More Effective Front-End Decision-Making for Pipe Renewal Projects
Abstract
1. Introduction
“How can decision-making in pipe renewal projects be improved by using a project model linking planning goals from the front-end to project execution and on to operation and asset management?”
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. General Decision-Making (Decision Theory)
2.2. Project Models
3. Methods
- A methodology to answer the research question was chosen. As a data source for the research, a literature review was considered appropriate.
- Planning stage, in which how the methodology would be executed was discussed.
- Execution stage, as presented in Figure 2.
- The research need was defined by a gap between the stated pipe renewal need and actual pipe renewal efforts.
- Problem definition was initiated based on professional observations and common statements in the water sector, followed by scoping and mapping to obtain an overview of relevant literature to further develop the research design. Inputs gained in parallel research aided in refining the problem definition and establishing a precise research question.
- The parallel research consisted of the following:
- Conversations with sector professionals to gain context understanding. This formed the direction of the first set of preliminary interviews.
- Preliminary interviews were conducted to identify the root cause of the backlog in pipe renewal. First, these were conducted assuming a technical cause. In the second round, they were conducted with an understanding that the problem is more complex than technical challenges.
- The first preliminary interviews sparked a search for literature related to operational decision-making for choosing technology. Later, the second set of preliminary interviews directed the search towards strategic and tactical decision-making in an organizational setting. This formed the basis of this article.
- In parallel to the literature search, a survey was conducted in 70 municipalities throughout Norway. The aim was to uncover the use of decision support systems and the knowledge of international decision-making models. This formed the assumption of a gap in decision-making for pipe renewal.
- Finally, the above steps led to a series of semi-structured interviews with Norwegian municipalities with the aim of uncovering the following:
- Normal practice for project execution regarding project models, decision-support tools, and use of trenchless technology (16 interviews).
- Decision-making processes in planning and projects leading up to technology choices (16 interviews).
- Stakeholder’s impact on pipe renewal projects (13 interviews).
- Project models and processes for pipe renewal (16 interviews).
- Results from the parallel research concluded on the need for a stand-ardized project process to mitigate limited human resources and varied competence in decision-making, impacting the ability to optimize pipe renewal projects [37]. The ambition to address this need formed the fi-nal problem definition.
- Development of a research design and a research question to bridge the gap identified in the problem definition.
- Keyword search for decision-making models for pipe renewal and decision support systems.
- Refinement of search covering decision-making models, in general, and DSS related to trenchless technology.
- Screening of abstracts.
- Thoroughly reading remaining abstracts.
- Snowball sampling from papers to elaborate on chosen topics.
- Data analysis and presentation of findings.
- General decision theory regarding project models.
- Decision models and DSS for trenchless technologies.
- Existing decision models and DSS for trenchless technologies relative to a generalized project process.
- Discussion of the results in order of generalized project processes, leading up to a tailored project model for pipe infrastructures.
