Interdependencies between Urban Transport, Water, and Solid Waste Infrastructure Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of Keywords and Selection of Infrastructure Elements
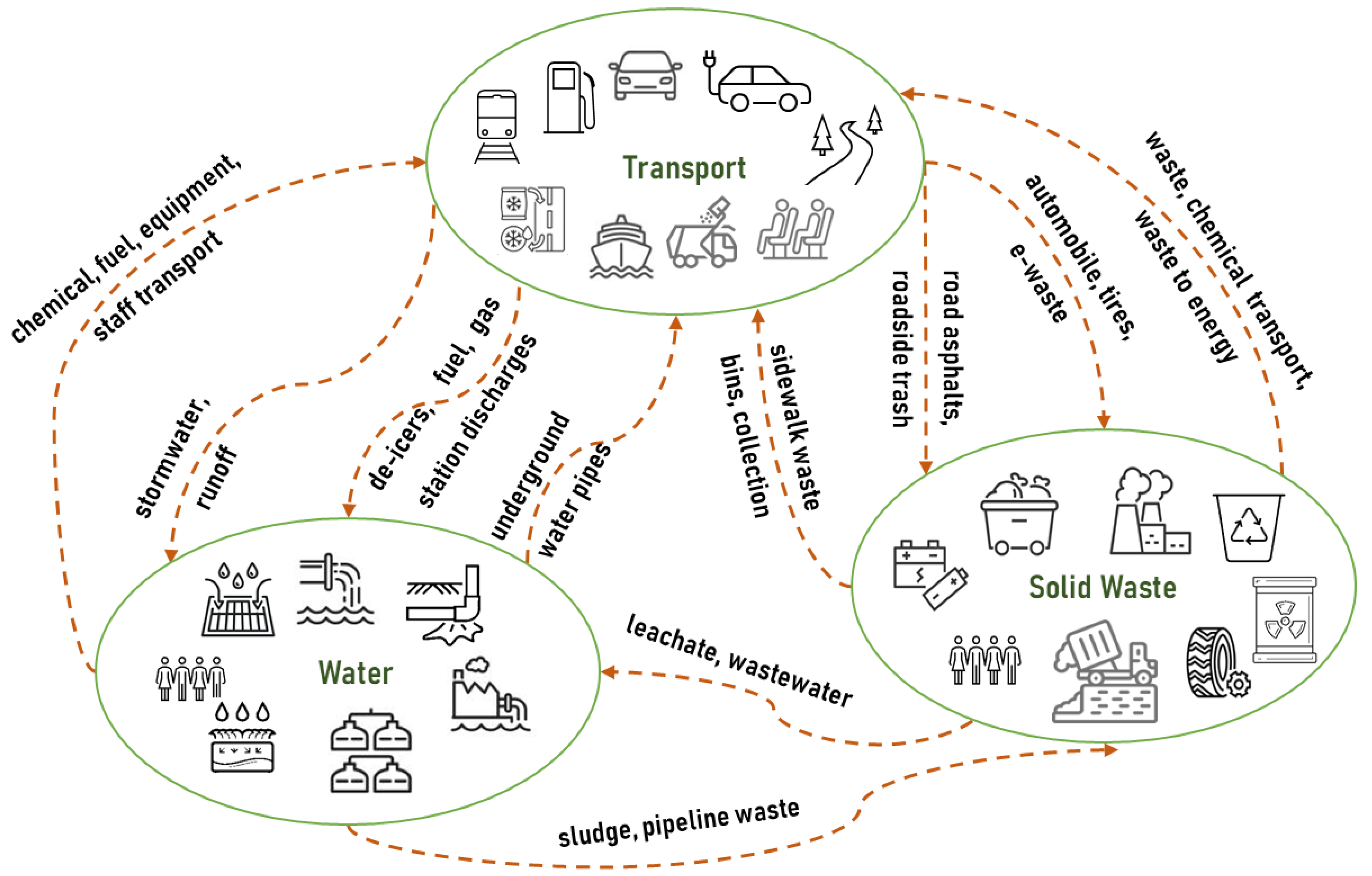
3. Interdependency Matrix for Transport, Water, and Solid Waste Infrastructure Systems
4. Understanding the Interdependencies between the Three Infrastructure Systems
4.1. Impacts of Transport on Water Infrastructure
4.2. Impacts of Transport on Solid Waste Infrastructure
4.3. Impacts of Water on Transport Infrastructure
4.4. Impacts of Solid Waste on Transport Infrastructure
4.5. Impacts of Water on Solid Waste Infrastructure
4.6. Impacts of Solid Waste on Water Infrastructure
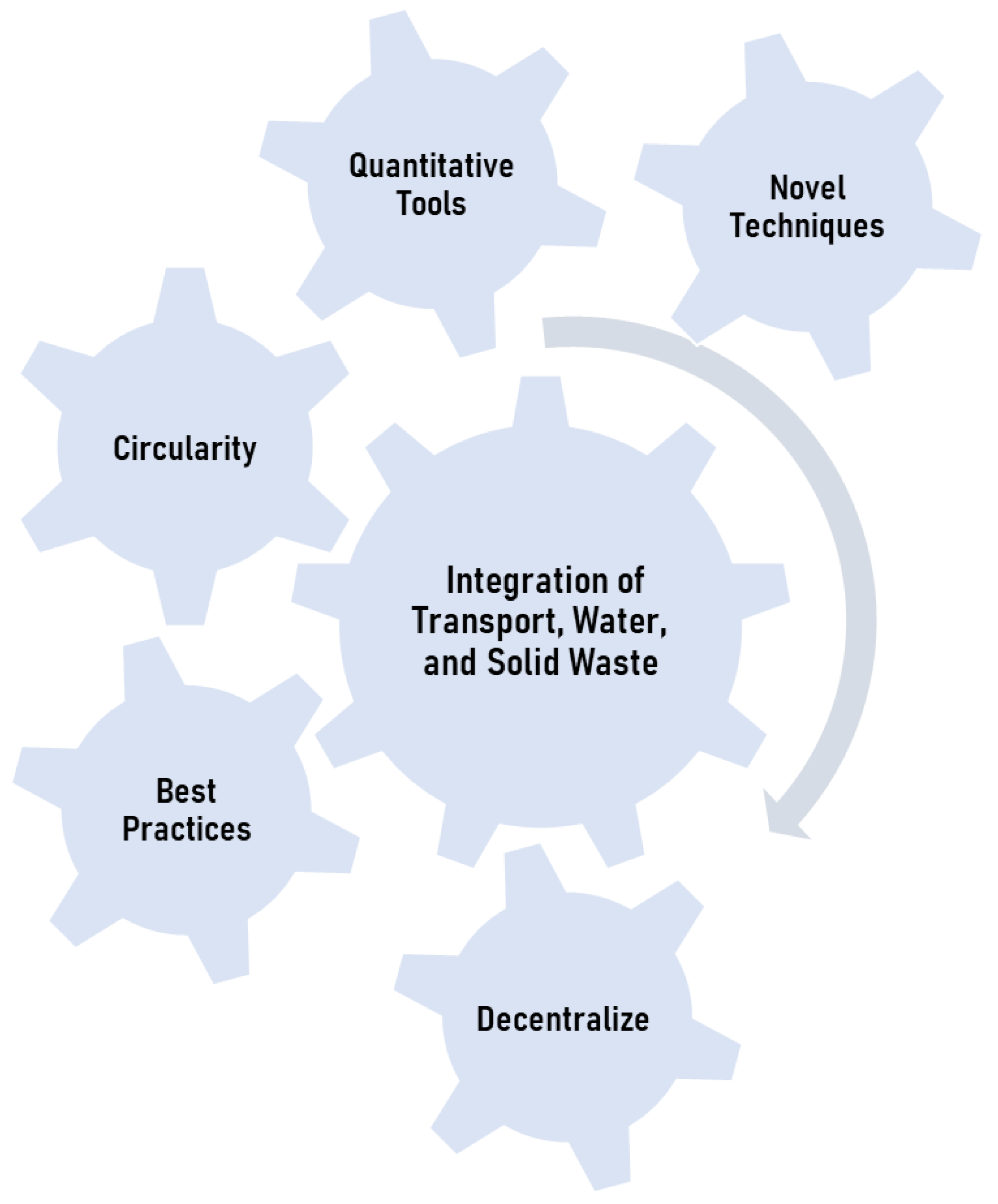
5. Opportunities and Moving Forward
5.1. Integrated and Decentralized Infrastructure Systems
5.2. Best Practices and Circular Economy Approach
5.3. Novel Techniques and Quantitative Tools
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derrible, S. An approach to designing sustainable urban infrastructure. MRS Energy Sustain. 2019, 5, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.M.; Peerenboom, J.P.; Kelly, T.K. Identifying, understanding, and analyzing critical infrastructure interdependencies. IEEE Control Syst. 2001, 21, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Derrible, S. Urban Engineering for Sustainability; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; 656p. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, J.; Hassel, H.; Cedergren, A. Vulnerability analysis of interdependent critical infrastructures: Case study of the Swedish railway system. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2011, 7, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wu, D.; Yin, Y.; Guan, Y. Optimal deployment of public charging stations for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2013, 47, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.C.; Kumar, A.; Zheng, H.; Agrawal, A.; Peeta, S. Integrated Framework to Capture the Interdependencies between Transportation and Energy Sectors Due to Policy Decisions; USDOT Region V Regional University Transportation Center Final Report; NEXTRANS Center: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.C.; Ersal, T.; Li, C.