Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Hydrolyzed Collagen from Sea Bass Skin on Skin Health: A 30-Day Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Product
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Subjects
2.5. Screening for Adverse Reactions
2.6. Facial Skin Assessment
2.7. Subject Self-Assessment Questionnaire
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Functional Properties of Hydrolyzed Collagen
3.2. Participant Characteristics
3.3. Facial Skin Assessments
3.4. Self-Perceived Satisfaction with Skin Improvements
3.5. Consumer Satisfaction with Product Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ideia, P.; Pinto, J.; Ferreira, R.; Figueiredo, L.; Spínola, V.; Castilho, P.C. Fish Processing Industry Residues: A Review of Valuable Products Extraction and Characterization Methods. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 3223–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti-Quijal, F.J.; Remize, F.; Meca, G.; Ferrer, E.; Ruiz, M.-J.; Barba, F.J. Fermentation in Fish and By-Products Processing: An Overview of Current Research and Future Prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 31, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Peng, X.-L.; Li, H.-R.; Liu, J.-X.; Cheng, J.-S.-Y.; Qi, X.-Y.; Ye, S.-J.; Gong, H.-L.; Zhao, X.-H.; Yu, J.; et al. Marine-Derived Collagen as Biomaterials for Human Health. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, M.-A.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Chifiriuc, M.-C.; Albulescu, R.; Tanase, C. Beneficial Effects of Food Supplements Based on Hydrolyzedm Collagen for Skin Care (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The Collagen Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Santivarangkna, C.; Rajput, M.S.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S. Valorization of Fish Byproducts: Sources to End-Product Applications of Bioactive Protein Hydrolysate. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1803–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachman, S.H.; Santoso, J.; Suseno, S.H. Antioxidant Activity and Potential Bioactive Peptides from Skin Protein Hydrolysate of Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares). J. Ilm. Perikan. dan Kelaut. 