Assessment of Ecological Suitability for Highway Under-Bridge Areas: A Methodological Integration of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Optimized Backpropagation Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
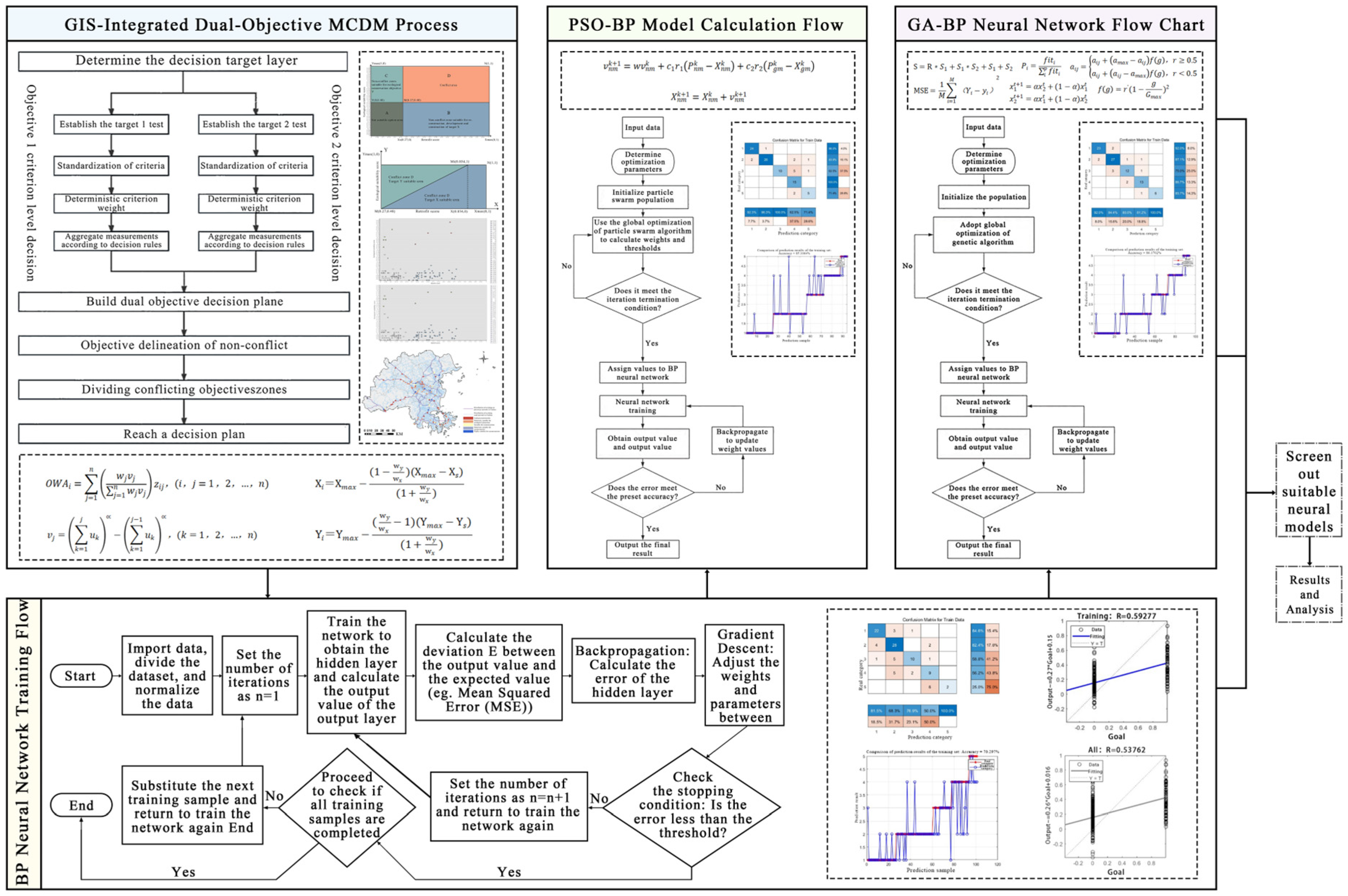
2. Method