-T.; Marshall, B.M.; Kundu, S.; Keoleian, G.A.; Peng, H.; Hiskens, I.A.; Stein, J.L. Sustainability, Resiliency, and Grid Stability of the Coupled Electricity and Transportation Infrastructures: Case for an Integrated Analysis. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2015, 21, 4015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wilkinson, S.; Dawson, R.J. A Spatial Network Model for Civil Infrastructure System Development. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 31, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, S.; Kelly, S.; Pant, R.; Hall, J.W. Evaluating the benefits of adaptation of critical infrastructures to hydrometeorological risks. Risk Anal. 2017, 38, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Danman, W.; Qiuwei, W.; Miadreza, S.; João, C. Interdependence between transportation system and power distribution system: A comprehensive review on models and applications. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2019, 7, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieker, S.; Cornel, P.; Wagner, M. Semi centralised supply and treatment systems: Integrated infrastructure solutions for fast growing urban areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2905–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepbasli, A. Low exergy (LowEx) heating and cooling systems for sustainable buildings and societies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, B.; Parshall, L.; Thompson, J.; Hammer, S.; Dickinson, J.; Modi, V. Spatial distribution of urban building energy consumption by end use. Energy Build. 2012, 45, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, A.; Ha, H. Buildings and Infrastructure from a Sustainability Perspective. In Sustainable and Healthy Communities Program—Theme 4.1.1; Internal EPA Report (EPA/600/X-14/369); US-EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; Ma, J.; Ahmad, N.; Hussain, K.; Waqas, M.; Liang, Y. Sustainable construction through energy management practices: An integrated hierarchal framework of drivers in the construction sector. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 90108–90127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, A.; Hummels, D.; Puzzello, L.; Avetisyan, M. Trade and the greenhouse gas emissions from international freight transport. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2013, 65, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatem, A.S.; Radwan, E.; Westerlund, K.; Cooper, D. Using a Traffic Simulation Model (VISSIM) with an Emissions Model (MOVES) to Predict Emissions from Vehicles on a Limited-Access Highway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 819–831. [Google Scholar]
- Van Fan, Y.; Perry, S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Lee, C.T. A review on air emissions assessment: Transportation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, H.C. Trends in on road transportation energy and emissions. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 514–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Ali, S.; Saud, S.; Shahzad, S.J.H. Transport CO2 emissions, drivers, and mitigation: An empirical investigation in India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S. Infrastructural Urbanism. Points and Lines: Diagrams and Projects for the City; Princeton Architectural Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, M. Review on modeling and simulation of interdependent critical infrastructure systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 121, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, S.; Kattan, L.; Jayasinghe, P.A.; Hettiaratchi, J.P.A.; Taron, J. Integrated infrastructure systems—A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Wild, A.; Muzyk, C. Developing a Method for Quantifying Transport Interdependencies; NZ Transport Agency research report 671 Contracted research organization—Tonkin & Taylor Lt.; NZ Transport Agency: Wellington, New Zealand, 2020.
- Zimmerman, R. Decision-making and the vulnerability of interdependent critical infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 10–13 October 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, P.; Dudenhoeffer, D.; Hartley, S.; Permann, M. Critical Infrastructure Interdependency Modeling: A Survey of US and International Research; Idaho National Laboratory: Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2006.
