Comprehensive Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid) Pollution in Agricultural and Urban Soils near an Oil Refining Facility: Distribution Patterns, Source Apportionment, Ecological Impact, and Probabilistic Health Risk Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
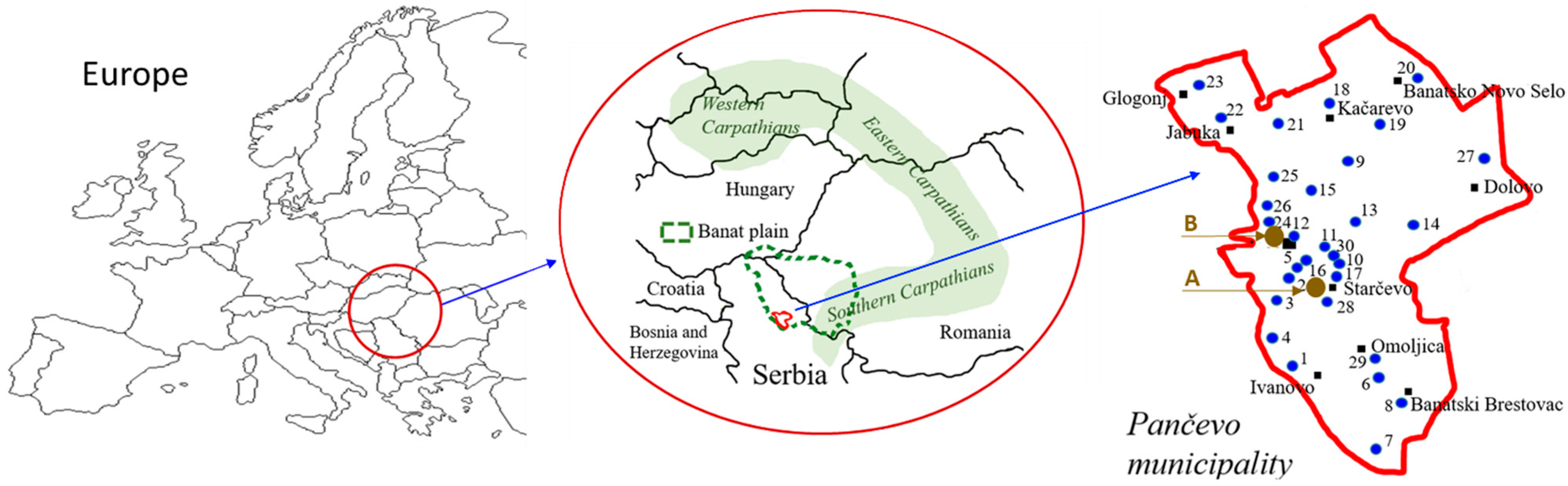
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Multivariate Data Analysis
2.4. Soil Pollution Indices
2.5. Source-Specific Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Monte Carlo Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
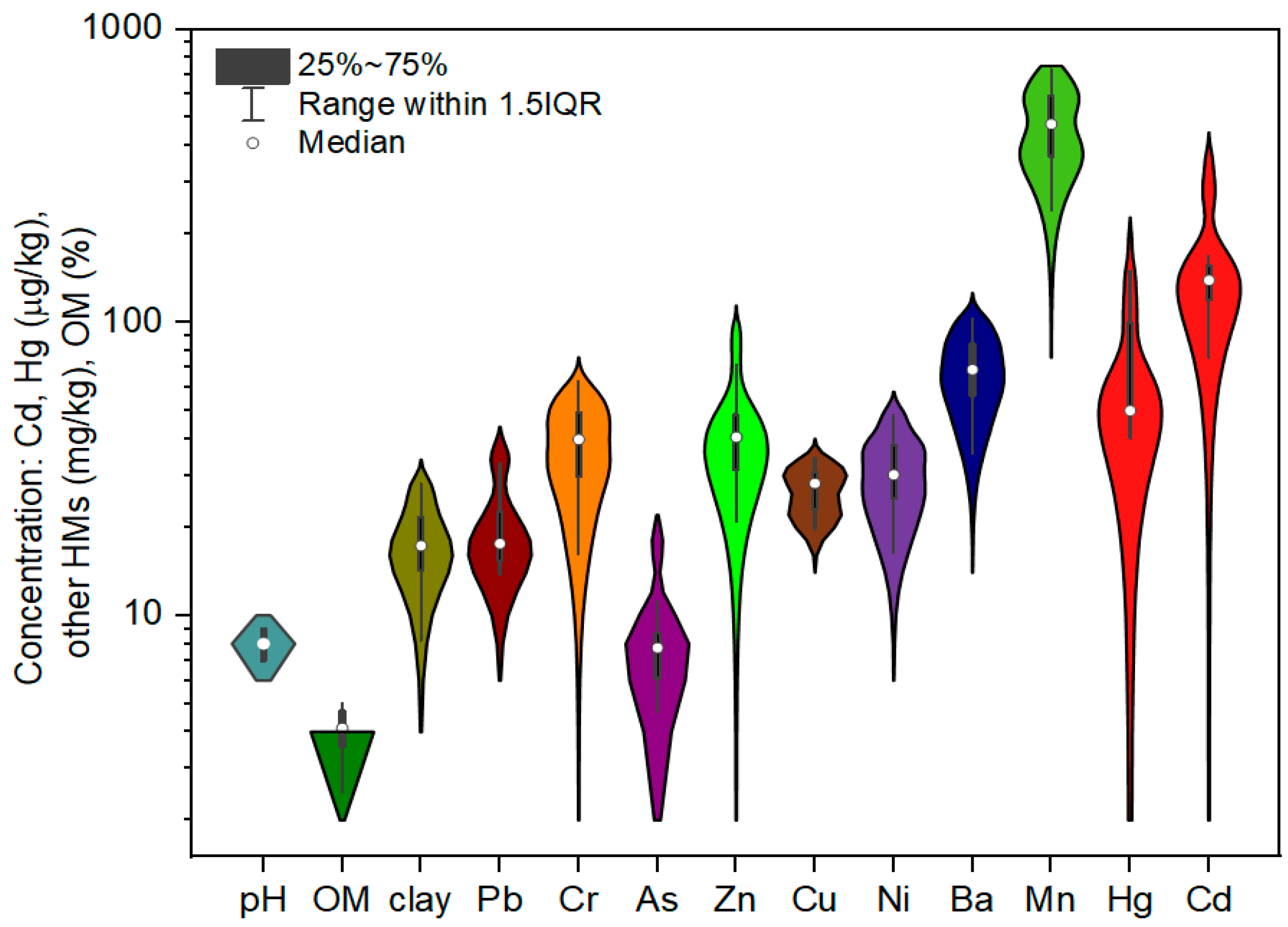
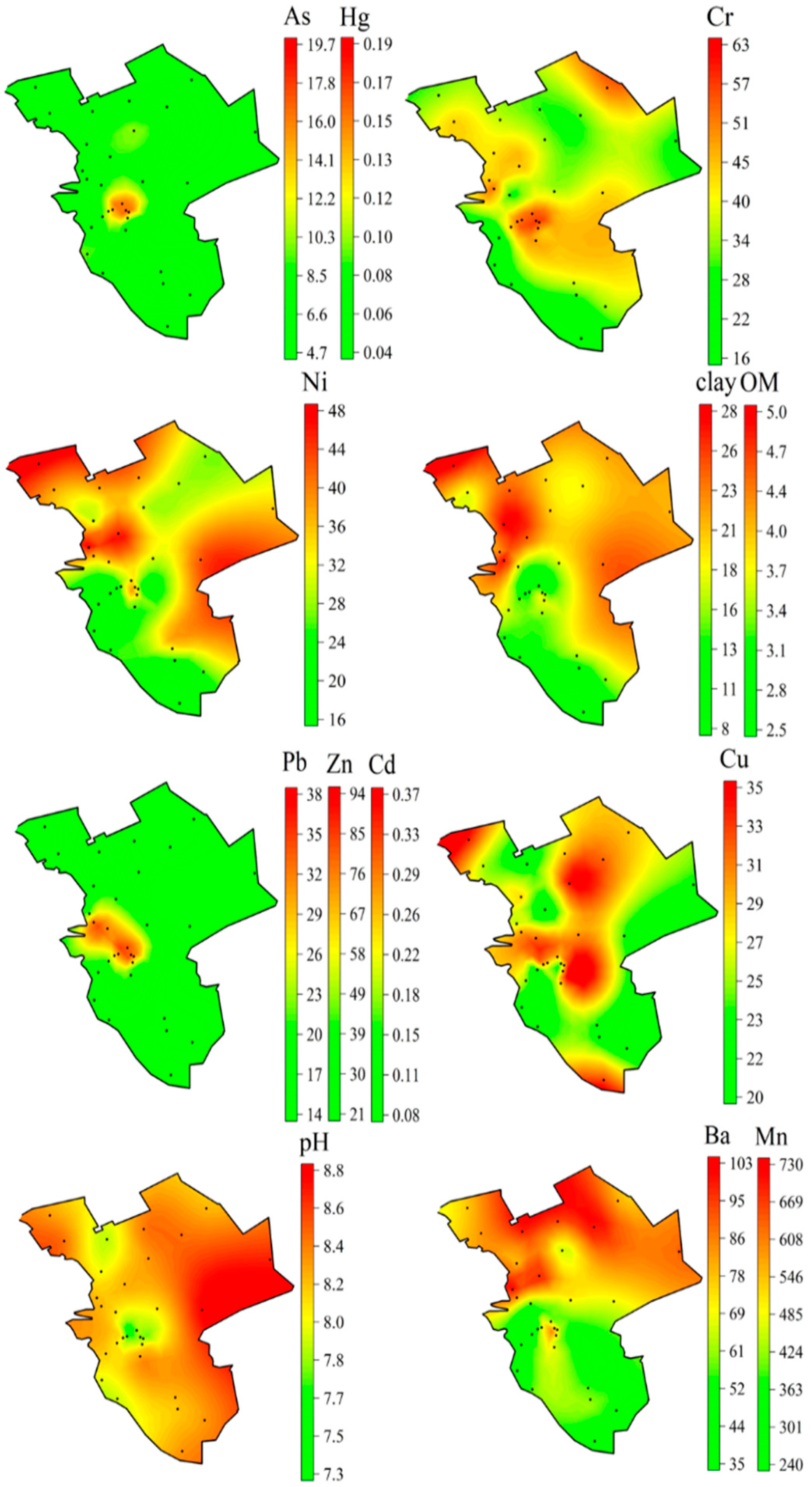
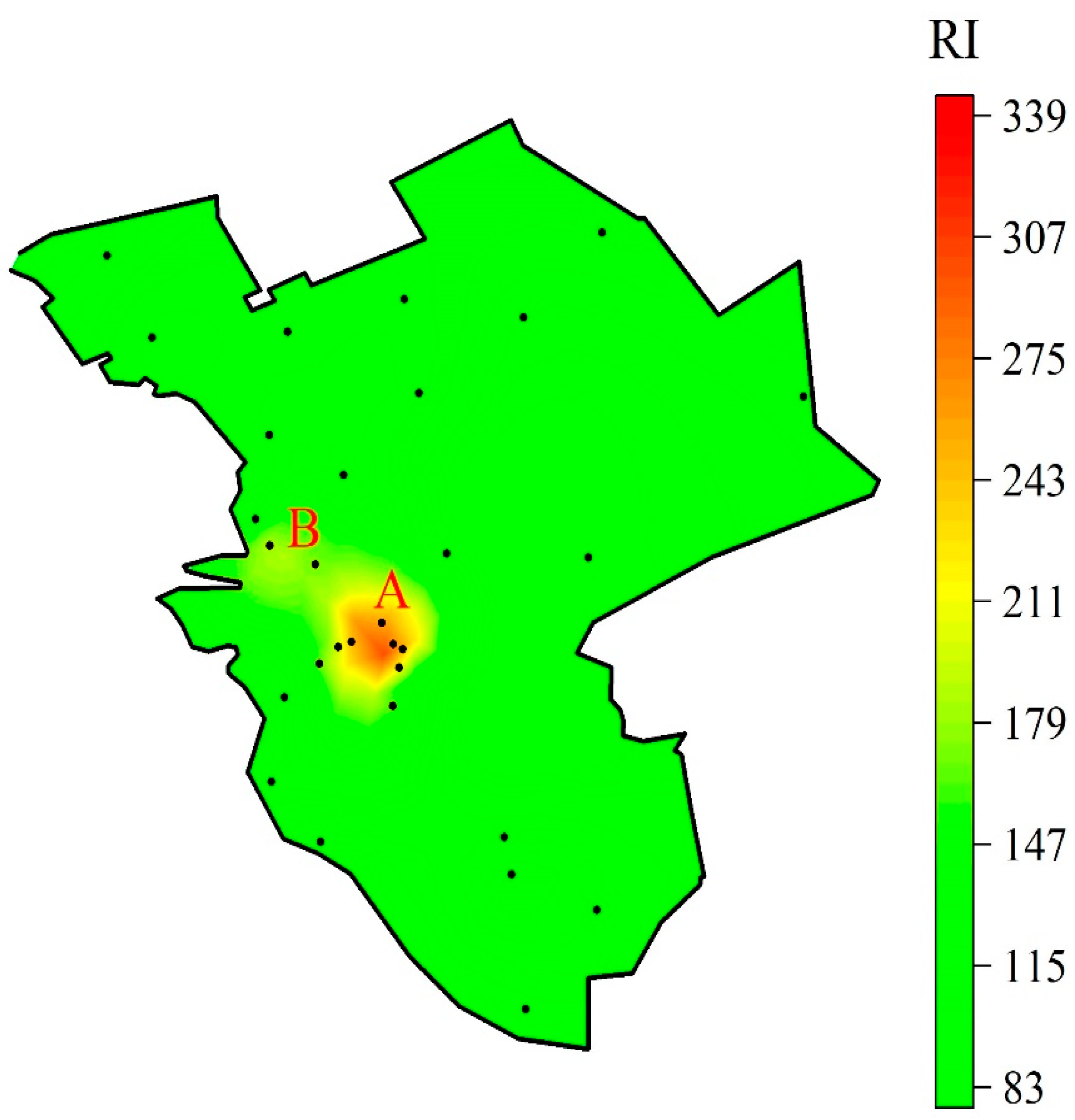
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Spatial Distribution of Soil HMs
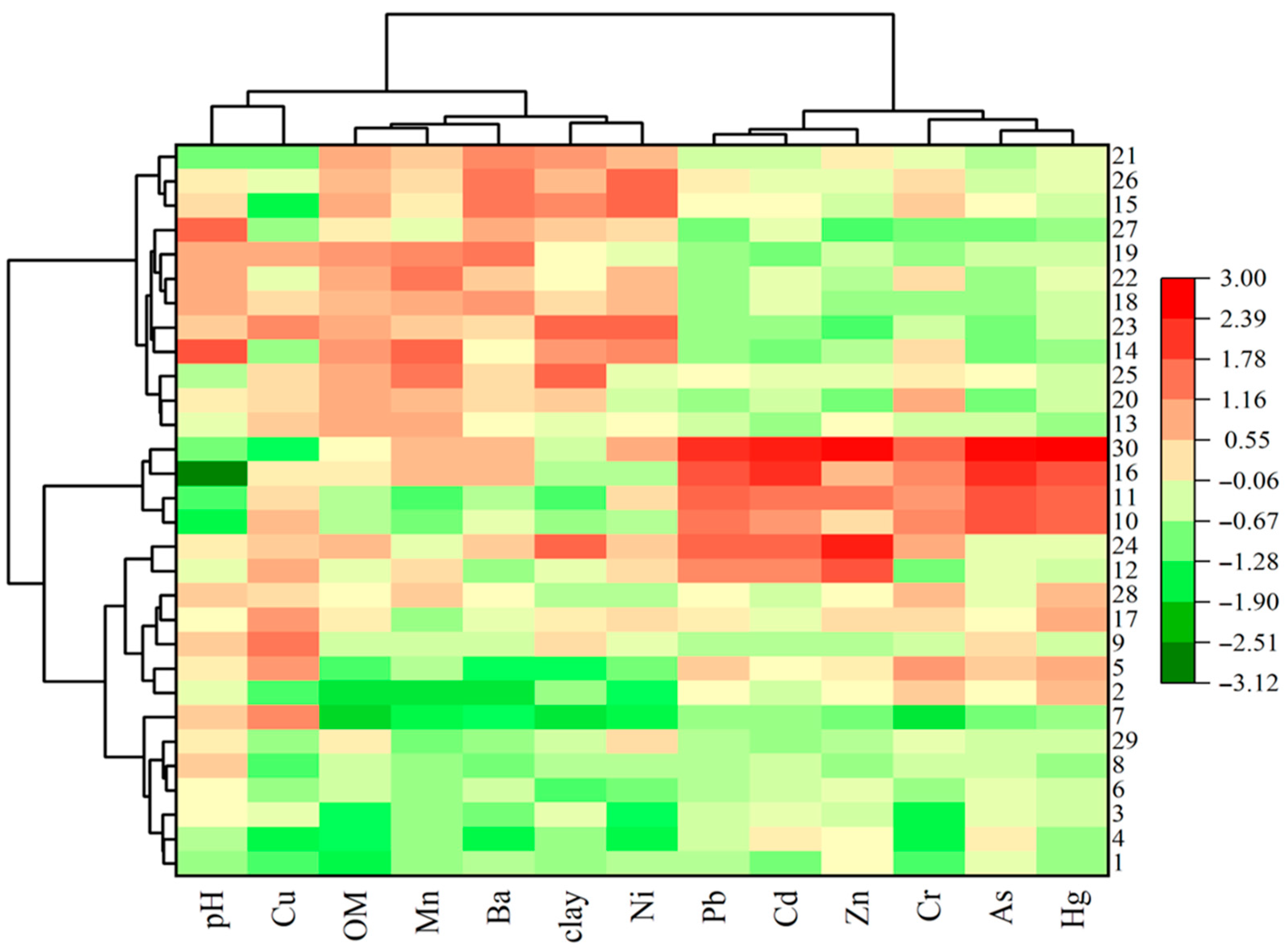
3.2. Source Analysis of HMs in Soil
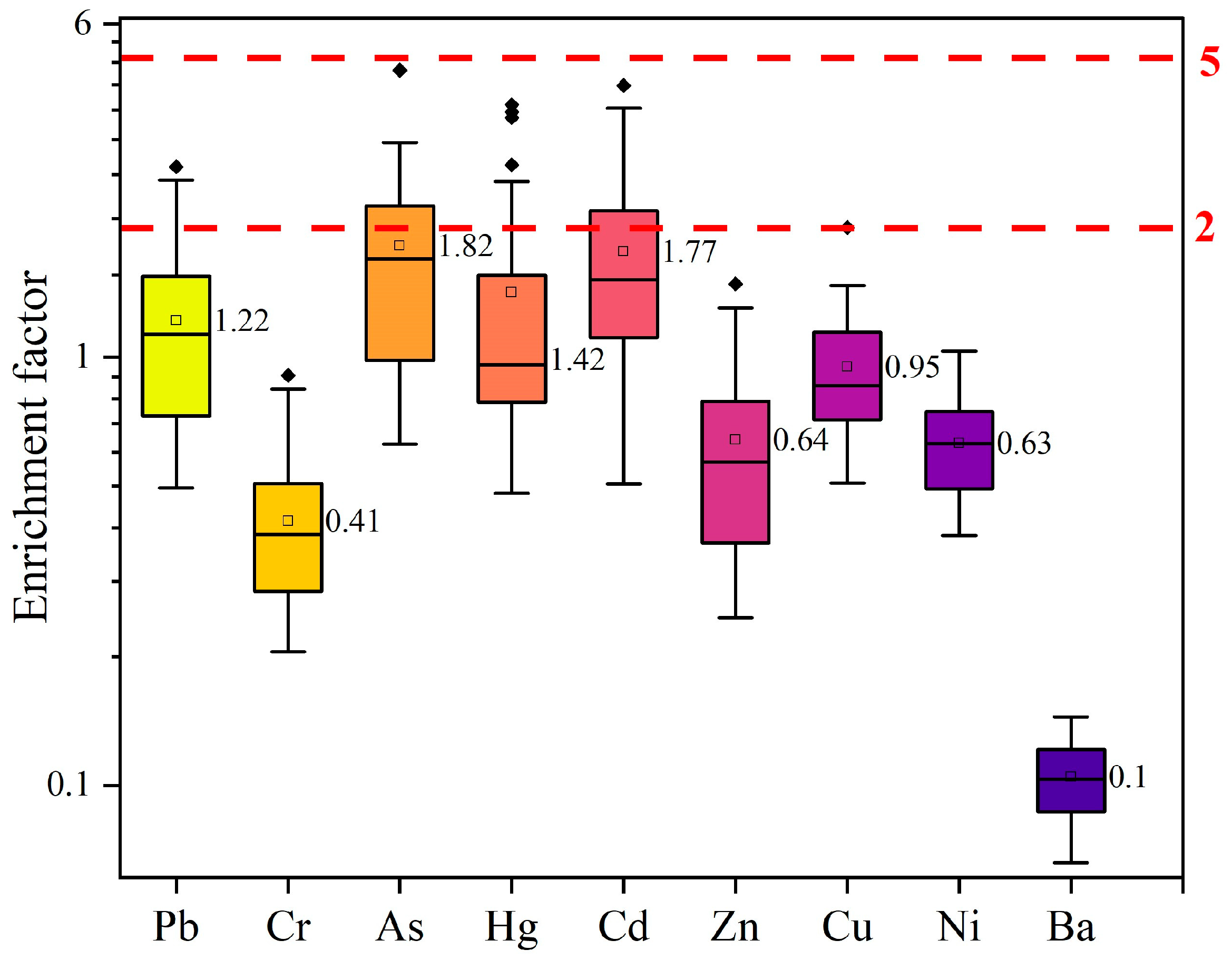
3.3. Assessment of Ecological Risks
3.4. Concentration-Based Health Risk Assessment
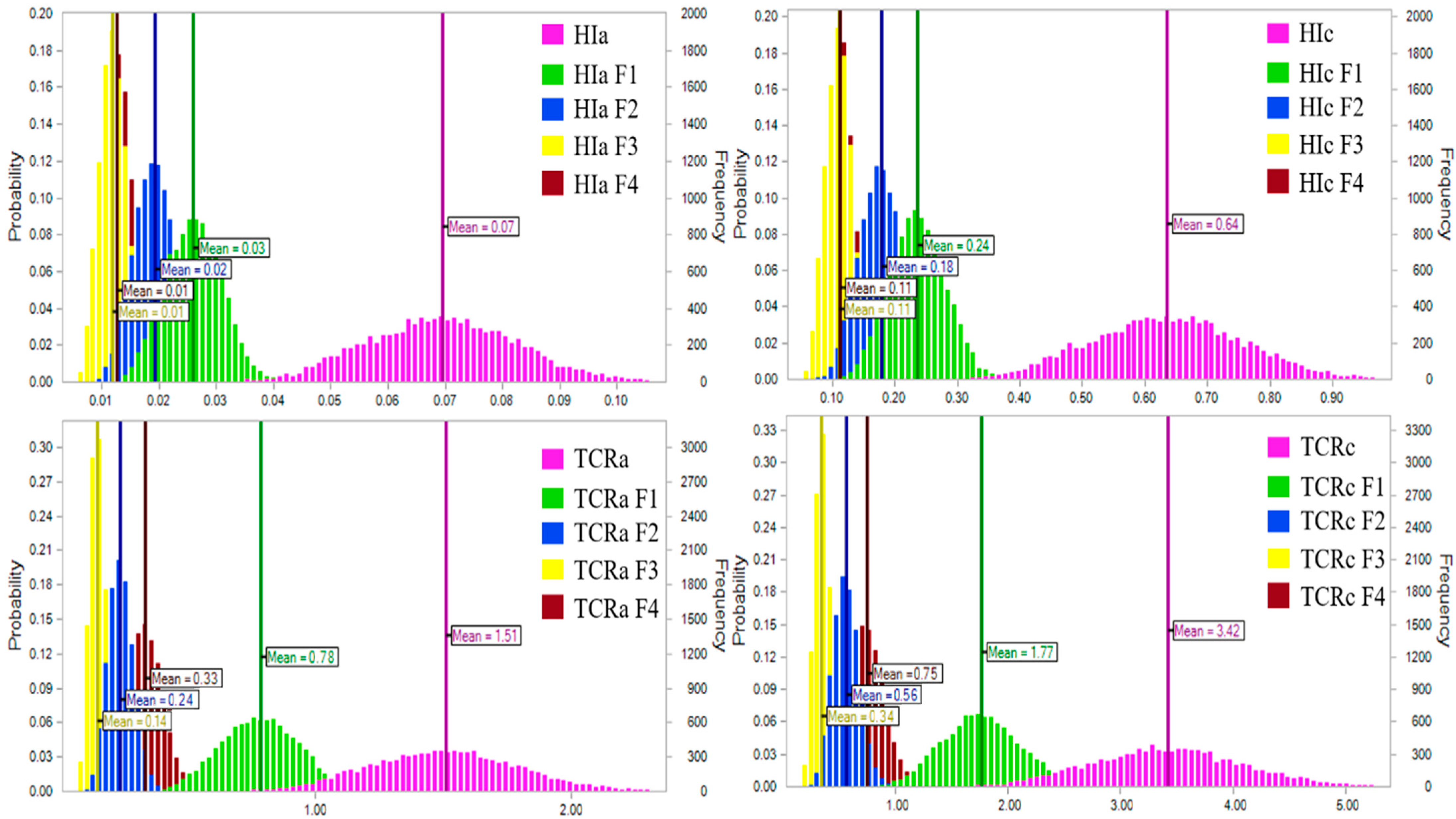
3.5. Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chang, S.X.; Collins, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Status Assessment and Probabilistic Health Risk Modeling of Metals Accumulation in Agriculture Soils across China: A Synthesis. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormoker, T.; Proshad, R.; Islam, S.; Ahmed, S.; Chandra, K.; Uddin, M.; Rahman, M. Toxic Metals in Agricultural Soils near the Industrial Areas of Bangladesh: Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment. Toxin Rev. 2019, 40, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, N.; Amini, A.; Dehbandi, R. Contamination, Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment and Quantitative Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Metals (PTMs) in Street Dust of a Highly Developed City in North of Iran. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, H.; Memarzadeh, M.; Naghizade Asl, F. Carcinogenic and Non-Carcinogenic Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Windborne Sediments from a Residential Area (Case Study: Tabas, Iran). Aeolian Res. 2024, 70–71, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, G.A.; Alves Martins, M.V.; Santos, L.M.G.; Neto, S.A.V.; Junior, F.B.; Geraldes, M.C.; Bergamaschi, S.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Patinha, C.; da Silva, E.F.; et al. Contamination by Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Agricultural Products Grown Around Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro State (SE Brazil). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2025, 89, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, W.; Zhou, C.; Long, K.; Zhang, Z. Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment and Grading Benchmark Estimation of Atmospheric PM2.5-Bound Heavy Metals in China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2025, 88, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković, J.; Bulatović, S.; Miletić, A.; Tadić, T.; Marković, B.; Nastasović, A.; Onjia, A. Source-Specific Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Groundwater of a Copper Mining and Smelter Area. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajković, I.; Sentić, M.; Miletić, A.; Vesković, J.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Ecological Risk of Potentially Toxic Elements in an Urban Shallow Lake Sediment. Chem. Ecol. 2024, 40, 1092–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlı, C.; Ustaoğlu, F.; Yazman, M.M.; Yüksel, B. Where Rivers Meet the Sea: Source Fingerprinting and Health Risk Mapping of Potentially Hazardous Elements in Sediments from the Çanakkale Strait Basin (Türkiye). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2026, 222, 118626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, Y.; Alshehri, F.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Alzahrani, H. Environmental Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils around Al-Janabeen Dam, Southwest Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, V.; Singh, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumari, G.