Spatially Explicit Analysis of Landscape Structures, Urban Growth, and Economic Dynamics in Metropolitan Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
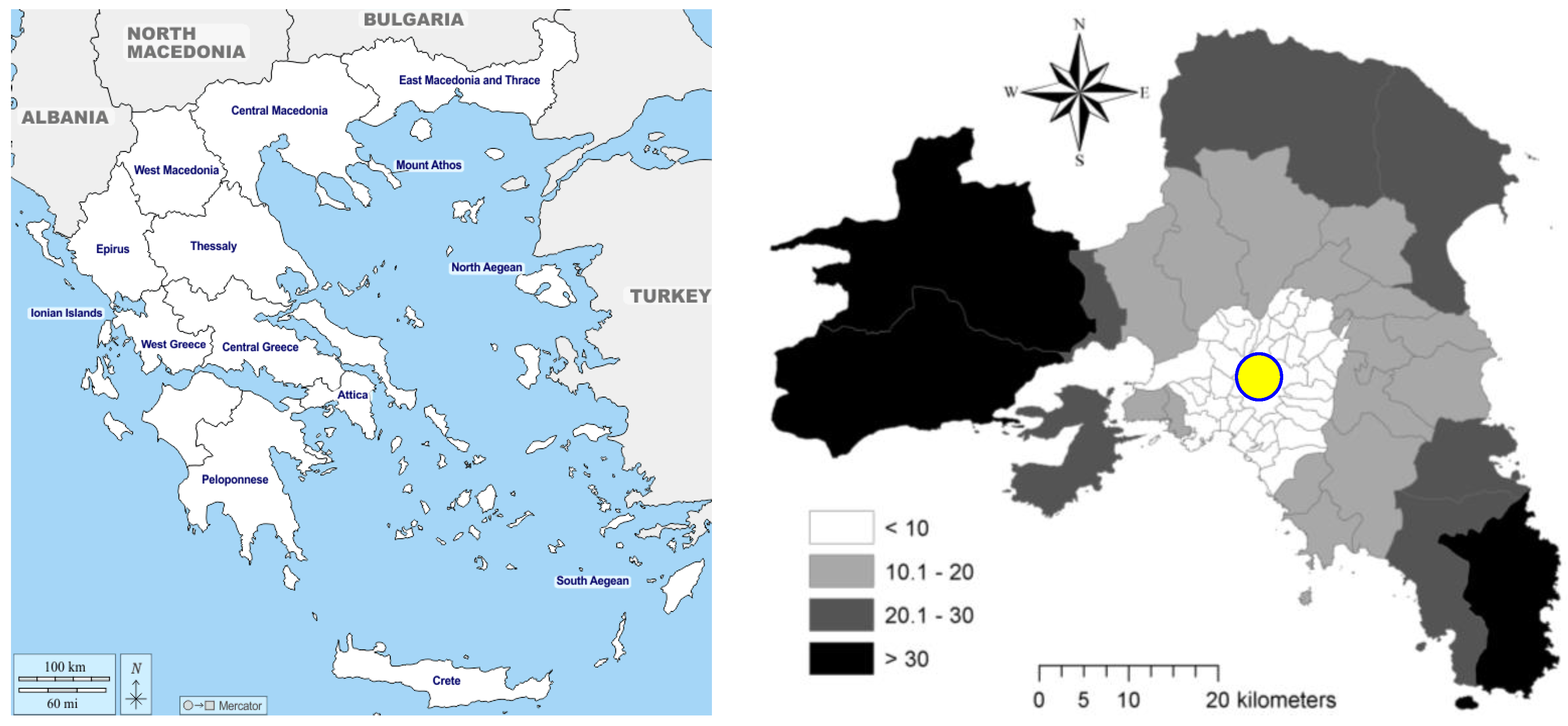
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Variables
- (a)
- The neighbor land infrastructure (i.e., road or railway), intended as a gross (indirect) metric (hereafter ‘Infr’) of the parcel accessibility, and computed from the parcel’s centroid and the closest point in the road axis or the closest railway station [96];
- (b)
- Downtown Athens (namely, Syntagma Square in the central settlement of Athens’s municipality); such an indicator (hereafter ‘DisA’, km) allows for evaluating the contribution of traditional (e.g., ‘centralized’) or more complex (e.g., ‘decentralized’) morphological structures to metropolitan growth, since settlements at moderate–low distances from Athens reflect the possible persistence of a traditional mono-centric model [97];
- (c)
- The Olympic Stadium of Athens, “Spyros Louis”, corresponding with Attica’s business district in Maroussi, northern Athens (hereafter ‘DisS’, km); low distances from the Olympic Stadium indicate the predominance of a settlement growth model centered on the economic expansion of the new Attica’s business district northeast of Athens, leveraging a dual metropolitan structure prodromal of polycentric development [98,99].
