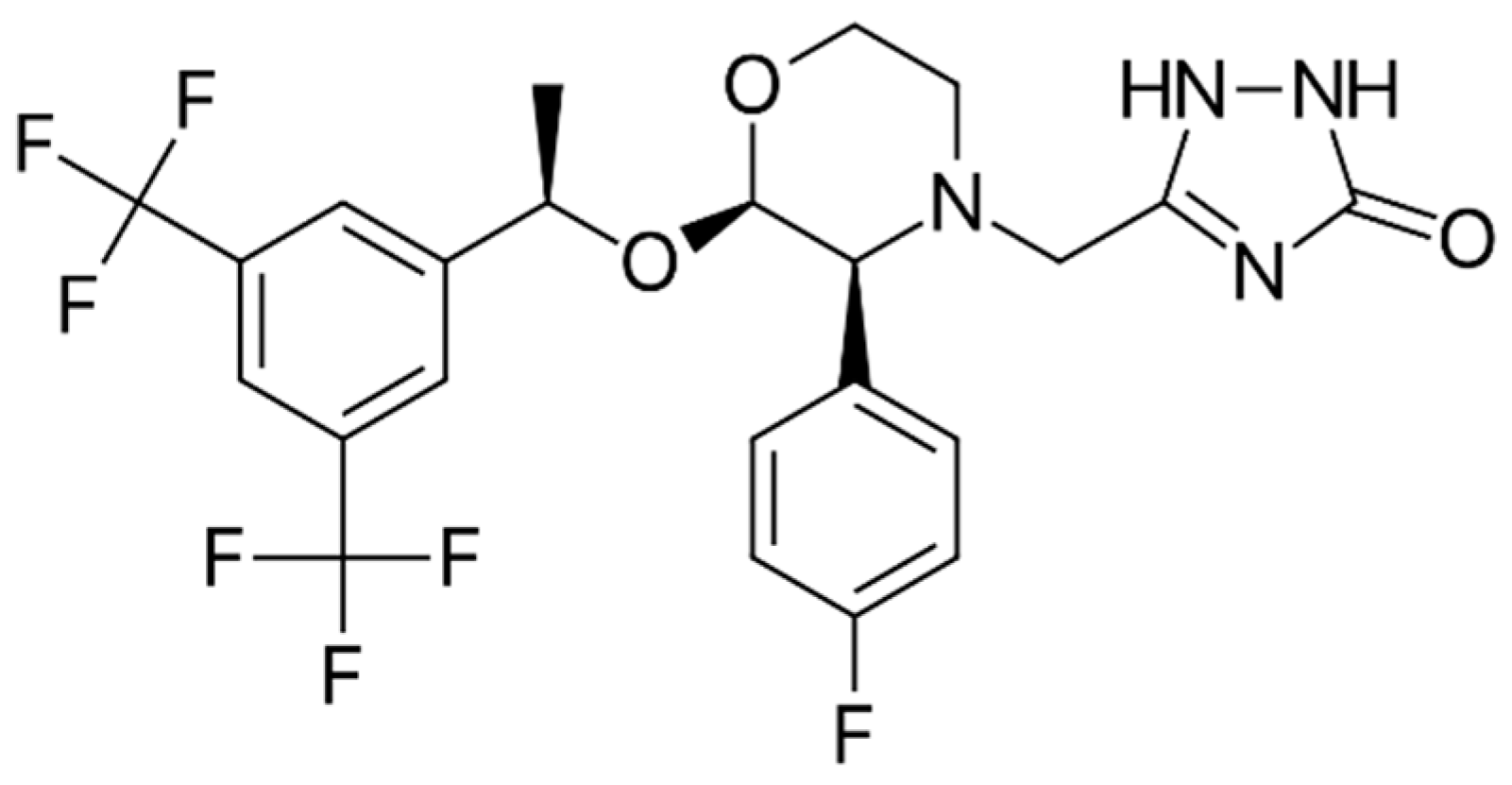
Evaluation of Dissolution Enhancement of Aprepitant Drug in Ternary Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions with Soluplus® and Poloxamer 188 Prepared by Melt Mixing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SD via Melt Mixing
2.3. Characterization of SD
2.3.1. Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.2. Hot Stage Polarized Light Microscopy (HSM)
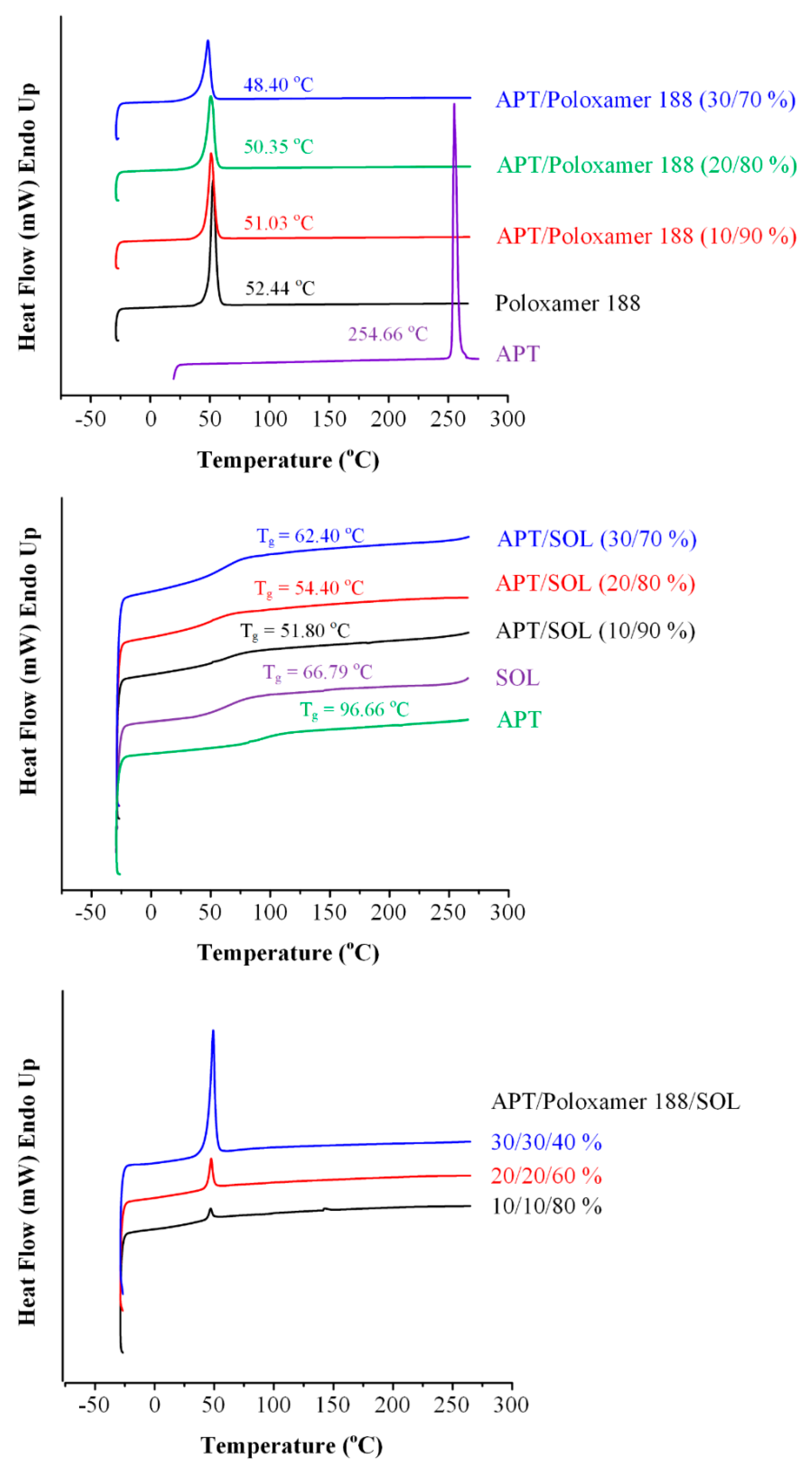
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
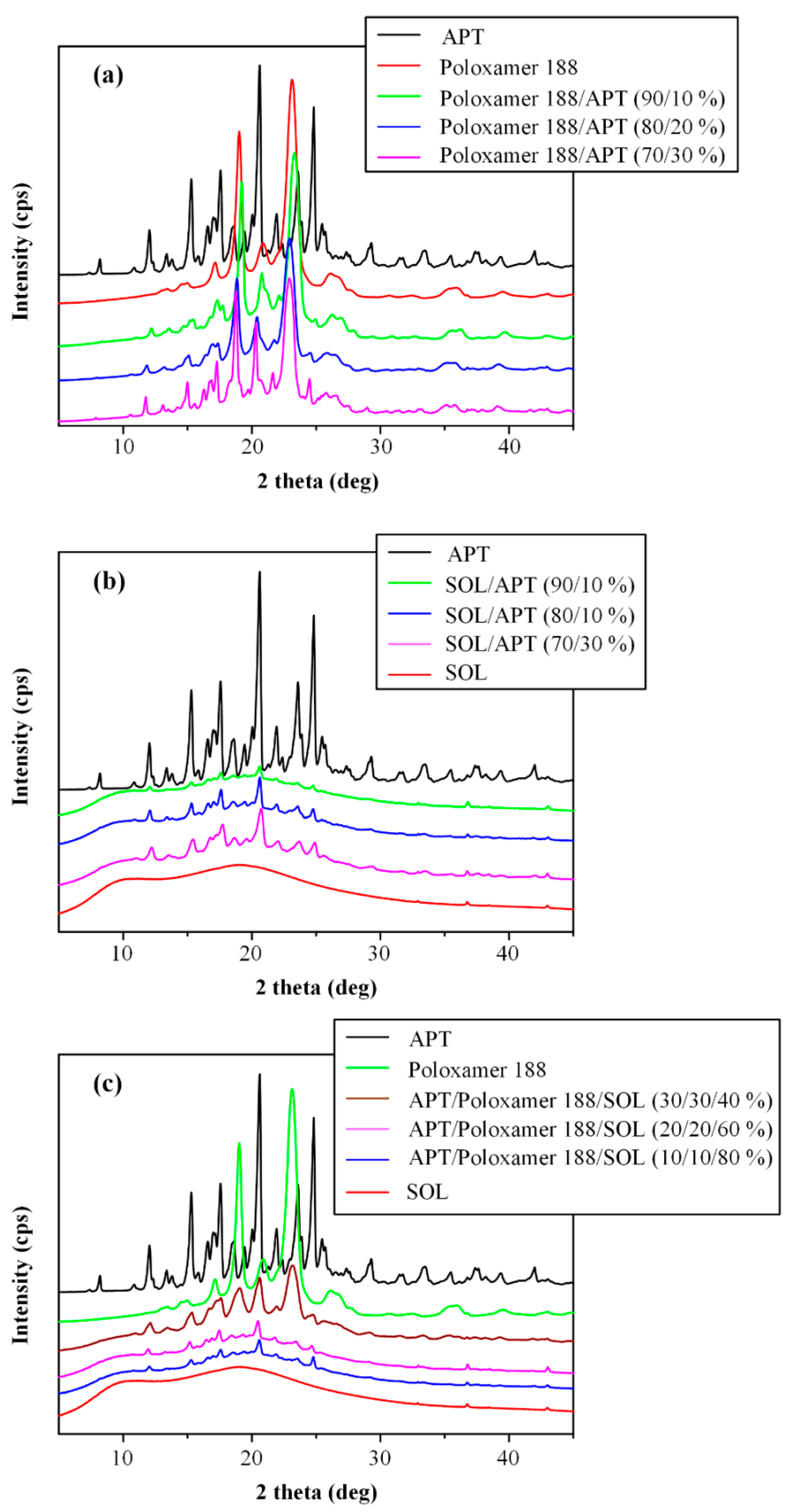
2.3.4. Wide Angle X-ray Diffractometry (WAXD)
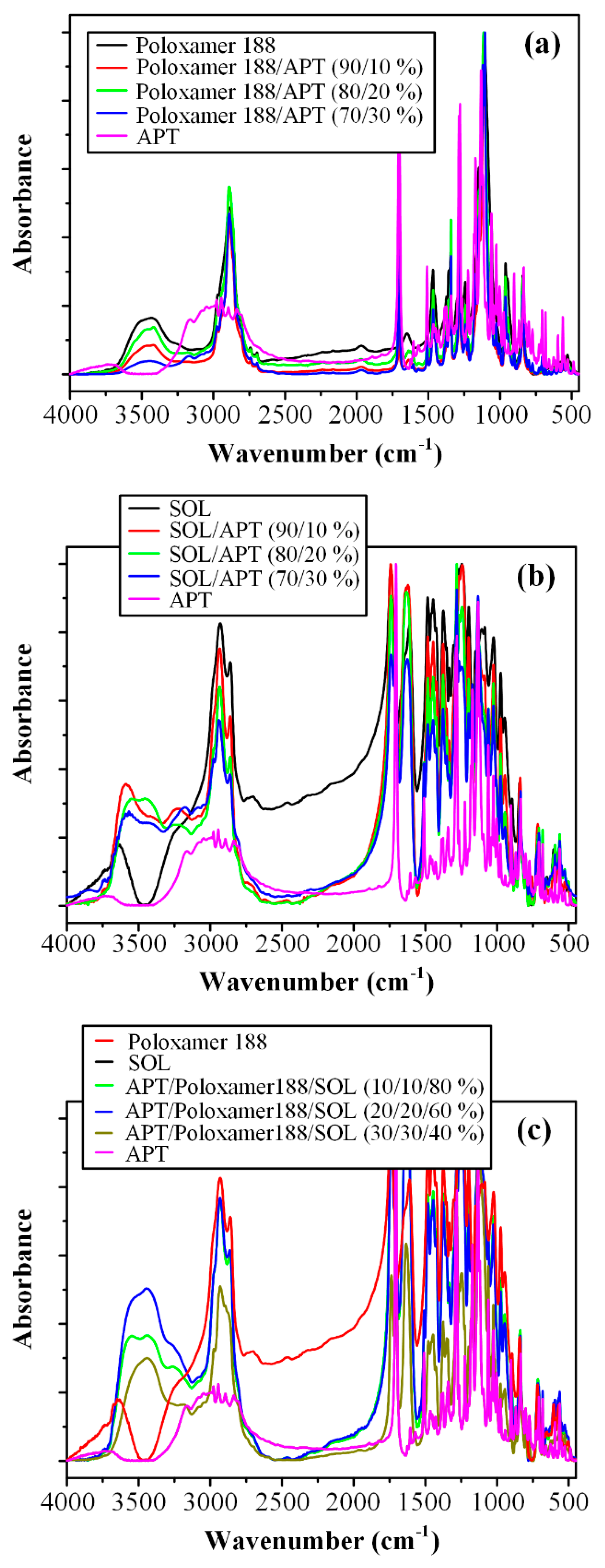
2.3.5. Fourier Transformation-Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
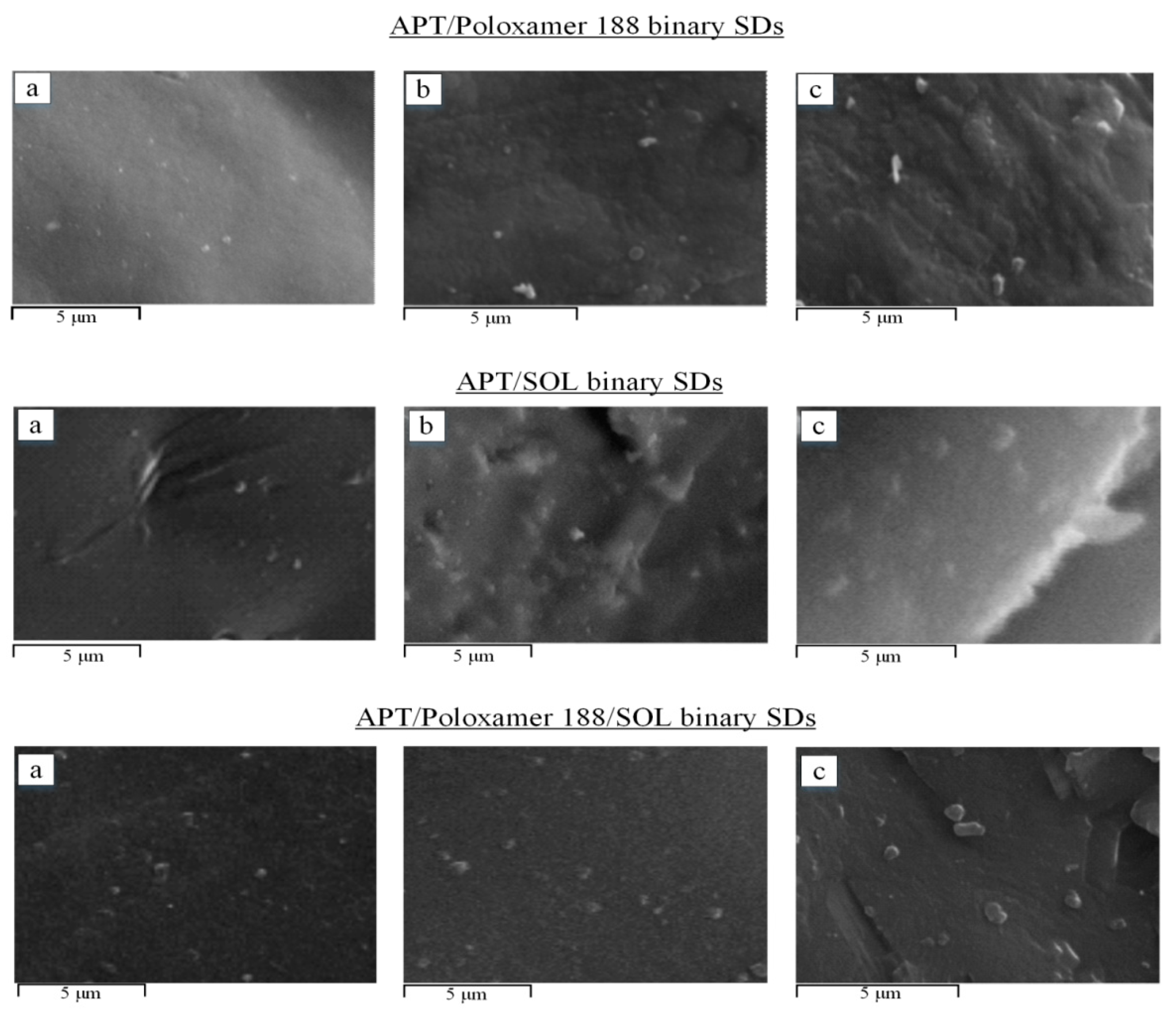
2.3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.7. Dissolution Studies
2.3.8. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
3. Results and Discussion
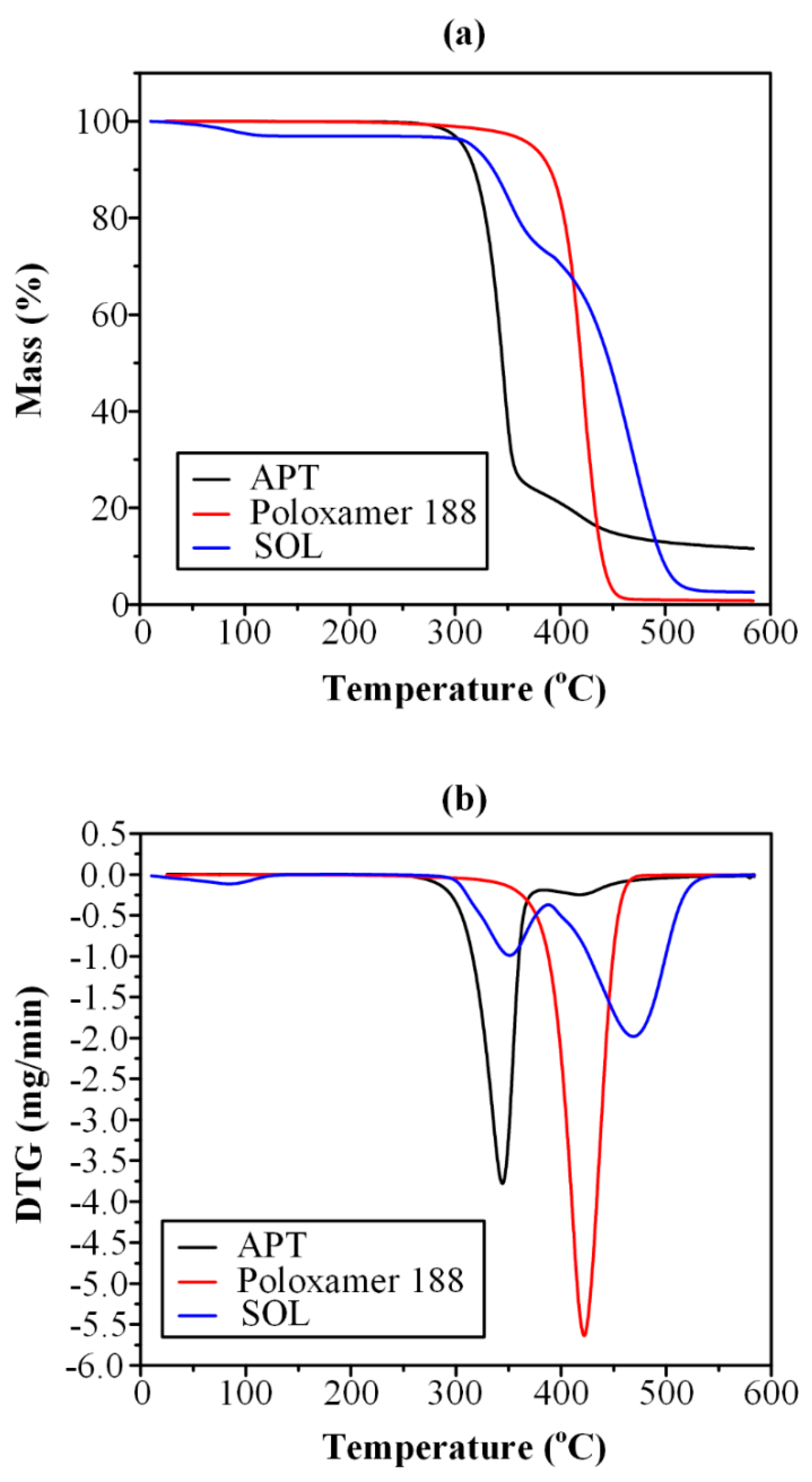
3.1. Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
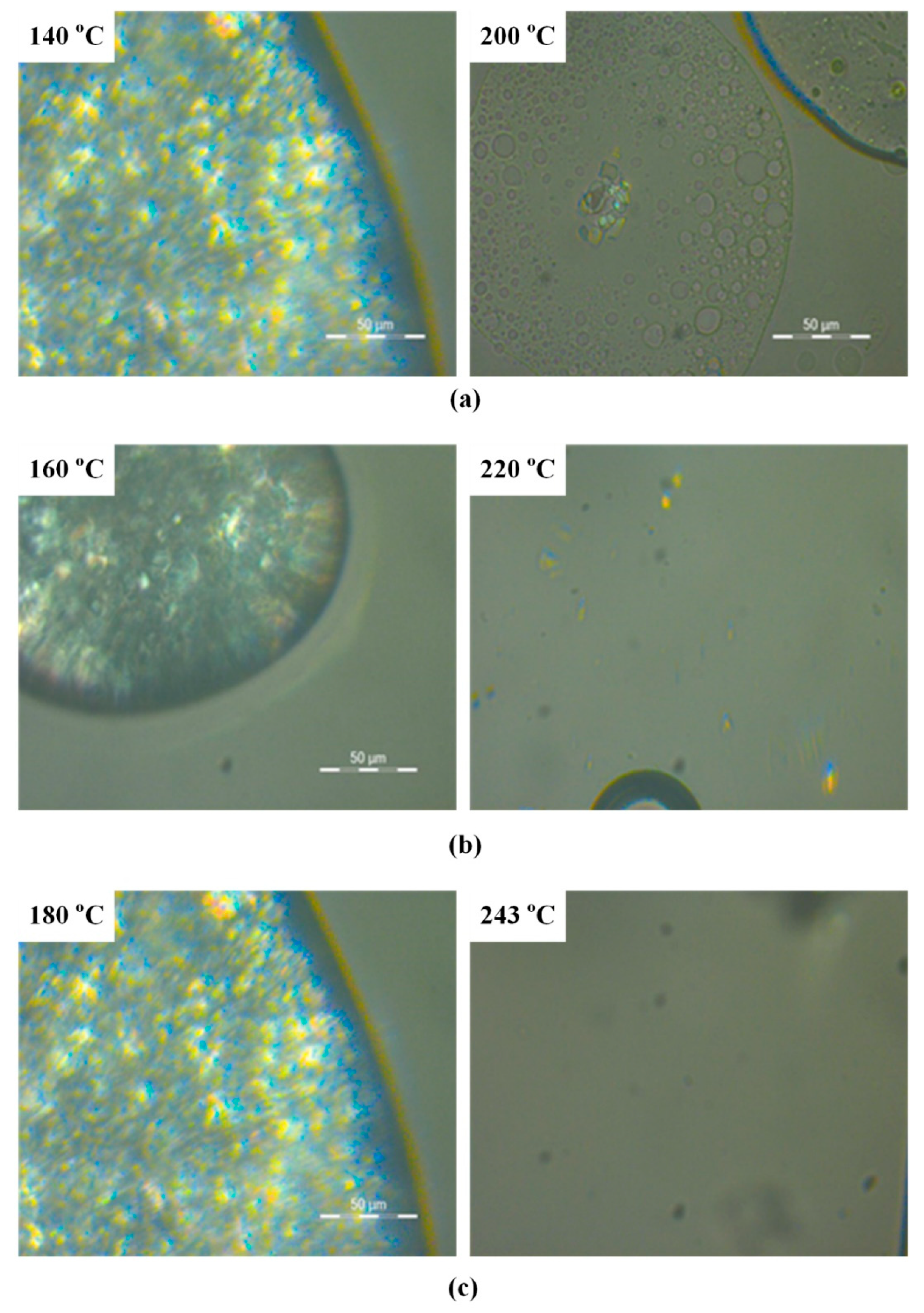
3.2. Hot Stage Polarized Light Microscopy (HSM)
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3.4. Fourier Transformation-Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Analysis
3.5. Wide Angle X-ray Diffractometry (WAXD) Analysis
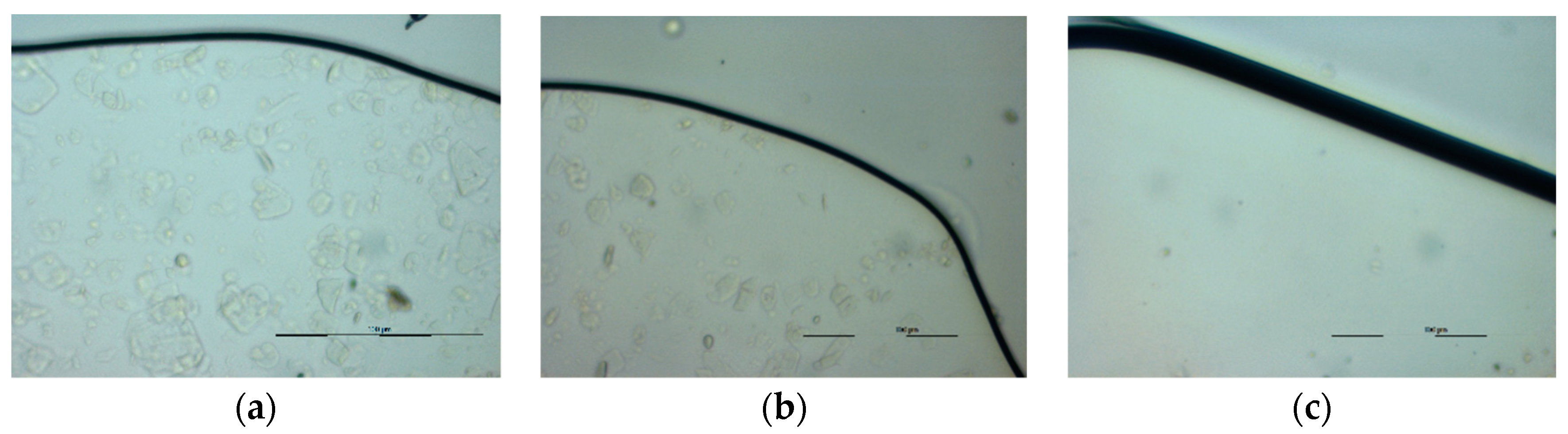
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
3.7. Dissolution Studies Results
4. Release Mechanism Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poli-Bigelli, S.; Rodrigues-Pereira, J.; Carides, A.D.; Julie Ma, G.; Eldridge, K.; Hipple, A.; Evans, J.K.; Horgan, K.J.; Lawson, F. Addition of the neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist aprepitant to standard antiemetic therapy improves control of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in Latin America. Cancer 2003, 97, 3090–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Loper, A.; Landis, E.; Hettrick, L.; Novak, L.; Lynn, K.; Chen, C.; Thompson, K.; Higgins, R.; Batra, U.; et al. The role of biopharmaceutics in the development of a clinical nanoparticle formulation of MK-0869: A Beagle dog model predicts improved bioavailability and diminished food effect on absorption in human. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 285, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aapro, M.; Carides, A.; Rapoport, B.L.; Schmoll, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Warr, D. Aprepitant and fosaprepitant: A 10-year review of efficacy and safety. Oncoloqist 2015, 20, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, V.T.; Yeo, W. Antiemetic therapy options for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press) 2011, 3, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cocquyt, V.; Van Belle, S.; Reinhardt, R.R.; Decramer, M.L.; O’Brien, M.; Schellens, J.H.; Borms, M.; Verbeke, L.; Van Aelst, F.; De Smet, M.; et al. Comparison of L-758,298, a prodrug for the selective neurokinin-1 antagonist, L-754,030, with ondansetron for the prevention of cisplatin-induced emesis. Eur. J. Cancer (Oxf. Engl.: 1990) 2001, 37, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, S.; Sharma, R.; Singh, K.; Rana, V. Aprepitant loaded solid preconcentrated microemulsion for enhanced bioavailability: A comparison with micronized Aprepitant. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.: Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 78, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Wu, Y. Understanding the effect of API properties on bioavailability through absorption modeling. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olver, I.; Shelukar, S.; Thompson, K.C. Nanomedicines in the treatment of emesis during chemotherapy: Focus on aprepitant. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, R.; Sharmab, S. Formulation optimization and evaluation of fast dissolving film of aprepitant by using design of experiment. Bull. Faculty Pharmacy, Cairo University 2018, 56, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.I.; Wang, R.W.; Newton, D.J.; Bakhtiar, R.; Lu, P.; Chiu, S.H.; Evans, D.C.; Huskey, S.E. Cytochrome P450 3A4 is the major enzyme involved in the metabolism of the substance P receptor antagonist aprepitant. Drug Metab. Dispos.: Biol. Fate Chem. 2004, 32, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Worku, Z.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Oral formulation strategies to improve solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1361–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Mitra, A. Crystalline nanosuspensions as potential toxicology and clinical oral formulations for BCS II/IV compounds. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shono, Y.; Jantratid, E.; Kesisoglou, F.; Reppas, C.; Dressman, J.B. Forecasting in vivo oral absorption and food effect of micronized and nanosized aprepitant formulations in humans. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. E.V 2010, 76, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, P.; Li, M.; Chen, G. Preparation and pharmacokinetic study of aprepitant-sulfobutyl ether-beta-cyclodextrin complex. Aaps Pharmscitech 2014, 15, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Angi, R.; Solymosi, T.; Otvos, Z.; Ordasi, B.; Glavinas, H.; Filipcsei, G.; Heltovics, G.; Darvas, F. Novel continuous flow technology for the development of a nanostructured aprepitant formulation with improved pharmacokinetic properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.: Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. E.V 2014, 86, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmpalexis, P.; Grypioti, A.; Eleftheriadis, G.K.; Fatouros, D.G. Development of a New Aprepitant Liquisolid Formulation with the Aid of Artificial Neural Networks and Genetic Programming. Aaps Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhara Rao, B.; Vidyadhara, S.; Sasidhar, R.; Chowdary, Y.A. Dissolution enhancement of poorly soluble drug aprepitant by hot melt extrusion method using hydrophilic polymer: A solid dispersion technique. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zou, M.; Piao, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, B.; Gao, Y.; Ma, N.; Cheng, G. Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Study of Aprepitant Solid Dispersions with Soluplus(R). Molecules 2015, 20, 11345–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumetcha, S.S.; Gutta, L.N.; Dhanala, H.; Yamili, S.; Challa, S.; Rudraraju, S.; Rudraraju, S.; Rudraraju, V. Hot melt extruded Aprepitant-Soluplus solid dispersion: Preformulation considerations, stability and in vitro study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puncochova, K.; Ewing, A.V.; Gajdosova, M.; Sarvasova, N.; Kazarian, S.G.; Beranek, J.; Stepanek, F. Identifying the mechanisms of drug release from amorphous solid dispersions using MRI and ATR-FTIR spectroscopic imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 483, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puncochova, K.; Vukosavljevic, B.; Hanus, J.; Beranek, J.; Windbergs, M.; Stepanek, F. Non-invasive insight into the release mechanisms of a poorly soluble drug from amorphous solid dispersions by confocal Raman microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.: Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. E.V 