Highway Rest Area Truck Parking Occupancy Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Case Study from Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Research Gap
1.3. Research Objectives
1.4. Manuscript Structure
2. Materials and Methods
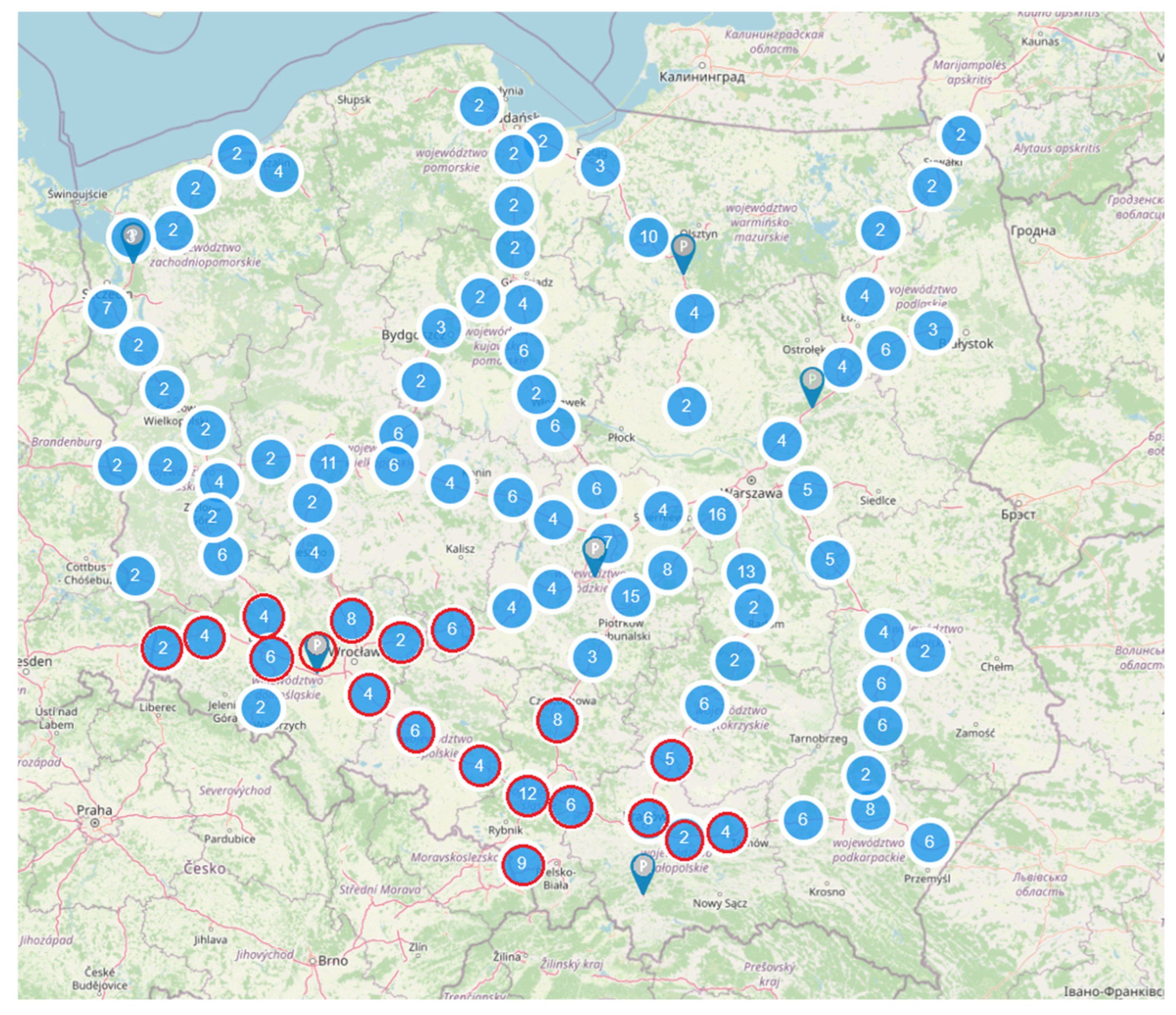
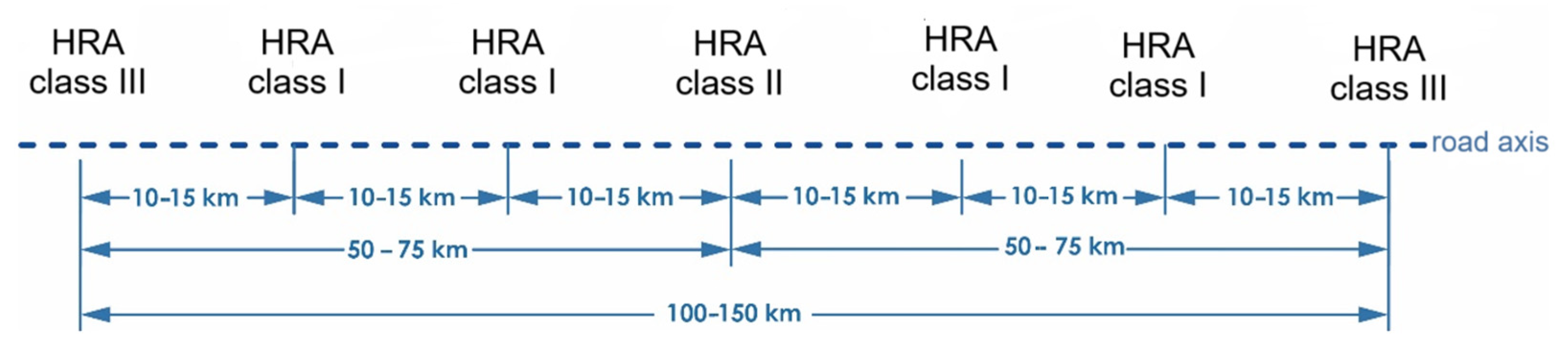
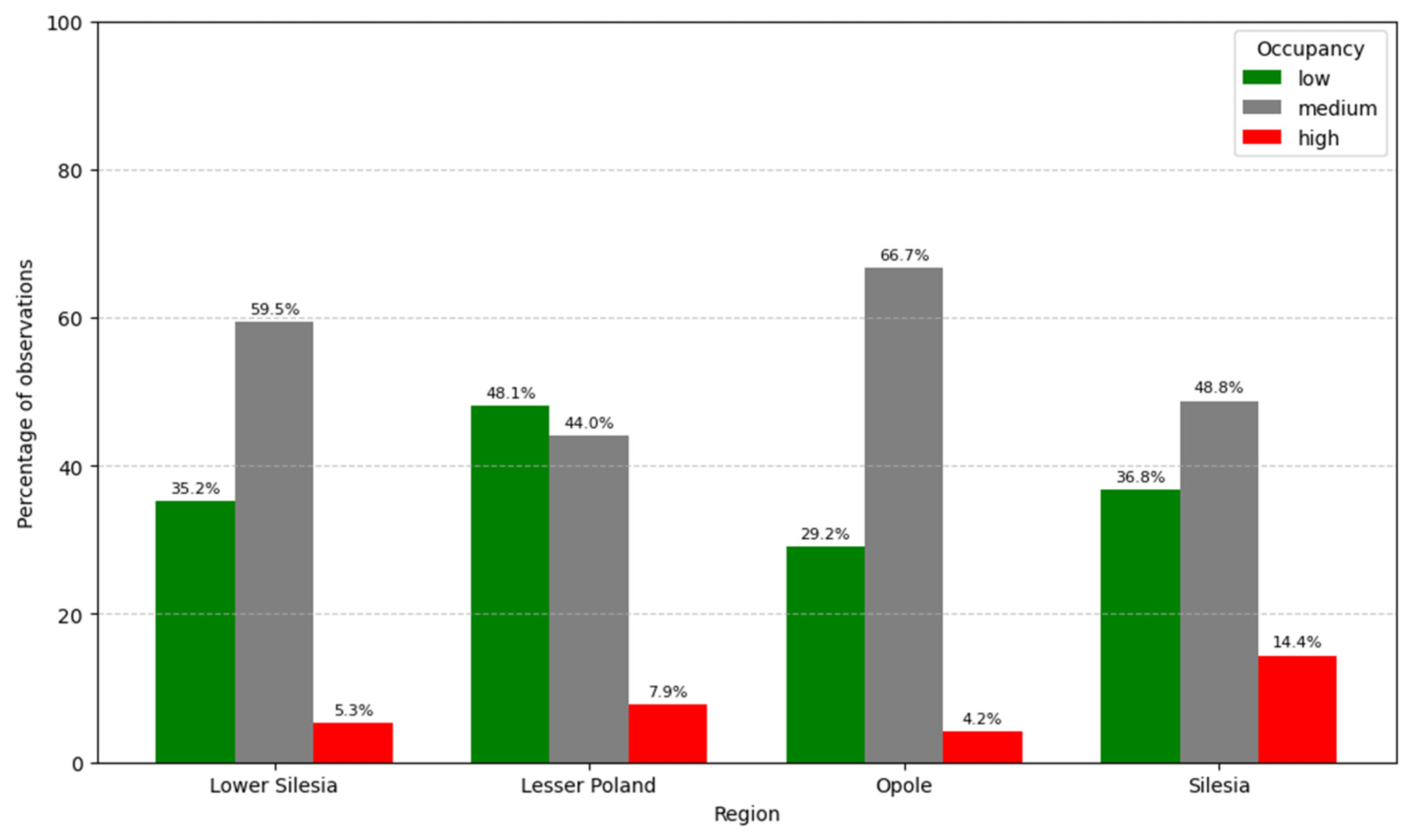
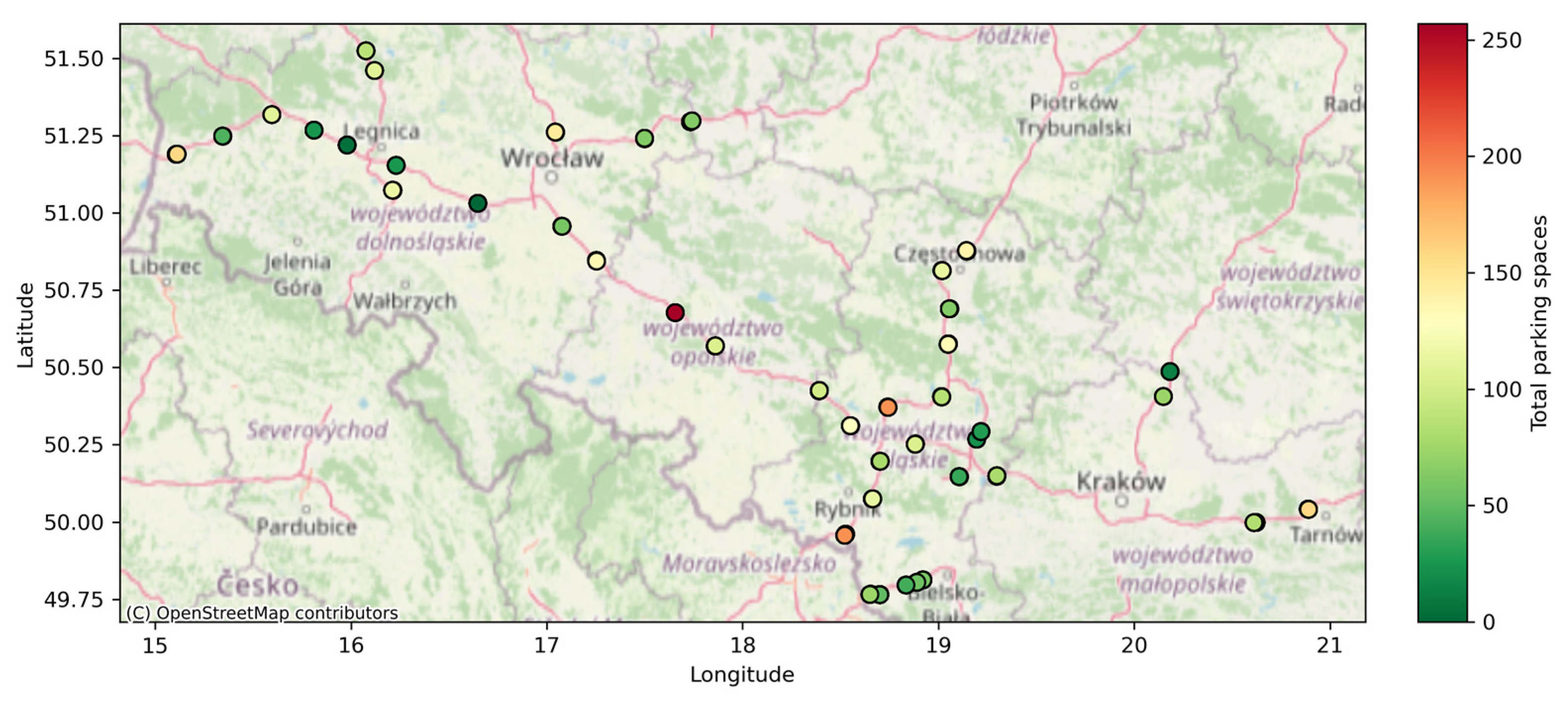
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Research Methodology
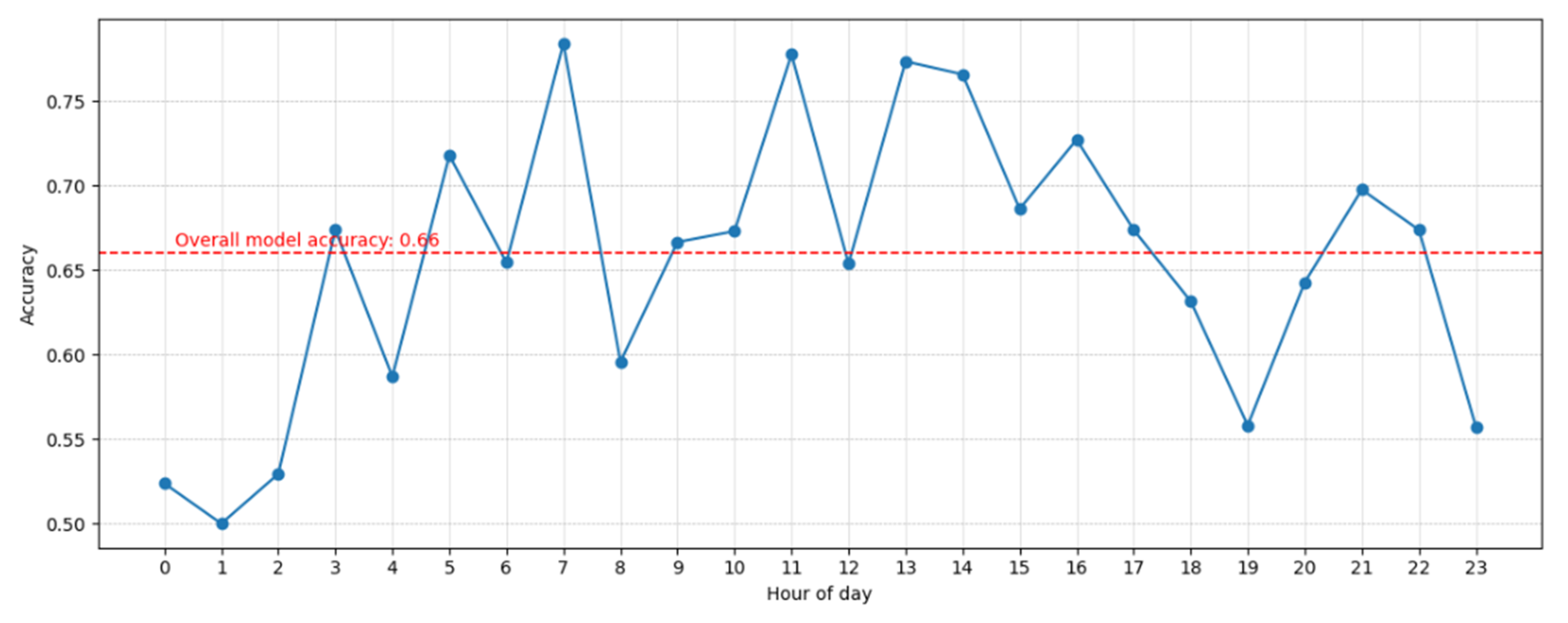
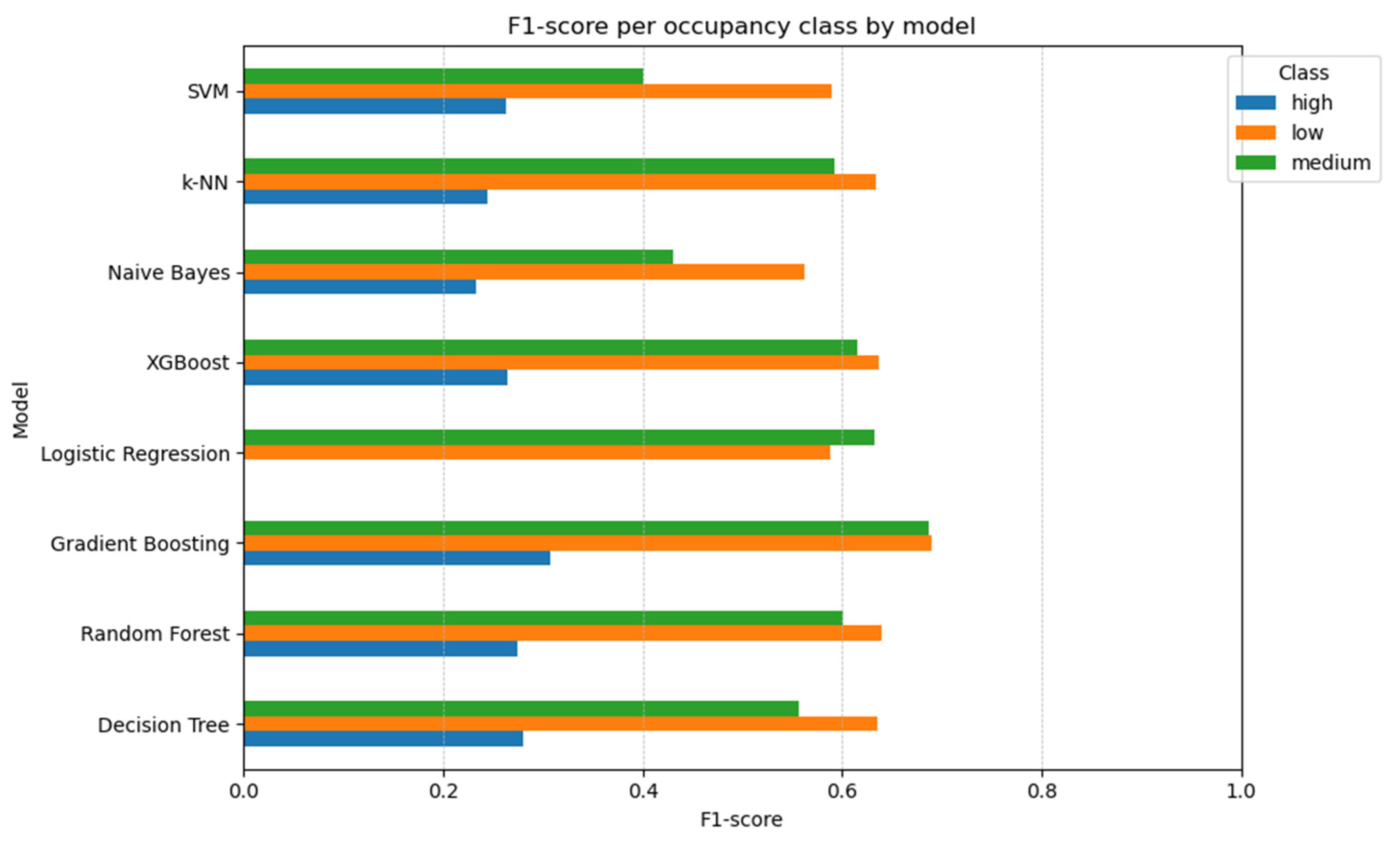
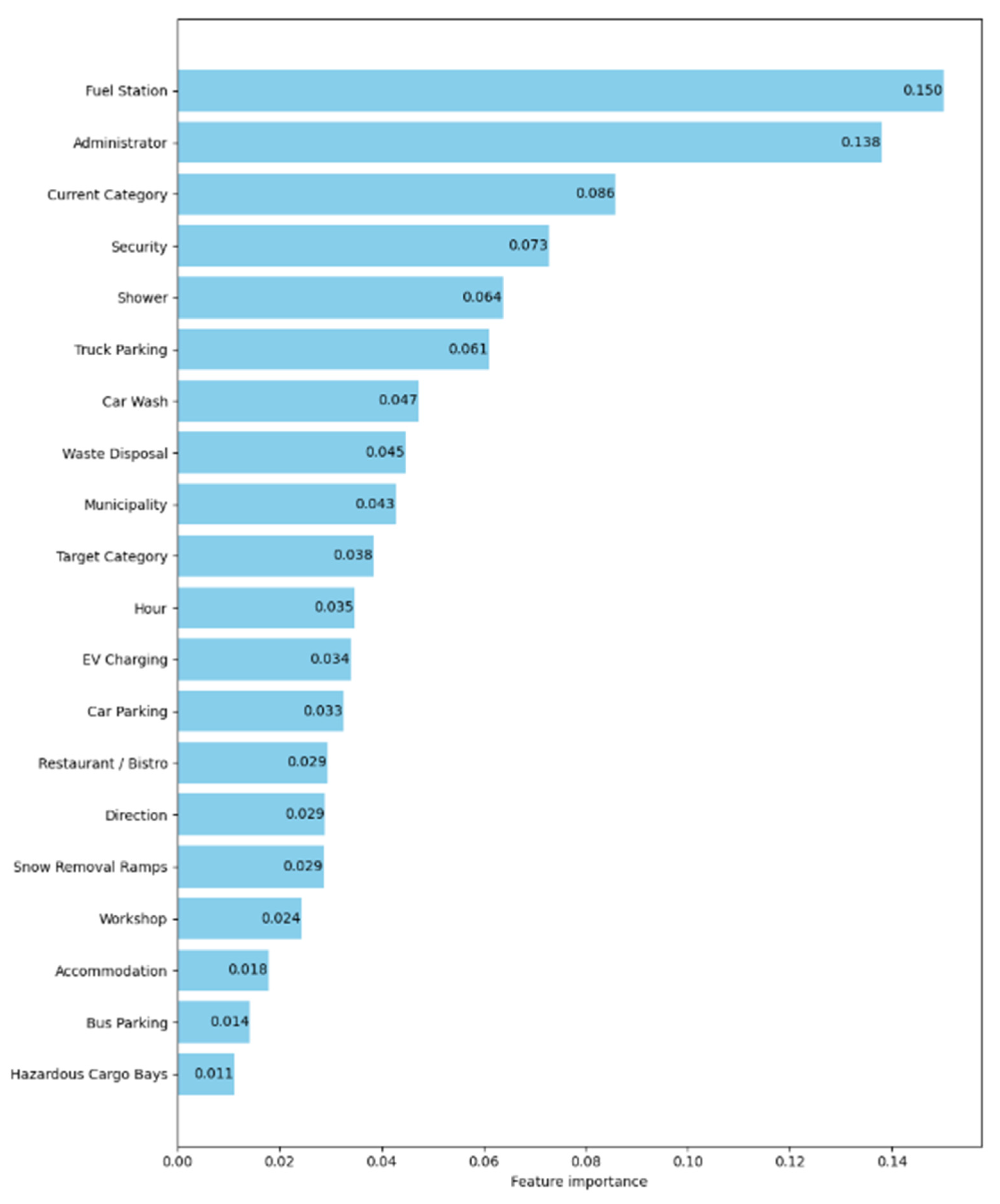
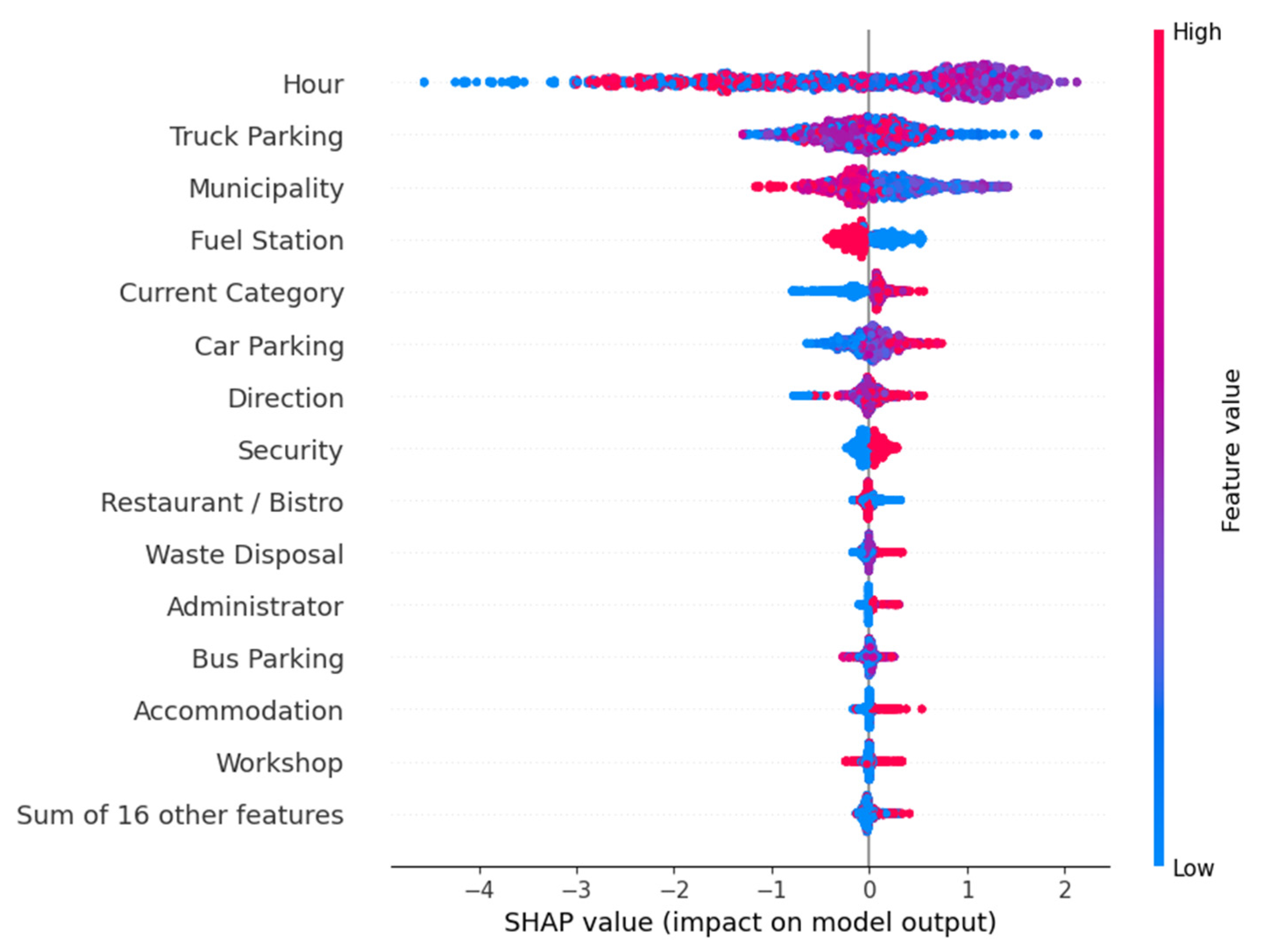
3. Results
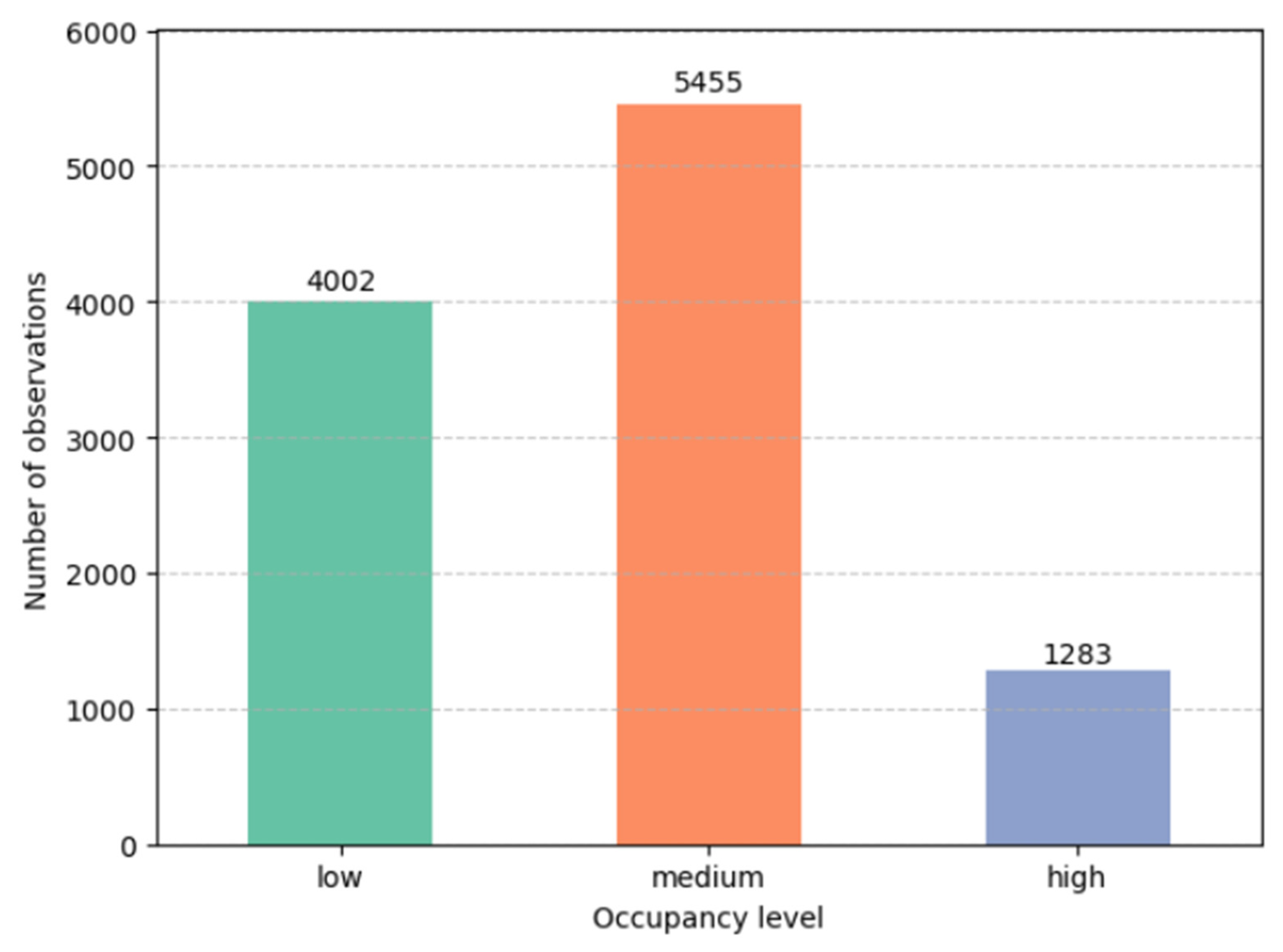
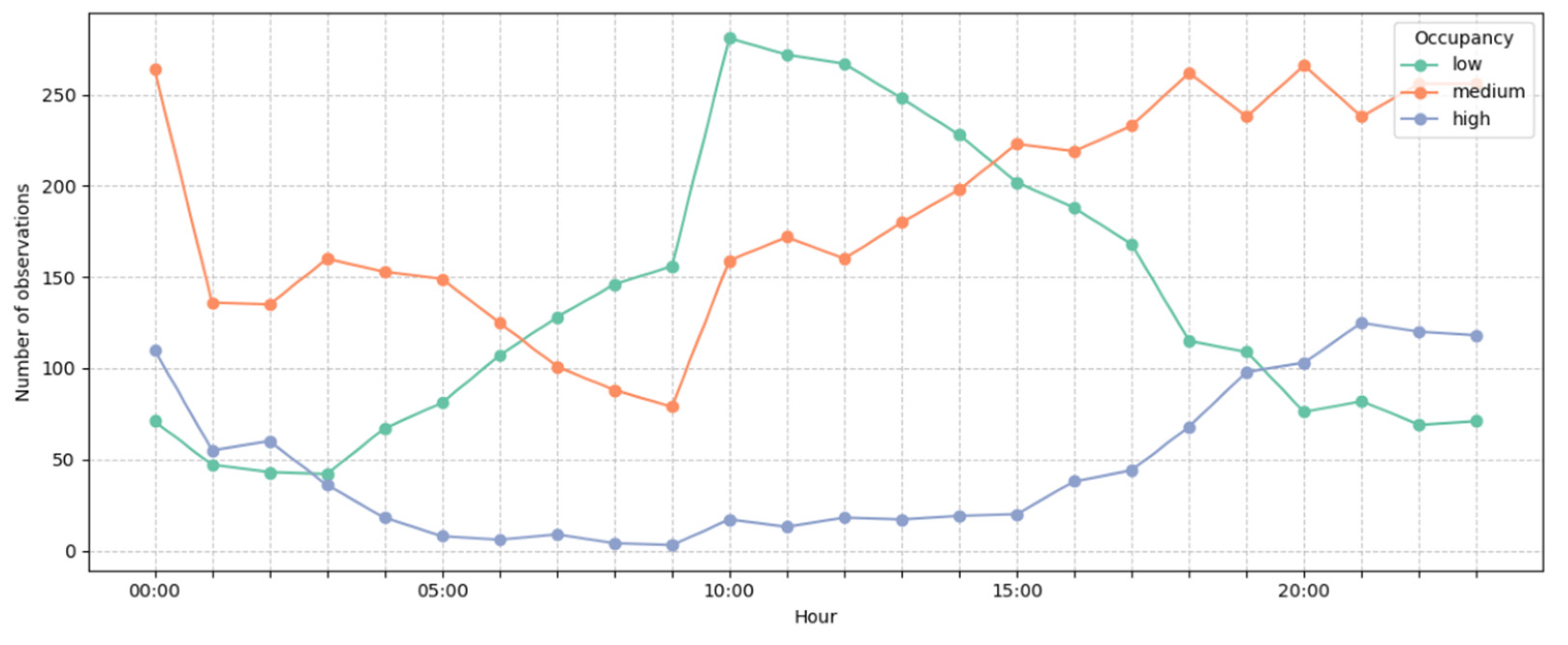
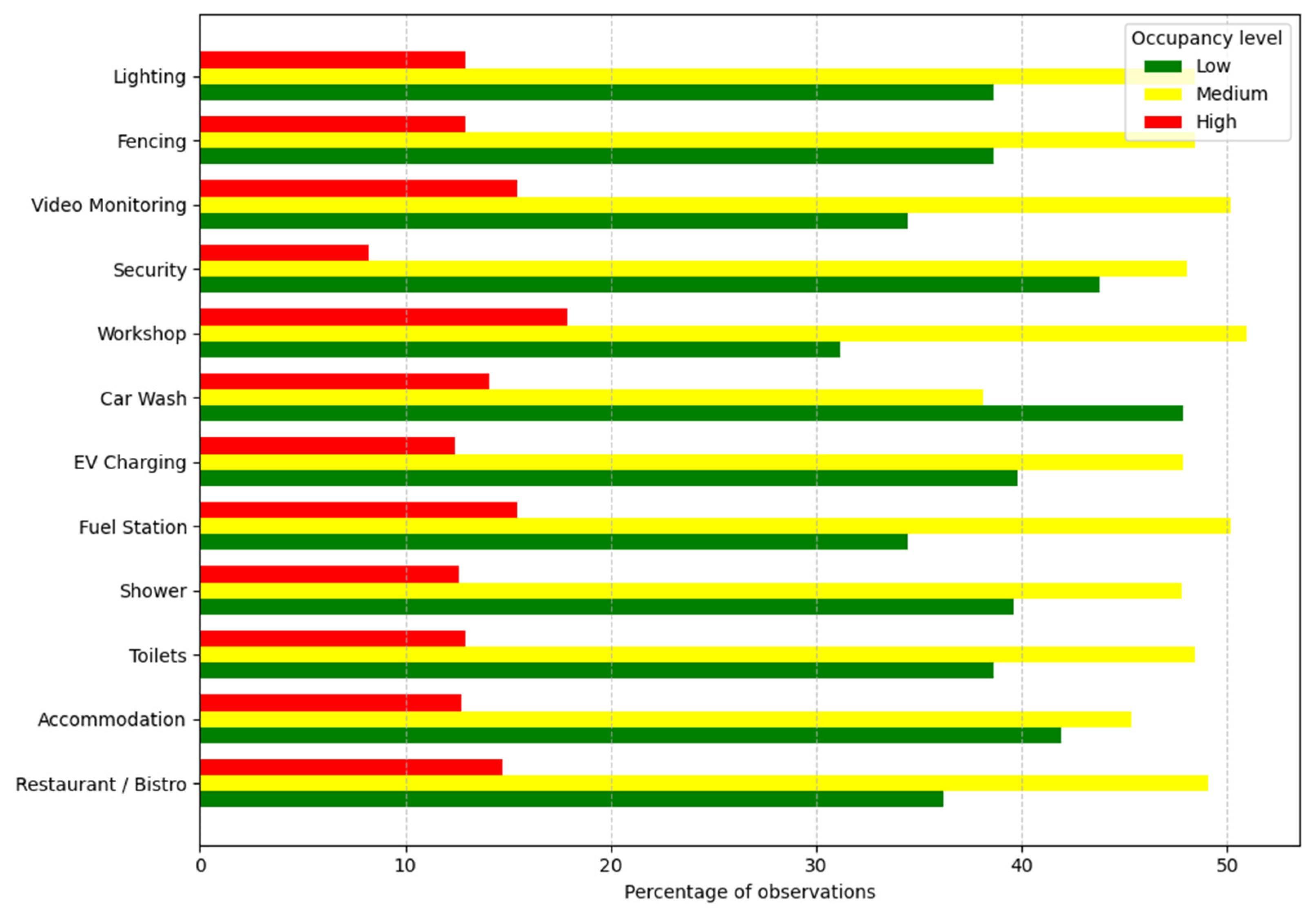
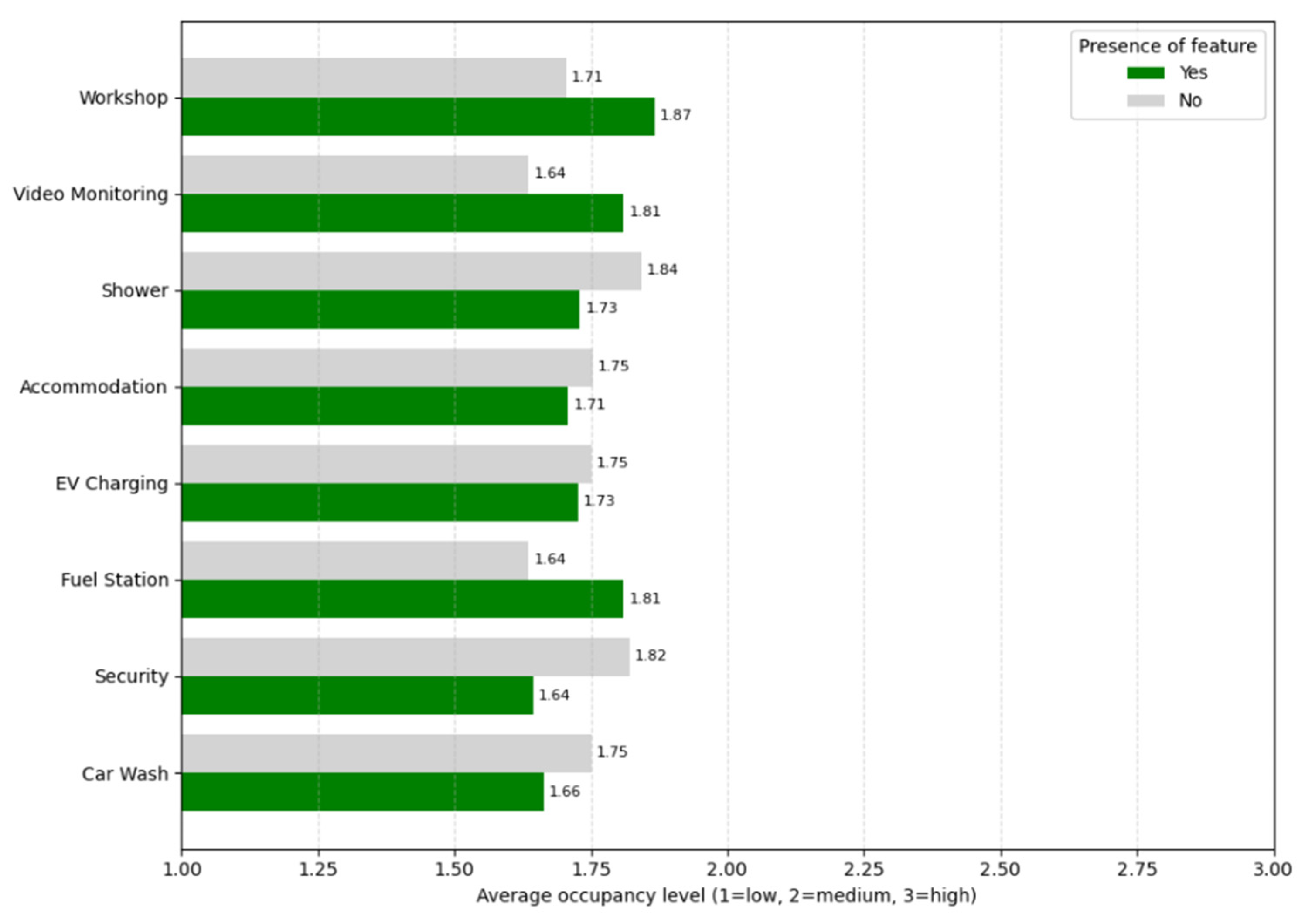
3.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
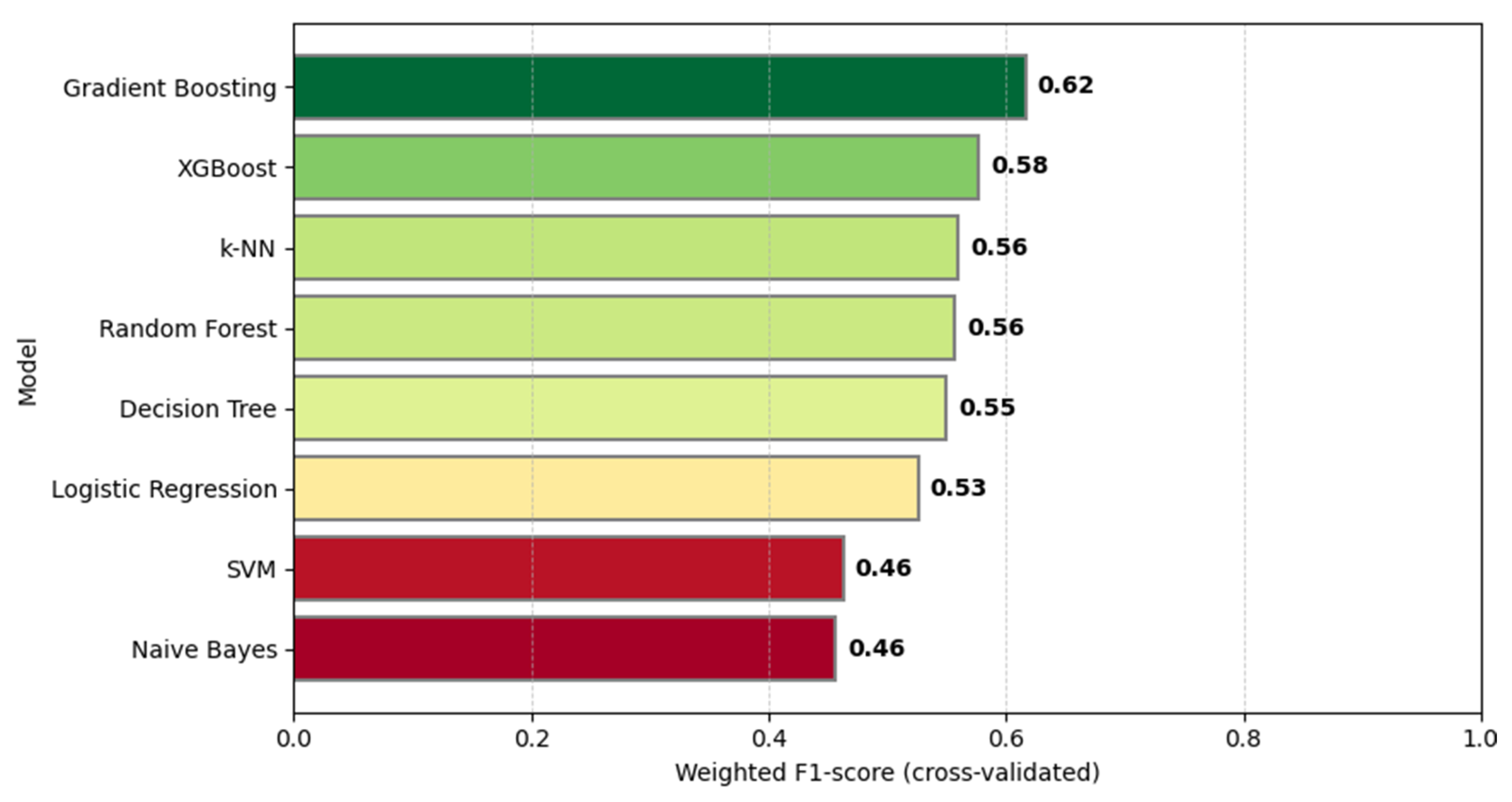
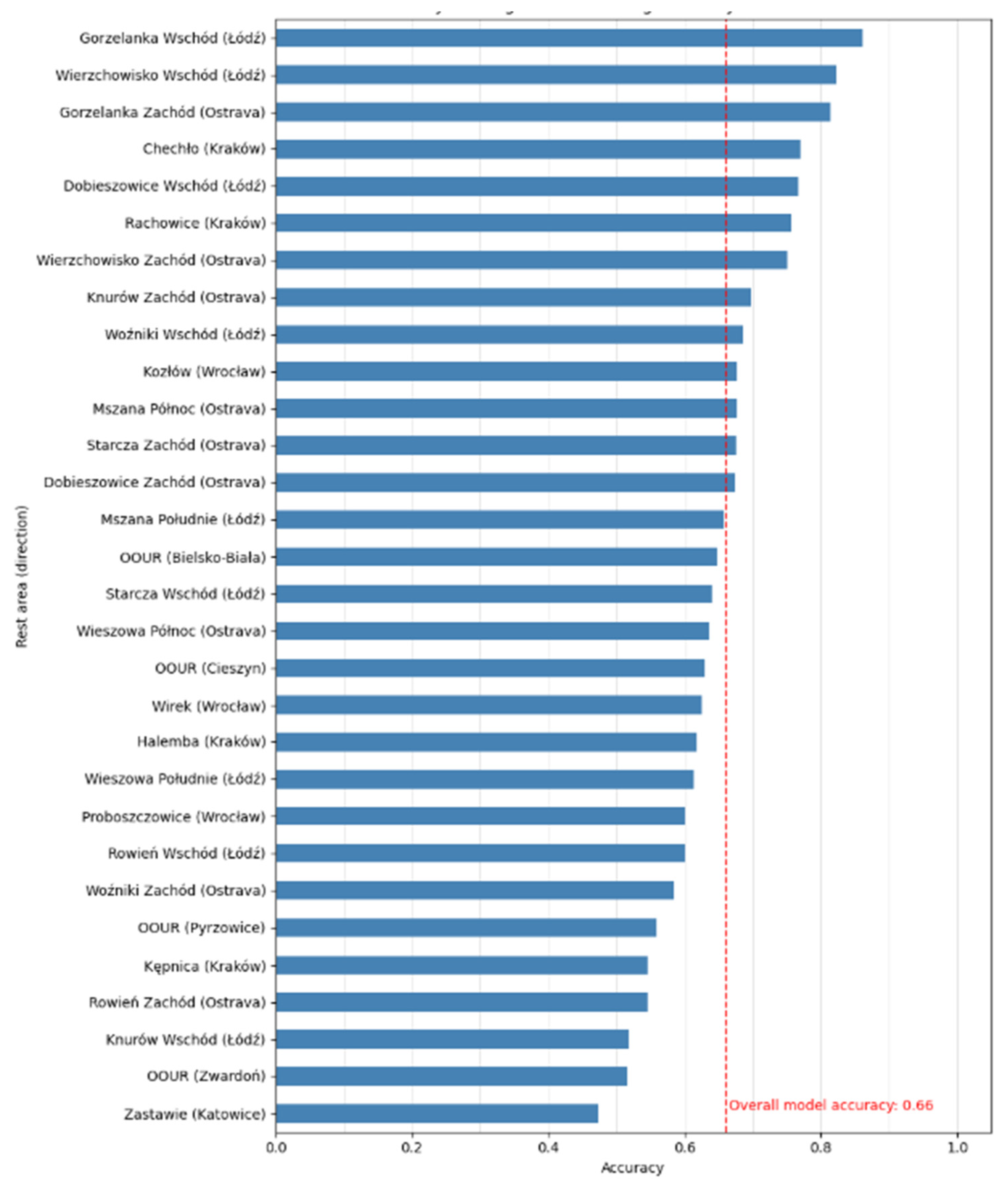
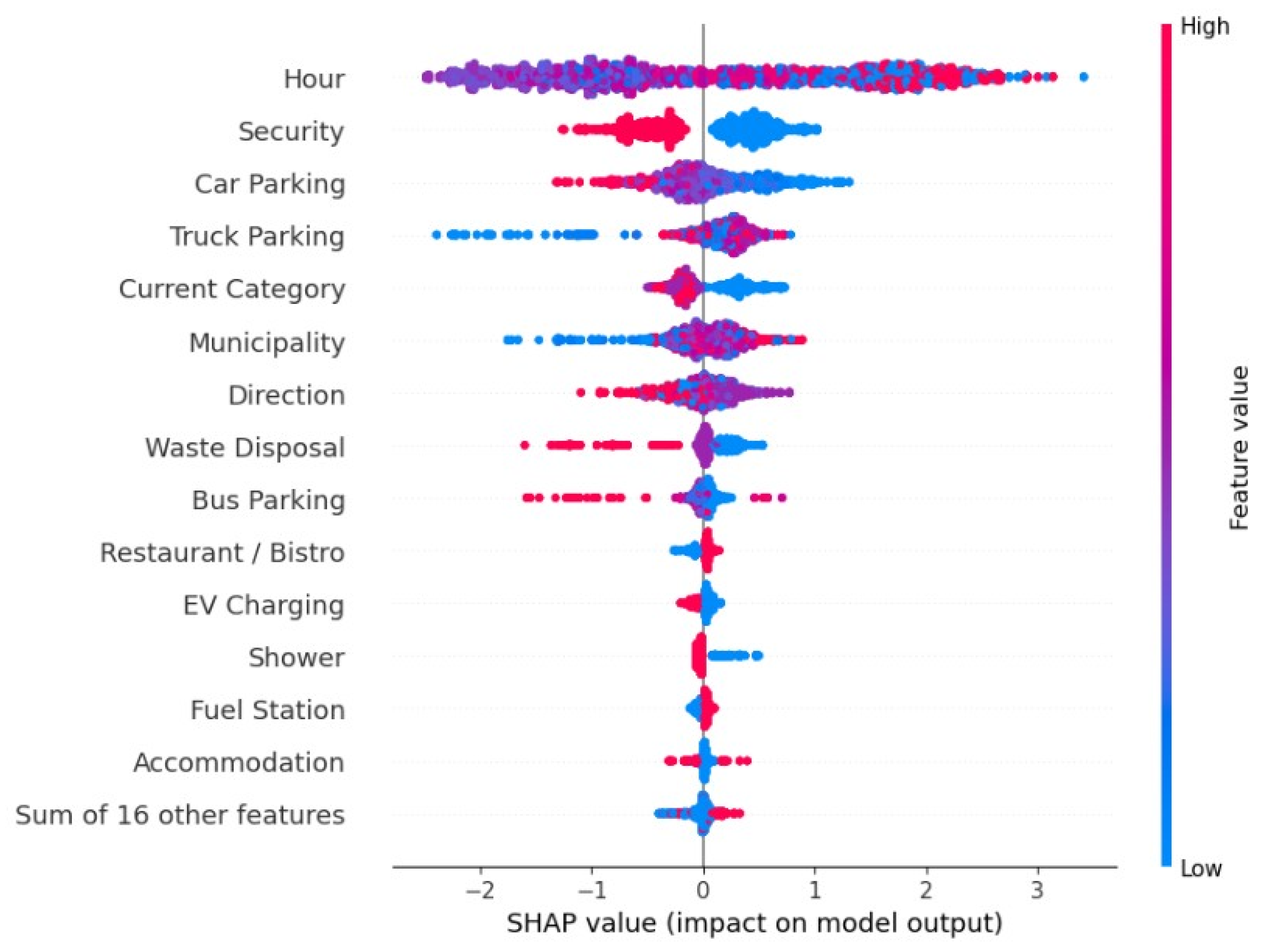
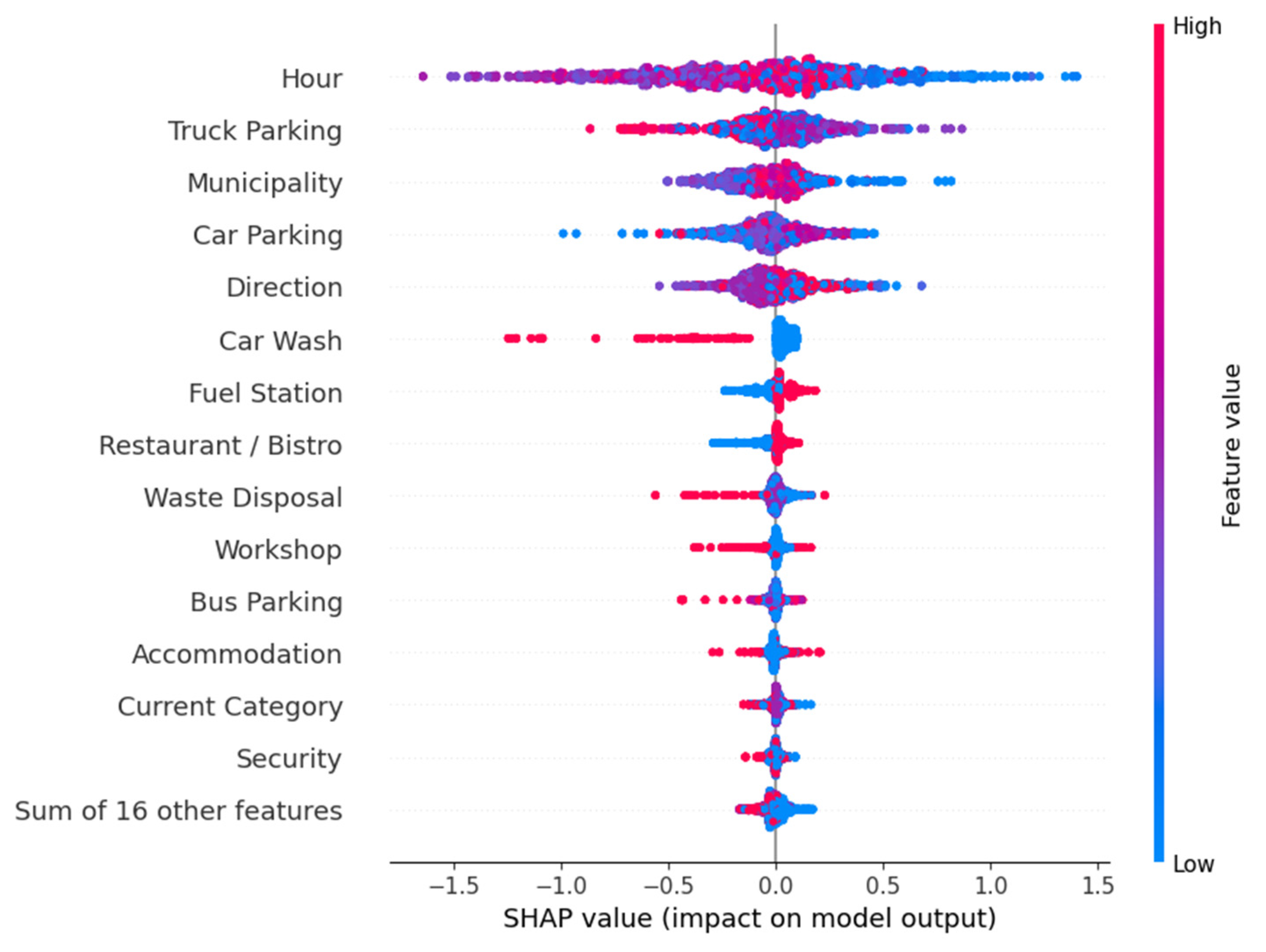
3.2. Results of Model Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ETC | electronic toll collection |
| HCV | Heavy Commercial Vehicles |
| HoS | Hours of Service |
| HRAs | Highway Rest Areas |
| RAs | Rest Areas |
| SSTPAs | Safe and Secure Truck Parking Areas |
References
- Cheng, G.; Cheng, R.; Pei, Y.; Han, J. Research on Highway Roadside Safety. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 6622360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/1012 of 7 April 2022 Supplementing Regulation (EC) No 561/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council with Regard to the Establishment of Standards Detailing the Level of Service and Security of Safe and Secure Parking Areas and to the Procedures for Their Certification. 