4. Results
4.1. Generalized Project Definitions and Models
4.2. Asset Management and Long-Term Planning
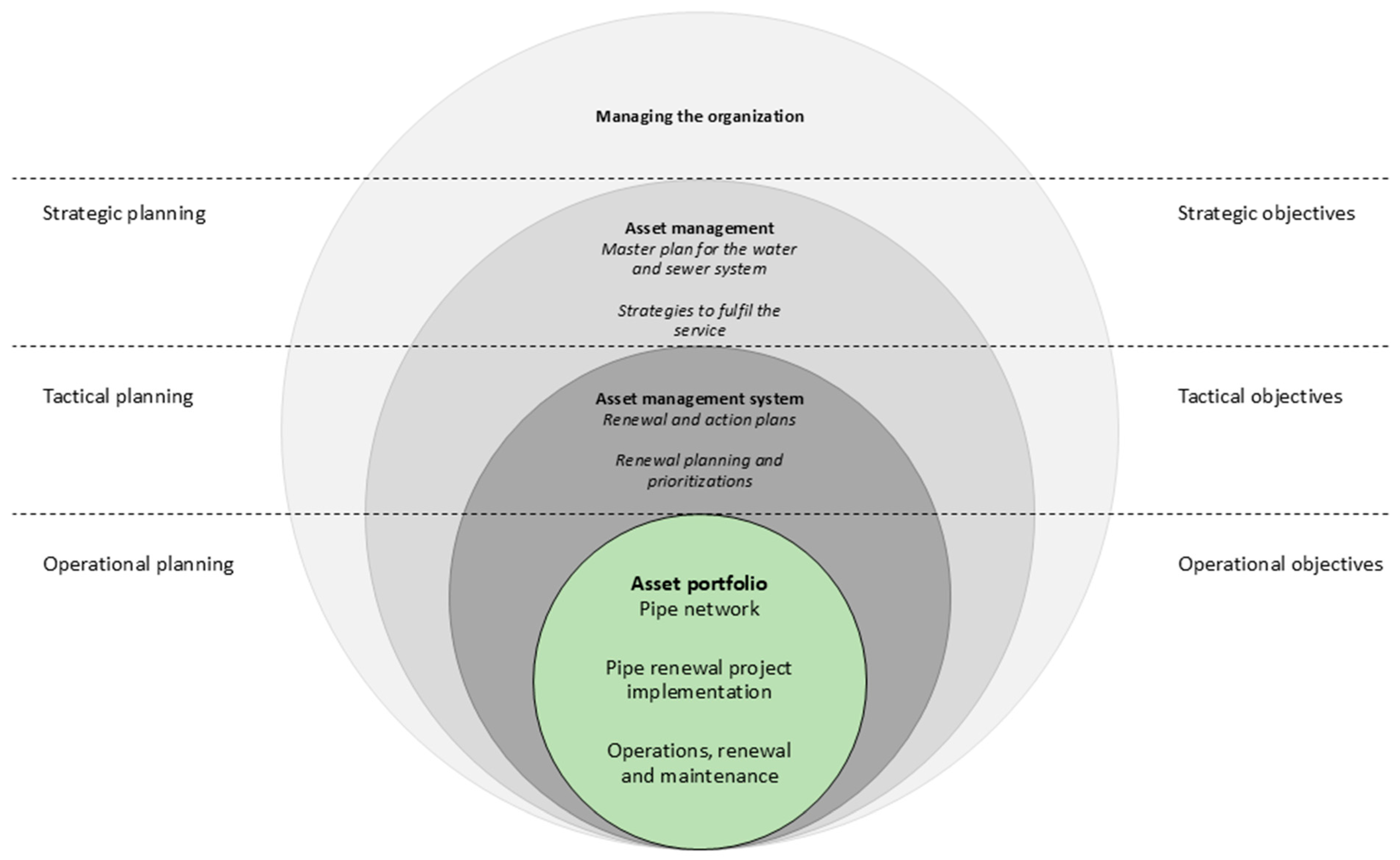
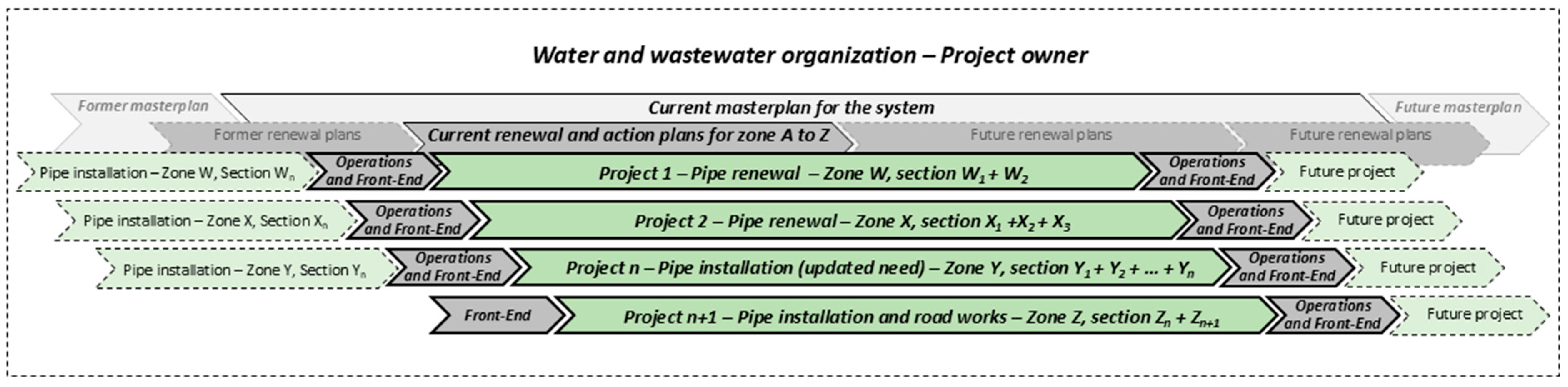
4.3. Reviewed Project Definitions
- Projects 1 and 2 represent the renewal of two and three sections in two different zones.
