Abstract
Local surface-depressed areas in an urban microrelief are geochemical traps for sediments deposited at the surface. These sediments accumulate pollutants over space and time. The aim of this study was to estimate the total amount of surface sediment in residential areas of small towns with different industrial specialisations. Snow-dirt sludge, snow, and surface sediment samples were collected in towns of the Sverdlovsk region, Russia: Alapaevsk, Kachkanar, Serov, and Verkhnyaya Pyshma. Snow and snow-dirt sludge were collected in the cold season, and surface sediment was collected in the warm season. This study was carried out in 2024. The solid matter of the samples was divided by sieving into particle size fractions: dust (<0.1 mm), fine sand (0.1–1 mm), and coarse sand (1–3 mm). The method used to estimate the total amount of sediment took into account data on the concentration of solid matter in snow-dirt sludge, the volume of melt water, and the contribution of the dust fraction in surface sediment and residential areas. The concentration of solid matter in snow-dirt sludge was about the same in the three cities (up to 6.6 g/L), but differed significantly in Kachkanar (60 g/L). The total amount of surface sediment per unit area was about the same in the three towns (1.1–1.4 kg/m2), but differed significantly in Kachkanar (10.8 kg/m2). The contribution of the dust fraction to the total amount of sediment was estimated to be 10–20% in the cities. The total amount of surface deposited sediments in the residential areas of the small towns was 1.6 × 107 t in Alapaevsk, 5.9 × 107 t in Kachkanar, 1.7 × 107 t in Serov, and 1.3 × 107 t in Verkhnyaya Pyshma. The values obtained for the total amount of surface sediments characterise the contemporary sedimentation processes in residential areas and the environmental quality of small towns.
1. Introduction
Approximately 60% of the world’s population now lives in urban areas [1]. That number will reach two-thirds of the global population by 2050. According to the 2020 census, most of Russia’s urban population lives in small towns [2]. The majority (72%) of Russian small towns have a population of less than 50,000, while 13% have between 50,000 and 100,000 inhabitants. A “monocity” concept has been implemented for most Russian small towns. Well-known examples of such monocities in Russia are Karabash, Kachkanar, Norilsk, and others [3,4,5]. Its main principle is that more than 20% of the population is employed in the main businesses of the city (“city-forming enterprises”). There are two types of locations in residential areas in Russian small cities: adjacent to industrial areas and at a considerable distance from industrial areas.
In the Sverdlovsk region of Russia, urbanisation has reached 86% and continues. Half of the population lives in small towns [6,7]. In the Sverdlovsk region, the main economic activity is mining, the processing of natural resources, and industrial production [7,8]. Due to the low diversity of enterprises, there is a limited profile of jobs, services (medical, entertainment, sports, shopping, etc.) and often an out-migration of the working-age population from small towns [9]. The economy of such towns is highly dependent on the presence of large companies, proximity to larger cities, or federal budget funds.
The existing local problems of the small town do not usually attract the attention of the general public in the region or country; information about what is happening in small towns does not reach people outside those towns. Ensuring the environmental quality of small towns is a similar problem. The main sources of pollution in small towns are the enterprises located there. Most small Russian towns are not included in the state environmental monitoring programme of the Federal Service for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring of Russia. The city-forming enterprise and the local department of the Federal Sanitary and Hygienic Service of Russia (Rospotrebnadzor), in cooperation with the city administration, are responsible for environmental monitoring and pollution control in residential areas of small towns. It is important to note that enterprises often carry out their own environmental impact assessments. The summary results of the analysis of the collected environmental data on small towns are published in the “Annual reports on the state of the environment in the region”, prepared by the relevant regional Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources. They often contain information on unfavourable environmental conditions in small towns [10]. However, it is not possible to carry out independent publicly available environmental monitoring in small towns due to the lack of open access data on the state of the environment in these towns. At the same time, the closure or shutdown of city-forming enterprises due to non-compliance with environmental standards can be disastrous for the economy of a town as a whole and for its residents. The environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles and approaches that take into account the interaction between a small city and its city-forming enterprises are still being developed in Russia.
Pollution in urban areas also comes from vehicle emissions, products of the weathering of soil, road abrasion, destruction of pavements and infrastructure objects, mineral anti-icing and traction materials for roads and sidewalks, etc. The solid particles from these sources are deposited on the surfaces and in the depressions of the microrelief, forming contemporary urban surface deposited sediment (USDS) [11]. The urban surface sediment is recognised by the US Environmental Protection Agency as a source of diffuse pollution and as the main carrier of diffuse pollution in the urban environment [12].
During the cold season in northern climates, urban sediment mixes with snow and forms snow-dirt sludge (SDS) [13]. SDS is formed on driveways, pavements, and roads [13]. During street and pavement cleaning, SDS is deposited in piles on roadsides and lawns (see Supplementary Materials). Part of SDS is transported from urban areas to dumps. In addition to the USDS material, SDS contains substances characteristic of the cold season (anti-icing materials, tyre studs, atmospheric dust, etc.) [13,14,15,16]. During spring snowmelt, some of the solid SDS material is transferred to the USDS, some is carried away by surface runoff, and some solid SDS material remains on the surfaces where SDS piles are stored.
