Experimental Insight into the Containment of Plastic Waste in Cement-Stabilised Soil as a Road Pavement Layer Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Methods
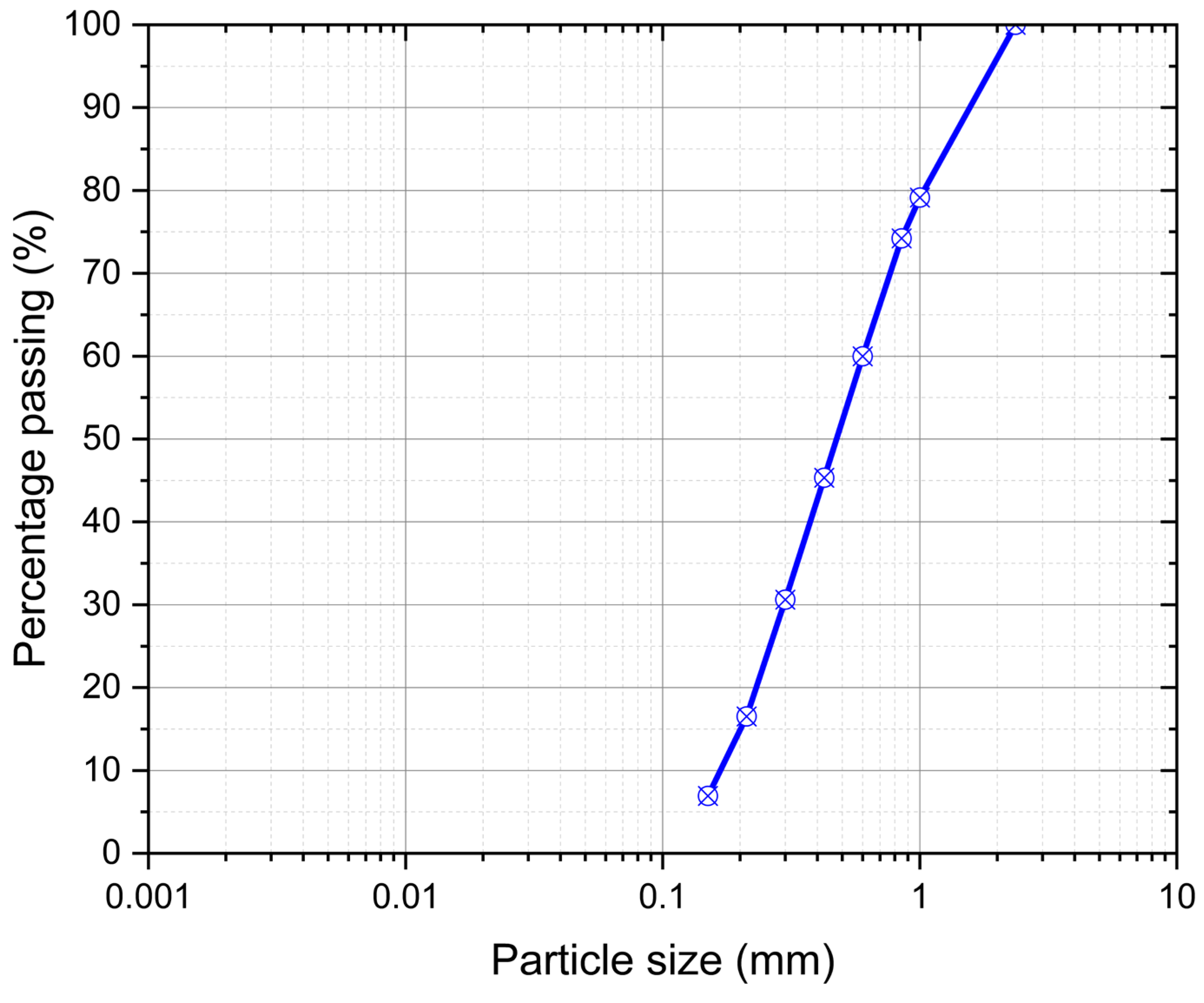
2.3. Geotechnical Properties of Natural Soil
