Abstract
Most damage-assessment strategies for dynamic systems only distinguish between undamaged and damaged conditions without recognizing the level or type of damage or considering unseen conditions. This paper proposes a novel framework for structural health monitoring (SHM) that combines supervised and unsupervised learning techniques to assess damage using a system’s structural response (e.g., the acceleration response of big infrastructures). The objective is to enhance the benefits of a supervised learning framework while addressing the challenges of working in an SHM context. The proposed framework uses a Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)/Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA) strategy that enables learning the distributions of known classes and the performance of probabilistic estimations on new incoming data. The methodology is developed and proposed in two versions. The first version is used in the context of controlled, conditioned monitoring or for post-damage assessment, while the second analyzes the single observational data. Both strategies are built in an automatic framework able to classify known conditions and recognize unseen damage classes, which are then used to update the classification algorithm. The proposed framework’s effectiveness is first tested considering the acceleration response of a numerically simulated 12-degree-of-freedom system. Then, the methodology’s practicality is validated further by adopting the experimental monitoring data of the benchmark study case of the Z24 bridge.
1. Introduction
Maintenance strategies have acquired increasing relevance in modern engineering. They play a crucial role in ensuring structural integrity, safety, and economic benefits for monitored assets while minimizing downtime, increasing productivity and extending service life. In particular, developing efficient predictive maintenance and monitoring procedures for damage detection is relevant in numerous fields, such as mechanical, civil, or aerospace engineering. In this context, structural health monitoring (SHM) is the discipline dedicated to designing and implementing damage identification strategies. It involves continuous or periodic monitoring to detect early signs of potential faults or deviations from normal operating conditions.
There are multiple ways to define the term “damage” according to the specific context and application. However, for the purpose of this study, which has a structural focus, “damage” is defined as any changes to the material and/or geometric properties of a system that permanently affect its performance. This includes, for example, intentional or unintentional changes to the boundary conditions and system connectivity, reductions in the stiffness of single or multiple system elements, or the loss of strength in supporting components [1]. The concept of damage involves a comparison between the reference, healthy condition of a system and an unknown, potentially damaged one. Such a comparison enables the identification of changes or deviations in a system’s properties and performance. Therefore, monitoring a system’s condition over time is crucial to detect any signs of this deviation and take appropriate actions to prevent further deterioration or catastrophic consequences.
Among the various strategies in SHM [2], the vibration-based approaches are among the most appealing [3,4]. They concentrate on gathering data directly from the dynamic response of the investigated system responses (e.g., displacement or acceleration), often without dealing with the construction of a model of the system or having prior knowledge. By focusing on the global response of the system, these methods have proven to be particularly effective for systems that have complex geometries or are made of materials that are not homogeneous. Given the collection of the system’s response via the use of sensors directly installed onto the structure, it is often possible to conduct short- or long-term monitoring campaigns, enabling real-time monitoring and online evaluations of any potential damages.
Such continuous monitoring of a system can be performed using either model-based or signal-based approaches. The model-based approach involves creating a physical or mathematical model that represents the dynamic behavior of the real system [5,6]. Real-time data are then used to update the parameters of the model so that its response accurately reproduces the measured one. The damage can be detected through a comparison between the data simulated via modeling and the real-time experimental data of the original system. However, while model-based strategies work well with simple systems, they become less reliable when dealing with articulated ones characterized by complex dynamics which are challenging to model [7].
On the other hand, recently developed machine learning tools have enhanced the opportunity to bypass the creation of complex and sophisticated models and to extract damage-sensitive parameters directly from the monitored dynamic response [8,9]. Such parameters are generally referred to as damage-sensitive features (DSFs) [10]. In this context, damage detection can be considered a problem of statistical pattern recognition, where the goal is to identify and characterize different behavioral and dynamic patterns in the DSFs [11], some of which are potentially associated with damage occurrence [12].
Selecting and estimating a reliable DSF is essential for the implementation of a successful statistical pattern recognition framework. The selected feature ought to be strongly correlated with the structural properties of the system, to detect structural changes due to the effect of damage, while being insensitive to changes due to noise or variations in operational and environmental conditions [13,14,15,16]. Modal parameters (e.g., natural frequencies or mode shapes [17]) and Auto Regressive model coefficients [18,19] are examples of popular and common DSFs often employed for structural health monitoring applications. However, in the last decade, new features, commonly used in a different domain, have been introduced and successfully implemented in damage detection problems: cepstral coefficients (CCs). These coefficients were first presented in 1962 by Bogert et al. in an attempt to coin a method able to identify the presence of an echo in a sound signal [20]. Oppenheim [21] addressed the discrete-time formulation of the cepstrum and its complex counterpart, the complex cepstrum. Despite such features being commonly used in acoustics [22,23], they have been successfully implemented in different forms and fields. They have been particularly successful in mechanical systems as features for detecting damage in bearing and gearboxes [24,25,26]. Several studies address them as features for monitoring the health conditions of civil and infrastructural systems [16,27,28,29,30], demonstrating how these features might represent valid alternatives to the most common approaches. In 2021, Morgantini et al. [31] investigated their connection to the modal characteristics of the structure and how they can be successfully used in a damage assessment strategy. The use of power cepstral coefficients as DSFs was further refined by Li et al. [32] in 2023. Li proposed a New Generalized Auto-Encoder integrated with a statistical-pattern-recognition-based approach that uses the cepstral coefficients extracted from structural acceleration responses as DSFs. It has been proven that the main advantages of the cepstral features consist of their natural dimensionality reduction and their simple and direct extraction process, from which follows a lower required user expertise and a lower computational burden.
This study addresses a supervised damage detection and classification framework using cepstral features as damage-sensitive features. Supervised learning is a machine learning paradigm in which labeled data are used to train classification or regression algorithms [33,34,35]. In the context of structural health monitoring and damage detection, supervised learning methods face limitations because they require information on both normal and damaged conditions during the learning process. For this reason, unsupervised approaches are usually preferred for these kinds of applications [36,37,38,39,40]. However, except for dynamic systems in a controlled environment, it is often impossible to have sufficient observations from the system in all the possible damage scenarios that could occur. The model would likely be trained on insufficient information and misclassify unknown damaged conditions. In particular, these data are rarely available for civil engineering structures for which it is neither reasonable nor cost-effective to intentionally damage them to provide training data [41].
The objective of this paper is to enhance the benefits of a supervised learning framework and address the challenges that arise while implementing these strategies in a structural health monitoring (SHM) context. The proposed approach is a new and innovative method that combines supervised tools within an unsupervised process. This method can automatically identify and classify unknown damage conditions and use them to strengthen the existing knowledge about the health condition of the system. The proposed framework is based on the use of a Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) [42]/Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA) [43] strategy that allows one to learn the distributions of known classes and to perform probabilistic estimations on new incoming acceleration data. The combination of dimensionality reduction via LDA and the probabilistic learning framework of PLDA applied on cepstral features has shown promising outcomes for speaker recognition applications and damage detection in civil systems [29,44,45]. The methodology is further developed here in an unsupervised hybrid approach and proposed in two versions. The first can be used in the context of controlled condition monitoring or for post-damage assessment in the case of well-known classes. The second is built in an automatic framework, where unknown damage classes, different from the healthy reference state, are recognized, classified, and used to update the classification algorithm via PLDA.
The sections below describe the proposed framework for damage detection and classification and its application. Section 2 presents the structural features adopted for this work and the theoretical background behind LDA and PLDA techniques, followed by the detailed functioning of the proposed algorithm. In Section 3, a numeric case study is presented to affirm the algorithm’s effectiveness, while Section 4 shows real-world application results using the Z24 bridge experimental dataset.
2. Methodology
The proposed methodology follows a statistical pattern recognition framework to detect and classify damage. It does so by comparing the cepstral features extracted from dynamic responses of the system in an unknown state against those extracted from the system in a healthy condition. Firstly, the methodology focuses on the extraction of the CCs from the acceleration responses of the monitored system, and then it creates a classification model based on the statistical distribution of the CCs representative of the healthy condition (training phase). Once the model is created, new incoming CCs, extracted from the system in an unknown state, are compared to the training ones (testing phase) and if the distributions do not match, the incoming data are labeled as damaged.