- (d)
- A proxy measure of local communities’ wealth (‘Poor’) implementing a dichotomous variable (0–1) derived from previous studies on the same area [100], and classifying the municipalities of metropolitan Athens as affluent (or economically disadvantaged) depending on the per capita income (below or above average) of the resident population estimated from official elaborations of tax declarations. Data for each municipality of the study area (n = 115) were assigned to each land parcel geographically belonging to that administrative unit;
- (e)
- The average elevation (meters at sea level) of each land parcel (‘Elev’) as an indirect indicator of natural amenities is more frequent at higher altitudes in the area, on average, because of the reduced human pressure. The variable was derived from a Digital Elevation Model (100 m spatial resolution) available for download and elaboration in raster format from the European Environment Agency and covering the study area homogeneously;
2.3. Local Regressions
3. Results
3.1. Parcel Size and Landscape Dynamics
3.2. Parcel Shape and Landscape Dynamics
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Model Diagnostics
3.4. Local Regressions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akkerman, A. Fuzzy Targeting of Population Niches in Urban Planning and the Fractal Dimension of Demographic Change. Urban Stud. 1992, 29, 1093–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, A.; Arnott, R.; Small, K.A. Urban Spatial Structure. J. Econ. Lit. 1998, 36, 1426–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, H.T.; Møller-Jensen, L.; Engelstoft, S. The End of Urbanization? Towards a New Urban Concept or Rethinking Urbanization. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2011, 19, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, L.; Drewett, R.; Klaassen, L.; Rossi, L.; Vijverberg, C. Urban Europe: A Study of Growth and Decline; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; ISBN 9780080231563. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, D. Counterurbanisation in England and Wales; Avebury: Aldershot, UK, 1990; ISBN 9781856280242. [Google Scholar]
- Antrop, M. Landscape Change and the Urbanization Process in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. Resurgent Metropolis: Economy, Society and Urbanization in an Interconnected World. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2008, 32, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.; Hull, A. The Futures of the City Region. Reg. Stud. 2009, 43, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.J.; Remøy, H. (Eds.) . Building Urban Resilience through Change of Use; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2018; ISBN 9781119231455. [Google Scholar]
- Coisnon, T.; Oueslati, W.; Salanié, J. Urban Sprawl Occurrence under Spatially Varying Agricultural Amenities. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2014, 44, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, A.; Salvati, L.; Sabbi, A.; Colantoni, A. Soil Resources, Land Cover Changes and Rural Areas: Towards a Spatial Mismatch? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Val, R.; Olmo, J. Growth in a Cross-Section of Cities: Location, Increasing Returns or Random Growth? Spat. Econ. Anal. 2015, 10, 230–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Partridge, M.D. When Are Cities Engines of Growth in China? Spread and Backwash Effects across the Urban Hierarchy. Reg. Stud. 2013, 47, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, N.E.; Liu, C.H.; Villupuram, S.V. Urban Economic Base as a Catalyst for Movements in Real Estate Prices. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2013, 43, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonakis, C.; Alexopoulos, G.; Garefalakis, A.; Garefalakis, S. Trends and New Elements in Urban Hierarchy Research: The Greek Paradigm. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2024, 72, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, A.J. Counterurbanisation in Western Europe. Prog. Plann. 1982, 17, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, M.D.; Rickman, D.S.; Ali, K.; Olfert, M.R. The Geographic Diversity of U.S. Nonmetropolitan Growth Dynamics: A Geographically Weighted Regression Approach. Land Econ. 2008, 84, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs-Crisioni, C.; Rietveld, P.; Koomen, E. The Impact of Spatial Aggregation on Urban Development Analyses. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 47, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, R. Von Thünen and Urban Sprawl. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1967, 57, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, L.; Molle, W.; Paelinck, J. Dynamics of Urban Development; Gower: Aldershot, UK, 1981; ISBN 9780566003783. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, A.; Kabisch, S.; Steinführer, A.; Bouzarovski, S.; Hall, R.; Ogden, P. Emergent Spaces of Reurbanisation: Exploring the Demographic Dimension of Inner-city Residential Change in a European Setting. Popul. Space Place 2010, 16, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorianopoulos, I.; Tsilimigkas, G.; Koukoulas, S.; Balatsos, T. The Shift to Competitiveness and a New Phase of Sprawl in the Mediterranean City: Enterprises Guiding Growth in Messoghia–Athens. Cities 2014, 39, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanko, M.; Barredo, J.I.; Lavalle, C.; McCormick, N.; Demicheli, L.; Sagris, V.; Brezger, A. Are European Cities Becoming Dispersed? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijker, R.A.; Haartsen, T. More than Counter-urbanisation: Migration to Popular and Less-popular Rural Areas in the Netherlands. Popul. Space Place 2012, 18, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgiotis, A.; Kyvelou, S.; Lainas, I. Industrial Location in Greece: Fostering Green Transition and Synergies between Industrial and Spatial Planning Policies. Land 2021, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, M. Polycentricity in Policies: The Greek Case. Built Environ. 2005, 31, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liasidou, S. Reviewing the Content of European Countries’ Official Tourism Websites: A Neo/Post-Fordist Perspective. Tour. Hosp. 2022, 3, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Ioannides, S.; Georgiou, M.; Voukkali, I.; Salvati, L.; Doukas, Y.E. Shaping Sustainable Cities: A Long-Term GIS-Emanated Spatial Analysis of Settlement Growth and Planning in a Coastal Mediterranean European City. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Ermini, B. Are Cities Truly Dispersed? A Long-Term Analysis of Vertical Profile of Settlements in Athens’ Metropolitan Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, C.; Musolesi, A. European Cities in the Process of Economic Integration: Towards Structural Convergence. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2007, 41, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.B. The Regional Economy, Spatial Structure and Regional Urban Systems. Reg. Stud. 2014, 48, 1926–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyvelou, S.S.; Gourgiotis, A. Landscape as Connecting Link of Nature and Culture: Spatial Planning Policy Implications in Greece. Urban Sci. 2019, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurría Gascón, J.L.; Nieto Masot, A. Rururban Partnerships: Urban Accessibility and Its Influence on the Stabilization of the Population in Rural Territories (Extremadura, Spain). Land 2020, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauchinger, L.; Reichenberger, A.; Goodwin-Hawkins, B.; Kobal, J.; Hrabar, M.; Oedl-Wieser, T. Developing Sustainable and Flexible Rural–Urban Connectivity through Complementary Mobility Services. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Wen, H. Spatial Spillover of House Prices: An Empirical Study of the Yangtze Delta Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonara, S.; Della Spina, L.; Stefano, D. Real Estate Values and Urban Quality: Definition of an Indicator. In New Metropolitan Perspectives. Post COVID Dynamics: Green and Digital Transition, between Metropolitan and Return to Villages Perspectives; Calabrò, F., Della Spina, L., Piñeira Mantiñán, M.J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 482, pp. 1082–1090. ISBN 9783031068249. [Google Scholar]
- Manola, M.; Tsatalbassoglou, A.-I.; Geronymou, K. The Cultural Monuments of the Italians in Rhodes and Their Use Today. Open J. Stud. Arts 2023, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, M.; Prete, C.; Viccaro, M.; Sijtsma, F.; Veneri, P.; Romano, S. Understanding the Role of Nature in Urban-Rural Linkages: Identifying the Potential Role of Rural Nature-Based Attractive Clusters That Serve Human Well-Being. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigkas, G.; Gourgiotis, A.; Derdemezi, E.-T. Spatial Planning Incompetence to Discourage Urban Sprawl on Greek Islands. Evidence from Paros, Greece. J. Coast. Conserv. 2022, 26, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussauw, K.; Neutens, T.; Witlox, F. Relationship between Spatial Proximity and Travel-to-Work Distance: The Effect of the Compact City. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 687–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N.; Schmid, C. The ‘Urban Age’ in Question. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2014, 38, 731–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravegias, N.; Doukas, Y.E. A Stategy for Rural Development in Greece: The Case of Island Areas. Reg. Peripher. 2012, 1, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinelli, L.; Black, D. Urbanization and Growth. J. Urban Econ. 2004, 56, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzar, S.; Ogden, P.; Hall, R.; Haase, A.; Kabisch, S.; Steinfiihrer, A. Splintering Urban Populations: Emergent Landscapes of Reurbanisation in Four European Cities. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 651–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Jaligot, R.; Chenal, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urbanization in Three Swiss Urban Agglomerations: Insights from Landscape Metrics, Growth Modes and Fractal Analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Bedoya, S.; Mora, A.; Vaca, A.; Estrella, A.; Herrera, M.