3. Results and Discussion
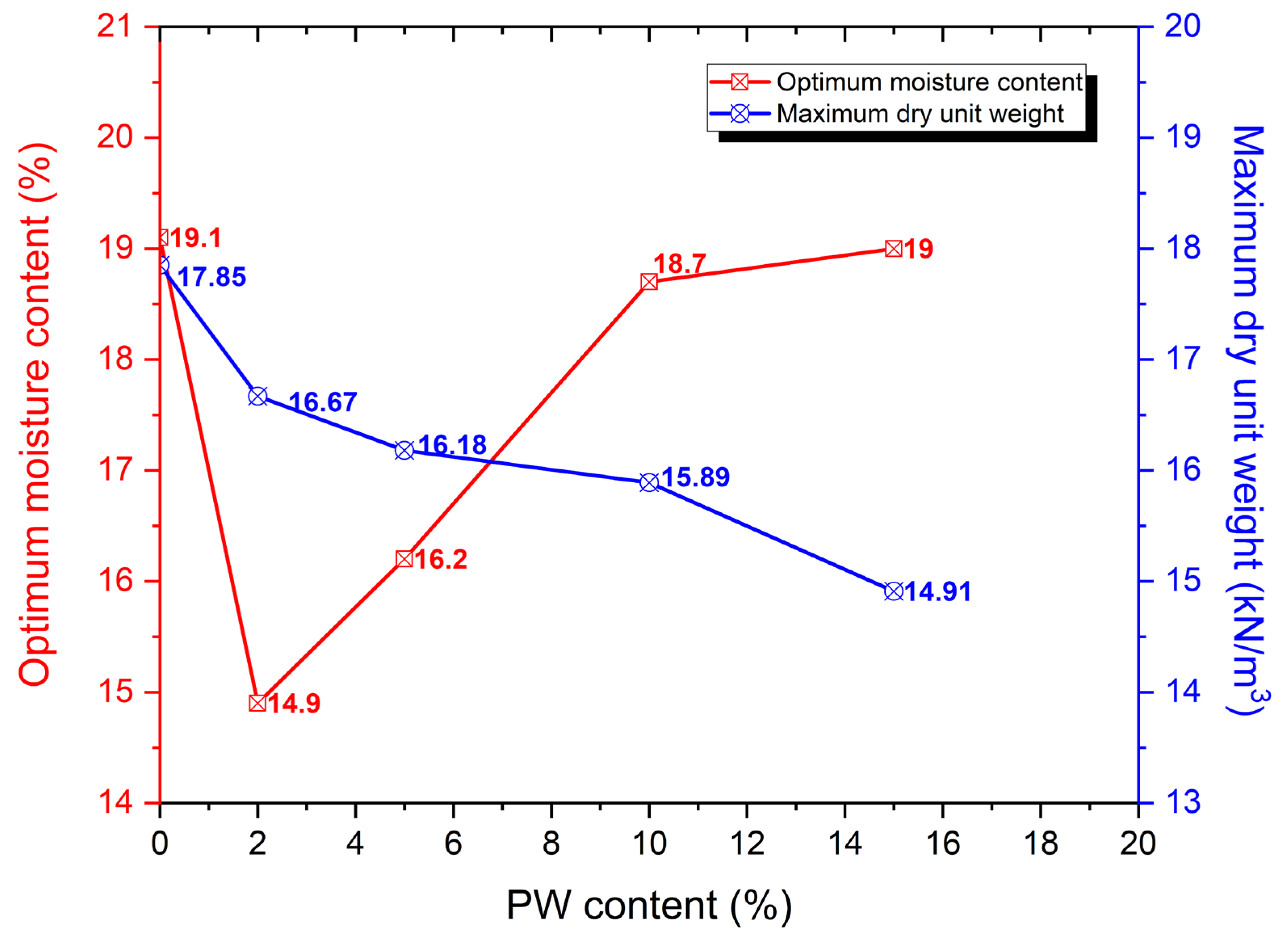
3.1. Compaction Characteristics
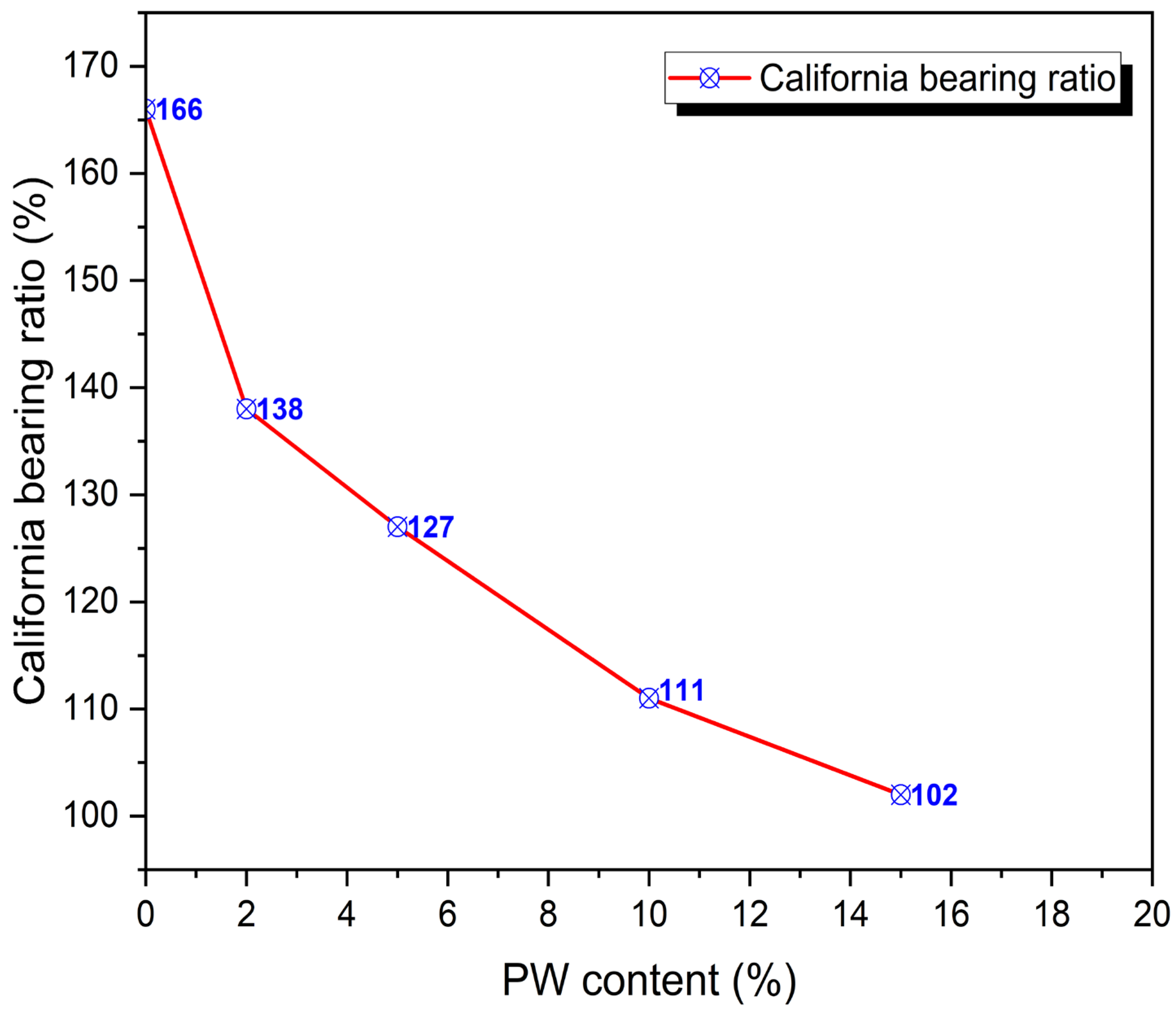
3.2. The California Bearing Ratio (CBR)
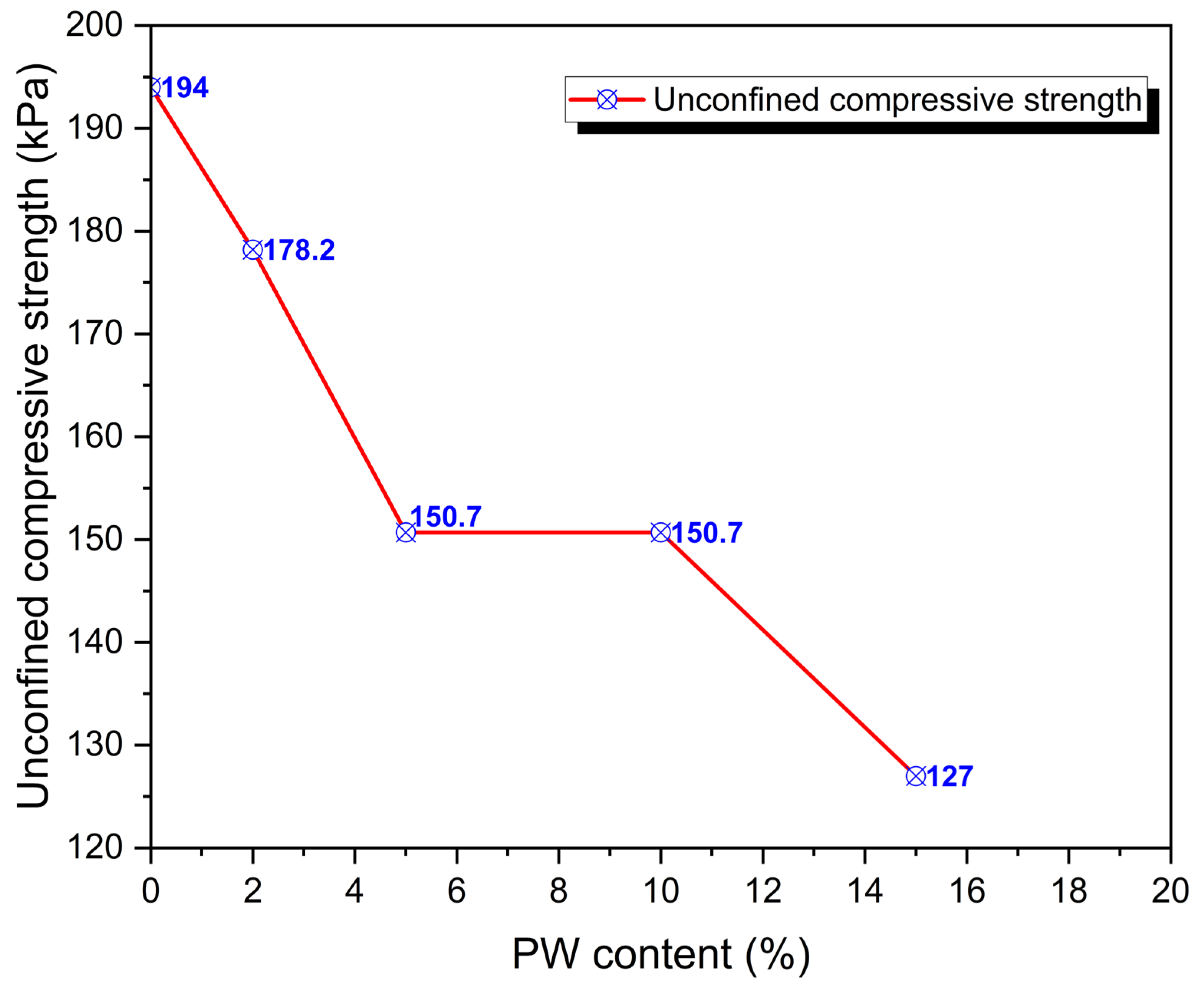
3.3. The Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS)
4. Conclusions
- The Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) characterises the soil as well-graded sand (SW), while the AASHTO Classification System classifies it as belonging in group A-2-6.
