | 5 (4–6) | 0.001 | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–6) | 0.10 | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–6) | 0.12 |
| ICU admission | 56 (51) | 15 (32) | 41 (66) | <0.001 | 37 (45) | 19 (73) | 0.01 | 41 (44) | 15 (100) | <0.0001 |
| ICU length of stay (days) a | 3 (2–5) | 1 (1–3) | 3 (2–6) | 0.002 | 2 (1–3) | 6 (3–11) | <0.0001 | 2 (1–3) | 9 (6–15) | <0.0001 |
| Received RRT | 18 (17) | 3 (6) | 15 (24) | 0.01 | 9 (11) | 9 (35) | 0.01 | 8 (9) | 10 (67) | <0.0001 |
| Received vasopressors b | 56 (51) | 15 (32) | 41 (66) | <0.001 | 37 (45) | 19 (73) | 0.01 | 41 (44) | 15 (100) | <0.0001 |
| Steroids prescribed | 19 (17) | 3 (6) | 16 (26) | 0.01 | 8 (10) | 11 (42) | <0.0001 | 6 (6) | 13 (87) | <0.0001 |
| Received ECMO | 2 (2) | 0 | 2 (3) | 0.51 | 0 | 2 (8) | 0.06 | 0 | 2 (13) | 0.02 |
| Hospital length of stay (days) a | 6 (3–8) | 4 (3–6) | 7 (5–11) | <0.001 | 5 (3–7) | 7 (6–14) | <0.0001 | 5 (3–7) | 18 (10–21) | <0.0001 |
| Died | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sykes, A.; Smith, S.; Stratton, H.; Staples, M.; Rosengren, P.; Brischetto, A.; Vincent, S.; Hanson, J. Lung Involvement in Patients with Leptospirosis in Tropical Australia; Associations, Clinical Course and Implications for Management. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120333
Sykes A, Smith S, Stratton H, Staples M, Rosengren P, Brischetto A, Vincent S, Hanson J. Lung Involvement in Patients with Leptospirosis in Tropical Australia; Associations, Clinical Course and Implications for Management. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(12):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120333
Chicago/Turabian StyleSykes, Adam, Simon Smith, Hayley Stratton, Megan Staples, Patrick Rosengren, Anna Brischetto, Stephen Vincent, and Josh Hanson. 2025. "Lung Involvement in Patients with Leptospirosis in Tropical Australia; Associations, Clinical Course and Implications for Management" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 12: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120333
APA StyleSykes, A., Smith, S., Stratton, H., Staples, M., Rosengren, P., Brischetto, A., Vincent, S., & Hanson, J. (2025). Lung Involvement in Patients with Leptospirosis in Tropical Australia; Associations, Clinical Course and Implications for Management. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(12), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120333