2016, 101, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikiaris, D.N. Solid dispersions, part I: Recent evolutions and future opportunities in manufacturing methods for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1501–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikiaris, D.N. Solid dispersions, part II: New strategies in manufacturing methods for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1663–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, C.; Nanaki, S.; Giliopoulos, D.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Kostoglou, M.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Bikiaris, D. Nanostructured Composites of Sodium Montmorillonite Clay and PEO Used in Dissolution Improvement of Aprepitant Drug by Melt Mixing. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, J.; Edinger, M.; Botker, J.; Baldursdottir, S.; Rantanen, J. Oscillatory Shear Rheology in Examining the Drug-Polymer Interactions Relevant in Hot Melt Extrusion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edueng, K.; Mahlin, D.; Bergstrom, C.A.S. The Need for Restructuring the Disordered Science of Amorphous Drug Formulations. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1754–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Morgan, D.J.; Mendham, A.P.; Pang, J.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. Drug-polymer intermolecular interactions in hot-melt extruded solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-Melt Extrusion: From Theory to Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation. Aaps Pharmscitech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.V.; Patil, H.; Repka, M.A. Contribution of hot-melt extrusion technology to advance drug delivery in the 21st century. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Boateng, J.S.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. A Review of Hot-Melt Extrusion: Process Technology to Pharmaceutical Products. Isrn Pharm. 2012, 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Nair, A.; Scoutaris, N.; Bradley, M.S.