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, S. Soil Heavy Metals Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment in Rohtak Urban Area, Haryana (India). Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-Specific Ecological Risk Analysis and Critical Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Road Dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Contamination, Sources and Health Risks of Toxic Elements in Soils of Karstic Urban Parks Based on Monte Carlo Simulation Combined with a Receptor Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebian, M.; Sobhanardakani, S.; Taghavi, L.; Ghoddousi, J. Analysis and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Surface Soils Collected from Various Land Uses around Shazand Oil Refinery Complex, Arak, Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzadeh, Z.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Marsan, F.A.; Padoan, E. Potentially Toxic Elements in the Middle East Oldest Oil Refinery Zone Soils: Source Apportionment, Speciation, Bioaccessibility and Human Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40573–40591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshahri, F.; El-Taher, A. Assessment of Heavy and Trace Metals in Surface Soil Nearby an Oil Refinery, Saudi Arabia, Using Geoaccumulation and Pollution Indices. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraki, H.; Keshavarzi, B.; Zarei, M.; Moore, F.; Abbasi, S.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Urban Street Dust in the Middle East Oldest Oil Refinery Zone: Oxidative Potential, Source Apportionment، and Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, W.J.; Deka, H. Ecological and Human Health Risk Associated with Heavy Metals (HMs) Contaminant Sourced from Petroleum Refinery Oily Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Fang, Q.; Miao, F.; Lin, Q. An