2.1. Feature Extraction
The proposed methodology employs cepstral coefficients as damage-sensitive features within an LDA/PLDA strategy. While LDA is adopted to project data into a coordinate system that enhances differences between different conditions, PLDA works as a classifier, evaluating the likelihood that incoming data belong to the seen classes. The choice of this strategy is rooted in the easiness of the implementation of these techniques and the fact that they are well known and used in the literature. Although they are supervised methods, the proposed algorithm uses these techniques in an overall unsupervised procedure, aiming to present not only a strategy to perform a binary differentiation of damaged/undamaged but also to classify different and unknown damage classes.
2.1.1. Cepstral Coefficients
Cepstral features are characterized by an easy, user-friendly, and almost parameter-less extraction process. They are obtained directly from the system’s response simply by taking the inverse discrete Fourier transform of the logarithm of the squared magnitude of the discrete Fourier transform of the acceleration time history, , (Equation (1)):
where and are the discrete Fourier transform and the inverse discrete Fourier transform, respectively. The simplicity of the extraction process grants optimal computational efficiency, suitable for real-time monitoring or large-scale applications, as well as requiring lower user expertise, as the decision-making is limited to the number of coefficients to extract. These reasons make cepstral coefficients appealing alternatives to the more commonly used DSFs. However, a drawback is that when using such features, the intuitive physical relationship between these coefficients and the system’s structural properties is less apparent, making interpreting the coefficients less intuitive.
From the analytical formulation, for which the reader is referred to [31], it is possible to better understand the connection to the structural properties as well as the input excitation and localization of the sensor. In particular, thanks to the presence of the logarithm in Equation (1), the coefficients are described as a sum of terms that separate the different contributions.
Figure 1 outlines in five essential steps the extraction process of the CCs from an input sampled signal (acceleration, for example). Each signal first undergoes a phase of framing, where the signal is divided into equal-length frames, followed by a windowing step, where a Hamming window is applied to each frame to reduce riddle effects at the frame’s onset and offset. From such windows it is then possible to extract the cepstral coefficients simply by calculating the log-power spectrum and, subsequently, applying the inverse discrete Fourier transform. The output of this process is a set of correlated coefficients characterizing the frequency content of the system in a concentrated time-dependent form. Because the first coefficient has proven to be particularly sensitive to the input force, it is a common rule to neglect it to highlight the contribution related to damage.
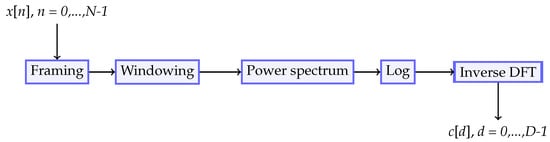
Figure 1.
Cepstral coefficient extraction procedure.
The extraction process highlights another important property of these coefficients. By analyzing small signal frames sequentially, these coefficients are capable of capturing variations caused by factors like input changes or evolving system properties. This makes them suitable for handling non-stationary signals with varying frequency components, making them an attractive option for describing systems characterized by complex dynamics or inputs.
2.1.2. Linear Discriminant Analysis
Linear Discriminant Analysis is a commonly used statistical tool utilized for dimensionality reduction and clustering. It was first formulated in 1936 by Fisher for two classes [46], and later on, in 1948 C.R Rao generalized it for multiple classes [47]. The objective of LDA is to find a hyperplane, known as latent space, that minimizes the inter-class variance while maximizing the variance between data of different classes.
Let be a training dataset containing N observations, where each observation is a column vector of length d. Each training sample belongs to one of the K classes of the training set. In the context of this work, the K classes represent different structural conditions, while d represents the dimension of the training vector, which corresponds to the number of CCs. Let be the set of all examples of class k, and let be the number of examples in class . The within-class and between-class scatter matrices, and , are computed, respectively, as
where and represent the mean vector of class k and the mean vector of the entire dataset, respectively. LDA aims to find the linear transformation that maximizes the between-class variance relative to the within-class variance. It can be shown that such a hyperplane can be found by solving the following eigenproblem:
The desired coordinate system is defined by the eigenvectors associated with the largest eigenvalues. The dimensionality of the latent space can be chosen by selecting the desired number g of components to keep. is the diagonal matrix that describes the change of coordinates from the original system to the latent space.
Therefore, LDA is trained on a set of known classes and finds the lowest dimensional space that enhances the separation between the classes. Once new incoming data arrive, they are projected into the subspace obtained from the training data. At this point, classification of the data can be performed. LDA could be also used for classification by computing the distance in the latent space between the data point and the centroids of the clusters and associating the new data to the nearest class. However, such a deterministic approach fails when the incoming data are part of a previously unseen class. In order to recognize unseen classes, a new, more flexible model is needed; one way to approach this problem is to use a probabilistic approach by adopting Probabilistic LDA.
2.1.3. Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis
PLDA is a probabilistic extended version of the previously presented LDA. It assumes that given data samples are generated from a normal distribution. The choice of such a distribution is rooted in the simplicity of its parameters and its computational implementation.
After the data are projected into the latent space, PLDA calculates the mean and standard deviation for each known class, creating a distribution for each class.
To better understand how PLDA works, let us consider an example in the data space and the corresponding class center . The PLDA model can be represented by the following expression:
where () represents the example of the class in the projected space, and () represents the class itself in the same latent space ( is the covariance matrix in the LDA-transformed latent space). Therefore, the example in the original data space is related to its latent representation via an invertible transformation .
Once the data have been projected into the latent space, PLDA computes the probability that the data come from one of the known classes by computing the probability that the data point belongs to the normal distribution that describes the class. Lastly, PLDA provides the log-likelihood ratio, also known as the PLDA score. To evaluate whether a point belongs to one of the known classes, the likelihood score is defined as the logarithm of R, the ratio between the likelihood of the point to be part of the same class and the likelihood to be of a different class.
Based on the score, it is possible to compare each new example with all the other examples; a PLDA score matrix is defined for each tested observation which is assigned to the class with the higher score.
2.2. Training
The first step of the proposed strategy involves the creation of a statistical model characterizing the system in its undamaged condition. The definition of such an initial model is obtained during the training phase, which consists of the following steps (Figure 2): (1) the extraction of the cepstral coefficients for all the observations in all the known classes characterizing the system; (2) a dimensionality reduction phase via the application of LDA; (3) the training of the PLDA classification model using the LDA projected components and the definition of the distribution of the PLDA scores for each class; (4) the identification of the thresholds characterizing the PLDA scores for the known classes.
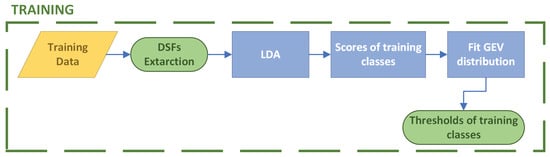
Figure 2.
Training phase flowchart.
Therefore, the first parameter to define is the number and type of classes used in the training phase to characterize the system’s health conditions. Since LDA finds the coordinate system in which classes are separated as much as possible (i.e., minimizing the within-class scatter while maximizing the variance between classes), it requires at least two classes to operate.
The strength of the proposed methodology lies in its capacity to autonomously recognize classes that may not have been encountered during the training phase. However, it does require a minimum of two known classes during training as a starting reference condition. This assumption necessitates a more detailed characterization of the system’s health condition beyond a single undamaged reference state. In the context of monitoring civil structural or mechanical systems, this is a reasonable hypothesis as the structure in its healthy condition can be further characterized according to different operational and environmental conditions that change the system’s dynamic behavior. Alternatively, it is possible to consider, in addition to the healthy state, low-intensity damaged conditions that could effectively characterize structures after a few years of operational use. In the present study, lower damage levels were considered additional classes for training the model, aiming to simulate real-life scenarios where structures encounter progressively severe damage, starting from minor damage. The identification and separation of this second class from the reference undamaged scenario can be achieved, when the information is not known beforehand, through a novelty detection unsupervised strategy that captures deviations in the chosen damage-sensitive features from this initial reference state. Once the second class is identified, it can be used in combination with the reference undamaged condition to initialize the proposed LDA/PLDA framework. At the same time, the number of components of the latent space is another crucial parameter for the simulation as it enhances class separation. The proposed algorithm autonomously evaluates the relevant components of LDA that effectively separate classes, following the procedure outlined in [43].