USDS represents a geochemical trap in the sedimentation cascade processes that occur in urban areas, together with the other components of this cascade (gutter sediments, stormwater drainage sediments, sediments deposited on roads, etc.) [17,18,19]. Places of the accumulation of USDS are puddles, surface water drains, etc. [20,21]. The accumulation of the solid particles occurs from the local catchment area represented by the conjugated segments of the surrounding landscape: road, green zone, sidewalk, parking spaces, etc. The urban sediment cocktail integrates pollution over time and space within the urban landscape [22,23].
Recently, various types of urban surface sediments have become the object of urban geochemical studies aimed at obtaining information on the environmental state. The analysis of the composition of different types of surface sediments is a new global trend [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Such studies allow for obtaining reliable information on the processes of pollution transfer in an urban environment, as well as for tracing pollution, identifying the sources of urban pollution, and performing source apportionment of pollutants [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
The accumulation of contemporary urban surface sediments is one significant environmental issue [26,28,30,34,35]. Citizens often associate surface sediments with mud, which has a negative impact on their perception of the urban environment. The problem is more serious than it may seem. Urban surface sediments contain high levels of particulate matter that accumulate heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, bacteria, and other potentially harmful substances [24,30,34,36,37]. Increases in the deposition of surface sediments lead to urban air pollution, pollution of urban water bodies and streams, loss of fertility of urban soils, wear and tear of urban infrastructure, and siltation of storm water drainage systems. Preventing increases in sediment accumulation in urban areas requires a significant increase in the cost of urban management measures. The other negative effect of sediment accumulation is an increase in the frequency of various diseases among the urban population, such as the following: respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and other diseases [26,28,36]. Therefore, contemporary sediments are one of the environmental risk factors for humans.
The amount of surface sediment deposited in residential areas of large Russian cities reaches 3.4 kg/m2 [21,38]. And the value of its production varies between 0.74 and 1.7 kg/m2/year [39]. Such estimates have not been made for small towns. Estimates of sediment accumulation and production in cities of other countries are much lower than those of Russian cities [28,35]. Knowledge of the total amount of sediment deposited in an urban area would be useful for city authorities and landowners in planning and developing urban management measures and cleaning techniques, to reduce the costs of maintaining the urban area.
The aim of this study was to assess the total amount of surface sediment deposited in residential areas of small towns. The study was carried out using the example of small towns in the Sverdlovsk region (Russia): Alapaevsk and the monocities of Kachkanar, Serov, and Verkhnyaya Pyshma. The following tasks were performed: (1) sampling of the environmental compartments involved in the formation of surface deposited sediment (USDS, SDS, and snow); (2) landscape analysis of the residential areas of the small towns; (3) particle size analysis of the solid phase of the collected samples of the environmental compartments; and (4) estimation of the residential areas of the towns.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Studied Towns
All the towns studied are located in the Urals, in the temperate continental climate zone. The cold season in this area lasts 160–170 days from mid-October to mid-April. During the cold season, there is a permanent snow cover of 40–60 cm. However, in some years, it exceeds 90 cm.
2.1.1. Alapaevsk
Alapaevsk was founded in 1639. It is one of the oldest cities in the Sverdlovsk region. The population of Alapaevsk is nearly 36,000. The city is located on the eastern side of the Middle Urals at the intersection of the Trans-Ural Plain and the West Siberian Lowland. The city is situated on the Neiva River. The relief of the city is dominated by large hills. The average temperature in January is −15.6 °C, in July—+18.7 °C. The average annual precipitation is 496 mm. At the beginning of the 18th century, metallurgical plants for smelting pig iron and copper were established at Alapaevsk. Copper production was stopped in 1801. The smelter was closed in 2008. At present, Alapaevsk has a wood processing, food, and engineering industry.
2.1.2. Kachkanar
Kachkanar was granted town status in 1968. The population of Kachkanar is almost 37,000. Kachkanar is located southwest of the mountain of the same name, on the eastern side of the Middle Urals in the watershed of the Isa and Vyja Rivers (tributaries of the Tura River). The relief of the city is mountainous with large differences in altitude. The city is mainly built on mountain terraces. The average temperature in January is −15.3 °C and in July it is +17.3 °C. The average annual precipitation is 467 mm. The main industry in Kachkanar is the production of iron ore. The Kachkanarsky Ore Mining and Processing Plant was established in 1963. The ore is mined in three open pits. It is one of Russia’s largest iron ore companies and the world’s only producer of Fe-V concentrate, sinter, and blast furnace pellets. Kachkanar has a power station that uses natural gas as fuel. Part of the town lies next to the quarry.
2.1.3. Serov
Serov was founded in 1893. The population of the town is about 93,000 people. Serov is located on the border between the Middle and Northern Urals, on the eastern side of the Ural Mountains. The Kakva River (a tributary of the Sosva River) flows through the city. The relief of the city is mostly flat. There are large hills in the north of the city. The average temperature in January is −16.2 °C and in July it is +18.0 °C. The average annual precipitation is 493 mm. The main industry is ferrous metallurgy, represented by the Serov Metallurgical Plant (founded in 1896), the Ferroalloy Plant (founded in 1958), and other metallurgy-related facilities. Wood processing is also developed in the town.