Integrated Method of Health Risk Assessment Based on Spatial Interpolation and Source Apportionment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, F.; Luo, X.; Feng, J.; He, J.; Xue, S. Geochemical Partitioning and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Soils Contaminated by Lead Smelting. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, K.; Lei, M. Human Health Risk Apportionment from Potential Sources of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Associated Uncertainty Analysis. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onjia, A.; Huang, X.; Trujillo González, J.M.; Egbueri, J.C. Editorial: Chemometric Approach to Distribution, Source Apportionment, Ecological and Health Risk of Trace Pollutants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1107465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Gupta, B.S.; Patidar, S.; Martinez-Villegas, N. Spatial Distribution and Source Identification of Metal Contaminants in the Surface Soil of Matehuala, Mexico Based on Positive Matrix Factorization Model and GIS Techniques. Front. Soil Sci. 2022, 2, 1041377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-González, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A.; Serrano-Gómez, M.; Castillo-Monroy, E.F.; Jiménez Ballesta, R.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Mapping Potential Toxic Elements in Agricultural and Natural Soils of the Piedemonte Llanero in Colombia. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, F.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, Source Investigation, and Risk Assessment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Areas with Intensive Anthropogenic Activities Using the Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Model Coupled with Self-Organizing Map (SOM). Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, T.; An, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Pu, Y.; Wang, G.; Jia, Y.; et al. Soil Potentially Toxic Element Pollution at Different Urbanization Intensities: Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk Assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletić, A.; Vesković, J.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Monte Carlo Simulation of Source-Specific Risks of Soil at an Abandoned Lead-Acid Battery Recycling Site. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 3313–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Martín, J.D. An Integrated Approach for Quantifying Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils near an Old Industrial Area. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, P.R.; De Pádua Melo, E.S.; Espindola, D.A.L.F.; Zoccal Garcia, D.A.; Aragão, V.; Pereira Ancel, M.A.; Pott, A.; Do Nascimento, V.A. Assessment of Metal (Loid) s in Fern Amauropelta Rivularioides (Fee), Soil, and River Water in a Peri-Urban Agriculture Area on the Brazil—Paraguay Border. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guan, Q.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, N. Contamination Characteristics, Source Apportionment, and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soil in the Hexi Corridor. Catena 2020, 191, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Shi, H.; Fei, Y.; Qi, J.; Mo, L. Research on Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil Based on Multi-Factor Source Apportionment: A Case Study in Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Source Apportionment of and Potential Health Risks Posed by Trace Elements in Agricultural Soils: A Case Study of the Guanzhong Plain, Northwest China. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, Q.; Cai, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment in Urban Parks at a Megacity of Central China. Toxics 2023, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment and Anthropogenic Sources Analysis of Heavy Metals in Different Types of Urban Road Dust. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 195, 106813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Ukah, B.U.; Ubido, O.E.; Unigwe, C.O. A Chemometric Approach to Source Apportionment, Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Industrial Soils from Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 3399–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, J. Source Apportionment and Spatial Distribution of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils: A New Exploration on Receptor and Geostatistical Models. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, B. Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk and Sources of Heavy Metals in Soils from a Typical Economic Development Area, Southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radomirović, M.; Miletić, A.; Onjia, A. Accumulation of Heavy Metal(Loid)s and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Sediment of the Prahovo Port (Danube) and Associated Risks. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thurkal, A.K.; Cerda, A. Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils of India and Ecological Risk Assessment: A State-of-the-Art. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Karmaker, S.C.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Rakib, M.A.; Saha, B.B. Enrichment, Sources and Ecological Risk Mapping of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of Dhaka District Employing SOM, PMF and GIS Methods. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 20460.
- Ene, A.; Moraru, S.S.; Moraru, D.I.; Pantelica, A.; Gosav, S.; Ceoromila, A.M. Major and Trace Element Accumulation in Soils and Crops (Wheat, Corn, Sunflower) around Steel Industry in the Lower Danube Basin and Associated Ecological and Health Risks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Darijani, T.; Alipour, V. Heavy Metal Pollution of Road Dust in a City and Its Highly Polluted Suburb; Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Specific Ecological and Health Risk Assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerizghi, T.; Guo, Q.; Tian, L.; Wei, R.; Zhao, C. An Integrated Approach to Quantify Ecological and Human Health Risks of Soil Heavy Metal Contamination around Coal Mining Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Heavy Metal Contamination Assessment and Probabilistic Health Risks in Soil and Maize near Coal Mines. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1004579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhu, D.; Yang, T.; Mao, C.; Huang, W.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y. Soil Heavy Metal Accumulation and Ecological Risk in Mount Wuyi: Impacts of Vegetation Types and Pollution Sources. Land 2025, 14, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Świercz, A.; Zajecka, E. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in the Urban Soils of the City of Skarzysko-Kamienna (Poland) with Regard to Land Use. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 13, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.C. Pollutant Source, Ecological and Human Health Risks Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils from Coal Mining Areas in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Shi, W. Source Apportionment and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils on a Large Scale in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 1413–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujre, N.; Mitra, S.; Soni, A.; Agnihotri, R.; Rangan, L.; Rene, E.R.; Sharma, M.P. Speciation, Contamination, Ecological and Human Health Risks Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils Dumped with Municipal Solid Wastes. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R. Effect of Different Industrial Activities on Soil Heavy Metal Pollution, Ecological Risk, and Health Risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); Office of Emergency and Remedial Response U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; p. 20450.