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. One-step continuous extrusion process for the manufacturing of solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Rana, M.M.; Boateng, J.S.; Mitchell, J.C.; Douroumis, D. Dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble APIs processed by hot-melt extrusion using hydrophilic polymers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.; Karavas, E.; Politis, S.; Docoslis, A.; Park, Y.; Stergiou, A.; Georgarakis, E. Effect of physical state and particle size distribution on dissolution enhancement of nimodipine/PEG solid dispersions prepared by melt mixing and solvent evaporation. AAPS J. 2006, 8, E623–E631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithani, K.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Slipper, I.J.; Mostafa, S.; Miolane, C.; Cuppok, Y.; Marchaud, D.; Douroumis, D. Sustained release solid lipid matrices processed by hot-melt extrusion (HME). Colloids Surf. Bbiointerfaces 2013, 110, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengale, S.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Lobmann, K. Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, J.M.; McGinity, J.W.; Williams, R.O., III. Enhancing bioavailability through thermal processing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, D. Investigating the molecular structures of solid dispersions by the simulated annealing method. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 554, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, J.; Krier, F.; Evrard, B. A review of pharmaceutical extrusion: Critical process parameters and scaling-up. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pang, H.; Guo, Z.; Lin, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, G.; Lu, M.; Wu, C. Interactions between drugs and polymers influencing hot melt extrusion. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadarin, A.B.; Potter, C.B.; Davis, M.T.; Iqbal, J.; Korde, S.; Pagire, S.; Paradkar, A.; Walker, G. Development of stability-enhanced ternary solid dispersions via combinations of HPMCP and Soluplus((R)) processed by hot melt extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.T.; Potter, C.B.; Mohammadpour, M.; Albadarin, A.B.; Walker, G.M. Design of spray dried ternary solid dispersions comprising itraconazole, soluplus and HPMCP: Effect of constituent compositions. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, S.; de Armas, H.N.; Roberts, C.J.; Van den Mooter, G. Characterization of ternary solid dispersions of itraconazole, PEG 6000, and HPMC 2910 E5. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Gala, U.; Chauhan, H. Classification of solid dispersions: Correlation to (i) stability and solubility (ii) preparation and characterization techniques. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H.; Atef, E. Amorphous stabilization and dissolution enhancement of amorphous ternary solid dispersions: Combination of polymers showing drug-polymer interaction for synergistic effects. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3511–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H.; Atef, E. Role of Molecular Interactions for Synergistic Precipitation Inhibition of Poorly Soluble Drug in Supersaturated Drug-Polymer-Polymer Ternary Solution. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, K.; Verreck, G.; Peeters, J.; Brewster, M.; Van Den Mooter, G. Increased physical stability and improved dissolution properties of itraconazole, a class II drug, by solid dispersions that combine fast- and slow-dissolving polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpalexis, P.; Koutsidis, I.; Karavas, E.; Louka, D.; Papadimitriou, S.A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Development of PVP/PEG mixtures as appropriate carriers for the preparation of drug solid dispersions by melt mixing technique and optimization of dissolution using artificial neural networks. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fousteris, E.; Tarantili, P.A.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D. Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)–poloxamer-188 solid dispersions prepared by hot melt extrusion. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 113, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw Oo, M.; Mandal, U.K.; Chatterjee, B. Polymeric behavior evaluation of PVP K30-poloxamer binary carrier for solid dispersed nisoldipine by experimental design. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, S.A.; Barmpalexis, P.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Optimizing the ability of PVP/PEG mixtures to be used as appropriate carriers for the preparation of drug solid dispersions by melt mixing technique using artificial neural networks: I. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Investigation into the Solid-State Properties and Dissolution Profile of Spray-Dried Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Rational Step toward the Design and Development of a Multicomponent Amorphous System. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3796–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Liang, Y.; Pan, W.; Gou, J.; Yin, T.