Once the training classes are chosen, 70% of each class’s data are picked randomly to be used to train the algorithm, while the remaining 30% are used later for testing. The cepstral coefficients are then extracted from the training data and employed to define the initial latent space using the LDA procedure. At this point, it is possible to calculate the initial thresholds of the training classes, which is the starting point for the testing phase. The computation of the thresholds is based on the analysis of the scores associated with the likelihood of training data belonging to their respective classes. By modeling these scores with the distribution that best fits the data, it is possible to define a limit value that enables the assessment of whether a new point belongs to a particular class.
To make things clear, let us consider two classes for the training phase. The algorithm computes the likelihood scores, hence, the probabilities, of the first class data to belong to the first class. In regards to this study, it was verified that the distribution that best modeled the scores is the generalized extreme value (GEV) distribution. Further details on this distribution can be found in [48]. The case studies treated in the following sections illustrate data distribution and the quality of fitting for each case. In this paper, the threshold of each class was set to the 95th percentile of the GEV distribution associated with the class. It is important to understand that the latent space and thresholds obtained from the training serve only as an initial model and will be updated as new data are classified, accommodating potential new classes.
After training the algorithm, the testing phase is conducted in two different ways. The first method involves analyzing data extracted from each new health condition as a set of available observations to be tested all together, to determine whether the group belongs to a known class. The second procedure simulates real-time monitoring, analyzing a single data point at a time to ascertain its class or identify if it belongs to an unseen class. Despite the apparent similarities between these two strategies, the algorithm exhibits notable differences depending on the method, and its performance can vary significantly. The subsequent sections delve into the description of these two testing types, highlighting their differences.
2.3. Testing Type 1
The first testing method is based on the idea that a group of data points, consisting of measurements collected with multiple sensors during a restricted period, is most likely representative of one health condition of the system. Therefore, this testing strategy assumes that the damage, if present, occurred before each data group was measured, and it works in block-examining a group of data points collected from a single scenario altogether.
For each class chosen for testing, the algorithm first extracts the cepstral coefficients and projects these features into the latent space defined during the training phase. This can be easily performed using the transformation matrix obtained during training.
Using PLDA, the likelihood scores for each data point are calculated, indicating the probability of each set of CCs belonging to each of the known classes.
Subsequently, the mean of the likelihood scores for the entire data group is calculated. This mean value provides an estimate of the probability of the entire group belonging to each of the known classes.
The algorithm then identifies the class the group is most likely to be a part of, comparing the mean likelihood score to the threshold of that class. If the likelihood score is below the threshold of one of the known classes, the observations are considered to belong to the identified class or, in the case of multiple classes meeting this requirement, to the most probable one. On the other hand, if the score exceeds all classes’ threshold values, the group of data is assumed to be representative of a previously unseen class. Consequently, a new class is created using these data, and the algorithm learns about this new class by updating the latent space and the thresholds acquired in the training phase, following the step described in Section 2.2. In this way, the subsequent groups of data are classified considering the newly created class. In order to better visualize the procedure, a graphical representation of the testing strategy is given in Figure 3.
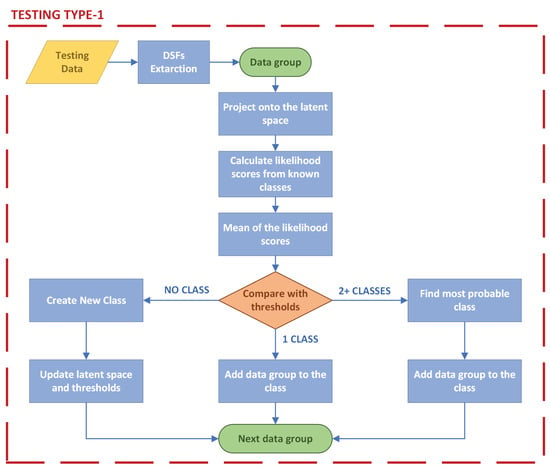
Figure 3.
Testing phase type 1 flowchart.
2.4. Testing Type 2
As an alternative to the previously described testing procedure, a second testing algorithm is proposed which analyzes each data point individually. The term “data point” refers to one set of cepstral coefficients obtained from a single observation.
The basic steps remain the same as those in the previous testing strategy: after extracting the features, the single data point is projected into the latent space, and the algorithm evaluates its belonging to the known classes, calculating the scores and comparing them with the thresholds. However, even if the overall procedure is quite similar, by considering one data point at a time a lot of complexity is added to the algorithm.
To begin, two new parameters must be defined: the number of consecutive non-classifiable points needed to create a new class (NCpnts) and the number of misclassifications allowed when creating a new class (Mis-NCpnts). The idea behind these parameters is that a previously unseen class will be recognized only when the algorithm cannot attribute, to any of the known classes, NCpnts consecutive points. At the same time, some observations might be missclassified as part of seen classes even if they are part of an unseen one, and Mis-NCpnts represents a safe margin of this happening.
Therefore, once the likelihood scores of one observation are computed and compared with the thresholds, there are three possible scenarios: the data point is recognized as part of (1) just one of the known classes, (2) of multiple classes, or (3) of none.
When a data point does not seem to belong to any of the seen classes, it is placed on a waiting line, and a counter (NC-counter), tracking the non-classifiable data points, is incremented. If the NC-counter reaches the previously defined value of NCpnts, the data points waiting in the queue are used to create a new class. The algorithm learns this new class by applying PLDA and re-computing the thresholds. Instead, if the counter is not equal to NCpnts, the algorithm proceeds to the next data point.
If the data point appears to belong to more than one of the known classes, it is labeled as transition data and put aside. Being part of multiple classes, the data could be representative of a transition phase between two different states of the system as well as an outlier of a particular damage scenario.
The third and final possibility happens when the data point belongs to one, and one only, of the seen classes. In this case, a second counter is needed to keep track of the number of data points recognized as part of the known classes (CD-counter). The primary purpose of this second counter is to update the thresholds not every time a data point is added to a specific class, but only when a group of data points is classified.
In this scenario, the algorithm places the data point on hold and increments the CD-counter, then moves to the next data point. If this counter reaches its defined limit value, the data points on hold are associated with the respective classes, and the thresholds, as well as the latent space, are updated. Moreover, both counters are reset to zero. This resetting of the NC-counter is crucial, as it ensures the previously explained misclassification margin. Because of this, the limit of the NC-counter is indeed equal to Mis-NCpnts.
Additionally, the CD-counter is used to define an interval for re-scanning unclassified data points. Every time the second counter reaches Mis-NCpnts, the previously unclassified data points are rechecked, as updates to the thresholds may impact their classification.
The limitation of the algorithm lies in the definition of the two parameters that limit the counters. The first, NCpnts, where higher values positively influence the accuracy of the threshold of a potential new class but make its creation less likely. On the other hand, the counter Mis-NCpnts is intuitively related to the dispersion of the data; it facilitates the generation of a new class but reduces the accuracy of thresholds for already defined classes. The choice of the values for the two parameters is closely related to the dataset and needs to be determined by the user.
The algorithm’s performance was evaluated using two quality indices: binary and multi-class. The binary performance index measures the ability of the strategy to discriminate between damaged and undamaged data, hence its damage detection capability. It is defined as the number of correct predictions, made as a binary choice between damaged and undamaged, over the total number of predictions (Equation (6)).