- Yuan, B.; Cao, H.; Du, P.; Ren, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H. Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements in a Typical Mining City. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, D.; Li, L. Multiple Pathway Exposure Risks and Driving Factors of Heavy Metals in Soil-Crop System in a Pb/Zn Smelting City, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, F.G.; de Souza, I.D.; Melo, E.S.d.P.; Ancel, M.A.P.; Garcia, D.A.Z.; Bogo, D.; Guimarães, R.d.C.A.; Gielow, K.d.C.F.; Oliveira, R.J.; Sanches, G.M.; et al. Assessment of Metal(Loid)s and Nonmetals Contamination in Soils of Urban Ecological Parks in Brazil: Implications for Ecological Risk and Human Health. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković, J.; Deršek-Timotić, I.; Lučić, M.; Miletić, A.; Đolić, M.; Ražić, S.; Onjia, A. Entropy-Weighted Water Quality Index, Hydrogeochemistry, and Monte Carlo Simulation of Source-Specific Health Risks of Groundwater in the Morava River Plain (Serbia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Novel Insights into Probabilistic Health Risk and Source Apportionment Based on Bioaccessible Potentially Toxic Elements around an Abandoned E-Waste Dismantling Site. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletić, A.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Exposure Factors in Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Sediment. Metals 2023, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In The Crust (ed. R.L. Rudnick). Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier-Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Li, C.; Tang, S.; Shang, G.; Yu, F.; Li, Y. Heavy Metal Concentration, Potential Ecological Risk Assessment and Enzyme Activity in Soils Affected by a Lead-Zinc Tailing Spill in Guangxi, China. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsamos, P.; Stefanou, S.; Noli, F. Assessment of Distribution of Heavy Metals and Radionuclides in Soil and Plants Nearby an Oil Refinery in Northern Greece. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, D.; Ding, D.; Wu, Y.; Wei, J.; Kong, L.; Long, T.; Fan, T.; Deng, S. Ecological-Health Risks Assessment and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils around a Super-Sized Lead-Zinc Smelter with a Long Production History, in China ☆. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.A. Comparison of Trace Element and Heavy Metal Concentrations of Top and Bottom Soils in a Complex Land Use Area. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 13, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoba, P.O.; Ogunkunle, C.O.; Folarin, O.O.; Oladele, F.A. Heavy Metal Pollution and Ecological Geochemistry of Soil Impacted by Activities of Oil Industry in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demİr, A.D. The Impacts of Long-Term Intensive Farming Applications on the Heavy Metal Concentrations in Soils. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 17, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, F.; Cui, L.; Jiao, Y. Source Apportionment and Ecological-Health Risks Assessment of Heavy Metals in Topsoil Near a Factory, Central China. Expo. Health 2021, 13, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, P.C.; John, K.; Kebonye, N.M.; Borůvka, L.; Vašát, R.; Drábek, O. A Geostatistical Approach to Estimating Source Apportionment in Urban and Peri-Urban Soils Using the Czech Republic as an Example. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Peng, S.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Shi, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, H.; Zeng, G. ming Source Apportionment and Spatial and Quantitative Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils from a Typical Chinese Agricultural County. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Shao, W.; Tian, J.; Luo, H.; Ni, F.; Shan, Y. Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Farmland Soils of a Typical Oasis City in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Risk Index | Equation * |
|---|---|
| Average daily dose (mg·kg−1·day−1): | |
| Hazard quotient and Hazard index: HI < 1 HI > 1 | |
| Carcinogenic risk and Total carcinogenic risk: TCR < 10–6 10–6 < TCR < 10–4 TCR > 10–4 |
| HMs | Mean | SD | Max | Min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | −0.37 | 0.46 | 0.58 | −0.89 |
| Cr | −1.89 | 0.53 | −1.13 | −3.09 |
| As | 0.16 | 0.56 | 1.45 | −0.62 |
| Hg | −0.27 | 0.67 | 1.34 | −0.91 |
| Cd | 0.13 | 0.60 | 1.44 | −0.83 |
| Zn | −1.31 | 0.55 | −0.09 | −2.26 |
| Cu | −0.66 | 0.25 | −0.28 | −1.09 |
| Ni | −1.22 | 0.44 | −0.55 | −2.11 |
| Ba | −3.79 | 0.42 | −3.18 | −4.72 |
| Mn | −0.50 | 0.44 | 0.15 | −1.44 |
| Percentage of samples in different categories * | ||||
| <0 | 0–1 | 1–2 | ||
| Pb | 76.7 | 23.3 | – | |
| Cr | 100 | – | – | |
| As | 33.3 | 53.3 | 13.3 | |
| Hg | 73.3 | 23.3 | 3.3 | |
| Cd | 46.7 | 36.7 | 16.7 | |
| Zn | 100 | – | – | |
| Cu | 100 | – | – | |
| Ni | 100 | – | – | |
| Ba | 100 | – | – | |
| Mn | 86.7 | 13.3 | – | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miletić, A.; Vesković, J.; Lučić, M.; Varol, M.; Crnković, D.; Potkonjak, N.; Onjia, A. Comprehensive Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid) Pollution in Agricultural and Urban Soils near an Oil Refining Facility: Distribution Patterns, Source Apportionment, Ecological Impact, and Probabilistic Health Risk Analysis. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100415
Miletić A, Vesković J, Lučić M, Varol M, Crnković D, Potkonjak N, Onjia A. Comprehensive Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid) Pollution in Agricultural and Urban Soils near an Oil Refining Facility: Distribution Patterns, Source Apportionment, Ecological Impact, and Probabilistic Health Risk Analysis. Urban Science. 2025; 9(10):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100415
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiletić, Andrijana, Jelena Vesković, Milica Lučić, Memet Varol, Dragan Crnković, Nebojša Potkonjak, and Antonije Onjia. 2025. "Comprehensive Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid) Pollution in Agricultural and Urban Soils near an Oil Refining Facility: Distribution Patterns, Source Apportionment, Ecological Impact, and Probabilistic Health Risk Analysis" Urban Science 9, no. 10: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100415
APA StyleMiletić, A., Vesković, J., Lučić, M., Varol, M., Crnković, D., Potkonjak, N., & Onjia, A. (2025). Comprehensive Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid) Pollution in Agricultural and Urban Soils near an Oil Refining Facility: Distribution Patterns, Source Apportionment, Ecological Impact, and Probabilistic Health Risk Analysis. Urban Science, 9(10), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100415










