1. Introduction
The development of a municipality, accompanied by increasing human activity, has significant environmental impacts [
1]. In the early 21st century, over half of the global population resided in urban areas. Projections indicate that by 2050, this proportion will surpass 60%, with the most significant urban expansion anticipated in Asia and Africa [
2]. This trend drives land cover changes, particularly the conversion of non-built land into built-up areas due to intensive development [
3]. Urban land expansion is a rapid and essentially irreversible process, primarily driven by population growth. Projections indicate that, over the course of the 21st century, the global extent of urban land may increase by approximately 1.8 to 5.9 times. This expansion is expected to be most pronounced in Africa and Asia, where urban growth rates are currently the highest [
4].
As land availability in municipality centers becomes limited, communities begin to expand residential areas into the periphery or peri-urban regions [
5]. According to [
1], peri-urban areas are highly vulnerable to land-use change issues, as these regions often experience rapid development as part of urban expansion. The expansion of peri-urban areas leads to significant land-use conversion, which must be accompanied by proper monitoring and anticipation strategies [
6]. Without these measures, the consequences of rapid urbanization have significant impacts on livelihoods, the environment, and urban development. Rapid urbanization increases transport costs, traffic congestion, and food prices while reducing access to essential services [
7]. Environmental consequences include biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, and pollution [
8]. However, Budiyantini and Pratiwi [
8] argue that several peri-urban areas lack proper development planning. This shortcoming is due to a limited understanding of the dual characteristics of peri-urban areas, which exhibit both urban and rural traits, and the weak comprehension of the interactions between these two spheres. Peri-urban areas are transitional zones between urban and rural landscapes, characterized by complex interactions and mixed land uses [
9,
10]. These areas face unique challenges due to urbanization pressures, including the conversion of agricultural land to built-up areas [
11]. Compared to megacities and metropolitan areas, the growth of secondary cities in developing countries has received less attention and faces disparities in development [
12,
13]. Current literature is limited and requires further investigation [
12,
14]. From the regional perspective, each secondary city in the region holds a distinguishable function in the regional system, such as an education center. Besides providing basic services for its inhabitants, a secondary city must prepare specific services to retain its function.
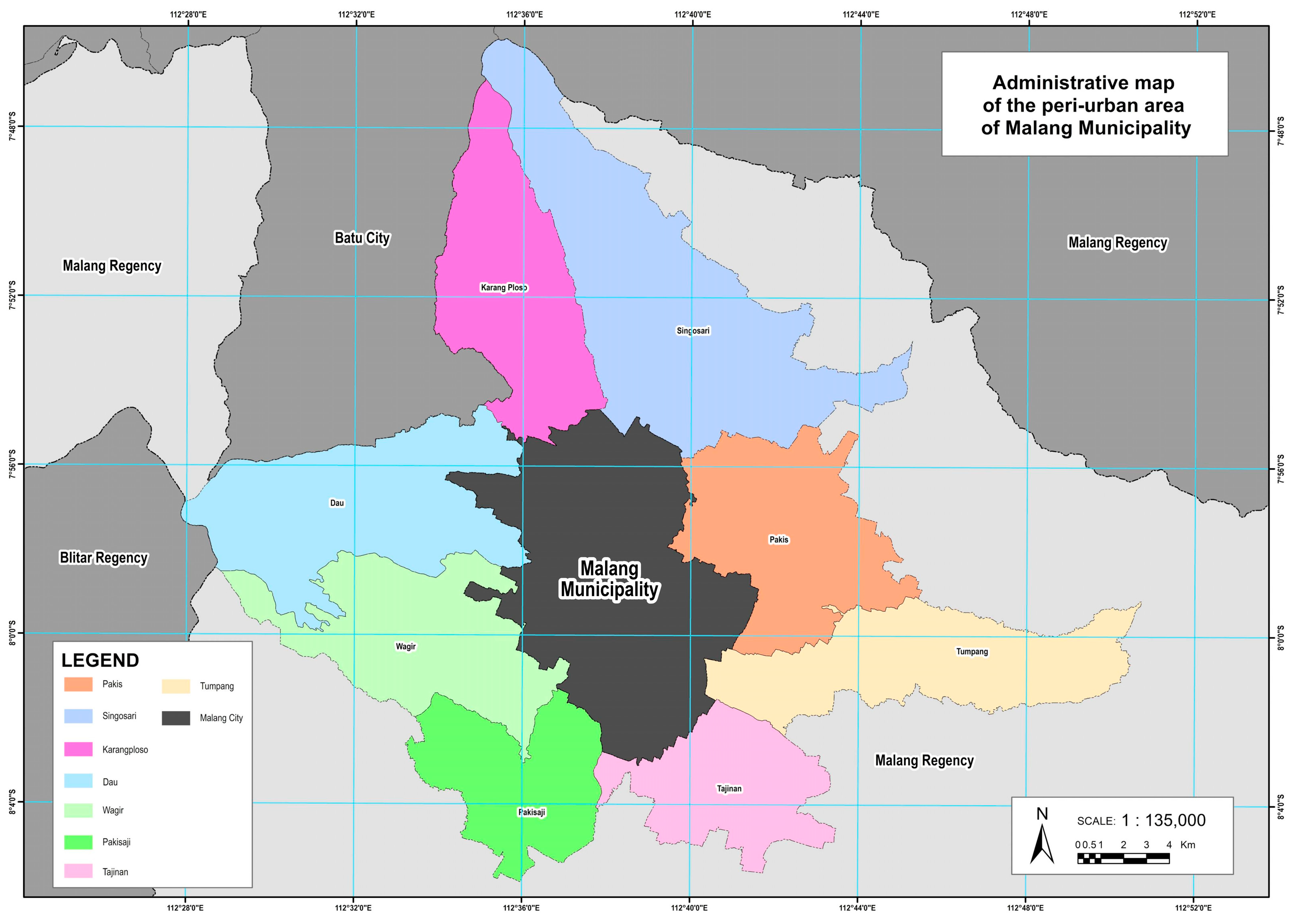
Malang Municipality serves as the central hub of the Malang Raya agglomeration, recognized as a potential metropolitan area in East Java and an integral part of the Gerbangkertosusila Megapolitan region [
15]. Malang ranks as the second-largest Municipality in East Java after Surabaya and serves as an agglomeration center. Urban development in Malang and its surroundings has formed a core urban area and satellite regions along its borders [
16]. Malang City has experienced significant urban development and sprawl, particularly from 2019 to 2023. This growth has led to changes in land use and increased built-up areas, especially in the northern districts of Lowokwaru and Blimbing [
17].
Population growth in urban areas drives increased housing demands, which often outpace the availability of urban land and cause rising land prices. Consequently, many people prefer to reside in the urban fringe [
15]. The expansion of Malang’s urban area beyond its administrative boundaries indicates urban sprawl, with built-up areas growing by 45% from 2004 to 2014 [
18].
This urban growth has resulted in uneven infrastructure distribution across the city, necessitating more balanced development to address housing and settlement needs [
19]. This trend is evident in the growing number of housing developments in Malang’s outskirts, where the residential space near the municipality center is limited. The emergence of low-density residential zones along Malang’s borders illustrates the urban sprawl phenomenon. Between 2006 and 2020, significant urban development occurred toward Malang’s periphery, especially into Malang Regency [
20].
The urban fringe of Malang has experienced significant residential development in recent decades due to land availability and lower costs. This trend is particularly evident in areas such as Tunggulwulung, where residential real estate increased by 112.8% between 2003 and 2019 [
21]. The emergence of slum settlements along Malang’s urban fringe illustrates a broader urban sprawl pattern, where protected or marginal zones are converted into residential areas without adequate infrastructure. This often leads to environmental degradation and deepens socio-economic challenges for peri-urban communities. The decision to settle in these areas is driven by interconnected factors such as economic hardship, large household sizes, and unaffordable housing in the city center. Despite inadequate facilities, peri-urban slums remain attractive due to lower living costs and access to informal employment, highlighting persistent spatial inequality in urban development [
22].
Eight Districts in Malang Regency, including Dau, Singosari, Karangploso, Pakis, Tumpang, Tajinan, Pakisaji, and Wagir, border Malang Municipality and have been directly affected by its growth [
23]. According to the 2030 land cover projection, these peri-urban districts are expected to experience a 30.8% increase in built-up areas, with approximately 11,950 hectares (22.7%) of land projected to be in mismatch with the designated spatial plan [
24]. Food crop production in Malang Regency has declined annually due to the conversion of farmland into residential and commercial areas. Between 2009 and 2021, Pakis lost 40.39 hectares of rice fields, and Singosari 71.84 hectares. Despite a permit ban since 2014, weak enforcement of spatial planning regulations has allowed the practice to continue [
25].
The rapid urban expansion in Malang is driven by various factors, including population growth, the concentration of economic activities, accessibility, real estate development, and spatial planning policies [
15]. In particular, population increase, high density, and migration are the primary drivers of urban growth in the city’s suburban areas [
25]. This expansion is further intensified by the role of the urban core as a service center, attracting continued development toward the periphery [
15]. The expansion is also influenced by good accessibility, the availability of pre-existing built-up land, and planned infrastructure projects such as the West Ring Road. Additionally, industrial development has stimulated further residential and commercial growth in adjacent areas. As a result, urban sprawl in Malang Municipality tends to follow a linear pattern along major transportation corridors [
18]. The peri-urbanization of secondary cities in Southeast Asia, exemplified by Malang, Indonesia, presents unique challenges. Urban sprawl in Malang’s western suburbs has led to a three-stage suburbanization process, resulting in agricultural involution and emerging poverty [
26]. Spatial transformation in Malang’s peri-urban areas varies, with the northern region experiencing higher transformation and a concentric development pattern [
27]. The expansion of urban settlements threatens peri-urban agriculture, as evidenced by the clustering patterns of agricultural conditions in Malang Regency [
28]. This phenomenon is not unique to Malang; similar processes are observed in other secondary cities, such as Surakarta, where significant changes in population, land use, and urban activities have occurred in peri-urban areas over the past decade [
29]. These studies highlight the complex challenges faced by secondary cities in managing peri-urban expansion and preserving agricultural land. In addition to its administrative and economic functions, Malang is recognized as a major education city in Indonesia, hosting over 60 higher education institutions, including leading public universities. This academic concentration drives a constant influx of students, generating high demand for housing, services, and infrastructure. As a result, land use in surrounding areas has changed rapidly, with residential zones converted into rental housing and informal businesses [
30].
Malang’s status as an education hub is also reflected in its urban policy through the slogan Tri Bina Citta, which places education at the core of its development vision. However, this concentration of student migration has also contributed to negative environmental impacts, such as increased CO
2 emissions and the reduction of green open spaces due to built-up land expansion [
31]. Moreover, pressure on land around academic centers has led to higher residential density, informal development, and the emergence of Urban heat island effects in campus-adjacent neighborhoods These dynamics highlight the unique and underexplored role of higher education as a catalyst of urban sprawl, particularly in secondary cities such as Malang [
30].
Given the dynamics and challenges of Malang’s peri-urban areas, this study analyzes urban sprawl morphology using the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI). A single dimensional approach is applied, focusing on spatial patterns such as edge-expansion, infilling, and leapfrogging to reflect urban dispersion and fragmentation. Temporally, this study adopts a longitudinal comparison, examining land cover changes over two periods: 2004–2014 and 2014–2024. Spatially, it operates at a micro-scale, focusing on eight peri-urban districts adjacent to Malang Municipality, using satellite imagery at sub-district level to track detailed land conversion. Several previous studies have successfully applied the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) to analyze urban growth patterns and spatial expansion modes. For instance, Tian et al. [
32] applied an improved LEI method to evaluate urban growth in Urumqi, China, integrating topological relationships among patches to accurately distinguish between infilling, edge-expansion, and outlying growth types. Their findings indicated that Urumqi’s expansion from 1990 to 2015 was dominated by edge-expansion, with increased compactness in later years.
Similarly, Wu et al. [
33] used LEI to examine the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration and found that different urban growth modes, including leapfrog, edge-expansion, and infilling, coexisted and alternated in dominance over three decades, supporting the spiral diffusion-coalescence hypothesis. The LEI helped reveal how urban sprawl led to landscape fragmentation and changing urban morphology in the region. Another application by [
34] in Alexandria, Egypt, demonstrated how LEI, combined with satellite imagery, could effectively identify landscape expansion trends in peri-urban areas, emphasizing the dominance of edge-expansion in rapidly developing zones. By adopting a similar approach, this research seeks to classify the morphological types of urban expansion in Malang’s peri-urban areas and evaluate their spatial implications between 2004 and 2014 and between 2014 and 2024.