- Project 3 represents a change in demand, such as urban transformation from industrial to residential use, requiring new installations.
- Project 4 is initiated by external stakeholders, such as road authority, resulting in joint infrastructure development.
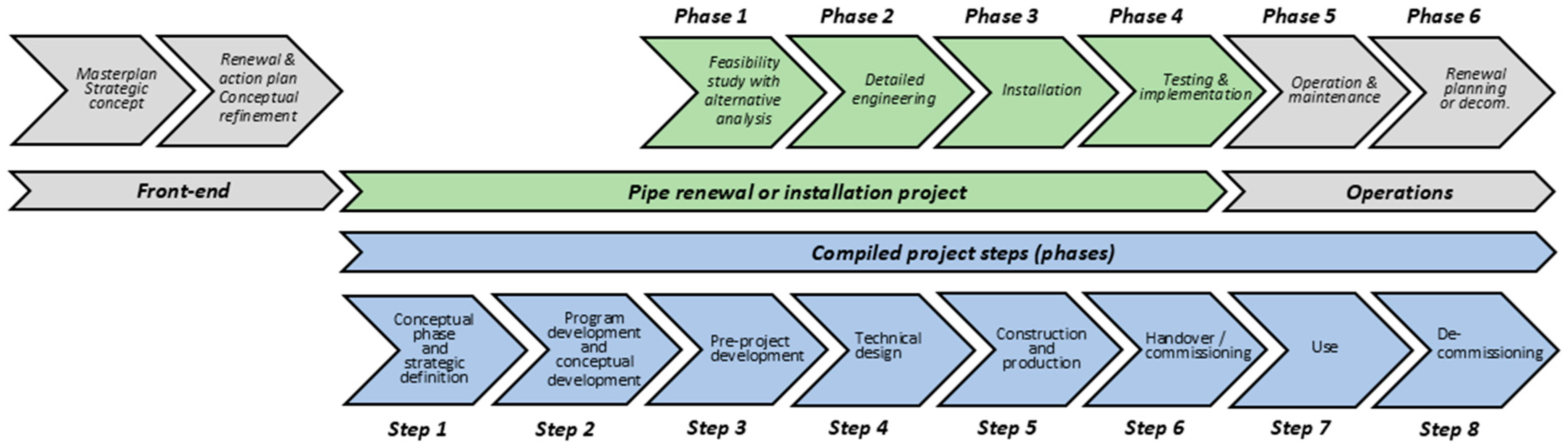
4.4. Step Models
4.5. Proposed Project Model for Pipe Renewal
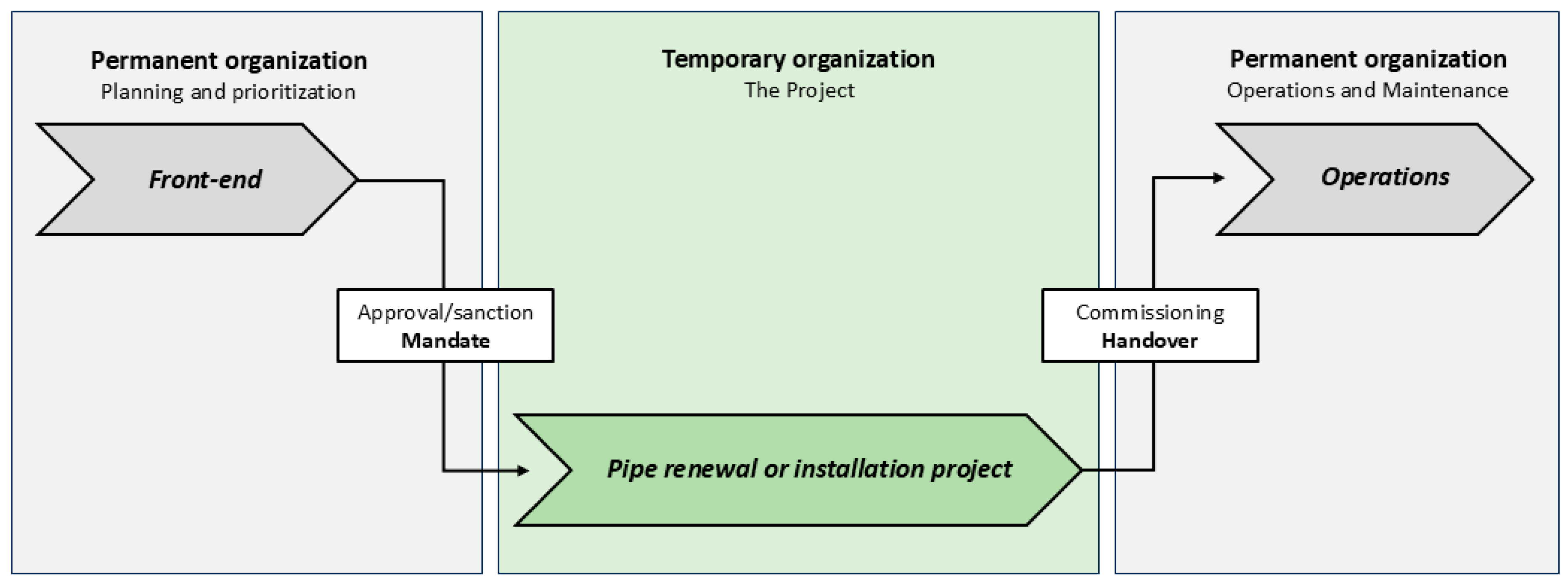
4.5.1. Project Implementation: Pipe Renewal or Installation
4.5.2. Operational Phases
5. Discussion
5.1. Asset Management and IAM-Planning
5.2. Project Definitions
5.2.1. General Project Definitions
5.2.2. Pipe Renewal Projects
5.3. Project Model for Pipe Renewal
Front-End of Pipe Renewal Projects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francisque, A.; Tesfamariam, S.; Kabir, G.; Haider, H.; Reeder, A.; Sadiq, R. Water mains renewal planning framework for small to medium sized water utilities: A life cycle cost analysis approach. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Shannon, B.; Deo, R.N.; Rathnayaka, S.; Hutchinson, C.R.; Zhao, X.L.; Kodikara, J. Classification of major cohorts of Australian pressurised cast iron water mains for pipe renewal. Aust. J. Water Resour. 2017, 21, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.A.; Valdes-Abellan, J. Pipe replacement by age only, how misleading could it be? Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2019, 19, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Caradot, N.; Cherqui, F.; Leitão, J.P.; Ahmadi, M.; Langeveld, J.G.; Le Gat, Y.; Scholten, L.; Roghani, B.; Rodríguez, J.P.; et al. Sewer asset management—State of the art and research needs. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadi, A.; Matthews, J.C.; Matthews, E. Environmental Impact Assessment of the Fabrication of Pipe Rehabilitation Materials. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2020, 11, 05019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, V.; Najafi, M.; Serajiantehrani, R. Environmental Impacts of Conventional Open-Cut Pipeline Installation and Trenchless Technology Methods: State-of-the-Art Review. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2020, 11, 03120001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, V.; Najafi, M.; Serajiantehrani, R. Sanitary sewer construction cost comparison between trenchless cipp renewal and open-cut replacement. In Proceedings of the International Structural Engineering and Construction, Limassol, Cyprus, 3–8 August 2020; Vacanas, Y., Danezis, C., Singh, A., Yazdani, S., Eds.; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvitsjøen, J.; Paus, K.H.; Bjerkholt, J.T.; Fergus, T.; Lindholm, O. Intensifying rehabilitation of combined sewer systems using trenchless technology in combination with low impact development and green infrastructure. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, Y.; Tesfamariam, S. Underground Sewer Networks Renewal Complexity Assessment and Trenchless Technology: A Bayesian Belief Network and GIS Framework. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2020, 11, 04019058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Canada. Census of Population. 2021. Available online: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/index-eng.cfm (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- United States Census Bureau U.S. Publication Clock. 2025. Available online: https://www.census.gov/popclock/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Saad, D.A.; Mansour, H.; Osman, H. Concurrent bilevel multi-objective optimisation of renewal funding decisions for large-scale infrastructure networks. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 14, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenskt Vatten Investeringsbehov Och Framtida Kostnader för Kommunalt Vatten Och Avlopp 2020, 54. Available online: https://vattenbokhandeln.svensktvatten.se/produkt/investeringsrapporten-2020/ (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Statistics Sweden. Population of Sweden per June 2025. 2025. Available online: https://www.scb.se/en/BE0101-en (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Holthe, A.B.K.; Reksten, H.; Svendsen, K.F.; Winther-Larsen, S.; Pedersen, S.; Bruaset, S.; Grande, C. Rapport 294 2025. 2025. Available online: https://norskvann.no/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Rapport294-_2025_Kommunalt_investeringsbehov_i_vann_og_avlop_2025_2045.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- SSB/Statistics Norway. Population of Norway. 2025. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/en/befolkning/folketall/statistikk/befolkning (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Maniar, S.H. Designing a Framework to Guide Renewal Engineering Decision—Making for Water and Wastewater Pipelines, Renewal. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2010. Available online: https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/items/f515b4d5-56af-4108-ae50-5b50bfce8054 (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- Matthews, J.C.; Selvakumar, A.; Sterling, R.; Condit, W. Analysis of Wastewater and Water System Renewal Decision-Making Tools and Approaches. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2012, 3, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M. Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection; The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-07-164088-6. [Google Scholar]
- SSB. Wastewater Pipe Network Statistics. 2019. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/en/statbank/table/11794 (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- SSB. Water Pipe Network Statistics. 2019. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/en/statbank/table/11792 (accessed on 6 October 2019).
- SSB. 11791: Utvalgte Nøkkeltall for Kommunalt Drikkevann (K) 2015–2021. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/statbank/table/11791 (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Aas, H.N.; Killingmo, E.; Busk, V. 221/2016 Smart Ledningsfornyelse—Bruk av NoDig-Metoder. 2016. Available online: https://va-kompetanse.no/butikk/a-221-smart-ledningsfornyelse-bruk-av-nodig-metoder/ (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Bruaset, S. Long-Term Sustainable Management of the Urban Water Pipe Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, R. Project Governance: A Practical Guide to Effective Project Decision Making; Kogan Page Publishers: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shiferaw, A.T.; Klakegg, O.J.; Haavaldsen, T. Governance of Public Investment Projects in Ethiopia. Proj. Manag. J. 2012, 43, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.; Kvalheim, E.V.; Volden, G.H.; Concept Rapport Nr. 50 Prosjektmodeller og Prosjekteierstyring i Statlige Virksomheter. Trondheim. 2016. Available online: https://www.ntnu.no/documents/1261860271/1262010703/CONCEPT_50_norsk_web.pdf/bc68f43d-262a-40d1-b9c9-dfeaff26d1a5?version=1.0 (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Vladeanu, G.; Matthews, J.C. Analysis of risk management methods used in trenchless renewal decision making. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 72, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazır, Ö. A review of analytical models, approaches and decision support tools in project monitoring and control. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S.O. Philosophical Perspectives on Risk; Virginia Tech: Blacksburg, Virginia, 2004; Available online: https://scholar.lib.vt.edu/ejournals/SPT/v8n1/hansson.html (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Jordanger, I.; Malerud, S.; Minken, H.; Strand, A.; Concept Rapport Nr. 18 Flermålsanalyser i Store Statlige Investeringsprosjekt. Trondheim. 2007. Available online: https://www.ntnu.edu/concept/concept-report-series (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Elliot, R. The Normative Side of Nature. Environ. Ethics. Brill 2009, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.A.; Orasanu, J.; Calderwood, R.; Zsambok, C.E. (Eds.) Decision Making in Action: Models and Methods; Ablex Pub: Norwood, NJ, USA, 1993; ISBN 0-89391-764-X. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, D.R.; Schindler, P.S. Business Research Methods, 12th ed.; McGraw-Hill/Irwin: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-07-352150-3. [Google Scholar]
- van Riel, W.; Langeveld, J.; Herder, P.; Clemens, F. Valuing information for sewer replacement decisions. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Casagrande, M.; Forte, G. Decision Making: A Theoretical Review. Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2022, 56, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaar, B.S.; Stevik, T.K.; Johansen, A. Barriers for pipe renewal—A comprehensive study. Urban Water J. 2023, 20, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, S.; Tucker, S.; Rahilly, M.; Davis, P.; Jarrett, R.; Po, M. Asset planning for water reticulation systems—The PARMS model. Water Supply 2003, 3, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moglia, M.; Burn, S.; Meddings, S. Parms-Priority: A Methodology for Water Pipe Replacement. (October). 2005. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/246044393_Parms-Priority_a_methodology_for_water_pipe_replacement (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- Matthews, J.C.; Allouche, E.N. Fully Automated Decision Support System for Assessing the Suitability of Trenchless Technologies. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2012, 3, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gauffre, P.; Baur, R. CARE-W: WP 3—Decision Support for Annual Rehabilitation Programmes D6—Criteria for the Prioritisation of Rehabilitation Projects, Water. 2002. Available online: https://www.sintef.no/contentassets/9e221cde66604461b90b4aa74dd62ca7/d06-care-w-criteria_for_arp.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Røstum, J. CARE-W Rehab Manager. 2004. Available online: https://www.sintef.no/contentassets/9e221cde66604461b90b4aa74dd62ca7/d14-user-manual-help-care-w.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Volden, G.H. Public project success as seen in a broad perspective.: Lessons from a meta-evaluation of 20 infrastructure projects in Norway. Eval. Program Plan. 2018, 69, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutchnik, A. Environmental and quality management systems and standards of churches and religious organizations. Sustain. Nexus Forum 2016, 24, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußler, M.; Borrmann, A. Model-based quality assurance in railway infrastructure planning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 109, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Norge Forvaltning av Anlegg og Verdier Oversikt, Prinsipper og Terminologi Asset Management Overview, Principles and Terminology. 