On the other hand, the multi-class performance index is linked to the classification of damage and the algorithm’s ability to differentiate between different damage classes. In addition to the ratio between the correct predictions and the overall predictions, it is important to assess whether the algorithm creates more or fewer classes than expected. For this reason, the value of the multi-class performance index is divided by a term dependent on the number of extra classes created or missed by the algorithm (Equation (7)). Therefore, in cases where many classes are created or where classes are not recognized, the results are strongly penalized as the index drops significantly.
Figure 4 shows a graphical representation of the second testing strategy.
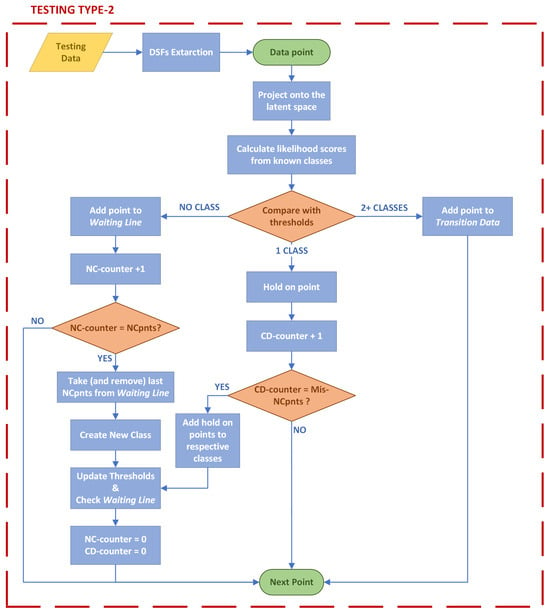
Figure 4.
Testing type 2 flowchart.
3. Case-Study 1: 12 DOF Numeric Dataset
The first case study, which serves as an initial benchmark to evaluate the proposed damage detection framework, involves a numerical simulation of a 12-DOF shear-type building presented by the IASC-ASCE SHM Task Group at the University of British Columbia. The structure is a quarter-scale model consisting of a four-story, two-bay by two-bay steel frame. Each bay measures 2.5 m, reaching an overall height of 3.6 m. Each floor is capable of translation in two horizontal directions, with only one rotation being unconstrained. The columns and beams are modeled as Euler–Bernoulli beams, while the braces are modeled as bars without bending stiffness.
The dataset comprises seven simulated scenarios, one undamaged and six damaged conditions. The severity of damage varies across these scenarios, with the first few representing more severe damage conditions and the later ones presenting minor damage. The damage was simulated by removing or modifying the stiffness in specific braces. In particular, in the first damage scenario, D1, all the braces from the first floor were removed, while the damage intensifies in condition D2, adding the absence of stiffness in the third-story braces. Scenario D3 simulates the absence of stiffness in only one of the first floor’s braces, the north brace on the west face of the structure. Scenarios D4 and D5 both involve a lack of stiffness in a first-story brace (the north brace on the west face) and one brace on the third floor (the west brace on the north face). In addition, D5 includes a weakened connection between a second-floor beam and a column. Lastly, D6 mirrors scenario D3 but only one-third of the brace’s stiffness is lost. For a visual representation of the damage scenarios, refer to Figure 5.
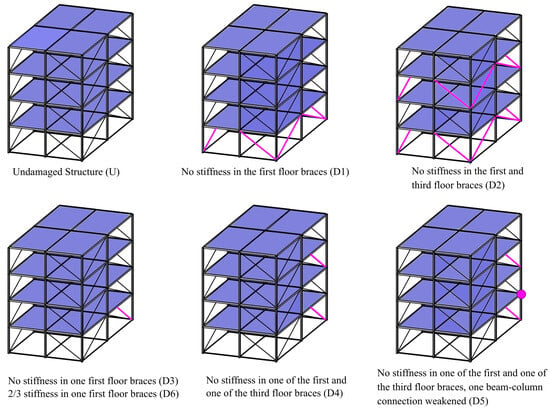
Figure 5.
Representation of the 12-DOF numerical model and of the six damaged conditions.
A comprehensive description of the structural conditions, resulting variations in the system’s natural modes, simulation procedures, and sensor placements, can be found in [29,49].
The system’s response is simulated at sixteen sensor locations with four sensors per floor; two of them are along the x direction and the other two are along the y direction. For each scenario, 1600 acceleration time histories (100 realizations per sensor) of about 100 s were simulated with a sampling frequency of 1 kHz.
3.1. Training Phase
The training phase was conducted considering two scenarios: the undamaged scenario and damaged condition D6, which is the least severe. As previously said, this choice emulates real-life applications, where if any information on the damaged structure is available it is probably regarding light damage. In this scenario, the algorithm aims to recognize the further damage that progressively occurs in the structure.
Given that the structure is numerically simulated, the influence of external factors (e.g., variations in environmental parameters or external excitations) on the system’s response is absent, except for a small variability introduced in the mass and stiffness quantities for each realization simulation and the addition of 5% Gaussian noise applied directly to the acceleration time histories. Therefore, the effect of the location of the sensors acquires a significant role. Given that the position of a sensor determines the capability of that sensor to capture particular natural modes of the structure, the readability of specific frequency content and its potential variations in the cepstral coefficients would change according to the sensor’s location.
From each time history, cepstral features were extracted [, , , ⋯, , ⋯, ], but, as foretold in Section 2.1, the first coefficient () was discarded. Figure 6 represents the scatter plot of the first two CCs extracted from the acceleration signals of the x-sensors of the undamaged condition. The figure highlights the CCs’ dependency on the sensors’ location: the features are not only divided by sensors but these sensors are grouped in pairs based on the floor. This results in four distinguishable clusters, emphasizing the overlap between data from sensors on the same floor. This pattern persists when considering more coefficients, as depicted in Figure 7, where the first five CCs from the sensors along the x-axis are plotted. Given the symmetry of the simulated system, the same trend is also present for the sensors distributed along the y-axis direction, but for the sake of brevity the results are presented only for the sensors in the x-direction.
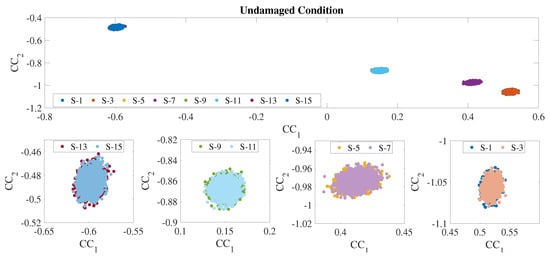
Figure 6.
First two CCs from the undamaged condition.
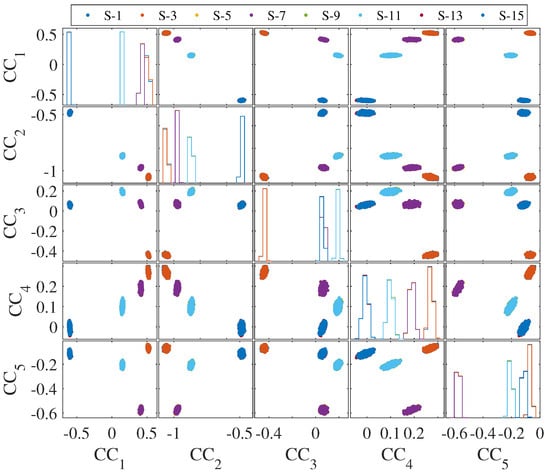
Figure 7.
Representation of the CCs extracted from U00.
This strong dependency on the sensor location necessitates different training approaches depending on whether one is implementing testing strategy type 1 or 2. In the first case, the effect of the sensors’ location is mitigated by analyzing all data simultaneously and considering the mean of the scores altogether. In this case, the algorithm tends to distinguish between damage conditions even if not all sensors contribute equally to differentiate classes.
On the contrary, the implementation of testing strategy type 2 requires more consideration because, when examining one data point at a time, the significant separation between data from different sensors makes the analysis challenging. Data from various sensors could be interpreted as representing different damage conditions, even when belonging to the same class of damage.
