Vascular Adhesion Protein 1 Mediates Gut Microbial Flagellin-Induced Inflammation, Leukocyte Infiltration, and Hepatic Steatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Adipocyte Cell Cultures, FLG Exposure, and Protein Extraction
2.3. Murine Tissue Collection, Multiplex ELISA, and Blood Analyses
2.4. Liver Fat Content Measurement
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative mRNA, Protein, Citrate Synthase, Xanthine Oxidase, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase 8, and AST and ALT Analyses
2.6. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.7. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing and the Analysis of the Gut Microbiota Composition
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
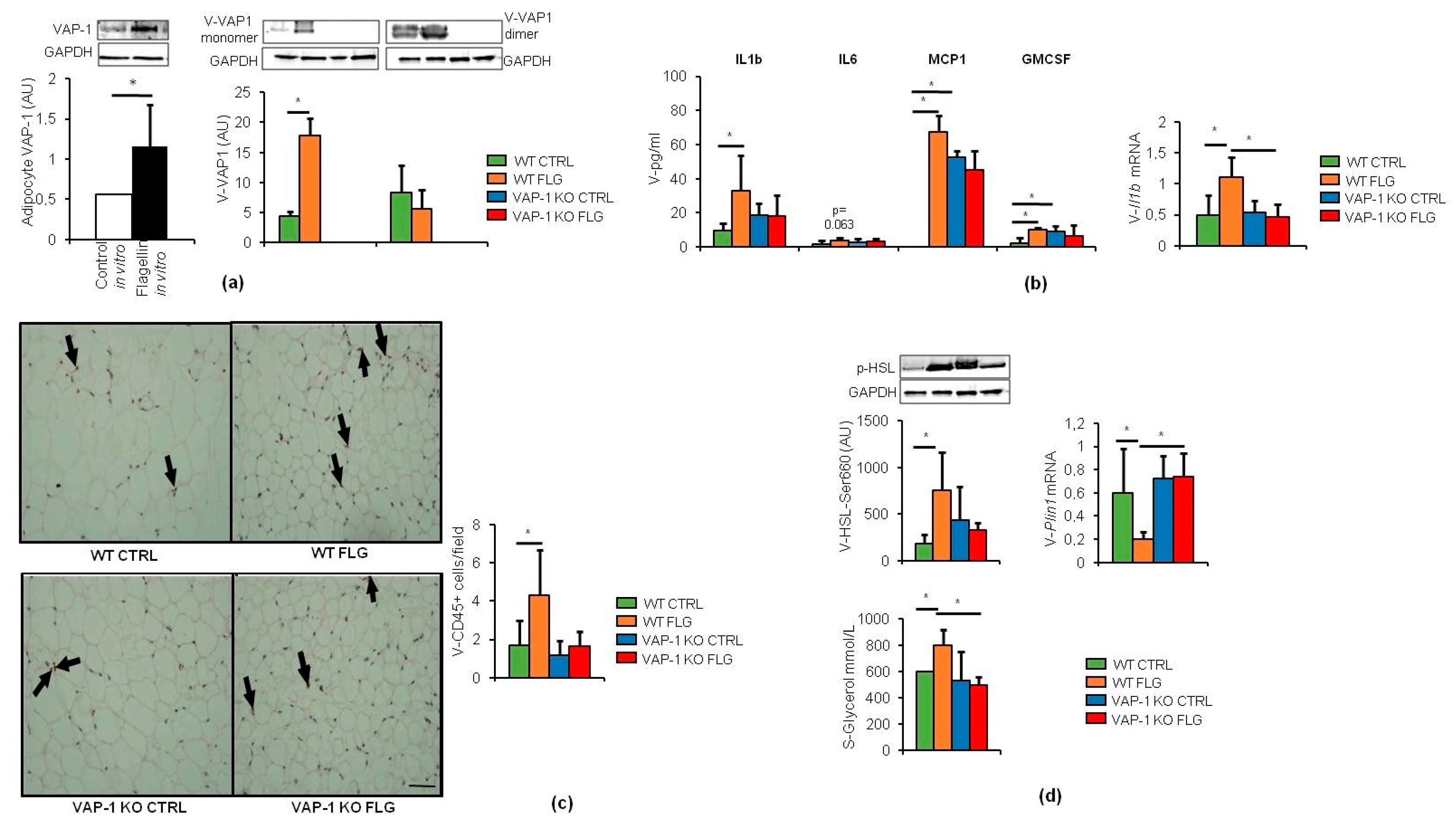
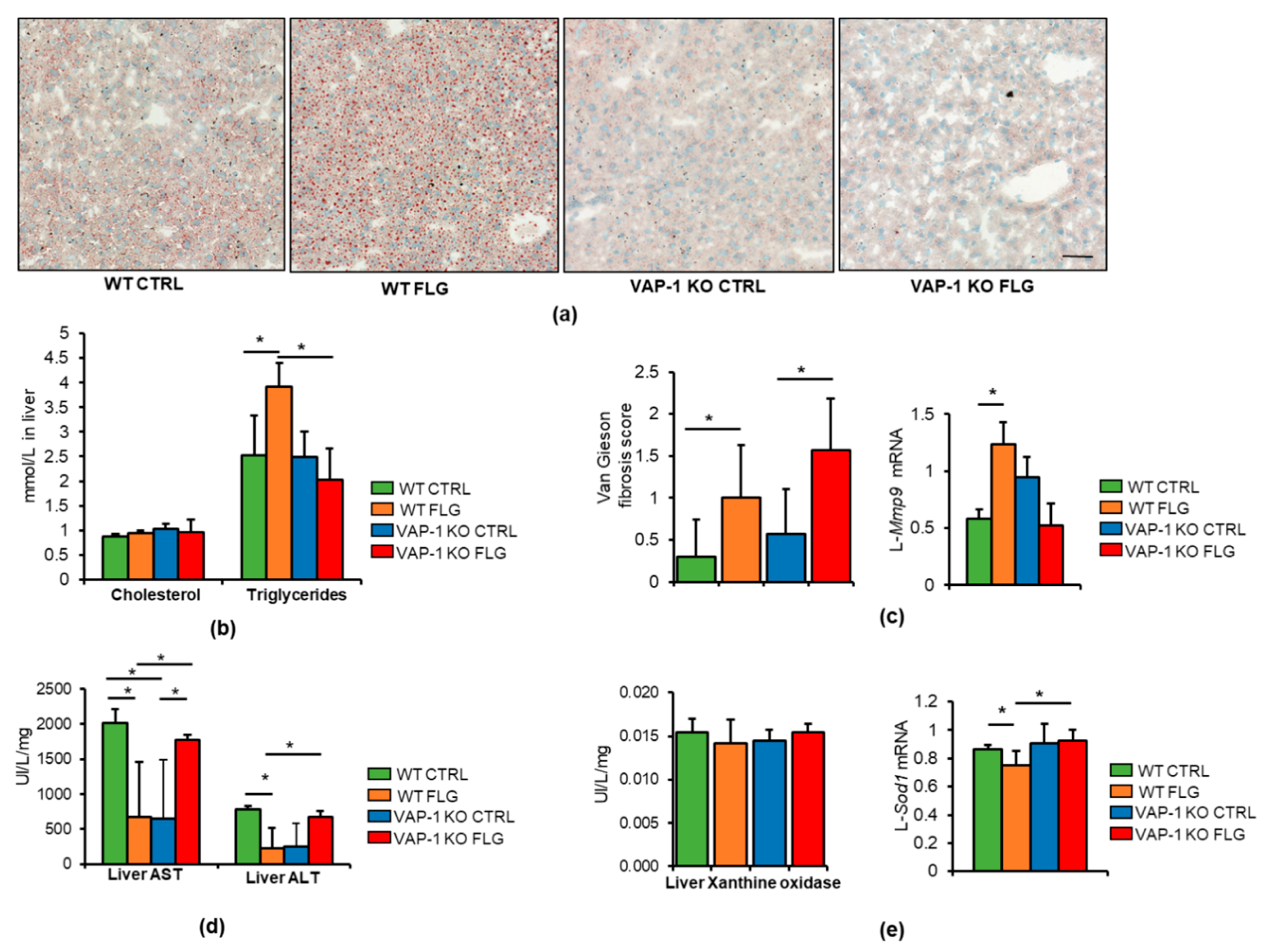
3.1. VAP-1 Mediated the FLG-Induced Inflammation and Lipolysis in VAT and Consequently Hepatic Fat Accumulation
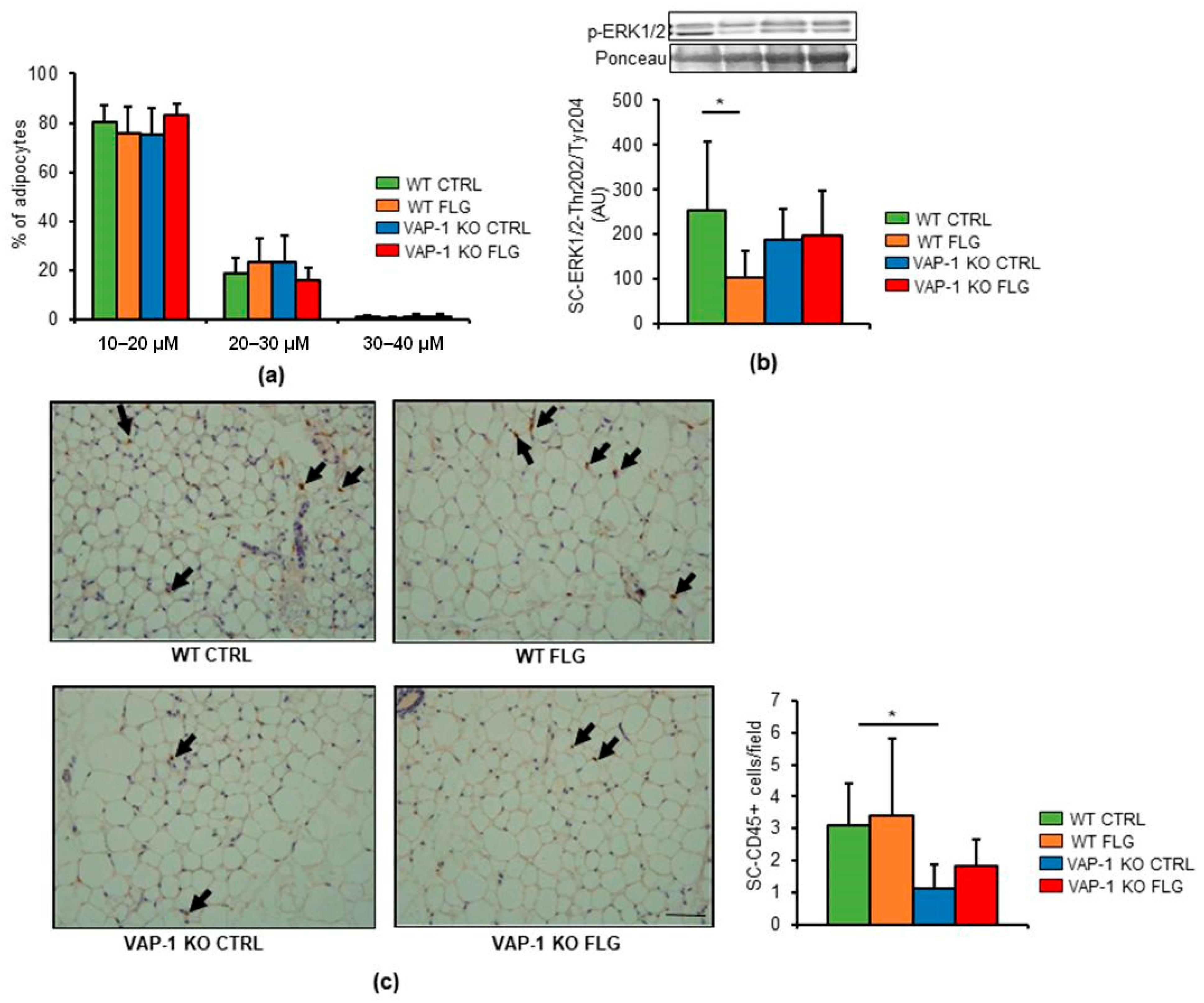
3.2. VAP-1 Mediated the FLG-Induced Decrease in ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in SAT
3.3. VAP-1 Knockout Modified the Gut Microbiota Composition and Intestinal Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, H.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Zenno, A.; Shi, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, L. The IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response is required for adipogenesis. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begriche, K.; Massart, J.; Robin, M.-A.; Bonnet, F.; Fromenty, B. Mitochondrial adaptations and dysfunctions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Barb, D.; Portillo-Sanchez, P.; Biernacki, D.; Lomonaco, R.; Suman, A.; Weber, M.H.; Budd, J.T.; Lupi, M.E.; Cusi, K. Metabolic and histological implications of intrahepatic triglyceride content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Thaiss, C.A.; Licona-Limon, P.; Flavell, R.A. Role of the intestinal microbiome in liver disease. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 46, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munukka, E.; Pekkala, S.; Wiklund, P.; Rasool, O.; Borra, R.; Kong, L.; Ojanen, X.; Cheng, S.M.; Roos, C.; Tuomela, S.; et al. Gut-adipose tissue axis in hepatic fat accumulation in humans. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahla, R.S.; Reddy, M.C.; Prasad, D.V.R.; Kumar, H. Sweeten PAMPs: Role of Sugar Complexed PAMPs in Innate Immunity and Vaccine Biology. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munukka, E.; Wiklund, P.; Partanen, T.; Välimäki, S.; Laakkonen, E.K.; Lehti, M.; Fischer-Posovzsky, P.; Wabitsch, M.; Cheng, S.; Huovinen, P.; et al. Adipocytes as a Link Between Gut Microbiota-Derived Flagellin and Hepatocyte Fat Accumulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chassaing, B.; Zhang, L.; Yeoh, B.S.; Xiao, X.; Kumar, M.; Baker, M.T.; Cai, J.; Walker, R.; Borkowski, K. Microbiota-dependent hepatic lipogenesis mediated by Stearoyl CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) promotes metabolic syndrome in TLR5-Deficient Mice. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Hepatocyte Toll-Like Receptor 5 Promotes Bacterial Clearance and Protects Mice Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Liver Disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 584–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedirko, V.; Tran, H.Q.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Stepien, M.; Trichopoulou, A.; Aleksandrova, K.; Olsen, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Carbonnel, F.; et al. Exposure to bacterial products lipopolysaccharide and flagellin and hepatocellular carcinoma: A nested case-control study. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, J.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, E.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, J.; et al. Over-activation of TLR5 signaling by high-dose flagellin induces liver injury in mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, C.J.; Shepherd, E.L.; Claridge, L.C.; Rantakari, P.; Curbishley, S.M.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Hubscher, S.G.; Reynolds, G.M.; Aalto, K.; Anstee, Q.M.; et al. Vascular adhesion protein-1 promotes liver inflammation and drives hepatic fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S. Vascular Adhesion Protein-1: A Cell Surface Amine Oxidase in Translation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 30, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.H.; Lu, L.-X.; Fan, H.; Kazachkov, M.; Jiang, Z.