2.1.4. Verkhnyaya Pyshma
Verkhnyaya Pyshma (founded 1854) is one of the agglomeration cities of Ekaterinburg. The population of Verkhnyaya Pyshma is about 74,000. Verkhnyaya Pyshma is located in the Middle Urals, on the eastern side of the Ural Mountains. The city’s relief is mostly hilly. The average temperature in January is −12.6 °C and in July it is +18.9 °C. The average annual precipitation is 535 mm. The city is currently undergoing active development with the construction of high-rise buildings and transport infrastructure. Copper ore has been mined and processed in Verkhnyaya Pyshma since 1854. The Plant for the Electrolytic Refining and Processing of Copper (currently Uralelectromed) was established in Verkhnyaya Pyshma in 1929. Currently, the other main industries of the town are machine building and metal processing.
The residential areas of each small town consist of blocks of multi-storey buildings (MSBs) and detached house development (DHD) areas.
2.2. Research Design
This study was conducted in the residential areas of the cities. The approach of the urban area survey was based on the results of previous studies [13,21,22]. Study sites were selected in both types of residential areas, MSB and DHD areas. Each study site represents a typical elementary landscape cell from which the urban residential area was composed. It has been proposed to define such a typical elementary landscape cell as an Elementary Urban Residential Landscape (EURL) [11]. In the current study, each EURL represents a part of the neighbourhood of the residential area and consists of the facade area adjacent to the urban street network and the courtyard area. The facade and courtyard areas of a cell consist of landscape functional zones. Figure 1 shows the structural organisation of the residential area of a small town.
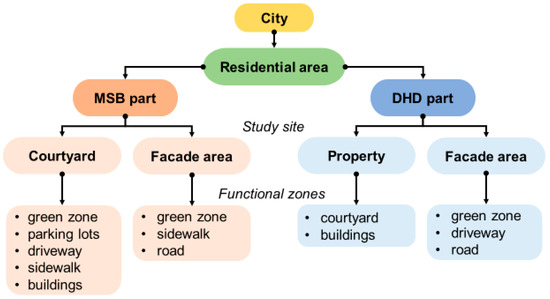
Figure 1.
The structural organisation of the residential area of each small Russian town.
An irregular grid was developed to select the location of the study sites in each town. The sites were randomly selected in the DHD and MSB parts and covered the whole residential area of the city. Figure 2 shows the location of the study sites in the towns in the cold and warm seasons. The sites had different periods of housing construction.
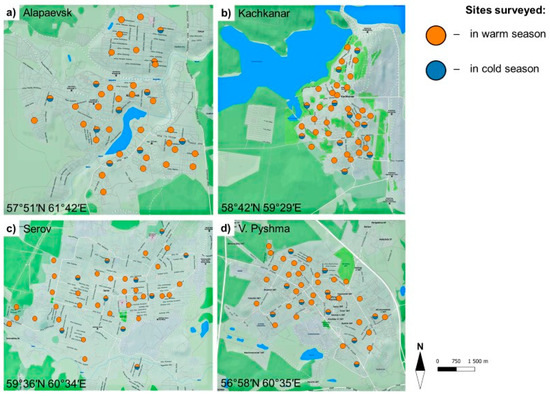
Figure 2.
The location of the study sites in the warm and cold seasons in Alapaevsk, Kachkanar, Serov, and Verkhnyaya Pyshma.
2.2.1. Sample Collection and Processing in the Cold Season
In the cold season, 10 sites (5 in DHD and 5 in MSB area) were surveyed. One snow sample and one SDS sample were collected at each site. In each town, 10 SDS and 10 snow samples were collected. The samples were collected at the end of the period of maximum snow accumulation—in March 2024.
Snow was collected from green areas (lawns) with undisturbed snow cover and without anthropogenic influences. Sampling was carried out with a cylindrical sampler (d = 10 cm). The thickness of the snow cover was measured. Snow cores were collected from 2 to 6 points, depending on the thickness of the snow cover at each site, and then combined into one sample. Soil, grass, and debris particles were removed from the bottom of the lifted snow core. The snow sampling points were located at a distance of 2–35 m (average about 10 m) from the vehicle zone (car park, road, and driveway areas). Snow samples were collected in the courtyard zone of the MSB area and in the façade zone of the DHD part of the residential area.
The SDS sample is a combined sample from 3 to 5 points on the study site. The SDS samples were collected from vehicle (road, driveway, and parking lot) and pedestrian (sidewalk) zones, as well as from SDS piles located along these zones. The SDS piles had been created on lawns as a result of surface cleaning of the other functional zones. SDS sampling was carried out in the courtyard of the MSB and in the façade zone of the DHD part of the residential area.
Snow and SDS samples were collected in 5-litre plastic containers with lids. The samples were not allowed to thaw during collection and transport to the laboratory. The collected samples were stored in an industrial refrigerator in the laboratory. The samples were then melted to a liquid at room temperature for 24 h. Tree branches, leaves, stone fragments, and other debris were then removed from the sample. The total volume of the melted sample was measured as the sum of the liquid (meltwater) and solid phases. The procedure for collecting and processing snow and SDS samples was in accordance with the requirements of Order N 524 of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment of Russia (30 July 2020).
The solid phase of the SDS samples was dried and then separated by dry sieving into particle size fractions <0.1 mm, 0.1–1 mm, 1–3 mm, and >3 mm. The granulometric subsamples obtained were weighted.
