Seismic Analysis of Historical Urban Walls: Application to the Volterra Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- analytical assessment of seismic vulnerability considering different scenarios of soil saturation by adopting proper soil imbibition models,
- (2)
- seismic NLS analysis using LEM,
- (3)
- seismic NLD analysis using FEM,
- (4)
- results comparison and discussion.
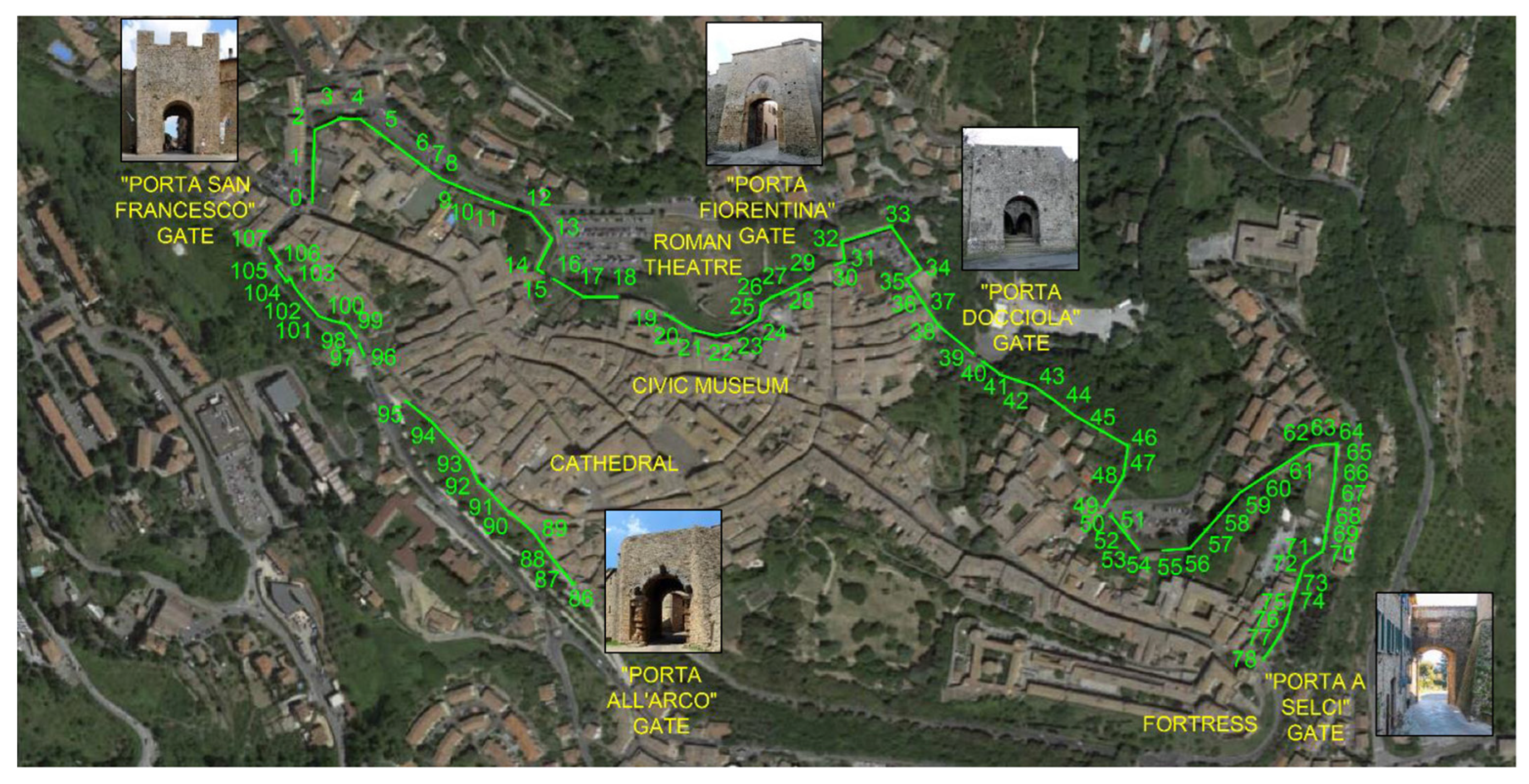
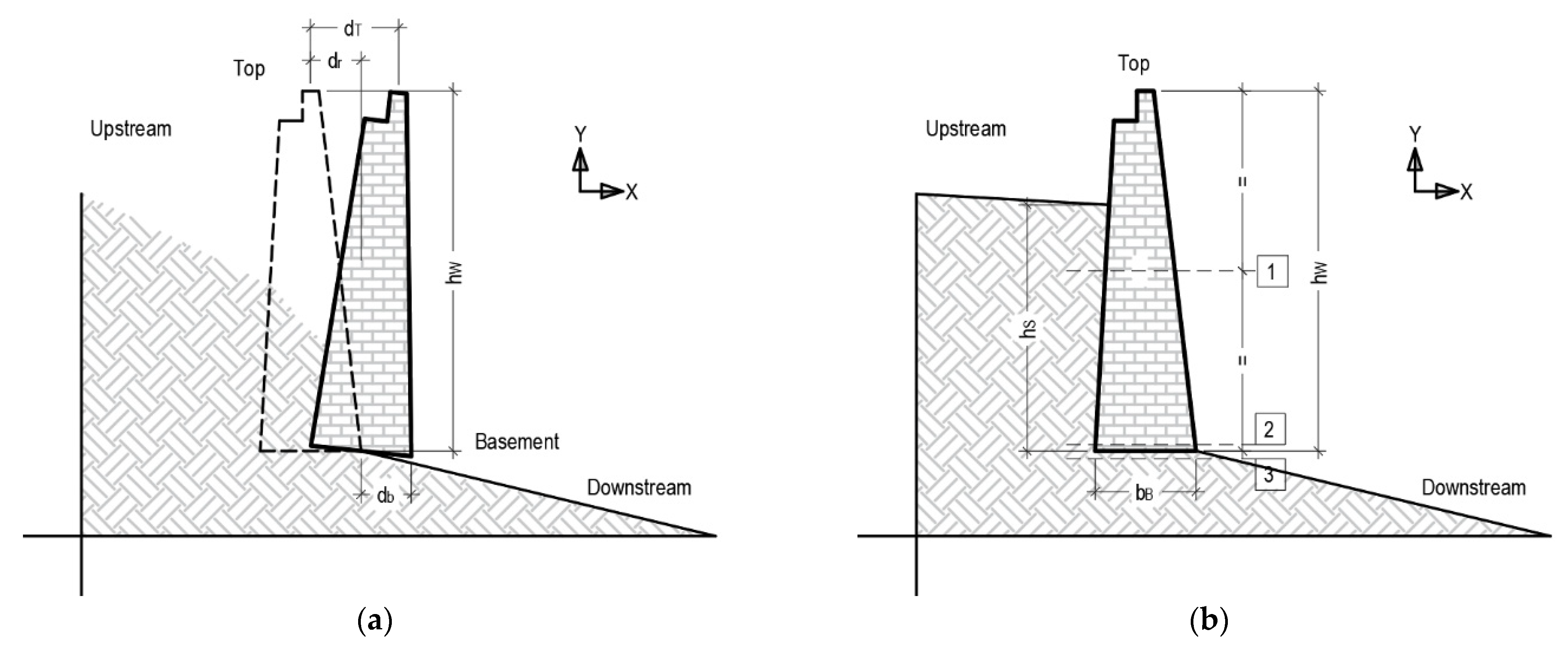
2. Case Study
- b average thickness of the wall.
- hw height of the wall, including the presence of railings.
- hs height of the backfill soil.
3. Analytical Assessments of Seismic Vulnerability
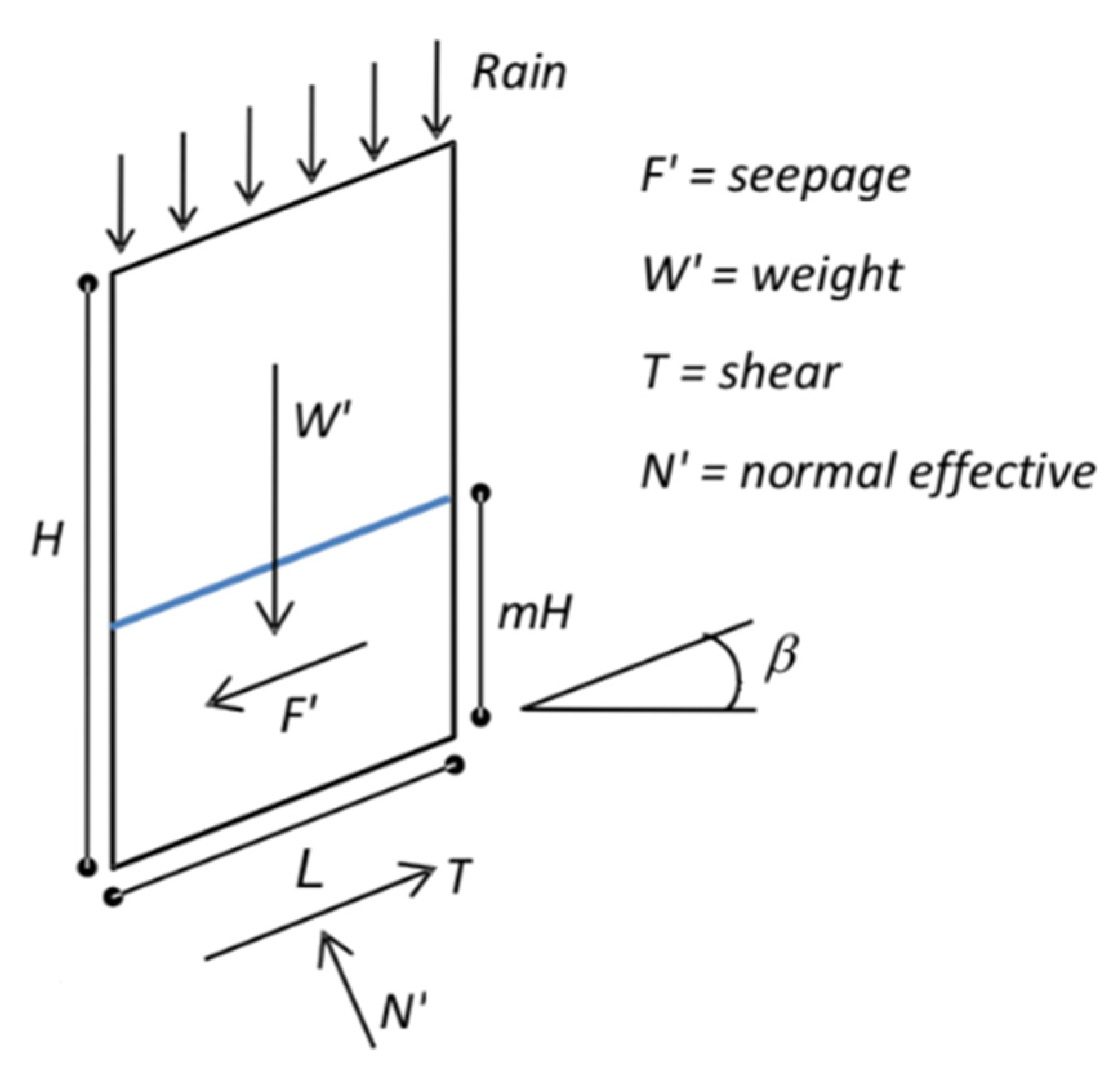
3.1. Moisture Effect
- h height of rainfall
- H height of the soil interested by the rainfall
- β* capacity of imbibition or percentage of filtered rain
- n soil porosity
- Sr saturation grade.
- Sr0 initial saturation grade
- β capacity of imbibition
- h height of rain.
- c’ψ initial apparent cohesion (Fredlund and Rahardjo) [69].
- α homogenization coefficient, here assumed as equal to 3, 40 [30].
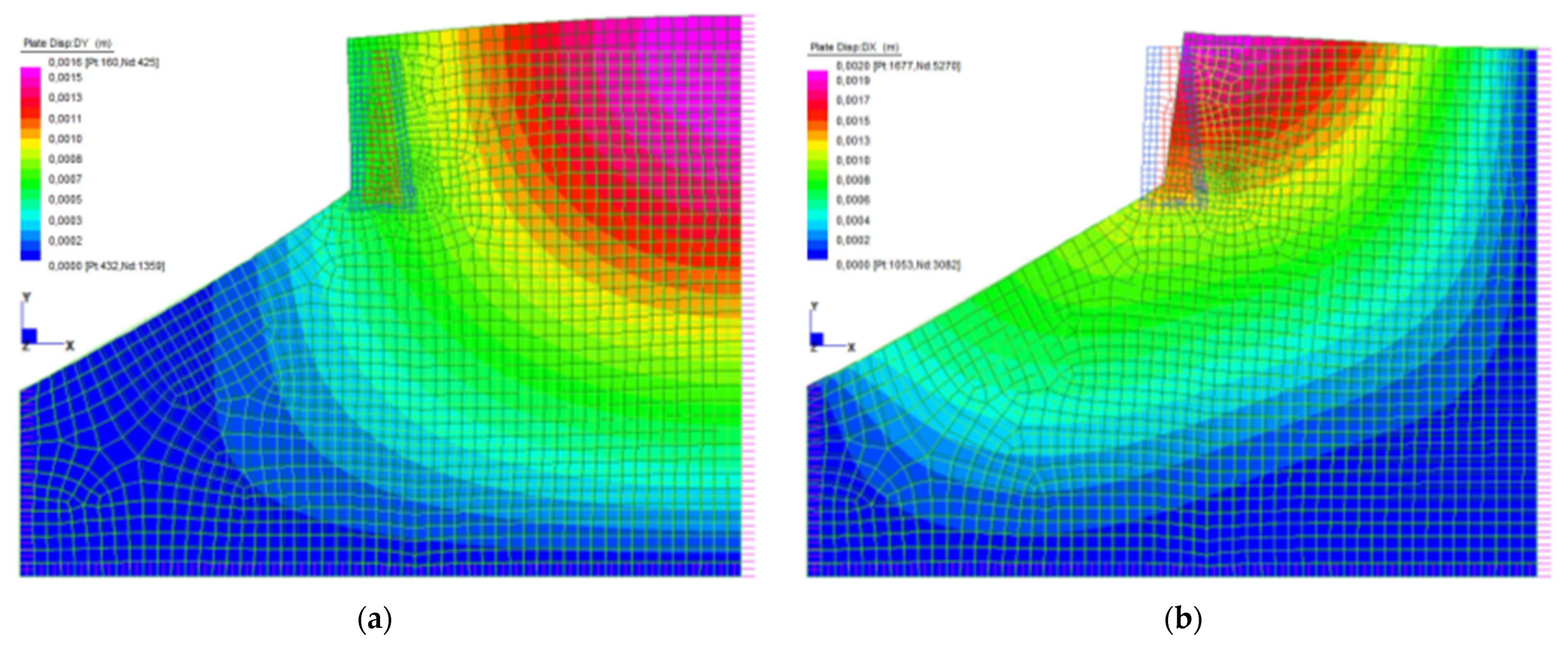
3.2. Seismic Analysis
4. Results
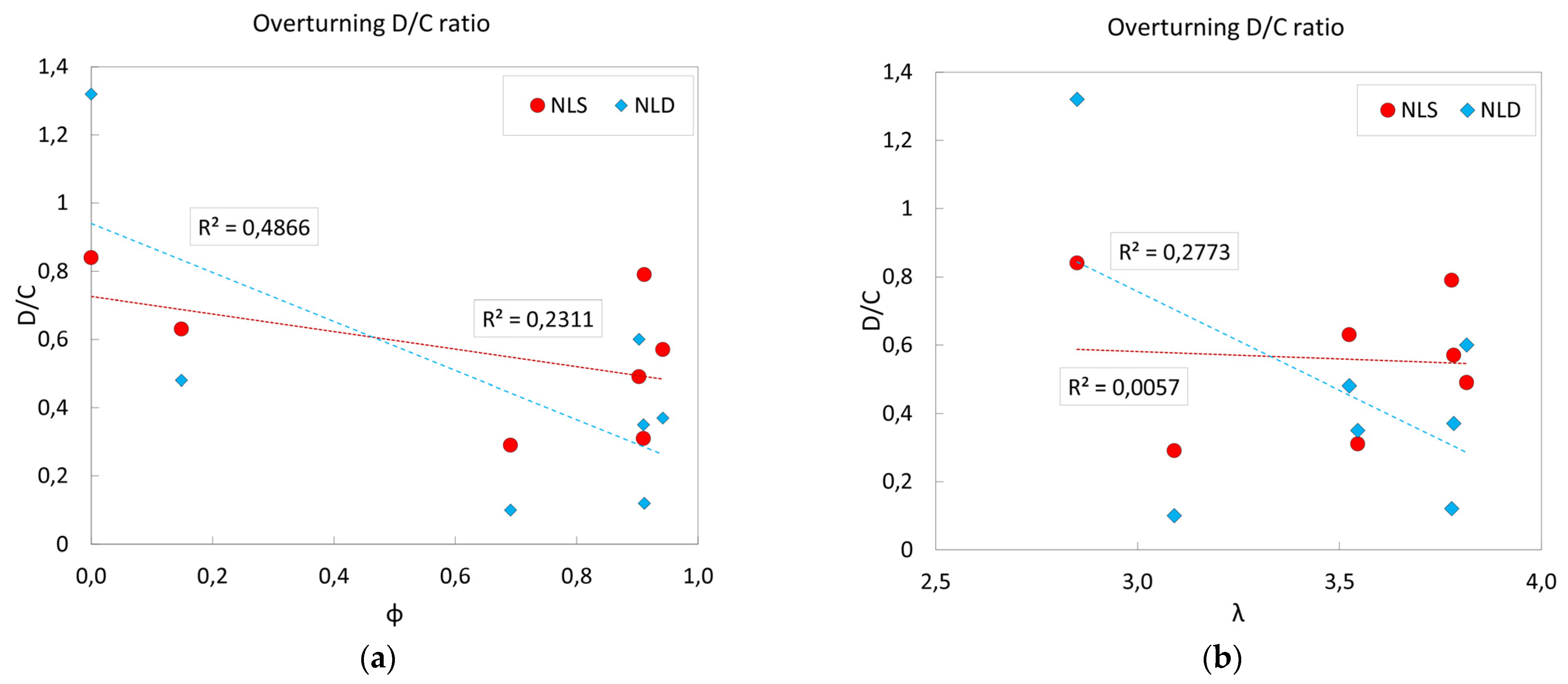
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreini, M.; de Falco, A.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Collapse of the Historic City Walls of Pistoia (Italy): Causes and Possible Interventions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Civil Structures: Selected Peer Reviewed Papers from the 3rd International Conference on Civil Engineering, Architecture and Building Materials (CEABM 2013), Jinan, China, 24–26 May 2013; Trans Tech Publication: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1389–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Andreini, M.; De Falco, A.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Recenti eventi di crollo in mura storiche urbane. In Proceedings of the Convegno di Ingegneria Forense, Crolli, Affidabilità Strutturale e Consolidamento (IF CRASC’15), Rome, Italy, 14–16 May 2015; pp. 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- De Falco, A.; Giresini, L.; Ruschi, P.; Sassu, M. Il Crollo Delle Mura Urbane Di Pistoia: Cause e Possibili Interventi. In Proceedings of the II Convegno di Ingegneria Forense v Convegno su Crolli, Affidabilità Strutturale, Consolidamento (IF CRASC’12), Pisa, Italy, 15–17 November 2012; pp. 