Á. Modelling the Relationship between Urban Expansion Processes and Urban Forest Characteristics: An Application to the Metropolitan District of Quito. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2020, 79, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, R.; Hynes, H.P. Sprawl In The 1990s. Urban Aff. Rev. 2003, 38, 325–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, E.; Rosentraub, M. Are Fragmentation and Sprawl Interlinked? Urban Aff. Rev. 2000, 35, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makse, H.A.; Andrade, J.S.; Batty, M.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E. Modeling Urban Growth Patterns with Correlated Percolation. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 7054–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.; Petschel-Held, G.; Leontidou, L. Urban Sprawl in Europe: Landscapes, Land-Use Change and Policy; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2007; ISBN 9781405139175. [Google Scholar]
- Sateriano, A. (Ed.) Urban Crisis: Social and Economic Implications for Southern Europe; Nova Science: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 9798891132429. [Google Scholar]
- Gourgiotis, A.; Stathakis, D. Urbanization Trends from Global to the Local Scale. In Geographical Information Science. Case Studies in Earth and Environmental Monitoring; Petropoulos, G.P., Chalkias, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 357–375. ISBN 9780443136054. [Google Scholar]
- Baxevani, M.; Tsiotas, D.; Kolkos, G.; Zafeiriou, E.; Arabatzis, G. Peri-Urban and Urban Green Space Management and Planning: The Case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Land 2024, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, S.; Vardopoulos, I.; Salvati, L. A Tale of a Shrinking City? Exploring the Complex Interplay of Socio-Demographic Dynamics in the Recent Development of Attica, Greece. Cities 2023, 132, 104089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Escrivà Saneugenio, F.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Homage (and Criticism) to the Mediterranean City. Regional Sustainability and Economic Resilience; River Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 9788770041775. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, S. A Critical Evaluation of the City Life Cycle Idea. Urban Geogr. 1991, 12, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, J.T. Planned Abandonment: The Neighborhood Life-cycle Theory and National Urban Policy. Hous. Policy Debate 2000, 11, 7–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounaridis, D.; Symeonakis, E.; Chorianopoulos, I.; Koukoulas, S. Incorporating Density in Spatiotemporal Land Use/Cover Change Patterns: The Case of Attica, Greece. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faka, A.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Maloutas, T.; Chalkias, C. Urban Quality of Life: Spatial Modeling and Indexing in Athens Metropolitan Area, Greece. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadimitriou, N.; Maloutas, T.; Arapoglou, V.P. Multiple Deprivation and Urban Development in Athens, Greece: Spatial Trends and the Role of Access to Housing. Land 2021, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavarnou, D.; Nanda, A. Which Attributes Influence the Housing Markets Across the Greek Islands? J. Real Estate Lit. 2014, 22, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiannidis, S.; Kalfas, D.; Papaevangelou, O.; Chatzitheodoridis, F.; Katsetsiadou, K.-N.; Lekkas, E. Integration of Climate Change Strategies into Policy and Planning for Regional Development: A Case Study of Greece. Land 2024, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatiou, K. Bridging the Gap between Tourism Development and Urban Planning: Evidence from Greece. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassi, A.; Siountri, K.; Papadaki, K.; Iliadi, A.; Ypsilanti, A.; Bakogiannis, E. The Greek Urban Policy Reform through the Local Urban Plans (LUPs) and the Special Urban Plans (SUPs), Funded by Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF). Land 2022, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.L. Land Use Planning and Green Environment Services: The Contribution of Trail Paths to Sustainable Development. Land 2023, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgiotis, A.; Tsilimigkas, G.; Haidarlis, M. (Eds.) Aménagement du Territoire et Ses Défis. Nouvelle Pensée Spatiale en Grèce et en France; Nomiki Bibliothiki: Athens, Greece, 2021; ISBN 9789606544460. [Google Scholar]
- Tsilimigkas, G.; Kizos, T.; Gourgiotis, A. Unregulated Urban Sprawl and Spatial Distribution of Fire Events: Evidence from Greece. Environ. Hazards 2018, 17, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Hoffmann, A.; Sandrin, P.; Doukas, Y.E. (Eds.) Climate Change in Regional Perspective. European Union and Latin American Initiatives, Challenges, and Solutions; United Nations University Series on Regionalism; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 27, ISBN 9783031493287. [Google Scholar]