2.1. Construction of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Model
2.1.1. Establishment of the Indicator System and Determination of Weights
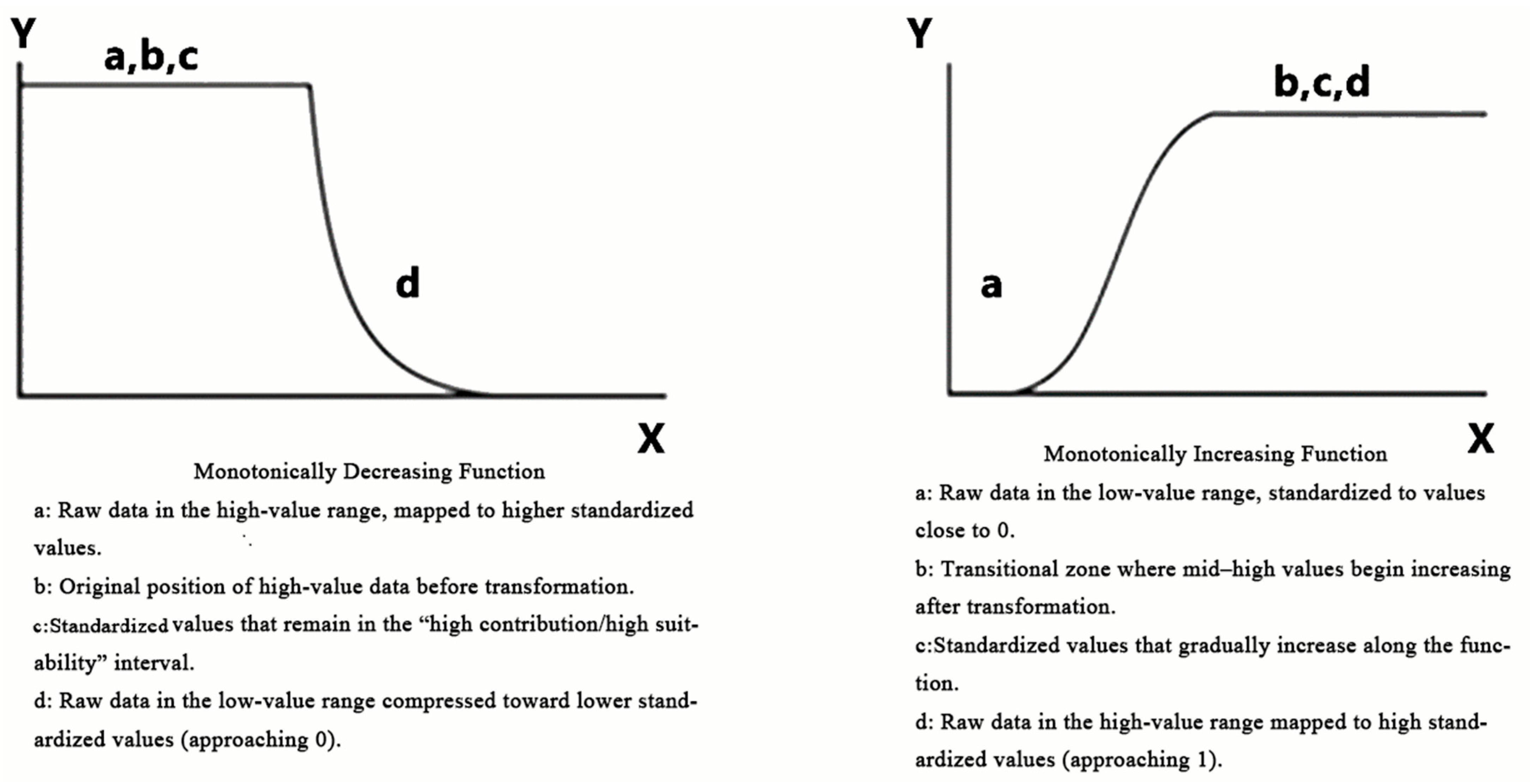
2.1.2. Data Standardization
2.1.3. OWA Aggregation Criterion Layer
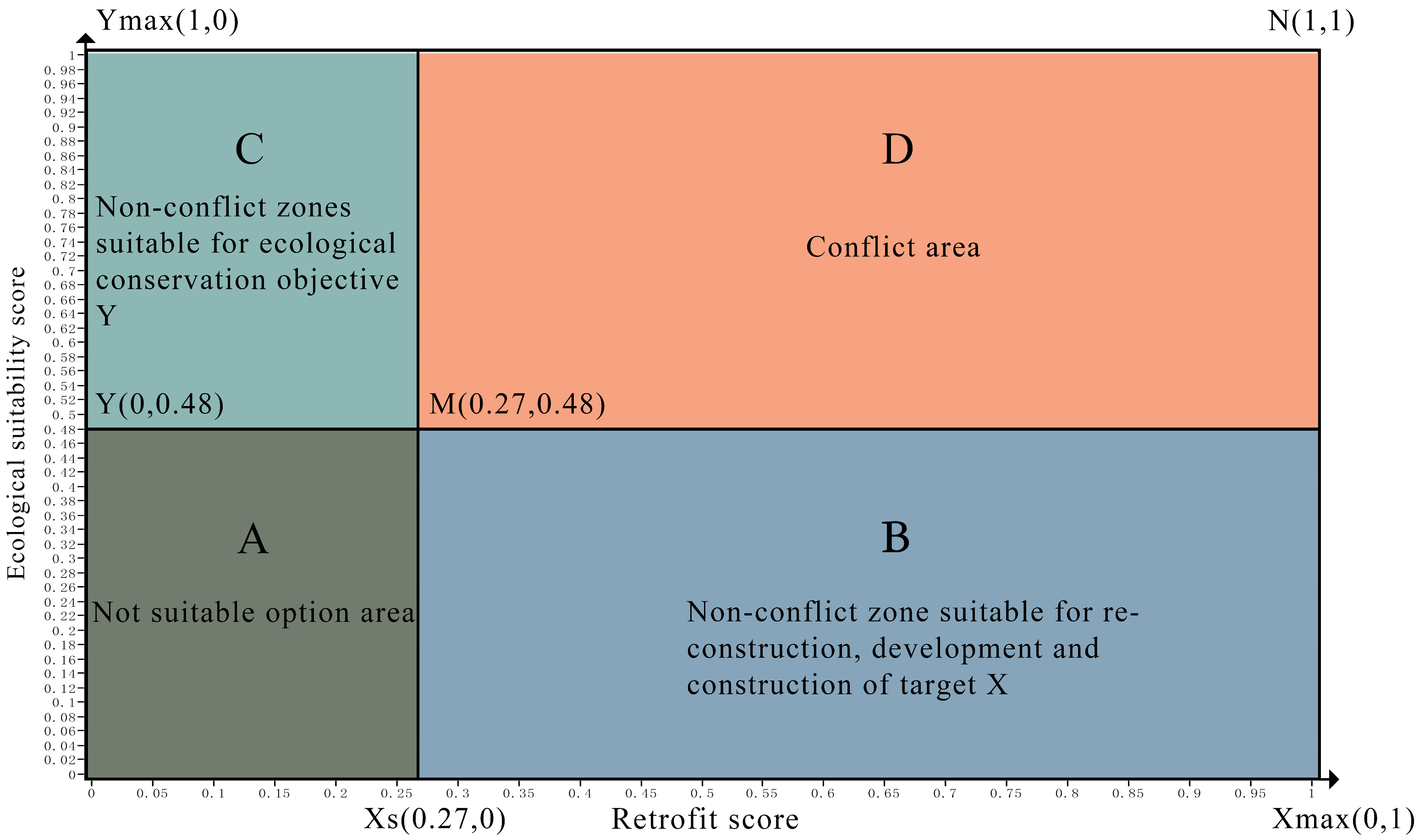
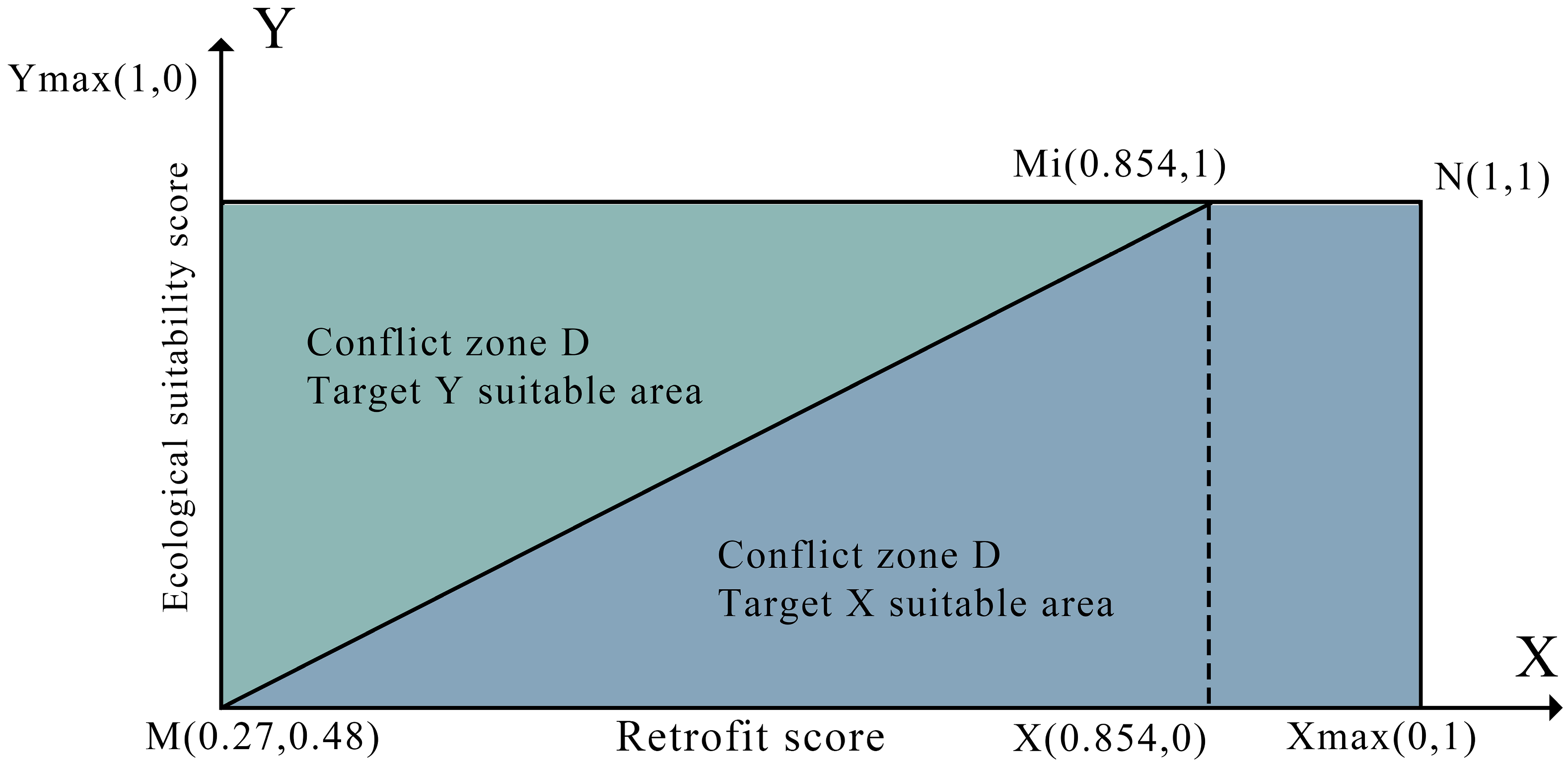