Several international studies have employed the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) to evaluate urban sprawl patterns in rapidly developing urban areas. For example, Thinh and Kamalipour [
35] examined formal and informal morphologies in Vietnam’s peri-urban zones, highlighting the spatial complexity of transitional urban landscapes. Likewise, studies in Iran [
36] and Ethiopia [
37] have demonstrated how peri-urban expansion is influenced by a combination of topography, land-use policy, and infrastructure availability. These works typically focus on general land-use changes, but relatively few have incorporated socio-functional factors such as the presence of universities, tourism centers, and retail-service corridors into the LEI framework. Moreover, most LEI applications have been conducted at macro or citywide scales, whereas fine-scale sub-district analysis in secondary cities remains underexplored.
This study seeks to address these gaps by applying LEI at the sub-district level in the peri-urban areas of Malang, Indonesia, and examining the spatial association between built-up area expansion and the presence of functional attractors such as educational institutions, tourism zones, and service–commercial corridors. The analysis involves multi-temporal land cover classification, LEI calculation and mapping, identification of urban growth typologies, including infilling, edge-expansion, and outlying, and an evaluation of the conformity of 2024 built-up land patterns with the Malang Regency Spatial Plan (RTRW) 2010–2030.
3. Results
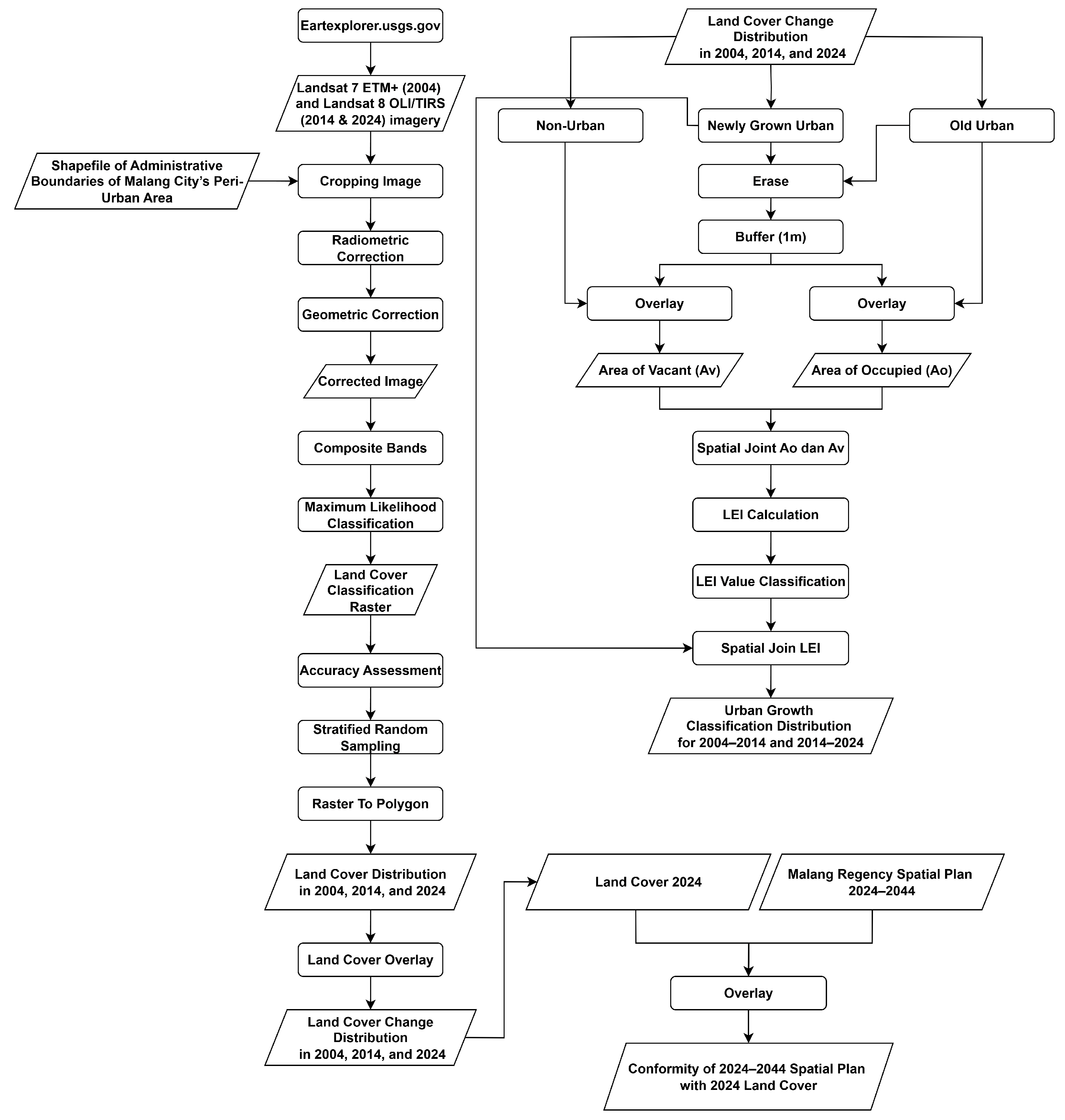
3.1. Land Cover Classification Results
The land cover classification was divided into two classes: built-up land and non-built-up land, using supervised classification with ArcGIS 10.8.1 software. The accuracy of the classification results was tested using Kappa Accuracy and Overall Accuracy calculations. For accuracy testing, 100 sample points were selected using stratified random sampling with the Accuracy Assessment Points feature in ArcGIS. In 2024, the accuracy for built-up land was 100%, while non-built-up land achieved 97.70%, with a Kappa value of 91.70%, indicating very high accuracy. In 2014, the accuracy for built-up land was 90%, while non-built-up land reached 98.89%, with a Kappa value of 88.89%, indicating good classification performance. In 2004, the accuracy for built-up land was 85.00%, while non-built-up land achieved 96.25%, with a Kappa value of 88.00%, indicating good accuracy, despite some misclassifications.
Overall, the analysis results show that the classification model provides good accuracy for land cover identification. According to [
49], an accuracy level of 85% is considered the minimum acceptable threshold for land cover mapping. Based on this benchmark, all classification results in 2004, 2014, and 2024 each exceeding or meeting the 85% threshold can be considered acceptable and reliable for identifying land cover types. This indicates that the classification model consistently performs well across all time periods analyzed.
3.2. Urban Expansion Analysis
Land cover in the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality has undergone significant changes over the past two decades. Changes in both built-up and non-built-up land cover have been influenced by various factors. The following figures provide a comparative overview of land cover data for the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality in the years 2004, 2014, and 2024.
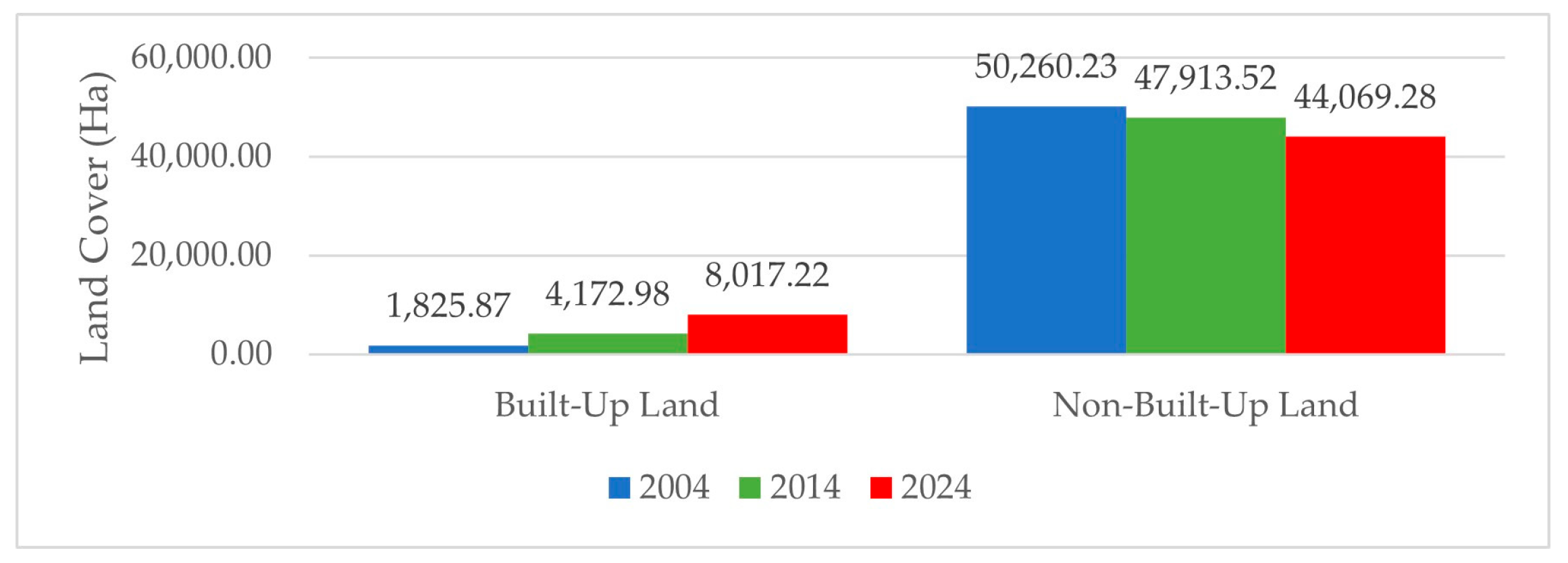
Figure 5 illustrates the change in land cover extent in Malang Municipality’s peri-urban area over a 20-year period. In general, there is a clear trend of increasing built-up land and decreasing non-built-up land over time. In 2004, built-up land covered only 1825.87 hectares, while non-built-up land dominated with 50,260.23 hectares. By 2014, the built-up area had increased significantly to 4172.98 hectares, whereas non-built-up land decreased to 47,913.52 hectares. A more pronounced change occurred between 2014 and 2024. In 2024, built-up land nearly doubled compared to 2014, reaching 8017.22 hectares, while non-built-up land further declined to 44,069.28 hectares. This pattern indicates an accelerating process of urbanization in the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality, particularly in the second decade. The significant increase in built-up land suggests mounting pressure on open spaces and agricultural land.
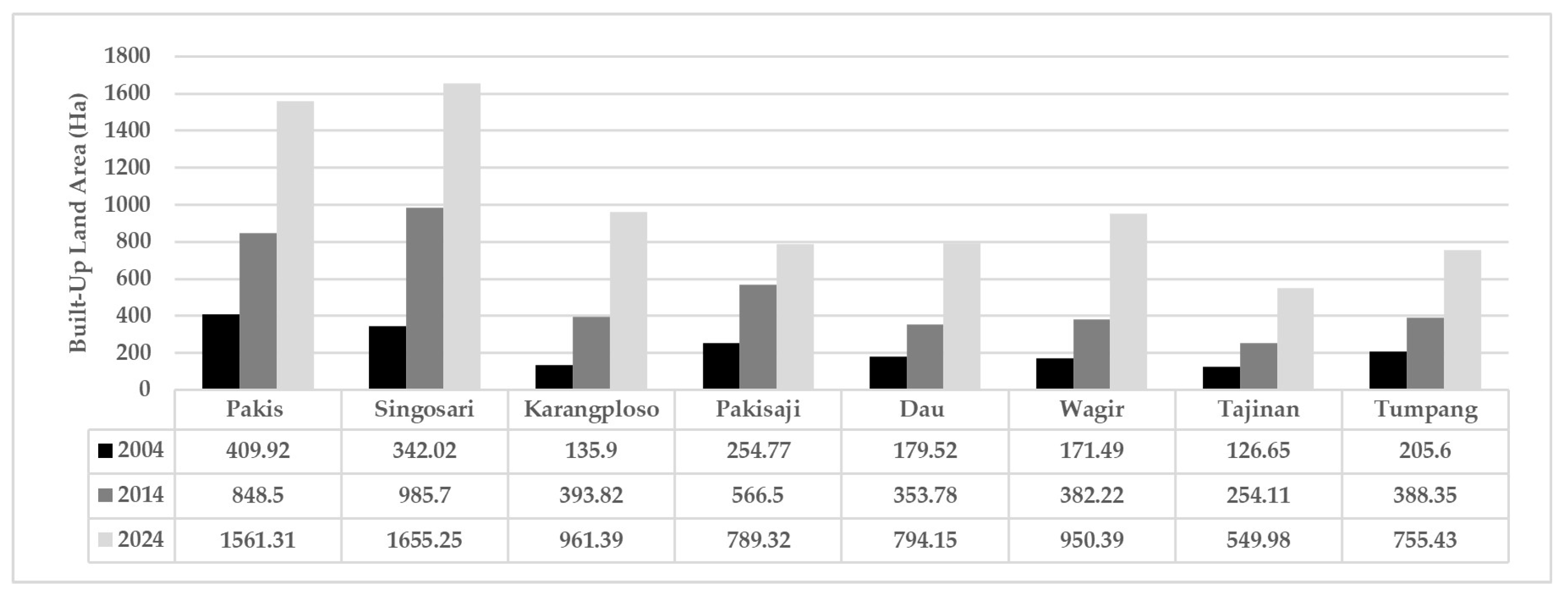
Figure 6 shows the expansion of built-up areas across several districts in Malang Municipality’s peri-urban region from 2004 to 2024. Overall, all districts experienced an increase in built-up land, although the rate of growth varied. In 2004, the built-up land in all districts was relatively low, with Pakis District having the largest area, at 409.92 hectares, followed by Singosari at 342.02 hectares. Other districts, such as Karangploso, Wagir, and Dau had less than 200 hectares of built-up land. By 2014, nearly all districts saw substantial increases. For example, built-up land in Pakis increased to 848.5 hectares, while Singosari reached 985.7 hectares. Karangploso and Pakisaji also recorded notable growth. The most significant increases occurred in 2024, with Singosari reaching the highest built-up area of 1655.25 hectares, followed by Pakis at 1561.31 hectares. Karangploso, Pakisaji, and Dau also showed sharp increases. Even districts that initially had the least built-up land, such as Tajinan and Tumpang, experienced considerable growth compared to previous years.