2.2.2. Sample Collection and Processing in the Warm Season
In total, 40 USDS samples were collected in the residential area of each town during the warm season. A total of 20 samples were collected in the MSB area and 20 in the DHD area. The USDS sample represents a combined sample of 3–5 points of the sedimentary material at each study site:
- Deposited along the roads (road dust) and in the drainage channels (see Supplementary Materials) in the façade part of the DHD type of the residential area;
- Deposited in the microrelief depressions on surfaces in the functional zones of parking, passage, driveway, sidewalk, and courtyard areas in the blocks of the MSB type.
During the field survey, the local catchment area for the USDS sampling site was defined the by the maximum surrounding elevations within the operator’s line of sight at the site.
The total mass of the sample was 1–1.5 kg. Sampling was carried out using a brush, shovel, and scoop. All USDS samples were collected in individual polyethylene bags with labels. Roots, rock fragments, glass, plastic, and other debris were removed from the collected samples. Samples were dried to air-dry condition in a desiccator at 59 °C and crushed.
The >3 mm fraction was removed from the sample by sieving and was not considered for further analysis as it represents large rock fragments. For particle size analysis, a representative subsample of the mass of 100–300 g was taken from the USDS sample using the quartering method. The subsample was then separated into three particle size fractions <0.1 mm, 0.1–1 mm, and 1–3 mm by dry sieving. The material from each fraction was weighted.
2.2.3. Field Landscape Survey
Field landscape surveys of the study sites were carried out in cold and warm seasons. The landscape analysis methodology was taken from previous research [12] and was adapted for the current study. A specific questionnaire was developed that included the landscape and operational characteristics of the site: functional zones, types of the surfaces, technical conditions of surfaces, traffic and parking load, characteristics of buildings, etc. Specific seasonal information for the cold season included the following: use of anti-icing materials, snow depth, etc. The information for the warm season included the characteristics of the local catchment area from which the sediment material was mobilised, such as the following: type of pavement, proportion of disturbed surfaces, quality of cleaning of functional zones, type of vegetation, etc.
2.3. Total Amount of Urban Surface Deposited Sediments
The total mass of the USDS in the urban environment is calculated according to the following equation:
where A is the total amount of the USDS, kg/m2, S is the total area of the residential zone of the town, m2, M1, M2, and M3 are the masses of the particle size fractions < 0.1 mm, 0.1–1 mm, and 1–3 mm per unit area, respectively [21].
The following assumptions were made. The dust fraction (<0.1 mm) in the USDS is evenly distributed over all functional landscape zones of the residential area of the city during the SDS formation in the cold season. During the cold season, SDS is either removed from the roads during sweeping or stored in piles close to where it forms and accumulates. The concentration of the USDS dust fraction under undisturbed snow cover on lawns and other surfaces remains the same as in early winter. The total mass of the USDS dust fraction is similar in the cold and warm seasons in the city due to the inhibition of USDS production and deposition during the cold season.
Taking into account the assumptions of uniform and complete mixing with snow in the functional zones of the residential area, the mass of the dust fraction per unit area is estimated from the SDS particle size composition data. Estimation by concentration of other size fractions in SDS is not applicable due to the low mixing rate with snow. The ratio between the particle size fractions can be estimated by analysing the USDS samples collected at the sites where the SDS was deposited.
Considering the above, the mass of dust (<0.1 mm), fine sand (0.1–1 mm), and coarse fractions (1–3 mm) per unit area was calculated using Equations (2)–(4).
where m is the concentration of solid sediment phase in melted SDS, kg/L; Cdf is portion of dust fraction in the solid phase of SDS; V is the volume of melt water received from undisturbed snow cover per unit area in L.
where k1 and k2 are the coefficients relating the mass of the coarse fraction to the dust fraction.
where k2 is the coefficient relating the mass of fine sand to the dust fraction.
2.4. Measurement of Total Residential Area
The total residential area of each city was delineated via satellite images using Google Earth tools and then measured. This area included MSB and DHD neighbourhoods with adjacent homesteads, road network, commercial areas (warehouses, garages, shops, etc.), administrative, and recreational areas (parks). The allocated area did not include large industrial areas, forest areas, and other areas that are not related to the residential area of the city. The areas of the functional zones (Figure 1) within the MSB and DHD parts were estimated on the basis of measurements of the areas of five randomly selected study sites in each part of the residential area of each city.
3. Results
3.1. The Features of the Studied Residential Areas
On the basis of the observations made in the residential areas of the towns studied, the following typical characteristics of the landscape functional zones were identified. The green zone is characterised by the presence of a pervious surface, lawn, bushes, trees, and other plantings. During the cold season, most of the green zone is covered with an undisturbed layer of snow. In DHD areas, the green zone is often outside the property boundary, between the property line and the road. A small driveway, often unpaved, is typically located within such a green zone in the DHD area. The courtyard zone of a DHD property includes the garden, main house, and various outbuildings. As this area is privately owned, it was not subject to inspection. The characteristics of the green zone in DHD and MSB areas are identical.
Areas adjacent to roads, sidewalks, and driveways both in facade and courtyard areas in the MSB neighbourhoods are used for storage of SDS in piles and heaps created during clean-up efforts. Illegal parking of vehicles was sometimes observed in green zones during the warm and cold seasons.
Photographs of the landscape of MSB and DHD areas of small towns and the collected environmental compartments are presented in the Supplementary Materials (S1–S19).