2023, 15, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żyga, J. Oral Collagen Supplements Intake on Improving Skin Structure and Function. J. Educ. Health Sport 2022, 12, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, A.; Kania, E.M.; Genovese, L.; Corbo, A.; Merone, G.; Luci, C.; Sibilla, S. Daily Oral Supplementation with Collagen Peptides Combined with Vitamins and Other Bioactive Compounds Improves Skin Elasticity and Has a Beneficial Effect on Joint and General Wellbeing. Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Hua, N.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Kan, K.-W.; Chen, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Kuan, C.-M. Oral Collagen Drink for Antiaging: Antioxidation, Facilitation of the Increase of Collagen Synthesis, and Improvement of Protein Folding and DNA Repair in Human Skin Fibroblasts. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8031795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; Joo, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.-U.; Chung, H.-C.; Kim, J.G. Low-Molecular-Weight Collagen Peptide Improves Skin Dehydration and Barrier Dysfunction in Human Dermal Fibrosis Cells and UVB-Exposed SKH-1 Hairless Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Visessanguan, W. Production and Characterization of Odorless Antioxidative Hydrolyzed Collagen from Seabass (Lates calcarifer) Skin Without Descaling. Waste Biomass Valor. 2018, 9, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Maibach, H.I. Degenerative Changes in Aging Skin—Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage, M.A., Miller, K.W., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). ICH Harmonised Guideline: Integrated Addendum to ICH E6(R1): Guideline for Good Clinical Practice E6(R2). 2016. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/E6_R2_Addendum.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Rajabimashhadi, Z.; Gallo, N.; Salvatore, L.; Lionetto, F. Collagen Derived from Fish Industry Waste: Progresses and Challenges. Polymers 2023, 15, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondero, L.; De Negri Atanasio, G.; Tardanico, F.; Lertora, E.; Boggia, R.; Capra, V.; Commeto, A.; Costamagna, M.; Fi, L.S.E.; Feletti, M.; et al. Unlocking the Potential of Marine Sidestreams in the Blue Economy: Lessons Learned from the EcoeFISHent Project on Fish Collagen. Mar. Biotechnol. 2025, 27, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish Collagen: Extraction, Characterization, and Applications for Biomaterials Engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Mis Solval, K.E. Recent Advancements in Marine Collagen: Exploring New Sources, Processing Approaches, and Nutritional Applications. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Segger, D.; Degwert, J.; Schunck, M.; Zague, V.; Oesser, S. Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, E.; Schunck, M.; Zague, V.; Segger, D.; Degwert, J.; Oesser, S. Oral intake of specific bioactive collagen peptides reduces skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Ko, E.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, B.G.; Shin, H.J.; Seo, D.B.; Lee, S.J.; Kim., B.J.; Kim, M.N. Effects of collagen tripeptide supplement on skin properties: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. J. Cosmet. Laser. Ther. 2014, 16, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, M.; Jabbari, M.; Navekar, R.; Farahmand, F.; Zeinalian, R.; Salehi-Sahlabadi, A.; Abbaszadeh, N.; Mokari-Yamchi, A.; Davoodi, S.H. Collagen supplementation for skin health: A mechanistic systematic review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2820–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Yoon, Y.C.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kang, Y.-H.; Shin, Y.C. Liquid Collagen from Freshwater Fish Skin Ameliorates Hydration, Roughness and Elasticity in Photo-Aged Skin: A Randomized, Controlled, Clinical Study. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2024, 18, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvonne, M.; Christiane, S.; Katrin, V.; Marianne, B.; Stepha, B.; Klaus-Peter, W. Evaluation of a Food Supplement with Collagen Hydrolysate and Micronutrients on Skin Appearance and Beauty Effects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, PlaceboControlled Clinical Study with Healthy Subjects. J. Clin. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.M.; Angelinetta, C.; Rizzi, G.; Praticò, A.; Villa, R. Evaluation of the Efficacy of a Hydrolyzed Collagen Supplement for Improving Skin Moisturization, Smoothness, and Wrinkles. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz, E.; Ruth, N.; Mammone, T.; Idowu, O.C. Investigating the Dual Functions of Butylated Hydroxytoluene, Vitamin E and Vitamin C as Antioxidants and Anti-Glycation Agents in Vitro: Implications for Skin Health. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2025, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivarsson, J.; Pecorelli, A.; Guiotto, A.; Souza, M.M.; Choudhary, H.; Brieva, P.; Ferrara, F.; Valacchi, G. Comparing UV and Diesel Cutaneous Damage and Evaluating the Protective Role of a Topical Antioxidant Mixture Containing Vitamin C, E and Ferulic Acid. Exp. Dermatol. 