Evaluation of Spectral Indices and Global Thresholding Methods for the Automatic Extraction of Built-Up Areas: An Application to a Semi-Arid Climate Using Landsat 8 Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
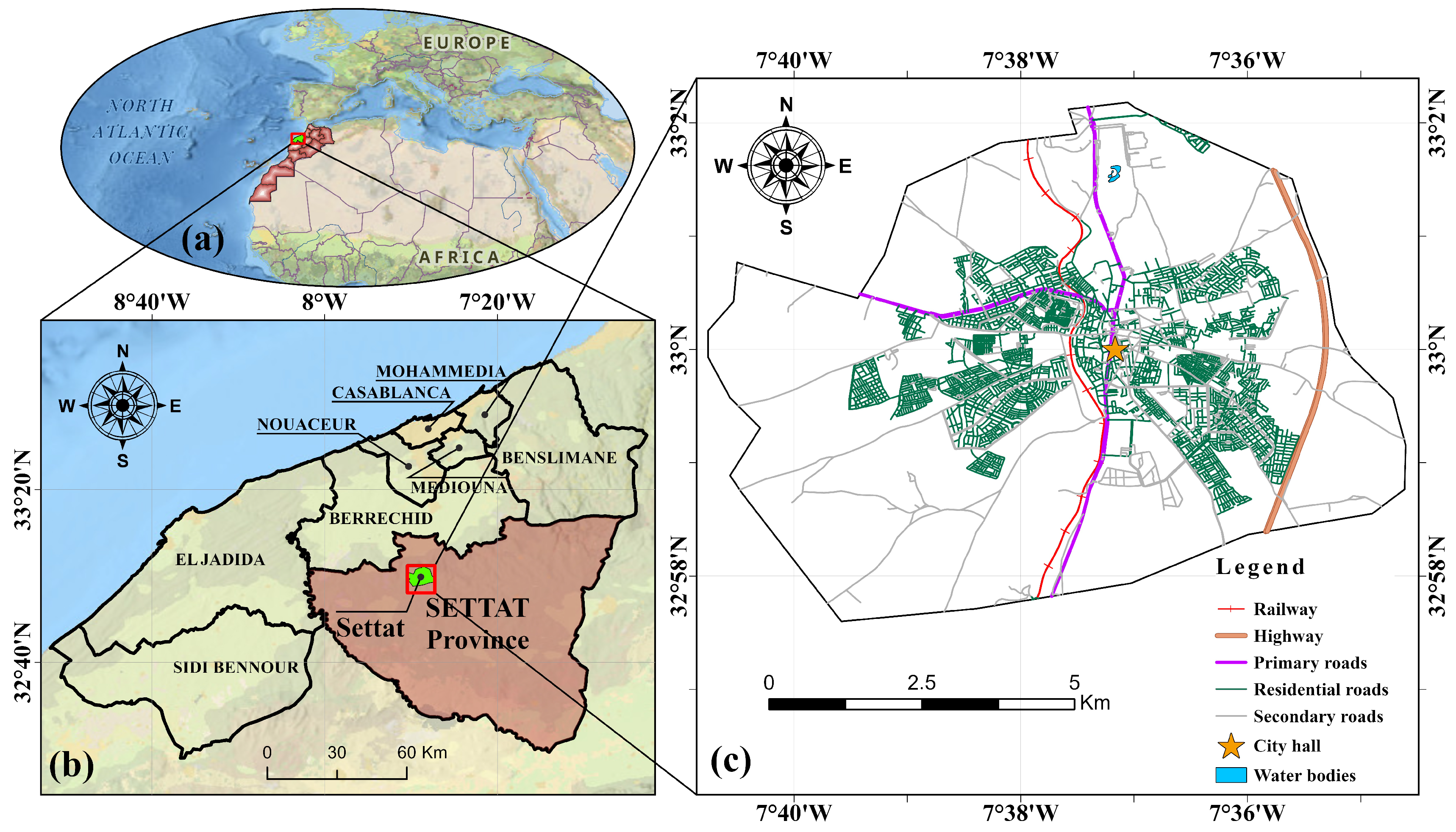
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Datasets
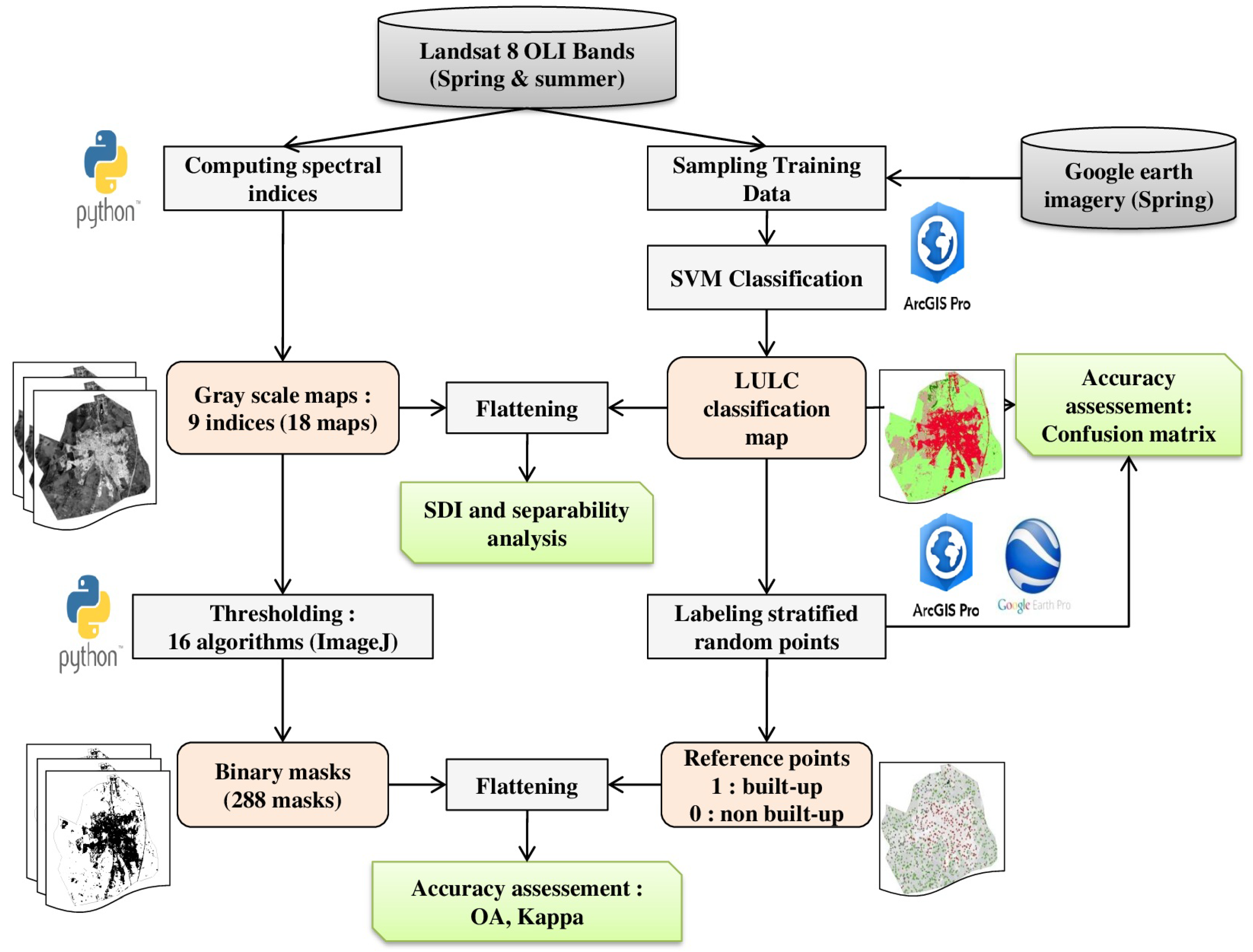
2.2. Methods
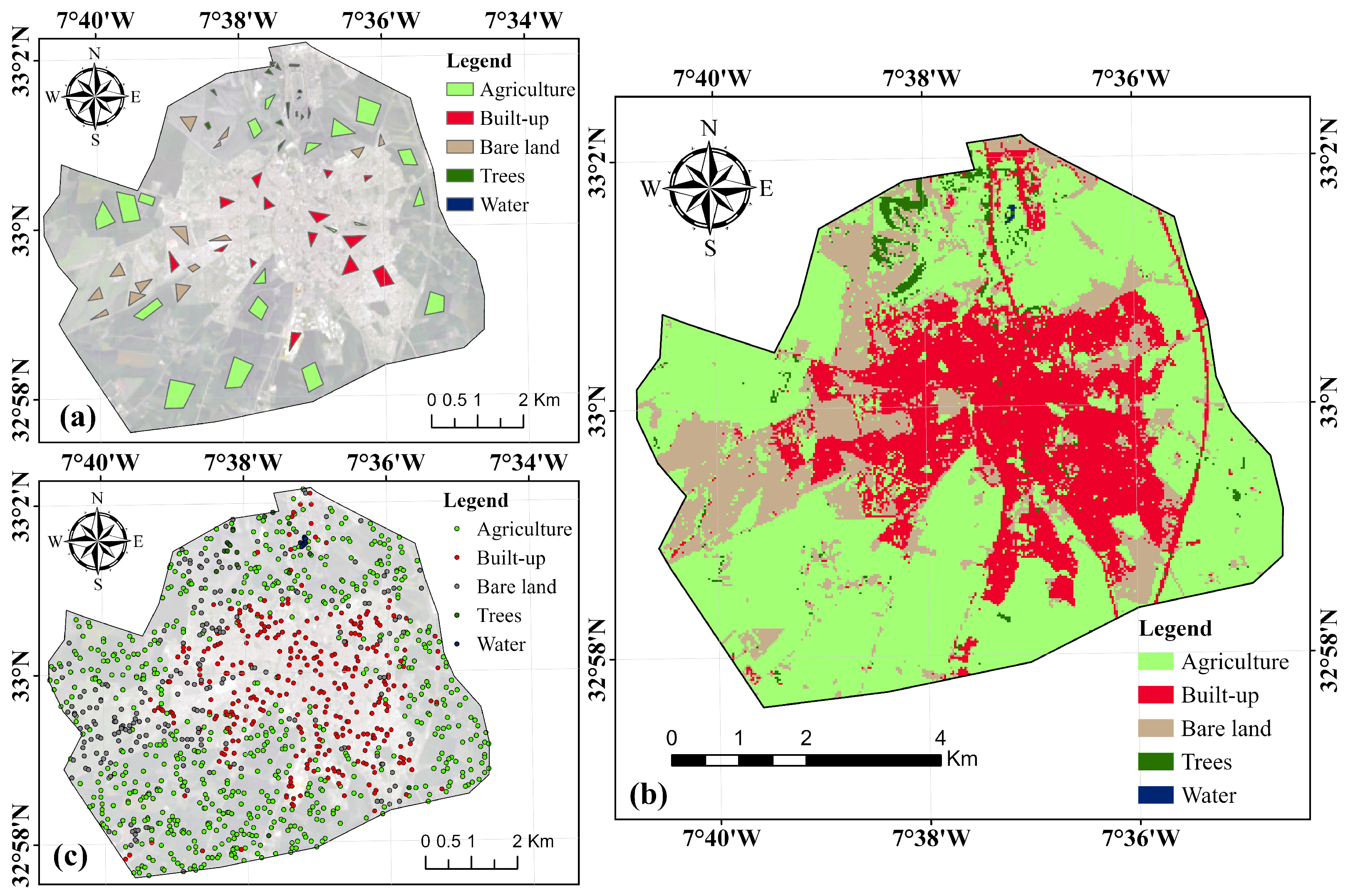
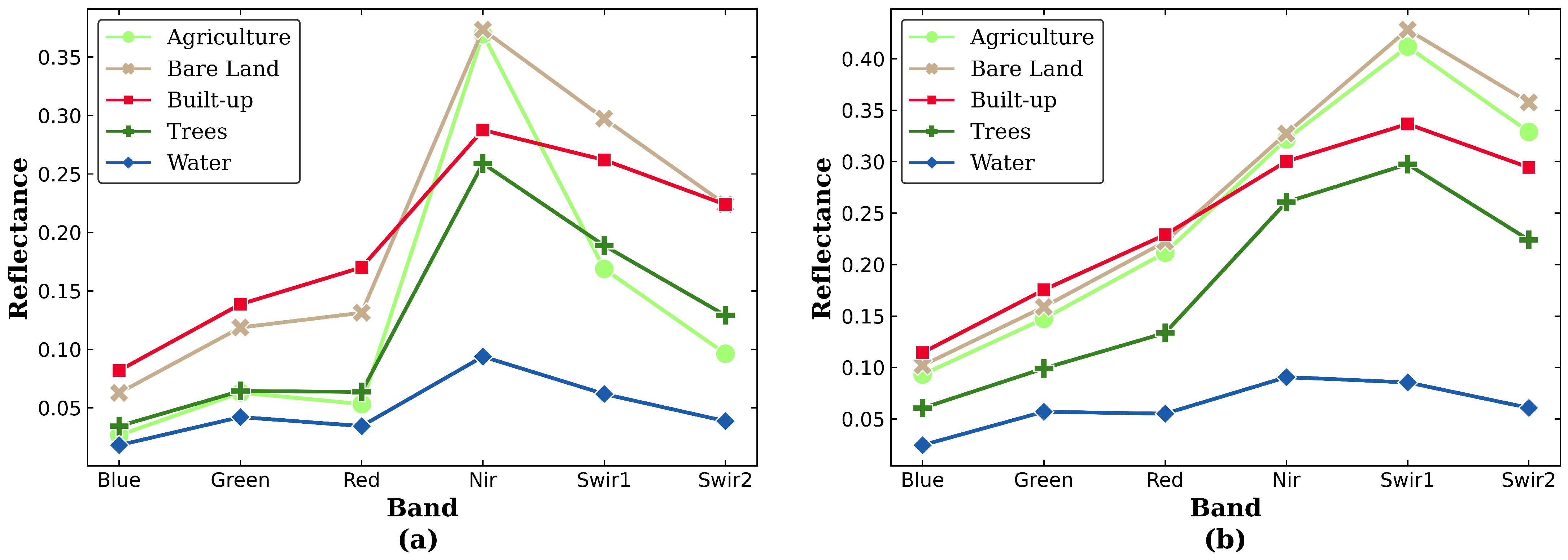
2.2.1. LULC Classification and Spectral Profiles
2.2.2. Spectral Indices
- Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI)
- Vis-red/green-NIR Built-up Indices (VrNIR-BI and VgNIR-BI)
- Swir Red index (SWIRED)
- Normalized Built-up Area Index (NBAI)
- Built-up Land Features Extraction Index (BLFEI)
- Built-Up Index (BUI)
- Combinational Biophysical Composition Index (CBCI)
- Perpendicular Impervious Surface Index (PISI)
- Enhanced Normalized Difference Impervious Surfaces Index (ENDISI)
2.2.3. Thresholding Methods
- Mean thresholding method
- Percentile thresholding method
- Otsu’s thresholding method