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolin, C. Preservation of Cultural Heritage and Resources Threatened by Climate Change. Geosciences 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissner, J.; Kilian, R.; Kotova, L.; Jacob, D.; Mikolajewicz, U.; Broström, T.; Ashley-Smith, J.; Schellen, H.L.; Martens, M.; Schijndel, J.; et al. Climate for Culture: Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Future Indoor Climate in Historic Buildings Using Simulations. Herit. Sci. 2015, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassu, M.; Andreini, M.; de Falco, A.; Giresini, L.; Puppio, M.L. Structural Protection after Landslide Phenomena: A Case Study in Northern Italy. In Civil Engineering and Urban Planning IV, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Urban Planning, CEUP 2015, Beijing, China, 25–27 July 2015; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppio, M.L.; Vagaggini, E.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Large-Scale Survey Method for the Integrity of Historical Urban Walls: Application to the Case of Volterra (Italy). Procedia Struct. Integr. 2020, 28, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, I.; Lagüela, S.; Fang, Q.; Arias, P. Introduction of the combination of thermal fundamentals and Deep Learning for the automatic thermographic inspection of thermal bridges and water-related problems in infrastructures. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 2022, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, M.; Giresini, L.; de Falco, A.; Sassu, M. Landslide Phenomena after Rainfalls in the Recent Case of Tellaro (Italy). In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Urban Planning, Beijing, China, 25–27 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R. Experimental Analysis and Modelling of Shallow Landslides. Landslides 2007, 4, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagaggini, E.; Ferrini, M.; Sassu, M.; Puppio, M.L. Modelling of Moisture Effect in Safety Evaluation of Soil-Interacting Masonry Wall Structures. In Computational Science and Its Applications, Proceedings of the 21st International Conference (ICCSA 2021), Cagliari, Italy, 13–16 September 2021; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12950, pp. 220–234. [Google Scholar]
- Santarsiero, G.; Masi, A.; Picciano, V.; Digrisolo, A. The Italian Guidelines on Risk Classification and Management of Bridges: Applications and Remarks on Large Scale Risk Assessments. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A.; Sousa, H.S.; Puppio, M.L.; Giresini, L.; Matos, J.C.; Sassu, M. Method for Sustainable Large-Scale Bridges Survey. In Proceedings of the IABSE Symposium, Guimaraes 2019: Towards a Resilient Built Environment Risk and Asset Management, Guimaraes, Portugal, 27–29 March 2019; pp. 1034–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Sassu, M.; Giresini, L.; Puppio, M.L. Failure Scenarios of Small Bridges in Case of Extreme Rainstorms. Sustain. Resilient Infrastruct. 2017, 2, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppio, M.L.; Novelli, S.; Sassu, M. Failure Evidences of Reduced Span Bridges in Case of Extreme Rainfalls the Case of Livorno. Frat. Ed Integrita Strutt. 