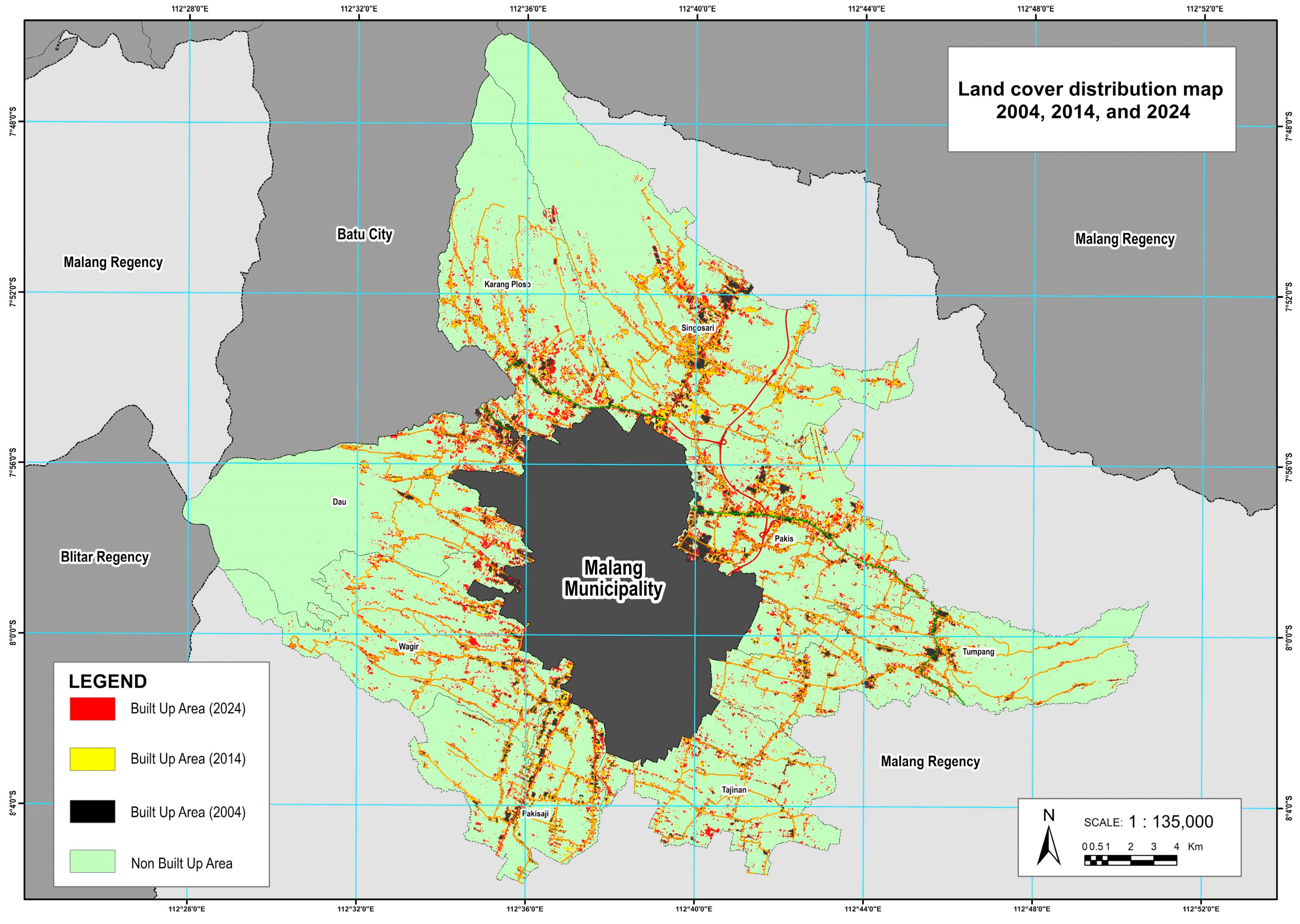
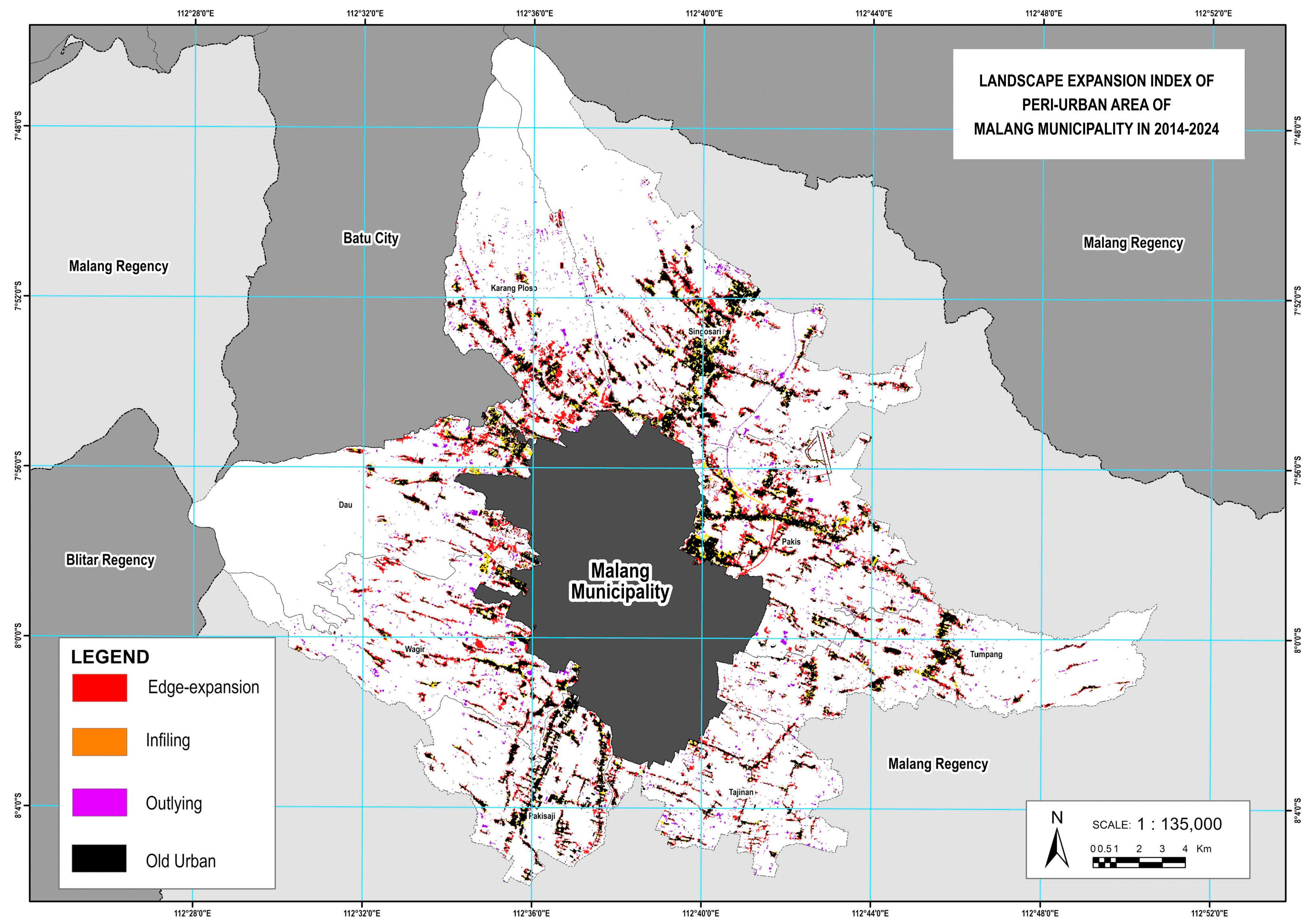
The highest increase in built-up land between 2004 and 2024 occurred in Singosari District, with an expansion of 1313.23 hectares, from 342.02 hectares in 2004 to 1655.25 hectares in 2024. Pakis District followed, with an increase of 1151.39 hectares (from 409.92 to 1561.31 hectares), while Karangploso grew by 825.49 hectares (from 135.90 to 961.39 hectares). This expansion indicates that these districts are emerging as new growth centers in the peri-urban area of Malang Municipality, driven by increasing demand for land for residential and economic activities. In contrast, the smallest growth was recorded in Tajinan District, where the built-up area increased by only 422.99 hectares over two decades, from 126.65 hectares in 2004 to 549.98 hectares in 2024. Tumpang District also experienced a relatively modest growth of 549.83 hectares. These disparities highlight the uneven nature of urban growth in Malang Municipality’s peri-urban areas. The spatial distribution of land cover change from 2004 to 2024 of the study area is shown in
Figure 7.
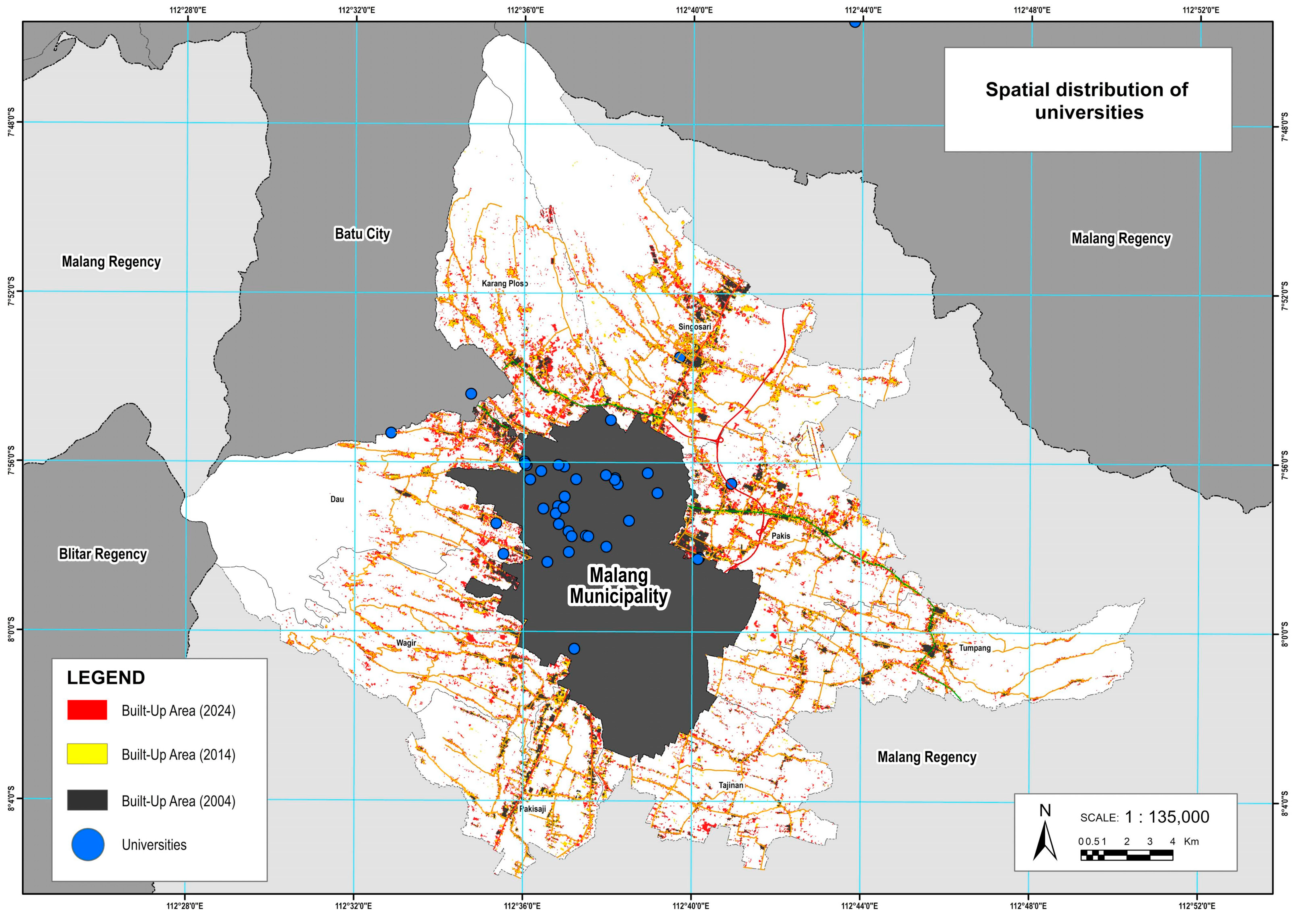
The spatial dynamics of built-up area expansion in Malang’s peri-urban region are also shaped by the concentration of higher education institutions. These institutions are predominantly located in the northern part of Malang City, in close proximity to peri-urban districts such as Karangploso, Pakis, Singosari, and Dau (
Figure 8). This geographic clustering appears to influence development patterns, as these districts consistently exhibited significant increases in built-up land from 2004 to 2024. The presence of universities in adjacent urban areas likely contributes to urban expansion through increased demand for housing, rental accommodations, commercial facilities, and supporting infrastructure to serve growing academic populations. The pattern observed in the spatial data suggests that education-driven urban growth plays an important role in intensifying land development pressure along the city’s northern fringe. This reinforces the trend of concentrated urban expansion in districts bordering academic centers, distinguishing these areas as active peri-urban growth corridors.