2014. Available online: https://online.standard.no/nb/ns-iso-55000-2014 (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Bruaset, S.; Becker, M.A.; Reksten, H.; Baade-Mathiesen, T. Kommunalt Investeringsbehov For Vann og Avløp 2021–2040. 2021. Norsk Vann BA, Vangsvegen 143, 2321, Hamar Tlf: 62 55 30 30 E-post: Post@norskvann.no www.norskvann.no. Available online: https://va-kompetanse.no/butikk/a-259-kommunalt-investeringsbehov-for-vann-og-avlop-2021-2040/ (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- Cardoso, M.A.; Poças, A.; Silva, M.S.; Ribeiro, R.; Almeida, M.C.; Brito, R.S.; Coelho, S.T.; Alegre, H. Innovation results of IAM planning in urbanwater services. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.; Coelho, S.T.; Alegre, H.; Cardoso, M.A.; Silva, M.S.; Ramalho, P.; Ribeiro, R.; Covas, D.; Poças, A.; Vitorino, D.; et al. Moving urban water infrastructure asset management from science into practice. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turban, E.; Aronson, J.; Llang, T. Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, 7th ed.; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005; ISBN -978-81-203-2961-4. [Google Scholar]
- Samset, K.; Strand, A.; Hendricks, V. Major Projects: Logical Minimalism, Rationality and Grand Choices. 2009. Available online: http://www.concept.ntnu.no (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Samset, K.; Volden, G.H. Front-end definition of projects: Ten paradoxes and some reflections regarding project management and project governance. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, N.O.E.; Nyström, J.; Pyddoke, R. Governance regimes for large transport infrastructure investment projects: Comparative analysis of Norway and Sweden. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2019, 7, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samset, K. Systems engineering in front-end governance of major public investment projects. Systems 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volden, G.H.; Samset, K. Governance of Major Public Investment Projects: Principles and Practices in Six Countries. Proj. Manag. J. 2017, 48, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volden, G.H. Up-Front Governance of Major Public Investment Projects. 2019. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11250/2635643 (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Tiltnes, S. Veileder for fasenormen «Neste Steg». 2015. Available online: http://www.bygg21.no/globalassets/dokumenter/nestesteg_fullversjon.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Klakegg, O.J. Project delivery models—Situational or fixed design? In Proceedings of the 2017 12th International Scientific and Technical Conference on Computer Sciences and Information Technologies (CSIT), Lviv, Ukraine, 5–8 September 2017; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruaset, S.; Rygg, H.; Sægrov, S. Reviewing the long-term sustainability of urban water system rehabilitation strategies with an alternative approach. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingl, V.; Geraldi, J. Errors, lies and misunderstandings: Systematic review on behavioural decision making in projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarian, M.; Yu, H.; Shiferaw, A.T.; Stevik, T.K. Do We Perform Systematic Literature Review Right? A Scientific Mapping and Methodological Assessment. Logistics 2023, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Norge. NS-ISO 55000:2024 (en) Asset Management Vocabulary, Overview and Principles. 