Experimental and Numerical Model Analysis of Pipe–Soil Interaction Under Typical Geohazard Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
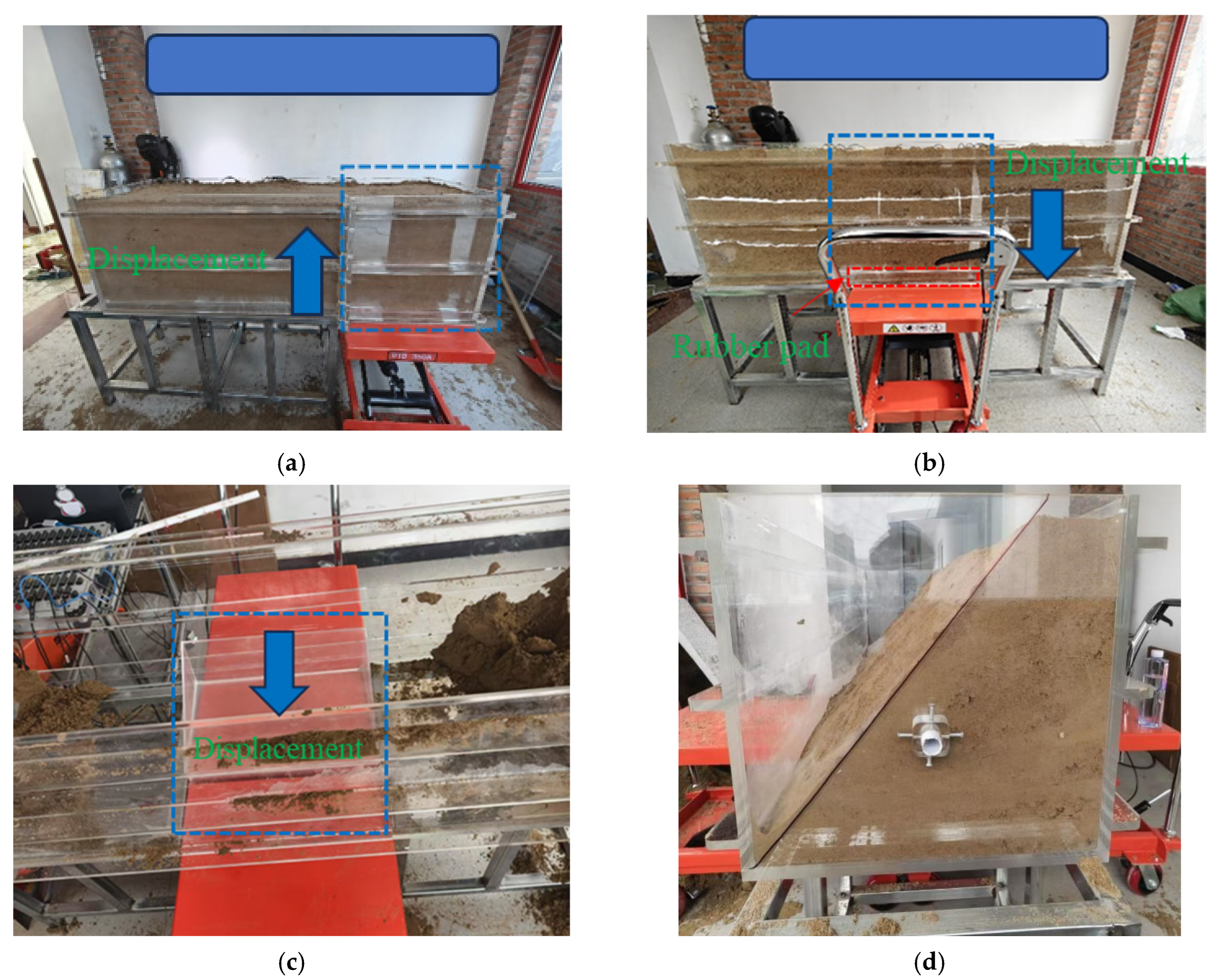
2. Pipe–Soil Interaction Test Apparatus
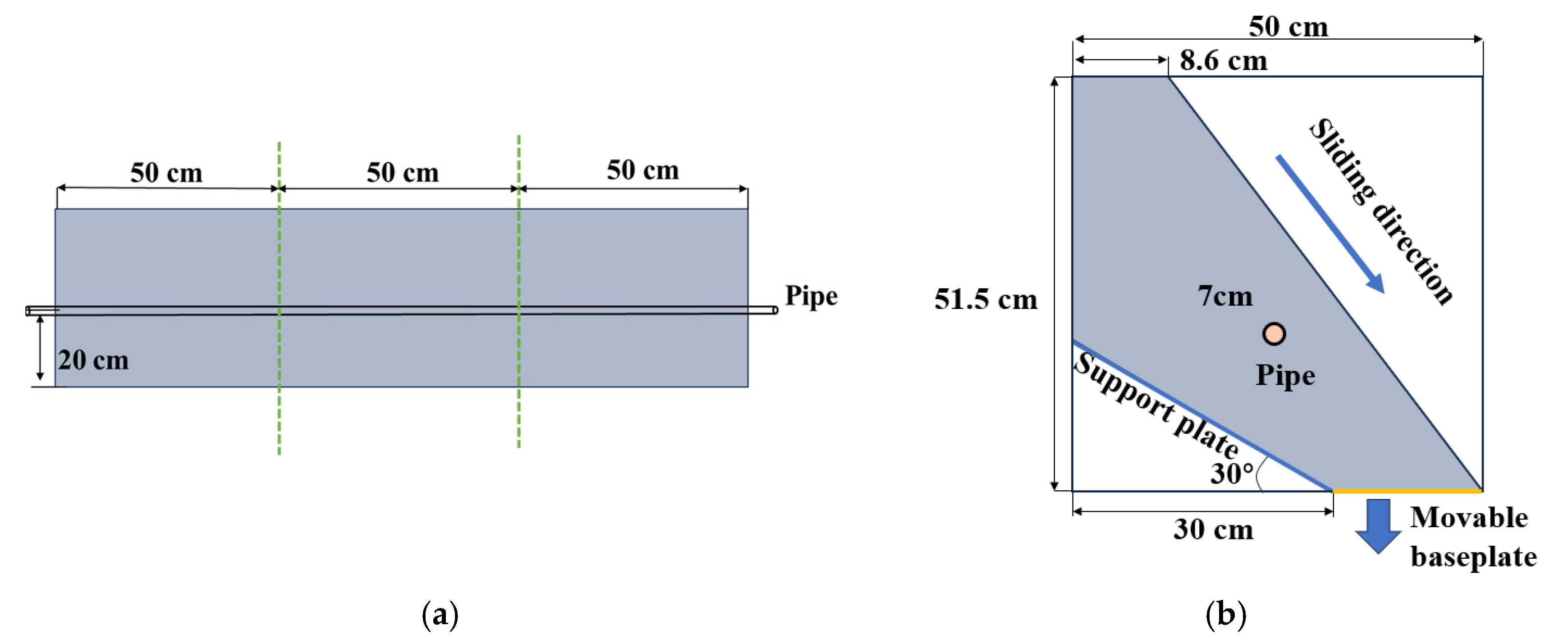
2.1. Apparatus Introduction
2.2. Test Materials
2.2.1. Test Pipe
2.2.2. Test Soil
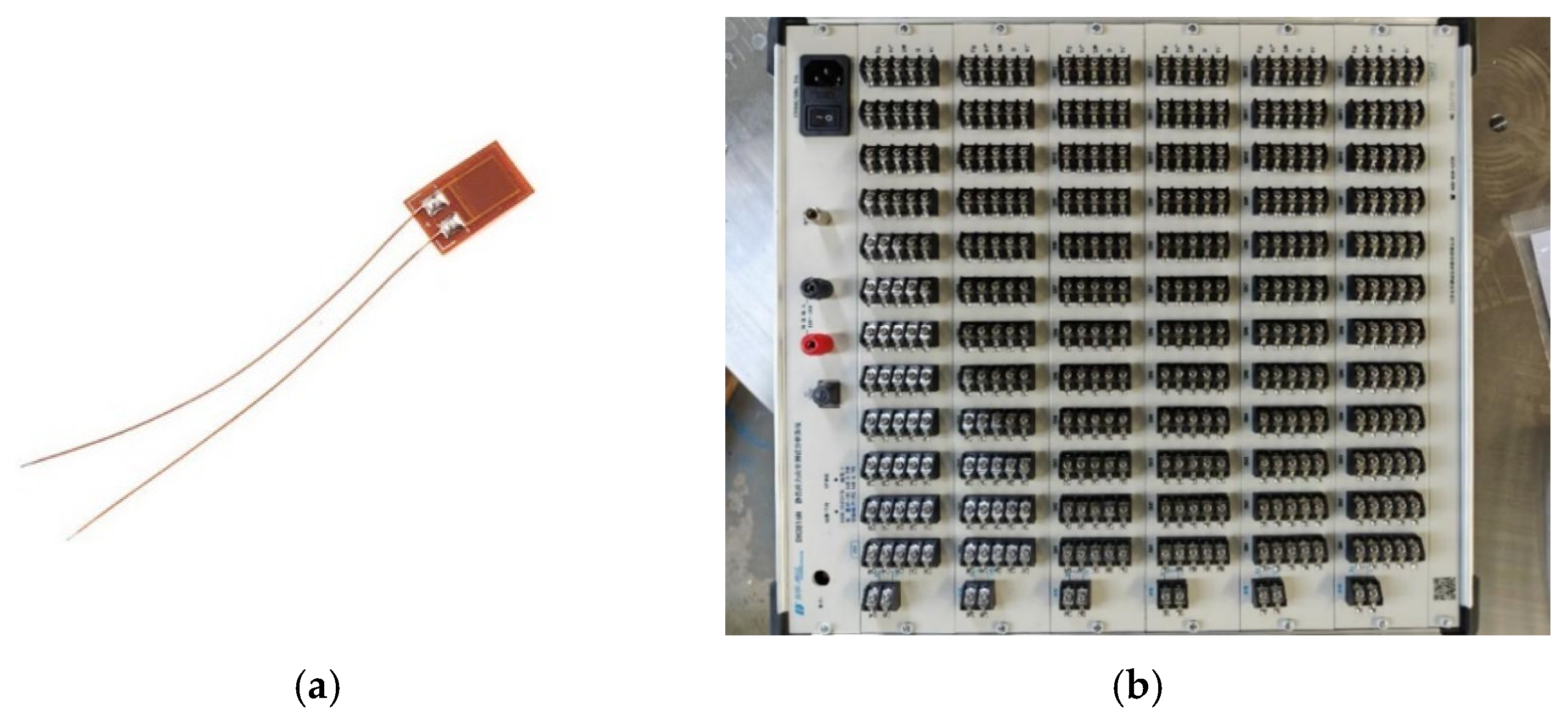
2.3. Data Acquisition Device and Monitoring Protocol
2.3.1. Data Acquisition Device
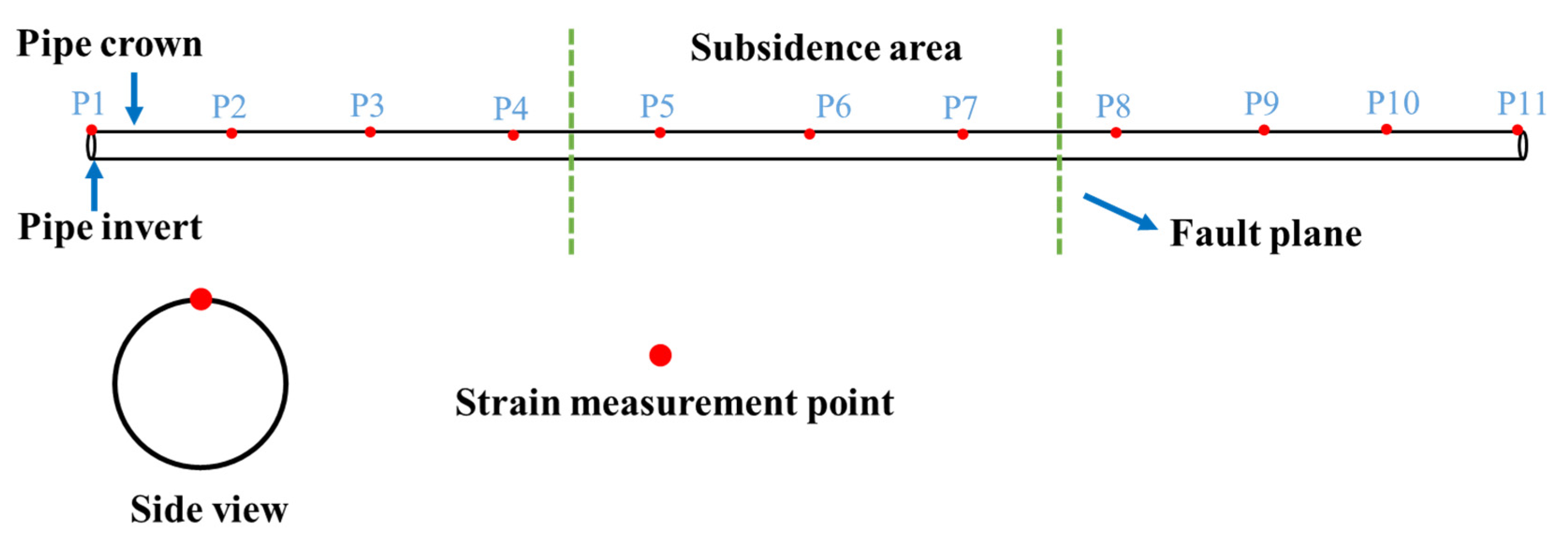
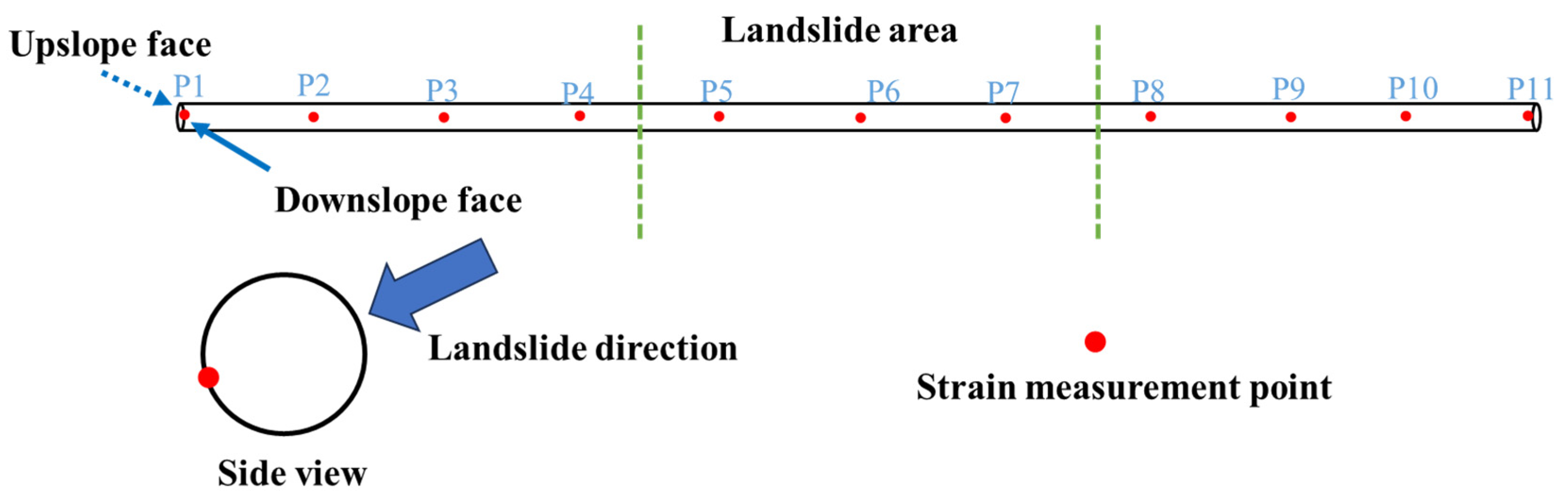
2.3.2. Monitoring Protocol
3. Pipe–Soil Interaction Test Results
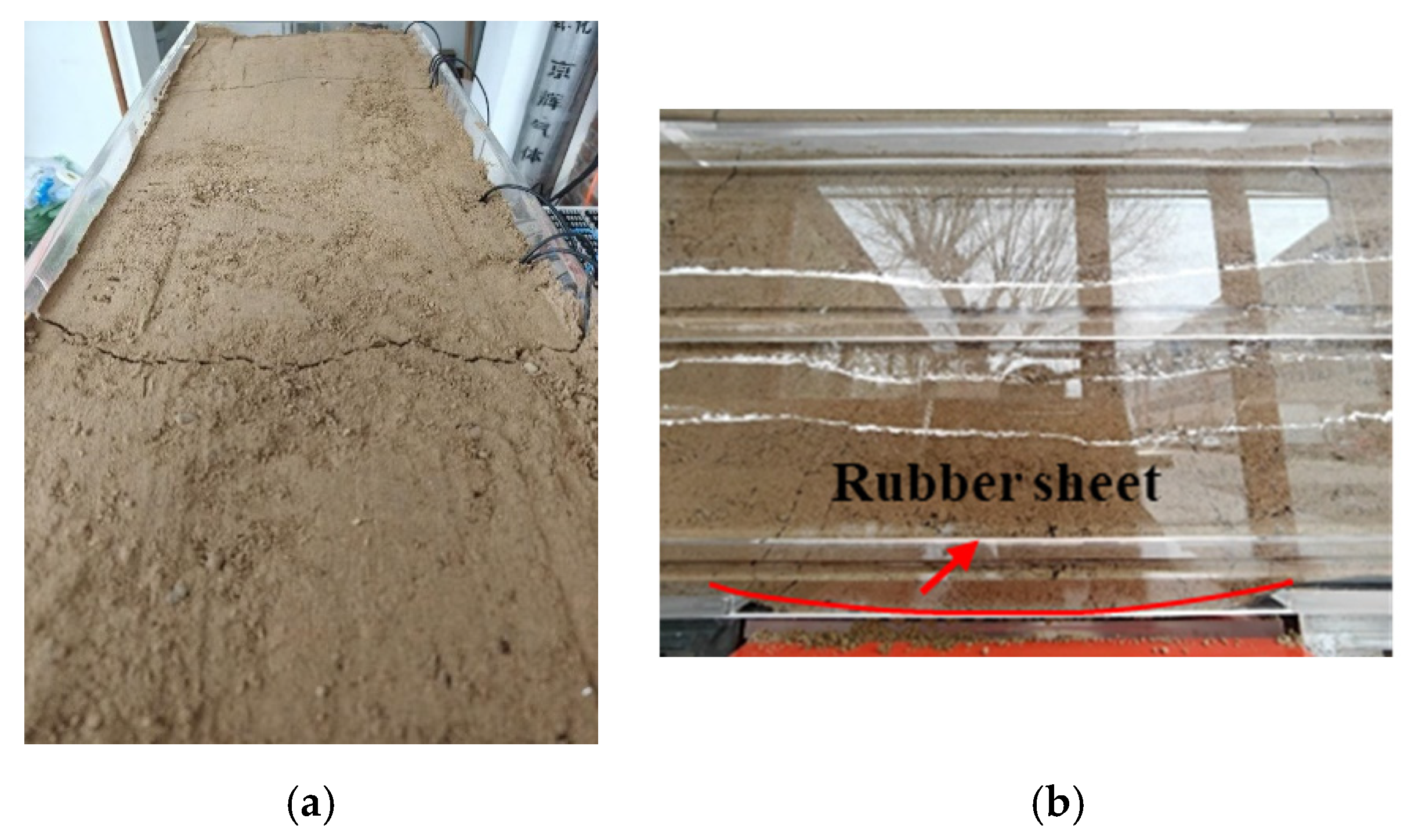
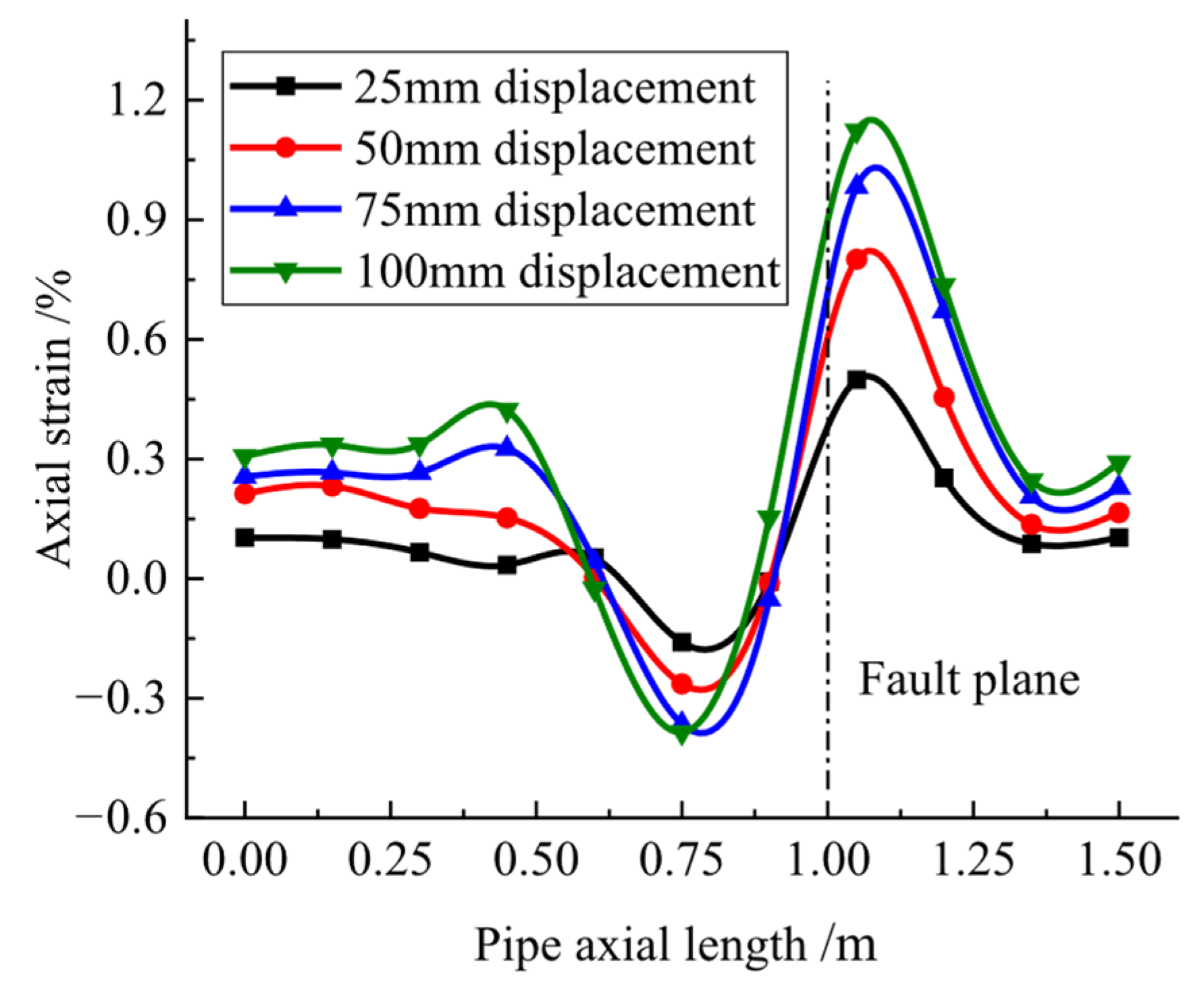
3.1. Test Results Under Fault Action
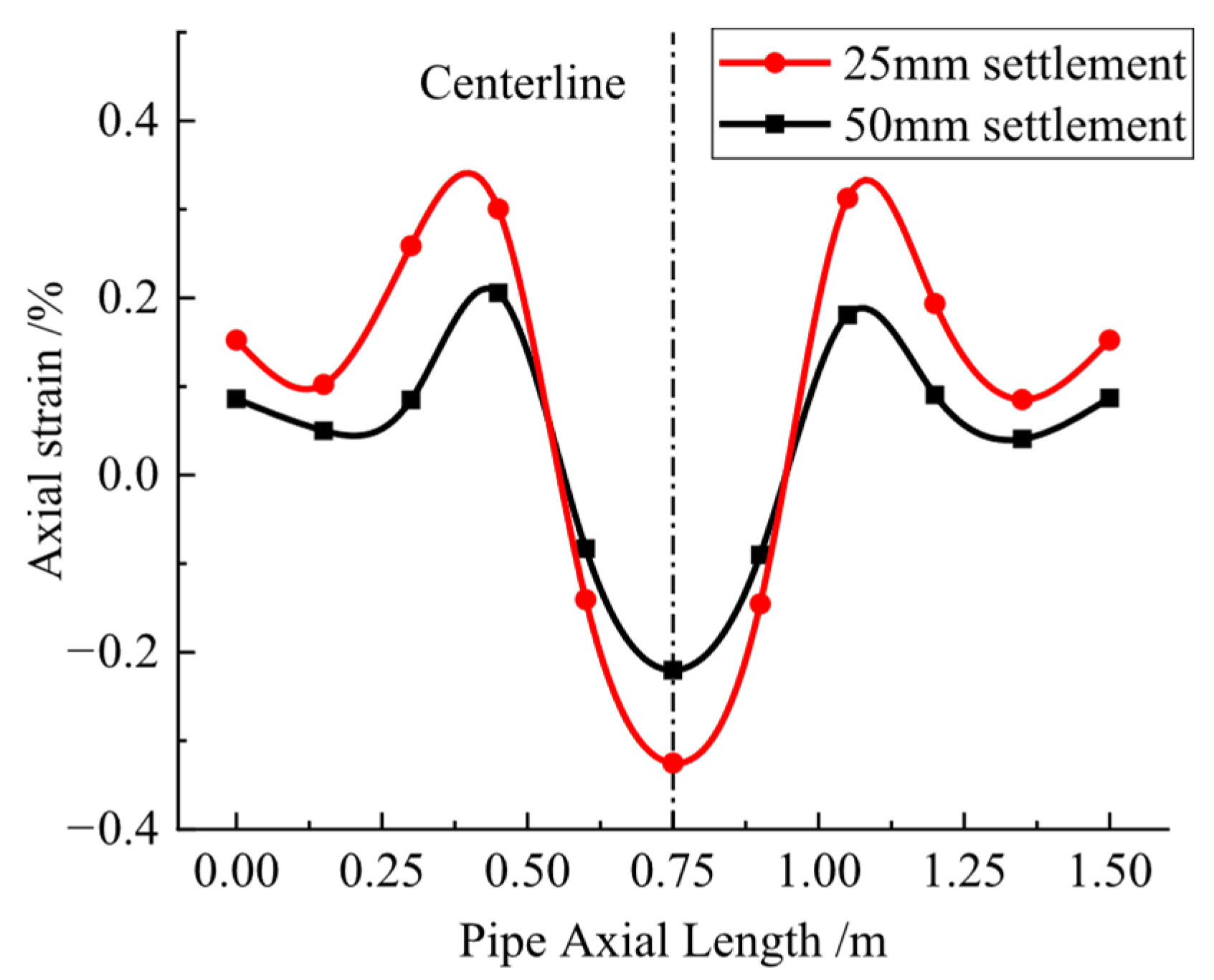
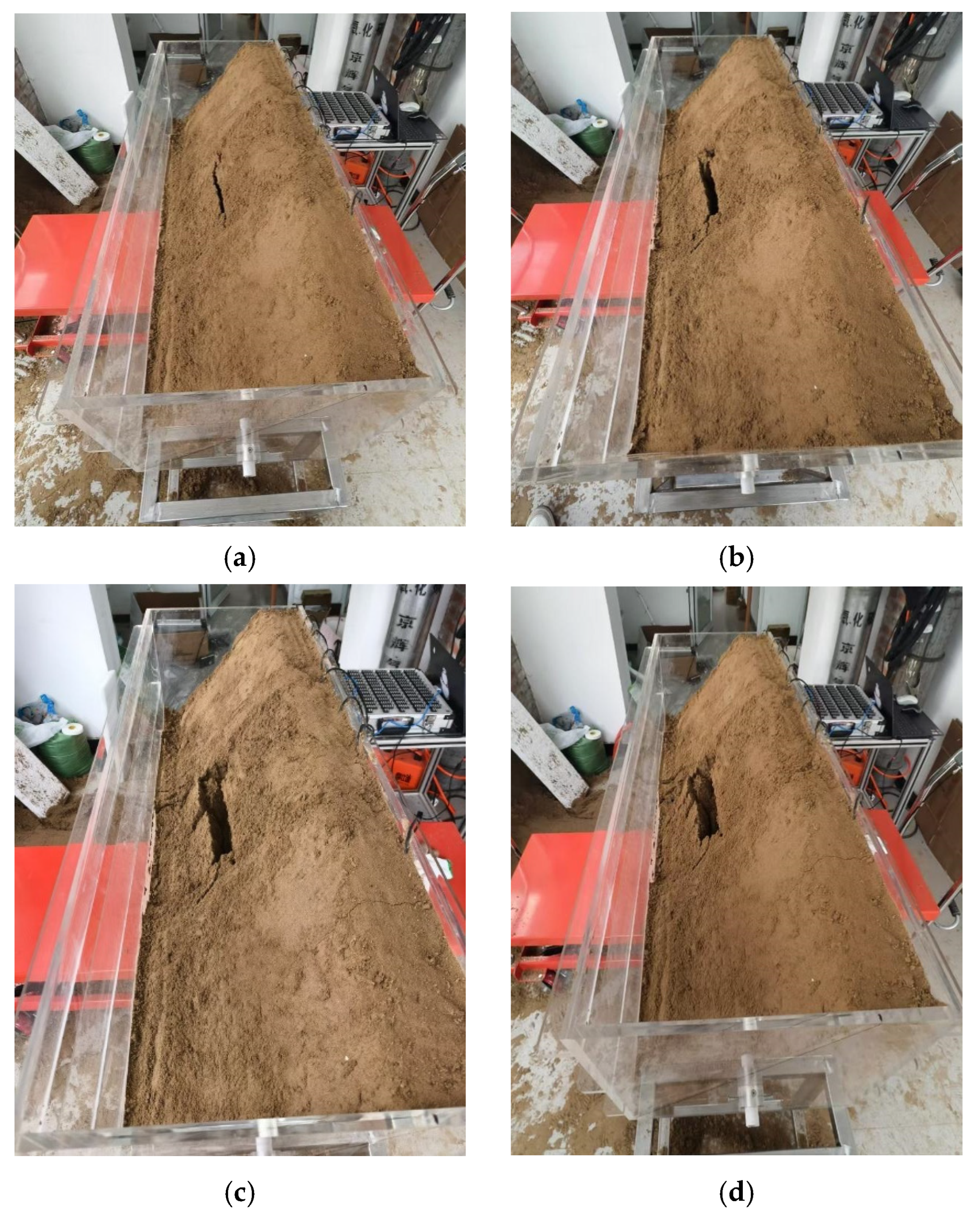
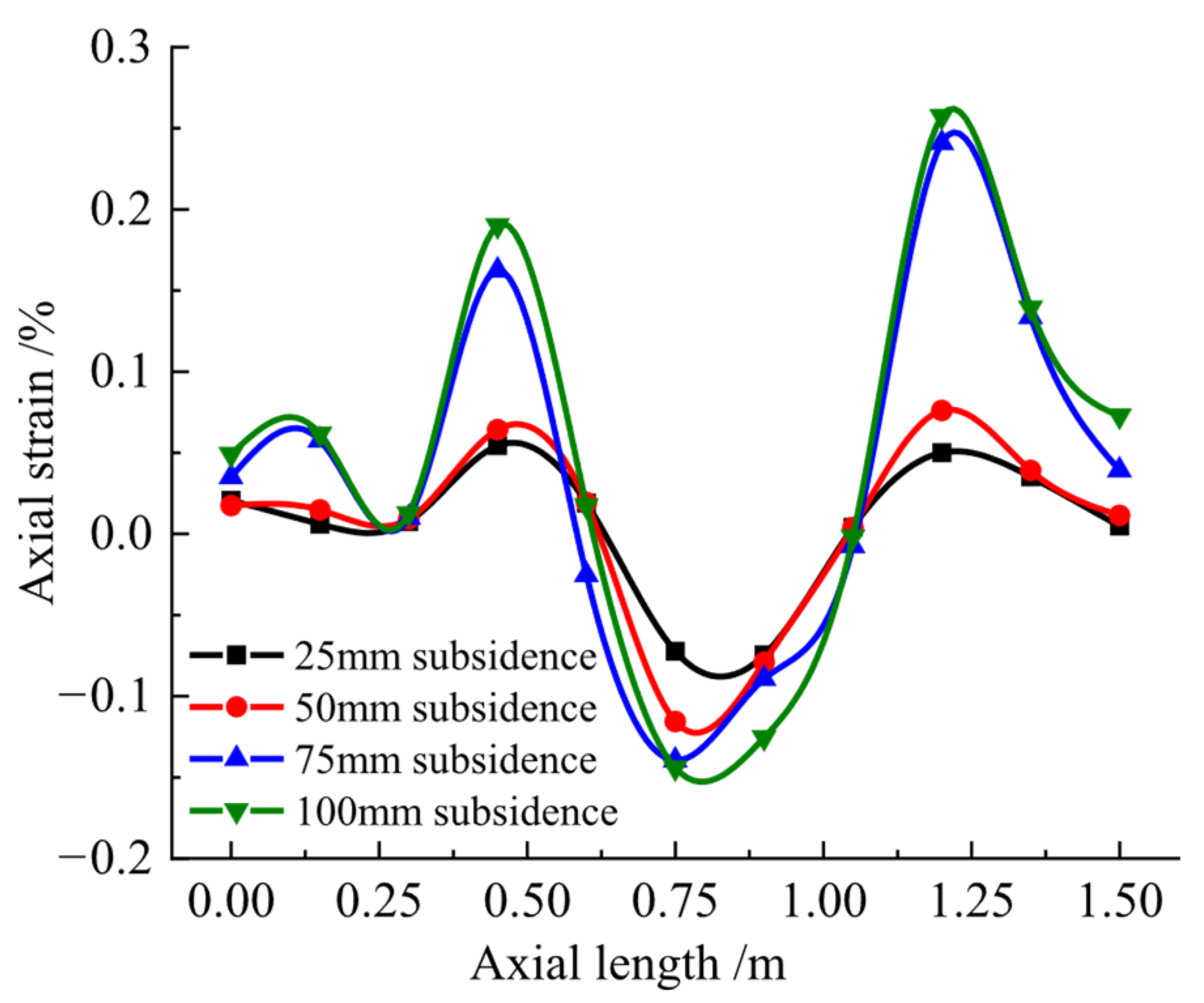
3.2. Test Results Under Settlement Action