For this reason, when using testing type 2, an analysis conducted using all sensors would not suit this dataset. Therefore, only sensors 9 and 13 (located on the third and fourth floor, respectively) were considered and separately used for the analysis, as they proved to be the most sensitive to changes in the system’s structural behavior related to the investigated damage effects. Figure 8 shows how CCs are differentiated by damage scenarios when considering data extracted from sensors 9 and 13. Notably, such a separation is absent when looking at damage scenarios D4 and D5. Since these scenarios are very similar and so are their effects on the system’s structural properties, the features are unable to differentiate between the two. Therefore, scenario D5 was excluded from the second testing type to enhance the results’ clarity and avoid a substantial impact on the multi-class index by preventing a halving effect due to the missed class.
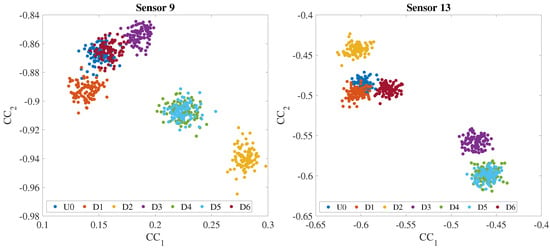
Figure 8.
First two CCs for sensor 9 and sensor 13 plotted by scenario.
Figure 9 shows the first two components of the latent space that was generated during the training phase, using only scenarios U0 and D6 as known classes. This latent space was later updated and expanded in the testing phase as data were classified and new classes were introduced. It is evident from the figure that LDA successfully projects the CCs onto a space where the classes are more compact and separated. The data features associated with the undamaged condition and the lighter damage scenario, D6, although distinguishable when looking only at the cepstral features in Figure 8, are further separated in the latent space. Figure 9 demonstrates the full potential of LDA by showcasing the first two LDA components of the projected CCs for sensor 13 when considering all the classes in the training phase. This is the expected latent space for the model when, at the end of the testing phase, all the new classes are recognized and included in updating the model. It becomes clear how the projections in the latent space are well distinguished for a multi-class scenario. There is a significant distance between damage conditions D1 and D2, which are the most severe. Additionally, D1 and D6 are more distinguishable from the undamaged scenario, as compared to when only cepstral features are considered (as seen in Figure 9). As the severity of the damage increases, clusters move further away from the reference undamaged condition, as expected. Only damaged conditions D4 and D5 remain difficult to separate, which is consistent with the small difference between the two scenarios (beam–column connection weakening).
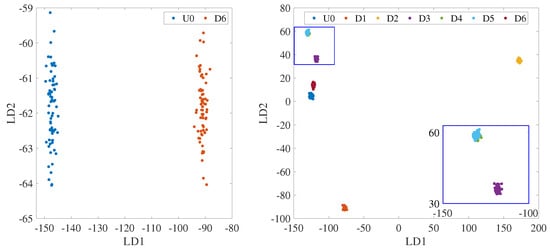
Figure 9.
First two components of the latent space. Data from sensor 13.
In order to complete the training phase, the thresholds for the training classes were established by following the procedure explained in Section 2.2. Figure 10 displays the density distribution of the scores, together with the fitting of the generalized extreme value distribution for training classes U0 and D6.
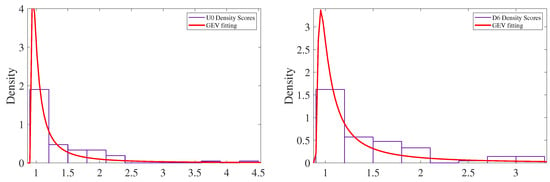
Figure 10.
Fitting of GEV distribution on the density distribution of the scores for training classes U0 and D6.
3.2. Testing Type 1
For the first testing strategy, the results are presented in the form of a table (Table 1). To simplify the interpretation of these results, each piece of information is explained step-by-step using the first two rows as an example. The first column identifies the scenario being analyzed. In this case, undamaged scenario U0 is in the first row and damaged condition D1 is in the second. The second column indicates if the class was included or not in the training phase. Since scenario U0 was part of the training classes, the second column indicates that class as “seen” in the training phase, while scenario D1 is considered unseen in the training phase. The third and fourth columns contain information about the performance of the classification model in the testing phase. The third column indicates if the tested observations belong to one of the existing classes (“Existing class”) or if it represents a new unseen condition (“New Class”). In this case, condition U0 is recognized as belonging to an existing class, while condition D1 is recognized as a class different from undamaged condition U0 and and scenario D6 used in the training. The indication “Existing class” is not limited to the classes considered in the training phase, but could also refer to a class previously encountered and created in the testing phase, as happens for scenario D5. Comparing the predicted class with the real class (fifth column), the last column indicates the correctness of the prediction.

Table 1.
Results testing type 1.
The results in Table 1 demonstrate the algorithm’s strong capability to differentiate between structural conditions. With the exception of class D5, which is associated with class D4, the algorithm consistently distinguishes between different scenarios. The challenge in distinguishing between classes D4 and D5 stems from the significant similarity between these two classes. This misclassification was expected, also given the LDA components displayed in the previous section (Figure 9), and therefore it is not considered a failure of the algorithm, impacting its performance. However, it is fundamental to point out that correct classification between D4 and D5 could be achieved by performing the training involving both classes. In fact, in such cases, LDA finds a coordinate system in which separation between those two classes is also maximized.
Another noteworthy aspect is the algorithm’s ability to recognize data from scenario D6. These data, used during the training phase, are the latest to be analyzed in the testing phase. The algorithm proves to be capable of distinguishing these data from other classes even when new classes have been added, subsequently altering the latent space.
3.3. Testing Type 2
As previously mentioned, testing strategy 2 was validated by solely focusing on data from sensors 9 and 13. Moreover, given the outcomes observed in the previous testing phase, damage scenario D5 was excluded from the classes considered. The focus of this analysis was to evaluate the optimal values of the input parameters, NCpnts, and Mis-NCpnts, to maximize the classification abilities of the algorithm. Understanding the role these parameters play in the final result is essential to assess the methodology’s reliability and possibly evaluate a general definition strategy. Therefore, multiple tests with different combinations of the parameters were carried out to understand and visualize the general response.
NCpnts, the number of unclassifiable points needed to create a new class, varied from 15 to 40 points with a step size of 5. Meanwhile, Mis-NCpnts, which defines both the frequency of updating the thresholds and the allowed misclassifications when creating a new class, ranged from 1 to 10 with increments of 2. These decisions derive from the dataset’s nature: since CCs are well grouped by scenario, data dispersion is low, making excessive increases in Mis-NCpnts unnecessary. On the other hand, increasing NCpnts signifies that the newly created classes would have more defined thresholds, but it simultaneously complicates the creation of a new class. Thus, the chosen range represents a balance between these two effects.
One important factor to consider in analyzing the data is the random selection of the training data. The algorithm is highly sensitive to changes in the training set, which could significantly impact results. To mitigate this impact, the simulation was performed 20 times for each parameter combination, randomly sampling the training data at each repetition and evaluating both the means of the performance indices and their standard deviations.
The indices were plotted as a surface interpolation of the outcomes obtained over the different parameter combinations. Figure 11 shows binary and multi-class performance indices when considering data from sensor 9. The algorithm demonstrates proficiency in the binary classification, distinguishing neatly between damaged and undamaged data and achieving a binary accuracy of around 93%. This result indicates that the binary performance index is not significantly affected by the two parameters.
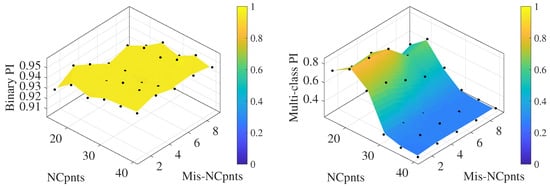
Figure 11.
Mean of the binary (left) and multi-class (right) performance indices using data from sensor 9.