- Minimum Error thresholding method
- K-means clustering method
- IsoData clustering method
- Intermodes thresholding method
- Minimum thresholding method
- Moments thresholding method
- Triangle thresholding method
- Rényi’s entropy and Shaboo’s thresholding method
- Maximum entropy
- Yen’s thresholding method
- Huang’s thresholding method
- Shanbhag’s thresholding method
- Li’s thresholding method
2.2.4. Separability Analysis
2.2.5. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Index-Based Maps
3.2. Separability Potential of SIs and Sensitivity to Seasonal Variations
3.3. Characteristics of Pixel Intensity Distributions
3.4. Accuracy Assessment
3.4.1. Thresholding Consistency
3.4.2. Overview of Highest Performing Binary Maps and Manual Thresholding
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
- The performance of an SI depends on the contrast it produces between BUAs and each of the other land covers. As a consequence, it can be deduced that the proportions of these land covers in an area of interest are also to be taken into consideration when adopting an index, as some SIs can distinguish BUAs from one or more particular land cover types better than others.
- Overall, SIs are better applied in wet conditions for semi-arid climate or regions with similar reflectance properties to the study area. Nonetheless, BLFEI, SWIRED, and BUI can achieve high accuracies in both wet and dry conditions, as they provide a balanced separability between BUAs and other land covers except water in both conditions. In contrast, ENDISI and NBAI resulted in poor separability and unimodal distributions in summer and, therefore, are deemed unsuitable in dry conditions.
- In terms of consistency, multiple thresholding methods are applicable in both dry and wet conditions when bimodal distributions are observed and can be reliable for automation processes. These methods are K-means, Huang, IsoData, Li, Moments, Otsu, Percentile, and Shanbhag. Other methods, such as Intermodes, Maximum entropy, Renyi’s entropy, Yen, Minimum error, Minimum, and Triangle, are not recommended when no evidence of the distribution of pixel values is available.