- The maximum dry unit weight, CBR and UCS increased when cement was applied to natural soil. This is attributed to chemical hydration during the reaction between cement and water, which gives rise to additional materials (C-S-H and C-A-H) that bound particles together and enhance strength. The cementing of soil particles, which played a vital role in enhancing its strength on the addition of cement, may have been activated by the pozzolanic reaction between the cement and soil particles.
- PW addition to the cement-stabilised mix at 2, 5, 10, and 15% by weight brings about a reduction in soil strength as PW content increased. This is due to a reduction in the friction angle and maximum dry density. The increase in the plastic content in the soil easily gives rise to shear deformation, causing it to fail under strain.
- The results obtained suggest that the cement-stabilised sample with no amount of PW displayed the highest strength when compared to the cement-stabilised samples with PW. However, the soil with 10% cement and 2% PW has a higher strength when compared to all the soil–cement–PW mixtures; and does not adversely affect the geotechnical properties of the cement-stabilised mix.
- The various samples with PW are suitable for use as subgrade, sub-base and base course materials, as they meet the strength requirements based on the Nigerian General Specifications for CBR. However, the soil with 10% cement and 2% PW is recommended since it performed better than the other soil–cement–PW mixtures.
- PW should be added optimally to stabilised soils to prevent a significant loss in durability and strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akinwumi, I.I.; Domo-Spiff, A.H.; Salami, A. Marine Plastic Pollution and Affordable Housing Challenge: Shredded Waste Plastic Stabilized Soil for Producing Compressed Earth Bricks. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2019, 11, e00241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoyera, P.O.; Adesina, A. Plastic Wastes to Construction Products: Status, Limitations and Future Perspective. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 12, e00330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, D.; Kang, S.Y.; Ma, G.; Oh, H.J. Application of Waste Plastic Films in Road Infrastructure and Construction. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 756723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, I.; Bagordo, F.; Grassi, T.; Panico, A.; De Donno, A. Occurrence of Microplastics in Tap and Bottled Water: Current Knowledge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Global Plastics Outlook Database: Policy Scenarios to 2060. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/newsroom/global-plastic-waste-set-to-almost-triple-by-2060.htm (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Darshan, R.; Gururaja, S. Design and fabrication of crusher machine for plastic wastes. Int. J. Mech. Product. Eng. 2017, 5, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Blettler, E.; Abrial, F.; Sivri, N.; Espinola, L. Freshwater Plastic Pollution: Recognizing Research Biases and Identifying Knowledge Gaps. Water Res. 2018, 143, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kehinde, O.; Ramonu, O.J.; Babaremu, K.O.; Justin, L.D. Plastic Wastes: Environmental Hazard and Instrument for Wealth Creation in Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.A.; Ologbonjaye, I.A.; Awosolu, O.; Alalade, O.E. Public and environmental health effects of plastic wastes disposal: A review. J. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2019, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA). Sustainable Development Challenges, World Economic and Social Survey. E/2013/50/Rev. 1; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rillig, M.C.; Lehmann, A. Microplastic in terrestrial ecosystems. Science 2020, 368, 1430–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lehmann, A.; Yang, G.; Leifheit, E.F.; Rillig, M.C. Effects of Microplastic Fibers on Soil Aggregation and Enzyme Activities Are Organic Matter Dependent. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 650155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of Microplastics in Water and Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundairo, T.O.; Olukanni, D.O.; Akinwumi, I.I.; Adegoke, D.D. A Review on Plastic Waste as Sustainable Resource in Civil Engineering Applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1036, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwaegbulam, C.; Nwannekanma, B.; Gbonegun, V. Environment: Producers’ Responsibility and Plastic Pollution Crisis. Available online: https://guardian.ng/property/producers-responsibility-and-plastic-pollution-crisis/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Evode, N.; Qamar, S.A.; Bilal, M.; Barceló, D.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Plastic Waste and Its Management Strategies for Environmental Sustainability. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 4, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, E.; Duda, P.; Duda, A.; Gorska, N.; Fenicki, A.; Molski, P. Characteristics of plastic waste processing in the modern recycling plant operating in Poland. Energies 2021, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, I.; Jenks, M.J.; Roelands, M.C.; White, R.J.; van Harmelen, T.; de Wild, P.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Beyond mechanical recycling: Giving new life to plastic waste. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15402–15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Worrell, E. Plastic recycling. In Handbook of Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Yanful, E.K.; Bassi, A.S. A review of plastic waste biodegradation. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, L.; Sasao, T.; Compernolle, T.; Van Passel, S.; De Jaeger, S. The effect of waste incineration taxation on industrial plastic waste generation: A panel analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, C.; Li, T.; Løvås, T. Surrogate reaction mechanism for waste incineration and pollutant formation. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 7030–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiounn, T.; Smith, R.C. Advances and approaches for chemical recycling of plastic waste. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierski, M.; Frère, D.; Le Maguer, G.; Bruzaud, S. Why Is There Plastic Packaging in the Natural Environment? Understanding the Roots of Our Individual Plastic Waste Management Behaviours. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharuddin, S.D.A.; Abnisa, F.; Daud, W.M.A.W.; Aroua, M.K. A review on pyrolysis of plastic wastes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shent, H.; Pugh, R.J.; Forssberg, E. A review of plastics waste recycling and the flotation of plastics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1999, 25, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Rani, A.; Khalid, N.; Qamar, S.A.; Bilal, M. Bioconversion of sugarcane molasses waste to high-value exopolysaccharides by engineered Bacillus licheniformis. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Yue, S.; Zhang, X. Insights into spatiotemporal distributions of trace elements in kelp (Saccharina japonica) and seawater of the western Yellow Sea, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Qamar, S.A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Bio-Based Active Food Packaging Materials: Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Petrochemical-Based Packaging Materials. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, P.; Kaur, D.P.; Raj, S.; Sorout, J. Recycling/Reuse of Plastic Waste as Construction Material for Sustainable Development: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 86156–86179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneke, F.I.; Shabangu, C. Green-efficient masonry bricks produced from scrap plastic waste and foundry sand. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 14, e00515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.M.H.; Ali, S.A. Reusing waste plastic bottles as an alternative sustainable building material. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2015, 24, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taafe, J.; O’Sullivan, S.; Rahman, M.E.; Pakrashi, V. Experimental characterization of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) bottle Ecobricks. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Sahat, S.; Hamid, B.; Kaamin, M.; Kesot, M.J.; Wen, L.C.; Xin, L.Y.; Ling, N.P.; Jia Lei, V.S. Application of plastic bottle as a wall structure for green house. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 7617–7621. [Google Scholar]
- Limami, H.; Manssouri, I.; Cherkaoui, K.; Saadaoui, M.; Khaldoun, A. Thermal performance of unfired lightweight clay bricks with HDPE & PET waste plastics additives. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101251. [Google Scholar]
- Limami, H.; Manssouri, I.; Cherkaoui, K.; Khaldoun, A. Study of the suitability of unfred clay bricks with polymeric HDPE & PET wastes additives as a construction material. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 100956. [Google Scholar]
- Alaloul, W.S.; John, V.O.; Musarat, M.A. Mechanical and thermal properties of interlocking bricks utilizing wasted polyethylene terephthalate. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2020, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kognole, R.; Shipkule, K.; Survase, K. Utilization of plastic waste for making plastic bricks. Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev. 2019, 3, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonone, P.; Devalkar, R. Green sustainable bricks made of fly ash and discarded polyethylene waste. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 6509–6516. [Google Scholar]
- Hemalatha, D. Reuse of waste plastics and demolition waste in the development of plastic paver block. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2019, 78, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Tawab, O.F.; Amin, M.R.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Abdel Wahab, M.; Abd El Rahman, E.N. Recycling waste plastic bags as a replacement for cement in production of building bricks and concrete blocks. J. Waste Resour. Recycl. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Seghiri, M.; Boutoutaou, D.; Kriker, A.; Hachani, M.I. The possibility of making a composite material from waste plastic. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, D. Experimental investigation on recycling of plastic wastes and broken glass in to construction material. Int. J. Creat. Res. Thoughts 2018, 6, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; Bhowmik, P.; Shaad, K. Use of waste plastic aggregation in concrete as a constituent material. Progress. Agric. 2016, 27, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.M.; Fatah Ahmed, B.A. Employment the plastic waste to produce the light weight concrete. Energy Procedia 2019, 157, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavhane, A.; Sutar, D.; Soni, S.; Patil, P. Utilisation of E-plastic waste in concrete. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 594–601. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yue, X.; Liu, X.; Tong, Y. Properties of self-compacting lightweight concrete containing recycled plastic particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 84, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Siddique, S.; Gupta, T. Fresh, strength, durability and microstructural properties of shredded waste plastic concrete. Iran J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2019, 43, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrmomtazi, A.; Dolati-Milehsara, S.; Lotfi-Omran, O.; Sadeghi-Nik, A. The Combined Effects of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Particles and Pozzolanic Materials on the Properties of Self-Compacting Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.M.; AL-Soudany, K.Y.; Ahmed, A.A. The Impact of Using Recycled Plastic Fibres on the Geotechnical Properties of Soft Iraqi Soils. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 433, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Neami, M.A.; Rahil, F.H.; Al-Ani, Y.H. Behavior of Cohesive Soil Reinforced by Polypropylene Fiber. Eng. Technol. J. 2020, 38, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, N.H.; Radhi, M.S.; Alsaad, A.J. Ecological Applications of Polyethylene Terephthalate Plastic in Producing Modified Subbase Soil. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1067, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhil, S.H.; Al-Soud, M.S.; Kudadad, R.M. Enhancing the Strength of Clay-Sand Mixture by Discrete Waste Plastic Strips. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2021, 24, 381–391. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, A.; Shaban, A.M.; Almuhanna, R.R. Performance of Lime-Treated Sandy Soils after Sustainable Reinforcement Using Waste Plastic Fibre. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1067, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, M.S. Utilization of Waste Plastic in Geotechnical Engineering Applications in Iraq: A Review. J. Tech. 2021, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.J.A.; Rasul, J.; Samin, M. Effects of Plastic Waste Materials on Geotechnical Properties of Clayey Soil. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotech. 2021, 8, 390–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, A.; Patel, M.S.; Jadhwar, N.B.; Khan, U.; Dhengare, S.W. Investigating the Application of Waste Plastic Bottle as a Construction Material: A Review. J. Adv. Res. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2015, 2, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaria, Y.; Sankhla, R. Use of Waste Plastic in Flexible Pavements-Green Roads. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 5, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkafle, M.H.; Khalifa, N.A. A Review on the Use of Waste Plastic Material in Pavement. Recent Trends Civ. Eng. Built Environ. 2021, 2, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, K.E.; Elghali, L.; Soerby, C.R. Development of New Materials for Secondary and Recycled Aggregates in Highway Infrastructure; TRL Rep. 598; TRL Limited: Crowthorne, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD) Report on Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/newsroom/plastic-pollution-is-growing-relentlessly-as-waste-management-and-recycling-fall-short.htm (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Sukhmanjit, R. A review study on the soil stablization with cement and lime. Int. J. Lat. Res. Eng. Comput. 2017, 5, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.A.; Nasir, H.; Alam, M.; Khan, S.W.; Ahmad, I. Performance of Subgrade Soil Blended with Cement and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9831615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Barua, A.; Chakraborty, S. Soil stabilization using cement as binder and nylon thread as reinforcement. Proc. Int. Conf. Plan. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadir, P.; Ranjbar, N. Clayey soil stabilization using geopolymer and Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solihu, H. Cement Soil Stabilization as an Improvement Technique for Rail Track Subgrade, and Highway Subbase and Base Courses: A Review. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2020, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkis, A.P.; Macid, S. Effect of Cement Amount on CBR Values of Different Soil. Eur. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andavan, M.S.; Nagasai, P. Soil Stabilisation Using Cement. Ann. Romanian Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Diana, W.; Hartono, E.; Muntohar, A.S. The Permeability of Portland Cement-Stabilized Clay Shale. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 650, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambri, N.; Ghazaly, Z. Peat Soil Stabilization Using Lime and Cement. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 34, 01034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, E.A.; Hashim, R.; Mahmud, H.B.; Muntohar, A.S. Stabilization of Residual Soil with Rice Husk Ash and Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, M.; Edeh, E. Stabilization of Ikpayongo Laterite with Cement and Calcium Carbide Waste. Glob. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2015, 20, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amu, O.O.; Fajobi, A.B.; Afekhuai, S.O. Stabilization potential of cement and fly ash mixture on expansive clay soil. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 5, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shahiri, J.; Ghasemi, M. Utilization of Soil Stabilization with Cement and Copper Slag as Subgrade Materials in Road Embankment Construction. Int. J. Transp. Eng. 2017, 5, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Arifin, Y.F.; Rahman, G. Stabilization of Soft Soil with Cement and Palm Kernel Shell Ash Admixture. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 280, 04011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ogirigbo, O.R.; Imafidon, D.; Ehiorobo, J.O. Chemical Stabilization of Deltaic Lateritic Soil Using Cement and Superplasticizer. NIPES J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2021, 3, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalo-Orden, H.; Linares-Unamunzaga, A.; Pérez-Acebo, H.; Díaz-Minguela, J. Advances in the Study of the Behavior of Full-Depth Reclamation (FDR) with Cement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, W.; Núñez, W.P.; Visser, A.T. A review of full-depth reclamation of pavements with Portland cement: Brazil and abroad. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, A.R.; Rahrovan, M. Full-Depth Reclamation Method for Rehabilitation of Streets Pavement in City of Sirjan: Mix Design and Bearing Capacity. J. Civ. Eng. Mater. App. 2020, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Akinwumi, I.I.; Booth, C.A.; Diwa, D.; Mills, P. Cement Stabilisation of Crude-Oil-Contaminated Soil. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 169, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzai, M.; Sharma, A. Soil Stabilization with Brick Kiln Dust and Waste Fiber. Int. J. Innov. Res. Adv. Stud. 2019, 6, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gowthami, D.; Sumathi, R. Expansive Soil Stabilization Using Plastic Fiber Waste Polypropylene. Int. J. Lat. Res. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Harini, V.; Harsha, R.; Dhanalakshmi, S. Effect on Properties of Expansive Soil by Using LDPE Plastic Wastes. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 5, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gangwar, P.; Tiwari, S. Stabilization of Soil with Waste Plastic Bottles. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3802–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayeb, A.; Attom, M. The Use of Shredded Plastic Water Bottles in Soil Stabilization. Eurasia Proc. Sci. Technol. Eng. Math. 2021, 13, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, P.; Kalra, S.; Ramakrishna, G.; Naik, J.S.; Sankar, K.G. An Experimental Study on Soil Properties by Inducing Plastic Strips. Int. J. Mod. Trends Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A. Soil Stabilization using Rice Husk Ash and Cement. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Waldman, W.R.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastic Research Should Embrace the Complexity of Secondary Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7751–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Shi, H. A review of microplastics in table salt, drinking water, and air: Direct human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbalaei, S.; Hanachi, P.; Walker, T.R.; Cole, M. Occurrence, sources, human health impacts and mitigation of microplastic pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36046–36063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Cai, Q. Source, migration and toxicology of microplastics in soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasing, M.; Amelung, W. Plastics in soil: Analytical methods and possible sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradney, L.; Wijesekara, H.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Obadamudalige, N.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kirkham, M.B. Particulate plastics as a vector for toxic trace-element uptake by aquatic and terrestrial organisms and human health risk. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galafassi, S.; Nizzetto, L.; Volta, P. Plastic sources: A survey across scientific and grey literature for their inventory and relative contribution to microplastics pollution in natural environments, with an emphasis on surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Hu, W.; Qin, X.; Yan, C.; Wang, H. The status and distribution characteristics of residual mulching film in Xinjiang, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C. Microplastic in terrestrial ecosystems and the soil? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6453–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, M.C.; Harms, H.; Schlosser, D. Prospects for microbiological solutions to environmental pollution with plastics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8857–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.K.; Raut, S. Microbial degradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE): A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Zhu, C.; Wang, C.; Gu, C. Occurrence and ecological impacts of microplastics in soil systems: A review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benítez, A.; Sanchez, J.J.; Arnal, M.L.; Müller, A.J.; Rodríguez, O.; Morales, G. Abiotic degradation of LDPE and LLDPE formulated with a pro-oxidant additive. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2013, 98, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gui, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Microplastics in the soil-groundwater environment: Aging, migration, and co-transport of contaminants–A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Guo, X.; Gao, S. Review of the artificially-accelerated aging technology and ecological risk of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Gooren, H.; Peters, P.; Salanki, T.; van der Ploeg, M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Geissen, V. Incorporation of microplastics from litter into burrows of Lumbricus terrestris. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Mao, R.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Olesen, K.B.; Borregaard, A.R.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics in urban and highway stormwater retention ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. A critical overview of the analytical approaches to the occurrence, the fate and the behavior of microplastics in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 65, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, S.; Sharma, K.; Sharma, G.; Singh, M.; Chadha, P. Sources, Fate, and Impact of Microplastics in Aquatic Environment. In Emerging Contaminants; Nuro, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-83962-418-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, M.H.; Ovi, F.M.; Akhter, F.; Barua, S.; Ahmed, M.; Nipa, T.J. Improvement of Sub Base Soil Using Sand-Cement Stabilization. Am. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 4, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Genazzini, C.; Giaccio, G.; Ronco, A.; Zerbino, R. Cement-Based Materials as Containment Systems for Ash from Hospital Waste Incineration. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.R.; Venkateswararao, T.; Ram, D.A.S. Use of Lime and Waste Plastic Fibers for Subgrade Stabilization. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2018, 8, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Google Maps. Available online: https://goo.gl/maps/kvzgJz86oASfNtGS9 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- ASTM D2216; Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- ASTM D854; Standard Test Method for Specific Gravity Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM C136; Standard Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D4318; Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit and Plasticity Index of Soils. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000.
- ASTM D2434; Permeability of Granular Soils (Falling Head). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000.
- ASTM D698; Standard Test Method for Compaction Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM D1883; Standard Test Method for California Bearing Ratio (CBR) of Laboratory-Compacted Soils. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM D293; Standard Test Method for Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- Nigerian General Specifications, Roads and Bridges; Federal Ministry of Works: Lagos, Nigeria, 1997.
- Structural Design of Flexible Pavements for Interurban and Rural Roads, TRH; Committee of Land Transport Officials, Ministry of Transport: Pretoria, South Africa, 1996.
- Overseas Road Note 31: A guide to the Structural Design of Bitumen-Surfaced Roads in Tropical and Sub-Tropical Countries; Transport Research Laboratory: Berkshire, UK, 1993.