2.1.4. Dual-Objective Decision Plane
2.2. Neural Network Optimization Model
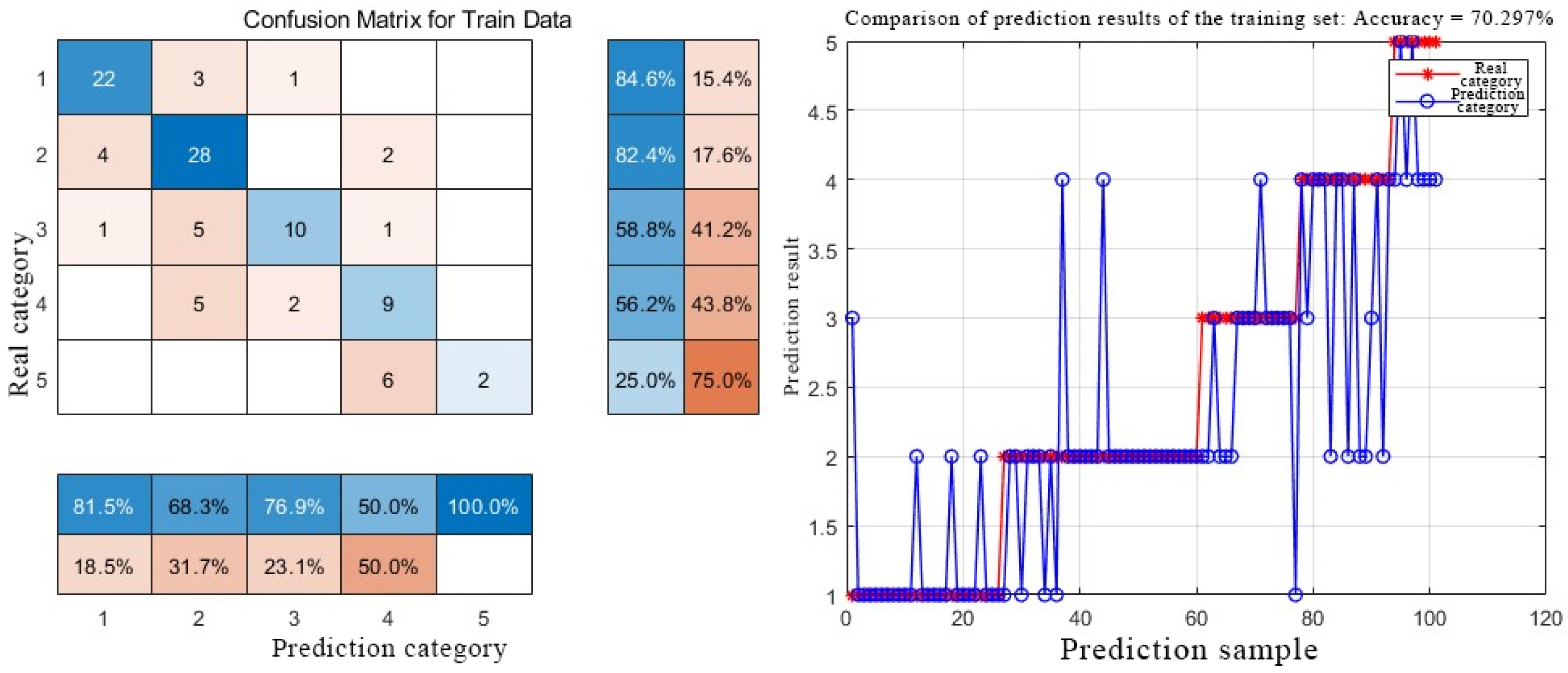
2.2.1. BP Neural Network
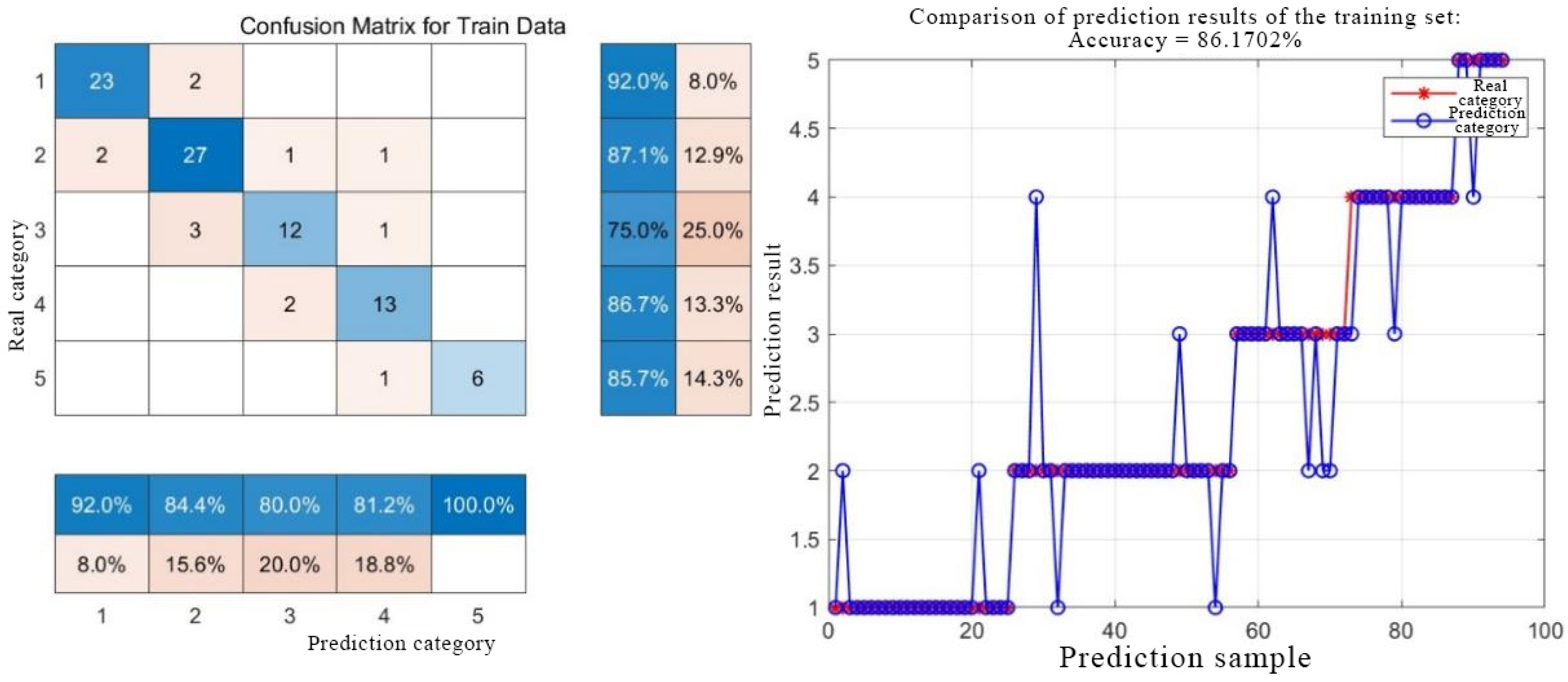
2.2.2. GA-BP Neural Network
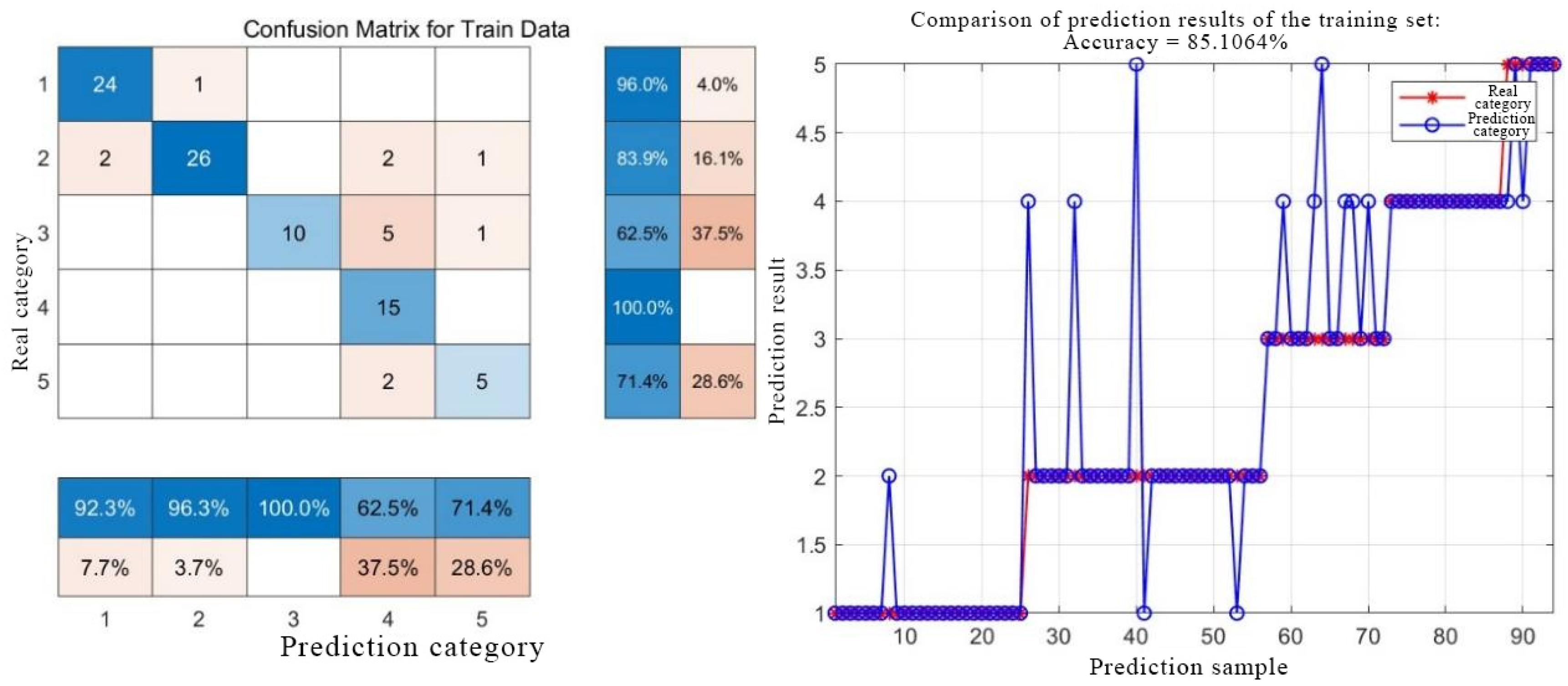
2.2.3. PSO-BP Neural Network
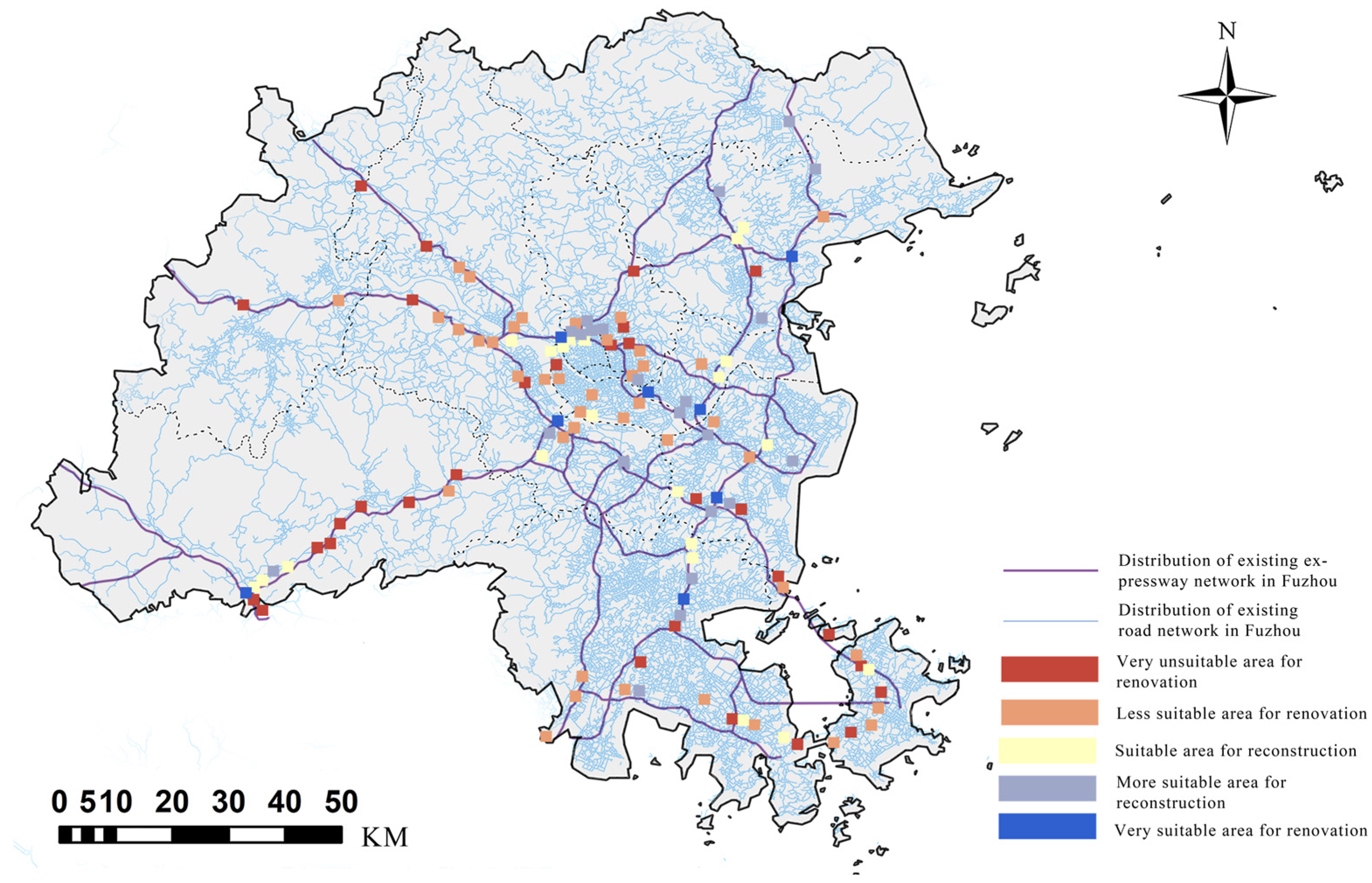