On the other hand, when evaluating the multi-class performance index, results vary significantly. Figure 11 shows how the multi-class index is strongly influenced by the number of points needed to create a new class (NCpnts). The accuracy ranges from 80% when 20 points are needed to around 30% when NCpnts exceed 30. It is noteworthy that when , every damage scenario is recognized, as a consequence of the index definition. Meanwhile, Mis-NCpnts does not appear to notably influence the output.
Another aspect to consider is the behavior of the standard deviations of binary and multi-class indices, shown in Figure 12. Regarding the binary index, results are almost unaffected by the random decision of training data, showing small standard deviation values for every parameter combination. On the other hand, this parameter significantly impacts the multi-class index.
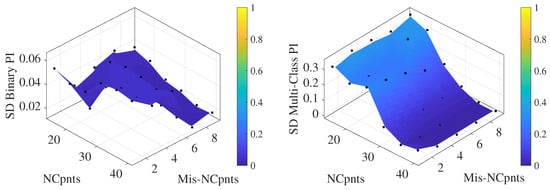
Figure 12.
Standard deviation of binary (left) and multi-class (right) performance indices using data from sensor 9.
Similar results were obtained from data collected by sensor 13. Figure 13 and Figure 14 depict the mean values of the performance indices obtained over 20 repetitions and their standard deviations. The binary classification shows high performance and reliability, being almost independent from both parameter combinations and the training set. In contrast, the multi-class index achieves slightly lower values compared to sensor 9, but, at the same time, it exhibits less dependence on Mis-NCpnts, showing a plateau for lower values of NCpnts.
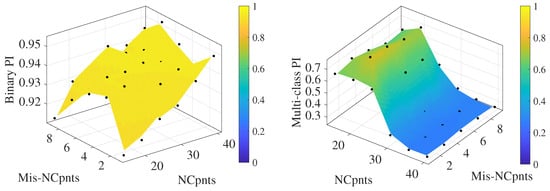
Figure 13.
Mean of the binary (left) and multi-class (right) performance indices using data from sensor 13.
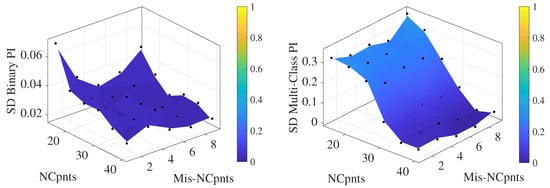
Figure 14.
Standard deviation of binary (left) and multi-class (right) performance indices using data from the sensor 13.
4. Case-Study 2: Z24 Bridge Experimental Data
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology for practical applications, experimental vibration data were used for verification. The selected dataset is a significant contribution to the field of vibration monitoring. It was provided by the European Brite EuRam research project BE-3157, System Identification to Monitor Civil Engineering Structures (SIMCES), in 1998. The project aimed to showcase the practicality of using vibration-based structural health monitoring on large civil infrastructures [50]. In addition, it sought to establish a unique dataset which could serve as a foundation for future research in the field. The project involved monitoring and progressive failure tests of a representative structure, the Z24 Bridge, over almost a year, from November 1997 to September 1998. For more details about the SIMCES project, the reader is referred to De Roeck [51]. The decision to use a dataset acquired in real-world conditions adds complexity to the analysis, as numerous elements come into play, making it closer to a real-world application.
4.1. The Z24 Bridge Dataset
The Z24 was a post-tensioned concrete two-cell box-girder Swiss bridge. With a main span of 30 m and two side spans of 14 m, it overpassed the A1 national highway between Bern and Zürich, connecting Utzenstorf and Koppigen. The ends were supported by a set of triple concrete columns connected with concrete hinges to the girder, while the intermediate supports were concrete piers clamped into the girder. Because all supports were rotated with respect to the longitudinal axis, the bridge was slightly skew.
In the last stages of the SIMCES project, Progressive Damage Tests (PDTs) took place over a month, shortly before the complete demolition of the bridge. Various damage scenarios were devised according to safety and feasibility requirements. These scenarios are listed in Table 2. The undamaged condition of the bridge was measured as a reference at first. The damage scenarios from D01 to D05 are considered “reversible” because the pier that was damaged, composed of four lowering scenarios (Table 2), was then restored to its original position. However, damage scenarios from D07 onwards are considered “irreversible” as per the study conducted by Brincker et al. in 2001 [52].

Table 2.
Chronological overview of applied scenarios.
The PDT database is divided into two sub-databases: Ambient Vibration Test (AVT) and Forced Vibration Test (FVT). In the AVT sub-database, the bridge was excited by an ambient load, whereas in the FVT sub-database, the bridge was excited by two shakers in a controlled way to reduce the influence of traffic-induced noise on the measurements. For more information on the PDTs and the positioning of the sensors, please refer to the work conducted by Kramer et al. [53]. For the present study, only the measurements collected during the AVT were considered.
The acceleration response of the bridge was measured considering accelerometers distributed over the entire bridge and divided into nine setups [53]. All the setups were designed to have 15 accelerometers on the deck (10 uni-axial accelerometers oriented in the vertical direction and 5 tri-axial ones) and 2 tri-axial accelerometers on the piles, except for setup number 5, which had no sensors on the piles. In addition, for all setups and in both sub-databases, three reference sensors (R1, R2, R3) were placed as shown in Figure 15.
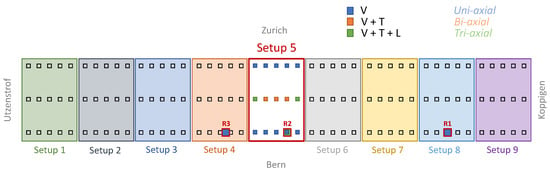
Figure 15.
PDT database: sensor placements for setup 5.
Data were collected at a sampling frequency of = 100 Hz, with each acceleration time history consisting of eight averages of 8192 samples. Consequently, the signal duration for each dataset amounted to 10 min and 55 s.
4.2. Training Phase
In the context of the Z24, the U01 and D06 classes were utilized during the training phase to create the initial statistical model. U01 refers to the undamaged condition, while D06, serving as the reference measure after reversible damages, represents a state where the structure, after light damages, was brought back to the original condition. However, it is important to note that D06 refers to a condition where the structural properties of the bridge have been affected by some previous damage, even though it has been restored to a “healthy state”. Therefore, the CCs extracted from this scenario may exhibit different behaviors compared to those obtained from U01.
For the present study, each time history was divided into four windows, from which 100 cepstral features were extracted. Then, as mentioned in the previous section, the first coefficient () was neglected.
Also in this case study, the location of the sensors plays a crucial role in distinguishing between damage classes. While this factor does not significantly affect the analysis when groups of data are used (testing strategy 1), it becomes a crucial element in the second testing type. Therefore, for the Z24 bridge study, the analysis was carried out using a single sensor setup. Specifically, the vertical sensors from setup 5 were used because they were located at the midspan of the bridge, making them the most sensitive to the different damage scenarios. Figure 15 displays the sensor information for setup 5.
Scenarios U01, D04, D06, D08, D13, and D14, highlighted in bold in Table 2, were considered for the testing analysis. These scenarios are representative of various damages in terms of types and severity, making them suitable for evaluating the classification performances of the algorithm. When considering additional scenarios, the performance tends to decline due to slight differences between damage conditions and resulting similarities in the cepstral features.
Figure 16 depicts, on the left, the first two CCs from the selected scenarios extracted considering the vertical sensors in setup 5. It can be noticed there is a considerable separation between undamaged condition U0 and the remaining scenarios. As expected, condition D6, the new reference condition, defined after the reversible damage scenarios, is separated from the original undamaged scenario, implying a sub-optimal restoration of the system to the original reference state. This separation between classes is particularly relevant in the second testing type, as the possibility of single data points being misclassified is reduced, thereby facilitating the recognition of unseen classes. On the other hand, the damage scenarios, even if sufficiently separated from the undamaged reference state, did not show a clear separation between each other. Figure 16 displays, on the right, the first two LDA components obtained when considering all the scenarios previously mentioned in the training phase (U01, D04, D06, D08, D13, and D14). This representation, as for the numerical case, is used to highlight the separation capabilities that the classification PLDA model will achieve in its learning updating strategy when able to recognize new unknown classes.