2018, 12, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A.; Sousa, H.S.; Matos, J.C.; Puppio, M.L.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Risk Management for Bridges: A Case Study of Unforeseen Failure Mode. In Proceedings of the IABSE Conference, Seoul 2020: Risk Intelligence of Infrastructures, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 9–10 November 2020; pp. 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A.; Puppio, M.L.; Sousa, H.S.; Giresini, L.; Matos, J.C.; Sassu, M. Detour-Impact Index Method and Traffic Gathering Algorithm for Assessing Alternative Paths of Disrupted Roads. J. Transp. Res. Board 2021, 2675, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J.; Woodruff, R.E.; Hales, S. Climate Change and Human Health: Present and Future Risks. Lancet 2006, 367, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, P.; Formichi, P.; Landi, F.; Marsili, F. Influence of Climate Change on Extreme Values of Rainfall. In Proceedings of the 12th International Multi-Conference on Society, Cybernetics and Informatics (IMSCI 2018), Orlando, FL, USA, 8–11 July 2018; Volume 1, pp. 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Vereecken, E.; Roels, S. Review of Mould Prediction Models and Their Influence on Mould Risk Evaluation. Build. Environ. 2012, 51, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiary, E.; Gardoni, P. Probabilistic seismic demand model and fragility estimates for rocking symmetric blocks. Eng. Struct. 2016, 114, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angela, D.; Magliulo, G.; Cosenza, E. Towards a reliable seismic assessment of rocking components. Eng. Struct. 2021, 230, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, E.G.; Paraskeva, T.S. Dimensionless fragility curves for rocking response to near-fault excitations. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 44, 2015–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busdraghi, P.; Veneri, F.; Iampieri, V. Senigallia Historic Town Walls: Materials and Stability Analyses. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 2, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Casapulla, C.; Giresini, L.; Argiento, L.U.; Maione, A. Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis of Rocking Masonry Corners Using Rigid Macro-Block Modeling. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2019, 19, 1950137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarino, F.; Oliveira, D.V.; Giresini, L. Wall-to-Horizontal Diaphragm Connections in Historical Buildings: A State-of-the-Art Review. Eng Struct 2019, 199, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giresini, L.; Solarino, F.; Paganelli, O.; Oliveira, D.V.; Froli, M. ONE-SIDED Rocking Analysis of Corner Mechanisms in Masonry Structures: Influence of Geometry, Energy Dissipation, Boundary Conditions. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 123, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, M.; de Falco, A.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Structural Damage in the Cities of Reggiolo and Carpi after the Earthquake on May 2012 in Emilia Romagna. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2014, 12, 2445–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, M.; de Falco, A.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Mechanical Characterization of Masonry Walls with Chaotic Texture: Procedures and Results of In-Situ Tests. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2014, 8, 376–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, M.; Pintucchi, B. A Review of Research on Seismic Behaviour of Irregular Building Structures since 2002. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2008, 6, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppio, M.L.; Giresini, L.; Doveri, F.; Sassu, M. Structural Irregularity: The Analysis of Two Reinforced Concrete (r.c.) Buildings. Eng. Solid Mech. 2019, 7, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassu, M.; Puppio, M.L.; Mannari, E. Seismic Reinforcement of a R.C. School Structure with Strength Irregularities throughout External Bracing Walls. Buildings 2017, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppio, M.L.; Pellegrino, M.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Effect of Material Variability and Mechanical Eccentricity on the Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Reinforced Concrete Buildings. Buildings 2017, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassu, M.; Giresini, L.; Bonannini, E.; Puppio, M.L. On the Use of Vibro-Compressed Units with Bio-Natural Aggregate. Buildings 2016, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giresini, L.; Puppio, M.L.; Taddei, F. Experimental Pull-out Tests and Design Indications for Strength Anchors Installed in Masonry Walls. Mater. Struct. 2020, 53, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borri, A.; Corradi, M.; de Maria, A.; Sisti, R. Calibration of a Visual Method for the Analysis of the Mechanical Properties of Historic Masonry. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2018, 11, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, P.B.; Mendes, N.; Ramos, L.F.; Oliveira, D.V. Analysis of Masonry Structures without Box Behavior. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2011, 5, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppio, M.L.; Giresini, L. Estimation of Tensile Mechanical Parameters of Existing Masonry through the Analysis of the Collapse of Volterra’s Urban Walls. Frat. Ed Integrità Strutt. 2019, 13, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantò, B.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M.; Caliò, I. Non-Linear Modeling of Masonry Churches through a Discrete Macro-Element Approach. Earthq. Struct. 