Figure 8 shows the spatial distribution of universities, emphasizing their concentration near rapidly expanding northern districts.
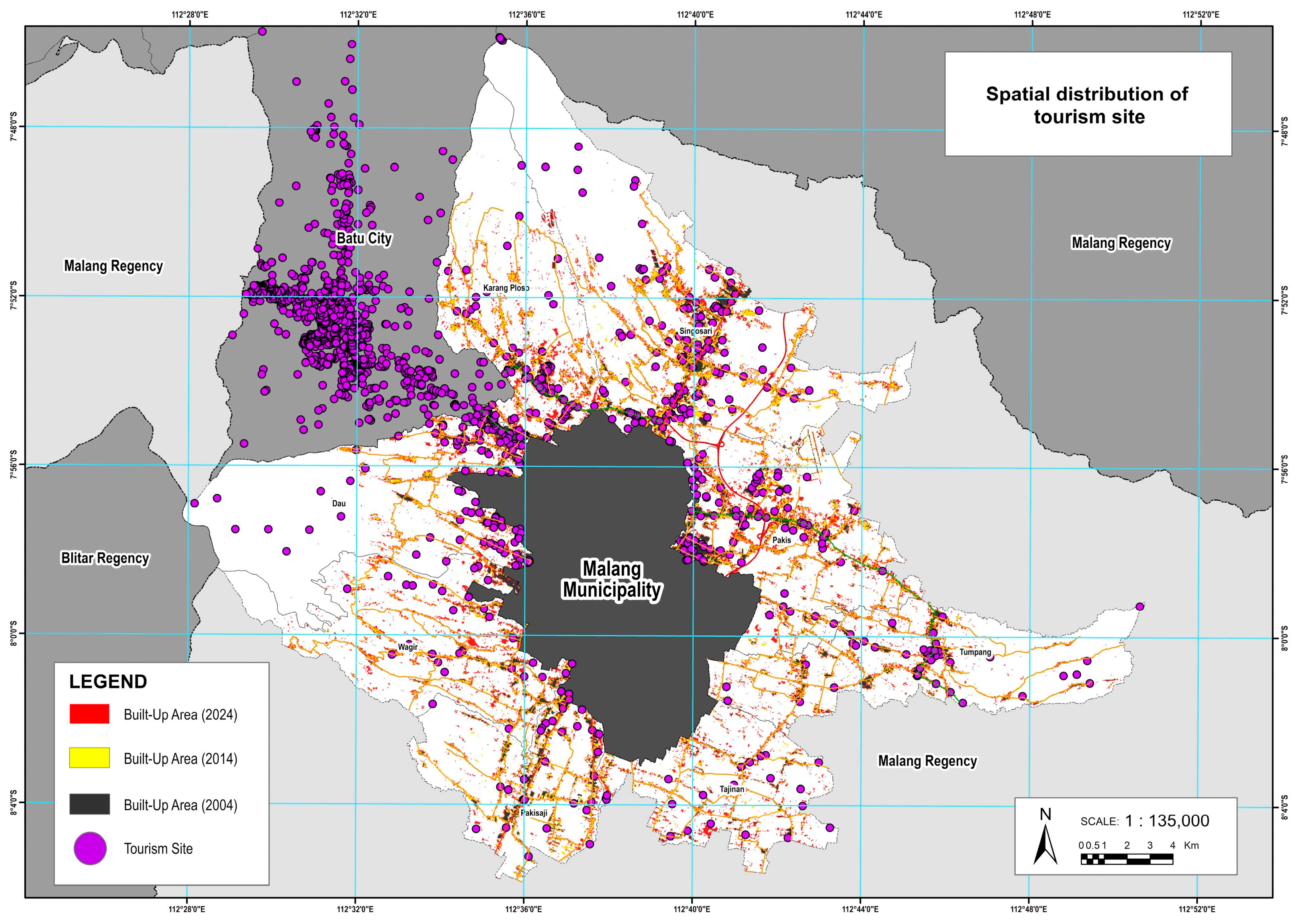
The development direction of Malang’s peri-urban areas is also influenced by the tourism sector. Batu City, with over 1200 tourism sites, drives growth in the neighboring districts of Karangploso and Dau, which directly border the city. The spatial concentration of tourism in northern Batu aligns with the significant increase in built-up land in these districts. Additionally, Malang’s peri-urban area hosts around 540 tourism points, mostly concentrated in the north, reinforcing development pressure in that region. Meanwhile, Tumpang District has also experienced notable growth, partly driven by the presence of local tourism destinations.
Figure 9 illustrates the clustering of tourism sites, particularly in the northern peri-urban region. The violet dots in
Figure 9 represents tourism sites.
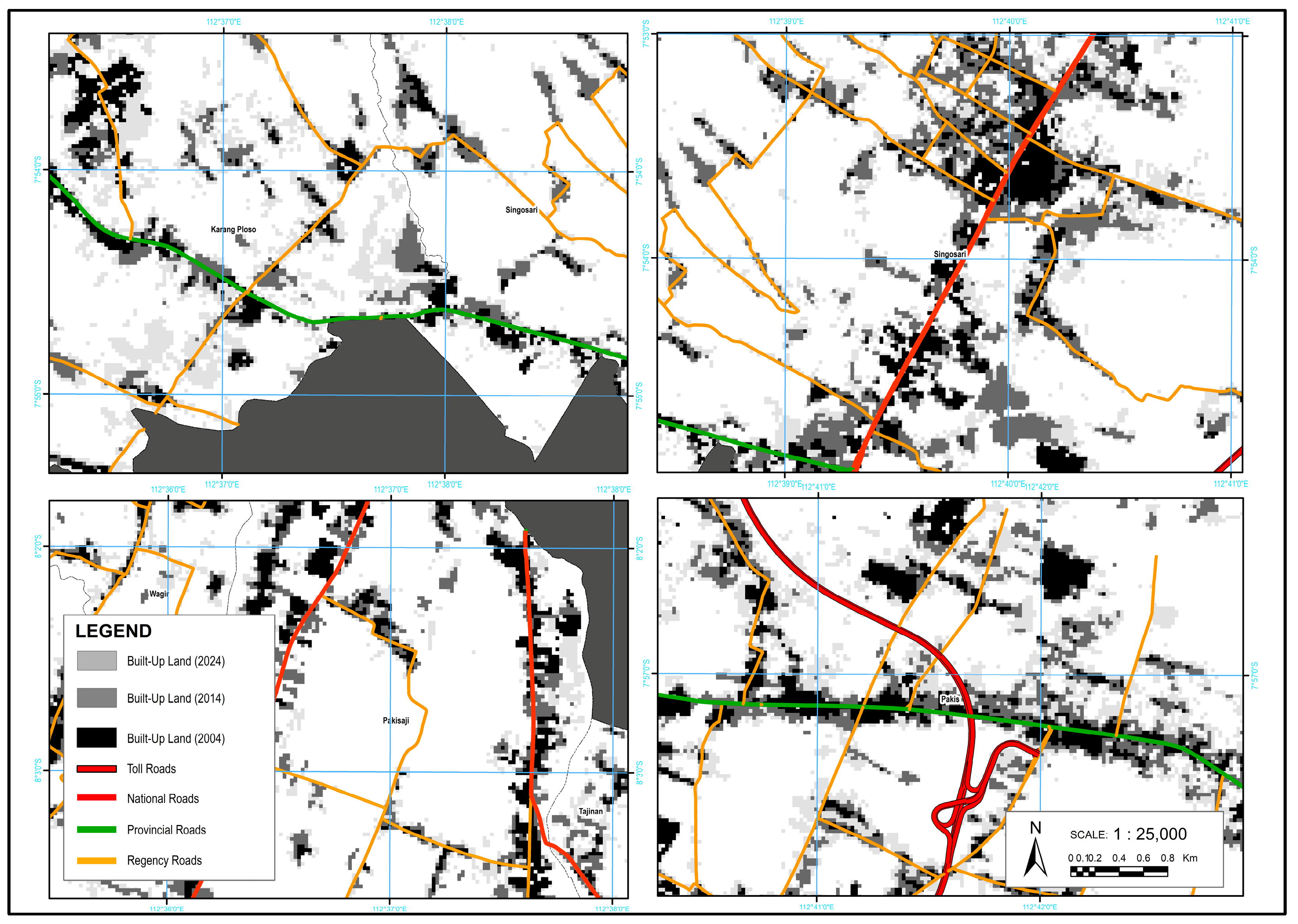
The expansion of built-up areas in the suburban region showed a strong pattern of following major road networks, as observed in Pakis, Pakisaji, Karangploso, and Singosari. This pattern is known as ribbon development, which refers to linear growth along main transportation corridors. This trend aligns with [
50], which highlights significant differences between northern and southern peri-urban Malang. The northern areas exhibit more compact and dense settlements, supported by better infrastructure and public services, while the southern areas remain more dispersed, particularly in highland zones such as Buring. However, improved accessibility, such as the construction of the Pandaan–Malang toll road, has begun to stimulate more compact development even in the southern region. These contrasts emphasize the need for balanced spatial planning to manage uneven growth and support sustainable development.
Figure 10 illustrates this ribbon development pattern, showing the concentration of built-up areas aligning closely with primary road networks. This spatial trend suggests that urban expansion in the peri-urban area is predominantly linear, following major transportation corridors. Such a pattern often indicates development driven by accessibility, where proximity to roads facilitates both residential and commercial growth along these axes.