2022. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2022/1012/oj/eng (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/276462 (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Brown, I.D. Driver Fatigue. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 1994, 36, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, A.; Kay, J.; Savolainen, P.T.; Gates, T.J. Effects of Public Rest Areas on Fatigue-Related Crashes. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2386, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, T.L.; Slavova, S.; Rock, P.J. Association between commercial vehicle driver at-fault crashes involving sleepiness/fatigue and proximity to rest areas and truck stops. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 126, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatni, F.; Ishak, S.Z.; Milad, A. Characteristics and Potential Impacts of Rest Areas Proximate to Roadways: A Review. Open Transp. J. 2021, 15, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crizzle, A.M.; Toxopeus, R.; Malkin, J. Impact of limited rest areas on truck driver crashes in Saskatchewan: A mixed-methods approach. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Pritchard, E.; Van Vreden, C.; Newnam, S.; Iles, R.; Xia, T. Factors Associated with Fatigued Driving among Australian Truck Drivers: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Yi, D.; Zou, F.; Zhou, Z.; Li, N.; Guo, F. Recognition of Vehicles Entering Expressway Service Areas and Estimation of Dwell Time Using ETC Data. Entropy 2022, 24, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Tang, J.; Luo, W. Short-term traffic flow prediction: An ensemble machine learning approach. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 74, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shang, Q.; Xie, T. A Hybrid Model for Short-Term Traffic Flow Prediction Based on Variational Mode Decomposition, Wavelet Threshold Denoising, and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. Complexity 2021, 2021, 7756299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provoost, J.; Wismans, L.; der Drift, S.V.; Kamilaris, A.; Keulen, M.V. Short Term Prediction of Parking Area states Using Real Time Data and Machine Learning Techniques. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesdwiady, A.; Soua, R.; Karray, F. Improving Traffic Flow Prediction With Weather Information in Connected Cars: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 9508–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Acebo, H.; Romo-Martín, A.; Findley, D.J. Spatial distribution and the facility evaluation of the service and rest areas in the toll motorway network of the European Union. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2022, 15, 821–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-Martín, A.; Pérez-Acebo, H. Analysis of the Location of Service and Rest Areas and their facilities in Spanish paying motorways. Transp. Res. Procedia 2018, 33, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Acebo, H.; Romo-Martín, A. SERVICE AND REST AREAS IN TOLL MOTORWAYS IN POLAND: STUDY OF DISTRIBUTION AND FACILITIES. Transp. Probl. 2019, 14, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodinskaja, J.; Bertulienė, L. Layout of Rest Areas and Their Infrastructure Development in the South-Eastern Region of Lithuania. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2020, 15, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hami, A.; Nojavan, A. Rest Areas Management; the Effect of Demographic Information into Users’ Preferences for Planning Parameters of Rest Areas. Int. J. Archit. Eng. Urban Plan. 2020, 30, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENevland, A.; Gingerich, K.; Park, P.Y. A data-driven systematic approach for identifying and classifying long-haul truck parking locations. Transp. Policy 2020, 96, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, K.; Mishra, S.; Paleti, R.; Golias, M.M.; Sarker, A.A.; Pujats, K. Truck Parking Utilization Analysis Using GPS Data. J. Transp. Eng. Part Syst. 2017, 143, 04017045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzyński, A.; Cieśla, M. APPLICATION OF A MACHINE LEARNING MODEL FOR FORECASTING FREIGHT RATE IN ROAD TRANSPORT. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2025, 126, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaru, R.; Cheng, Y.; Parker, S.; Perry, E.; Ran, B.; Ahn, S. Truck Parking Usage Prediction with Decomposed Graph Neural Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H. Estimating Vehicle Turn-In Rate of Expressway Rest Areas via ETC Gantry Data—An ADPC-GMM Approach. Prome-Traffic Transp. 