- The use of BLFEI in combination with the Minimum method was found to be the most effective approach under wet conditions in semi-arid climates. Likewise, the use of BLFEI in combination with either Li, Huang, Triangle, Otsu, K-means, or IsoData is the most effective approach under dry conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hejazi, M.; Wise, M.; Vernon, C.; Iyer, G.; Chen, W. Global urban growth between 1870 and 2100 from integrated high resolution mapped data and urban dynamic modeling. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Corbane, C.; Freire, S.; Batista e Silva, F. Built-up areas are expanding faster than population growth: Regional patterns and trajectories in Europe. J. Land Use Sci. 2022, 17, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Zeleňáková, M.; Vranayová, Z.; Fathy, I. Evaluating the impact of urban growth on the design of storm water drainage systems. Water 2020, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, M.A.; Morshed, S.R.; Morshed, S.Y. Impacts of land use-based carbon emission pattern on surface temperature dynamics: Experience from the urban and suburban areas of Khulna, Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 22, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.N.; Akter, K.S.; Faridatul, M.I. Assessing the Impact of Urban Expansion on Carbon Emission. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2024, 23, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Stouffs, R. Human-earth system dynamics in China’s land use pattern transformation amidst climate fluctuations and human activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyadeyi, O.A.; Oyadeyi, O.O. Towards inclusive and sustainable strategies in smart cities: A comparative analysis of Zurich, Oslo, and Copenhagen. Res. Glob. 2025, 10, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaïd, F.; Apeaning, R.; Arora, A. Advancing Cities’ Resilience: A Comprehensive Review and Mapping of Research. In Climate-Resilient Cities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Z. ASI: An artificial surface Index for Landsat 8 imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, N.P.; Savaglio, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dumba, B. Future of urban remote sensing and new sensors. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 56, 2281073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, N.; Kanthe, A.; Gangane, J.; Padiya, P.; Sumithra, T. A Complete Study of Remote Sensing-Sentinel-2 Satellite Data for Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Analysis. Panam. Math. J. 2025, 35, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.A.; Hailu, B.T.; Suryabhagavan, K.V. Evaluation of spectral built-up indices for impervious surface extraction using Sentinel-2A MSI imageries: A case of Addis Ababa city, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2022, 8, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z. Combinational build-up index (CBI) for effective impervious surface mapping in urban areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, P.K.; Rajpal, N.; Mehta, R.; Mishra, V. Urban land cover and land use classification using multispectral sentinal-2 imagery. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 81, 36853–36867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M. Unsupervised object-based spectral unmixing for subpixel mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 318, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Cheng, Q.; Peng, H.; Altan, O.; Li, Y.; Ara, I.; Huq, E.; Ali, Y.; Saleem, N. Review of spectral indices for urban remote sensing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2021, 87, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Pandey, P. A review on spectral indices for built-up area extraction using remote sensing technology. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozdani, S.E.; Johnson, B.; Chen, D. Comparing Deep Neural Networks, Ensemble Classifiers, and Support Vector Machine Algorithms for Object-Based Urban Land Use/Land Cover Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, R.; Aniss, M.; Jamal, C. Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Remote Sensing and Urban Application: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. In Proceedings of the 4th Edition of International Conference on Geo-IT and Water Resources 2020, Geo-IT and Water Resources 2020, Hoceima, Morocco, 11–12 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunig, H.; Wolf, N.; Naumann, S.; Siegmund, A.; Jürgens, C.; Uysal, C.; Maktav, D. Land use/land cover classification for applied urban planning-the challenge of automation. In Proceedings of the 2011 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Munich, Germany, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Polykretis, C.; Grillakis, M.G.; Alexakis, D.D. Exploring the impact of various spectral indices on land cover change detection using change vector analysis: A case study of Crete Island, Greece. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. Classification and change detection of built-up lands from Landsat-7 ETM+ and Landsat-8 OLI/TIRS imageries: A comparative assessment of various spectral indices. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 56, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, H.; Song, Q.; Zheng, K. A novel index for impervious surface area mapping: Development and validation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, K.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Sun, M. Combinational biophysical composition index (CBCI) for effective mapping biophysical composition in urban areas. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 41224–41237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, M.M.; Mirza, J.F.; Mumtaz, R.; Hussain, E. Development of New Indices for Extraction of Built-Up Area and Bare Soil from Landsat Data. Open Access Sci. Rep. 2012, 1, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kaimaris, D.; Patias, P. Identification and area measurement of the built-up area with the Built-up Index (BUI). Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2016, 5, 1844–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; He, L. Enhanced normalized difference index for impervious surface area estimation at the plateau basin scale. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 016502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhennache, R.; Bouden, T.; Taleb-Ahmed, A.; Cheddad, A. A new spectral index for the extraction of built-up land features from Landsat 8 satellite imagery. Geocarto Int. 2019, 34, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As-Syakur, A.R.; Adnyana, I.W.S.; Arthana, I.W.; Nuarsa, I.W. Enhanced built-up and bareness index (EBBI) for mapping built-up and bare land in an urban area. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2957–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyoosh, A.K.; Ghosh, S.K. Development of a modified bare soil and urban index for Landsat 8 satellite data. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Mapping global urban areas from 2000 to 2012 using time-series nighttime light data and MODIS products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumaran, N.; Vaithegi, S. Image segmentation by using thresholding techniques for medical images. Comput. Sci. Eng. Int. J. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sekertekin, A. A survey on global thresholding methods for mapping open water body using Sentinel-2 satellite imagery and normalized difference water index. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Fan, H.; Tong, X.; Liu, J. A forest type-specific threshold method for improving forest disturbance and agent attribution mapping. Giscience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1624–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, U.; d’Angelo, P.; Schwind, P.; Karlshöfer, P.; Müller, R.; Zepp, S.; Wiesmeier, M.; Reinartz, P. Soil reflectance composites—improved thresholding and performance evaluation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M. A comparative analysis of index-based methods for impervious surface mapping using multiseasonal Sentinel-2 satellite data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3682–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohamad, H.; Alshwesh, I.O. Evaluation of Index-Based Methods for Impervious Surface Mapping from Landsat-8 to Cities in Dry Climates; A Case Study of Buraydah City, KSA. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, C.; He, L.; Hou, M.; Shi, T. A comparative study of impervious surface extraction using Sentinel-2 imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, 274–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekertekin, A.; Abdikan, S.; Marangoz, A.M. The acquisition of impervious surface area from LANDSAT 8 satellite sensor data using urban indices: A comparative analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Thinh, N.X.; Li, C. Preliminary comparative assessment of various spectral indices for built-up land derived from Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2A MSI imageries. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Seasonal effects of impervious surface estimation in subtropical monsoon regions. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Tian, J.; Dong, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, N.; Xi, Y. An impervious surface spectral index on multispectral imagery using visible and near-infrared bands. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Cheng, T.; Fu, H.; Li, D.; Huang, X. Emerging issues in mapping urban impervious surfaces using high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günen, M.A.; Atasever, U.H. Remote sensing and monitoring of water resources: A comparative study of different indices and thresholding methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HCP. Monographie de la Province de Settat; Technical Report; Haut Commissariat du Plan du Royaume du Maroc: Casablanca, Morocco, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Driouech, F. Distribution des précipitations hivernales sur le Maroc dans le cadre d’un changement climatique: Descente d’échelle et incertitudes. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse-INPT, Toulouse, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- DGM. Maroc-Etat du climat en 2023; Technical Report; Direction Général de Météorologie-Ministér de l’Equipement et de l’Eau: Casablanca, Morocco, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- HCP. Recessement Général de la Population et de l’Habitat 2024; Technical Report; Haut Commissariat du Plan du Royaume du Maroc: Casablanca, Morocco, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, A.; Lacey, J.; Mecklenburg, S.; Ross, J.; Siqueira, A.; Killough, B.; Szantoi, Z.; Tadono, T.; Rosenavist, A.; Goryl, P.; et al. CEOS analysis ready data for Land (CARD4L) overview. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 7407–7410. [Google Scholar]
- John, S.; Varghese, A. Analysis of support vector machine and maximum likelihood classifiers in land cover classification using Sentinel-2 images. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2022, 88, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; N, H. Land use and land cover classification using machine learning algorithms in google earth engine. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 16, 3057–3073. [Google Scholar]
- Capolupo, A.; Monterisi, C.; Tarantino, E. Landsat images classification algorithm (LICA) to automatically extract land cover information in Google Earth Engine environment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Wiegand, C. Distinguishing vegetation from soil background information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1977, 43, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, M.; Sankur, B.L. Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosko, B.; Toms, M. Fuzzy Thinking: The New Science of Fuzzy Logic; Hyperion New York: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 288. [Google Scholar]