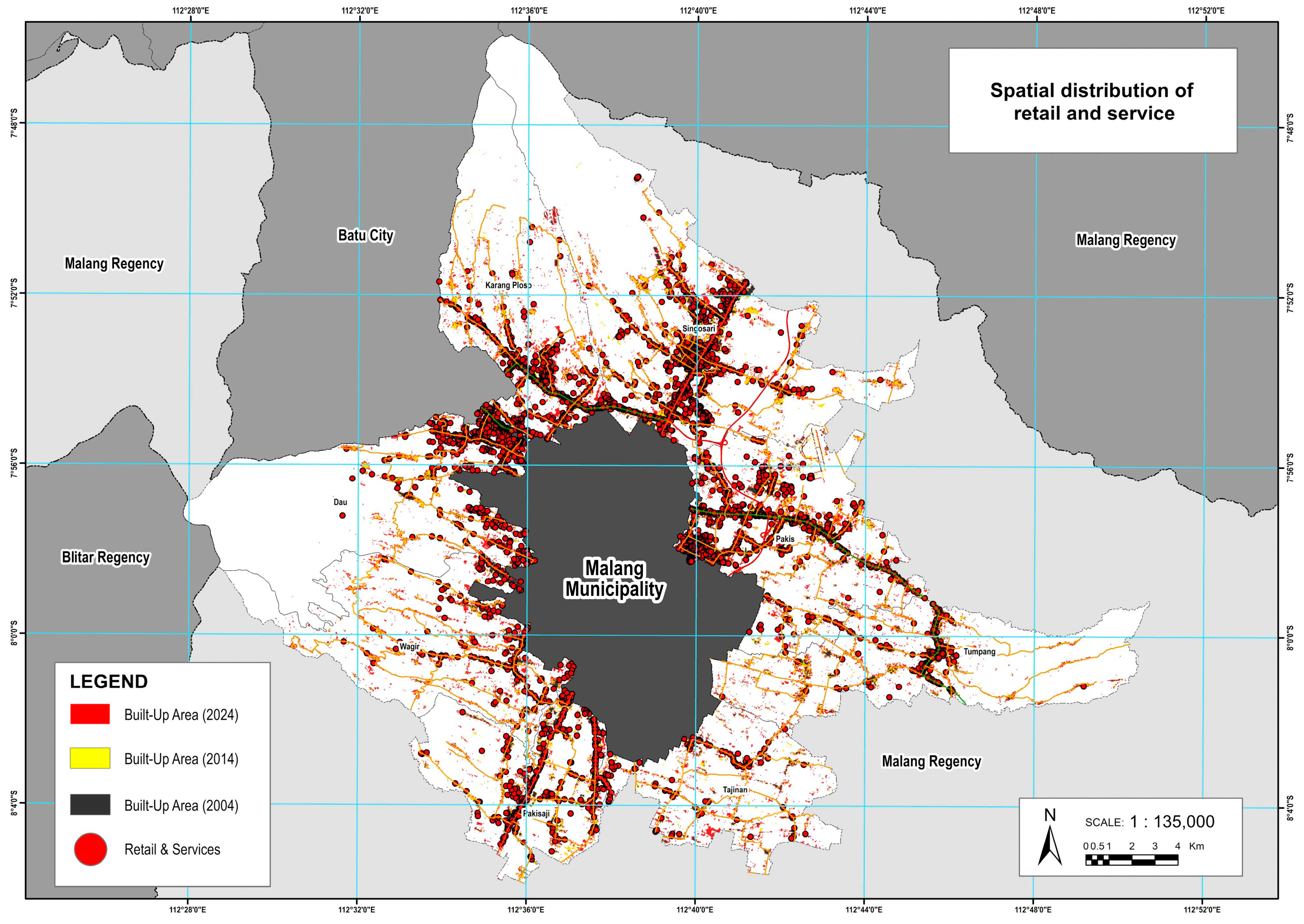
Moreover, this ribbon-like expansion is reinforced by the concentration of retail and service functions, which predominantly occur along national and provincial roads. A total of 3762 retail and service locations were recorded across Malang’s peri-urban areas, with a notable clustering along major road corridors. These establishments, such as shops, kiosks, workshops, and minimarkets, tend to form linear commercial strips that enhance accessibility and attract further residential development. The close relationship between road infrastructure, economic activity, and built-up expansion illustrates the role of transportation networks not only as mobility corridors but also as drivers of land-use change. This reinforces the dominance of ribbon development in shaping urban growth in Malang’s peri-urban region. As shown in
Figure 11, the spatial distribution of retail and service activities clearly follows the road network, visually confirming their linear, corridor-based arrangement and their influence on surrounding urban land use.
These findings carry significant implications for peri-urban land governance. The expansion of built-up land in Malang’s peri-urban areas is notably concentrated along major transportation corridors and in proximity to key urban functions, such as higher education hubs, tourism centers, and retail and service concentrations. In districts such as Karangploso, Dau, Singosari, and Pakis, rapid growth is influenced by the clustering of universities in the northern part of Malang, the presence of over 1200 tourism sites in adjacent Batu City, and the distribution of more than 3700 retail and service locations, mostly aligned along national and provincial roads.
3.3. LEI Calculation and Classification 2004–2014
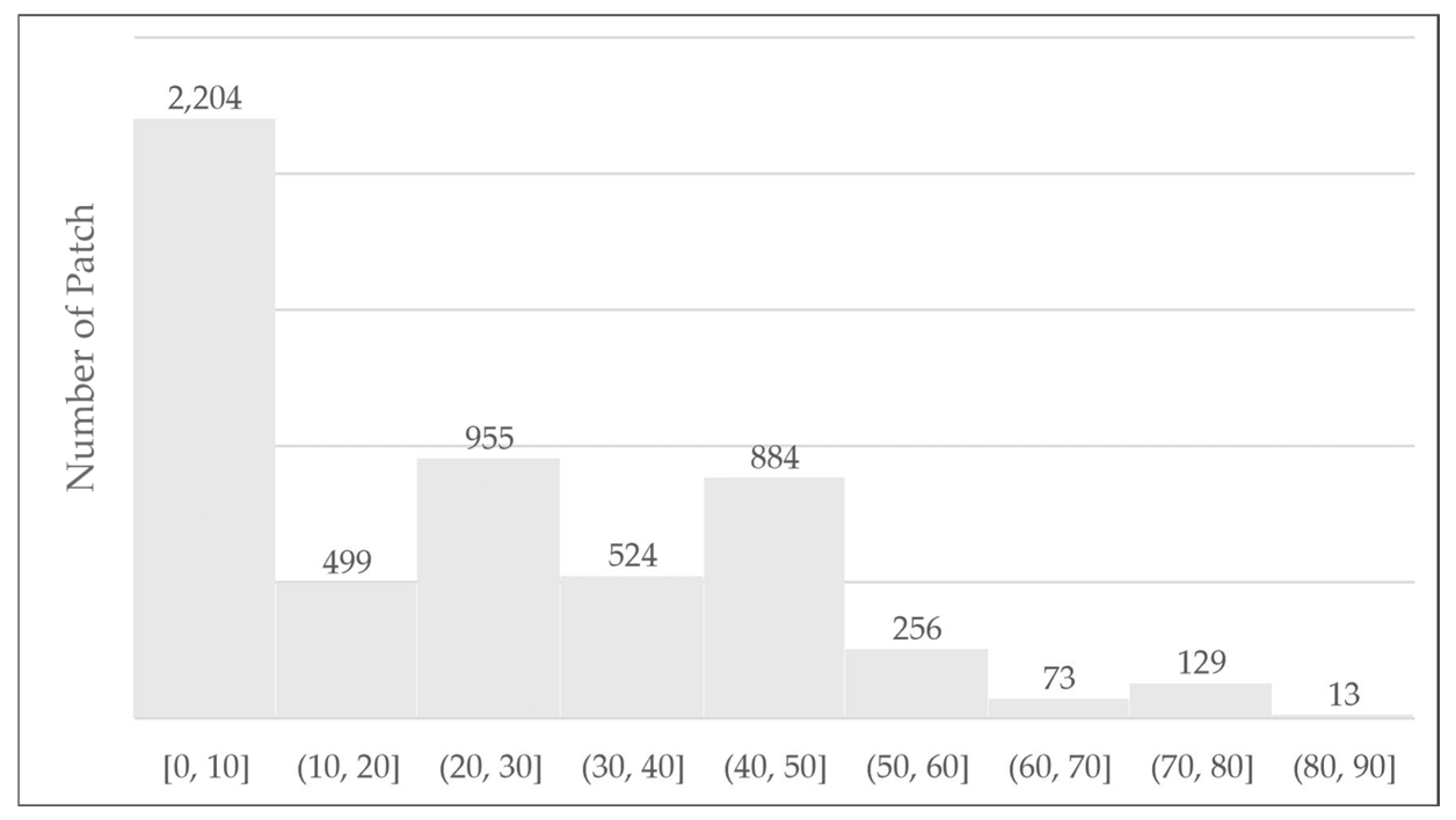
The distribution of patch numbers (
Figure 12) based on the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) indicates that most land expansion in the study area falls within the LEI range of 0–10, totaling 2204 patches. This reflects a dominance of the outlying growth pattern, characterized by developments that are not directly connected to existing built-up areas. Additionally, a substantial number of patches were found in the 20–30 and 40–50 LEI ranges 955 and 884 patches, respectively, which represent the edge-expansion type, or the outward expansion from the edges of existing built-up areas.
Moderate numbers of patches were observed in the LEI ranges of 10–20 and 30–40, indicating peripheral-oriented expansion, but at lower intensity. Conversely, higher LEI values (above 50) showed a significant decline in patch numbers: only 256 patches in the 50–60 range, decreasing to 73 (60–70), 129 (70–80), and 13 (80–90). This downward trend suggests that infilling development within unbuilt spaces of existing urban areas remained relatively limited.
Figure 13 revealed that the dominant expansion type in the study area was edge-expansion, covering 1725.37 ha. This indicates a trend of urban growth extending from the edges of already developed areas. Outlying expansion, representing disconnected development from urban cores, spanned 611.65 ha, an early indicator of urban sprawl. In contrast, infilling covered only 175.88 ha, highlighting the minimal effort toward densifying existing built-up zones. This underscores a preference for developing new land on urban peripheries rather than optimizing internal urban spaces.
Table 1 presents the distribution of LEI according to district. Based on this analysis, Singosari Subdistrict recorded the highest expansion, with 680.95 ha of built-up area added, predominantly through edge-expansion (499.89 ha), showing growth from existing centers. Pakis followed with 471.10 ha, also led by edge-expansion (328.32 ha). Meanwhile, Tajinan had the smallest expansion, only 138.83 ha, reflecting slower urban growth. These patterns indicate an uneven spatial distribution, with subdistricts such as Singosari and Pakis likely benefiting from better infrastructure and proximity to urban cores, experiencing more extensive growth compared to rural or less accessible areas such as Tajinan. As visualized in
Figure 14, the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) map for the 2004–2014 period highlights the spatial concentration of edge-expansion typologies in key subdistricts.
3.4. LEI Calculation and Classification 2014–2024
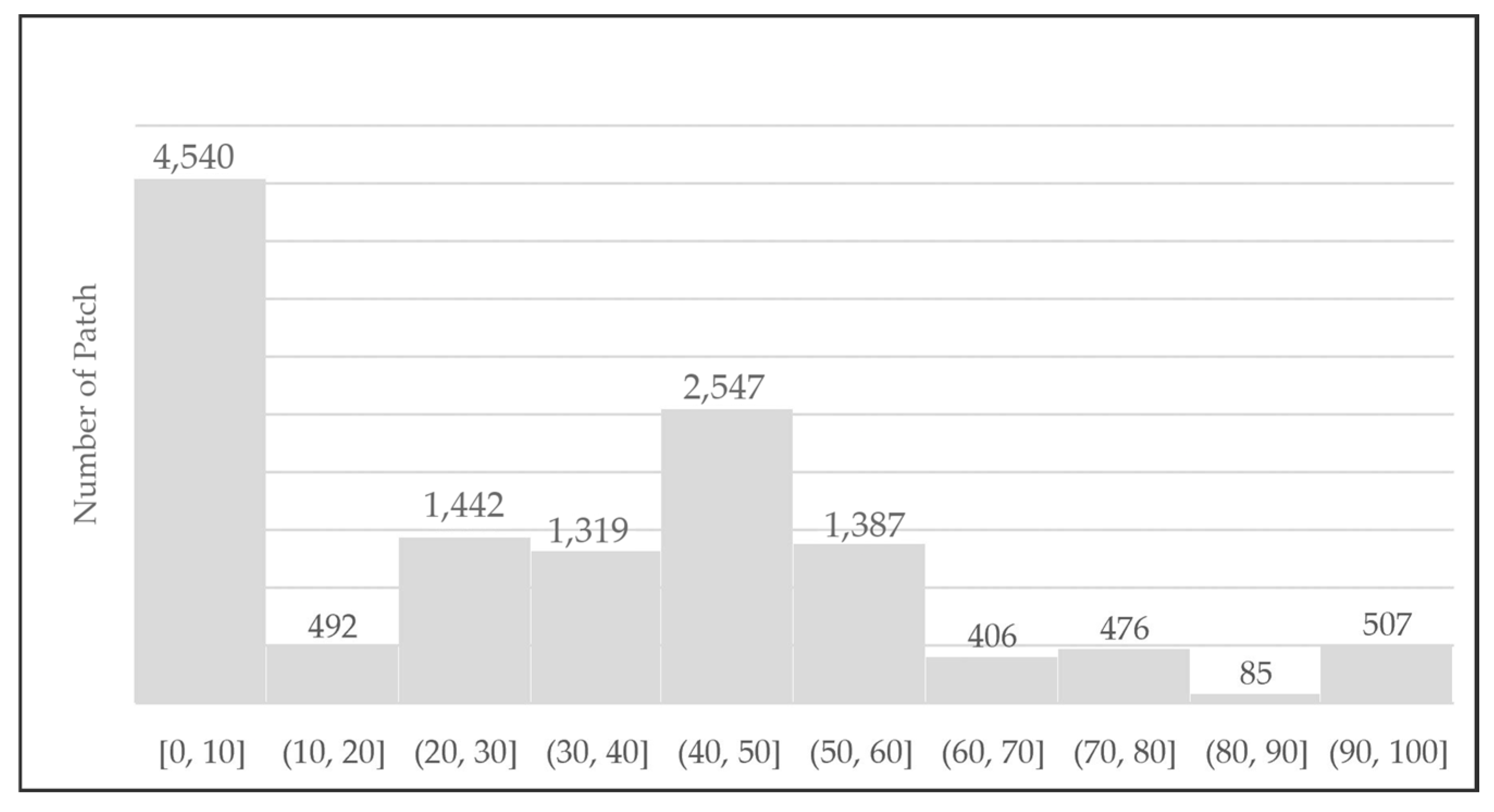
Figure 15 illustrates the fragmentation pattern of land and urban development over the past decade. The diagram shows that most patches fall into the smaller size categories, with the highest concentration found in the 0–10 ha range, totaling 4540 patches. A significant peak is also observed in the 40–50 ha category, with 2547 patches, indicating a considerable number of medium-sized patches. Other ranges, such as 30–40 ha and 50–60 ha, also show substantial figures, with 1319 and 1387 patches, respectively. Overall, this trend reveals that patch sizes are still predominantly small to medium, while larger patches are less common; for instance, only 507 patches are found in the 90–100 ha range.