3.2. Size of the Residential Area of the City
The total size of the residential area of the cities and the number of the studied sites per square kilometre in the warm/cold season (in brackets) are as follows:
| 13.6 km2 (3/1) |
| 6.3 km2 (6/2) |
| 17.9 km2 (2/1) |
| 11.6 km2 (3/1) |
Table 1a,b show the values of the area of the EURL and its functional zones for the MSB and DHD types in the cities studied, as well as the average portion of the area of the functional zone.

Table 1.
a. The values of the area of the EURL and its functional zones for the MSB type of the residential area (mean/std. dev./min-max) and the mean proportion of the area of the functional zone (impervious surface: parking lot, driveway, sidewalk). b. The values of the area of the EURL and its functional zones for the DHD type of the residential area (mean/std. dev./min-max) and the mean proportion of the area of the functional zone.
On average, buildings (houses, utility buildings, garages, etc.) occupy about 15% of the residential area.
3.3. Results of the Landscape Analysis
During the cold season, traces of the use of anti-icing materials were observed on roads, driveways, and sidewalks at seven study sites in Kachkanar and two sites in Serov. The highest snow depth was at Kachkanar and Serov (60 cm), and the lowest at Alapaevsk (35 cm).
During the warm season, the proportion of disturbed surfaces of the study sites and their catchments was assessed (Table 2). Most of the study sites were characterised by a high proportion of disturbed areas at Alapaevsk, Kachkanar, and Serov. At the same time, the proportion of disturbed areas in the catchment of these cities varied in the range of 10–50%. In Verkhnyaya Pyshma, the area of the study site and the catchment area was the least disturbed compared to the other cities studied.

Table 2.
Proportion of disturbed surfaces of the studied sites.
3.4. Content of Solid Matter in the SDS
Table 3 shows the mean concentrations of the solid matter in the SDS in the DHD and MSB areas of the towns. There is no significant difference in the solid matter content in the SDS between the DHD and the MSB areas of the towns, with the exception of Serov. The solid matter content in the SDS in the MSB area is more than twice as high as in the DHD area in Serov. The concentration of solid matter in Kachkanar is almost 10 times higher than in the other towns.

Table 3.
The mean content of the solid matter in SDS samples in MSB and DHD areas of the towns.
3.5. Particle Size Composition of the Solid Matter in USDS and SDS
Figure 3 shows the particle size composition of the solid matter in the USDS and the SDS in the four towns. Differences are observed between the various mass concentrations of the particle size fractions depending on the season. In the USDS, the contribution of fine (0.1–1 mm) and coarse (1–3 mm) sand fractions is on average 20% and 6% higher, respectively, than in the SDS. The average content of the dust fraction (<0.1 mm) in the SDS varies between 21 and 31%, depending on the town. The content of the dust fraction is on average 11% lower in the USDS than in the SDS.
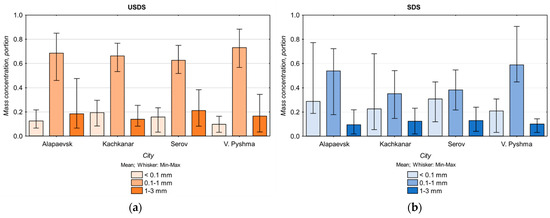
Figure 3.
Particle size composition (mass concentration) of the solid matter (with min and max values) in the USDS (a) and in the SDS samples (b) in the towns.
3.6. Assessment of Total and Specific Amount of USDS
Table 4 shows the values of the parameters of the model (Section 2.3), which are necessary for the assessment of the total amount of USDS, as well as the results of the assessment of the specific amount of USDS.

Table 4.
The values of the parameters of the model for the assessment of the total amount of the USDS, and the results of the assessment of the specific amount of USDS.
The following values were obtained for the concentrations of the fine sand (M2) and the coarse sand (M3) particle size fractions in the USDS:
| M2 = 0.94, M3 = 0.25 kg/m2, |
| M2 = 7.13, M3 = 1.52 kg/m2, |
| M2 = 0.68, M3 = 0.23 kg/m2, |
| M2 = 0.95, M3 = 0.22 kg/m2. |
The total size of the residential area (excluding roofs) and the total amount of the USDS in it are:
| S = 11.5 km2 | A = 1.6 × 107 t, |
| S = 5.4 km2 | A = 5.9 × 107 t, |
| S = 15.0 km2 | A = 1.7 × 107 t, |
| S = 9.7 km2 | A = 1.3 × 107 t. |
The total amount of the USDS per unit area in Alapaevsk, Serov, and Verkhnyaya Pyshma is in the range of 1.1–1.4 kg/m2, while in Kachkanar, the value stands out—10.8 kg/m2. The contribution of the dust fraction is estimated at 10–20% depending on the city.
4. Discussion
The assessment of the total amount of USDS was carried out for the small towns located in the climate zone with a long cold season and stable snow cover. An approach was applied that took into account data on the accumulation of USDS in all functional zones of the residential area of each town, the content of the solid matter in the SDS, and the particle size composition of the USDS.
It is easy to identify and collect USDS in the MSB and the DHD areas of the cities during the warm season. In DHD areas, sediments are usually carried by surface runoff and collected in drainage channels along the road (see Supplementary Materials). The residential MSB residential areas built in the second half of the 20th century did not have a subsurface stormwater drainage network in the courtyard area. It was assumed that surface runoff from the courtyard area would be discharged into the street network storm sewer system.