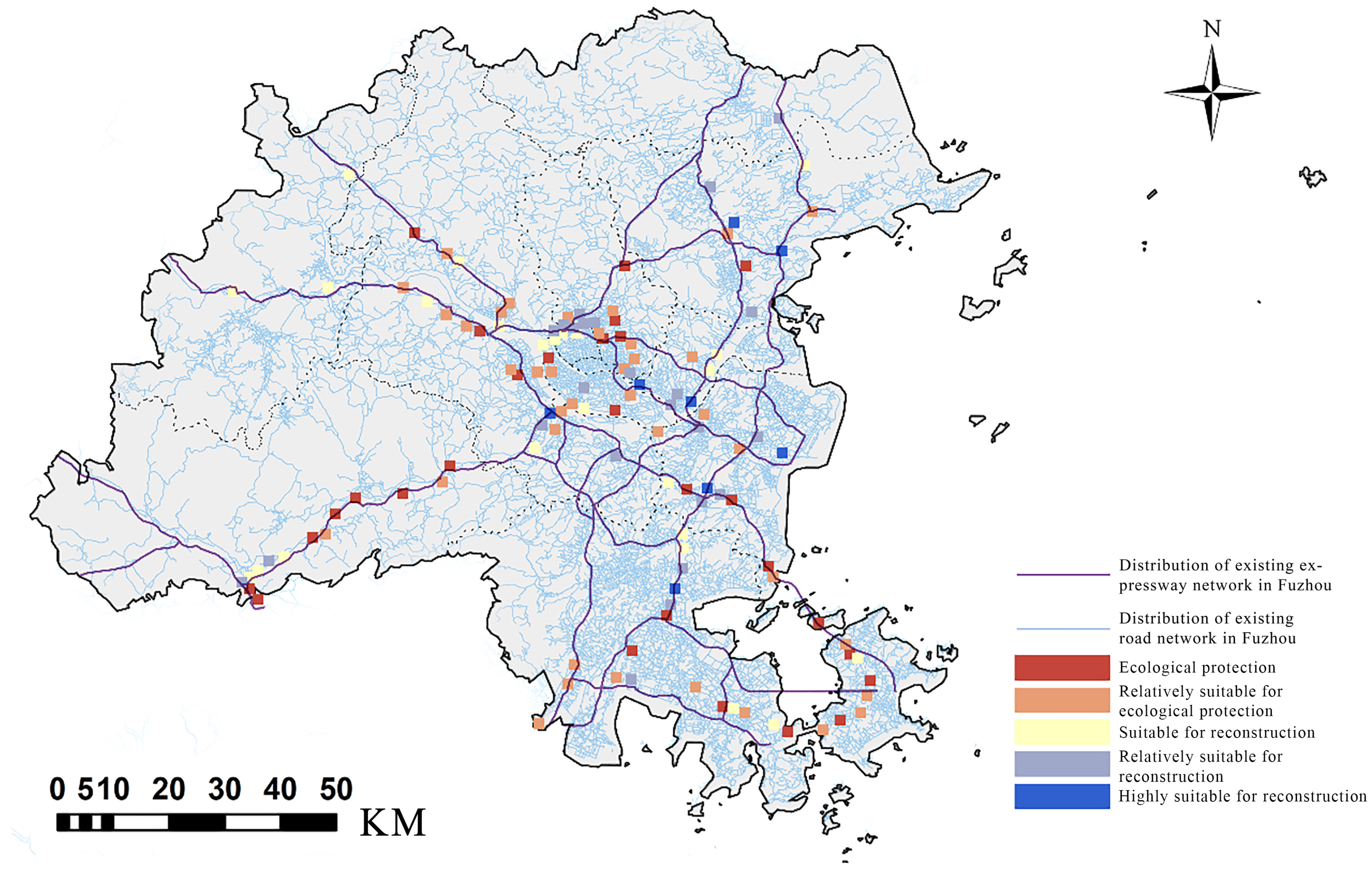
2.3. GIS Spatial Analysis and Visualization
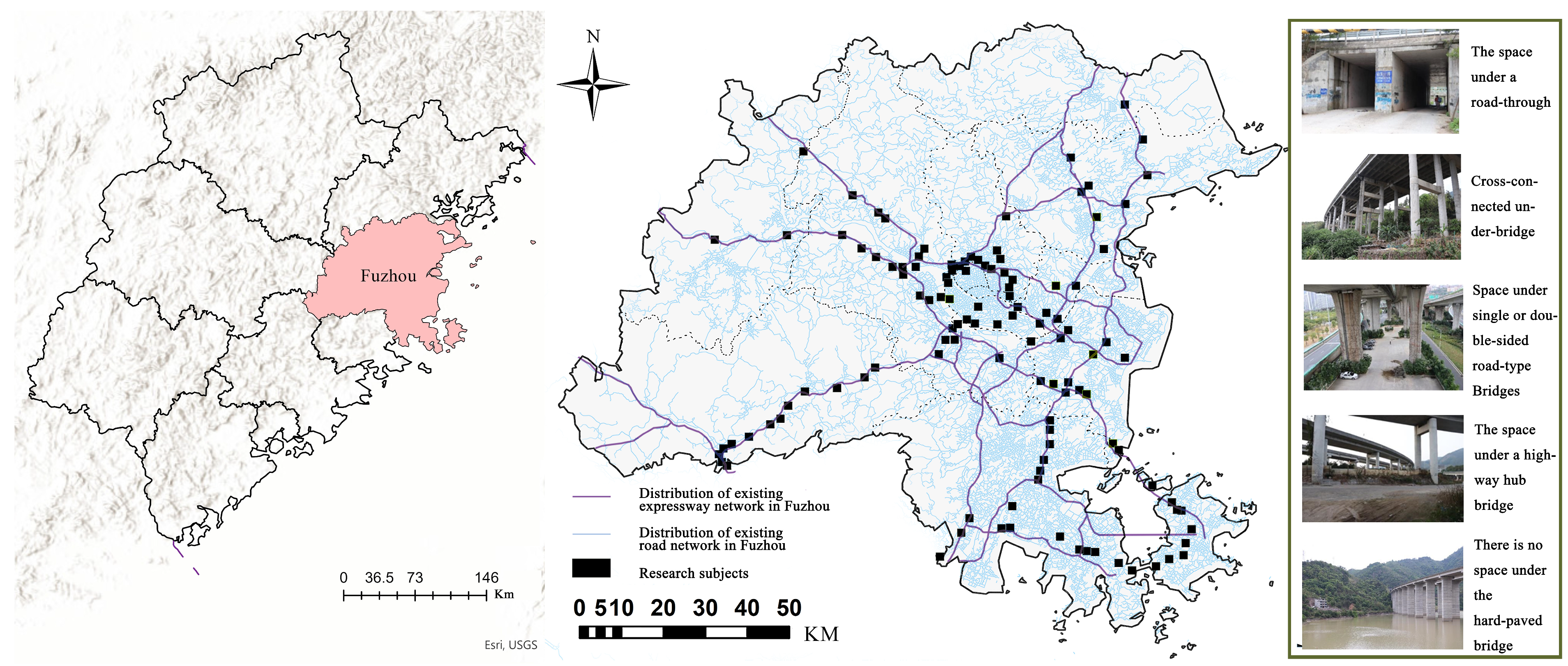
2.4. Empirical Region Selection
3. Research Results
3.1. Preliminary Evaluation Results of Dual-Objective MCDM
3.1.1. Calculation of Indicators and Weights
3.1.2. Aggregated Results of the Criterion Layer