Figure 16 shows that the edge-expansion type dominates with the largest area, totaling 6499 hectares. This suggests that urban expansion in the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality primarily occurs by extending the boundaries of existing built-up areas. The outlying pattern follows, covering 3842 hectares, indicating the emergence of new developments that are spatially detached from existing urban centers. Meanwhile, infilling, which represents the densification of already developed areas by filling vacant spaces, accounts for 2861 hectares. These findings suggest that urban growth in the peri-urban region is largely driven by edge-expansion, indicative of an urban sprawl pattern. Nevertheless, both outlying and infilling processes also play important roles in shaping the urban landscape.
Table 2 shows varying urban growth patterns across subdistricts, with edge-expansion emerging as the most dominant LEI type throughout all areas. This confirms that most of the urban development in Malang’s peri-urban regions expands from pre-existing built-up zones. The subdistricts with the largest total expansion are Pakis (781.99 ha) and Singosari (796.52 ha), reflecting rapid urban growth. Both areas exhibit significant expansion through edge-expansion, amounting to 504.42 ha in Pakis and 488.99 ha in Singosari. Although infilling and outlying also contribute to land development in these districts, their extents are comparatively smaller.
Figure 17 provides a spatial visualization of the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) types across Malang’s peri-urban districts.
Conversely, Pakisaji (304.86 ha) and Tajinan (322.01 ha) display relatively lower total expansion, indicating more limited growth. However, the edge-expansion pattern remains the primary mode of development, with lesser contributions from infilling and outlying. Notably, Wagir (590.12 ha) and Singosari (796.52 ha) also exhibit substantial outlying areas, totaling 146.35 ha and 143.38 ha, respectively. This signifies the emergence of new settlements or urban zones developing independently of the existing built-up environment.
3.5. Urban Growth Typology
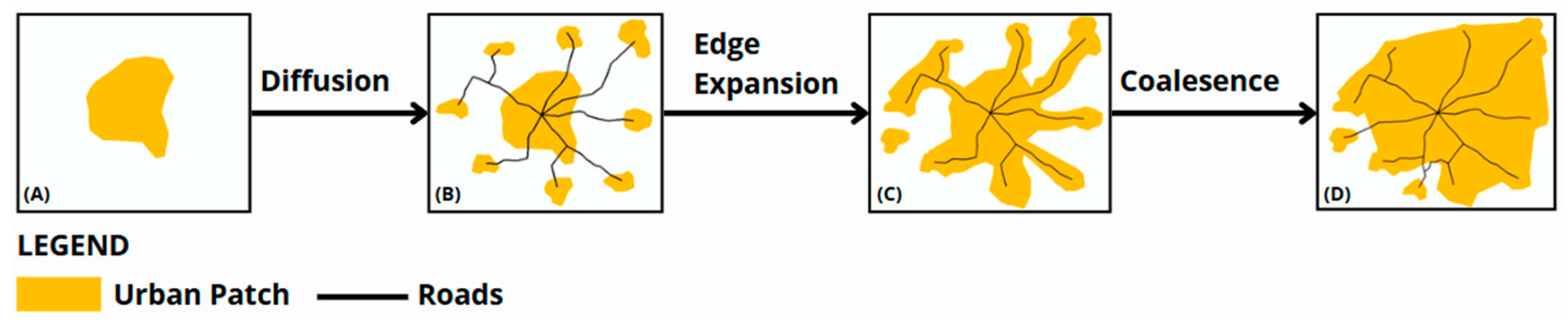
During 2004–2014, the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality exhibited characteristics of the early urban sprawl phase, corresponding to the diffusion phase in the urban growth cycle. This phase is marked by scattered, unconnected developments and the emergence of isolated new growth zones. The dominance of LEI values in the 0–10 range (2204 patches) confirms this, reflecting prevalent outlying development.
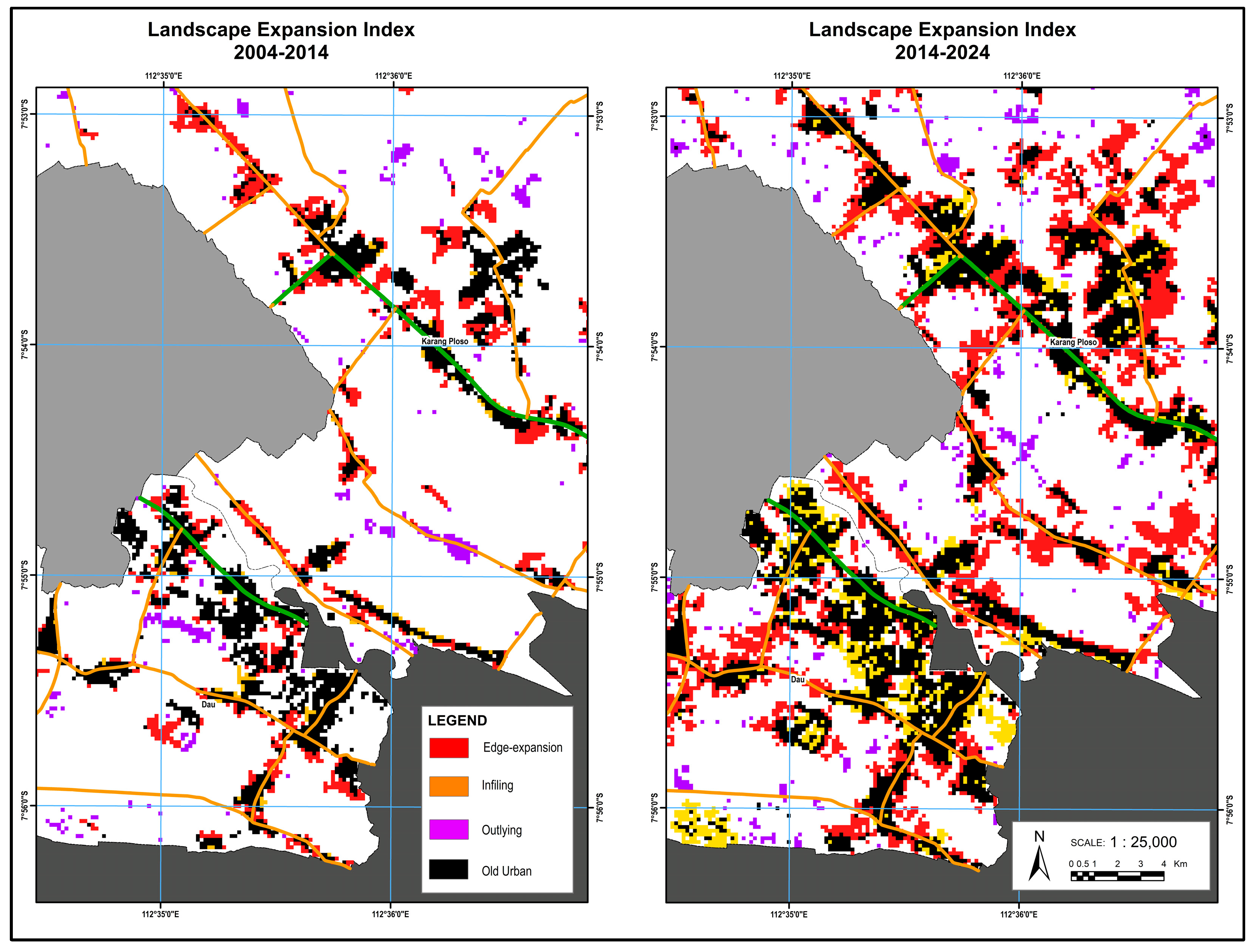
While edge-expansion was also substantial (1725.37 ha), it mainly represented linear growth along existing boundaries. The relatively small area of infilling (175.88 ha) further illustrates the lack of consolidation. Spatial disparities were evident, with subdistricts such as Singosari and Pakis showing the largest expansion, highlighting unequal growth patterns driven by access and infrastructure. From 2014 to 2024, the municipality entered the coalescence phase. This is characterized by the merging of previously scattered patches into a more consolidated urban form. Edge-expansion saw a dramatic increase (6499 ha), suggesting intensified growth from existing urban edges. Infilling also rose sharply to 2861 ha, reflecting a shift toward space optimization and compact development, aligned with smart growth principles.
Despite this consolidation, outlying development remained significant (3842 ha), particularly in suburban areas with available land. This duality-structured consolidation alongside persistent scattered growth indicates a transitional phase between sprawl and controlled urban form. Singosari and Pakis continued to lead urban growth, with rising contributions from infilling and outlying development. Even less expansive areas such as Pakisaji and Tajinan exhibited growth through edge-expansion and infilling, though at a smaller scale. These observed spatial dynamics reflect the alternating diffusion and coalescence phases theorized in urban growth literature, where cities undergo periodic cycles of outward expansion, followed by consolidation. Importantly, such transitions may not occur uniformly across space. Certain subdistricts may progress through these phases faster than others, depending on urbanization intensity and infrastructure access [
51]. As shown in
Figure 18, which illustrates the phase shift of urban expansion in Malang Municipality between 2004 and 2014 and between 2014 and 2024, the dominance of edge-expansion in the first period begins to shift toward increased infilling and continued outlying growth in the second, marking the gradual movement from diffusion to coalescence.
Outlying or leapfrog development reflects the emergence of isolated residential clusters, often initiated by developers targeting peripheral agricultural lands. Over time, these areas integrate into the urban fabric via edge-expansion, stressing infrastructure and spatial governance. Such trends warrant increased oversight by Malang Regency authorities.