During the field study, we observed less surface sediment accumulation in the new MSB areas in Verkhnyaya Pyshma, where USDS was almost completely removed to the subsurface drainage channels. Infrastructure facilities in the residential areas built after the 2010s, such as in Verkhnyaya Pyshma, were better designed than in older areas in all the cities studied. Illegal parking is also prohibited in new districts.
In DHD areas, houseowners store construction materials such as gravel and sand in piles without cover on the lawns and passages of the façade area (see Supplementary Materials). Such uncovered materials contribute to the production of fine particles in an urban area. In the DHD area, the roads are unpaved or gravelled, which also contributes to the formation of the fine particles. Local industrial byproducts are often used as construction materials, especially in road construction, such as slag from the sinter plant in Serov and material from quarry dumps in Kachkanar. Such industrial byproducts are also used as anti-icing material in these towns.
During the cold season, the majority of snow and SDS is removed from the roads, driveways, sidewalks, and parking lots. The snow and SDS are piled up on the roadsides and lawns. At the time of the study in the cold season, the piles of snow and SDS were up to 4 m high in some sites in the towns. The piles began to melt in some sites, resulting in surface sediment runoff in residential areas and ice formation on roads, driveways, and sidewalks. Traces of atmospheric deposition of industrial origin, i.e., undisturbed snow of a dark grey colour, were observed in Kachkanar.
The grid of study sites designed for the research can be characterised as representative of a small town, taking into account the relatively small area of the residential part of the towns. The number of sites in each town was comparable to other studies [24]. Moreover, such an irregular grid can be considered close to regular, subject to the peculiarities of contemporary sediments as a geoindicator. Industrial, transport, recreational, and commercial areas, as well as gardens in the city were not studied. The possibility of bias in the study grid was minimised by the following principles: (1) a summer USDS sample was taken in one local catchment; (2) the design and execution of the field studies were guided by the fact that the grid would evenly cover the entire residential area of the town. The apparent visual concentration of sampling sites (Figure 2) in Kachkanar was due to the small size of the town, while the number of samples taken was the same as in larger cities [22].
The method of estimating the area of a residential zone of a town in Google Maps is quite rough. Errors can be caused by the measurement of areas by the tool used and the operator. However, since as all the measurements were made by the same operator using a consistent methodology, the results obtained can be considered valid for the purpose of this study. The results obtained allow the towns to be compared in terms of the amount of sediment.
The design of green zones with vegetation cover is intended to reduce the intensity of solid material supply in residential areas. On average, the green zone occupies about 50% of the MSB area. Such a share of the green zone of small towns corresponds to the results obtained for the residential area of the large Russian cities [11]. According to the results of the landscape study, there was illegal parking in the green zone in almost all study areas.
As the property area occupies the largest part (about 65%) of the DHD area, roads and driveways do not have hard surfaces, and the storm drains are mainly not designed in the DHD area of the town; it can be hypothesised that the surface runoff transfers solid particles outside the property area.
The presence of disturbed surfaces in residential areas has been identified as a contributing factor to the supply of solid matter. Under certain circumstances, the production of USDS can increase by up to fourfold, depending on the season [39]. The majority of disturbed surfaces were found in areas featuring roads, driveways, sidewalks, and parking lots.
The uniformity of pollution in the residential areas of each town can be inferred from the fact that there is no significant difference in the content of solid matter in the SDS between the MSB and DHD areas. The exception is Serov, where the content of solid matter in SDS is 2.5 times lower in DHD areas than in MSB areas (Table 3). This may be related to the poor removal of snow and SDS piles from DHD areas in Serov.
The relatively high content of solid matter in the SDS in Kachkanar may be related to the intensive use of mineral anti-icing materials on roads, driveways, and sidewalks. In addition, in Kachkanar, compared to other towns, dust originates from the pit mines and ore processing industrial sites as result of atmospheric transport. In addition, the value of surface runoff is higher due to the sloping relief in Kachkanar. It can be hypothesised that the intensity of the sediment cascade processes in Kachkanar is higher than in others. Thus, the largest part of the sedimentary material remains deposited on the terraces on which the residential area was built. According to field observations and background information analysis, Kachkanar is the town where all the factors involved in the formation of the contemporary urban surface sediment converged.
The particle size composition of USDS in small towns differs from that in large cities [23]. In small towns, the contribution of the dust fraction is lower, and the coarse sand fraction is higher than in large cities. In addition, the dust content in SDS and USDS differs significantly between towns. The high content of the dust fraction in the SDS (> 20%) may be partly due to the atmospheric supply of particulate matter with falling snow. The large variation in the content of the dust and the fine sand fractions in the SDS indicates the heterogeneity of the particle size composition within the residential area of the town. In small towns, the contribution of the dust fraction to SDS is lower and the coarse sand fraction is higher than in large cities [13].
The total amount of USDS per unit area in Alapaevsk, Serov, and Verkhnyaya Pyshma is almost three times lower than that value in Ekaterinburg (3.2 kg/m2) [28]. However, in Russian cities, this amount varies in the range of 1.7–3.4 kg/m2 [27]. The obtained value of the total amount of USDS per unit area in the small town is quite high, taking into account that the area of small town is much lower than that of large city. At the same time, the total amount of USDS per unit area in Kachkanar (10.8 kg/m2) is almost 10 times higher than in other small towns and more than 3 times higher than in Ekaterinburg. The accumulation of the surface sediments in a small town occurring due to the poor management, deteriorating urban infrastructure, and poorly maintained spaces is many times greater than in a large city.