- Zhang, P.; Peeta, S. A generalized modeling framework to analyze interdependencies among infrastructure systems. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2011, 45, 553–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrible, S. Urban infrastructure is not a tree: Integrating and decentralizing urban infrastructure systems. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2017, 44, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, R.J.; Beyeler, W.E.; Conrad, S.H.; Brodsky, N.S.; Kaplan, P.G.; Brown, T. Defining Research and Development Directions for Modeling and Simulation of Complex, Interdependent Adaptive Infrastructures; NISAC, Sandia National Laboratories, Infrastructure Complexity R & D Group: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2003.
- Hughes, T. Human-Built World: How to Think about Technology and Culture; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dudenhoeffer, D.D.; Permann, M.R.; Manic, M. CIMS: A framework for infrastructure interdependency modeling and analysis. In Proceedings of the 2006 Winter Simulation Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 3–6 December 2006; pp. 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esugel, I.; Nan, C.; Dietz, S. System of Systems approach for interdependent critical infrastructures. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 679–686. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.W.; Otto, A.; Hickford, A.J.; Nicholls, R.J.; Tran, M. A framework for analysing the long-term performance of interdependent infrastructure system. In The Future of National Infrastructure a System-of-System Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Karagoz, S.; Aydin, N.; Simic, V. End-of-life vehicle management: A comprehensive review. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu, V.H.S.; Da Costa, M.G.; Da Costa, V.X.; De Assis, T.F.; Santos, A.S.; D’Agosto, M.D.A. The Role of the Circular Economy in Road Transport to Mitigate Climate Change and Reduce Resource Depletion. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tri, P.T.; Visvanathan, C.; Jegatheesan, V. Biological treatment of oily wastewater from gas stations by membrane bioreactor. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 5, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghamitra, P.; Mazumder, D.; Mukherjee, S. Treatment of wastewater containing oil and grease by biological method- a review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Berawala, N.; Patil, Y. Automobile service station waste assessment and promising biological treatment alternatives: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Cappello, S.; Yakimov, M.M.; Polizzi, A.; Torregrossa, M. Biological approaches to the treatment of saline oily waste (waters) originated from marine transportation. Chem. Eng. 2012, 27, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, T.R.; Adebambo, O.; Del Aguila Feijoo, M.C.; Elhaimer, E.; Hossain, T.; Edwards, S.J.; Morrison, C.E.; Romo, J.; Sharma, N.; Taylor, S.; et al. Chapter 27—Environmental Effects of Marine Transportation. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 505–530. [Google Scholar]
- Springer, S. Waste Management in Transportation: The Present and the Future. Transp. Res. Board 2000, 1–9, A1F07-Committee on Waste Management in Transportation. Available online: https://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/millennium/00145.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Hu, L.M.; Dong, S.B.; Li, X.M.; Ouyang, X.D. Pollution Source from Gas Stations and Preventive Measures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 361–363, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Hussain, R.; Shah, S.M.; Bibi, S.; Ahmad, S.R.; Shahzad, A.; Zamir, A.; Rauf, Z.; Noshad, A.; Ahmad, L. Composition, impacts, and removal of liquid petroleum waste through bioremediation as an alternative clean-up technology: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, A.; Srivastava, P. Automobile Waste and Its Management. Res. J. Chem. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, R.G.; Rocha, C.L.; Felipe, F.L.S.; Cezario, F.T.; Correia, P.J.; Rezaei-Gomari, S. Tire waste management: An overview from chemical compounding to the pyrolysis-derived fuels. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andeobu, L.; Wibowo, S.; Grandhi, S. A Systematic Review of E-Waste Generation and Environmental Management of Asia Pacific Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhd Moktar MF, H.; Salman MF, N.; Rizzuddin, M.A.; Abdul Kadir, M.A.; Sanik, M.E. Drive-Thru Trash Bin. Multidiscip. Appl. Res. Innov. 2022, 3, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Araya, F.; Faust, K.M.; Kaminsky, J.A. Agent-Based Model of Hosting Communities’ Perceptions of Water and Wastewater Infrastructure during the German Refugee Crisis. J. Manag. Eng. 2021, 37, 4021035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, M.; Borremans, A.; Dubgorn, A.; Shaban, A. Nuclear Waste Transportation: Quality Assurance and Control. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 54, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Biofuels securing the planet’s future energy needs. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Gardy, J.; Demirbas, A.; Rashid, U.; Budzianowski, W.M.; Pant, D.; Nizami, A.S. Waste to biodiesel: A preliminary assessment for Saudi Arabia. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes SD, C.; Zhou, J.L.; Li, W.; Long, G. Progress in manufacture and properties of construction materials incorporating water treatment sludge: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ahmad, K.; Alam, M. Sustainable management of water treatment sludge through 3‘R’ concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, S.T.S. Bioreactor Landfills: Do They Work? In Proceedings of the 2nd ANZ Conference on Environmental Geotechnics, Newcastle, Australia, 28–30 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Erses, A.S.; Onay, T. Accelerated landfill waste decomposition by external leachate recirculation from an old landfill cell. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafius, D.R.; Varga, L.; Jude, S. Infrastructure Interdependencies: Opportunities from Complexity. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2020, 26, 4020036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carhart, N.J.; Rosenberg, G. A Framework for Characterising Infrastructure Interdependencies. Int. J. Complex. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 1, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, A.W.; Kvasnak, A.; Segale, J. Integrated Infrastructure Management Systems: Small Urban Area’s Experience. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2003, 9, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfawy, M.R. Integration of Municipal Infrastructure Asset Management Processes: Challenges and Solutions. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2008, 22, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourabi, H.; Nam, T.; Walker, S.; Gil-Gracia, J.R.; Mellouli, S.; Nahon, K.; Pardo, T.A.; SchollH, J. Understanding Smart Cities: An Integrative Framework. In Proceedings of the 2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2012; pp. 2289–2297. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Samra, S.; Ahmed, M.; Hammad, A.; Zayed, T. Multi-objective framework for managing municipal integrated infrastructure. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 4017091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metayer, G.; Torres-Machi, C.; Bastias, A. A proposed framework for the integrated management of municipal infrastructure. In Construction Research Congress 2020: Infrastructure Systems and Sustainability; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 846–855. [Google Scholar]
- Araya, F.; Vasquez, S. Challenges, drivers, and benefits to integrated infrastructure management of water, wastewater, stormwater and transportation systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orehounig, K.; Evins, R.; Dorer, V. Integration of decentralized energy systems in neighbourhoods using the energy hub approach. Appl. Energy 2015, 154, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Integrated, Decentralized Wastewater Management for Resource Recovery in Rural and Pe-ri-Urban Areas. Resources 2017, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lieshout, R.N. Integration, Decentralization and Self-Organization: Towards Better Public Transport. Ph.D. Thesis, Erasmus Research Institute of Management, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, D.K.S. Canadian waste tire practices and their potential in sustainable construction. Dalhous. J. Interdiscip. Manag. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, R.; Juaidi, A.; Assad, M.; Salameh, T.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Energy Recovery from Waste Tires Using Pyrolysis: Palestine as Case of Study. Energies 2020, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfayez, S.; Suleiman, A.; Nehdi, M. Recycling Tire Rubber in Asphalt Pavements: State of the Art. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cai, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, K. Evaluation of engineering properties and environmental effect of recycled waste tire-sand/soil in geotechnical engineering: A compressive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 126, 109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, M.; Uddin, M.N.; Chowdhury, J.I.; Ahmed, S.F.; Uddin, M.N.; Mofiur, M.; Uddin, M.A. A review of the recent development, challenges, and opportunities of electronic waste (e-waste). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 4513–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Global E-Waste Management: Urban Mining towards a Sustainable Future and Circular Economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, P.; Cialani, C.; Ulgiati, S. A Review on Circular Economy: The Expected Transition to a Balanced Interplay of Environmental and Economic Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A new sustainability paradigm. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariatli, F. Linear Economy Versus Circular Economy: A Comparative and Analyzer Study for Optimization of Economy for Sustainability. Visegrad J. Bioeconomy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Otero, J.; Boks, C.; Pettersen, I.N. Consumption in the Circular Economy: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.V.; Lee, C.T.; Lim, J.S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Le, P.T.K. Cross-disciplinary approaches towards smart, resilient and sustainable circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modoi, O.C.; Mihai, F.C. E-Waste and End-of-Life Vehicles Management and Circular Economy Initiatives in Romania. Energies 2022, 15, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, W.; Braungart, M. Remaking the Way We Make Things: Cradle to Cradle; North Point Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Khairul, N.I.; Azmatun, A.; Nadia, R. Identification of Technical and Biological Nutrients (cradle-to-cradle) to-wards Environmental Sustainability: A Case study of an Electrical and Electronic Equipment Industry in Malaysia. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 2010, 36, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, F.; Luisi, P.L. The Systems View of Life: A Unified Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mestre, A.; Cooper, T. Circular Product Design. A Multiple Loops Life Cycle Design Approach for the Circular Economy. Des. J. 2017, 20, 1620–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, E.V.; Murphy, D.; Stefan, H.G. Increase of urban lake salinity by road deicing salt. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 406, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Jungwirth, S. The Search for ‘Greener’ Materials for Winter Road Maintenance Operations, Sustainable Winter Road Operations; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 378–401. [Google Scholar]
- Uliasz-Misiak, B.; Winid, B.; Lewandowska-Śmierzchalska, J.; Matuła, R. Impact of road transport on groundwater quality. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 824, 153804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zari, M.P.; Hecht, K. Biomimicry for Regenerative Built Environments: Mapping Design Strategies for Producing Ecosystem Services. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Yeow, L.W.; Cheah, L.; Derrible, S. Assessing water circularity in cities: Methodological framework with a case study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 178, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, M. Autonomous Vehicles: The Next Big Trend in the Waste, Recycling Industry? Waste 360 Technology Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.waste360.com/fleets-technology/autonomous-vehicles-next-big-trend-waste-recycling-industry (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Abdallah, M.; Abu Talib, M.; Feroz, S.; Nasir, Q.; Abdalla, H.; Mahfood, B. Artificial intelligence applications in solid waste management: A systematic research review. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Alam, G.; Jamal, A.; Shaik, F. Recent advances in applications of artificial intelligence in solid waste management: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Vaid, U. Emerging role of artificial intelligence in waste management practices. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 889, 12047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, S.; Barnett, K.; Aslani, B. Decentralized resource allocation for interdependent infrastructures resilience: A cooperative game approach. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2021, 28, 3394–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotmans, J.; van Asselt, M.; Vellinga, P. An integrated planning tool for sustainable cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2000, 20, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, J. The future of systems integration within civil infrastructure: A review and directions for research. INCOSE Int. Symp. 2016, 26, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrible, S.; Cheah, L.; Arora, M.; Yeow, L.W. Urban Metabolism. In Urban Informatics; Shi, W., Goodchild, M.F., Batty, M., Kwan, M.P., Zhang, A., Eds.; The Urban Book Series; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.; Pincetl, S.; Bunje, P. The study of urban metabolism and its applications to urban planning and design. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, A.; Derrible, S. Interrelationships between electricity, gas, and water consumption in large-scale buildings. J. Ind. Ecol. 2021, 25, 932–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infrastructure | Elements |
|---|---|
| Transport | Roads, bridges, airports, ports, waterways, tunnels, parking lots, gas stations, rail, transit stations, automobiles and parts, and passengers. |
| Water | Potable water, wastewater and stormwater, water pipelines and drainage systems, treatment facilities including buildings, and workforce. |
| Solid waste | Solid waste, garbage collection trucks, garbage bins, treatment facilities, including buildings, and workforce. |
| Transport | Water | Solid Waste | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport | Cell # 1 to Cell # 3 |
|
|
| Water |
| Cell # 5 |
|
| Solid Waste |
|
| Cell # 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayasinghe, P.A.; Derrible, S.; Kattan, L. Interdependencies between Urban Transport, Water, and Solid Waste Infrastructure Systems. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8040076
Jayasinghe PA, Derrible S, Kattan L. Interdependencies between Urban Transport, Water, and Solid Waste Infrastructure Systems. Infrastructures. 2023; 8(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayasinghe, Poornima A., Sybil Derrible, and Lina Kattan. 2023. "Interdependencies between Urban Transport, Water, and Solid Waste Infrastructure Systems" Infrastructures 8, no. 4: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8040076
APA StyleJayasinghe, P. A., Derrible, S., & Kattan, L. (2023). Interdependencies between Urban Transport, Water, and Solid Waste Infrastructure Systems. Infrastructures, 8(4), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8040076







