Towards Smart Wildfire Prevention: Development of a LoRa-Based IoT Node for Environmental Hazard Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Transmission Frequency: This specifies the center channel within the Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) band.
- Bandwidth (BW): This impacts the transmission rate and sensitivity of the system; typical values are 125 kHz, 250 kHz, and 500 kHz.
- Code Rate (CR): This refers to the ratio of data bits to the total number of bits transmitted, including error correction bits. LoRa uses Forward Error Correction (FEC) coding at a variable rate between 4/5 and 4/8, allowing for better noise immunity.
- Spreading Factor (SF): This represents the encoded bits per chirp, ranging from 7 to 12. A higher SF means a larger chirp time and smaller bit rate, but higher sensitivity and range.
- A low-cost and energy-efficient environmental monitoring node, using LoRa communication, for deployment in remote wildfire prevention.
- The integration of multiple environmental sensors capable of capturing critical parameters related to wildfire prevention.
- Designing a modular and easy-to-use dashboard for real-time data visualization and analysis.
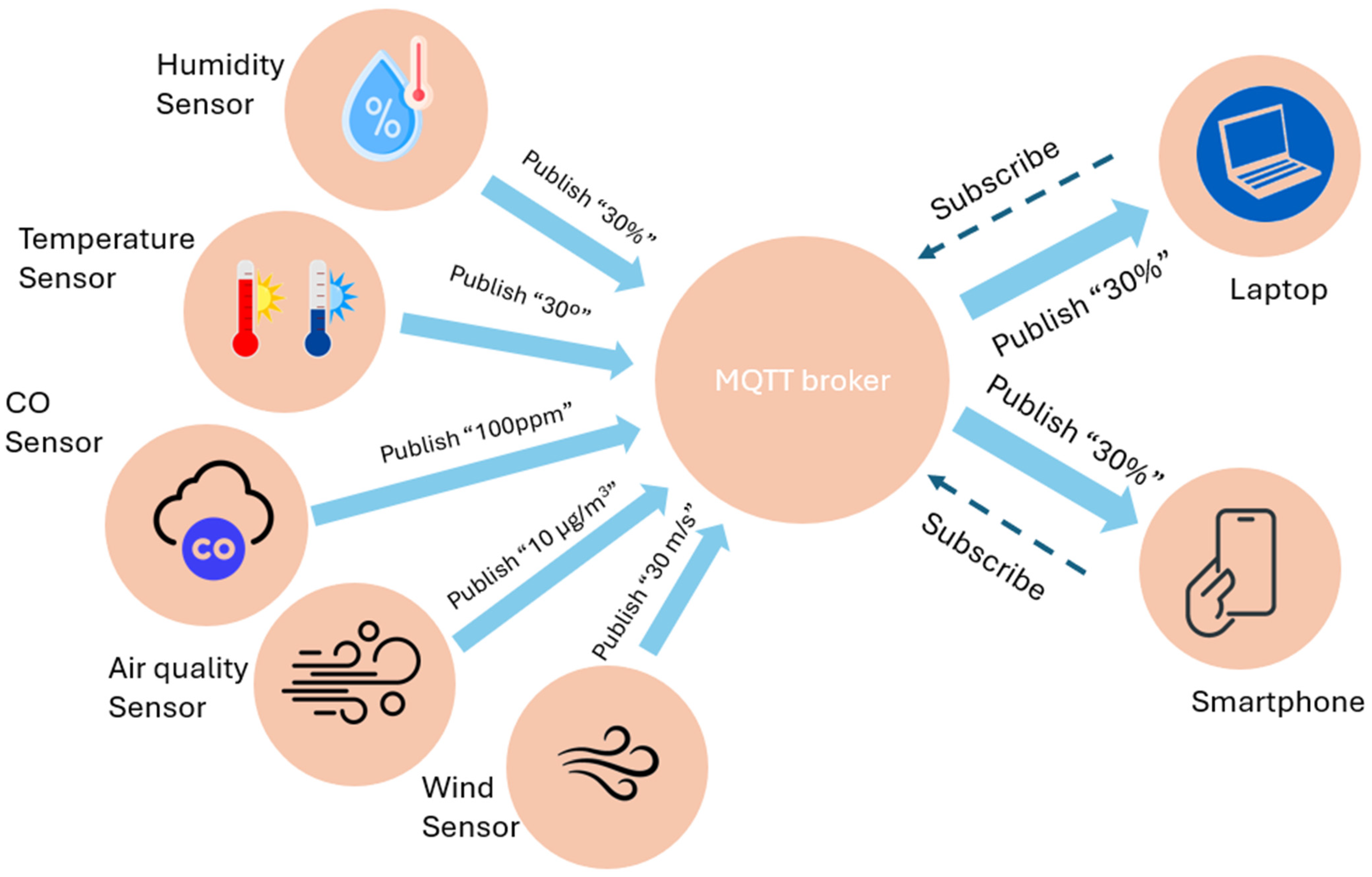
- Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication, focusing on Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) and Node Red.