2024. Available online: https://online.standard.no/nb/ns-iso-55000-2024 (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Egger, P.; Rauch, W.; Kleidorfer, M. Comparison of Multi-Criteria Decision Support Methods for Integrated Rehabilitation Prioritization. Water 2017, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsaas, B.T.; Kristensen, K.H.; Van Veen, A.R.; Johansen, A.; Torp, O. Prosjekteringsprosesser—Verdiskaping, Bærekraft og Kompleksitet; Fagbokforlaget: Bergen, Norway, 2024; ISBN 978-82-450-3902-3. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.; Vo, H.; Samset, K.; Edkins, A. The front-end of projects: A systematic literature review and structuring. Prod. Plan. Control 2019, 30, 1137–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, A.T. Front-End Project Governance—Choice of Project Concept and Decision-Making—An International Perspective. 2013. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11250/232749 (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- RIBA RIBA Plan of Work 2020 Overview. RIBA 2020, 66, Portland Place, London, W1B 1AD, 146. Available online: https://www.riba.org/media/syneeeto/2020ribaplanofworkoverviewpdf.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Kerwin, S.; Adey, B.T. Optimal Intervention Planning: A Bottom-Up Approach to Renewing Aging Water Infrastructure. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossalam, A.; Arafa, M. The role of project manager in benefits realization management as a project constraint/driver. HBRC J. 2016, 12, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volden, G.H.; Samset, K. A Close-up on Public Investment Cases. Lessons from Ex-post Evaluations of 20 Major Norwegian Projects; Ex Ante Akademisk Forlag. 2017. Available online: http://www.concept.ntnu.no (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Brillinger, A.-S.; Els, C.; Schäfer, B.; Bender, B. Business model risk and uncertainty factors: Toward building and maintaining profitable and sustainable business models. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruaset, S.; Sægrov, S. Using the multiple scenario approach for envisioning plausible futures in long-term planning and management of the urban water pipe systems. Eur. J. Futures Res. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Așchilean, I.; Giurca, I. Choosing a Water Distribution Pipe Rehabilitation Solution Using the Analytical Network Process Method. Water 2018, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.A.; Santos Silva, M.; Coelho, S.T.; Almeida, M.C.; Covas, D.I.C. Urban water infrastructure asset management—A structured approach in four water utilities. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2702–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşchilean, I.; Badea, G.; Giurca, I.; Naghiu, G.S.; Iloaie, F. Determining Priorities Concerning Water Distribution Network Rehabilitation. Energy Procedia 2017, 112, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.; Strand Alfredsen Larsen, A.; Klakegg, O.J.; Welde, M. Cost estimation in major public projects front-end phase: An empirical study on how to improve current practices. Proj. Leadersh. Soc. 2025, 6, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagherouit, W.; Bennis, S.; Bengassem, J. A Fuzzy Expert System for Prioritizing Rehabilitation of Sewer Networks. Comput. -Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 26, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelo, D.; Mandri-Perrott, C.; House, S.; Schwartz, J.Z. An Alternative Approach to Project Selection: The Infrastructure Prioritization Framework; 2016; Volume 40. Available online: https://thedocs.worldbank.org/en/doc/844631461874662700-0100022016/original/160423InfrastructurePrioritizationFrameworkFinalVersion.