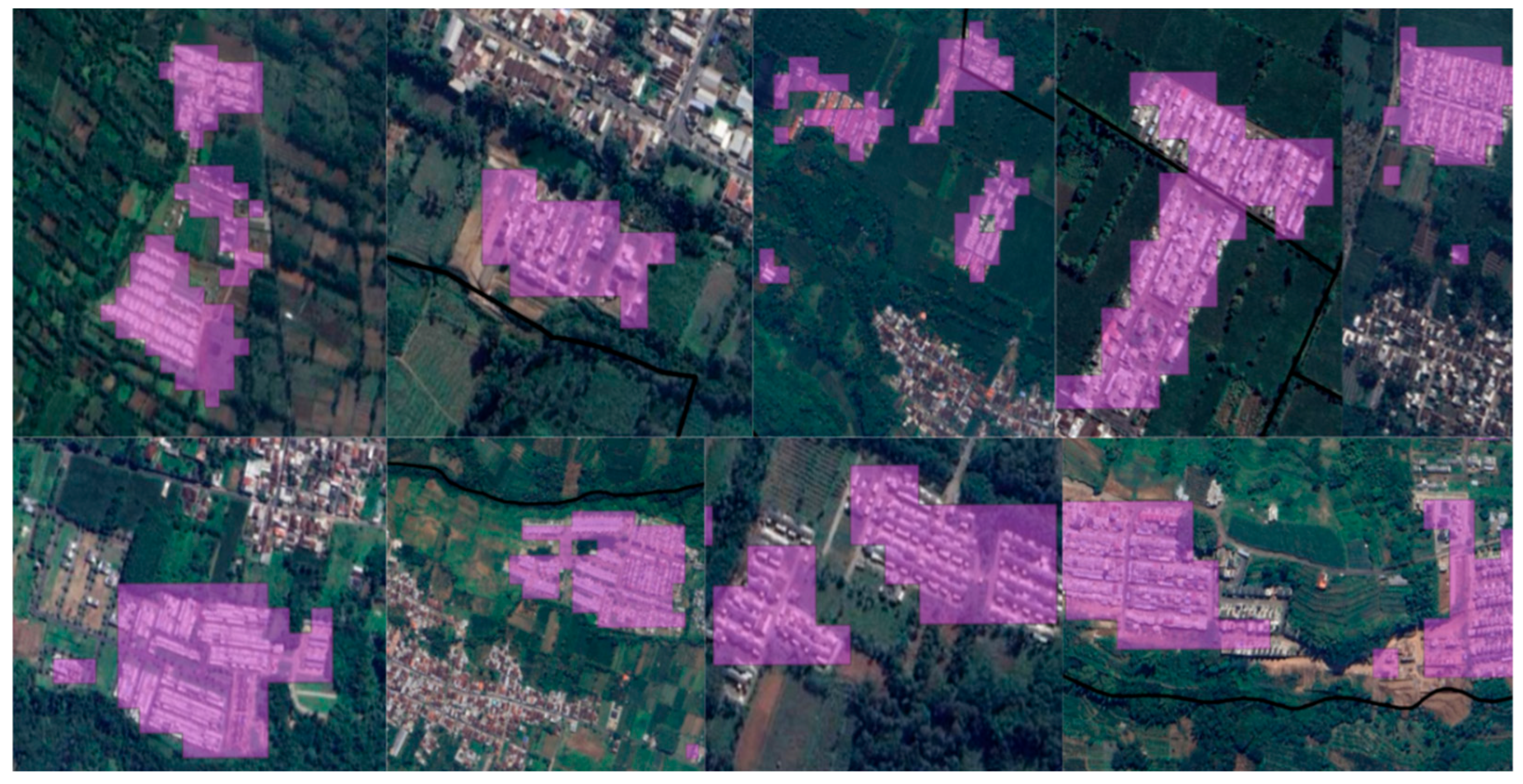
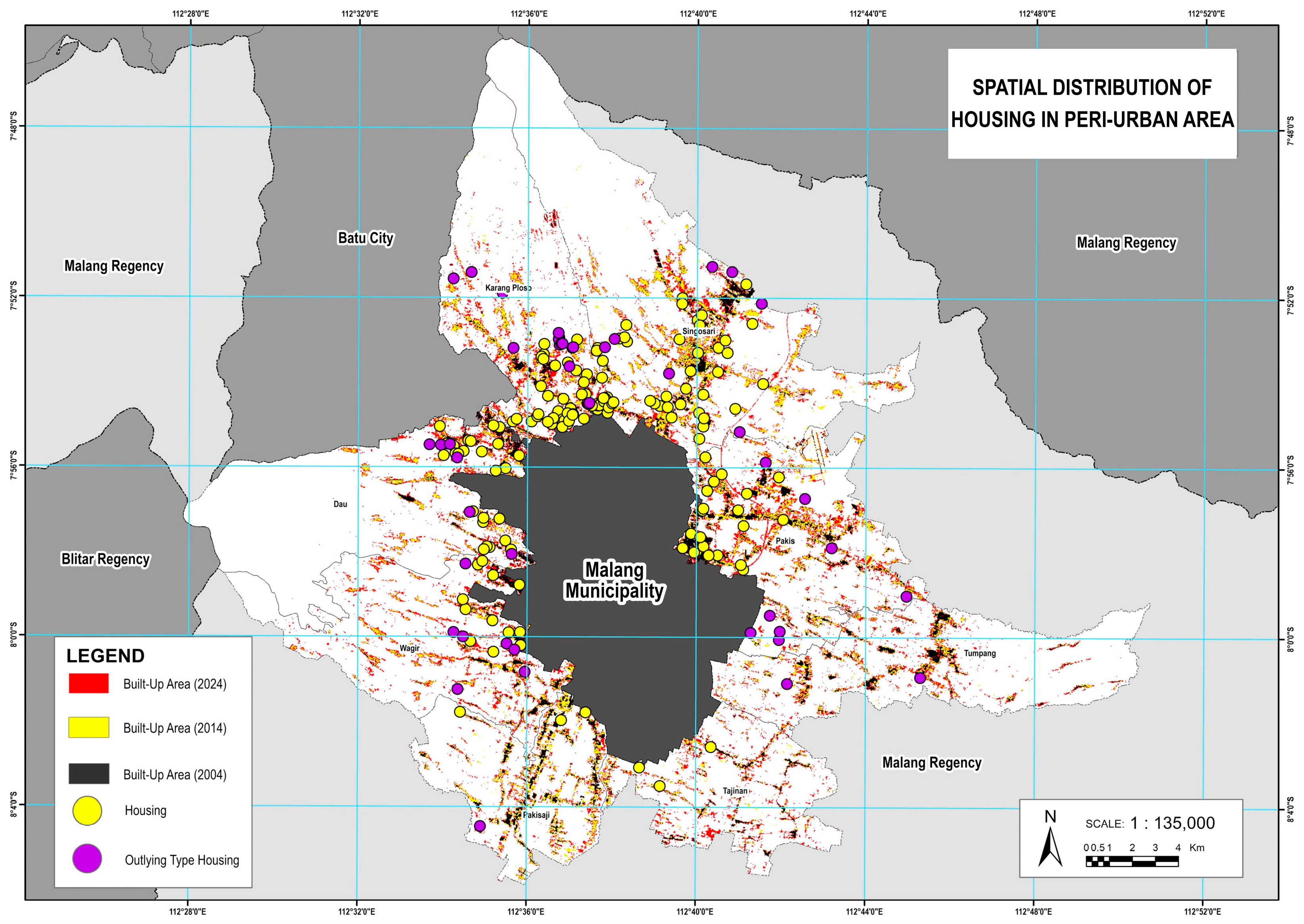
High-resolution satellite imagery from Google Earth was used as a base map (
Figure 19) to support visual interpretation, while spatial classification was conducted using Landsat imagery. Based on the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) classification, many areas identified as “outlying” were found to be housing estates developed by private developers. From a total of 242 housing estates located in the peri-urban area of Malang City, 48 were classified as outlying patches. This indicates that approximately 19.8% of the identified residential developments exhibit a spatial detachment from the existing urban core, often surrounded by agricultural or undeveloped land. The high proportion of outlying-type housing suggests a pattern of leapfrog development, in which residential expansion occurs in disconnected patches beyond the edge of continuous urban growth. This trend reflects the role of speculative land development and weak spatial planning enforcement, leading to fragmented urbanization and increased pressure on peri-urban ecosystems and infrastructure services.
As illustrated in
Figure 20, which shows the spatial distribution of housing across the peri-urban region, the scattered nature of these developments highlights the urgency of strengthening spatial planning controls. Without more effective land-use governance, leapfrog development is likely to persist, undermining efforts toward compact, sustainable, and infrastructure-efficient urban expansion.
A parallel phenomenon was observed in West Surabaya, where unchecked outlying residential development transformed farmland into elite housing, triggering urban sprawl. Consequences included diminished water catchment areas, flooding, traffic congestion, noise, and air pollution, compounded by rising land demand and dense settlements at the municipality’s fringe [
52]. The prevalence of outlying development (LEI = 0) in the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality is largely associated with the proliferation of developer-led housing clusters, which are typically separated from the main urban core by agricultural or forested land. This finding is in line with [
53], reporting leapfrog development in Ho Chi Minh City, which occurred near major infrastructure corridors and new industrial zones. However, unlike the informal sprawl patterns observed in cities such as Hanoi or Bahir Dar, most outlying settlements in Malang were found to be formally constructed residential estates. These developments reflect planned but spatially detached urban expansion driven by land price disparities and speculative investments near future infrastructure projects.
4. Discussion
Based on land cover change data from 2004 to 2024, the peri-urban area of Malang Municipality has experienced rapid growth in built-up areas, increasing from 1825.87 ha (4%) to 8017.22 ha (15.39%). This increase reflects high urbanization pressure over the past two decades. The most rapid growth occurred in Singosari, Pakis, and Karangploso Districts, which are also the main centers of municipality expansion. Conversely, Tajinan and Tumpang Districts showed slower growth. Although all regions experienced an increase in built-up areas, the growth rate was uneven.
Urban sprawl has become a pressing global concern, especially in developing countries, where rapid population growth, fragmented spatial planning, and socio-economic disparities often drive low-density urban expansion. A global study by Behnisch et al. [
54] found that regions in Southeast Asia and West Africa have experienced the most significant increases in sprawl since 1990, closely associated with accelerated urban transitions and weak spatial governance. These global patterns are echoed in Malang Municipality, where land conversion pressure remains high and poses a serious challenge to sustainable land-use and spatial planning.
The expansion of built-up areas in Malang Municipality’s peri-urban region from 2004 to 2024 demonstrates significant but uneven growth across districts. The most rapid increases occurred in Singosari, Pakis, and Karangploso, indicating their emergence as new peri-urban growth centers. This expansion is largely driven by the proximity to major urban functions such as higher education institutions, tourism destinations (especially in nearby Batu City), and clusters of retail and service activities. The development pattern follows a ribbon-like form, with built-up areas spreading along main transportation corridors, supported by improved infrastructure and accessibility. Northern peri-urban areas tend to grow more compactly due to better access to urban services, while southern areas remain more dispersed. These patterns highlight the need for balanced spatial planning to manage growth pressures, reduce spatial disparities, and support sustainable urban development in Malang’s peri-urban region. These spatial dynamics reflect similar findings in other urban regions, such as peri-urban Cairo [
34], where accessibility, infrastructure, and land value significantly influence urban expansion.
However, recent trends indicate emerging development of built-up area in Kendungkandang District, which borders Tajinan and Tumpang Districts. Between 2016 and 2022, this zone recorded the highest increase in built-up land area, 167.4 hectares, with a 30.9% expansion rate. This directional growth is supported by available land and infrastructure in the area [
19]. This trend aligns with the predicted land cover changes in Kedungkandang District. The simulation forecasts an increase of 146.78 hectares in built-up areas from 2016 to 2036 [
55]. The model thus supports the observed and expected pattern of southeastern urban growth, reinforcing the notion that future expansion will continue to intensify in this direction.
During the two decades from 2004 to 2024, the peri-urban area of Malang Municipality experienced significant changes in built-up land expansion patterns. Based on the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI) results for the 2004–2014 period, expansion was dominated by edge-expansion and outlying types, indicating an initial diffusion phase with scattered and sporadic growth. In the 2014–2024 period, expansion increased sharply, with continued dominance of edge-expansion, accompanied by a surge in infilling type, signaling a transition toward the coalescence phase. However, the high outlying values in the second period indicate that diffusion is still ongoing. The peri-urban area of Malang Municipality shows a transition from diffusion toward coalescence. Growth patterns characterized by the outlying or leapfrog development type show the tendency of new residential clusters emerging, separate from existing urban areas. This pattern is generally dominated by housing developers choosing agricultural land or open space on the Municipality’s outskirts, where land is still available. For example, in China, urban sprawl has moved from scattered edge developments to more compact and regulated forms in peri-urban areas, influenced by strategic infrastructure and economic zones [
56]. However, the transitional phase often coexists with ongoing leapfrog development, as developers continue to target cheap peri-urban lands.