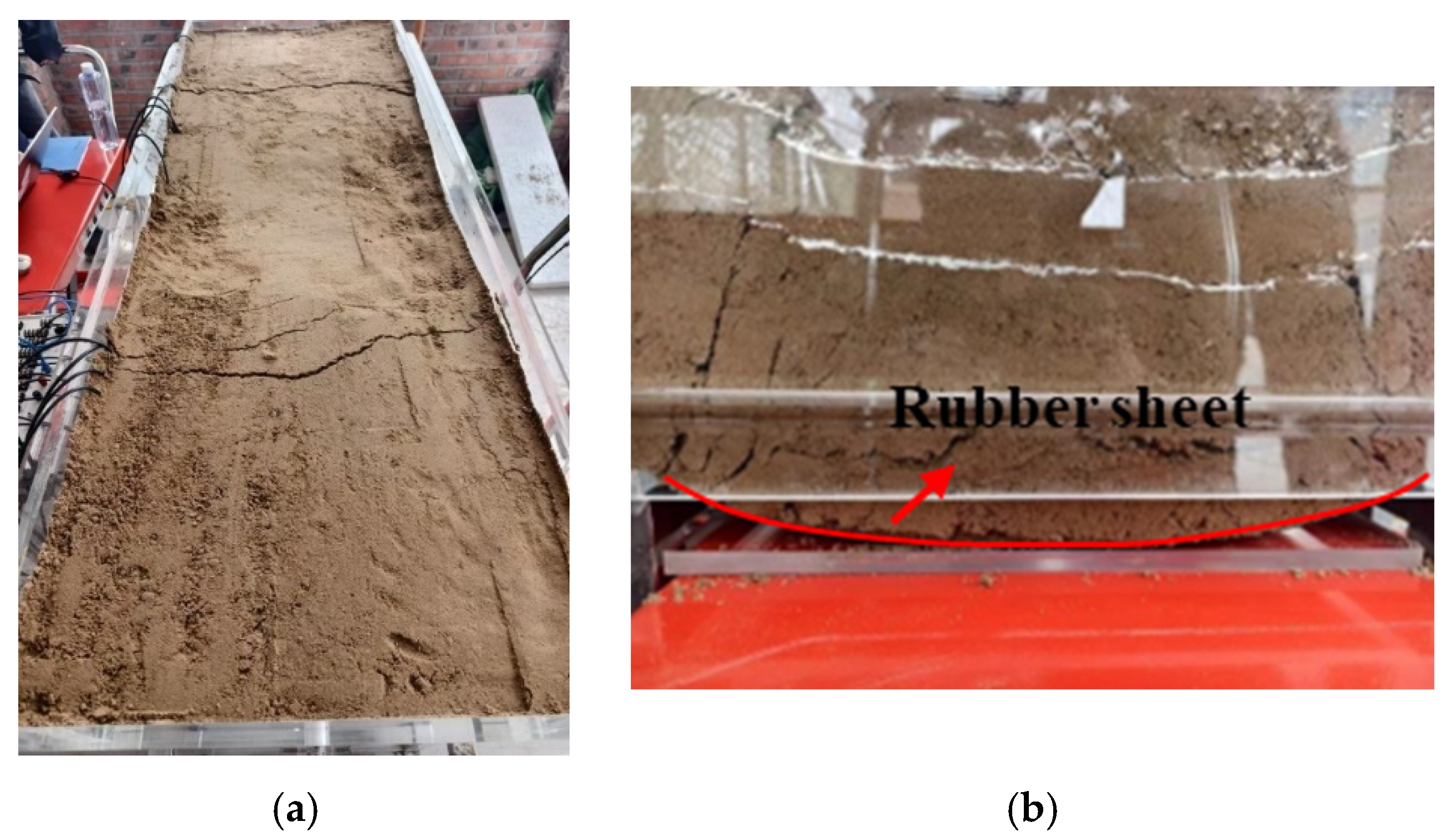
3.3. Test Results Under Landslide Action
4. Multifaceted Numerical Simulation Model
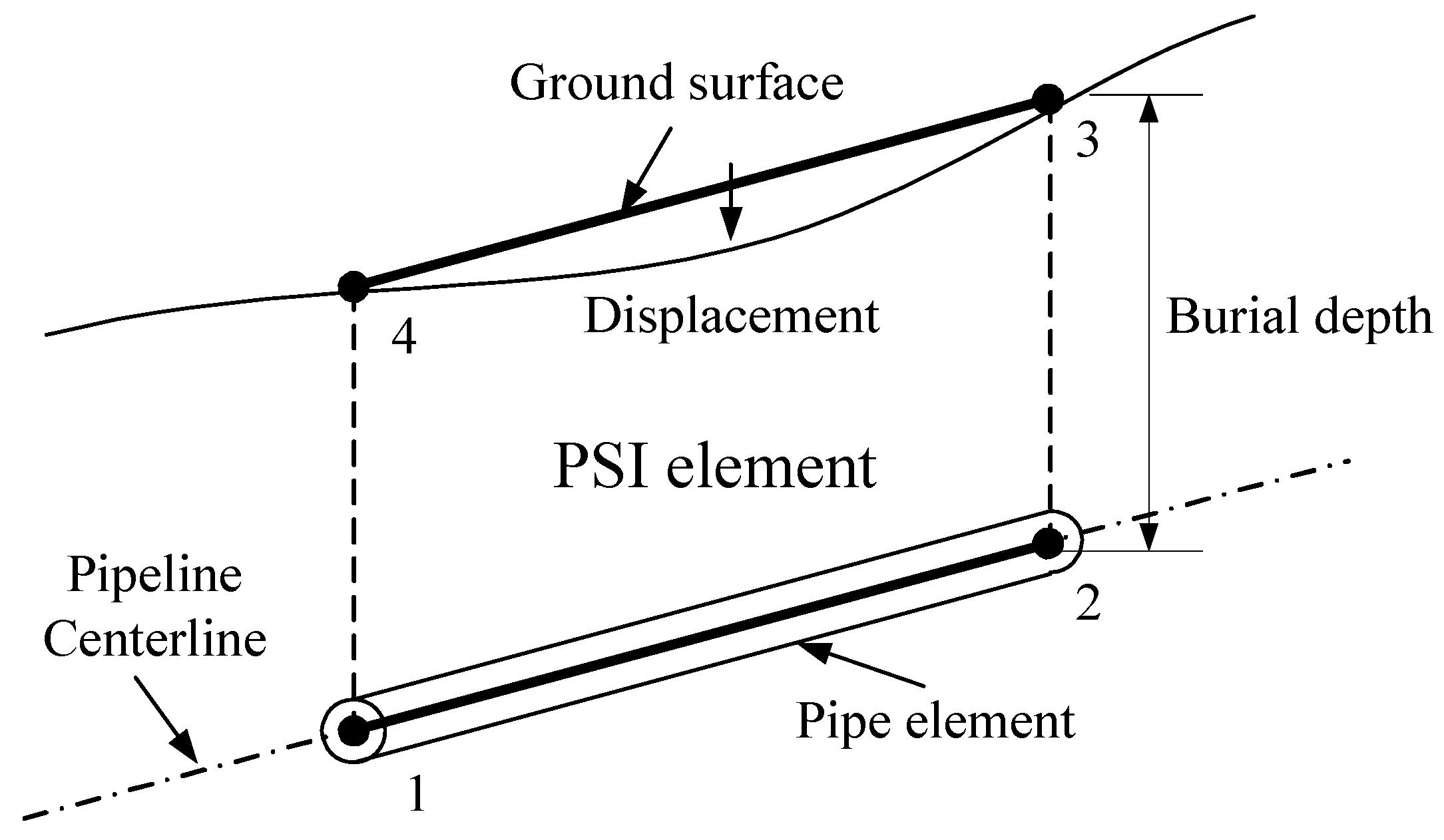
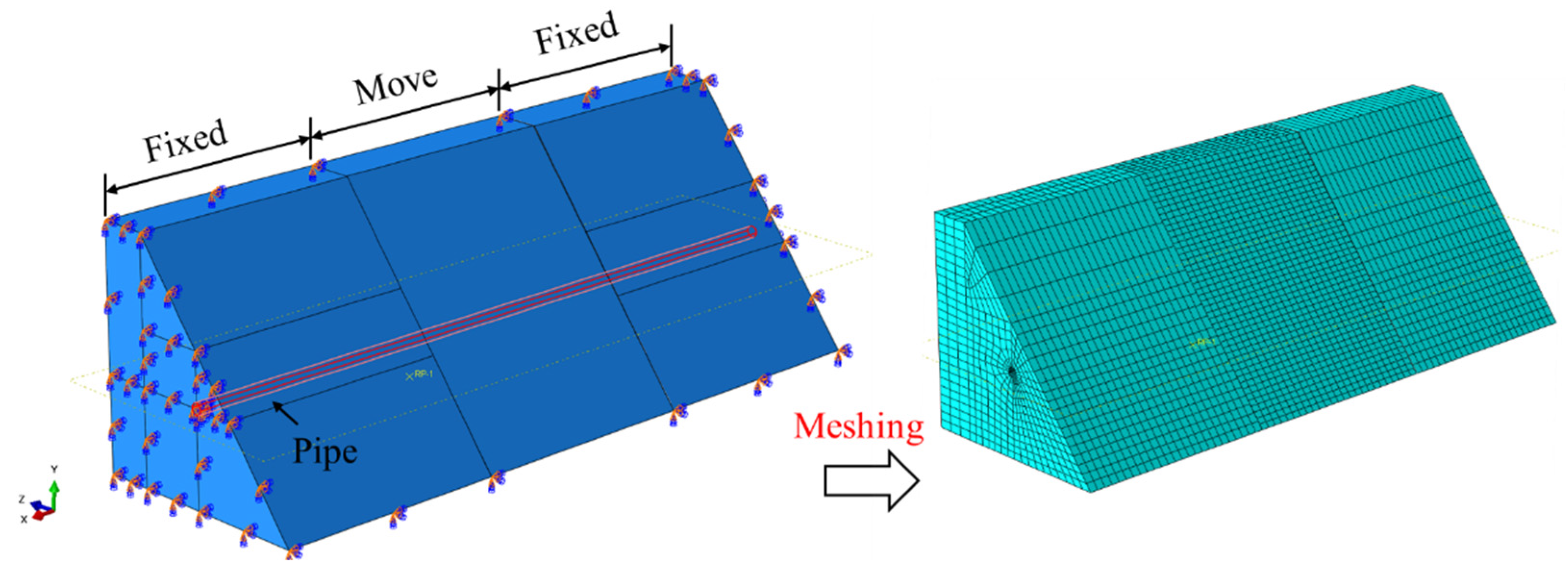
4.1. Soil Spring-Based Pipe–Soil Coupling Model
4.1.1. Soil Spring Constitutive Model
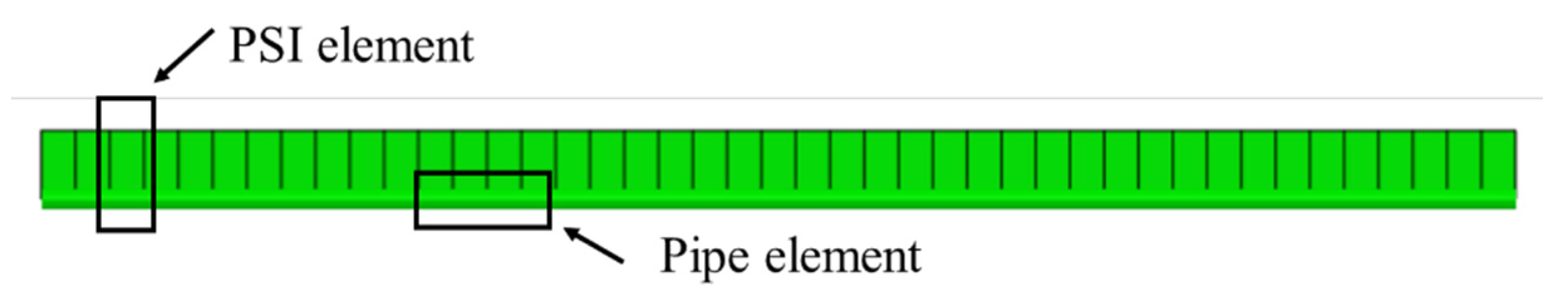
4.1.2. Introduction of the Finite Element Model
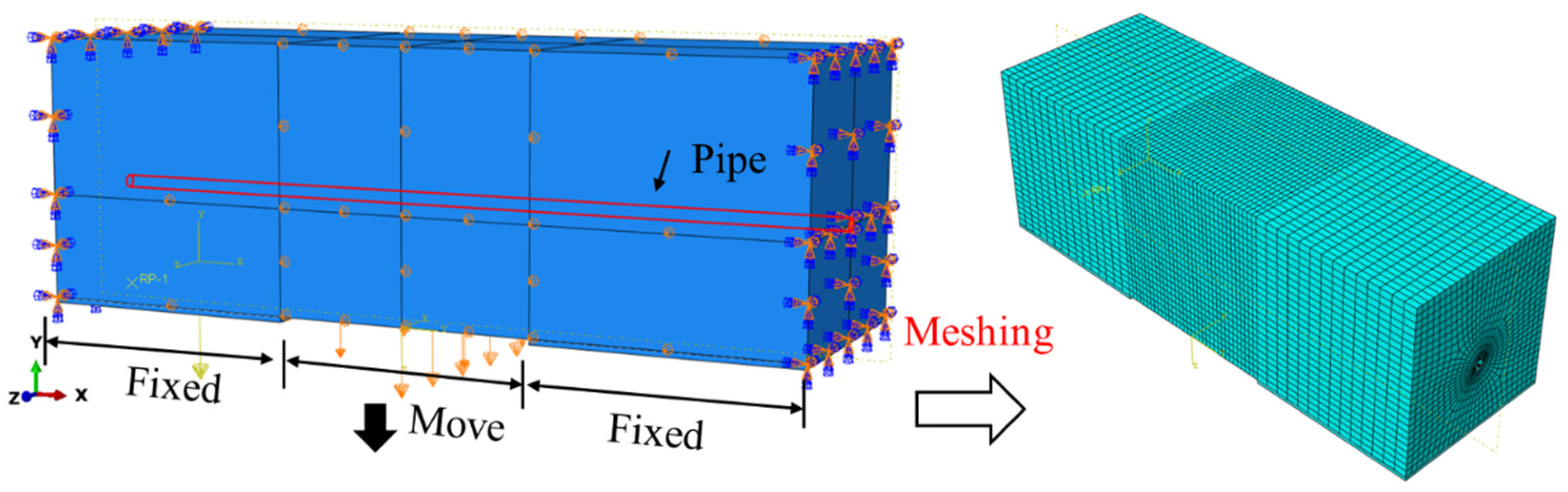
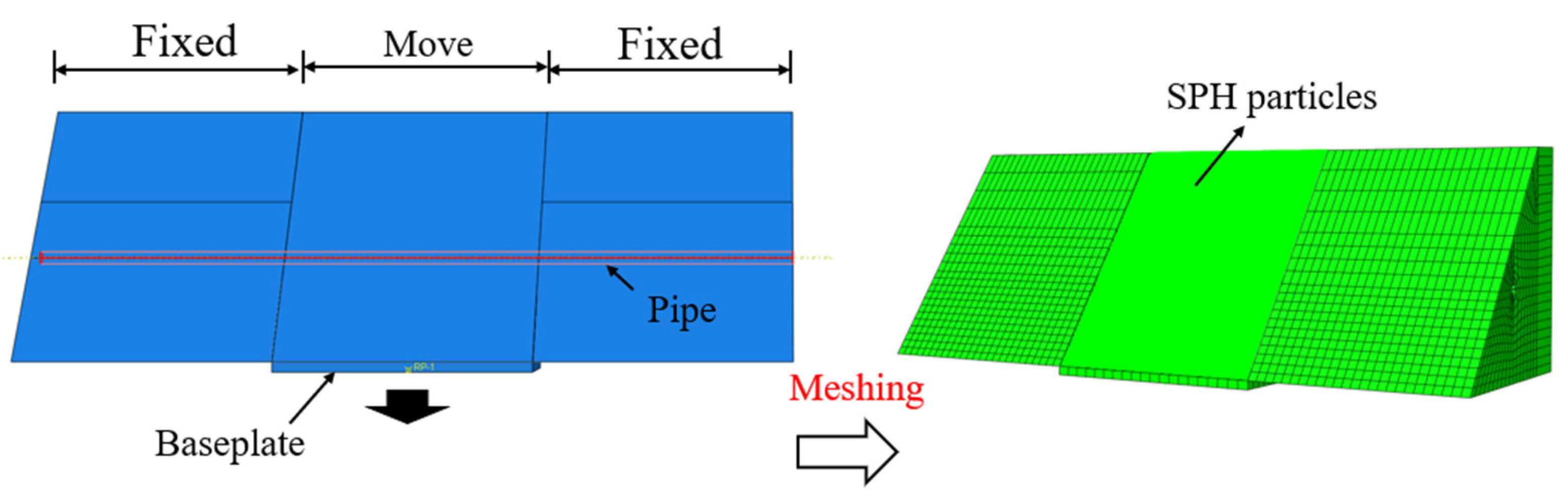
4.2. Traditional FEM Pipe–Soil Coupling Model
4.2.1. FEM Method
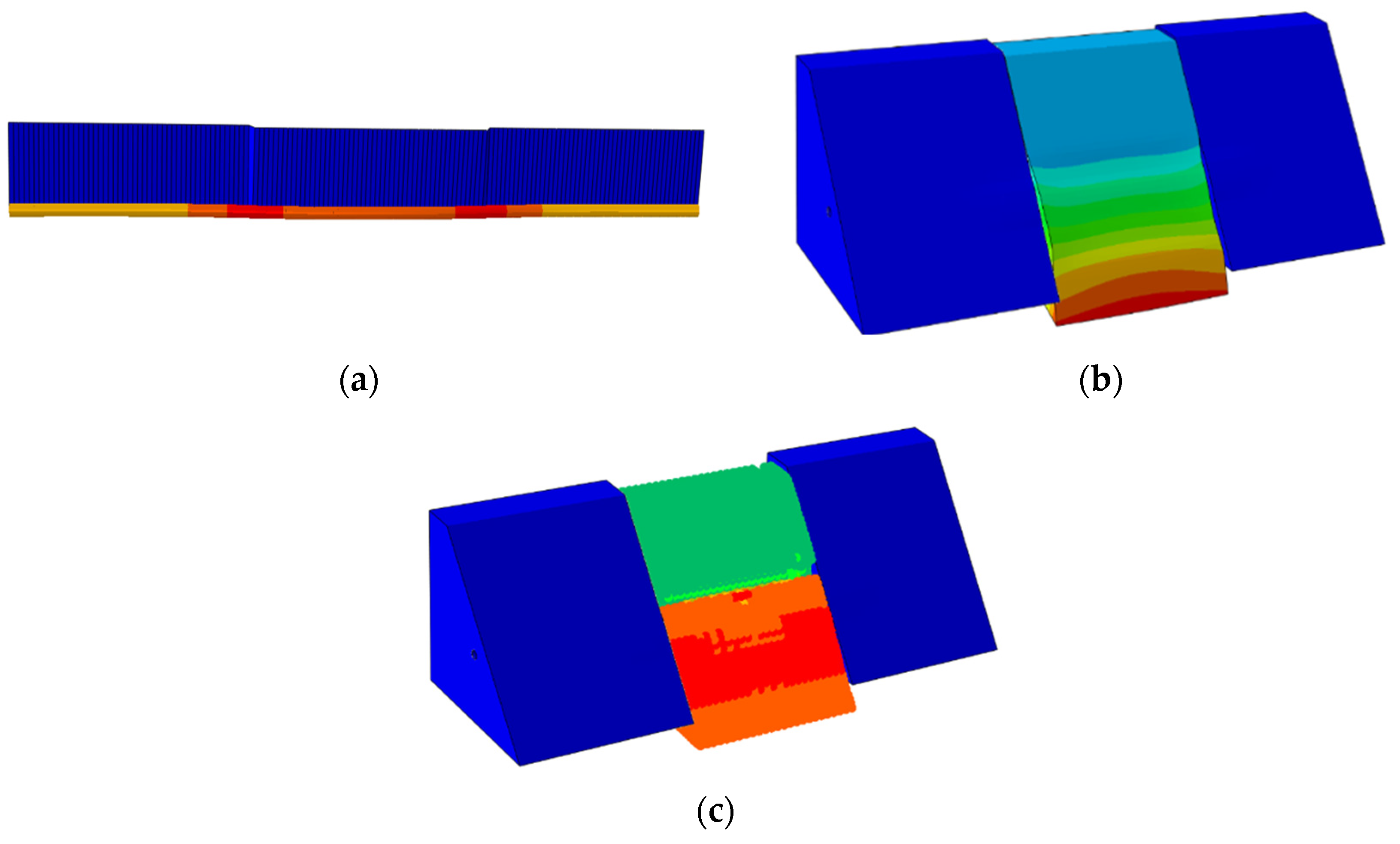
4.2.2. Introduction of the Finite Element Model
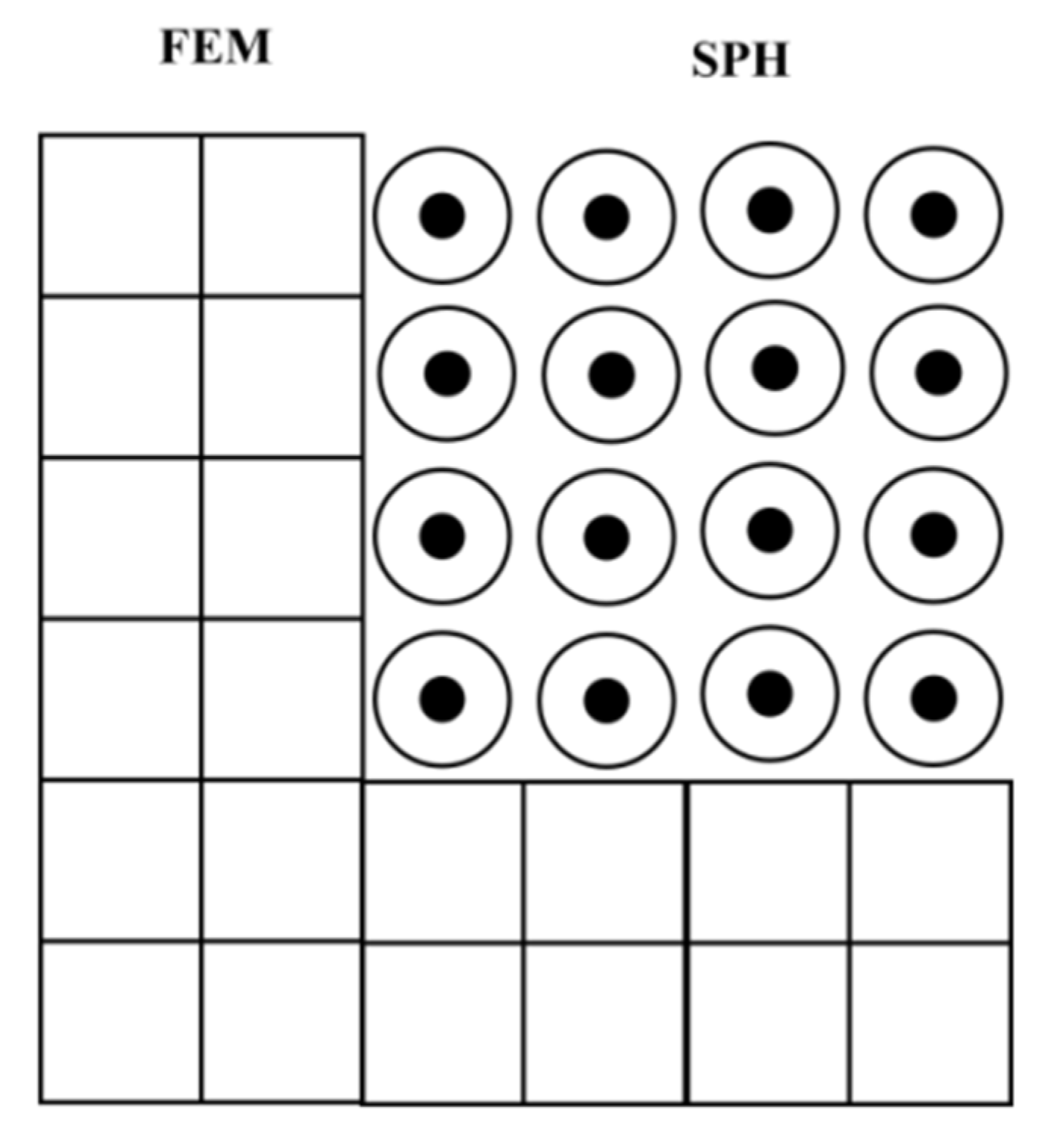
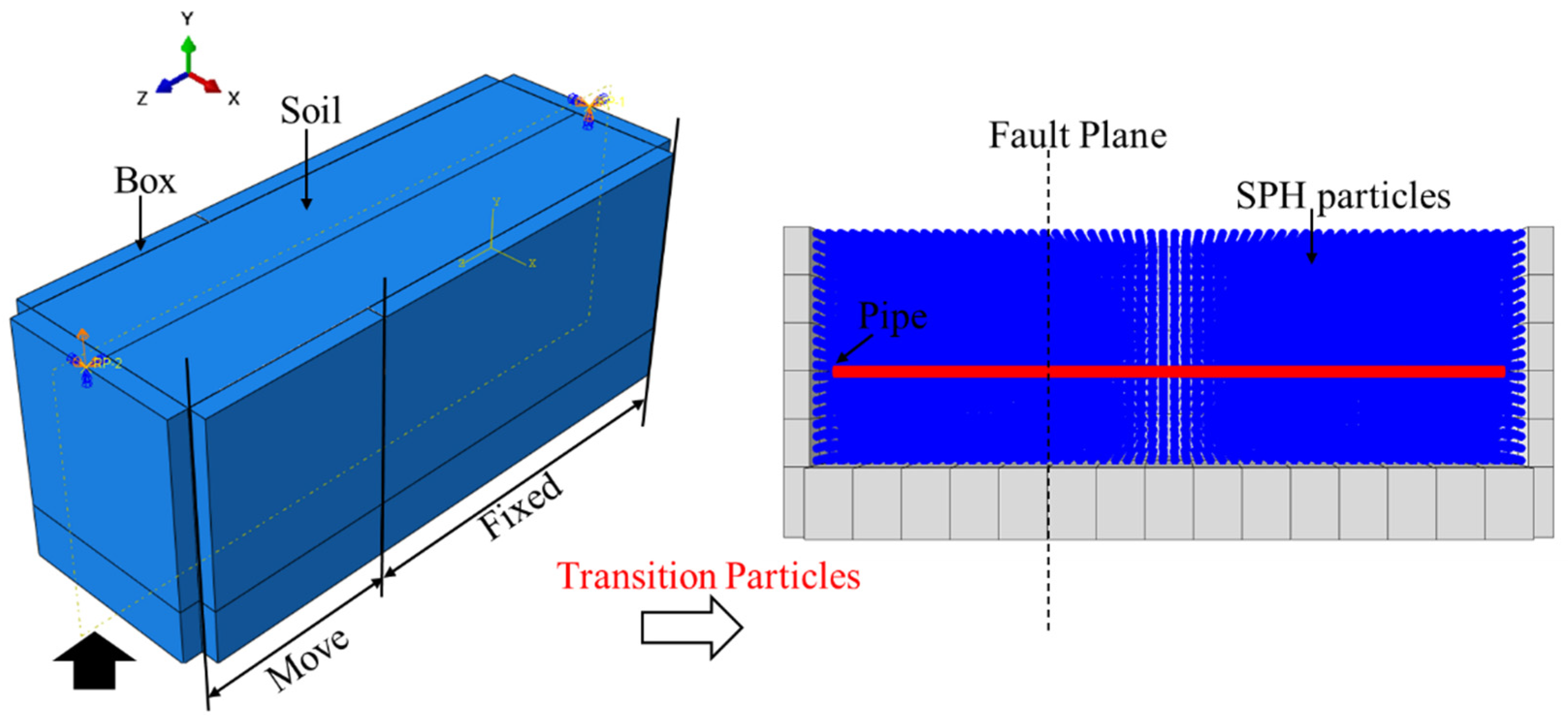
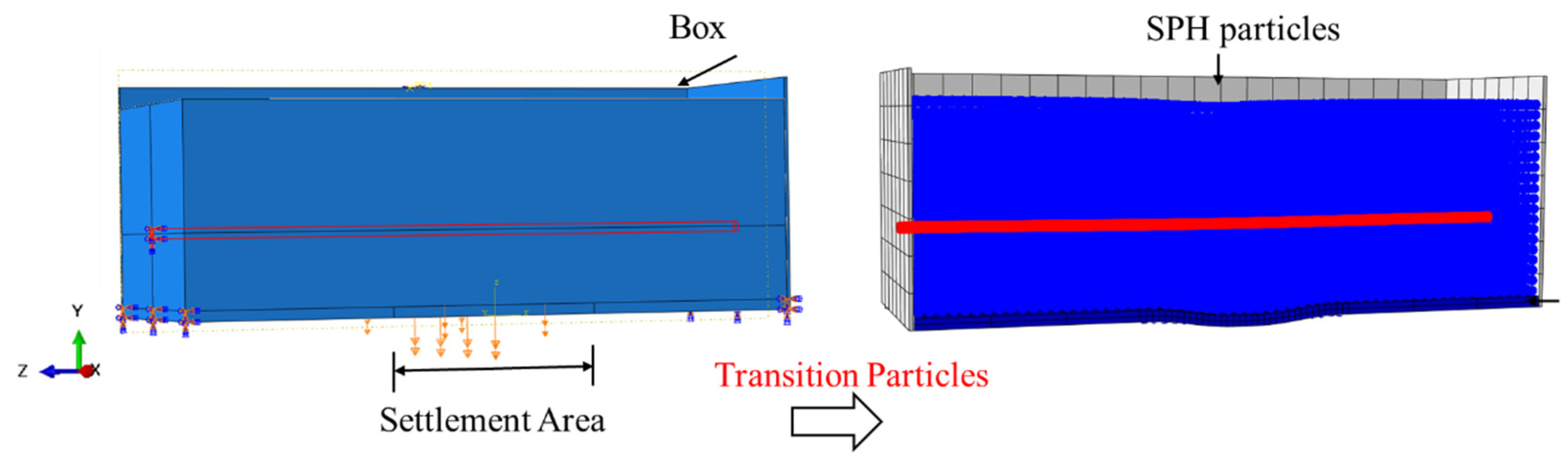
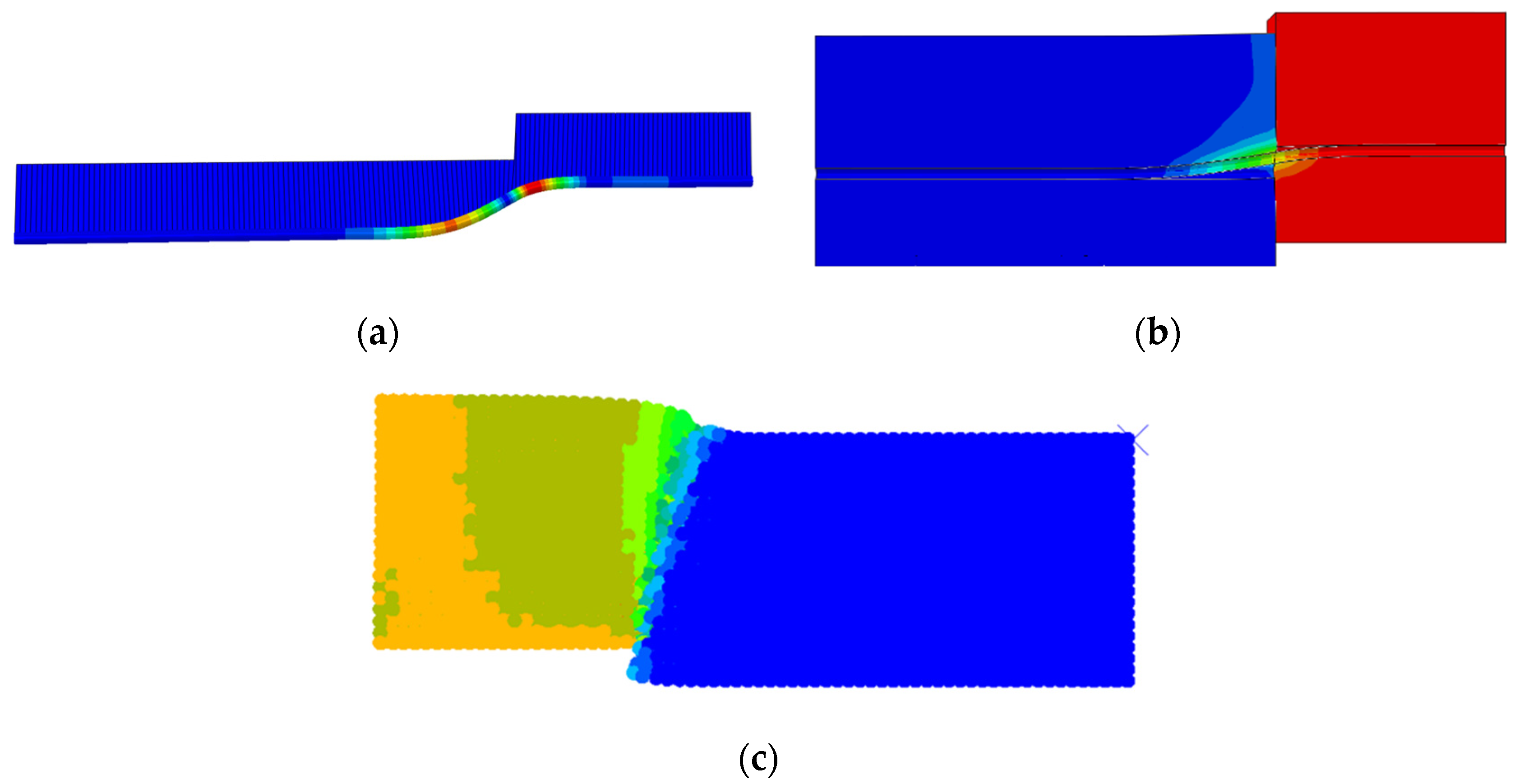
4.3. SPH-FEM Pipe–Soil Coupling Mode
4.3.1. SPH Method
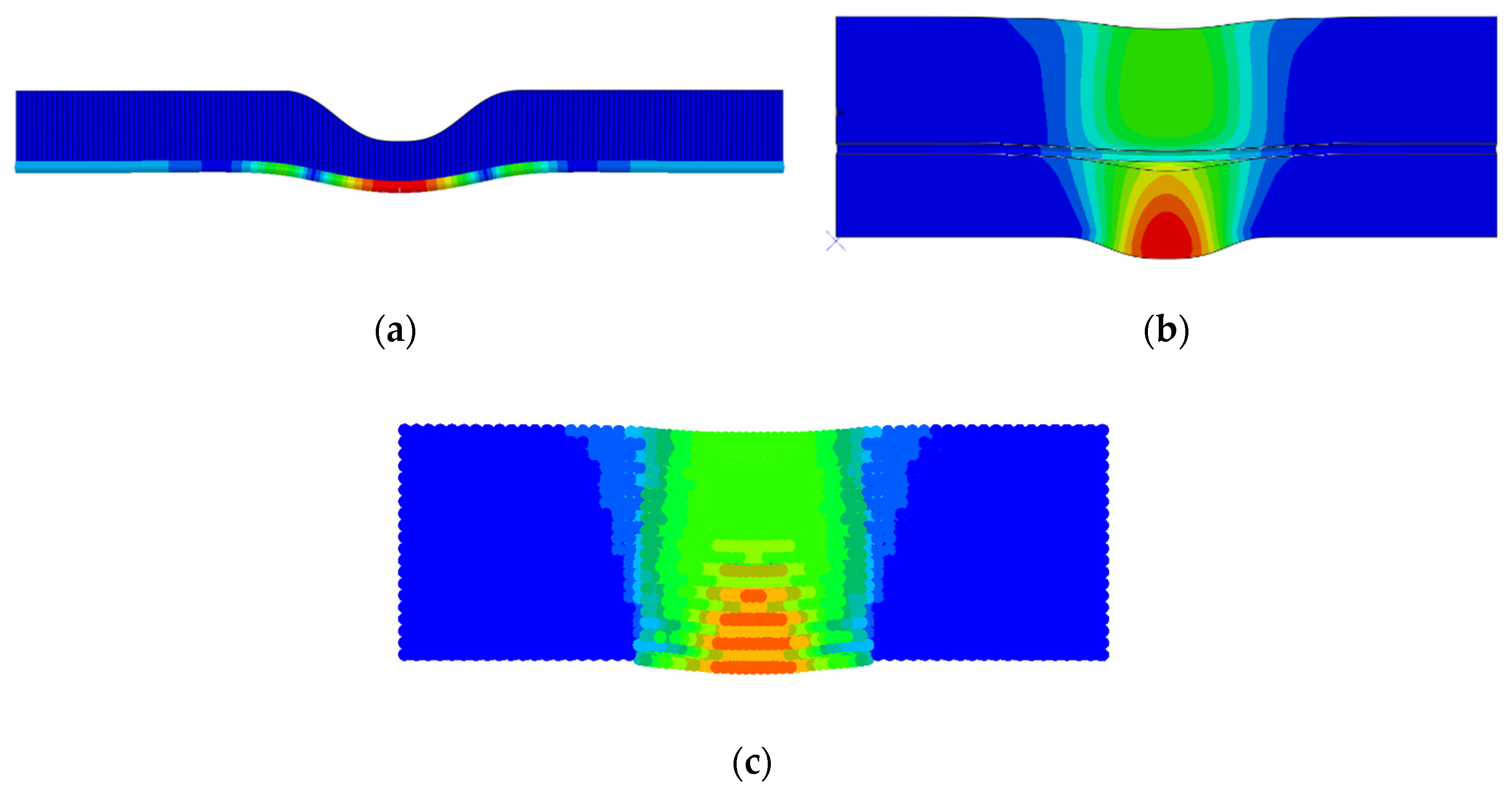
4.3.2. Introduction of the Finite Element Model