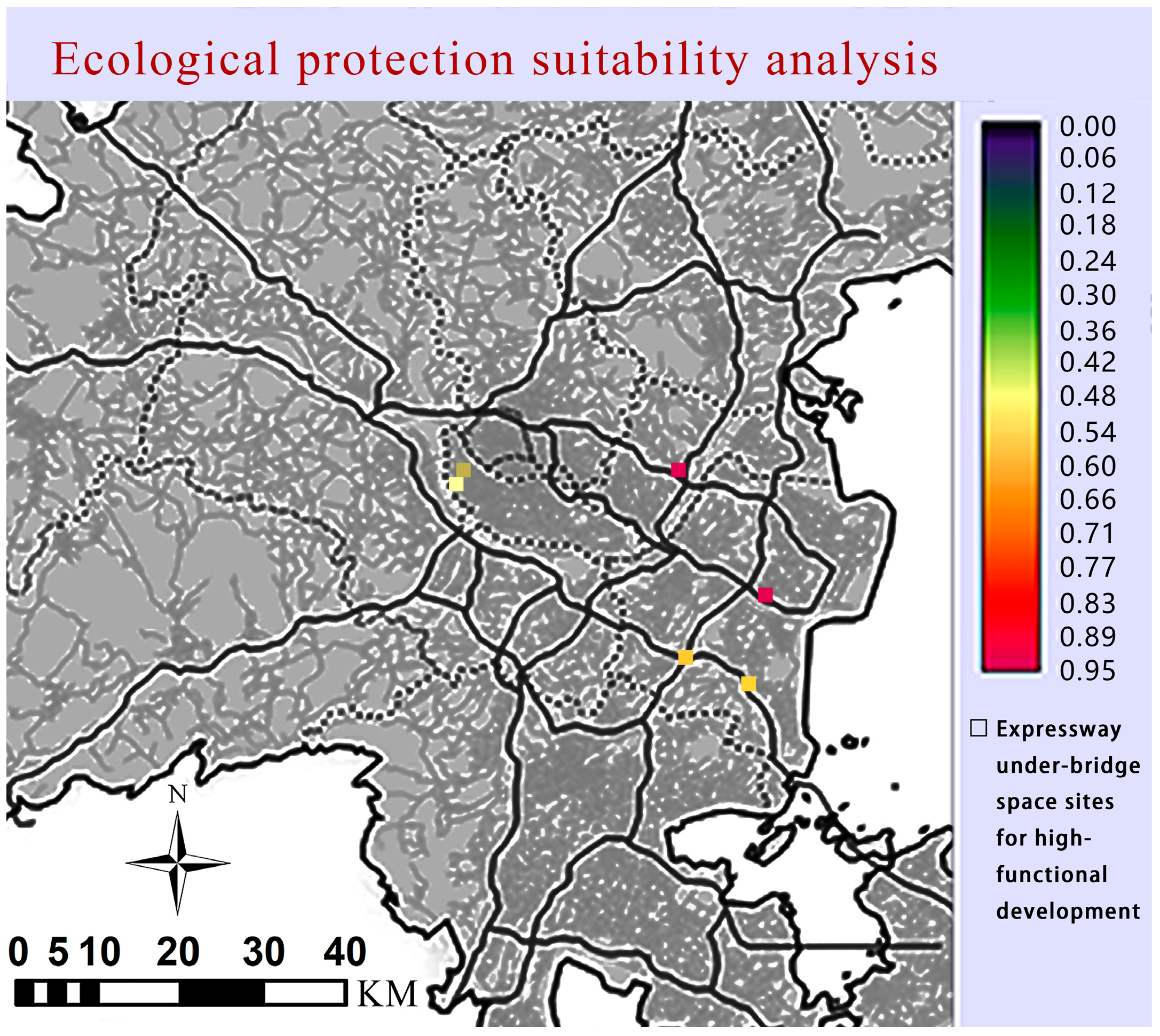
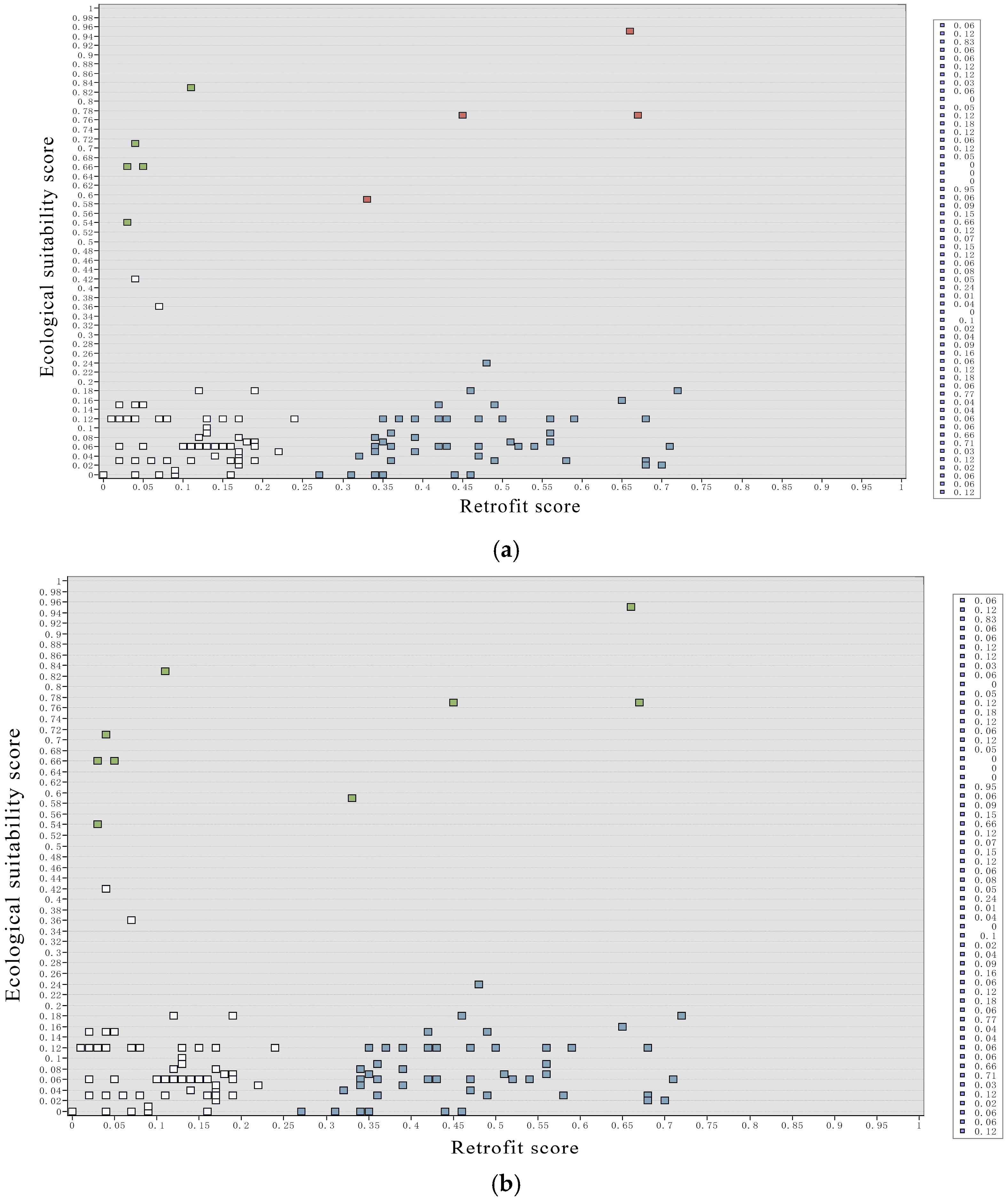
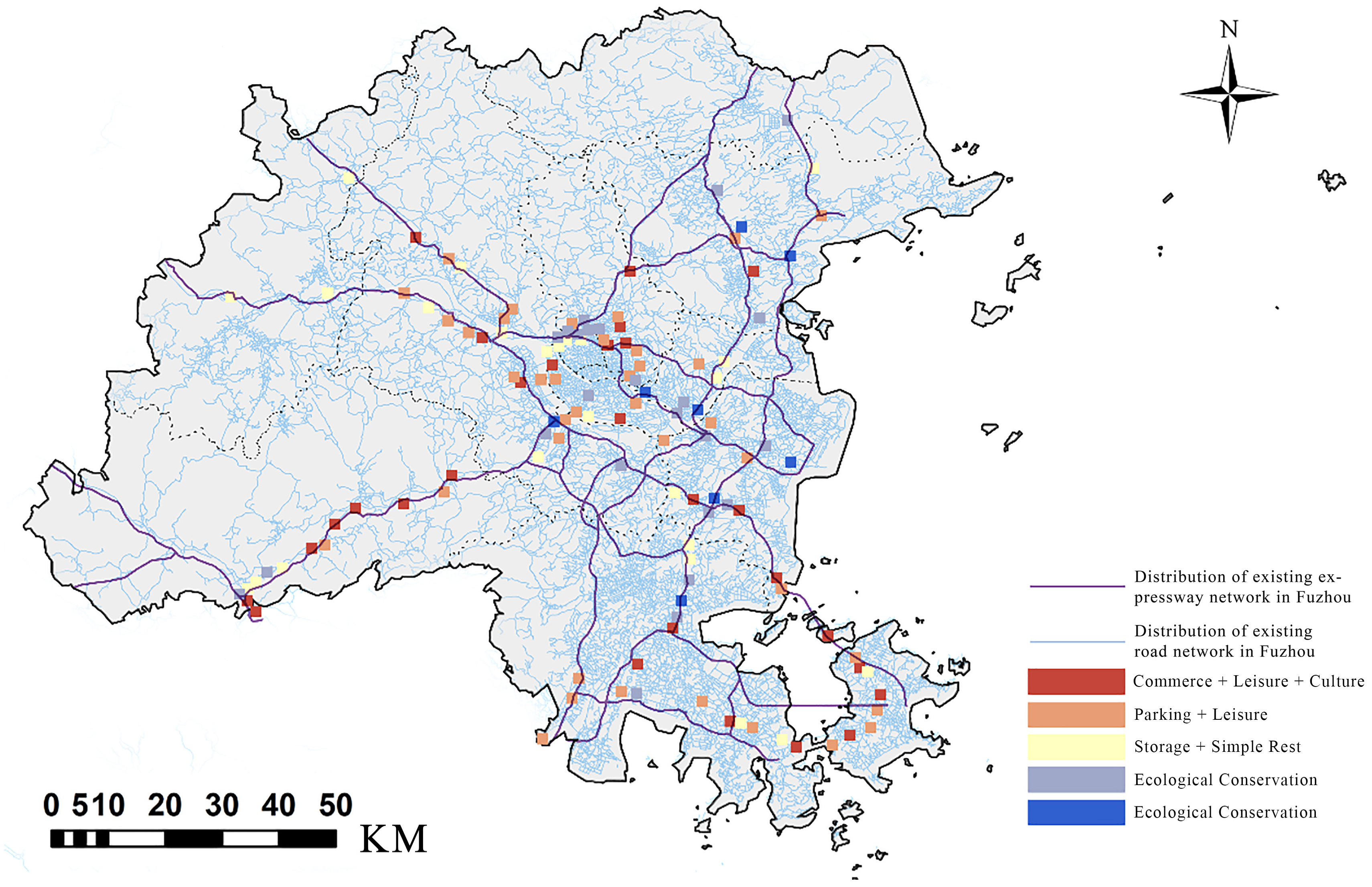
3.1.3. Decision Analysis and Characteristics of the Underground Space Under the Fuzhou Highway Bridge
- Systematic Division Based on the Dual-Objective Decision Plane
- 2.