2025, 34, e70069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, Z.; Waliullah, S.; Rastogi, D.; Pant, S. Vitamin E and Human Health: An Update. Glob. J. Health Sci. Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, J.M.; Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weschawalit, S.; Thongthip, S.; Phutrakool, P.; Asawanonda, P. Glutathione and its antiaging and antimelanogenic effects. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljšak, B.; Dahmane, R.G.; Godić, A. Intrinsic skin aging: The role of oxidative stress. Acta Dermatovenerol. Alp. Pannonica Adriat. 2012, 21, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.; Kim, S.-H.; Joo, K.-M.; Lim, S.-H.; Shin, J.-H.; Roh, J.; Kim, E.; Park, C.W.; Kim, W. Oral Intake of Enzymatically Decomposed AP Collagen Peptides Improves Skin Moisture and Ceramide and Natural Moisturizing Factor Contents in the Stratum Corneum. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.; Krug, L.; Ramsey, D.L.; Safaei, A.; Aspley, S. Beneficial Effects of Multi-Micronutrient Supplementation with Collagen Peptides on Global Wrinkles, Skin Elasticity and Appearance in Healthy Female Subjects. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 1599–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katta, R.; Desai, S.P. Diet and dermatology: The role of dietary intervention in skin disease. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Romera-Vilchez, M.; Montero-Vilchez, T.; Herrero-Fernandez, M.; Rodriguez-Pozo, J.-A.; Jimenez-Galvez, G.; Morales-Garcia, C.; Buendia-Eisman, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Impact of Exposome Factors on Epidermal Barrier Function in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Hwang, B.F.; Chen, C.P. Acute dermal effects of solar UV irradiation and efficacy of sunscreen use. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2022, 34, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
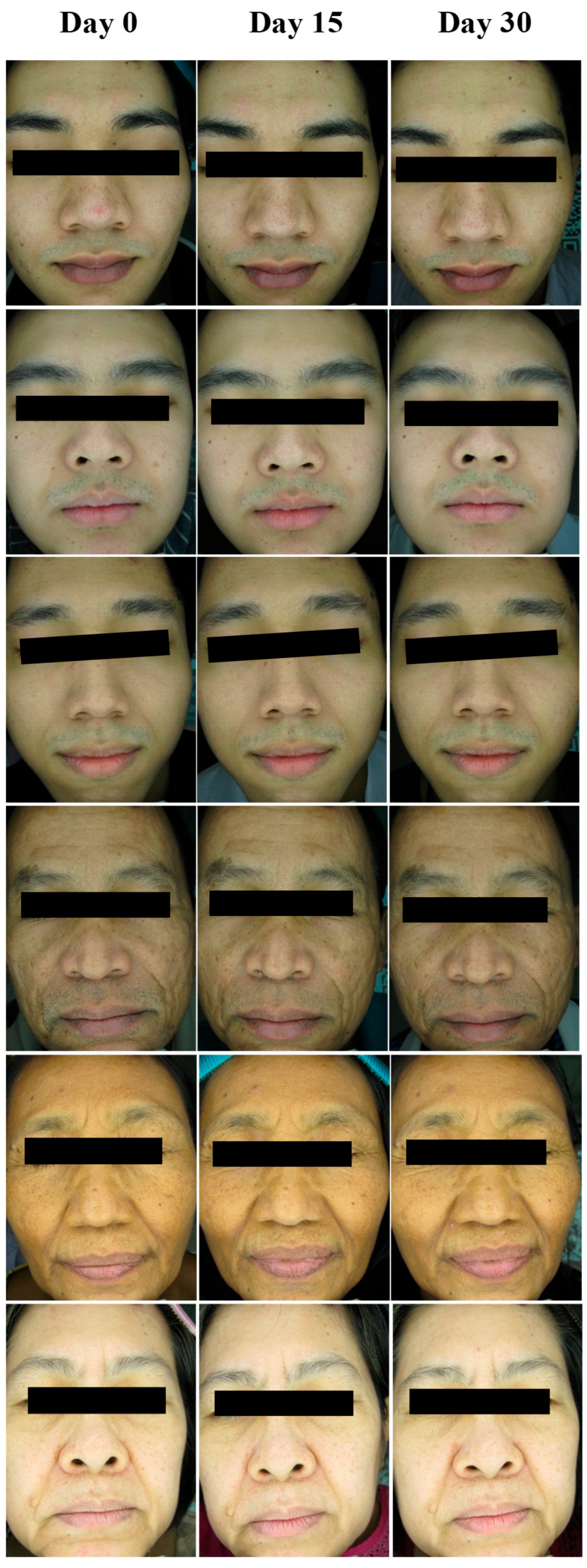
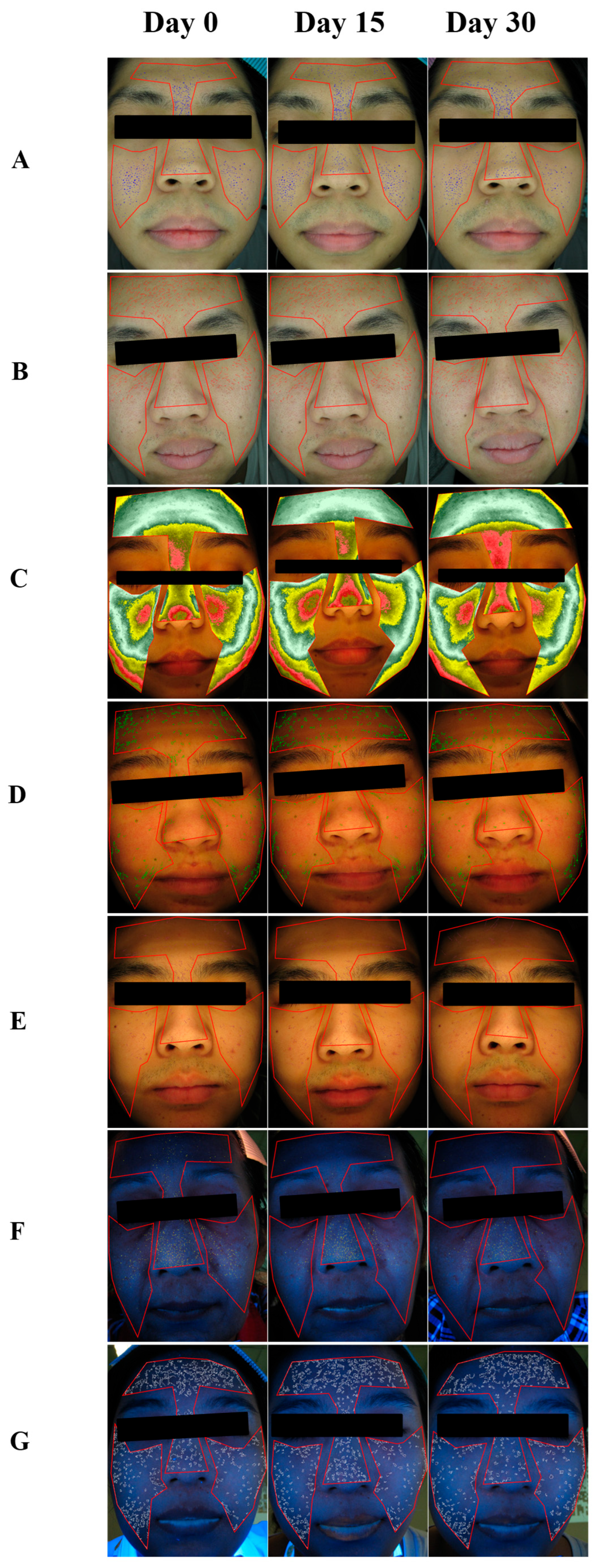
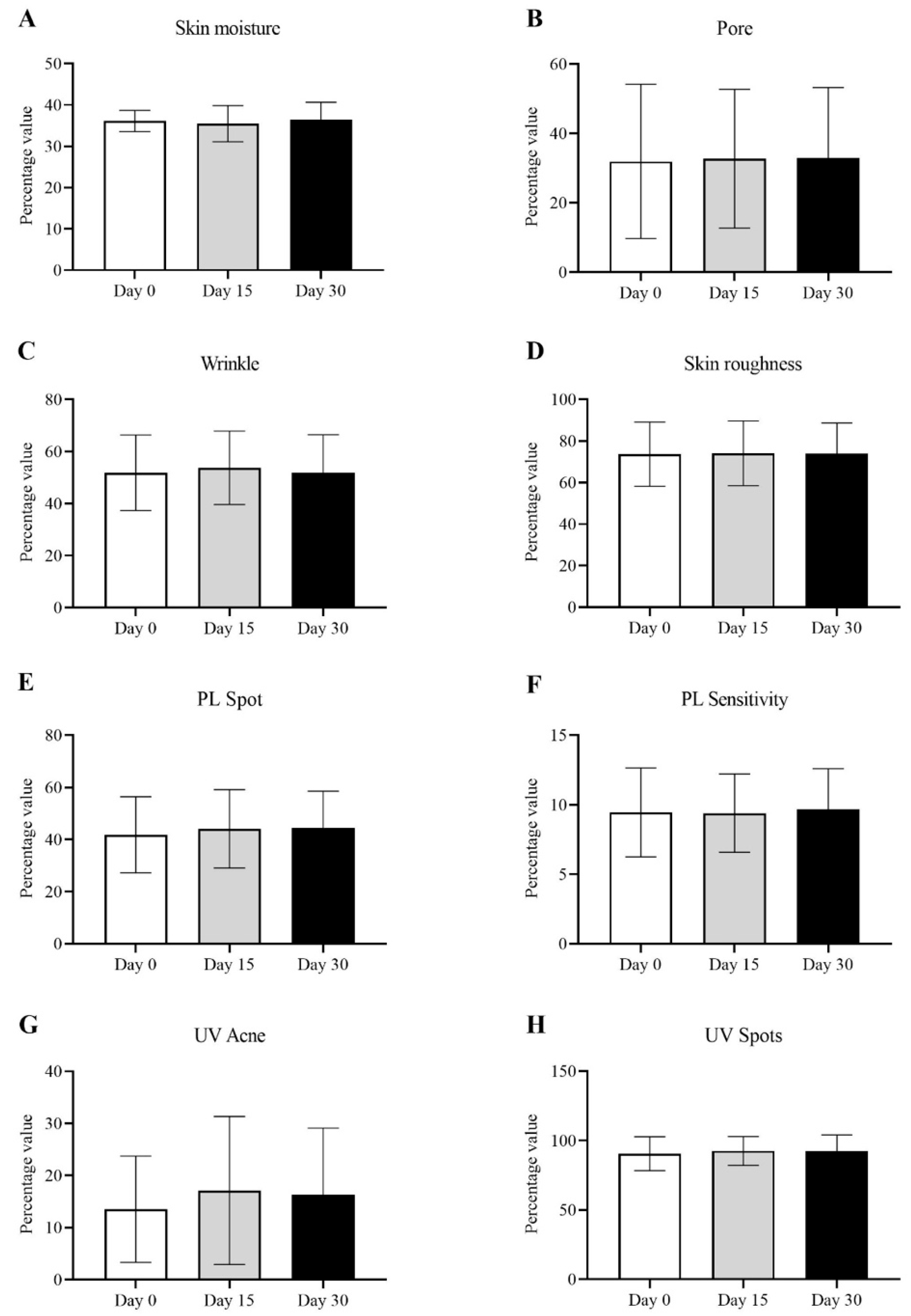
 ), pore size reduction (
), pore size reduction ( ), wrinkles reduction (
), wrinkles reduction ( ), skin roughness reduction (
), skin roughness reduction ( ), PL spots reduction (
), PL spots reduction ( ), PL sensitivity reduction (
), PL sensitivity reduction ( ), UV acne reduction (
), UV acne reduction ( ), and UV spots reduction (
), and UV spots reduction ( ) after consumption of product for 15 days.