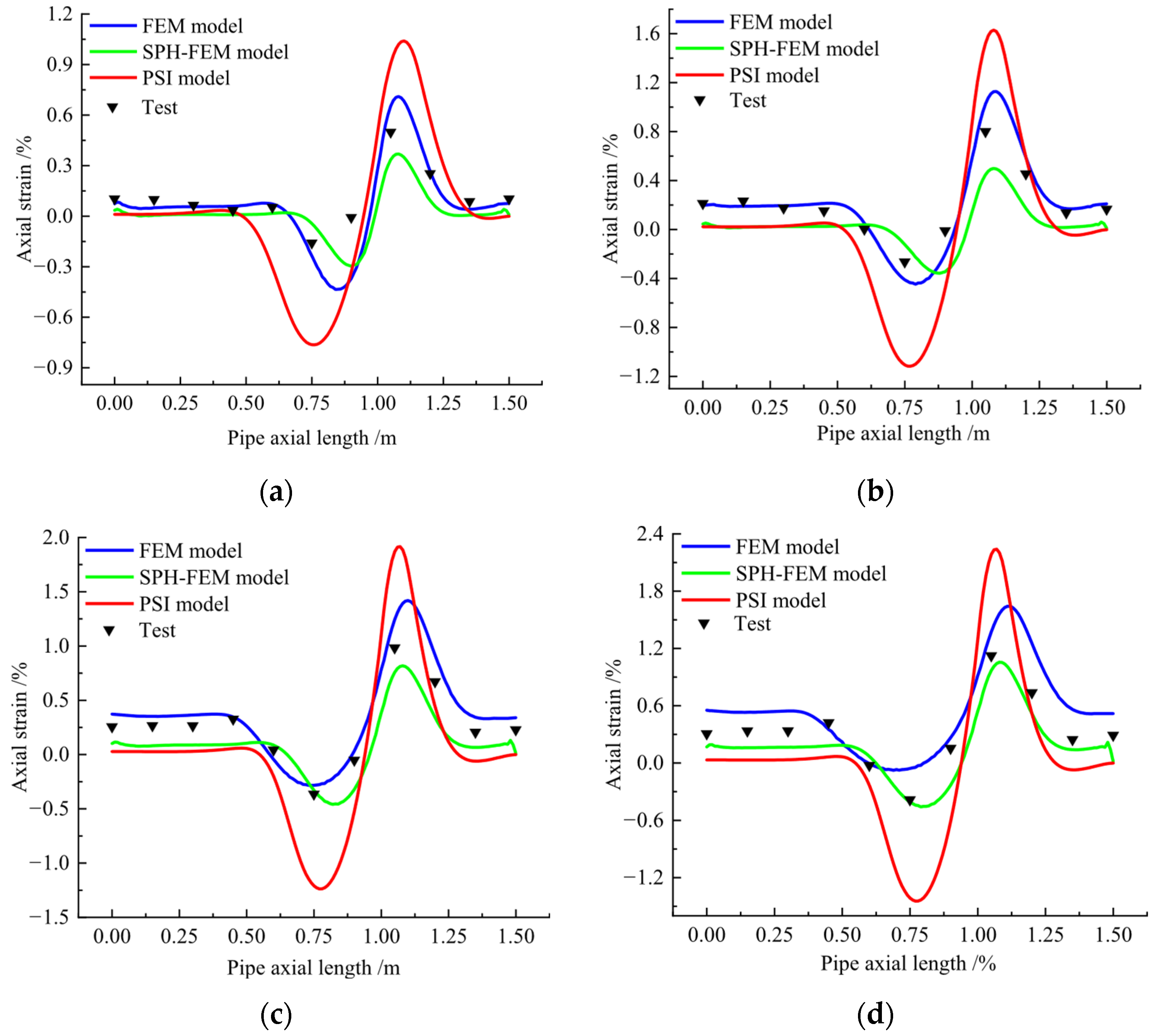
5. Analysis of Numerical Simulation and Experimental Results
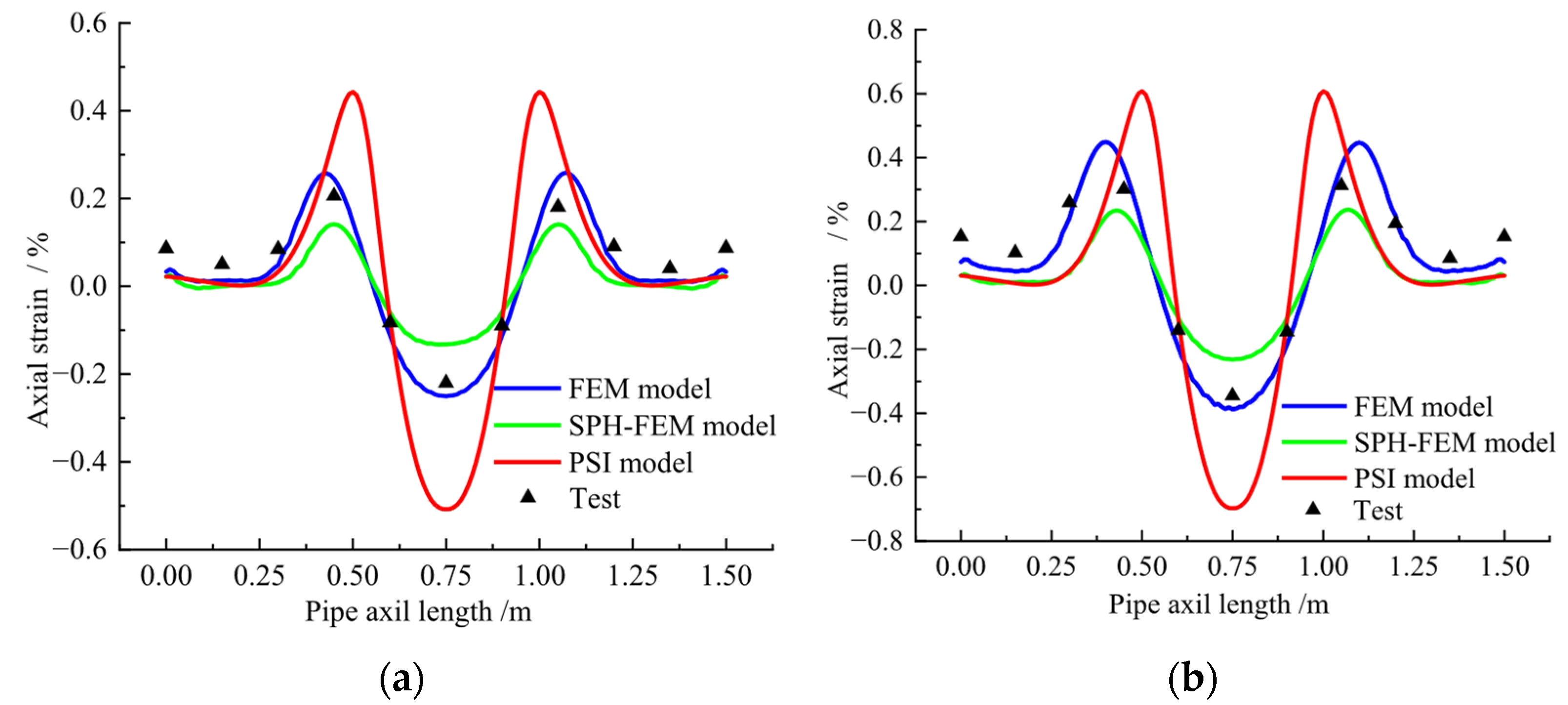
5.1. Fault Action
5.2. Settlement Action
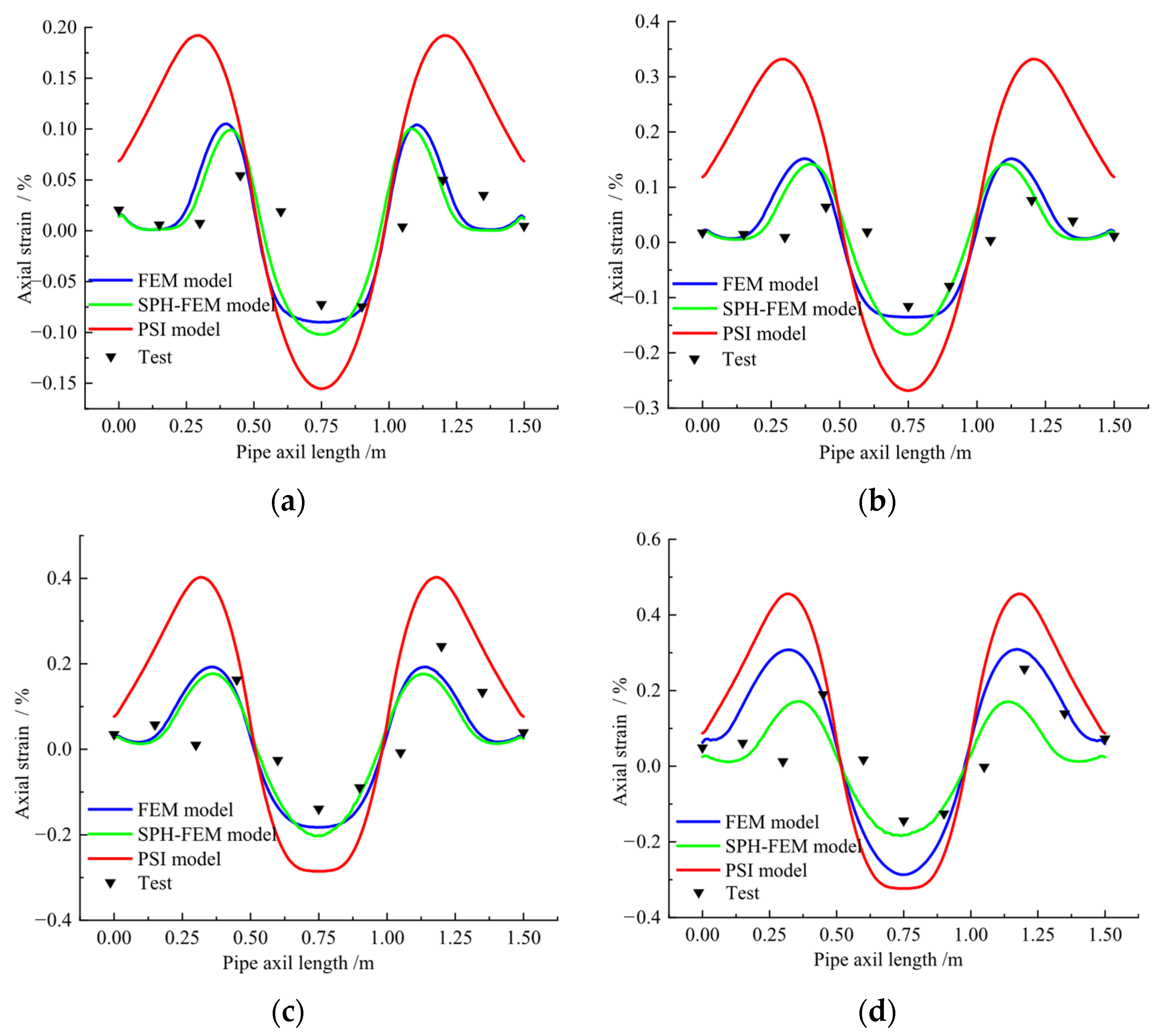
5.3. Landslide Action
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, T.W.; Liu, X.B.; Huang, W.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Strain response study of CFRP pre-reinforced pipelines under reverse fault displacement. China Pet. Pet. Mach. 2023, 51, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Tu, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Fu, G.; Qiu, R.; Liao, Q.; Xu, N. Role of oil and gas pipelines in the construction of a new energy system with multi-energy integration. Oil Gas Storage Transp. 2025, 44, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Analysis of Pipeline Stress State and Risk Assessment Under Slope Conditions. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jang, J. The behavior analysis of buried pipeline: Considering longitudinal permanent ground deformation. In Pipelines 2001: Advances in Pipelines Engineering and Construction; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, S.; Hassani, N.; Fukuda, K. A new proposal for simplified design of buried steel pipes crossing active faults. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2001, 30, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Symans, M.D.; O’Rourke, M.J.; Abdoun, T.H.; O’Rourke, T.D.; Palmer, M.C.; Stewart, H.E. Numerical modeling of buried HDPE pipelines subjected to normal faulting: A case study. Earthq. Spectra 2013, 29, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yu, Z.; Tong, L. Strain demand in areas of mine subsidence. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 24–28 September 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 391–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, B.L. Research on Digital Twin Technology for Pipeline Structures in Geological Hazard Zones. Master’s thesis, China University of Petroleum (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Numerical analysis of pipeline responses to ground subsidence. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L. Failure mechanism analysis of buried pipelines subjected to slope movement: Numerical modeling and parametric study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 111, 104453. [Google Scholar]
- Karamitros, D.K.; Bouckovalas, G.D.; Kouretzis, G.P. Numerical simulation of fault-pipeline interaction and its effects on design. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, B.; Liu, J. Interaction of pipelines with landslides: Analysis of mechanical properties at different strengths. Vibroeng. Procedia 2024, 57, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. Ministry of Housing and the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- American Lifelines Alliance (ALA). Guidelines for the Design of Buried Steel Pipe; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, K.; Zhang, J. Application of ABAQUS in Geotechnical Engineering; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Yan, F.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.M.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, S. Mechanism and flow process of debris avalanche in mining waste dump based on improved SPH simulation. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Imin, R. A kernel derivative free SPH method. Results Appl. Math. 2023, 17, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalotti, L.D.G.; Klapp, J.; Gesteira, M.G. The mathematics of smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) consistency. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 2021, 7, 797455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

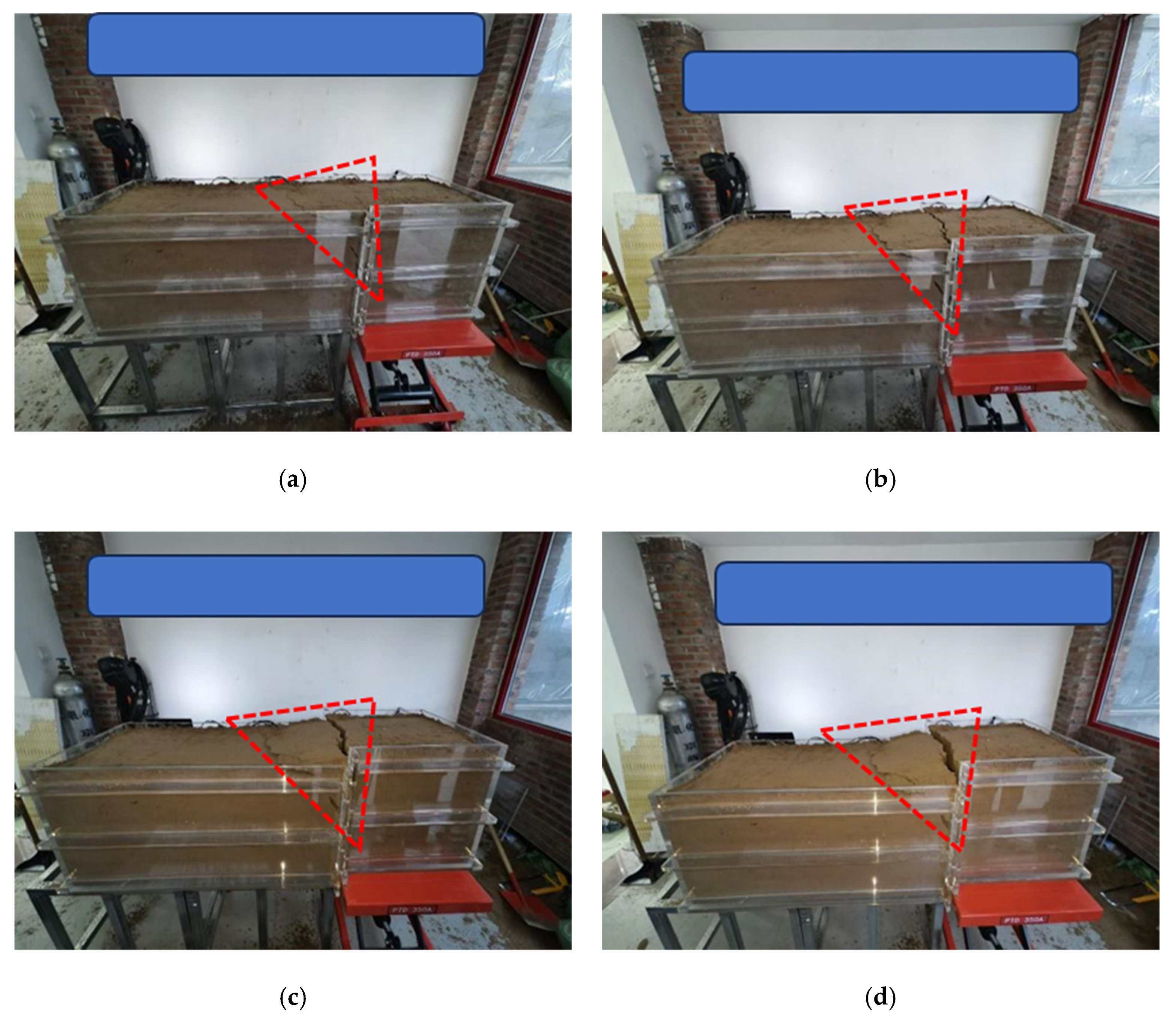



| Density | Elasticity Modulus | Poisson’s Ratio | Length | Diameter | Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1400 kg/m3 | 3500 MPa | 0.38 | 2 m | 25 mm | 1.5 mm |
| Horizontal Coordinate/mm | Settlement | |
|---|---|---|
| 25 mm | 50 mm | |
| −250 | 0 | 0 |
| −200 | 8.58 | 17.06 |
| −150 | 15.67 | 30.52 |
| −100 | 21.10 | 40.69 |
| −50 | 23.60 | 46.98 |
| 0 | 25.00 | 50.00 |
| 50 | 23.58 | 46.80 |
| 100 | 20.64 | 40.25 |
| 150 | 15.21 | 30.12 |
| 200 | 8.47 | 16.95 |
| 250 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, N.; Kong, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Experimental and Numerical Model Analysis of Pipe–Soil Interaction Under Typical Geohazard Conditions. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110286
Shi N, Kong T, Liu X, Zhang H. Experimental and Numerical Model Analysis of Pipe–Soil Interaction Under Typical Geohazard Conditions. Infrastructures. 2025; 10(11):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110286
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Ning, Tianwei Kong, Xiaoben Liu, and Hong Zhang. 2025. "Experimental and Numerical Model Analysis of Pipe–Soil Interaction Under Typical Geohazard Conditions" Infrastructures 10, no. 11: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110286
APA StyleShi, N., Kong, T., Liu, X., & Zhang, H. (2025). Experimental and Numerical Model Analysis of Pipe–Soil Interaction Under Typical Geohazard Conditions. Infrastructures, 10(11), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10110286