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Tang, X. Effect of supersaturation on the oral bioavailability of paclitaxel/polymer amorphous solid dispersion. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bao, J.; Shi, X.; Sheng, X.; Su, W. Preparation, Optimization, and in vitro—In vivo Evaluation of Febuxostat Ternary Solid Dispersion. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, D.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Stergiou, A.; Pavlidou, E.; Karavas, E.; Kanaze, F.; Georgarakis, M. Physicochemical studies on solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs: Evaluation of capabilities and limitations of thermal analysis techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 439, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaze, F.I.; Kokkalou, E.; Niopas, I.; Georgarakis, M.; Stergiou, A.; Bikiaris, D. Dissolution enhancement of flavonoids by solid dispersion in PVP and PEG matrixes: A comparative study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, E.; Bikiaris, D.; Thomas, T.; Katsos, V.; Xenakis, A. Hydrophilic Matrices as Carriers in Felodipine Solid Dispersion Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 181, pp. 149–152, Progress in Colloid and Polymer Science. [Google Scholar]
- Docoslis, A.; Huszarik, K.L.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.; Stergiou, D.; Georgarakis, E. Characterization of the distribution, polymorphism, and stability of nimodipine in its solid dispersions in polyethylene glycol by micro-Raman spectroscopy and powder X-ray diffraction. AAPS J. 2007, 9, E361–E370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, M.; Docoslis, A.; Bikiaris, D. Combining SEM, TEM, and micro-Raman techniques to differentiate between the amorphous molecular level dispersions and nanodispersions of a poorly water-soluble drug within a polymer matrix. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Docoslis, A.; Georgarakis, M.; Bikiaris, D. The effect of physical state on the drug dissolution rate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 95, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Haruna, Y.; Otsuk, M. Dissolution process analysis using model-free Noyes–Whitney integral equation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Vigouroux, F.; Reed, W.F. Dissolution Kinetics of Polymer Powders. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
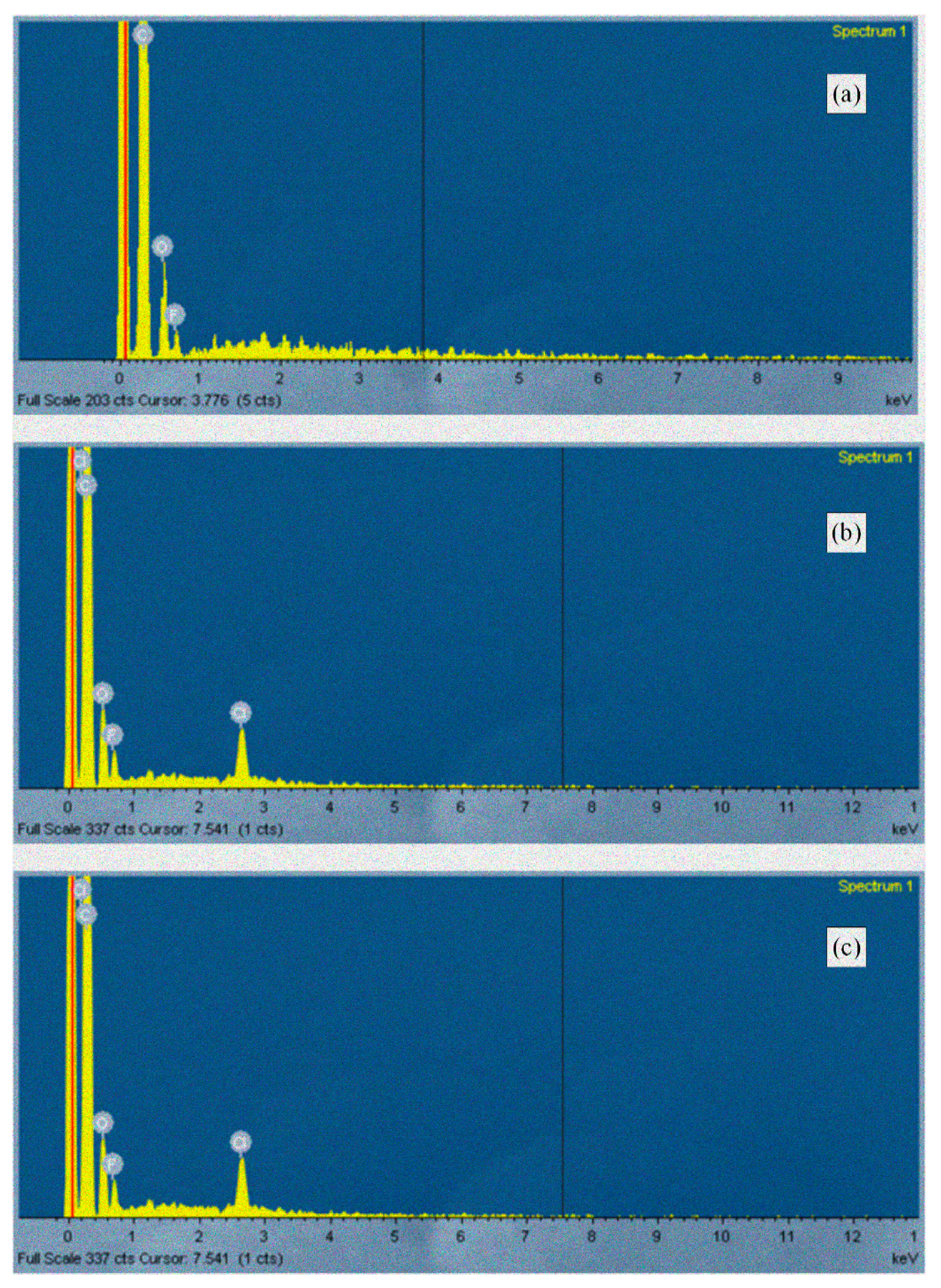
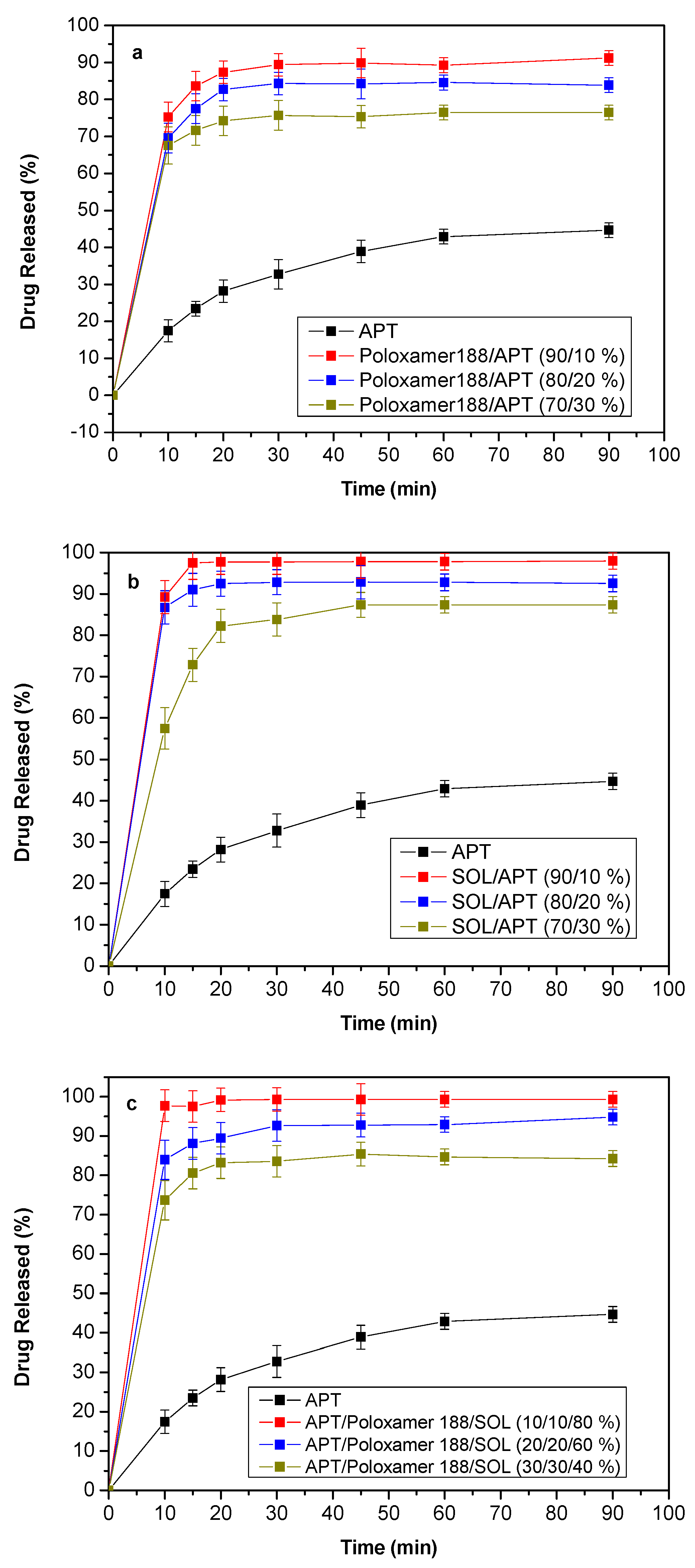