) after consumption of product for 15 days.
 ), pore size reduction (
), pore size reduction ( ), wrinkles reduction (
), wrinkles reduction ( ), skin roughness reduction (
), skin roughness reduction ( ), PL spots reduction (
), PL spots reduction ( ), PL sensitivity reduction (
), PL sensitivity reduction ( ), UV acne reduction (
), UV acne reduction ( ), and UV spots reduction (
), and UV spots reduction ( ) after consumption of product for 15 days.
) after consumption of product for 15 days.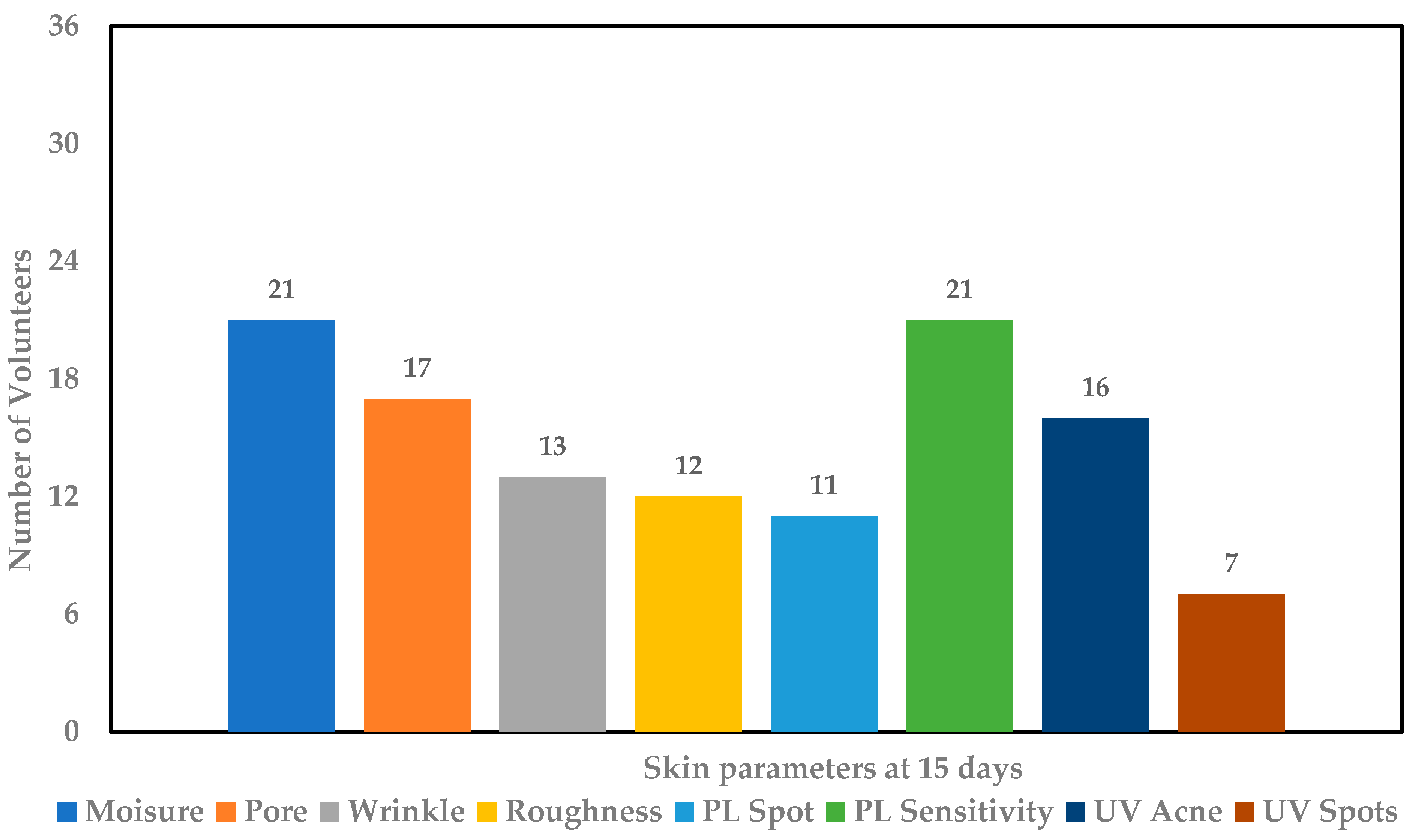
 ), pore size reduction (
), pore size reduction ( ), wrinkles reduction (
), wrinkles reduction ( ), skin roughness reduction (
), skin roughness reduction ( ), PL spots reduction (
), PL spots reduction ( ), PL sensitivity reduction (
), PL sensitivity reduction ( ), UV acne reduction (
), UV acne reduction ( ), and UV spots reduction (
), and UV spots reduction ( ) after consumption of product for 30 days.
