Quantification of Urban Groundwater Recharge: A Case Study of Rapidly Urbanizing Guwahati City, India
Abstract
1. Introduction
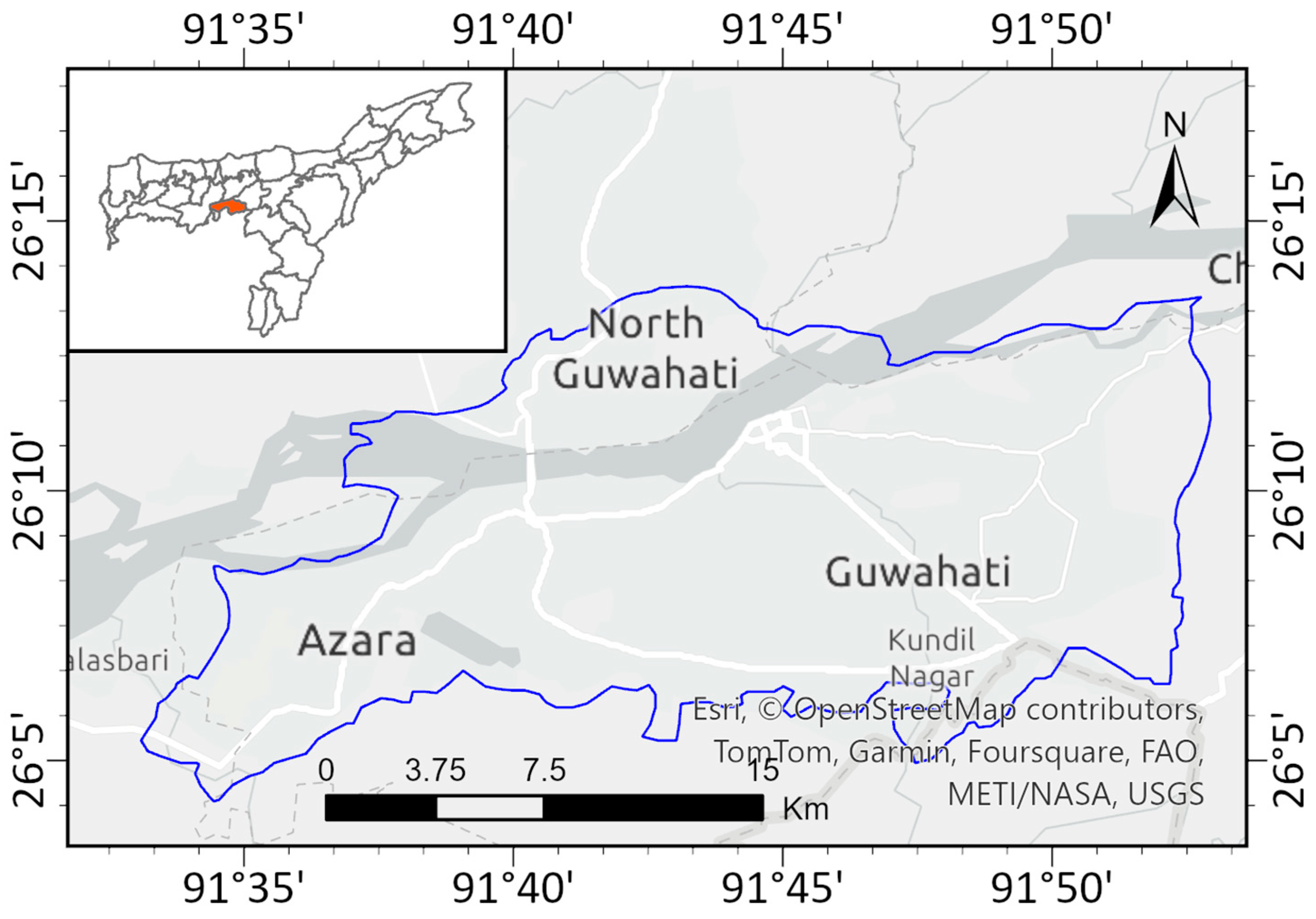
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Assessments of Natural Groundwater Recharge
3.2. Assessments of Urban Groundwater Recharge
4. Results
4.1. Total Natural Groundwater Recharge
4.2. Total Urban Groundwater Recharge
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Gun, J. Groundwater resources sustainability. In Global Groundwater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 331–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sarami-Foroushani, T.; Balali, H.; Movahedi, R.; Kurban, A.; Värnik, R.; Stamenkovska, I.J.; Azadi, H. Importance of good groundwater governance in economic development: The case of western Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 21, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.J.S.; Schneider, M.; Elango, L. The state-of-the-art estimation of groundwater recharge and water balance with a special emphasis on India: A critical review. Sustainability 2021, 14, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, G.; Lu, S.; Sang, L.; Meng, G.; Chen, L.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of urbanization on the water cycle in the Shiyang River basin: Based on a stable isotope method. HESS 2023, 27, 4437–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Slater, L.; Wilby, R.L.; Faulkner, D. Contribution of urbanisation to non-stationary river flow in the UK. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, D.N. Groundwater recharge in urban areas. Atmos. Environ. Part B 1990, 24, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakode, H.B.; Baier, K.; Jha, R.; Azzam, R. Impact of urbanization on groundwater recharge and urban water balance for the city of Hyderabad, India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.R.; Ismail, Z.B.; Niksokhan, M.H.; Ramli, A.H.; Sidek, L.M.; Dayarian, M.A. Investigating the effective factors influencing surface runoff generation in urban catchments—A review. Desalin. Water Treat 2019, 164, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshtawi, T.; Evers, M.; Tischbein, B. Quantifying the impact of urban area expansion on groundwater recharge and surface runoff. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 826–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, H.T.L.; Pathirana, A. Urbanization and climate change impacts on future urban flooding in Can Tho city, Vietnam. HESS 2013, 17, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppath, N.; Raviraj, A.; Kannan, B.; Sellamuthu, K.M. Estimation of groundwater recharge using water table fluctuation method. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 3404–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnig, M.; Moeck, C.; Radny, D.; Schirmer, M. Impact of urbanization on groundwater recharge rates in Dübendorf, Switzerland. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutsch, M.; Rieckermann, J.; Krebs, P. Quantification of sewer leakage: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prigiobbe, V.; Giulianelli, M. Quantification of sewer leakage by a continuous tracer method. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineeth, V.; Ramachandran, P. Components of urban ground water recharge in Bengaluru, India. Urban Water J. 2022, 20, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Tubau, I.; Vázquez-suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; Valhondo, C.; Criollo, R. Quantification of groundwater recharge in urban environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammal, M.; Archambeau, P.; Erpicum, S.; Orban, P.; Brouyère, S.; Pirotton, M.; Dewals, B. Technical note: An operational implementation of recursive digital filter for base flow separation. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 8528–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherl, R.K.; Salgado, M.J.H.; Ramgraber, M.; Moeck, C.; Schirmer, M. Estimating surface runoff and groundwater recharge in an urban catchment using a water balance approach. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 2411–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lerner, D.N.; Barrett, M.H.; Tellam, J.H. Quantification of groundwater recharge in the city of Nottingham, UK. Environ. Geol. 1999, 38, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Tambe, J.A.; Dehury, B.N.; Tiwari, A.N. Impact of urbanization on the groundwater regime in a fast growing city in central India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 146, 339–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; Tubau, I.; Sanchez-Vila, X.; Soler, A. An approach to identify urban groundwater recharge. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGWA. Consolidated MoJS Guideline to Regulate and Control Groundwater Extraction in India. Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India. 2023. Available online: https://cgwa-noc.gov.in/ (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Madhok, A.K. Enhancing water Use Efficacy. Central Water Commission, Roorkee Water Conclave, 2020, p. 159. Available online: https://www.iitr.ac.in/rwc2020/pdf/theme_concepts_abstracts-book.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Tomer, S.K.; Sekhar, M.; Balakrishnan, K.; Malghan, D.; Thiyaku, S.; Gautam, M.; Mehta, V.K. A model-based estimate of the groundwater budget and associated uncertainties in Bengaluru, India. Urban Water J. 2021, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Jain, K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Gupta, V.; Varade, D.; Singh, H.; Narayan, A.B.; Budillon, A. Analyzing urbanization induced groundwater stress and land deformation using time-series Sentinel-1 datasets applying PSInSAR approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GMDW & SB. Guwahati Metropolitan Drinking Water and Sewerage Board. 2024. Available online: https://gmdwsb.assam.gov.in/ (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Roy, I. Hydrogeological framework and impact of urbanization on groundwater regime in greater Guwahati area, Assam, NER. CGWB. Unpublished work. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Climate Engine. On-Demand Insights from Climate and Earth Observations Data. 2024. Available online: https://www.climateengine.org (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Beven, K. The era of infiltration. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGWB. Report of the Groundwater Resource Estimation Committee. Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation. Government of India, Faridabad. 2015. Available online: https://cgwb.gov.in/ (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Lerner, D.N.; Issar, A.S.; Simmers, I. Groundwater recharge: A guide to understanding and estimating natural recharge. In IAH International Contributions to Hydrogeology, 8th, ed.; Taylor and Francis: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Vystavna, Y.; Diadin, D.; Rossi, P.M.; Gusyev, M.; Hejzlar, J.; Mehdizadeh, R.; Huneau, R. Quantification of water and sewage leakages from urban infrastructure into a shallow aquifer in East Ukraine. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiswirth, M.; Hötzl, H. The Impact of Leaking Sewers on Urban Groundwater. Available online: https://users.pfw.edu/isiorho/G300Eiswirth-Hoetzl_IAH_Nottingham_1997.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Wilopo, W.; Putra, D.P.E. Groundwater recharge estimation using groundwater level fluctuation patterns in unconfined aquifer of Yogyakarta City, Indonesia. Kuwait J. Sci. 2021, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Michael, H.A.; Voss, C.I.; Sikdar, P.K. Impacts on groundwater recharge areas of megacity pumping: Analysis of potential contamination of Kolkata, India, water supply. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1340–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, S.N.; Mukherjee, A.; Rangarajan, R.; Scanlon, B.R.; Malakar, P.; Verma, S. Long-term groundwater recharge rates across India by in situ measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddin, S.; Rateb, A.; Graaf, I.D.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Ni-Meister, W.; Choudhury, R. Impact of urbanization on land use and land cover change in Guwahati city, India and its implication on declining groundwater level. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J. The impacts of urbanization on groundwater systems and recharge. AQUA Mundi. 2010, 1, 2719. [Google Scholar]
- Siddik, M.S.; Tulip, S.S.; Rahman, A.; Islam, M.Z.; Haghighi, A.T.; Mustafa, S.M.T. The impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge in northwestern Bangladesh. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Agency | Total Water Supply (MLD) |
|---|---|
| GMC | 45 |
| Guwahati Jal Board | 9.5 |
| JNNURM | 2 |
| JICA | 10 |
| Total | 66.5 |
| Month | Rainfall (mm) | Evapotranspiration (mm) | Runoff (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 31.6 | 36.72 | 1.11 |
| February | 50.4 | 50.11 | 2.27 |
| March | 5.3 | 25.25 | 1.0 |
| April | 103.4 | 108.65 | 9.45 |
| May | 293.4 | 125.31 | 55.39 |
| June | 499.8 | 92.47 | 109.51 |
| July | 168.8 | 136.84 | 44.89 |
| August | 152.8 | 121.22 | 4.98 |
| September | 81.4 | 115.07 | 10.55 |
| October | 155.6 | 101.6 | 8.62 |
| November | 0.0 | 51.35 | 0.0 |
| December | 0.0 | 31.73 | 0.0 |
| Total | 1542.5 | 996.3 | 247.8 |
| Geomorphic Unit | Area (km2) | Paved Area (km2) | Area Available for Recharge (km2) | Rainfall Available for Recharge (mm) | Rainfall Infiltration Factor * | Total Recharge (MCM/yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alluvial plains | 254.56 | 155.9 | 98.66 | 298.4 | 0.22 | 6.47 |
| Residual hills | 73.44 | 27.1 | 46.34 | 298.4 | 0.11 | 1.52 |
| Total | 328 | 183 | 145 | 7.99 |
| Surface Water Body | Geomorphic Unit | Area (km2) | Water Available (days) | Seepage Factor (mm/day) * | Total Recharge (MCM/yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deepor Beel | Alluvial plains | 4.1 | 365 | 1.4 | 2.09 |
| Sarusola and Borsola Beel | Alluvial plains | 1.38 | 365 | 1.4 | 0.72 |
| Dighali Pukhuri | Alluvial plains | 0.04 | 365 | 1.4 | 0.02 |
| Silsako Beel | Alluvial plains | 0.55 | 365 | 1.4 | 0.28 |
| Total | 6.07 | 3.11 |
| Source | Population | Actual Water Supply (MLD) | Consumptive Use (MLD) | Potential Wastewater Production (MLD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water supply | 501,094 | 56.53 | 10.02 | 46.61 |
| Groundwater | 674,906 | 91.11 | 13.5 | 77.61 |
| Assessment Year | Investigating Agency | Groundwater Recharge (MCM/yr) |
|---|---|---|
| 2004–2006 | CGWB | 116.27 |
| 2017 | CGWB | 95.38 |
| 2022 | CGWB | 53.52 |
| 2022 | Present study | 55.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dutta, J.; Choudhury, R.; Nath, B. Quantification of Urban Groundwater Recharge: A Case Study of Rapidly Urbanizing Guwahati City, India. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040187
Dutta J, Choudhury R, Nath B. Quantification of Urban Groundwater Recharge: A Case Study of Rapidly Urbanizing Guwahati City, India. Urban Science. 2024; 8(4):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040187
Chicago/Turabian StyleDutta, Jayashri, Runti Choudhury, and Bibhash Nath. 2024. "Quantification of Urban Groundwater Recharge: A Case Study of Rapidly Urbanizing Guwahati City, India" Urban Science 8, no. 4: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040187
APA StyleDutta, J., Choudhury, R., & Nath, B. (2024). Quantification of Urban Groundwater Recharge: A Case Study of Rapidly Urbanizing Guwahati City, India. Urban Science, 8(4), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040187