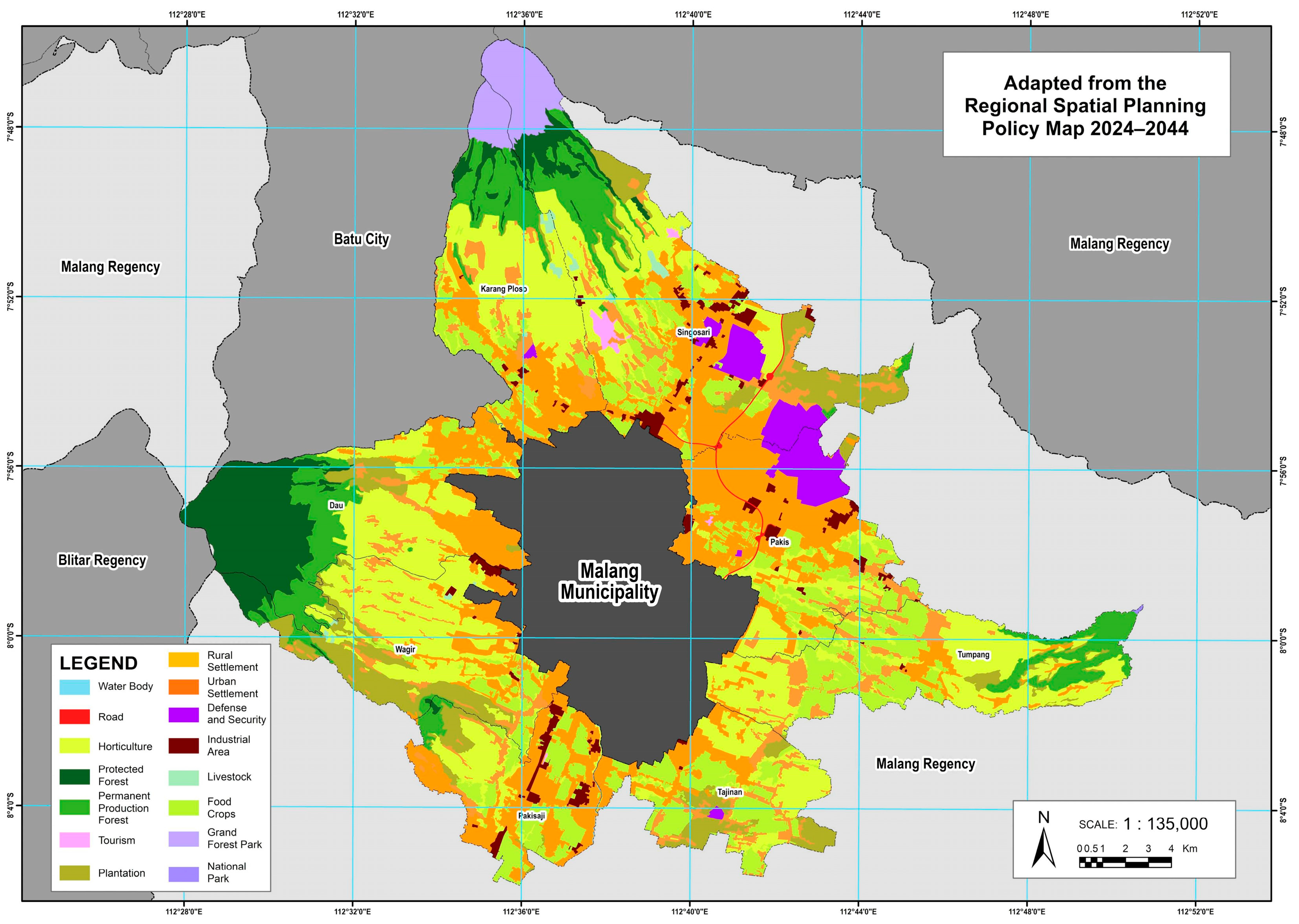
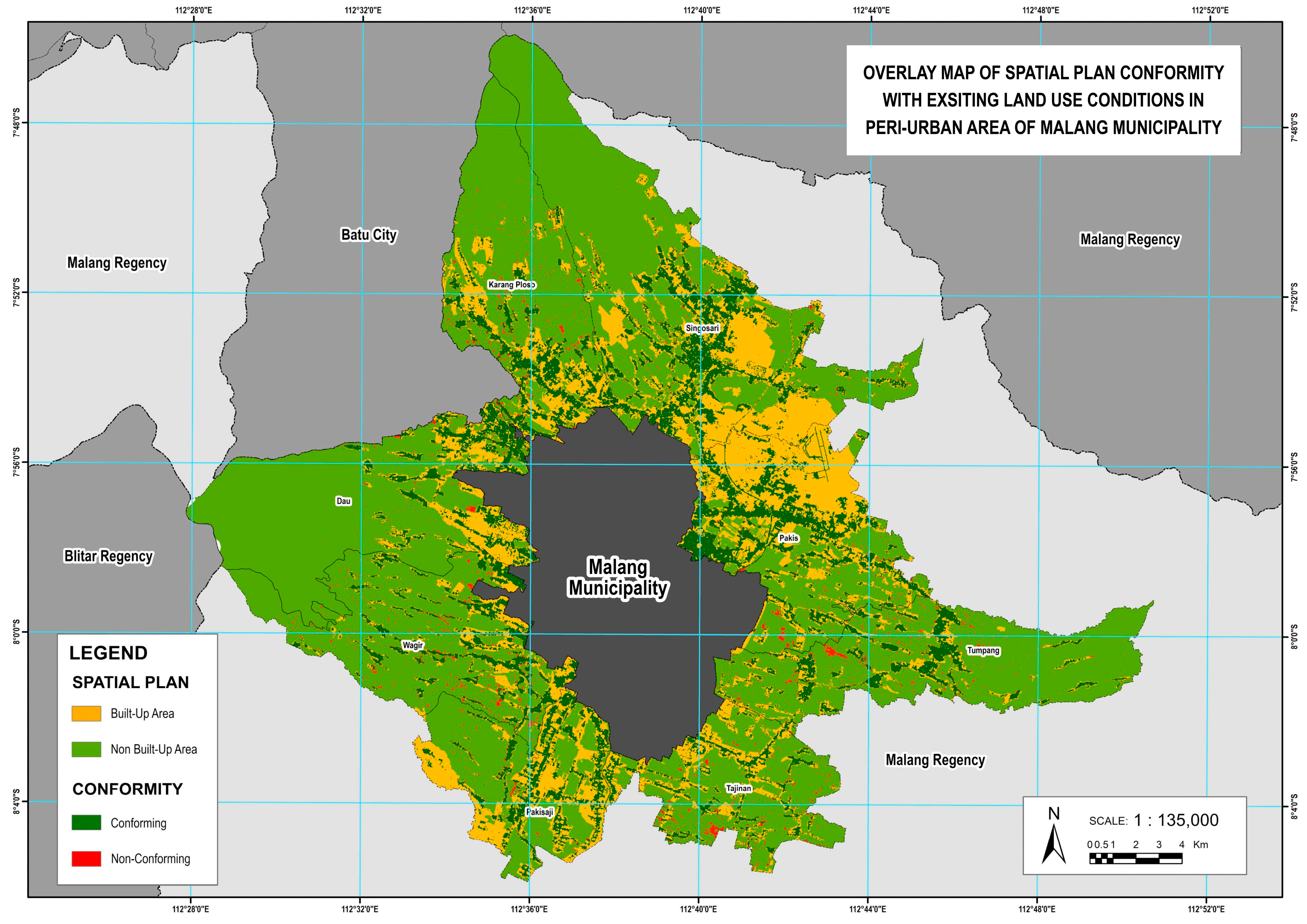
The inconsistency between the spatial plan and the existing conditions in the peri-urban areas of Malang Municipality reflects the increasing development pressure on non-built-up lands. In the 2024–2044 Municipality Spatial Plan, conformity was assessed by overlaying the existing conditions. The total area of land that has been converted into built-up areas, whether residential or for other uses, reaches 677.29 hectares. Wagir District recorded the highest amount of land-use inconsistency at 146.24 hectares. In this area, large portions of plantation and horticultural land have been converted into built-up areas. The 2024–2044 Spatial Plan was just ratified on April 30, 2024, yet it already shows inconsistency, particularly in protected forests and food crop lands designated as Sustainable Food Agriculture Zones. A total of 172.38 hectares of sustainable food agriculture zones have been converted into built-up areas. This spatial mismatch between planned and actual land use is not unique to Malang. In many cities across South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa, unregulated sprawl has directly threatened food-producing areas. A systematic review [
57] underscores that urban expansion in these regions often occurs on prime agricultural land due to weak governance and land speculation, thus posing long-term risks to food security.
This figure reflects the extent of land-use conversion pressures, even in areas that are supposed to be protected and preserved as productive agricultural lands. Tumpang District has the highest converted sustainable food agriculture zones area at 35.16 hectares, followed by Tajinan, at 31.21 hectares, and Karangploso, at 29.26 hectares. These three districts show high levels of change, likely driven by residential development needs. Dau and Pakisaji report the smallest sustainable food agriculture zone conversions, at 9.56 hectares and 5 hectares, respectively, but still form part of the overall land-use deviation pattern. This indicates that the functional deviation of sustainable food agriculture zone lands is not confined to just one or two areas, but is fairly widespread across nearly all peri-urban districts of Malang Municipality.
This ongoing land-use conversion correlates with a steady decline in annual rice production in Malang Regency. Between 2021 and 2024, rice production continuously decreased from 481,187 tons in 2021 to 480,063 tons in 2022, 466,909 tons in 2023, and sharply dropped to 394,149 tons in 2024 [
58]. This downward trend aligns with the reduction in agricultural land, particularly in zones officially designated for sustainable food production. It highlights the growing conflict between spatial planning and land-use reality, where development needs increasingly undermine long-term food security and agricultural sustainability. As shown in
Figure 21, which presents the overlay map of the 2024–2044 Spatial Plan and existing land use, the analysis highlights significant spatial mismatches that threaten the integrity of agricultural zones and raise concerns about future food security. The data underscores the urgent need for improved spatial governance and enforcement mechanisms to align land-use practices with planning objectives and to safeguard sustainable agriculture in the face of urban expansion.
In Government Regulation Number 68 of 2010 concerning Procedures for Community Roles in Spatial Planning, it is explained that the community actively participates in land-use planning, land use, and land-use control [
59]. In Government Regulation Number 15 of 2010 concerning the Implementation of Spatial Planning, it is also explained that the procedure for preparing spatial plans must involve the community in formulating the concept of spatial planning [
60]. Based on these regulations, the control of space utilization should be carried out through community involvement in a more interactive system between the government and the community.
To manage the rapid and often disorganized expansion of built-up areas in the peri-urban zones of Malang Regency that directly border Malang Municipality, the government must adopt stronger spatial planning measures. One strategic approach is the establishment of an Urban Growth Boundary (UGB) of peri-urban areas to limit areas for urban development from those designated for environmental protection, agriculture, or other non-urban functions. This is critical, considering the loss of 172.38 ha of sustainable food agriculture zones and a total of 677.29 ha of converted productive land.
The implementation of UGB can follow two main approaches: forward-looking, based on realistic urban development needs, and protective, based on safeguarding ecologically and economically sensitive areas. In parallel, stricter enforcement of spatial regulations is needed to curb ribbon development and leapfrog patterns [
61]. Residential growth should be directed toward compact, infrastructure-supported clusters rather than fragmented sprawl. The Government of Malang Regency should accelerate the completion of the Detailed Spatial Plans of urban fringe areas. Additionally, Malang Regency should consistently monitor land conversion, especially in areas affected by infrastructure megaprojects such as toll roads and the Singosari Strategic Economic Zone (SEZ), which will be essential to align future development with sustainable land-use objectives and to maintain ecological balance across the urban fringe.
Further research is necessary to examine the factors driving the expansion of built-up areas in the peri-urban region of Malang Municipality, including population growth, socioeconomic conditions, strategic location, accessibility, and infrastructure availability. Additionally, studies should consider physical and economic characteristics such as topography, disaster-prone zones, and land value to better understand the direction and pattern of future urban development. These patterns underscore the need for balanced and evidence-based spatial planning that integrates infrastructure development, economic functions, and land-use control. Future research should consider applying logistic regression or spatial modeling techniques to better quantify the relationships between spatial expansion patterns and their underlying drivers, supporting more sustainable urban growth management. Moreover, it is important to classify the peri-urban areas more rigorously using established delineation methods, such as morphological or functional approaches, to address one of the limitations of this study, which applied administrative boundaries that may not fully capture the complexity of peri-urban dynamics.
5. Conclusions
Over the past two decades, the peri-urban area of Malang Municipality has experienced rapid, yet spatially irregular expansion of built-up land. Subdistricts such as Singosari, Pakis, and Karangploso have emerged as primary urban growth centers due to their strategic proximity to infrastructure, urban services, and economic functions. Additionally, the increasing development in Kedungkandang District indicates a spatial shift toward southeastern expansion, aligning with land cover change projections for the period 2016–2036. Using the Landscape Expansion Index (LEI), this study identified a transitional shift in urban growth morphology, from a diffusion phase dominated by scattered outlying expansion, toward a coalescence phase, marked by increasing edge-expansion and infilling development. Nevertheless, the persistence of outlying patterns highlights ongoing leapfrog developments, particularly in peri-urban areas with weak spatial control and abundant available land.
The spatial overlay analysis between actual land use and the Malang Regency Spatial Plan (2024–2044) revealed a significant planning discrepancy, with 677.29 hectares of non-built areas, including 172.38 hectares of protected sustainable food agriculture land, having been converted into built-up areas. This raises serious concerns regarding spatial plan enforcement and long-term environmental and food security risks. To address these challenges, stronger spatial governance is urgently needed. Strategies should include the implementation of Urban Growth Boundaries (UGBs), the acceleration of Detailed Spatial Plan formulation, and enhanced community participation, as stipulated by national spatial planning regulations. These approaches are essential for managing urban expansion while safeguarding ecological functions and agricultural productivity.
The scientific contribution of this study lies in its integrative approach, combining LEI-based sprawl typology analysis, spatial policy evaluation, and urban function mapping using both remote sensing and point-of-interest (POI) data. This multidimensional method offers valuable insights for understanding and managing peri-urban growth in rapidly urbanizing regions. Future research should apply spatial modeling techniques to quantify the influence of socio-economic, physical, and policy-related variables, thereby supporting more adaptive and sustainable spatial planning practices in peri-urban landscapes.