- Akinwumi, I. Soil Modification by the Application of Steel Slag. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2014, 58, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 197; Cement—Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. BSI: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Bowles, J.E. Engineering Properties of Soils and Their Measurement, 4th ed.; Mc Graw-Hill Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-00-7911-266-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kassa, R.B.; Workie, T.; Abdela, A.; Fekade, M.; Saleh, M.; Dejene, Y. Soil Stabilization Using Waste Plastic Materials. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 10, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Goel, A.; Tangri, A. Stabilization of Subgrade Soil by Using Alccofine and Waste Bottle Plastic Strips. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar]
- Yohanna, P.; Badamasi, A.; Ishola, K.; Odoh, K.C.; Abdulkadir, M.N.; Fwangshak, G.M. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Sisal Fibre and Waste Plastic Strips in Structural Strength Improvement of Tropical Black Clay. J. Eng. Stud. Res. 2022, 28, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Amena, S.; Chakeri, D. A Study on the Effects of Plastic Waste Strips and Lime on Strength Characteristics of Expansive Soil. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusinski, J.; Bhattacharja, S. Effectiveness of Portland cement and lime in stabilizing clay soils. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 1999, 1652, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Kumar, A. Strength Characterization of Cement Stabilized and Fiber Reinforced Clay–Pond Ash Mixes. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2016, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Guney Olgun, C.; Firoozi, A.A.; Baghini, M.S. Fundamentals of Soil Stabilization. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 2017, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, B.S.; Thi, N.N.; Thanh, N.D. An Experimental Study on Unconfined Compressive Strength of Soft Soil-Cement Mixtures with or without GGBFS in the Coastal Area of Vietnam. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, E.; Prabandiyani Retno Wardani, S.; Setyo Muntohar, A. The Effect of Cement Stabilization on the Strength of the Bawen’s Siltstone. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 195, 03012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wardani, S.P.R.; Muntohar, A.S. Perbaikan Tanah, 1st ed.; LP3M: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2018; ISBN 978-602-7577-68-8. [Google Scholar]
- Niyomukiza, J.B.; Bitekateko, A.; Nsemerirwe, J.; Kawiso, B.; Kiwanuka, M. Investigating the Effect of PET Plastic Bottle Strips on the Strength and Compressibility Properties of Clayey Soil. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 894, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.; Kalra, S.; Singh, H. Stabilization of Clayey Soil Using Lime and Plastic Fiber in Sub Grades. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 2118–2123. [Google Scholar]


| Property | % |
|---|---|
| Lime (CaO) | 60.87 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | 5.36 |
| Soluble silica (SiO2) | 20.55 |
| Iron oxide (Fe2O3) | 4.00 |
| Chloride (Cl2) | <0.1 |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 0.74 |
| Sulphuric anhydride (SO3) | 1.83 |
| Insoluble residue | 2.93 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| AASHTO Classification System | A-2-6 |
| Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) | SW |
| Specific gravity | 2.56 |
| Liquid limit (LL) | 38% |
| Plastic limit (PL) | 21.9% |
| Plasticity index (PI) | 16.11% |
| Natural moisture content | 25% |
| Maximum dry unit weight | 17.0 kN/m3 |
| Optimum moisture content (OMC) | 19.56% |
| Coefficient of permeability | 1.85 × 10−3 cm/s |
| Unsoaked CBR | 1.7% |
| Unconfined compressive strength (qu) | 133.0 kPa |
| S/N | Description | OMC (%) | Maximum Dry Unit Weight (kN/m3) | CBR (%) | UCS (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soil + 10% cement + 0% PW | 19.1 | 17.85 | 166 | 194.0 |
| 2 | Soil + 10% cement + 2% PW | 14.9 | 16.67 | 138 | 178.2 |
| 3 | Soil + 10% cement + 5% PW | 16.2 | 16.18 | 127 | 150.7 |
| 4 | Soil + 10% cement + 10% PW | 18.7 | 15.89 | 111 | 150.7 |
| 5 | Soil + 10% cement + 15% PW | 19.0 | 14.91 | 102 | 127.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akinwumi, I.; Soladoye, O.; Ajayi, V.; Epelle, P. Experimental Insight into the Containment of Plastic Waste in Cement-Stabilised Soil as a Road Pavement Layer Material. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7120172
Akinwumi I, Soladoye O, Ajayi V, Epelle P. Experimental Insight into the Containment of Plastic Waste in Cement-Stabilised Soil as a Road Pavement Layer Material. Infrastructures. 2022; 7(12):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7120172
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkinwumi, Isaac, Oluwatomisin Soladoye, Victor Ajayi, and Promise Epelle. 2022. "Experimental Insight into the Containment of Plastic Waste in Cement-Stabilised Soil as a Road Pavement Layer Material" Infrastructures 7, no. 12: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7120172
APA StyleAkinwumi, I., Soladoye, O., Ajayi, V., & Epelle, P. (2022). Experimental Insight into the Containment of Plastic Waste in Cement-Stabilised Soil as a Road Pavement Layer Material. Infrastructures, 7(12), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7120172