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Sitzenfrei, R.; Rauch, W.; Kleidorfer, M. Integrated rehabilitation planning of urban infrastructure systems using a street section priority model. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, J.; Carriço, N.; Covas, D. Lessons Learnt from the Application of MCDA Sorting Methods to Pipe Network Rehabilitation Prioritization. Water 2022, 14, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, A.; Eik-Andresen, P.; Ekambaram, A. Stakeholder Benefit Assessment—Project Success through Management of Stakeholders. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 119, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch-Juan, E.; Cabrera, E.; Gómez, E.; del Teso, R. Improving the communication with stakeholders: The infrastructure degradation index and the infrastructure histogram. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riel, W.; van Bueren, E.; Langeveld, J.; Herder, P.; Clemens, F. Decision-making for sewer asset management: Theory and practice. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, R.; Herz, R.; Kropp, I. CARE-S WP6 D19 Multi-criteria Decision Support. Dresden. 2005. Available online: https://www.sintef.no/contentassets/dcbdfcc90c044a4aa8abf26d8edfee60/d19_care-s__wp6_report.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Rolstadås, A.; Olsson, N.; Langlo, J.A.; Johansen, A. (Eds.) Praktisk Prosjektledelse Fra idé Til Gevinst, 3rd ed.; Fagbokforlaget: Bergen, Norway, 2023; ISBN 978-82-450-4523-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gdanski, S.-K.D.; Wilk, B.J. Possible Ways to Improve Infrastructure Project Governance on Front-End and Planning Phase. July. 2016. Available online: https://bibsys-almaprimo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1bgnrh8/BRAGE11250/2399226 (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- Daulat, S.; Rokstad, M.M.; Klein-Paste, A.; Langeveld, J.; Tscheikner-Gratl, F. Challenges of integrated multi-infrastructure asset management: A review of pavement, sewer, and water distribution networks. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 20, 546–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katko, T.S.; Juuti, P.S.; Schwartz, K.; Rajala, R.P. (Eds.) Water Services Management and Governance; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; Volume 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skaar, B.S.; Stevik, T.K.; Johansen, A.; Shiferaw, A.T. More Effective Front-End Decision-Making for Pipe Renewal Projects. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110290
Skaar BS, Stevik TK, Johansen A, Shiferaw AT. More Effective Front-End Decision-Making for Pipe Renewal Projects. Infrastructures. 2025; 10(11):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110290
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkaar, Bjørn Solnes, Tor Kristian Stevik, Agnar Johansen, and Asmamaw Tadege Shiferaw. 2025. "More Effective Front-End Decision-Making for Pipe Renewal Projects" Infrastructures 10, no. 11: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110290
APA StyleSkaar, B. S., Stevik, T. K., Johansen, A., & Shiferaw, A. T. (2025). More Effective Front-End Decision-Making for Pipe Renewal Projects. Infrastructures, 10(11), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110290