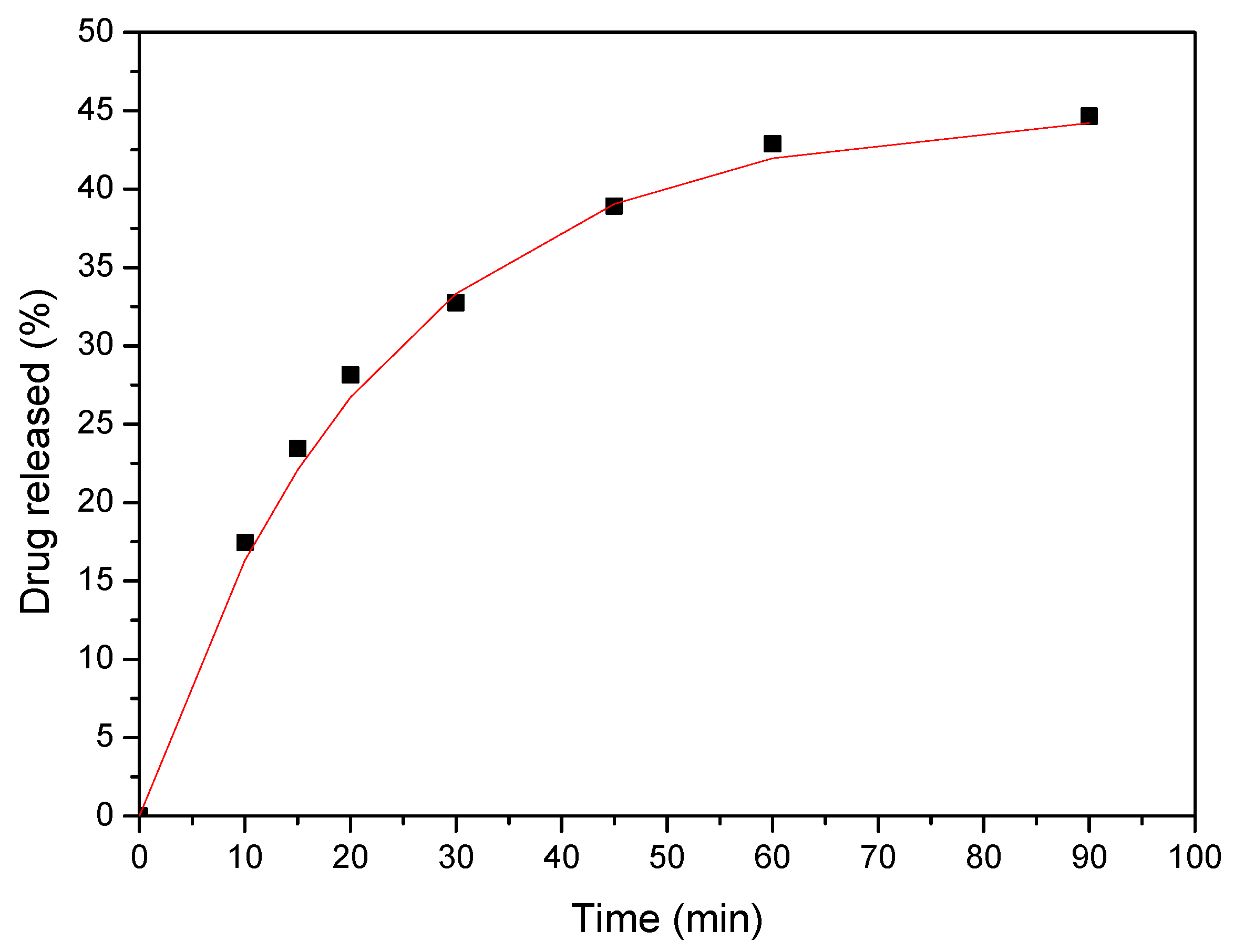
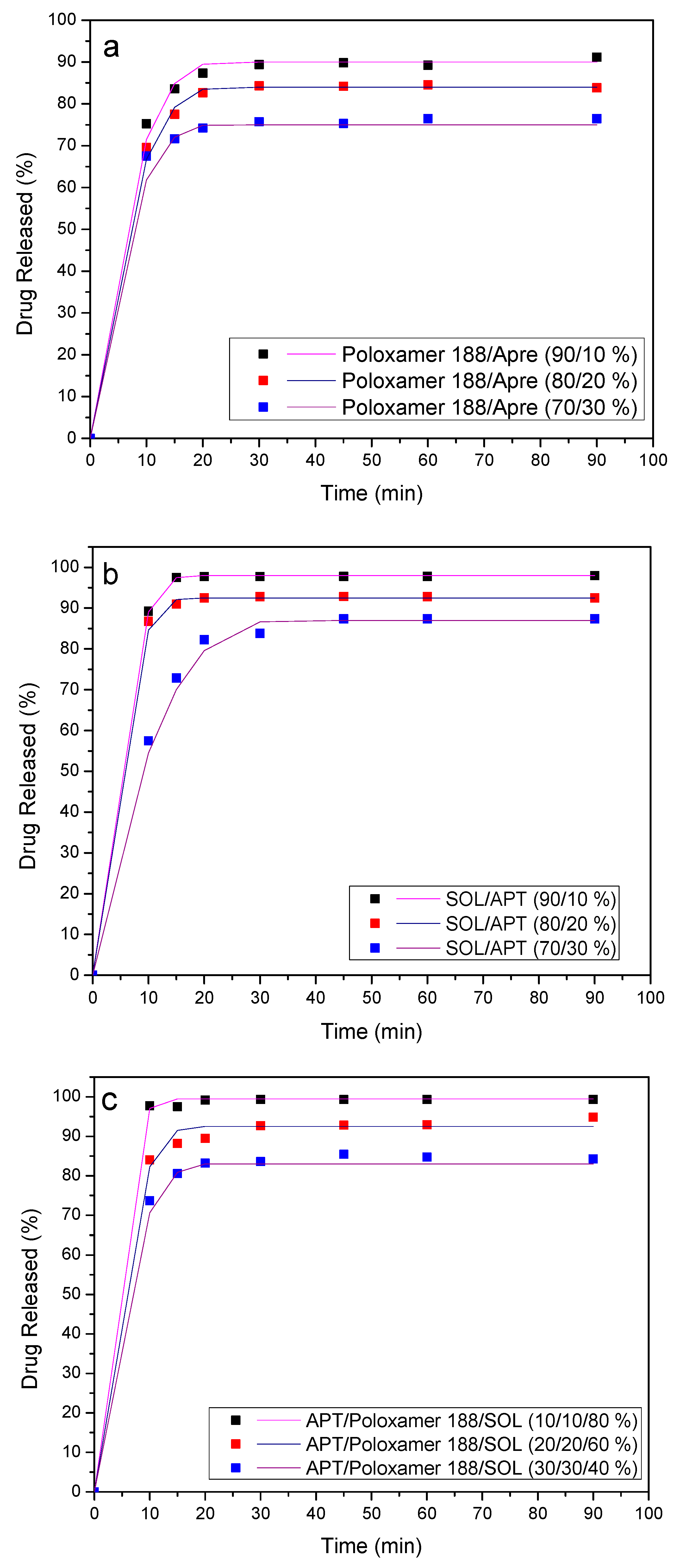
| Sample | Temperature (°C) | Mixing Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Binary SDs | ||
| Poloxamer/APT (90/10 w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| Poloxamer/APT (80/20 w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| Poloxamer/APT (70/30 w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| SOL/APT (90/10 w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| SOL/APT (80/20 w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| SOL/APT (70/30 w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| Ternary SDs | ||
| SOL/Poloxamer/APT (80/10/10 w/w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| SOL/Poloxamer/APT (60/20/20 w/w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
| SOL/Poloxamer/APT (40/30/30 w/w/w) | 160.0 | 15.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nanaki, S.; Eleftheriou, R.M.; Barmpalexis, P.; Kostoglou, M.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D. Evaluation of Dissolution Enhancement of Aprepitant Drug in Ternary Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions with Soluplus® and Poloxamer 188 Prepared by Melt Mixing. Sci 2019, 1, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci1020048
Nanaki S, Eleftheriou RM, Barmpalexis P, Kostoglou M, Karavas E, Bikiaris D. Evaluation of Dissolution Enhancement of Aprepitant Drug in Ternary Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions with Soluplus® and Poloxamer 188 Prepared by Melt Mixing. Sci. 2019; 1(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci1020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleNanaki, Stavroula, Rodanthi Maria Eleftheriou, Panagiotis Barmpalexis, Margaritis Kostoglou, Evangelos Karavas, and Dimitrios Bikiaris. 2019. "Evaluation of Dissolution Enhancement of Aprepitant Drug in Ternary Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions with Soluplus® and Poloxamer 188 Prepared by Melt Mixing" Sci 1, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci1020048
APA StyleNanaki, S., Eleftheriou, R. M., Barmpalexis, P., Kostoglou, M., Karavas, E., & Bikiaris, D. (2019). Evaluation of Dissolution Enhancement of Aprepitant Drug in Ternary Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions with Soluplus® and Poloxamer 188 Prepared by Melt Mixing. Sci, 1(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci1020048