) after consumption of product for 30 days.
 ), pore size reduction (
), pore size reduction ( ), wrinkles reduction (
), wrinkles reduction ( ), skin roughness reduction (
), skin roughness reduction ( ), PL spots reduction (
), PL spots reduction ( ), PL sensitivity reduction (
), PL sensitivity reduction ( ), UV acne reduction (
), UV acne reduction ( ), and UV spots reduction (
), and UV spots reduction ( ) after consumption of product for 30 days.
) after consumption of product for 30 days.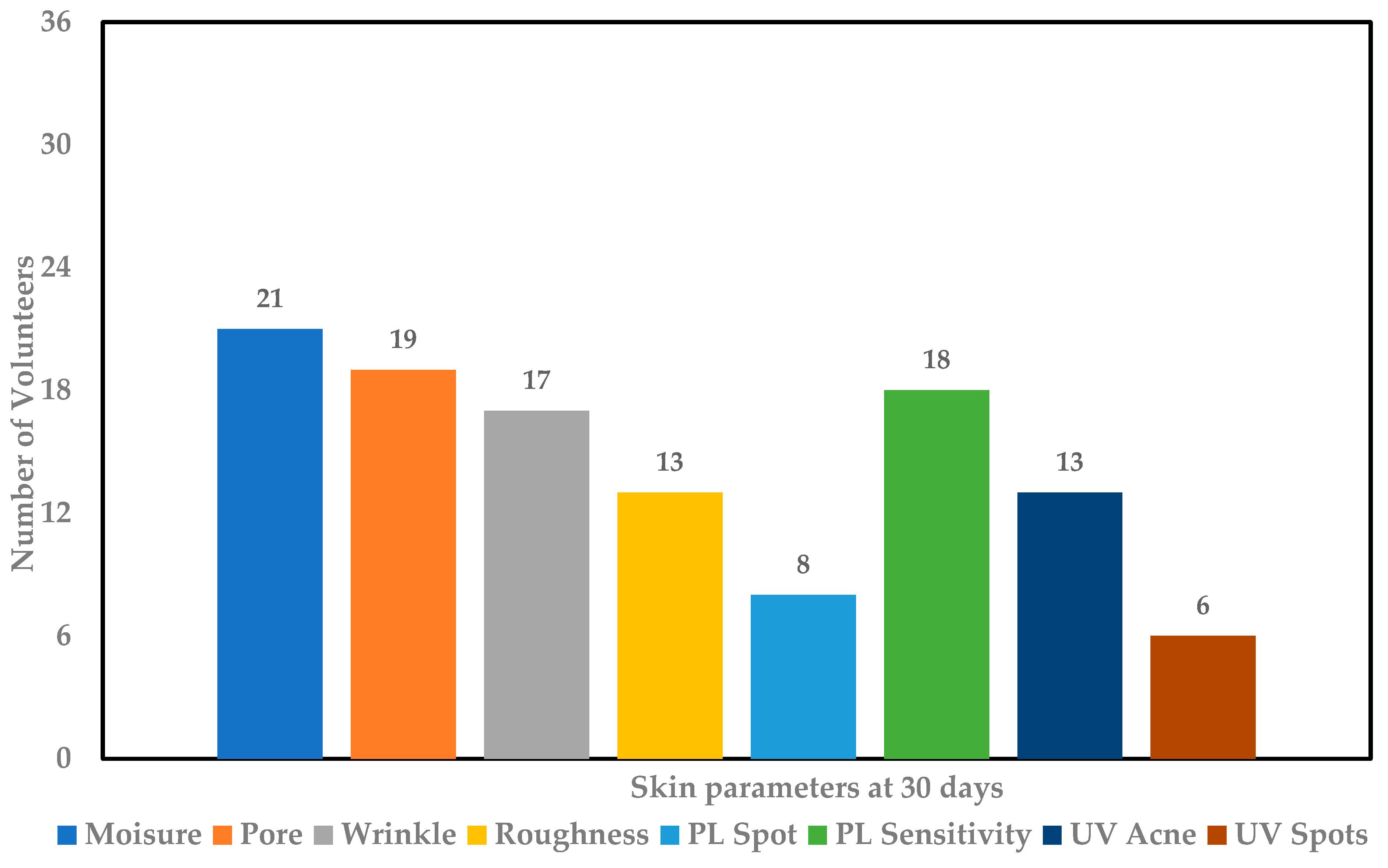
 ), pore size reduction (
), pore size reduction ( ), wrinkles reduction (
), wrinkles reduction ( ), skin roughness reduction (
), skin roughness reduction ( ), PL spots reduction (
), PL spots reduction ( ), PL sensitivity reduction (
), PL sensitivity reduction ( ), UV acne reduction (
), UV acne reduction ( ), and UV spots reduction (
), and UV spots reduction ( ) after consumption of product for 30 days.
) after consumption of product for 30 days.
 ), pore size reduction (
), pore size reduction ( ), wrinkles reduction (
), wrinkles reduction ( ), skin roughness reduction (
), skin roughness reduction ( ), PL spots reduction (
), PL spots reduction ( ), PL sensitivity reduction (
), PL sensitivity reduction ( ), UV acne reduction (
), UV acne reduction ( ), and UV spots reduction (
), and UV spots reduction ( ) after consumption of product for 30 days.