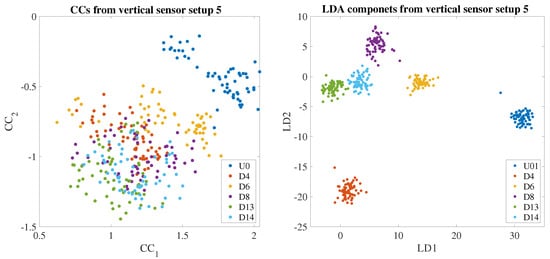
Figure 16.
Comparison between CCs (left) and LDA (right) extracted from the vertical sensors of setup 5.
4.3. Testing Type 1
Following the same strategy described in Section 3.2, Table 3 shows the results obtained from the classification based on grouped data.

Table 3.
Results testing type 1.
The algorithm demonstrates its ability to classify previously encountered data as well as to recognize new classes, resulting in good performances in various scenarios. However, it is important to note that in scenario D14, the algorithm classified it in the same class as D13. This is because the two scenarios represent the same damage, but with different intensities. Therefore, the misclassification error can be expected. Therefore, if the algorithm performance is tested considering its ability to recognize the same damage typology, the prediction can be considered correct.
Table 4 illustrates the prediction results of the model when considering all the damage scenarios for testing. The algorithm demonstrates the ability to differentiate between various scenarios, with only a few instances of misclassification occurring between similar scenarios in terms of severity and type. The classes from D11 onward are all associated with the same damage condition. This outcome is expected, as these refer to the most severe damage scenarios, and differentiation between them is challenging due to the overall structural damage characterizing the bridge. Therefore, this does not significantly impact the algorithm’s positive performance.

Table 4.
Results testing type 1.
4.4. Testing Type 2
Following the same validation process proposed for the numeric case study (Section 3.3), the second testing strategy was implemented in the experimental Z24 PDT dataset. The nature of the dataset implies many more complications to the analysis, as it is characterized by external disturbances, changes in environmental conditions, and small progressive cumulative damages, resulting in not-well-isolated damage classes. On these grounds, the focus of the analysis is on the data collected in a particular setup (setup 5) and in selected damage scenarios, as described in Section 4.2.
After training the model with scenarios U01 and D06, the algorithm was tested using classes U01, D04, D08, D06, D08, D13, and D14 (Table 2), where the last and most severe two are part of the same damage typology and therefore should be recognized as the same class. The algorithm’s performance was evaluated on both its damage detection capability, using the (Equation (6)), and its damage classification proficiency, thanks to (Equation (7)).
A multivariate sensitivity analysis was conducted to evaluate the optimal combination of parameters, NCpnts and Mis-NCpnts, maximizing the performances. In particular, the number of points needed to create a new class varied from 20 to 50 points, with a step of 5, while Mis-NCpnts ranged from 10 to 25, with the same step. It is clear how the parameters’ ranges are wider with respect to the numerical case study. The more dispersed data justify this choice, requiring a safer misclassification margin to recognize new classes and reliable thresholds when those classes are created.
In order to mitigate the strong influence of the random sampling of training data on the results, 20 simulations were performed for each combination of parameters, and the means and standard deviations of the results were calculated. The results can be appreciated in Figure 17 and Figure 18.
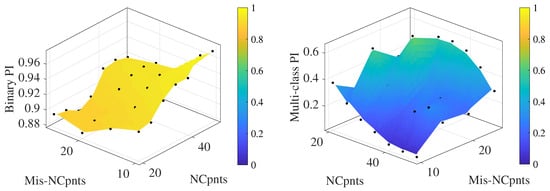
Figure 17.
Mean of the binary (left) and multi-class (right) performance indices using data from setup 5.
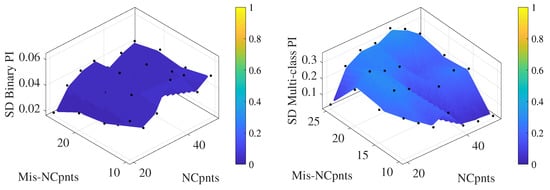
Figure 18.
Standard deviation of binary (left) and multi-class (right) performance indices using data from sensor 9.
The algorithm successfully recognizes the presence of damage as a binary choice between labeling the new data as damaged or undamaged. The binary performance index shows high values overall, around 92% accuracy, even reaching an astonishing 97%, with minimal standard deviations.
On the other hand, as expected, the classification of new data is more challenging for the real study case. The multi-class performance index appears to be quite dependent on the parameter combinations. Nonetheless, it reaches accuracy performance indexes of 60%. The standard deviation for the multi-class case shows a higher dependence on the repetition with respect to the binary case, highlighting a higher sensitivity towards the choice of the sampling of the training data used. At the same time, it demonstrates the presence of cases where the model is able to correctly classify the tested observations with an accuracy up to almost 90%.
5. Conclusions
The present study addresses a novel damage assessment strategy for dynamic systems that adopts a hybrid supervised–unsupervised methodology to identify and classify known and unknown healthy and damaged conditions. The strategy relies on training a Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis model starting from cepstral features extracted from the measurement responses of the system, projected into a latent space where the class separation is maximized. The classification model is then used to evaluate the health condition of structural systems.
The classification performance of the model was evaluated based on its capacity to identify the presence of damage as a binary decision and to classify it, even in the case of new damage conditions. The framework being proposed takes into account two testing strategies.
The first method analyzes groups of data altogether, assuming that all data in the same block represent the same condition. This approach is useful for condition monitoring scenarios where the damage conditions are already known or for post-processing damage assessment. The second methodology, on the other hand, considers the analysis of a single incoming observation data point, offering a damage assessment strategy compatible with real-time monitoring strategies.
The proposed method was evaluated using two testing strategies on a simulated shear-type model with plate number 12-DOF. Following the first testing approach, the model was trained on the undamaged scenario and the lighter damaged condition, and it demonstrated excellent performance in distinguishing between the known scenarios and other damaged conditions. It proved to be able to recognize the classes seen in the training phase correctly and, at the same time, identify unknown classes, update the prior knowledge of the model, and recognize them afterward. Even when analyzing one data point at a time, the model offered a robust classification accuracy for the binary and the multi-class case with performance indexes above 90% and 80%, respectively, for the optimal algorithm’s parameters.
A comparable set of results could be observed for the experimental data collected from the Z24 bridge. The model proved to correctly identify the different damage categories and differentiate them from the undamaged reference condition, processing the data by group and for a single point at a time.