- Glasbey, C.A. An analysis of histogram-based thresholding algorithms. CVGIP Graph. Model. Image Process. 1993, 55, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, W. Operations useful for similarity-invariant pattern recognition. J. ACM (JACM) 1962, 9, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 1975, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, J.; Illingworth, J. Minimum error thresholding. Pattern Recognit. 1986, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, S.A.; Tariq, H. K-means cluster analysis for image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, P.; Gopal, G.; Kumar, R. Image Segmentation using K-means clustering and Thresholding. Image 2016, 3, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Ridler, T.; Calvard, S. Picture thresholding using an iterative selection method. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern 1978, 8, 630–632. [Google Scholar]
- Prewitt, J.M.; Mendelsohn, M.L. The analysis of cell images. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1966, 128, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H. Moment-preserving thresolding: A new approach. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1985, 29, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zack, G.W.; Rogers, W.E.; Latt, S.A. Automatic measurement of sister chromatid exchange frequency. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1977, 25, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rényi, A. On the foundations of information theory. Rev. L’Institut Int. Stat. 1965, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Wilkins, C.; Yeager, J. Threshold selection using Renyi’s entropy. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, J.N.; Sahoo, P.K.; Wong, A.K. A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1985, 29, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, T. A new method for grey-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Signal Process. 1980, 2, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.C.; Chang, F.J.; Chang, S. A new criterion for automatic multilevel thresholding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.K.; Wang, M.J.J. Image thresholding by minimizing the measures of fuzziness. Pattern Recognit. 1995, 28, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, A.G. Utilization of information measure as a means of image thresholding. CVGIP Graph. Model. Image Process. 1994, 56, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tam, P.K.S. An iterative algorithm for minimum cross entropy thresholding. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1998, 19, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwanga, S.S.; Ndambuki, J.M. Accuracy assessment of land use/land cover classification using remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Geosci. 2017, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Estépar, R.S.J.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Diaz, A.; Ross, J.C.; Murayama, S.; Silverman, E.K.; Hatabu, H.; Washko, G.R. Kurtosis and skewness of density histograms on inspiratory and expiratory CT scans in smokers. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2011, 8, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
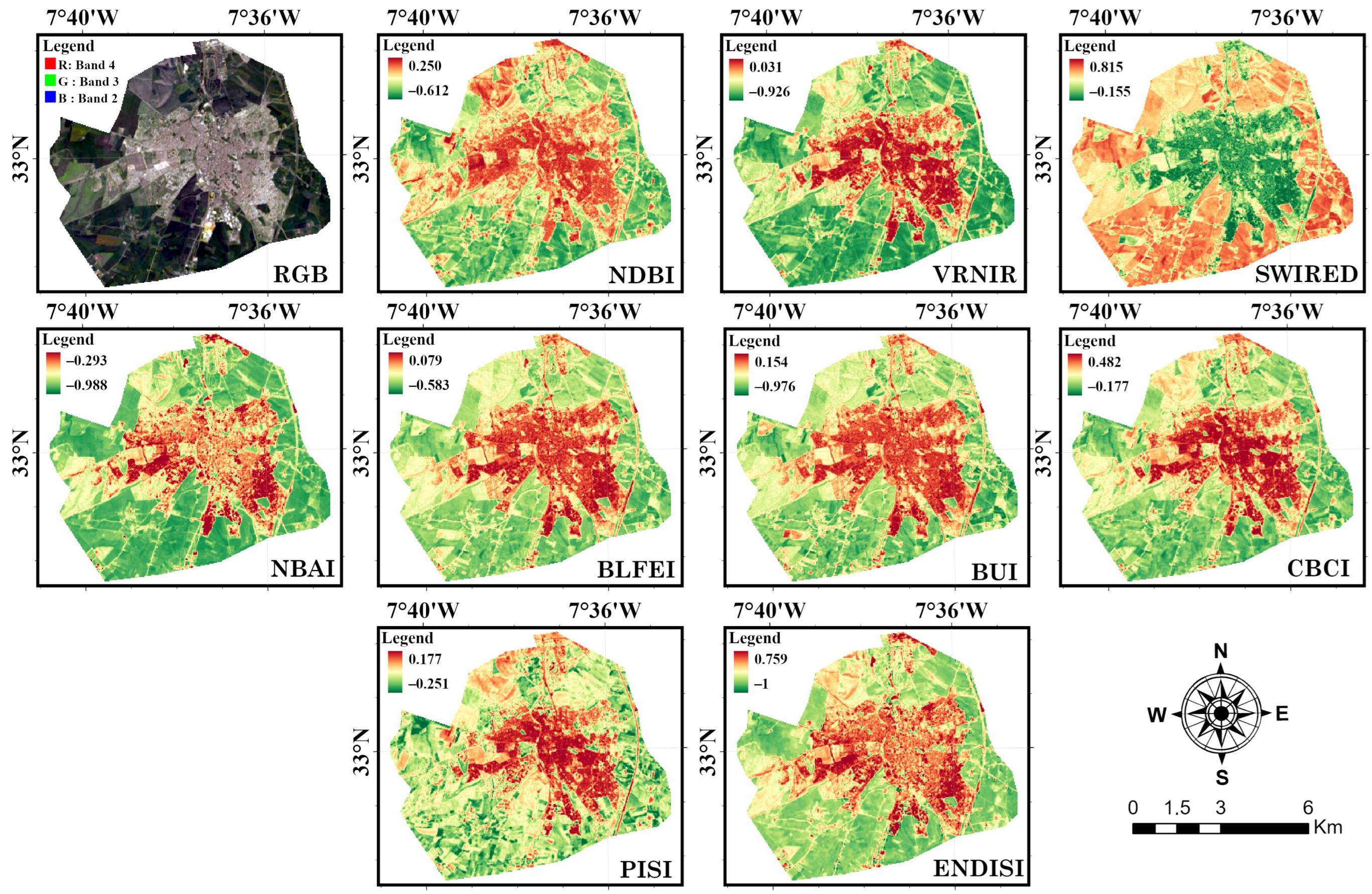
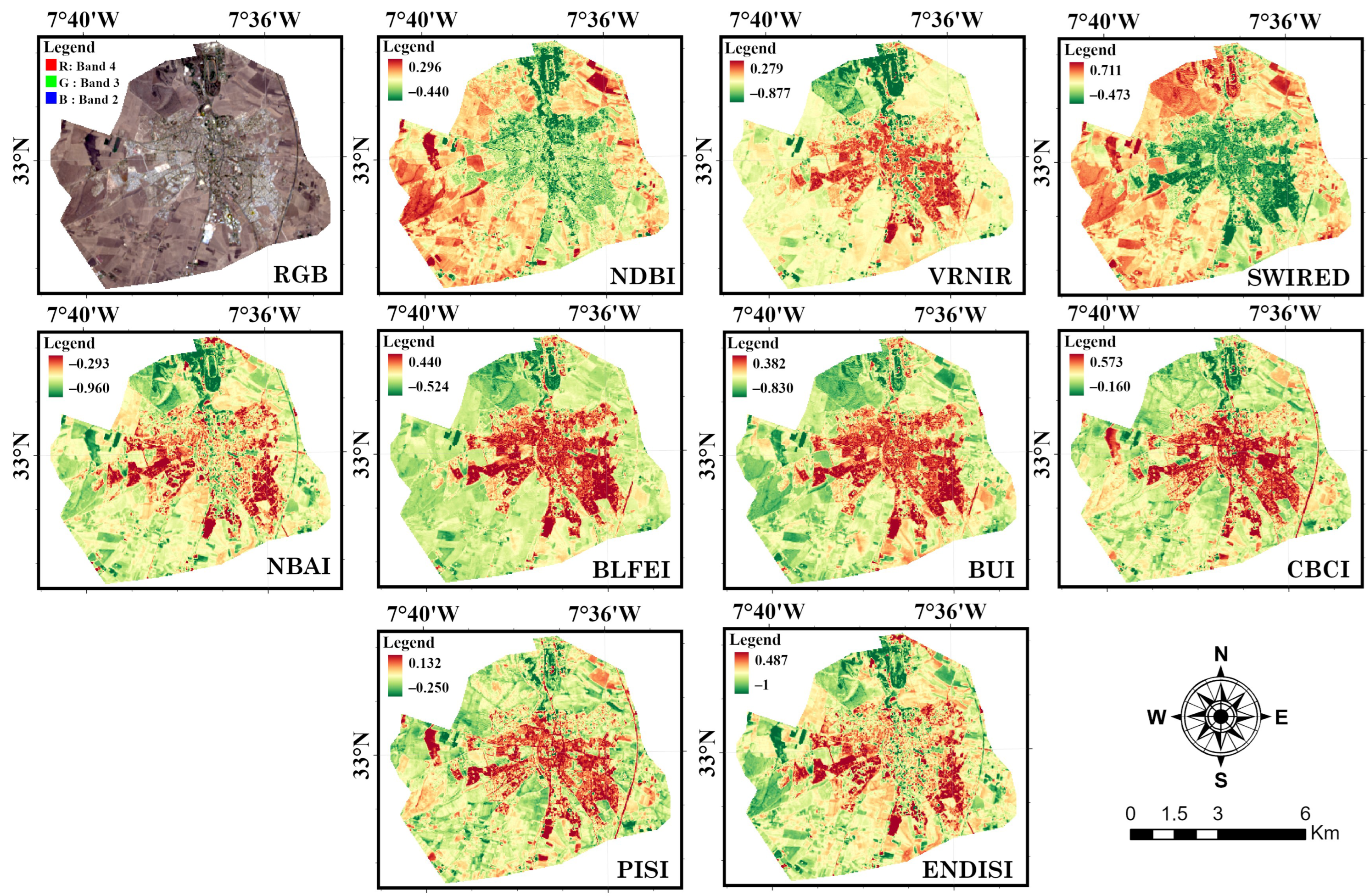
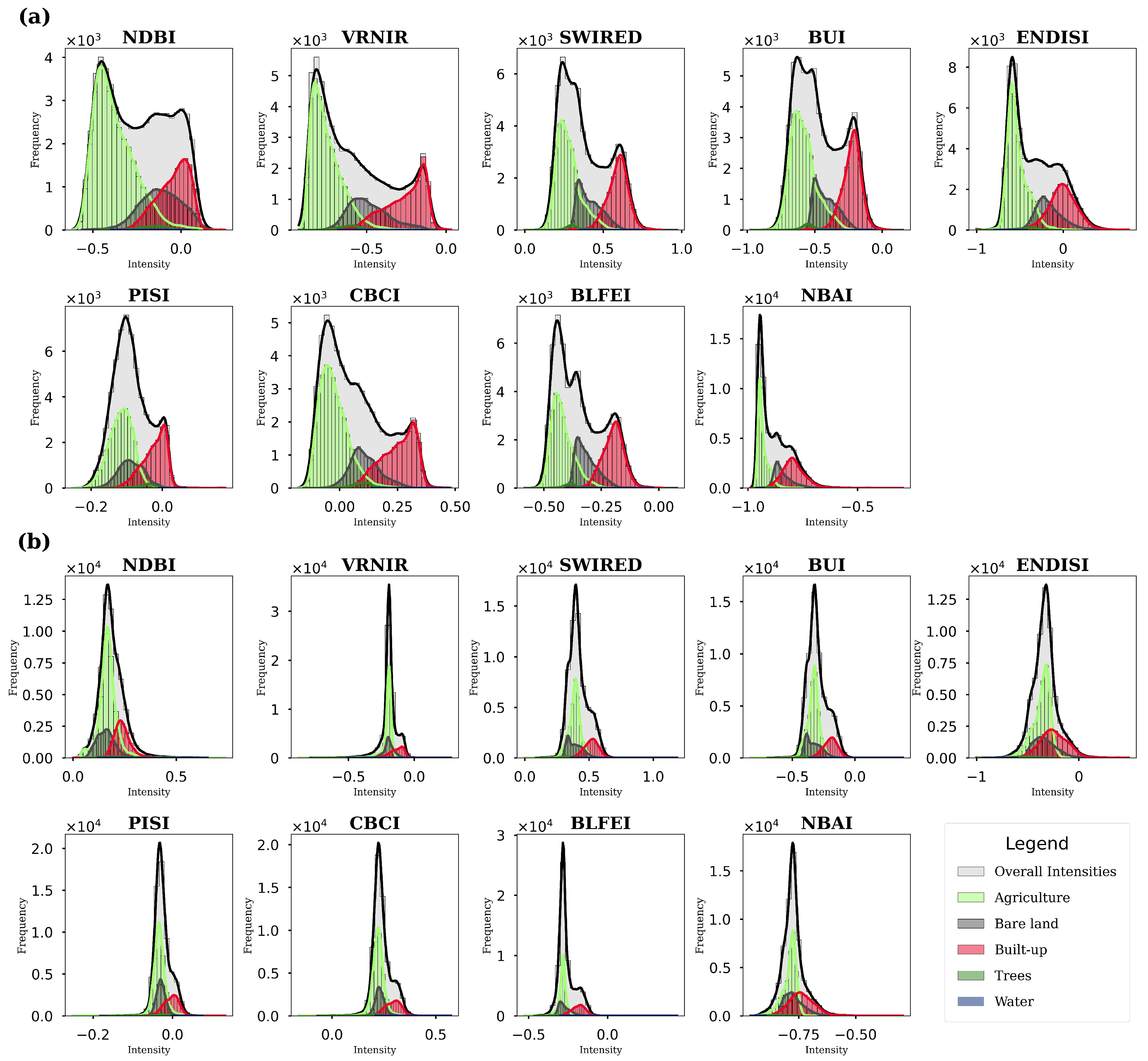


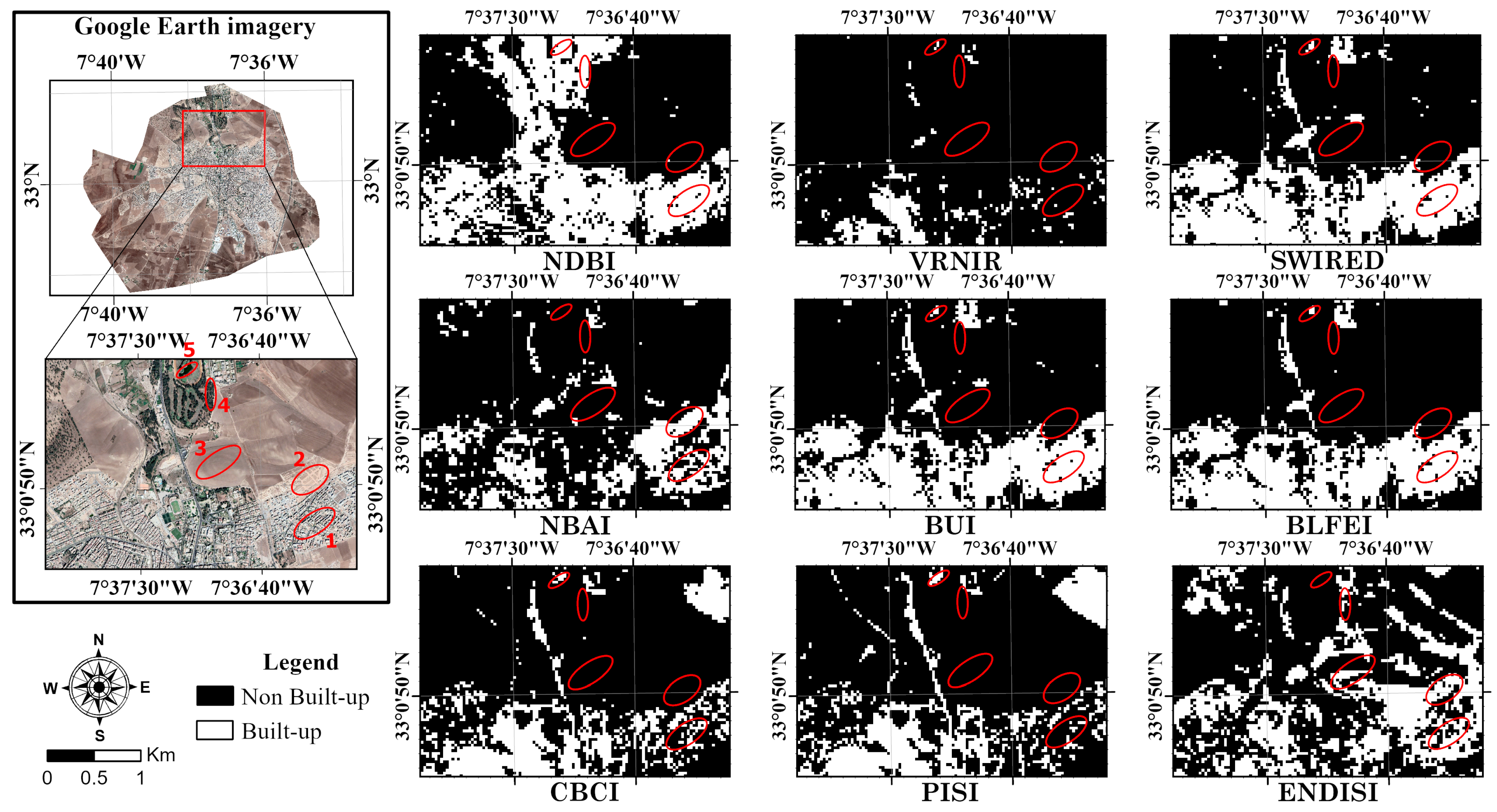
| Date of Capture | Scene ID | Cloud Cover |
|---|---|---|
| 24 March 2021 (Spring) | LC08_L2SP_202037_20210324_20210402_02_T1 | 0.02% |
| 14 July 2021 (Summer) | LC08_L2SP_202037_20210714_20210402_02_T1 | 0.21% |
| Class | Agriculture | Built-Up | Bare Land | Trees | Water | UA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 630 | 14 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 96.18 |
| Built-up | 3 | 286 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 97.95 |
| Bare Land | 20 | 17 | 196 | 0 | 0 | 84.12 |
| Trees | 4 | 0 | 2 | 14 | 0 | 70.00 |
| Water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 100.00 |
| PA (%) | 95.89 | 90.22 | 94.23 | 77.78 | 100.00 |
| Index | Built-Up/Agriculture | Built-Up/Bare Land | Built-Up/Trees | Built-Up/Water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Spring | Summer | Spring | Summer | Spring | Summer | |
| NDBI | 1.57 | 0.67 | 0.34 | 0.83 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.57 |
| VRNIR | 2.15 | 0.56 | 0.89 | 0.51 | 1.67 | 1.16 | 0.51 | 0.01 |
| SWIRED | 2.14 | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.08 | 2.03 | 1.67 | 0.19 | 0.28 |
| BUI | 2.10 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 1.08 | 2.02 | 1.66 | 0.19 | 0.27 |