-J.; Jalkanen, S.; Stolen, C. Involvement of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase-mediated deamination in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Newell, F.S.; Wabitsch, M.; Tornqvist, H.E. Human SGBS cells—A unique tool for studies of human fat cell biology. Obes. Facts 2008, 1, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalto, K.; Maksimow, M.; Juonala, M.; Viikari, J.; Jula, A.; Kähönen, M.; Jalkanen, S.; Raitakari, O.T.; Salmi, M. Soluble vascular adhesion protein-1 correlates with cardiovascular risk factors and early atherosclerotic manifestations. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintala, A.; Riikonen, I.; Toivonen, A.; Pietilä, S.; Munukka, E.; Pursiheimo, J.-P.; Elo, L.L.; Arikoski, P.; Luopajärvi, K.; Schwab, U.; et al. Early fecal microbiota composition in children who later develop celiac disease and associated autoimmunity. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Gonzalez Peña, A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bour, S.; Caspar-Bauguil, S.; Iffiu-Soltesz, Z.; Nibbelink, M.; Cousin, B.; Miiluniemi, M.; Salmi, M.; Stolen, C.; Jalkanen, S.; Casteilla, L.; et al. Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase/vascular adhesion protein-1 deficiency reduces leukocyte infiltration into adipose tissue and favors fat deposition. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.; Baber, J.; Fujii, T.; Coito, A.J. Matrix metalloproteinases in liver injury, repair and fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Plessis, J.; van Pelt, J.; Korf, H.; Mathieu, C.; van der Schueren, B.; Lannoo, M.; Oyen, T.; Topal, B.; Fetter, G.; Nayler, S.; et al. Association of Adipose Tissue Inflammation with Histologic Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; et al. Frontline Science: Nasal epithelial GM-CSF contributes to TLR5-mediated modulation of airway dendritic cells and subsequent IgA response. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Deyama, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Morita, M. Toll like receptor 5 ligand induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in mouse osteoblastic cells. Biomed. Res. 2012, 33, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 461S–465S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechner, R.; Zimmermann, R.; Eichmann, T.O.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Haemmerle, G.; Lass, A.; Madeo, F. FAT SIGNALS—Lipases and lipolysis in lipid metabolism and signaling. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekkala, S.; Munukka, E.; Kong, L.; Pöllänen, E.; Autio, R.; Roos, C.; Wiklund, P.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Wabitsch, M.; Alen, M.; et al. Toll-like receptor 5 in obesity: The role of gut microbiota and adipose tissue inflammation. Obesity 2015, 23, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S. The case of visceral fat: Argument for the defense. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Gastaldelli, A. The Subtle Balance between Lipolysis and Lipogenesis: A Critical Point in Metabolic Homeostasis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9453–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrin, K.A.; Roth Flach, R.J.; DiStefano, M.T.; Matevossian, A.; Friedline, R.H.; Jung, D.; Kim, J.K.; Czech, M.P. IL-1 signaling in obesity-induced hepatic lipogenesis and steatosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirovski, G.; Dorn, C.; Huber, H.; Moleda, L.; Niessen, C.; Wobser, H.; Schacherer, D.; Buechler, C.; Wiest, R.; Hellerbrand, C. Elevated systemic monocyte chemoattractrant protein-1 in hepatic steatosis without significant hepatic inflammation. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2011, 91, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.S. Obesity, Visceral Fat, and NAFLD: Querying the Role of Adipokines in the Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011, 2011, 592404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, L.; Morin, N.; Enrique-Tarancon, G.; Prevot, D.; Lafontan, M.; Testar, X.; Zorzano, A.; Carpéné, C. Tyramine and vanadate synergistically stimulate glucose transport in rat adipocytes by amine oxidase-dependent generation of hydrogen peroxide. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 342–349. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Zhong, S.; Xie, K.; Yu, D.; Yang, R.; Gong, D.-W. Hepatic ALT isoenzymes are elevated in gluconeogenic conditions including diabetes and suppressed by insulin at the protein level. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuno-Lambarri, N.; Barbero-Becerra, V.J.; Uribe, M.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C. Mitochondrial molecular pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A proteomics approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolen, C.M.