2024, 36, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yu, S.; Ye, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Predicting the vehicle turn-in rates of highway service area: A random forest approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Bilbao, Spain, 24–28 September 2023; pp. 1349–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, J. Estimation of the Percentage of Mainline Traffic Entering Rest Area Based on Bp Neural Network. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 13, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, F.; Lv, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. Prediction of Entering Percentage into Expressway Service Areas Based on Wavelet Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54562–54574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, N.S. An Introduction to Kernel and Nearest-Neighbor Nonparametric Regression. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. The optimality of naive Bayes. In Proceedings of the International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, FLAIRS, Sandestin Beach, FL, USA, 19 May 2024; pp. 562–567. [Google Scholar]
- OpenStreetMap Project. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Biedrońska, J. (Ed.) Projektowanie Obiektów Motoryzacyjnych; Wyd. 2. in Monografia/[Politechnika Śląska], no. 262; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.S.; McCabe, G.P.; Craig, B.A. Introduction to the Practice Of Statistics, 9th ed.; Freeman, W.H., Ed.; Macmillan Learning: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A.P. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: And Sex and Drugs and Rock ‘n’ roll, 4th ed.; Sage: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, W. Python for Data Analysis: Data Wrangling with Pandas, NumPy, and Jupyter, 3rd ed.; O’Reilly: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher, J.D.; Tierney, B. Data science. In the MIT Press Essential Knowledge Series; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Müller, A.; Nothman, J.; Louppe, G.