) after consumption of product for 30 days.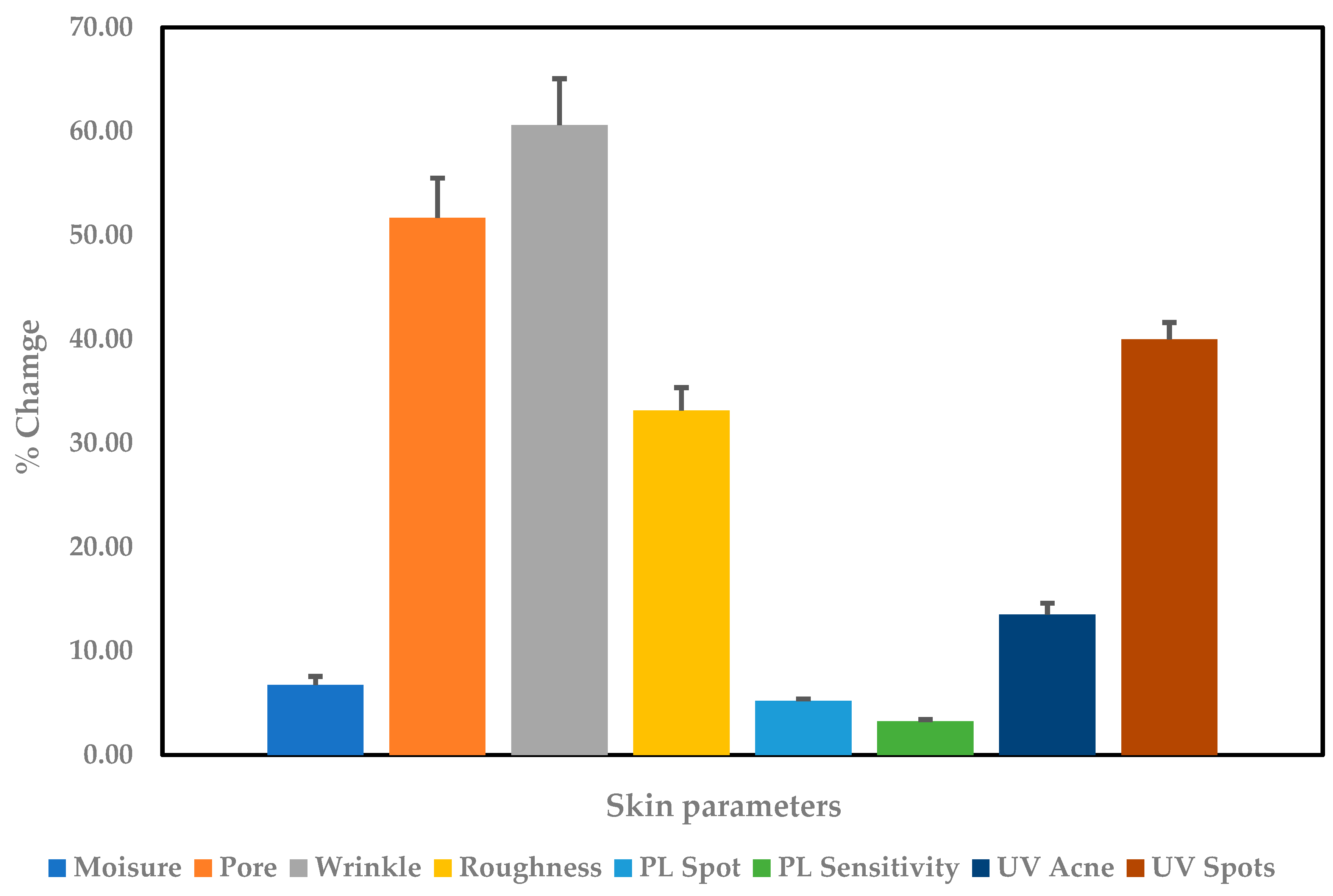


| Ingredients | C-Shortz® Content (%) w/v |
|---|---|
| Hydrolyzed fish skin collagen | 15 |
| Concentrated white grape juice | 3 |
| Vitamin C | 0.08 |
| Vitamin E | 0.02 |
| L-glutathione | 0.06 |
| Psyllium husk | 0.50 |
| Stabilizer (INS 466) Coloring agent (INS 133) Sweeteners (sucralose and dextrose) Citric acid Flavoring Nature-identical flavoring substances |
| Parameters | Number of Participants (n = 36) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | ||
| 21–30 | 26 | 72.22 |
| 51–60 | 9 | 25.00 |
| 61–70 | 1 | 2.78 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 22 | 61.11 |
| Male | 14 | 38.89 |
| History of allergy | ||
| Food | 1 | 2.78 |
| Drug | 2 | 5.55 |
| None | 33 | 91.67 |
| History of skin care use | ||
| Serum | 3 | 8.33 |
| Gel | 2 | 5.56 |
| Lotion | 1 | 2.78 |
| None | 30 | 83.33 |
| Skin concern | ||
| Dark spots | 9 | 25.00 |
| Acnes/scars | 7 | 19.44 |
| Wrinkles | 6 | 16.67 |
| Pitted scars | 6 | 16.67 |
| Pores | 3 | 8.33 |
| Dry skin | 2 | 5.55 |
| Freckles | 2 | 5.56 |
| Sensitive skin | 1 | 2.78 |
| Event Type | Definition | Observation Window | Reporting Mechanism | Responsible Staff | Number of Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Event (AE) | abnormal acne flare-ups, red rashes, itching, facial or periorbital swelling, vomiting, diarrhea, or other symptoms indicating an adverse reaction to the product were considered | Entire study duration 1–30 days | Participant self-report, clinical observation recorded in case report form | Clinical research coordinators | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wunnoo, S.; Jakkawanpitak, C.; Rajagopal, R.S.; Amnuaikit, T. Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Hydrolyzed Collagen from Sea Bass Skin on Skin Health: A 30-Day Clinical Trial. Sci 2025, 7, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7040134
Wunnoo S, Jakkawanpitak C, Rajagopal RS, Amnuaikit T. Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Hydrolyzed Collagen from Sea Bass Skin on Skin Health: A 30-Day Clinical Trial. Sci. 2025; 7(4):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7040134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWunnoo, Suttiwan, Chanawee Jakkawanpitak, Rajeev Shankar Rajagopal, and Thanaporn Amnuaikit. 2025. "Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Hydrolyzed Collagen from Sea Bass Skin on Skin Health: A 30-Day Clinical Trial" Sci 7, no. 4: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7040134
APA StyleWunnoo, S., Jakkawanpitak, C., Rajagopal, R. S., & Amnuaikit, T. (2025). Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Hydrolyzed Collagen from Sea Bass Skin on Skin Health: A 30-Day Clinical Trial. Sci, 7(4), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7040134