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Kurkijarvi, R.; Bono, P.; Alitalo, K.; Jalkanen, S. Origins of serum semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikoff, T.; Gophna, U. Oscillospira: A Central, Enigmatic Component of the Human Gut Microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Primer Sequence 5′ > 3′ |
|---|---|
| mACTB fwd | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG |
| mACTB rev | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| mIL1B fwd | TGTGAAATGCCACCTTTTGA |
| mIL1B rev | GGTCAAAGGTTTGGAAGCAG |
| mMMP9 fwd | AGACGACATAGACGGCATCC |
| mMMP9 rev | CTGTCGGCTGTGGTTCAGT |
| mPLIN fwd | TGAAGCAGGGCCACTCTC |
| mPLIN rev | GACACCACCTGCATGGCT |
| mSOD1 fwd | CAGGACCTCATTTTAATCCTCAC |
| mSOD1 rev | TGCCCAGGTCTCCAACAT |
| mTLR5 fwd | AAGTTCCGGGGAATCTGTTT |
| mTLR rev | GCATAGCCTGAGCCTGTTTC |
| mTjp1 fwd | GAGCGGGCTACCTTACTGAAC |
| mTjp1 rev | GTCATCTCTTTCCGAGGCATTAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toivonen, R.; Vanhatalo, S.; Hollmén, M.; Munukka, E.; Keskitalo, A.; Pietilä, S.; Elo, L.; Huovinen, P.; Jalkanen, S.; Pekkala, S. Vascular Adhesion Protein 1 Mediates Gut Microbial Flagellin-Induced Inflammation, Leukocyte Infiltration, and Hepatic Steatosis. Sci 2021, 3, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010013
Toivonen R, Vanhatalo S, Hollmén M, Munukka E, Keskitalo A, Pietilä S, Elo L, Huovinen P, Jalkanen S, Pekkala S. Vascular Adhesion Protein 1 Mediates Gut Microbial Flagellin-Induced Inflammation, Leukocyte Infiltration, and Hepatic Steatosis. Sci. 2021; 3(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleToivonen, Raine, Sanja Vanhatalo, Maija Hollmén, Eveliina Munukka, Anniina Keskitalo, Sami Pietilä, Laura Elo, Pentti Huovinen, Sirpa Jalkanen, and Satu Pekkala. 2021. "Vascular Adhesion Protein 1 Mediates Gut Microbial Flagellin-Induced Inflammation, Leukocyte Infiltration, and Hepatic Steatosis" Sci 3, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010013
APA StyleToivonen, R., Vanhatalo, S., Hollmén, M., Munukka, E., Keskitalo, A., Pietilä, S., Elo, L., Huovinen, P., Jalkanen, S., & Pekkala, S. (2021). Vascular Adhesion Protein 1 Mediates Gut Microbial Flagellin-Induced Inflammation, Leukocyte Infiltration, and Hepatic Steatosis. Sci, 3(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010013