- Vardopoulos, I.; D’Agata, A.; Escrivà Saneugenio, F.; Salvati, L. Sprawl and the City: Realizing a Sustainable Mediterranean Urbanization; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 9798895300060. [Google Scholar]
- Grekousis, G.; Manetos, P.; Photis, Y.N. Modeling Urban Evolution Using Neural Networks, Fuzzy Logic and GIS: The Case of the Athens Metropolitan Area. Cities 2013, 30, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, M.R. Forecasting Land-Use Changes in Mashhad Metropolitan Area Using Cellular Automata and Markov Chain Model for 2016–2030. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Ma, Q.; Du, C.; Hu, G.; Shang, C. Rapid Urbanization in a Mountainous Landscape: Patterns, Drivers, and Planning Implications. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 2449–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, A.; Bauer, D.M.; Bell, K.P.; Loftin, C.S.; Nelson, E.J. Using Landscape Metrics to Characterize Towns along an Urban-Rural Gradient. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2937–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lu, H.; Wu, L.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Cao, L. Automatic Extraction for Land Parcels Based on Multi-Scale Segmentation. Land 2024, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; He, S.; Lian, J.; Bie, Q.; Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Xie, Y. Detailed Mapping of Urban Land Use Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Lanzhou. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Chang, R.; Zeng, H.; Bai, X. Dynamic Simulation Patterns and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Ecol. Modell. 2022, 464, 109850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadonna, A.; Rostagno, A.; Beltramo, R. Improving the Landscape and Tourism in Marginal Areas: The Case of Land Consolidation Associations in the North-West of Italy. Land 2020, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, F.; Praticò, S.; Piovesan, G.; Chiarucci, A.; Argentieri, A.; Modica, G. Characterizing Historical Transformation Trajectories of the Forest Landscape in Rome’s Metropolitan Area (Italy) for Effective Planning of Sustainability Goals. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4708–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S. Effects of Urbanization on Farmland Size and Diversified Farm Activities in Japan: An Analysis Based on the Land Parcel Database. Land 2020, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacamán Ochoa, C.; Ferrer Jiménez, D.; Mata Olmo, R. Green Infrastructure Planning in Metropolitan Regions to Improve the Connectivity of Agricultural Landscapes and Food Security. Land 2020, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.; Fernandes, C.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Farinha-Marques, P. A Diagnostic Framework for Assessing Land-Use Change Impacts on Landscape Pattern and Character—A Case-Study from the Douro Region, Portugal. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 228, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Feng, R.; Wang, L. Fractal Characteristic Analysis of Urban Land-Cover Spatial Patterns with Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Images in Shenzhen City (1988–2015). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Weng, M. A Fractal Approach to Urban Boundary Delineation Based on Raster Land Use Maps: A Case of Shanghai, China. Land 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, X.; Fu, D. Examining the Satellite-Detected Urban Land Use Spatial Patterns Using Multidimensional Fractal Dimension Indices. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5152–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitner, A.; Fialkowski, M. Entropy of the Land Parcel Mosaic as a Measure of the Degree of Urbanization. Entropy 2021, 23, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Dale, P.; Ding, X.; Lu, Y. Urban Parcel Grouping Method Based on Urban Form and Functional Connectivity Characterisation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.; Santé-Riveira, I.; Crecente-Maseda, R.; Redondo, C.D.; Trinidad, J.P.; López, J.P.; Biempica, R.D.; Ferreira Neto, J.A. A New Spatial Criteria Method to Delimit Rural Settlements towards Boundaries Equity: Land Use Optimization for Decision Making in Galicia, NW Spain. Land 2022, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, M.; Biczkowski, M.; Leśniewska-Napierała, K.; Nalej, M.; Napierała, T. Impairing Land Registry: Social, Demographic, and Economic Determinants of Forest Classification Errors. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Zhong, M.; Safdar, M. Evaluating Locational Preference of Urban Activities with the Time-Dependent Accessibility Using Integrated Spatial Economic Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Fiscal Ecological Cost of Land in China: Estimation and Regional Differences. Land 2022, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legras, S.; Cavailhès, J. Environmental Performance of the Urban Form. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2016, 59, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopiou, D.; Giannopoulos, K.; Anagnostellos, K.; Tselentis, B.; Mavridoglou, G. SWOT Analysis of the Tourist Sector on Paros Island, Greece. In Proceedings of the WIT Transactions on the Built Environment. 3rd International Conference on Coastal Cities and their Sustainable Future, Rome, Italy, 11–13 September 2019; pp. 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Maravegias, N.; Doukas, Y.E.; Petides, P. Climate Change Concerns and the Role of Research and Innovation in the Agricultural Sector: The European Union Context. In Climate Change in Regional Perspective. European Union and Latin American Initiatives, Challenges, and Solutions; Ribeiro Hoffmann, A., Sandrin, P., Doukas, Y.E., Eds.; United Nations University Series on Regionalism, Vol. 27; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 135–151. ISBN 9783031493287. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agata, A.; Cudlin, P.; Vardopoulos, I.; Schinaia, G.; Corona, P.; Salvati, L. Assessing the Spatial Coherence of Forest Cover Indicators from Different Data Sources: A Contribution to Sustainable Development Reporting. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, A.; Madusanka, N.B.S.; Abenayake, C.; Mahanama, P.K.S. A Modeling Framework: To Analyze the Relationship between Accessibility, Land Use and Densities in Urban Areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkartzios, M. ‘Leaving Athens’: Narratives of Counterurbanisation in Times of Crisis. J. Rural Stud. 2013, 32, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agata, A.; Ciaschini, C.; Mosconi, E.M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Vardopoulos, I.; Scarpitta, D.; Alhuseen, A.M.A.; Salvati, L. The Latent Shift from Monocentric to Polycentric Settlement Models. In Urban Crisis: Social and Economic Implications for Southern Europe; Sateriano, A., Ed.; Nova Science: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 9798891132429. [Google Scholar]
- Davri, A.I.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Detsikas, S.E.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Faka, A. Spatial Distribution of Noise Levels in the Historic Centre of Athens in Greece Using Geoinformation Technologies. In Geographical Information Science. Case Studies in Earth and Environmental Monitoring; Petropoulos, G.P., Chalkias, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 429–454. ISBN 9780443136054. [Google Scholar]
- Sotiriou, G.; Petropoulou, C. Socio-Spatial Inequalities, and Local Struggles for the Right to the City and to Nature—Cases of Urban Green Parks in Athens. Land 2022, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Ferrara, A.; Chelli, F. Long-Term Growth and Metropolitan Spatial Structures: An Analysis of Factors Influencing Urban Patch Size under Different Economic Cycles. Geogr. Tidsskr. J. Geogr. 2018, 118, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Titterington, D.M. Neural Networks: A Review from a Statistical Perspective. Stat. Sci. 1994, 9, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiotas, D. City-Size or Rank-Size Distribution? An Empirical Analysis on Greek Urban Populations. Theor. Empir. Res. Urban Manag. 2016, 11, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Oshan, T.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.; Fotheringham, A. Mgwr: A Python Implementation of Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression for Investigating Process Spatial Heterogeneity and Scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Batty, M.; Longley, P.A. Diffusion-Limited Aggregation and the Fractal Nature of Urban Growth. Pap. Reg. Sci. Assoc. 1989, 67, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niavis, S.; Tsiotas, D. Decomposing the Price of the Cruise Product into Tourism and Transport Attributes: Evidence from the Mediterranean Market. Tour. Manag. 2018, 67, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkos, G.E.; Tsirivis, A.S. Sustainable Development of the European Electricity Sector: Investigating the Impact of Electricity Price, Market Liberalization and Energy Taxation on RES Deployment. Energies 2023, 16, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recanatesi, F.; Clemente, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Ranalli, F.; Zitti, M.; Salvati, L. A Fifty-Year Sustainability Assessment of Italian Agro-Forest Districts. Sustainability 2015, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yue, H.; Li, Z. Examining the Influences of Air Quality in China’s Cities Using Multi-scale Geographically Weighted Regression. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 1444–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Partridge, M.D.; Olfert, M.R. Can Geographically Weighted Regressions Improve Regional Analysis and Policy Making? Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2007, 30, 300–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkos, G.; Zisiadou, A. The Effects of Climate Change to Weather-Related Environmental Hazards: Interlinkages of Economic Factors and Climate Risk. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Malekzadeh, N. Driving Factors of Formation, Development, and Change of Spatial Structure in Metropolitan Areas: A Systematic Review. J. Urban Manag. 2020, 9, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliocca, N.; McConnell, V.; Walls, M.; Safirova, E. Zoning on the Urban Fringe: Results from a New Approach to Modeling Land and Housing Markets. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2012, 42, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorianopoulos, I.; Pagonis, T.; Koukoulas, S.; Drymoniti, S. Planning, Competitiveness and Sprawl in the Mediterranean City: The Case of Athens. Cities 2010, 27, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutridi, E.; Tsiotas, D.; Christopoulou, O. Examining the Spatial Effect of “Smartness” on the Relationship between Agriculture and Regional Development: The Case of Greece. Land 2023, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, M. Spatial Integration as A Factor Of Overcoming The Crisis In South-East Of Europe. Sustain. Dev. Cult. Tradit. J. 2013, 1, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.W.; Rihan, M.; Ishtiaque, M.; Shahfahad. Analyses of Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Change and Built-up Expansion in the Suburb of a Metropolitan City: Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Delhi NCR Using Landsat Datasets. J. Urban Manag. 2020, 9, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidley, T. Measuring Sprawl. Urban Aff. Rev. 2016, 52, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Báez, P.; Cabrera-Barona, P.; Bogaert, J. Characterizing Landscape Patterns in Urban-Rural Interfaces. J. Urban Manag. 2021, 10, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiraglia, D.; Ceccarelli, T.; Bajocco, S.; Perini, L.; Salvati, L. Unraveling Landscape Complexity: Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Landscape Pattern Dynamics (1954–2008) in Contrasting Peri-Urban and Agro-Forest Regions of Northern Italy. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Mori, T. Structural Stability and Evolution of Urban Systems. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1997, 27, 399–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiraglia, D.; Ceccarelli, T.; Bajocco, S.; Salvati, L.; Perini, L. Linking Trajectories of Land Change, Land Degradation Processes and Ecosystem Services. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Georgescu, M.; Wu, J. Impacts of Landscape Changes on Local and Regional Climate: A Systematic Review. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1269–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, R.; Quaranta, G.; Rontos, K.; Cudlin, P.; Salvati, L. Investigating Metropolitan Hierarchies through a Spatially Explicit (Local) Approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckner, J.K. Urban Sprawl: Diagnosis and Remedies. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2000, 23, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P. The Future of the Metropolis and Its Form. Reg. Stud. 1997, 31, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, M.D.; Rickman, D.S.; Ali, K.; Olfert, M.R. Do New Economic Geography Agglomeration Shadows Underlie Current Population Dynamics across the Urban Hierarchy? Pap. Reg. Sci. 2009, 88, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J.; Carter, C.; Reed, M.R.; Larkham, P.; Adams, D.; Morton, N.; Waters, R.; Collier, D.; Crean, C.; Curzon, R.; et al. Disintegrated Development at the Rural–Urban Fringe: Re-Connecting Spatial Planning Theory and Practice. Prog. Plann. 2013, 83, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, E.; Papadas, C.T. Spatial Connectivity and Regional Economic Resilience in Turbulent Times. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiotas, D.; Polyzos, S. Transportation Networks And Regional Development: The Conceptual And Empirical Framework In Greece. Sustain. Reg. Dev. Sci. J. 2024, 1, 15–39. [Google Scholar]
- Miceikienė, A.; Skauronė, L.; Krikštolaitis, R. Assessment of the Financial Autonomy of Rural Municipalities. Economies 2021, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakos, G.; Rontos, K.; Vavoura, C.; Vavouras, I. The Impact of Recent Economic Crises on Income Inequality and the Risk of Poverty in Greece. Economies 2023, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


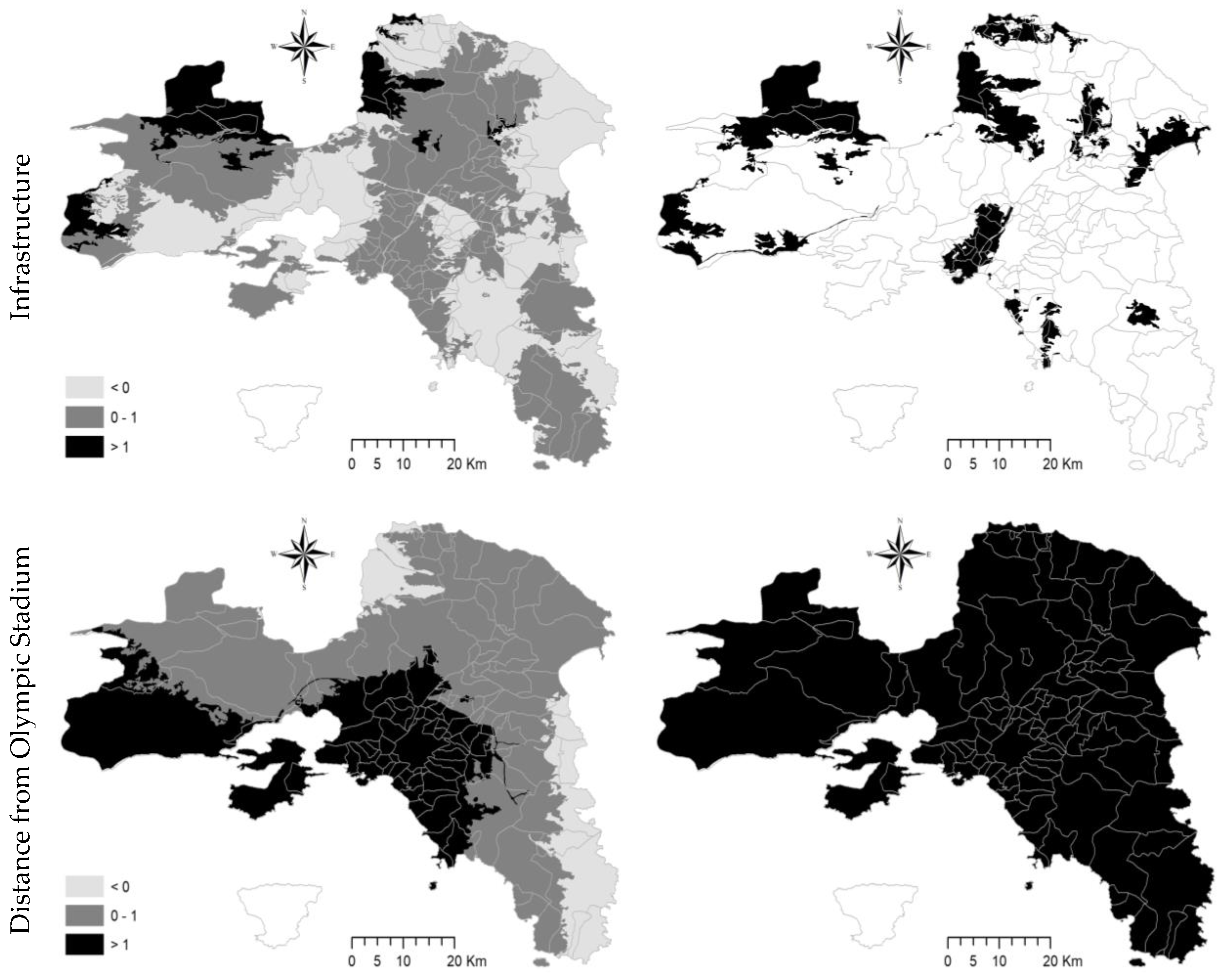


| Predictor | OLS | MGWR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estim. | St.Err | p | Avg. | St.Dev | I (m) | Min | Med. | Max | M/A | |
| 1990 | ||||||||||
| Infr | 0.042 | 0.032 | 0.083 | 0.490 | 0.2 | −1.419 | 0.030 | 2.286 | 0.36 | |
| Poor | 0.059 | 0.030 | * | 0.034 | 0.014 | 2.4 | 0.010 | 0.039 | 0.052 | 1.15 |
| DisA | 0.026 | 0.034 | 0.055 | 0.011 | 5.0 | 0.028 | 0.060 | 0.067 | 1.09 | |