2017, 12, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppio, M.L.; Vagaggini, E.; Giresini, L.; Sassu, M. Landslide Analysis of Historical Urban Walls: Case Study of Volterra, Italy. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2021, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Skalomenos, K.; Zhang, D. Seismic fragility analysis of masonry structures considering the effect of mainshock-aftershock sequences. Eng. Struct. 2023, 275, 115287, ISSN 0141-0296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansoni, C.; da Silva, L.C.M.; Marques, R.; Pampanin, S.; Lourenço, P.B. SLaMA-URM method for the seismic vulnerability assessment of UnReinforced Masonry structures: Formulation and validation for a substructure. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105487, ISSN 2352-7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isık, E.; Harirchian, E.; Arkan, E.; Avcil, F.; Günay, M. Structural Analysis of Five Historical Minarets in Bitlis (Turkey). Buildings 2022, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Khadka, S.S. Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Old Brick Masonry Buildings: A Case Study of Dhulikhel. In Recent Trends in Wave Mechanics and Vibrations; Dimitrovová, Z., Biswas, P., Gonçalves, R., Silva, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malomo, D.; DeJong, M.J. A Macro-Distinct Element Model (M-DEM) for simulating in-plane/out-of-plane interaction and combined failure mechanisms of unreinforced masonry structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 51, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar for Crustal Deformation Analysis, with Application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Gili, J.A.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Corominas, J.; Serral, D. Interferometric SAR Monitoring of the Vallcebre Landslide (Spain) Using Corner Reflectors. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasa, L.; Corsini, G.; Diani, M.; Libera Battagliere, M.; Sassu, M.; Puppio, M.L. Territorial Scale Monitoring of Civil Infrastructures through Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Natural Hazards & Infrastructure (ICONHIC 2022), Athens, Greece, 5–7 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Budillon, A.; Schirinzi, G. Remote Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure Based on TomoSAR. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Porcu, M.C.; Lundgren, P.; Soccodato, F.; Salzer, J.; Fielding, E.; Burgmann, R.; Milillo, G.; Perissin, D.; Biondi, F. The ongoing destabilization of the Mosul dam as observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 6279–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łacny, Ł.; Ścisło, Ł.; Guinchard, M. Application of Probabilistic Power Spectral Density Technique to Monitoring the Long-Term Vibrational Behaviour of CERN Seismic Network Stations. Vib. Phys. Syst. 2020, 31, 2020311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montisci, A.; Porcu, M.C. A Satellite Data Mining Approach Based on Self-Organized Maps for the Early Warning of Ground Settlements in Urban Areas. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, Y.; Chen, W.; Kang, D.; Zhang, C. Rapid mapping of seismic intensity assessment using ground motion data calculated from early aftershocks selected by GIS spatial analysis. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martakis, P.; Reuland, Y.; Imesch, M.; Chatzi, E. Reducing uncertainty in seismic assessment of multiple masonry buildings based on monitored demolitions. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 4441–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazizi, A.H.; Tahghighi, H. Influence of soil–structure interaction on seismic demands of historic masonry structure of Kashan Grand Bazaar. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 21, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaydin, M.; Erturk, E.; Genc, A.F.; Okur, F.Y.; Altunisik, A.C.; Tavsan, C. FE model updating and seismic performance evaluation of a historical masonry clock tower. Earthq. Struct. 2022, 22, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, P.; Caliò, I.; Fiorini, N.; Occhipinti, G.; Spina, D.; Tombari, A. Seismic response of nonlinear soil-structure interaction systems through the Preisach formalism: The Messina Bell Tower case study. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 3485–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunişik, A.C.; Genç, A.F.; Ertürk, E.; Günaydin, M.; Okur, F.Y.; Sevİm, B. Soil–Structure Interaction and Earthquake Input Models Effect on the Structural Response of the Santa Maria Church and Guesthouse Building. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022. Published online 29 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drougkas, A.; Verstrynge, E.; Szekér, P.; Heirman, G.; Bejarano-Urrego, L.-E.; Giardina, G.; Van Balen, K. Numerical Modeling of a Church Nave Wall Subjected to Differential Settlements: Soil-Structure Interaction, Time-Dependence and Sensitivity Analysis. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2020, 14, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Azadi, M.R.E.; Hoveidaie, N. Assessing Seismic Behavior of a Masonry Historic Building considering Soil-Foundation-Structure Interaction (Case Study of Arge-Tabriz). Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2020, 14, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piro, A.; de Silva, F.; Parisi, F.; Di Santolo, A.S.; Silvestri, F. Effects of soil-foundation-structure interaction on fundamental frequency and radiation damping ratio of historical masonry building sub-structures. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 1187–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, C.J. Soil-Structure Interaction Vol. 3 Influence of Ground Water; NUREG/CR-4588 BNL-NUREG-51983 Vol. 3; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez, E.; Lopez-Caballero, F.; Modaressi-Farahmand-Razavi, A. Inelastic dynamic soil-structure interaction effects on moment-resisting frame buildings. Eng. Struct. 2013, 51, 166–177, ISSN 0141-0296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liratzakis, A.; Tsompanakis, Y. Impact of Soil Saturation Level on the Dynamic Response of Masonry Buildings. Front. Built Environ. 2018, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalicata, L.M.; Rotisciani, G.M.; Desideri, A.; Casini, F.; Thorel, L. Physical modelling of piles under lateral loading in unsaturated soils. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Unsaturated Soils (E-UNSAT 2020), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R. Modelling Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides at Different Scales Using SLIP—Part I. Procedia Eng. 2016, 158, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R. Modelling Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides at Different Scales Using SLIP—Part II. Procedia Eng. 2016, 158, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Kuwano, J.; Kuwano, R. Effects of Saturation on Shear Strength of Soils. Soils Found. 1991, 31, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.; Rahardjo, H. Soil Mechanics for Unsatured Soils; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R.; Terrone, A. Application of the SLIP Model. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 9, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R.; Losi, G.L. Rainfall-Induced Shallow Landslides: A Model for the Triggering Mechanism of Some Case Studies in Northern Italy. Landslides 2009, 6, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, L. SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS PROGRAM, Version 5.1; SSAP 5.1(2022); Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí: San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1998-3:2005; Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance2014–Part 3: Assessment and Retrofitting of Buildings. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- Borselli, L.; Castelli, G.; Secchi, G.; Nsabiyumva, J.; Preti, F. Optimal Design of Terraced Landscapes: Sensitivity Analysis of Geomechanical and Bio-Mechanical Parameters. In Proceedings of the International Forum on Land Degradation, Soil Conservation and Sustainable Development (LASOSU 2021), Dalian, China, 21–23 August 2021; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Straus7 Release 2.4. Available online: https://www.hsh.info/MainR24_IE_Civile.html (accessed on 10 February 2021).