- GIS Scatter Plot Division
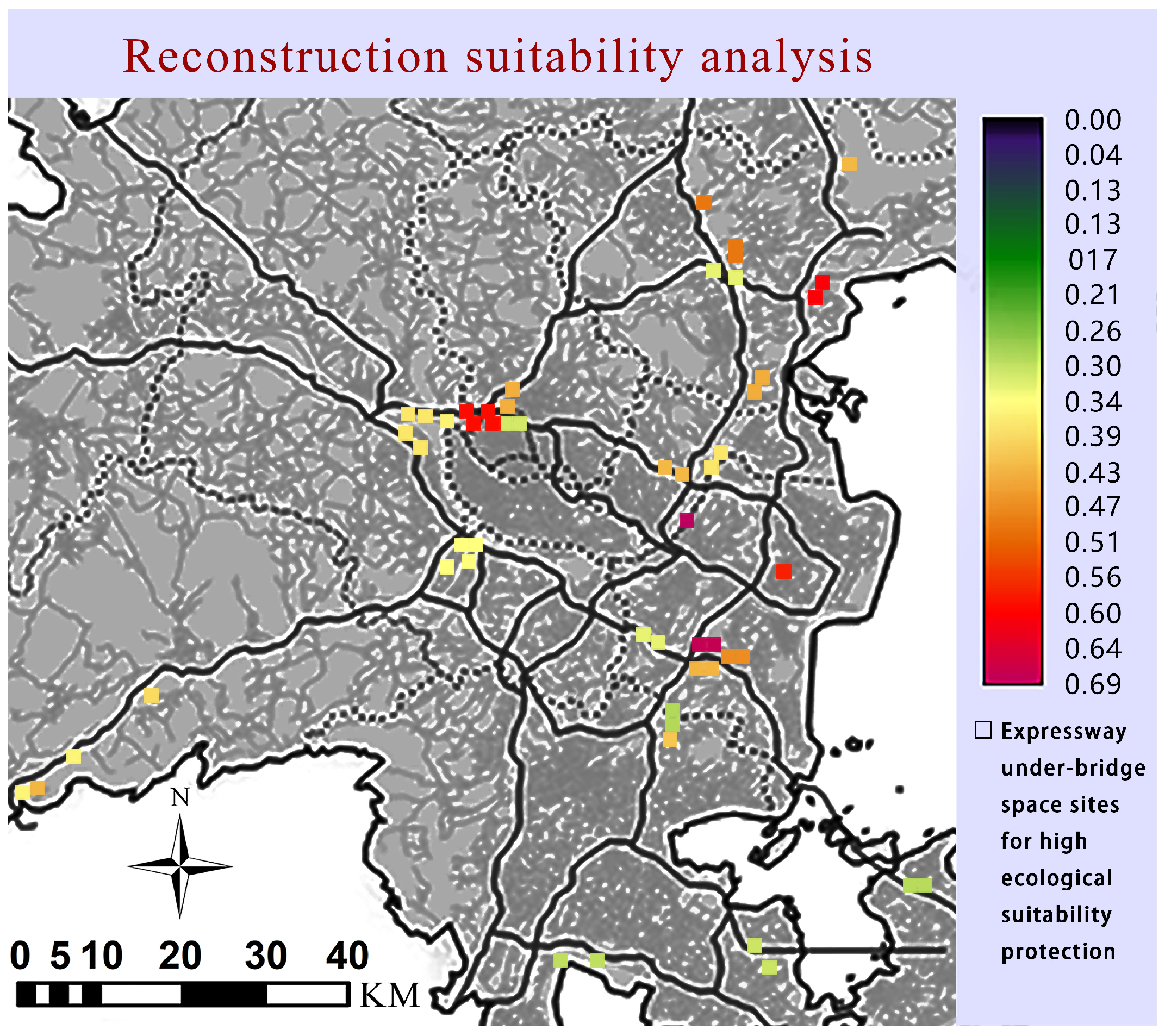
3.1.4. Preliminary Assessment of Overall Suitability
3.2. Optimization of Neural Network Model
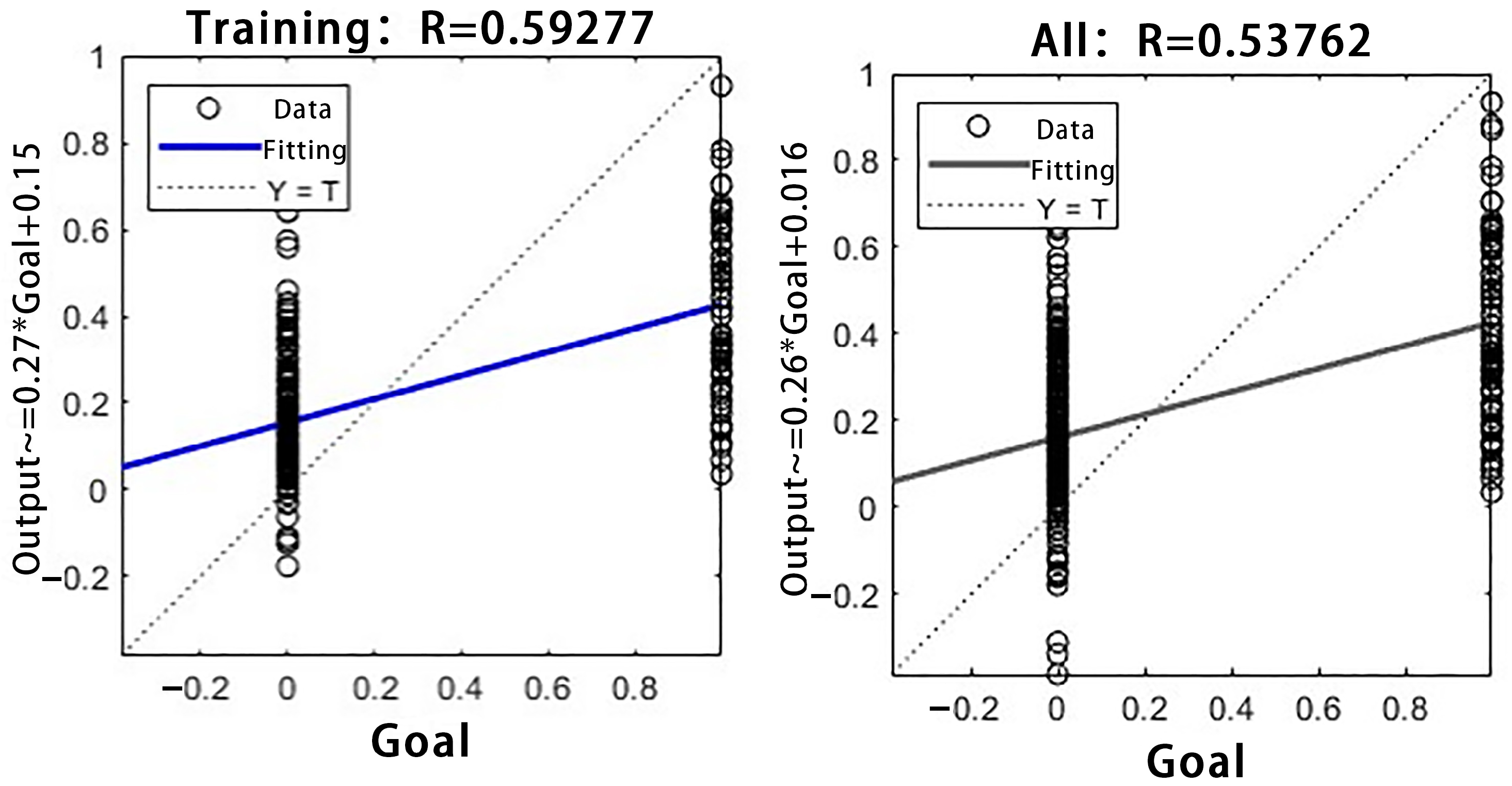
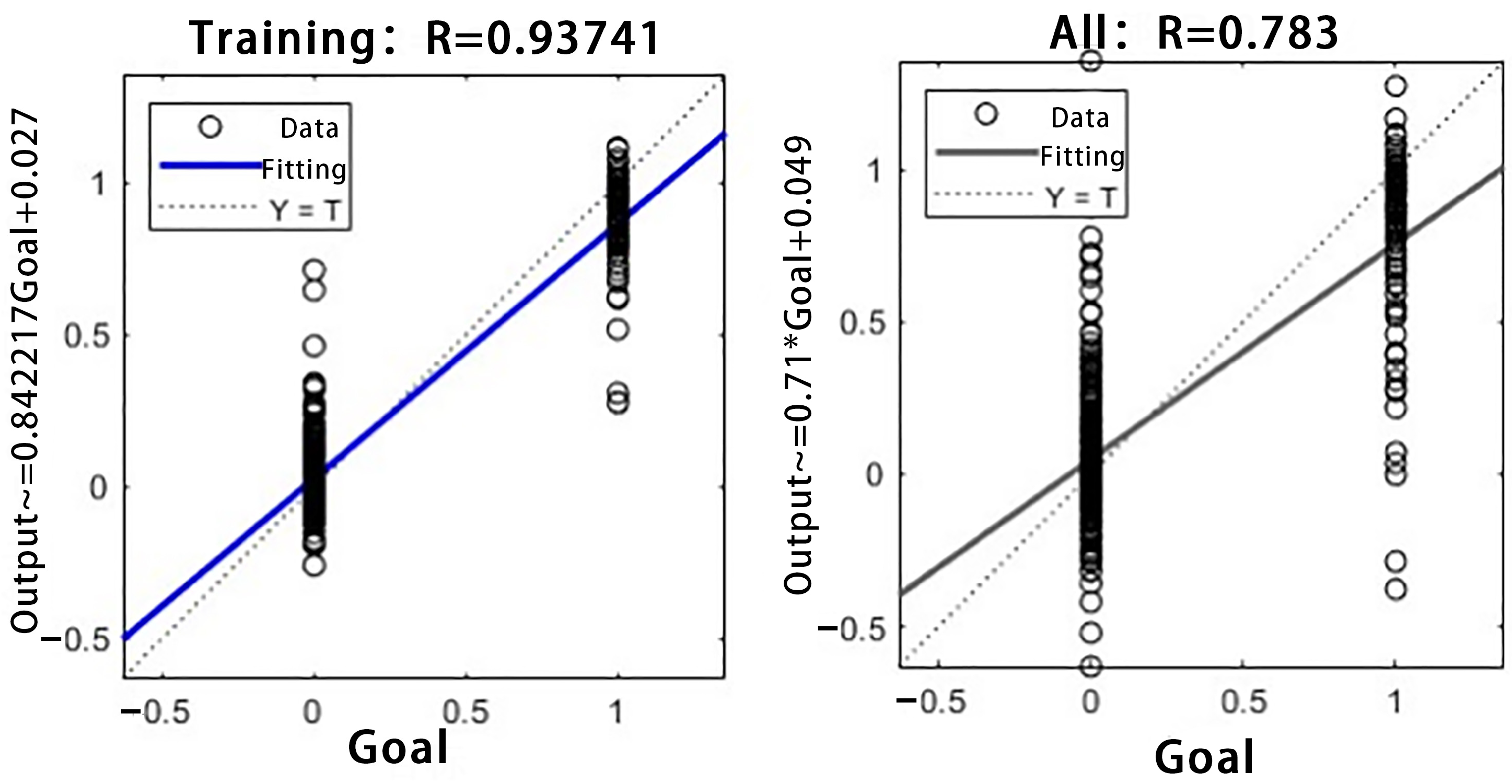
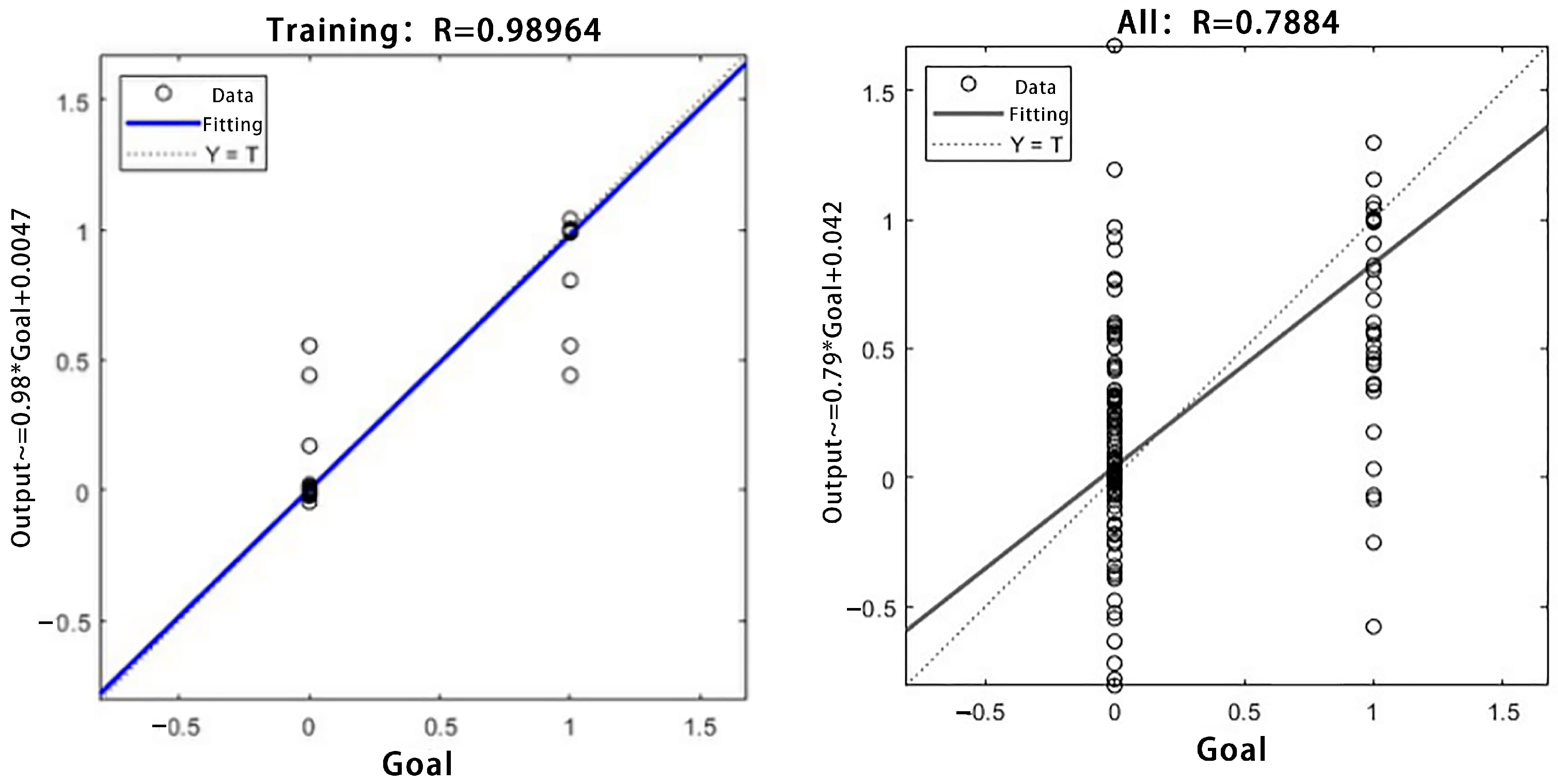
3.2.1. Model Prediction Results
3.2.2. Comparison Between Single Model and Combined Model
3.3. Comprehensive Suitability Assessment
- Very suitable for renovation (accounting for 6%)
- 2.
- Highly suitable for renovation (accounting for 12%)
- 3.
- Generally suitable for renovation (accounting for 26.1%)
- 4.
- More suitable for ecological protection (accounting for 30.6%)
- 5.
- Ecological protection (accounting for 25.3%)
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantitative Model for Assessing the Suitability of Space Renovation Under Bridges
4.2. Evaluation of the Suitability of Space Renovation Under Bridges
4.3. Differential Utilization Potentials of Under-Bridge Space Typologies
4.4. Planning Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trancik, R. Finding Lost Space: Theories of Urban Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zhu, Y.X. Analysis on Three Ways for the Reuse of Urban Corner Space under Viaduct. Urban. Archit. 2023, 20, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.N. Study on the Landscape Construction Under the South Approach Bridge of Nanjing Yangtze River Bridge Basedon the Concept of Landscape Ecology. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Architecture and Engineering, Zhangjiakou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.W.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.Z. The influence of urban elevated bridges on the dispersion and distribution of particulate matter. China J. Highw. Eng. 2022, 35, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Oltra-Carrió, R.; Sòria, G.; Bianchi, R.; Paganini, M. Impact of spatial resolution and satellite overpass time on evaluation of the surface urban heat island effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 117, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.J. Numerical Simulation of the Air Environment in the Street Canyon at the Crossroads Of Urban Roads with Viaducts. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Jinzhong, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vlassova, L.; Perez-Cabello, F.; Nieto, H.; Martín, P.; Riaño, D.; Riva, J.d.l. Assessment of Methods for Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from Landsat-5 TM Images Applicable to Multiscale Tree-Grass Ecosystem Modeling. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4345–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.-H. Reserch on Vegetation Change in Su-Hua Expressway based on GF-1 Remote Sensing Data. Highway 2024, 69, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.; Shao-huai, Y.; Fei, Y. Monitoring and Analysis of Typical Vegetation Parameters in Expressway Road Area Based on Time Series Sentinel-2 images. Highway 2023, 68, 344–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.; Li, B.S.; Pu, F.C.; Gu, X.F.; Wang, X.W. Evaluation of DynamicL and Scape Along Jiuzhi-Maerkang Expressway Based on Digital Twin Scenari. Highway 2024, 69, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Seven Cases of Renovation and Upgrading of Bridge Underspace Abroad. Available online: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_8574101 (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Anonymous. Under Bridges Vol. 2: What Can a City Do with Four Spaces the Size of Central Parks Under Bridges? Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1808689325204881466&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Anonymous. Under the Bridge Space Vol.3: Skating, Boating, Running, Daydreaming. Can These Happen in the Space Under the Bridge? Available online: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_8676960 (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Yin, W. “Scrap Materials” Reimagining the Urban Landscape: A Study on Micro-Updates in Urban Design—The Case of the Underground Space Under the Garden Bridge in Xinchanggang Central Area. Housing 2023, 163, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y. The Research on Innovative Commercial Space and Landscape Under Urban Viaduct. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.M.; Zhou, H.L.; He, Y.Q. Study on the Renewal of the Space Under the Bridge Based on Behavioral Requirements—Taking the Chengdu Fuqing Sports Space as an Example. Intell. Build. City Inf. 2023, 1, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, M.; Matthews, K.; Jones, D. Vegetated Fauna Overpass Disguises Road Presence and Facilitates Permeability for Forest Microbats in Brisbane, Australia. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatriz, P.D.A.; Thiago, S.F.S. Beyond the park and city dichotomy: Land use and land cover change in the northern coast of São Paulo (Brazil). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 189, 352–361. [Google Scholar]
- McGregor, M.E.; Wilson, S.K.; Jones, D.N. Vegetated fauna overpass enhances habitat connectivity for forest dwelling herpetofauna. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 4, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, R.; Mittermeier, J.C.; Roll, U. Combining culturomic sources to uncover trends in popularity and seasonal interest in plants. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.H. Space Utilization and Landscape Under Urban Elevated Bridges (Revised Edition); Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: WuHan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarian Ronizi, S.R.; Mokarram, M.; Negahban, S. Investigation of Sustainable Rural Tourism Activities with Different Risk: A GIS-MCDM Case in Isfahan, Iran. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2021EA002153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Paul, I.; Sarkar, B. Geotourism site suitability assessment by a novel GIS-based MCDM method in the Eastern Duars region (Himalayan foothill) of West Bengal, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Mondal, M.; Sarma, U.S.; Podder, S.; Gayen, S.K. Tourism Suitability Assessment in Malbazar Block using principal component analysis and analytical hierarchy process. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, K.H.; Woldemariam, G.W. GIS-based ecotourism potentiality mapping in the East Hararghe Zone, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Wang, Q.; Wei, D.J. A Novel Hybrid Model Combining BPNN Neural Network and Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.L.; Guo, X. Ecological environment value assessment and ecological civilization in the Changjiang River basin. Water Environ. J. 2024, 38, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Han, Y. Ecological security assessment of urban park landscape using the DPSIR model and EW-PCA method. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 31301–31321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wen, X.; He, P. Surface Soil Moisture Estimation Using a Neural Network Model in Bare Land and Vegetated Areas. J. Spectrosc. 2023, 2023, 5887177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Qian, X.; Jian, D. Research and application of GIS-based multiple-criteria decision making method for dual objectives. J. Chongqing Univ. 2021, 44, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, L.; Ding, G. Research on the Summer Micro-Environment and Human Comfort under Elevated Bridges in Hot and Humid Area. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.H. Potential Tapping and Utilization of Remaining Space in the Process of Urban Renewal: A Case Study of Underbridge Space. Landsc. Archit. 2023, 30, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, J.W. Study on Humanize Design of Urban Overpass Accessory Space. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M. Research on the Spatial Landscape Planning and Design of the Urban Expressway Viaduct—Take Xi’an as an Example. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Han, C.P.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J.J.; Bu, T.M. Analyzing Landscape Preference in Under-Bridge Spaces Based on Different Travel Modes: A Study on Urban Viaduct Landscapes in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2025, 19, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkoog, N.A.M.; Kyu, L.J. A study for utilization of under space of urban bridge. J. Korea Intitute Spat. Des. 2012, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, J.; Luo, M.; Zhou, X. Commercial Value Assessment of “Grey Space” under Overpasses: Analytic Hierarchy Process. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4970697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, F.J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W. Distance-decay pattern and spatial differentiation of expressway flow:An empirical study using data of expressway toll station in Fujian Province. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.; Tong, L. Research on residents activity survey and satisfaction evaluation on public open space of rural areas in severe cold regions. China Sci. 2015, 10, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.T.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, D.W.; Rong, J.H. Research on Under-Bridge and its Public Demand Evaluation in Mega City Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Beijing. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2023, 38, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Study on the Quality of Urban Overhead Visual Space. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, K.Y.; Cinn, E. A Study on the Strategies for the Vitalization of the Spaces under Han River Bridges. J. Korea Intitute Spat. Des. 2019, 14, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, C. Challenges and Potentials: Environmental Assessment of Particulate Matter in Spaces Under Highway Viaducts. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Cai, C.X.; Min, L.; Peng, X.-L. Study on methodology of ecological suitability assessment ofvurban landuse: An example of Pingxiang. Geogr. Res. 2007, 26, 782–788+859. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.F.; Huang, H. Evaluation and Characteristics Analysis of the Production living-ecological Space Suitability in Chenzhou Prefecture. Land Resour. Her. 2023, 20, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, F.F.; Wu, N.Y.; Yangjian, H. Land Suitability Evaluation and Development Planning in Lingnan Hilly Areas: A Case Study of the Large Scientific Facilities Cluster in Guangming Science City. Intell. City 2022, 8, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.W.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Gong, C. A GA-BP Neural Network Regression Model for Predicting Soil Moisture in Slope Ecological Protection. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Cao, J.; Chao, L.; Li, Y. Study on Comprehensive Assessment of Water-Resource Safety Based on Improved TOPSIS Coupled with GA-BP. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 105, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Fang, K. Adaptability assessment of the Enning road heritage district in China based on GA-BP neural network. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Fan, Z.Y. Evaluation of urban green space landscape planning scheme based on PSO-BP neural network model. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 7141–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. WSN Localization Technology Based on Hybrid GA-PSO-BP Algorithm for Indoor Three-Dimensional Space. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Peng, F. Network traffic prediction algorithm research based on PSO-BP neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Systems Research and Mechatronics Engineering (ISRME), Zhengzhou, China, 11–13 April 2015; pp. 1239–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qin, D.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Li, P.; Liu, B.; Gong, P.; Yang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Land Use and Landscape Pattern Evolution in the Economic Belt of the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieian, M.; Kianfar, A. Guiding public policy in gray spaces: A meta-study on land ownership conflicts (1987–2022). Cities 2024, 147, 104803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, L. Research of Interaction Mechanism between Comprehensive Transport and Territorial Space. Railw. Transp. Econ. 2025, 47, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochop, M.; Konecna, J.; Podhrazska, J.; Kyselka, I. Support of Development of Landscape Not-Production Functions in Spatial Planning and Land Consolidation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Public Recreation and Landscape Protection—With Nature Hand in Hand, Krtiny, Czech Republic, 1–3 May 2016; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Komarzyńska-Świeściak, E.; Kozlowski, P. The acoustic climate of spaces located under overpasses in the context of adapting them for outdoor public events—A pilot case study. Bud. I Archit. 