| DisS | 0.372 | 0.049 | * | 0.477 | 0.065 | 7.3 | 0.361 | 0.491 | 0.604 | 1.03 |
| Elev | −0.153 | 0.051 | * | −0.219 | 0.031 | −7.1 | −0.264 | −0.213 | −0.181 | 0.97 |
| Urb | 0.105 | 0.180 | 0.306 | 0.010 | 30.6 | 0.286 | 0.305 | 0.327 | 1.00 | |
| Agr | 0.248 | 0.198 | 0.472 | 0.004 | 118.0 | 0.465 | 0.472 | 0.479 | 1.00 | |
| For | 0.256 | 0.225 | 0.547 | 0.045 | 12.2 | 0.468 | 0.549 | 0.617 | 1.00 | |
| Adj-R2 | 0.083 | 0.178 | ||||||||
| AIC | 3097 | 3027 | ||||||||
| n | 1123 | |||||||||
| 2018 | ||||||||||
| Infr | 0.067 | 0.030 | * | 0.276 | 0.675 | 0.4 | −1.133 | 0.104 | 3.057 | 0.38 |
| Poor | −0.012 | 0.028 | −0.017 | 0.043 | −0.4 | −0.069 | −0.019 | 0.052 | 1.12 | |
| DisA | 0.015 | 0.032 | 0.063 | 0.011 | 5.7 | 0.04 | 0.066 | 0.077 | 1.05 | |
| DisS | 0.230 | 0.045 | * | 0.284 | 0.032 | 8.9 | 0.225 | 0.28 | 0.361 | 0.99 |
| Elev | 0.119 | 0.047 | * | 0.157 | 0.258 | 0.6 | −0.435 | 0.143 | 1.212 | 0.91 |
| Urb | −0.214 | 0.146 | −0.374 | 0.054 | −6.9 | −0.493 | −0.364 | −0.262 | 0.97 | |
| Agr | −0.148 | 0.150 | −0.348 | 0.043 | −8.1 | −0.431 | −0.331 | −0.281 | 0.95 | |
| For | −0.206 | 0.164 | −0.383 | 0.009 | −42.6 | −0.402 | −0.381 | −0.372 | 0.99 | |
| Adj-R2 | 0.095 | 0.300 | ||||||||
| AIC | 3348 | 3131 | ||||||||
| n | 1220 | |||||||||
| Predictor | OLS | MGWR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estim. | St.Err | p | Mean | St.Dev | I (m) | Min | Med. | Max | M/A | |
| 1990 | ||||||||||
| Infr | −0.110 | 0.033 | * | −0.090 | 0.064 | −1.4 | −0.165 | −0.116 | 0.015 | 1.29 |
| Poor | −0.037 | 0.030 | 0.073 | 0.115 | 0.6 | −0.077 | 0.047 | 0.223 | 0.64 | |
| DisA | −0.061 | 0.034 | * | 0.013 | 0.052 | 0.3 | −0.067 | −0.012 | 0.115 | −0.92 |
| DisS | −0.407 | 0.049 | * | −0.376 | 0.360 | −1.0 | −2.181 | −0.309 | 0.899 | 0.82 |
| Elev | 0.200 | 0.051 | * | 0.252 | 0.065 | 3.9 | 0.127 | 0.260 | 0.373 | 1.03 |
| Urb | 0.002 | 0.182 | −0.139 | 0.005 | −27.8 | −0.147 | −0.140 | −0.127 | 1.01 | |
| Agr | −0.028 | 0.199 | −0.139 | 0.006 | −23.2 | −0.148 | −0.140 | −0.121 | 1.01 | |
| For | −0.059 | 0.227 | −0.207 | 0.005 | −41.4 | −0.218 | −0.206 | −0.199 | 1.00 | |
| Adj-R2 | 0.067 | 0.336 | ||||||||
| AIC | 3117 | 2806 | ||||||||
| n | 1123 | |||||||||
| 2018 | ||||||||||
| Infr | −0.087 | 0.031 | * | −0.014 | 0.199 | −0.1 | −0.679 | −0.018 | 0.689 | 1.29 |
| Poor | 0.018 | 0.029 | −0.001 | 0.007 | −0.1 | −0.009 | −0.003 | 0.012 | 3.00 | |
| DisA | 0.063 | 0.033 | * | −0.043 | 0.167 | −0.3 | −0.544 | −0.013 | 0.255 | 0.30 |
| DisS | 0.169 | 0.046 | * | 0.006 | 0.137 | 0.0 | −0.358 | −0.010 | 0.384 | −1.67 |
| Elev | −0.397 | 0.048 | * | −0.225 | 0.710 | −0.3 | −6.039 | −0.065 | 0.244 | 0.29 |
| Urb | 0.327 | 0.149 | * | 0.241 | 0.002 | 120.5 | 0.235 | 0.240 | 0.245 | 1.00 |
| Agr | 0.253 | 0.153 | * | 0.234 | 0.047 | 5.0 | 0.024 | 0.242 | 0.341 | 1.03 |
| For | 0.404 | 0.167 | * | 0.293 | 0.007 | 41.9 | 0.281 | 0.294 | 0.303 | 1.00 |
| Adj-R2 | 0.067 | 0.753 | ||||||||
| AIC | 3386 | 1859 | ||||||||
| n | 1220 | |||||||||
| Variable | Land Parcel | |
|---|---|---|
| Size (Area) | Shape (Fractal Index) | |
| 1990 | ||
| R2 (MGWR vs. OLS) | 2.14 | 5.01 |
| AIC (MGWR vs. OLS) | 0.98 | 0.90 |
| No. of significant predictors (OLS) | 3 | 4 |
| No. of significant predictors (MGWR) | 3 | 4 |
| 2018 | ||
| R2 (MGWR vs. OLS) | 3.16 | 11.24 |
| AIC (MGWR vs. OLS) | 0.94 | 0.55 |
| No. of significant predictors (OLS) | 3 | 7 |
| No. of significant predictors (MGWR) | 3 | 7 |
| Predictor | Area | Fractal Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2018 | 1990 | 2018 | |
| Infr | 0.05 | 0.04 * | 0.68 * | 0.09 * |
| Poor | 0.99 * | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.98 |
| DisA | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.58 * | 0.25 * |
| DisS | 0.42 * | 0.57 * | 0.04 * | 0.17 * |
| Elev | 0.90 * | 0.07 * | 0.57 * | 0.04 * |
| Urb | 1.00 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 1.00 * |
| Agr | 1.00 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.26 * |
| For | 0.61 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vardopoulos, I.; Maialetti, M.; Scarpitta, D.; Salvati, L. Spatially Explicit Analysis of Landscape Structures, Urban Growth, and Economic Dynamics in Metropolitan Regions. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040150
Vardopoulos I, Maialetti M, Scarpitta D, Salvati L. Spatially Explicit Analysis of Landscape Structures, Urban Growth, and Economic Dynamics in Metropolitan Regions. Urban Science. 2024; 8(4):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040150
Chicago/Turabian StyleVardopoulos, Ioannis, Marco Maialetti, Donato Scarpitta, and Luca Salvati. 2024. "Spatially Explicit Analysis of Landscape Structures, Urban Growth, and Economic Dynamics in Metropolitan Regions" Urban Science 8, no. 4: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040150
APA StyleVardopoulos, I., Maialetti, M., Scarpitta, D., & Salvati, L. (2024). Spatially Explicit Analysis of Landscape Structures, Urban Growth, and Economic Dynamics in Metropolitan Regions. Urban Science, 8(4), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040150