The total amount of USDS per city inhabitant was 446 kg in Alapaevsk, 1584 kg in Kachkanar, 177 kg in Serov, and 171 kg in Verkhnyaya Pyshma, of which the dust fraction was 129, 364, 55, and 36 kg, respectively. These values are an order of magnitude or more than the amount of road sediment per city inhabitant in the city of Prince George, Canada (9 kg) [28]. The population of Prince George is about the same as that of Serov or Verkhnyaya Pyshma. A similar estimate was made for Ekaterinburg (the city with a population of about 1.5 million people)—36 kg of the USDS per inhabitant [38]. Residents of small Russian towns are more exposed to dust than, for example, people living in Prince George (Canada) or in large cities.
The main sources of uncertainty in the assessment of the total amount of surface deposited sediment in the studied towns are as follows:
- Lack of or limited data on the sediment supply and the sediment yield;
- Inaccuracy in the measurement of residential and functional zone areas using Google Earth tools;
- The subjectivity of the operator’s estimates during the landscape survey;
- Lack of data on the mass distribution of particle size fractions by season;
- Uneven distribution of sediment material on the surfaces in the residential area of the city.
The representativeness of this study is enhanced by the fact that the most typical residential areas of each city and an equal number of sites in relation to the MSB and DHD areas were taken into account when selecting the survey sites. The cities surveyed are located in climatic conditions typical for most of Russia.
5. Conclusions
The total amount of surface deposited sediment in small towns varies greatly (up to 10 times). The content of the dust fraction, which represents the greatest environmental hazard for residents, also varies considerably. The highest value of USDS accumulation was observed in the city characterised by mining specialisation and located in the immediate vicinity of a territory of raw material extraction (a part of the city is located close to the mining area).
The total amount of USDS was evenly distributed between the MSB and DHD parts of the residential areas of the towns, though the landscaping and maintenance techniques and population density of these areas are very different. The method developed earlier for determining the total amount of USDS is appropriate for small towns.
The main sources of USDS in the small towns studied include the following: unpaved roads, eroded soils, illegal parking on lawns, disturbed paved areas, and anti-icing materials (including materials from quarry dumps and byproducts of the metallurgical industry). In small towns, a large amount of USDS is concentrated in a small area.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/urbansci8040178/s1, Figures S1–S19.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev) and A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko); methodology, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev) and A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko); validation, G.M. and A.S. (Andrian Seleznev); formal analysis, A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko); field study, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev), V.G., A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko), and G.M.; resources, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev); laboratory analyses, V.G. and N.I.; data curation, A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko); writing—original draft preparation, A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko); writing—review and editing, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev), G.M., and M.Y.H.; visualisation, A.S. (Andrew Shevchenko) and N.I.; supervision, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev); project administration, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev); funding acquisition, A.S. (Andrian Seleznev). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 24-17-20036.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Urbanization of Least Developed Countries Leads to the Growth of Megacities. Available online: https://news.un.org/ru/story/2022/04/1422732 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Federal State Statistics Service. Population Census. Available online: https://eng.rosstat.gov.ru/storage/mediabank/SDDS_Population..pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Humphreys, D. Challenges of Transformation: The Case of Norilsk Nickel. Resour. Policy 2011, 36, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshikova, E.; Fetisov, V.; Karavaeva, T.; Blinov, S.; Belkin, P.; Vaganov, S. Reducing the Negative Technogenic Impact of the Mining Enterprise on the Environment through Management of the Water Balance. Minerals 2020, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanov, M.V.; Marichev, M.S.; Minkina, T.M.; Mandzhieva, S.S.; Nevidomskaya, D.G. Assessment of the Impact of Industry-Related Air Emission of Arsenic in the Soils of Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2023, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal State Statistics Service. Population in Sverdlovsk Region. Available online: https://66.rosstat.gov.ru/storage/mediabank/Числ.%20н-я_МО_%202024.xlsx (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Federal State Statistics Service. Cities of the Sverdlovsk Region. Available online: https://rosstat.gov.ru/bgd/regl/b12_14t/IssWWW.exe/Stg/ural/02-00.htm (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Ministry of Investment and Development of the Sverdlovsk Region. Development of Monocities. List of Monoprofile Municipalities Located in the Sverdlovsk Region. Available online: https://mir.midural.ru/razvitie-monogorodov (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. What Are Some of the Challenges of Rural and Small Town America? Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2014-06/documents/ref_herman_081612.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Government of the Sverdlovsk Region. Resolution N 602-PP, 13 September, 2018. On the State Report “On the State and Environmental Protection of the Sverdlovsk Region in 2017”. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/550183685?marker=3NRUJ76§ion=text (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- Yarmoshenko, I.; Malinovsky, G.; Baglaeva, E.; Seleznev, A. A Landscape Study of Sediment Formation and Transport in the Urban Environment. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Polluted Runoff: Nonpoint Source (NPS) Pollution. Nonpoint Source Highlights Reports. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/nps/highlights (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- Seleznev, A.; Yarmoshenko, I.; Malinovsky, G.; Ilgasheva, E.; Baglaeva, E.; Ryanskaya, A.; Kiseleva, D.; Gulyaeva, T. Snow-Dirt Sludge as an Indicator of Environmental and Sedimentation Processes in the Urban Environment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, O.A.; Arafat, M.; Uddin, M.S. Physical and Economic Impacts of Studded Tyre Use on Pavement Structures in Cold Climates. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2021, 3, tdab022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, L.; Shi, X. Environmental Impacts of Chemicals for Snow and Ice Control: State of the Knowledge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2751–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Traffic-Related Metals in Urban Snow Cover: A Review of the Literature Data and the Feasibility of Filling Gaps by Field Data Collection. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Brierley, G.; Cadol, D.; Coulthard, T.J.; Covino, T.; Fryirs, K.A.; Grant, G.; Hilton, R.G.; Lane, S.N.; Magilligan, F.J.; et al. Connectivity as an Emergent Property of Geomorphic Systems. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 44, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, K.L.; Vietz, G.J.; Fletcher, T.D. Urban Sediment Supply to Streams from Hillslope Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.G.; Owens, P.N. Sediments in Urban River Basins: A Review of Sediment–Contaminant Dynamics in an Environmental System Conditioned by Human Activities. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleznev, A.A.; Yarmoshenko, I.V.; Shevchenko, A.V.; Malinovsky, G.P. Rationale for the Ecological Geoindicator Role of Contemporary Surface Sediments of Dust and Dirt in Urban Environment. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2023, 48, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleznev, A.A.; Yarmoshenko, I.V.; Malinovsky, G.P. Assessment of Total Amount of Surface Sediment in Urban Environment Using Data on Solid Matter Content in Snow-Dirt Sludge. Environ. Process. 2019, 6, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleznev, A.A.; Yarmoshenko, I.V.; Malinovsky, G.P. Urban Geochemical Changes and Pollution with Potentially Harmful Elements in Seven Russian Cities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleznev, A.; Rudakov, M. Some geochemical characteristics of puddle sediments from cities located in various geological, geographic, climatic and industrial zones. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 14, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezberdaya, L.; Chernitsova, O.; Lychagin, M.; Aseeva, E.; Tkachenko, A.; Kasimov, N. Pollution of a Black Sea coastal city: Potentially toxic elements in urban soils, road dust, and their PM10 fractions. J Soils Sediments 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathne, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Transformation Processes of Metals Associated with Urban Road Dust: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1675–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.N.; Blake, W.H.; Gaspar, L.; Gateuille, D.; Koiter, A.J.; Lobb, D.A.; Petticrew, E.L.; Reiffarth, D.G.; Smith, H.G.; Woodward, J.C. Fingerprinting and Tracing the Sources of Soils and Sediments: Earth and Ocean Science, Geoarchaeological, Forensic, and Human Health Applications. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.; Pereira, J.A.; Poleto, C.; De Lima, J.L.M.P.; Gonçalves, F.A.; Alvarenga, L.A.; Isidoro, J.M.P.G. Assessment of Loose and Adhered Urban Street Sediments and Trace Metals: A Study in the City of Poços de Caldas, Brazil. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.N.; Caley, K.A.; Campbell, S.; Koiter, A.J.; Droppo, I.G.; Taylor, K.G. Total and Size-Fractionated Mass of Road-Deposited Sediment in the City of Prince George, British Columbia, Canada: Implications for Air and Water Quality in an Urban Environment. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojiljkovic, A.; Kauhaniemi, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Kupiainen, K.; Karppinen, A.; Denby, B.R.; Kousa, A.; Niemi, J.V.; Ketzel, M. The Impact of Measures to Reduce Ambient Air PM10; Concentrations Originating from Road Dust, Evaluated for a Street Canyon in Helsinki. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11199–11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, H.M.; Taylor, K.G.; Rothwell, J.; Byrne, P. Characterisation of Road-Dust Sediment in Urban Systems: A Review of a Global Challenge. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 4194–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froger, C.; Ayrault, S.; Evrard, O.; Monvoisin, G.; Bordier, L.; Lefèvre, I.; Quantin, C. Tracing the Sources of Suspended Sediment and Particle-Bound Trace Metal Elements in an Urban Catchment Coupling Elemental and Isotopic Geochemistry, and Fallout Radionuclides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28667–28681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhu, D.Z.; Loewen, M.R.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Van Duin, B.; Chen, L.; Mahmood, K. Particle Size Distribution of Total Suspended Sediments in Urban Stormwater Runoff: Effect of Land Uses, Precipitation Conditions, and Seasonal Variations. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z. Vanadium in Modern Sediments of Urban Lakes in the North of Russia: Natural and Anthropogenic Sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Theller, L.; Gitau, M.W.; Engel, B.A.; Harbor, J.M. Urbanization Impacts on Surface Runoff of the Contiguous United States. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, K.L.; Vietz, G.J.; Fletcher, T.D. Global Sediment Yields from Urban and Urbanizing Watersheds. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 168, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on Pollution and Health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, N.; Straif, K.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L. The IARC Monographs on the carcinogenicity of crystalline silica. La Med. Del Lav. 2011, 102, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Card of the Project of Fundamental and Prospecting Scientific Research Supported by the Russian Scientific Foundation. Available online: https://grant.rscf.ru/prjcard_int?18-77-10024 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Shevchenko, A.V.; Seleznev, A.A.; Malinovsky, G.P.; Yarmoshenko, I.V. Modeling Sediment Production in Urban Environments: Case of Russian Cities. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 16, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).