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. arxiv 2011, arXiv:1201.0490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Benjain, R.-K.; Fernando, P.; Brian, G.; Matthias, B.; Jonathan, F.; Kyle, K.; Jessica, H.; Jason, G.; Sylvain, C.; et al. Jupyter Notebooks—A Publishing Format for Reproducible Computational Workflows; International Conference on Electronic Publishing: Göttingen, Germany, 2016; Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:36928206 (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- VanderPlas, J. Python Data Science Handbook: Essential Tools for Working with Data, 1st ed.; O’Reilly: Beijing, China; Boston, MA, USA; Farnham, UK; Sebastopol, CA, USA; Tokyo, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rokach, L.; Maimon, O. Data Mining with Decision Trees: Theory and Applications, 2nd ed.; In Series in Machine Perception and Artificial Intelligence; World Scientific: Singapore, 2014; Volume 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 1st ed.; In Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. arxiv 2020, arXiv:2010.16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; in NIPS’17. Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.04938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaisy, A.; Kirkemo, Z.; Veneziano, D.; Dorrington, C. Traffic Use of Rest Areas on Rural Highways: Recent Empirical Study. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2255, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ohno, S.; Nakamura, F. Analysis on drivers’ parking lot choice behaviors in expressway rest area. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, F.; Shi, C.; Yang, X. Quantitative Estimation and Analysis of Spatiotemporal Delay Effects in Expressway Traffic Accidents. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, D.; Song, D.; Shen, X.; Wang, W.; Li, G. Spatial and temporal distribution of expressway and its relationships to land cover and population: A case study of Beijing, China. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2014, 32, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, S.; Maget, C.; Spangler, M.; Bogenberger, K. Truck Parking Occupancy Prediction: XGBoost-LSTM Model Fusion. Front. Future Transp. 2021, 2, 693708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channamallu, S.S.; Kermanshachi, S.; Rosenberger, J.M.; Pamidimukkala, A. Parking occupancy prediction and analysis—A comprehensive study. Transp. Res. Procedia 2023, 73, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
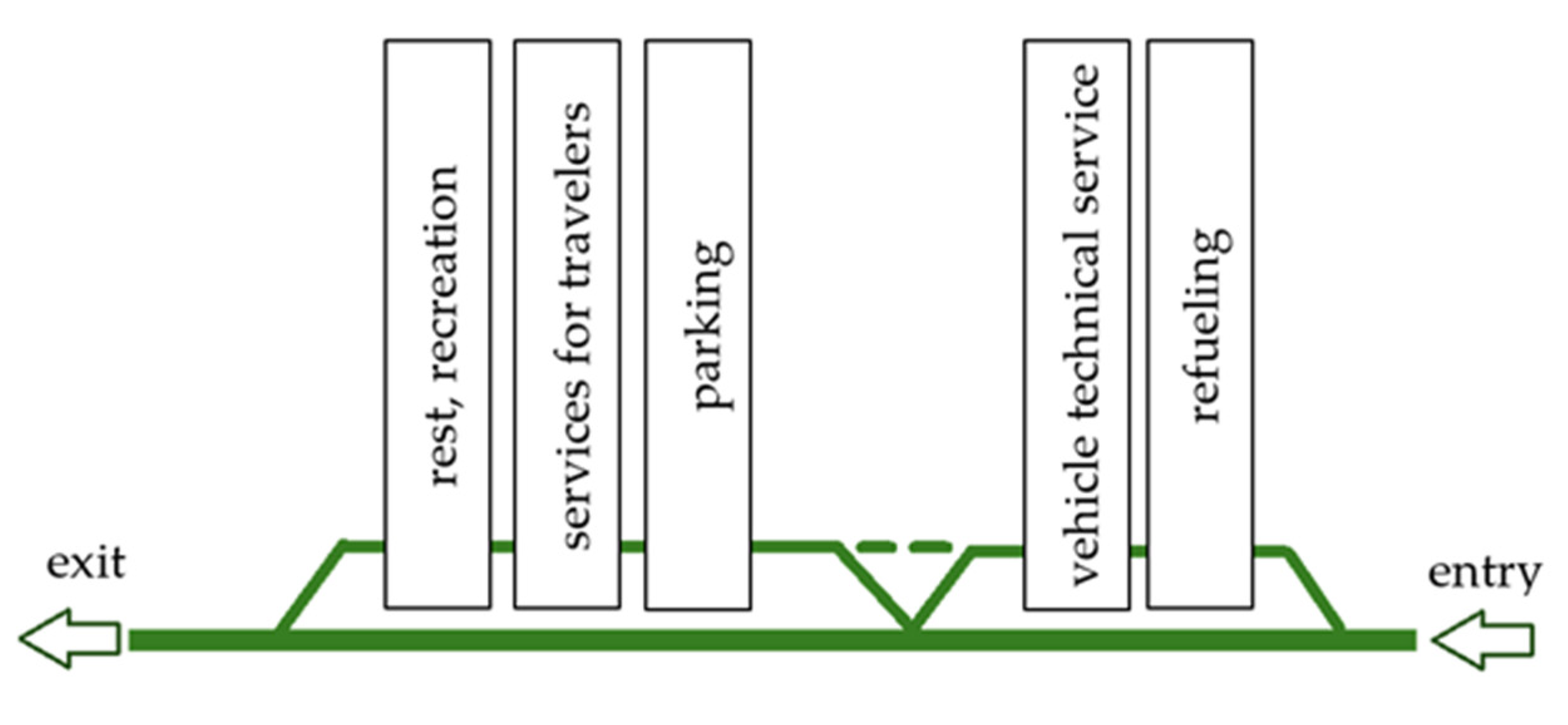
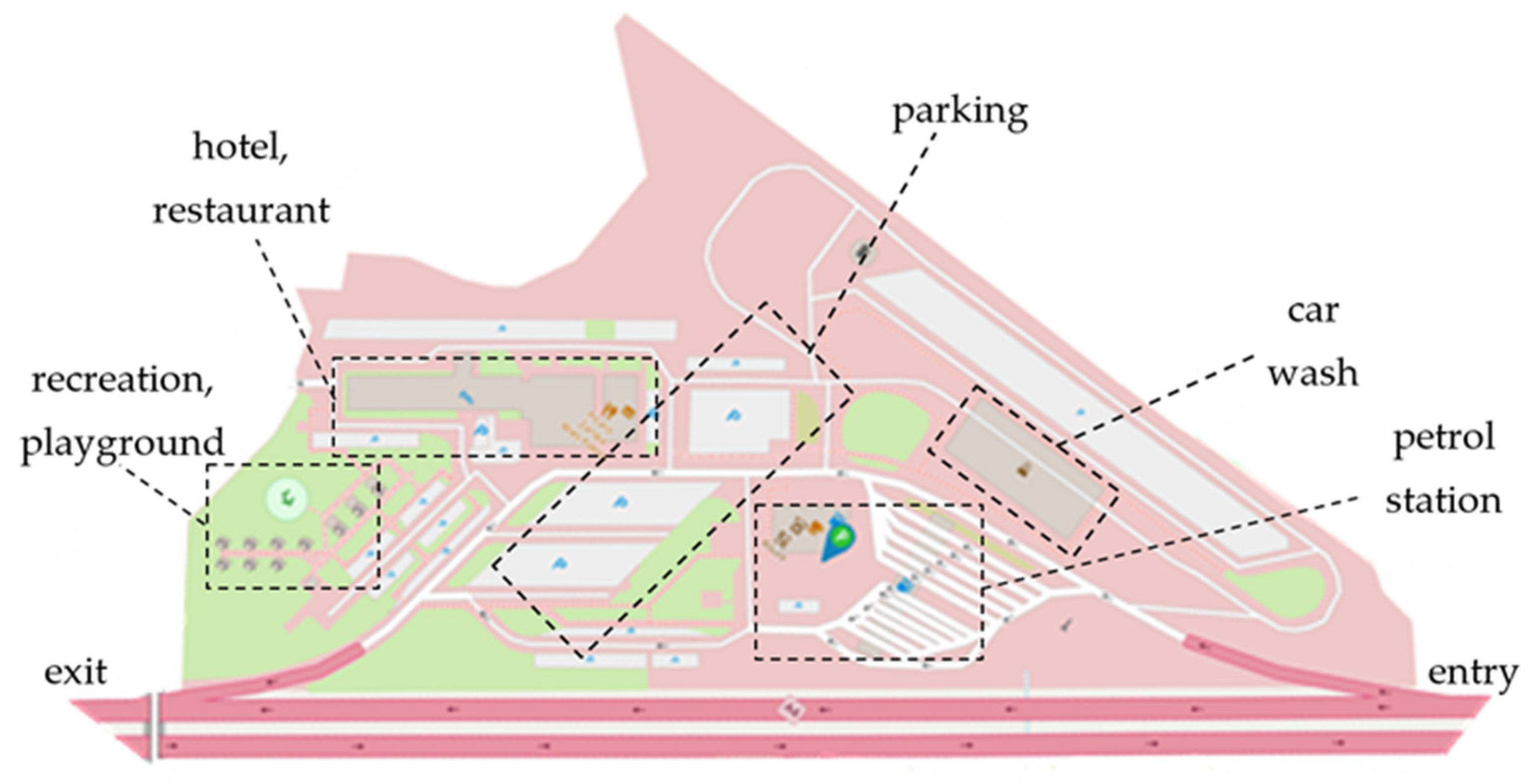
| Type of Facility | HRA Class I | HRA Class II | HRA Class II |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area Surface | up to 1.5 ha | 1.5–3.0 ha | 3.0–4.5 ha |
| Parking spaces for passenger cars | + | + | + |
| Parking spaces for trucks | + | + | + |
| Sanitary facilities | + | + | + |
| Water collection point | + | + | + |
| Pedestrian bridge for car inspection | + | + | + |
| Fuel station | - | + | + |
| Catering services (fast-food) | - | + | + |
| Service station | - | - | + |
| Catering services (restaurant) | - | - | + |
| Accommodation services | - | - | + |
| Characteristic | Low Occupancy (L) | Moderate Occupancy (M) | Full Occupancy (F) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A small percentage of the parking spaces are currently occupied | A significant portion of the parking lot is in use, but spaces are still available | Most or all of the parking spaces are occupied |
| Estimated occupancy | 0–30% filled (approximate range, may vary slightly) | 31–70% filled | 71–100% filled |
| Driver implication |
|
|
|
| App visualization | Shown in green to indicate availability | Marked in yellow or orange to signal caution | Shown in red, indicating unavailability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budzyński, A.; Cieśla, M. Highway Rest Area Truck Parking Occupancy Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Case Study from Poland. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10070151
Budzyński A, Cieśla M. Highway Rest Area Truck Parking Occupancy Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Case Study from Poland. Infrastructures. 2025; 10(7):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10070151
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudzyński, Artur, and Maria Cieśla. 2025. "Highway Rest Area Truck Parking Occupancy Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Case Study from Poland" Infrastructures 10, no. 7: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10070151
APA StyleBudzyński, A., & Cieśla, M. (2025). Highway Rest Area Truck Parking Occupancy Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Case Study from Poland. Infrastructures, 10(7), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10070151