In the future, it is planned to upgrade the framework to explore the possibility of conducting the training phase using only the undamaged condition and gradually introducing transitional intermediate damage scenarios, investigating a progressively increasing degradation event for the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani), E.M.T., R.B., S.M., A.C. (Antonio Culla), N.R. and A.C. (Antonio Carcaterra); methodology, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani), E.M.T. and R.B.; software, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani), E.M.T. and R.B.; validation, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani), E.M.T. and R.B.; formal analysis, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi) and L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani); investigation, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani), E.M.T. and R.B.; data curation, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani) and E.M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani) and E.M.T.; writing—review and editing, L.S. (Lorenzo Stagi), L.S. (Lorenzo Sclafani), E.M.T., R.B., S.M., A.C. (Antonio Culla), N.R. and A.C. (Antonio Carcaterra); supervision, E.M.T., R.B., S.M., A.C. (Antonio Culla), N.R. and A.C. (Antonio Carcaterra); project administration, E.M.T., R.B., S.M., A.C. (Antonio Culla), N.R. and A.C. (Antonio Carcaterra). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The numerical data used in the present work can be reproduced following the detailed information provided by the authors in [29]. The experimental data from the Z24 bridge were provided by the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely acknowledge the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Structural Mechanics Section, for providing the data collected within the SIMCES project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. An introduction to structural health monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehbaghi, V.R.; Noroozinejad Farsangi, E.; Noori, M.; Yang, T.; Li, S.; Nguyen, A.; Málaga-Chuquitaype, C.; Gardoni, P.; Mirjalili, S. A critical review on structural health monitoring: Definitions, methods, and perspectives. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 29, 2209–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qiao, P. Vibration-based damage identification methods: A review and comparative study. Struct. Health Monit. 2011, 10, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Xia, Y. Review on the new development of vibration-based damage identification for civil engineering structures: 2010–2019. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 491, 115741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownjohn, J.M.; Xia, P.Q.; Hao, H.; Xia, Y. Civil structure condition assessment by FE model updating: Methodology and case studies. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2001, 37, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friswell, M.; Mottershead, J.E. Finite Element Model Updating in Structural Dynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1995; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Cabboi, A.; Gentile, C.; Saisi, A. From continuous vibration monitoring to FEM-based damage assessment: Application on a stone-masonry tower. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Garrett, J.H., Jr.; Oppenheim, I.J.; Soibelman, L.; Harley, J.B.; Shi, J.; Jin, Y. Toward data-driven structural health monitoring: Application of machine learning and signal processing to damage detection. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2013, 27, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibaduiza Burgos, D.A.; Gomez Vargas, R.C.; Pedraza, C.; Agis, D.; Pozo, F. Damage identification in structural health monitoring: A brief review from its implementation to the use of data-driven applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafas, K.; Kiremidjian, A.S. Extraction of a series of novel damage sensitive features derived from the continuous wavelet transform of input and output acceleration measurements. Proc. Sens. Smart Struct. Technol. Civil Mech. Aerosp. Syst. 2014, 9061, 386–394. [Google Scholar]
- Worden, K.; Manson, G.; Fieller, N.R. Damage detection using outlier analysis. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 229, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. Structural Health Monitoring: A Machine Learning Perspective; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, E.; Manson, G.; Worden, K.; Pierce, S. Features for damage detection with insensitivity to environmental and operational variations. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 468, 4098–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, D.; Jankowski, K.; Rees, B.; Farrar, C.; Flynn, G. Identifying Environmental-and Operational-Insensitive Damage Features. In Data Science in Engineering, Volume 9: Proceedings of the 39th IMAC, A Conference and Exposition on Structural Dynamics 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, D.H.; Yi, T.H.; Zhang, G.H.; Han, J.G. Eliminating environmental and operational effects on structural modal frequency: A comprehensive review. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2022, 29, e3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronci, E.M.; Betti, R.; De Angelis, M. Damage detection in a RC-masonry tower equipped with a non-conventional TMD using temperature-independent damage sensitive features. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 15, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Ryu, Y.S.; Cho, H.M.; Stubbs, N. Damage identification in beam-type structures: Frequency-based method vs mode-shape-based method. Eng. Struct. 2003, 25, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Pakzad, S.N. Autoregressive statistical pattern recognition algorithms for damage detection in civil structures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 31, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernagozzi, G.; Achilli, A.; Betti, R.; Diotallevi, P.P.; Landi, L.; Quqa, S.; Tronci, E.M. On the use of multivariate autoregressive models for vibration-based damage detection and localization. Smart Struct. Syst. Int. J. 2021, 27, 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Bogert, B.P. The quefrency alanysis of time series for echoes: Cepstrum, pseudoautocovariance, cross-cepstrum and saphe cracking. Proc. Symp. Time Ser. Anal. 1963, 209–243. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, A.V.; Schafer, R.W. Discrete-Time Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 878–882. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.; Mermelstein, P. Comparison of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1980, 28, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Jamil, M.; Rahman, M. Speaker identification using mel frequency cepstral coefficients. Variations 2004, 1, 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Nelwamondo, F.V.; Marwala, T.; Mahola, U. Early classifications of bearing faults using hidden Markov models, Gaussian mixture models, mel-frequency cepstral coefficients and fractals. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2006, 2, 1281–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Benkedjouh, T.; Chettibi, T.; Saadouni, Y.; Afroun, M. Gearbox fault diagnosis based on mel-frequency cepstral coefficients and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Its Applications, Oran, Algeria, 8–10 May 2018; pp. 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.R.; Jen, K.K.; Shen, Y.T. Application of cepstrum and neural network to bearing fault detection. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, L.; Betti, R.; Beigi, H. A structural health monitoring strategy using cepstral features. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 4526–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.F.; Bittencourt, T.N.; Ribeiro, D.; Carvalho, H. Feasibility of Applying Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients in a Drive-by Damage Detection Methodology for High-Speed Railway Bridges. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronci, E.M.; Beigi, H.; Betti, R.; Feng, M.Q. A damage assessment methodology for structural systems using transfer learning from the audio domain. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 195, 110286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Y. Drive-by bridge damage detection using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients and support vector machine. Struct. Health Monit. 2023, 22, 14759217221150932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgantini, M.; Betti, R.; Balsamo, L. Structural damage assessment through features in quefrency domain. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Morgantini, M.; Betti, R. Structural damage assessment through a new generalized autoencoder with features in the quefrency domain. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, P.; Cord, M.; Delany, S.J. Supervised learning. In Machine Learning Techniques for Multimedia: Case Studies on Organization and Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 21–49. [Google Scholar]
- Perfetto, D.; Rezazadeh, N.; Aversano, A.; De Luca, A.; Lamanna, G. Composite Panel Damage Classification Based on Guided Waves and Machine Learning: An Experimental Approach. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Broer, A.; Chiachío, J.; Benedictus, R.; Loutas, T.H.; Zarouchas, D. Intelligent health indicator construction for prognostics of composite structures utilizing a semi-supervised deep neural network and SHM data. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugate, M.L.; Sohn, H.; Farrar, C.R. Unsupervised learning methods for vibration-based damage detection. In Proceedings of the 18th International Modal Analysis Conference–IMAC, San Antonio, TX, USA, 7–10 February 2000; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cha, Y.J. Unsupervised machine and deep learning methods for structural damage detection: A comparative study. Eng. Rep. 2022, e12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveri, N.; Carcaterra, A. Unsupervised identification of damage and load characteristics in time-varying systems. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2015, 27, 531–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, N.; de Oliveira, M.; Perfetto, D.; De Luca, A.; Caputo, F. Classification of Unbalanced and Bowed Rotors under Uncertainty Using Wavelet Time Scattering, LSTM, and SVM. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaça, M.J.; Cardoso, E.L.; de Medeiros, R. A systematic approach to find the hyperparameters of artificial neural networks applied to damage detection in composite materials. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmadi, H.; Entezami, A. Application of supervised learning to validation of damage detection. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2021, 91, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, P.; Pardalos, P.M.; Trafalis, T.B.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Pardalos, P.M.; Trafalis, T.B. Linear discriminant analysis. In Robust Data Mining; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S. Probabilistic linear discriminant analysis. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2006: 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; Proceedings, Part IV 9. pp. 531–542. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-vectors: Robust dnn embeddings for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthram, A.; Saravanakumar, K.K.; Huynh, J.; Beigi, H. Multi-modal emotion detection with transfer learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.07065. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.A. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R. The utilization of multiple measurements in problems of biological classification. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1948, 10, 159–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, S.; Nadarajah, S. Extreme Value Distributions: Theory and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.A.; Lam, H.F.; Katafygiotis, L.S.; Beck, J.L. Phase I IASC-ASCE structural health monitoring benchmark problem using simulated data. J. Eng. Mech. 2004, 130, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, B.; De Roeck, G. One-year monitoring of the Z24-Bridge: Environmental effects versus damage events. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2001, 30, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeck, G.D. The state-of-the-art of damage detection by vibration monitoring: The SIMCES experience. J. Struct. Control 2003, 10, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, R.; Andersen, P.; Cantieni, R. Identification and level I damage detection of the Z24 highway bridge. Exp. Tech. 2001, 25, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, C.; De Smet, C.; De Roeck, G. Z24 bridge damage detection tests. In IMAC 17, the International Modal Analysis Conference; Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; Volume 3727, pp. 1023–1029. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).