2021, 20, 63–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M.; Brown, K.G.; Ng, K.; Cortes, M.; Kosson, D. The importance of recognizing Buffer Zones to lands being developed, restored, or remediated: On planning for protection of ecological resources. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part A-Curr. Issues 2024, 87, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K. Research on the Ecological Strategies in Landscape Design and Planning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Building, Materials and Civil Engineering (GBMCE 2011), Shangri La, China, 22–23 August 2011; pp. 1805–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhani, P. Analysis of ecological network structure and biological function continuity in Jajrud Protected Area. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 27, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Du, X. Green Renewal Strategies for Urban Elevated Grey Transportation Infrastructure: A Case Study of the Space Under the Ningbo-Dongguan Expressway in Wenzhou. Cent. China Archit. 2025, 43, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S. Exploration of Underground Space Development and Utilization from the Perspective of Urban Renewal: A Review of “Urban Renewal and Planning and Design of Underground Space Expansion and Renovation”. Mod. Urban Stud. 2025, 4, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y. Renewal Strategies and Practices of Urban Infrastructure under the Concept of Green Development. Planner 2025, 41, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
| Destination Layer | Quasi-Measurement Layer | Index Level | Measurement Unit | Data Type | Data Sources | Expected Weight | Source of Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functional development objective | Renovation suitability (C1) | head room | m | Quantitative | Field measurement, actual value | 0.07969 | [32,33,34] |
| The vertical projected area enclosed by the bridge boundary | m2 | Quantitative | Field measurement, actual value | 0.17182 | [35,36] | ||
| Nighttime lighting | lamp | Qualitative | Number of street lamps: 1–5 | 0.10375 | [35,37] | ||
| Environmental Aesthetics (C2) | The population of the surrounding residents | Ten thousand people | Quantitative | Actual value/10,000 people | 0.06497 | [38,39] | |
| Type of people participating in the surrounding activities | class | Qualitative | Field investigation:Number of population types: 0–3 | 0.04660 | [38,40] | ||
| regional culture characteristics | class | Qualitative | Field investigation:Number of cultural characteristic types: 0–10 | 0.09025 | [32,41] | ||
| Surrounding landscape resources | class | Qualitative | Field investigation:Number of landscape types: 0–10 | 0.05273 | [32,41] | ||
| Convenience and Security (C3) | traffic accessibility | km | Quantitative | GIS analysis of road network density 1–5 | 0.11542 | [36,42] | |
| Activity safety | vehicle | Quantitative | Field investigation:Daily traffic volume: 1–5 | 0.09934 | [37] | ||
| Space noise | dB | Quantitative | Field investigation: Actual value of the decibel meter | 0.07558 | [37] | ||
| air pollutant | mg/m3 | Quantitative | Field investigation:Pollutant Detection Instrument Implementation Mechanism | 0.09985 | [37,43] | ||
| Ecological protection goals | Environmental ecology (C4) | Distribution of surrounding water systems | m | Quantitative | GIS analysis of water flow distance and spatial distance | 0.16260 | [30,44,45,46] |
| The distribution of basic farmland in the surrounding area | m | Quantitative | GIS analysis of the spatial distance between farmland | 0.36520 | [30,44,46] | ||
| The current status of vegetation and its conservation value | % | Quantitative | GIS analysis of spatial vegetation coverage | 0.47220 | [35,36,42] |
| Degree of Suitability for Renovation | Types of Space Under the Bridge | Number (of Seats) | Percentage (%) | Remarks | For Example | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very suitable | Highway hub type, Cross-connected type | 8 | 6% | Good lighting, cultural resources, low traffic volume | Qiantang Hub |  |
| Highly suitable | Cross-connected type, Single and double-sided road-facing type | 16 | 12% | Good lighting, cultural resources, low traffic, good safety | Fuzhou G1505 Ring Expressway |  |
| Generally suitable | Cross-connected type | 35 | 26.1% | Poor lighting, scarce cultural resources, average safety | Chuangxia Grand Bridge |  |
| More suitable for ecological protection | Road-penetration spaces | 41 | 30.6% | Poor lighting, heavy traffic, suitable for ecological protection | The Bancheng Interchange of the Ningbo-Dongguan Expressway |  |
| Ecological protection | Poor-accessibility ecological spaces | 34 | 25.3% | Poor access, high ecological value, few human interferences | Yuxi Bridge |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ren, W.; Peng, D. Assessment of Ecological Suitability for Highway Under-Bridge Areas: A Methodological Integration of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Optimized Backpropagation Neural Networks. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9120528
Han Y, Huang S, Zhao S, Zhang X, Chen Y, Wu Z, Huang Y, Ren W, Peng D. Assessment of Ecological Suitability for Highway Under-Bridge Areas: A Methodological Integration of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Optimized Backpropagation Neural Networks. Urban Science. 2025; 9(12):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9120528
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yiwei, Shuhong Huang, Siyan Zhao, Xinyu Zhang, Yanbing Chen, Zhenhai Wu, Yuanhao Huang, Wei Ren, and Donghui Peng. 2025. "Assessment of Ecological Suitability for Highway Under-Bridge Areas: A Methodological Integration of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Optimized Backpropagation Neural Networks" Urban Science 9, no. 12: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9120528
APA StyleHan, Y., Huang, S., Zhao, S., Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Wu, Z., Huang, Y., Ren, W., & Peng, D. (2025). Assessment of Ecological Suitability for Highway Under-Bridge Areas: A Methodological Integration of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Optimized Backpropagation Neural Networks. Urban Science, 9(12), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9120528