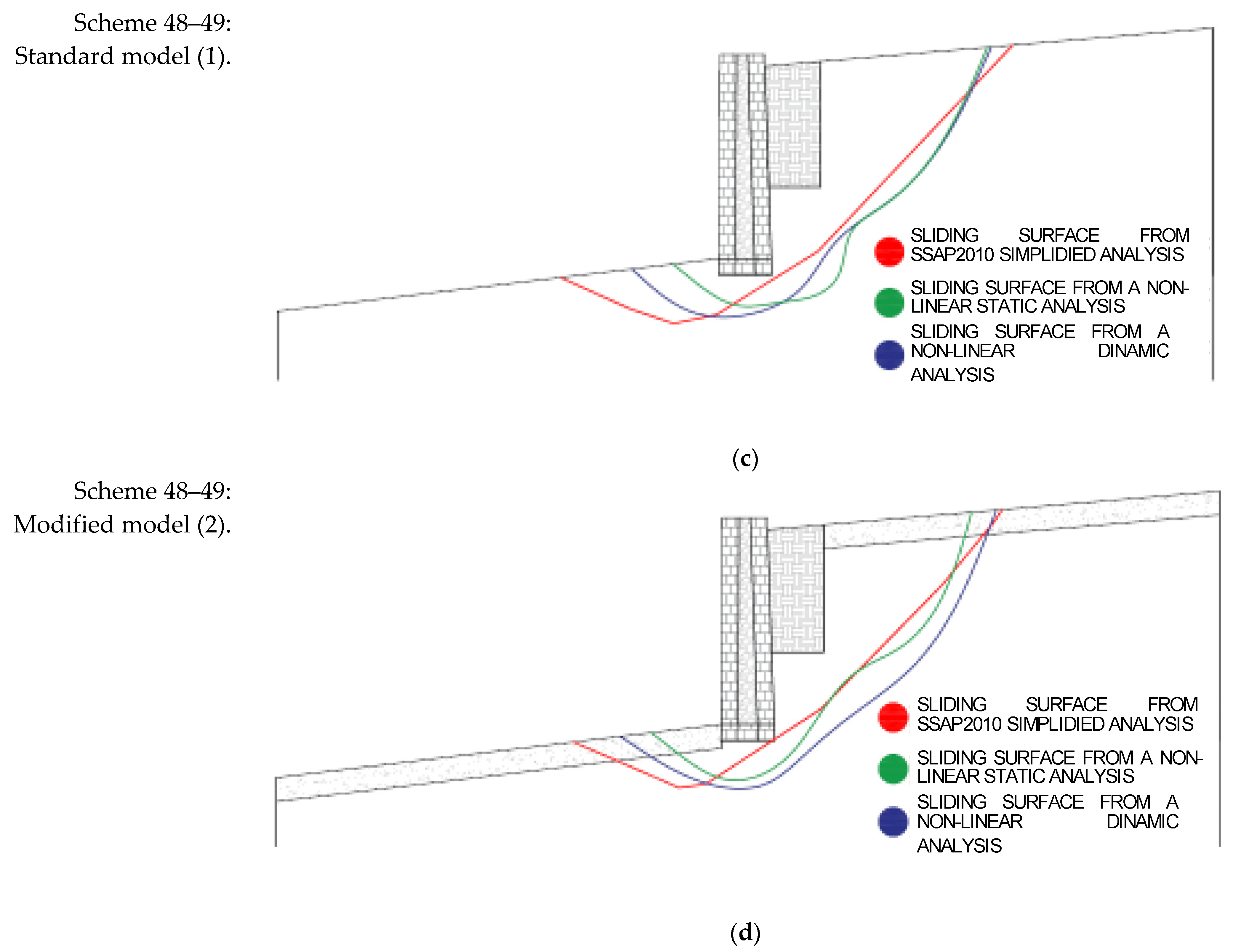

| Section | Sketch | Pictures |
|---|---|---|
| 32–33 λ = 3.81 φ= 0.90 | 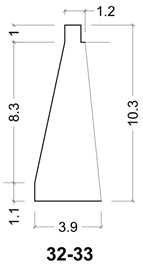 |  |
| 48–49 λ = 3.78 φ= 0.94 | 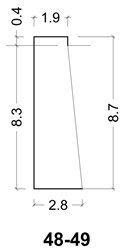 |  |
| 50 λ = 2.85 φ= 0.00 | 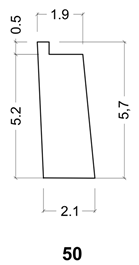 |  |
| 61–62 λ = 3.52 φ= 0.15 | 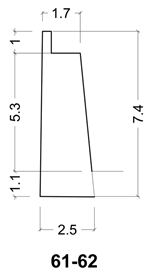 |  |
| 71–72 λ = 3.09 φ= 0.69 |  |  |
| 87 λ = 3.55 φ= 0.91 |  |  |
| 92–93 λ = 3.78 φ= 0.9 |  |  |
| dSLCg | dSLV | dSLD | dSLI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incipient collapse | 0.9 × dSLCg | hw/100 | Expert judgement |
| Model | |
|---|---|
| (a) standard | (b) with imbibition |
| Uniform soil in dry conditions. | Stratum of saturated soil with a depth equal to 1.00 m and uniform soil |
| Foot print S | Foot print I |
| Combination 1 | Combination 2 | Combination 3 | Combination 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ax | +ax | +ax | −ax | −ax |
| ay | +ay | −ay | +ay | −ay |
| Section | λ | φ | Δµ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32–33 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 0.50 |
| 48–49 | 3.8 | 0.9 | −0.23 |
| 50 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 5.83 |
| 61–61 | 3.5 | 0.1 | 1.00 |
| 71–72 | 3.1 | 0.7 | 0.75 |
| 87 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 1.50 |
| 92–93 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Concu, G.; Deligia, M.; Sassu, M. Seismic Analysis of Historical Urban Walls: Application to the Volterra Case Study. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8020018
Concu G, Deligia M, Sassu M. Seismic Analysis of Historical Urban Walls: Application to the Volterra Case Study. Infrastructures. 2023; 8(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleConcu, Giovanna, Mariangela Deligia, and Mauro Sassu. 2023. "Seismic Analysis of Historical Urban Walls: Application to the Volterra Case Study" Infrastructures 8, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8020018
APA StyleConcu, G., Deligia, M., & Sassu, M. (2023). Seismic Analysis of Historical Urban Walls: Application to the Volterra Case Study. Infrastructures, 8(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8020018