| ENDISI | 1.72 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.41 | 2.14 |
| PISI | 1.34 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 1.00 | 1.01 |
| CBCI | 2.02 | 0.92 | 1.01 | 0.89 | 1.19 | 0.90 | 0.38 | 0.75 |
| BLFEI | 2.28 | 1.42 | 1.21 | 1.05 | 1.97 | 1.67 | 0.06 | 0.34 |
| NBAI | 1.76 | 0.59 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 1.66 | 1.30 | 2.44 | 2.39 |
| Index | Standard Deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Spring | Summer | Spring | Summer | |
| NDBI | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 1.40 | −1.25 | 6.05 |
| VRNIR | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.57 | −2.18 | −0.93 | 12.58 |
| SWIRED | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 0.48 | −0.89 | 0.54 |
| BUI | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 0.38 | −0.99 | 0.71 |
| ENDISI | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 0.44 | −0.66 | 2.38 |
| PISI | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.31 | −0.01 | −0.41 | 5.25 |
| CBCI | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.55 | −0.02 | −0.80 | 3.84 |
| BLFEI | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.53 | 0.87 | −0.84 | 1.32 |
| NBAI | 0.07 | 0.05 | 1.09 | 1.09 | 1.46 | 5.32 |
| Index | Season | Threshold | OA (%) | Kappa (%) | ATM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATM | Manual | ATM | Manual | ATM | Manual | |||
| NDBI | Spring | −0.11215 | −0.16703 | 81.49 | 80.57 | 53.91 | 56.15 | Percentile |
| Summer | 0.20855 | 0.21272 | 83.30 | 84.13 | 60.00 | 60.10 | Percentile | |
| VRNIR | Spring | −0.47940 | −0.38573 | 88.01 | 89.50 | 71.09 | 71.91 | Shanbhag |
| Summer | −0.17484 | −0.16076 | 80.90 | 86.19 | 52.32 | 61.44 | Percentile | |
| SWIRED | Spring | 0.49814 | 0.49438 | 93.39 | 93.47 | 82.80 | 83.09 | Minimum |
| Summer | 0.44645 | 0.45980 | 89.17 | 90.41 | 73.02 | 75.01 | Huang & Shanbhag | |
| BUI | Spring | −0.34257 | −0.32459 | 92.81 | 93.55 | 81.69 | 83.23 | Minimum |
| Summer | −0.26458 | −0.25523 | 89.67 | 90.58 | 73.90 | 75.49 | Huang | |
| ENDISI | Spring | −0.19280 | −0.19998 | 85.78 | 85.78 | 65.42 | 65.68 | Max Entropy |
| Summer | −0.28870 | −0.25905 | 75.70 | 78.92 | 39.26 | 41.00 | Percentile | |
| PISI | Spring | −0.05830 | −0.05483 | 87.77 | 88.18 | 68.88 | 69.28 | Renyi’s Entropy |
| Summer | −0.01663 | −0.01462 | 83.88 | 84.38 | 59.03 | 59.40 | Huang & Shanbhag | |
| CBCI | Spring | 0.13308 | 0.15883 | 88.68 | 89.91 | 72.27 | 73.71 | Percentile |
| Summer | 0.25985 | 0.26006 | 86.77 | 86.69 | 65.41 | 65.66 | IsoData | |
| BLFEI | Spring | −0.26332 | −0.26856 | 93.97 | 94.13 | 84.29 | 84.84 | Minimum |
| Summer | −0.23654 | −0.22596 | 91.57 | 91.74 | 77.77 | 78.06 | Li | |
| NBAI | Spring | −0.84534 | −0.84341 | 86.94 | 87.60 | 67.74 | 68.95 | Percentile |
| Summer | −0.75589 | −0.75377 | 79.25 | 80.50 | 44.16 | 45.18 | Moments | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harrak, Y.; Rachid, A.; Aguejdad, R. Evaluation of Spectral Indices and Global Thresholding Methods for the Automatic Extraction of Built-Up Areas: An Application to a Semi-Arid Climate Using Landsat 8 Imagery. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030078
Harrak Y, Rachid A, Aguejdad R. Evaluation of Spectral Indices and Global Thresholding Methods for the Automatic Extraction of Built-Up Areas: An Application to a Semi-Arid Climate Using Landsat 8 Imagery. Urban Science. 2025; 9(3):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030078
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarrak, Yassine, Ahmed Rachid, and Rahim Aguejdad. 2025. "Evaluation of Spectral Indices and Global Thresholding Methods for the Automatic Extraction of Built-Up Areas: An Application to a Semi-Arid Climate Using Landsat 8 Imagery" Urban Science 9, no. 3: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030078
APA StyleHarrak, Y., Rachid, A., & Aguejdad, R. (2025). Evaluation of Spectral Indices and Global Thresholding Methods for the Automatic Extraction of Built-Up Areas: An Application to a Semi-Arid Climate Using Landsat 8 Imagery. Urban Science, 9(3), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9030078