- The existence of a proof-of-concept demonstrating the relevance of this system in providing early wildfire prevention capabilities and ultimately aiding in wildfire protection.
- Firmware implementation of wildfire safety rule: 30-30-30 [7].
2. State of the Art and Related Works
2.1. State of the Art
- Smart Cities: The implementation of IoT in cities has helped to improve the efficiency and quality of services at an urban level, improving quality of life for its citizens. It has uses in areas such as waste management, public safety, mobility, and energy saving [15]. Smart cities are one of the “children” of the IoT, playing a key role in the development of smarter and more sustainable cities.
- Digital Health: Monitoring biomedical sensors has been one of the areas of greatest applicability for IoT. Biomedical sensors can measure various physiological parameters of patients and send this data to a central monitoring unit. This revolution has allowed, for example, patients with chronic illnesses or recovering from surgery to be monitored remotely [16].
- Industrial IoT: The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is an extension of the IoT that focuses on the interconnection of industrial assets with Information Technology (IT). Through IIoT, sensors and devices are being incorporated into industrial machinery and equipment to collect data in real time, which can be analyzed and used to improve the efficiency and productivity of industry. Some examples of where IIoT is already being applied in industry include machine monitoring and equipment maintenance forecasting [17].
- Smart Earth: As an integral part of the IoT, Smart Earth technologies aim to collect environmental data from a wide variety of sensors, including land, water, and air sensors, satellites, and monitoring devices [18]. The primary objective is to conserve and protect the planet, as well as to prevent potential human disasters, including tsunamis, floods, earthquakes, and fires [19].
2.2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
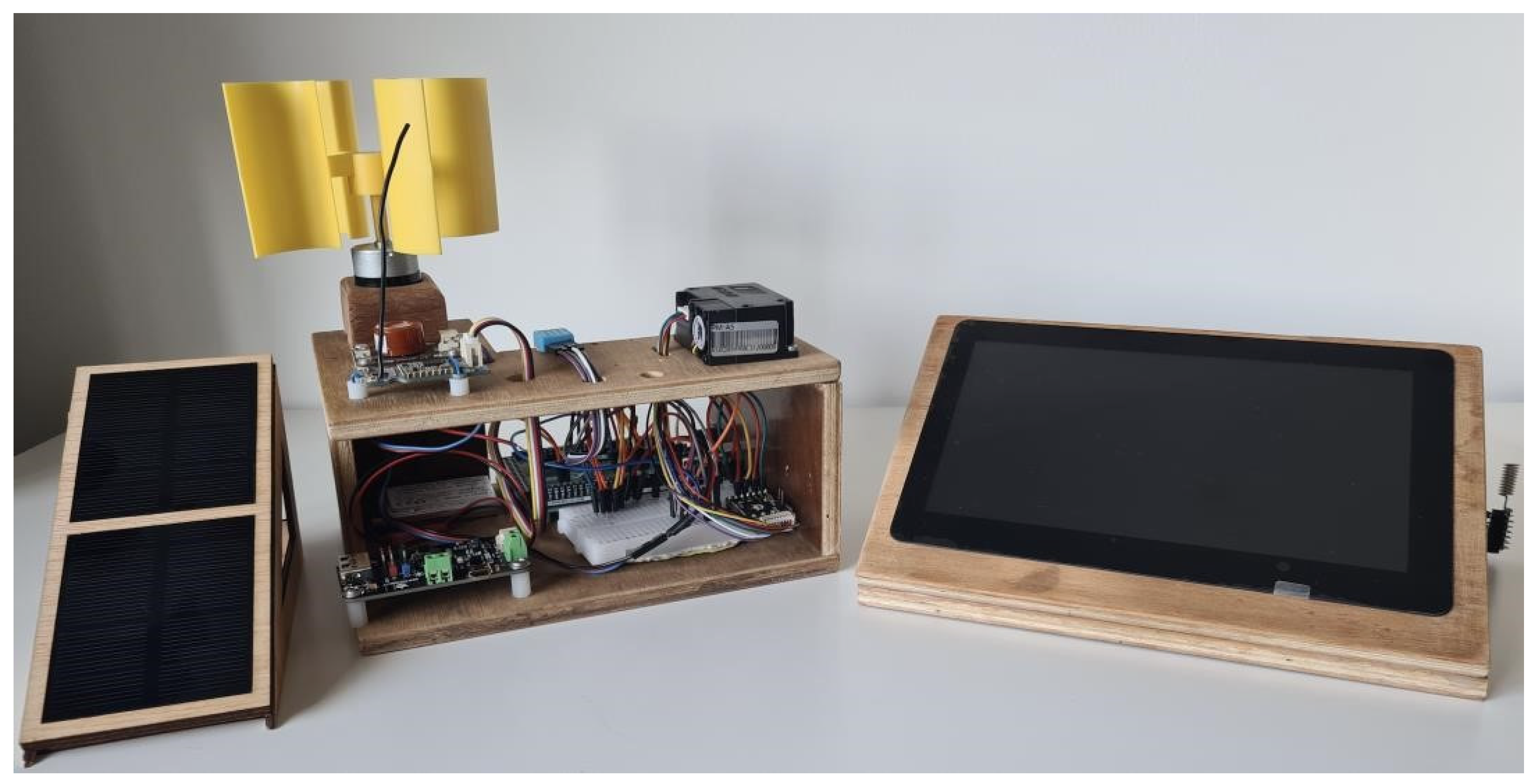
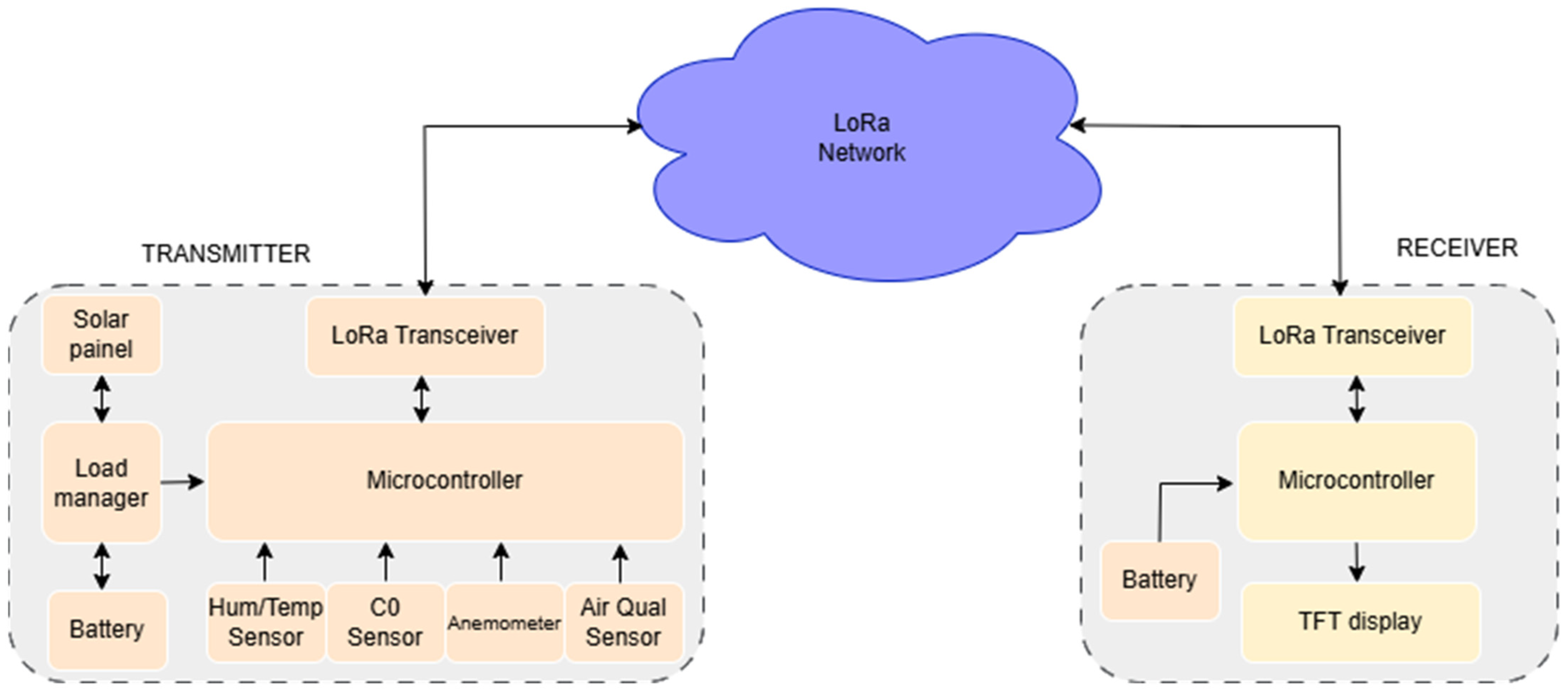
3.1. System Implementation and Hardware Setup
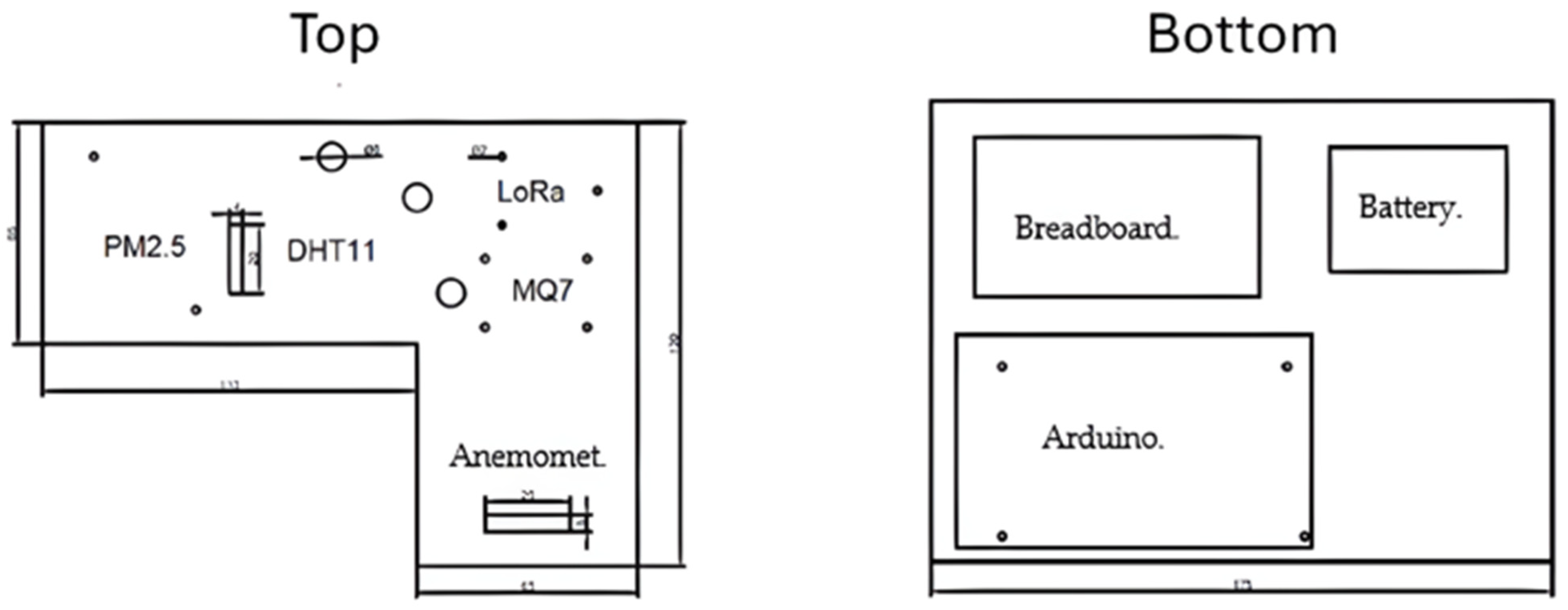
3.1.1. Controllers
3.1.2. Sensors
- PM10—particles whose aerodynamic diameter is less than 10 µm; coarse inhalable particles (2.5 to 10 µm).
- PM2.5 particles are fine inhalable particles (<2.5 µm).
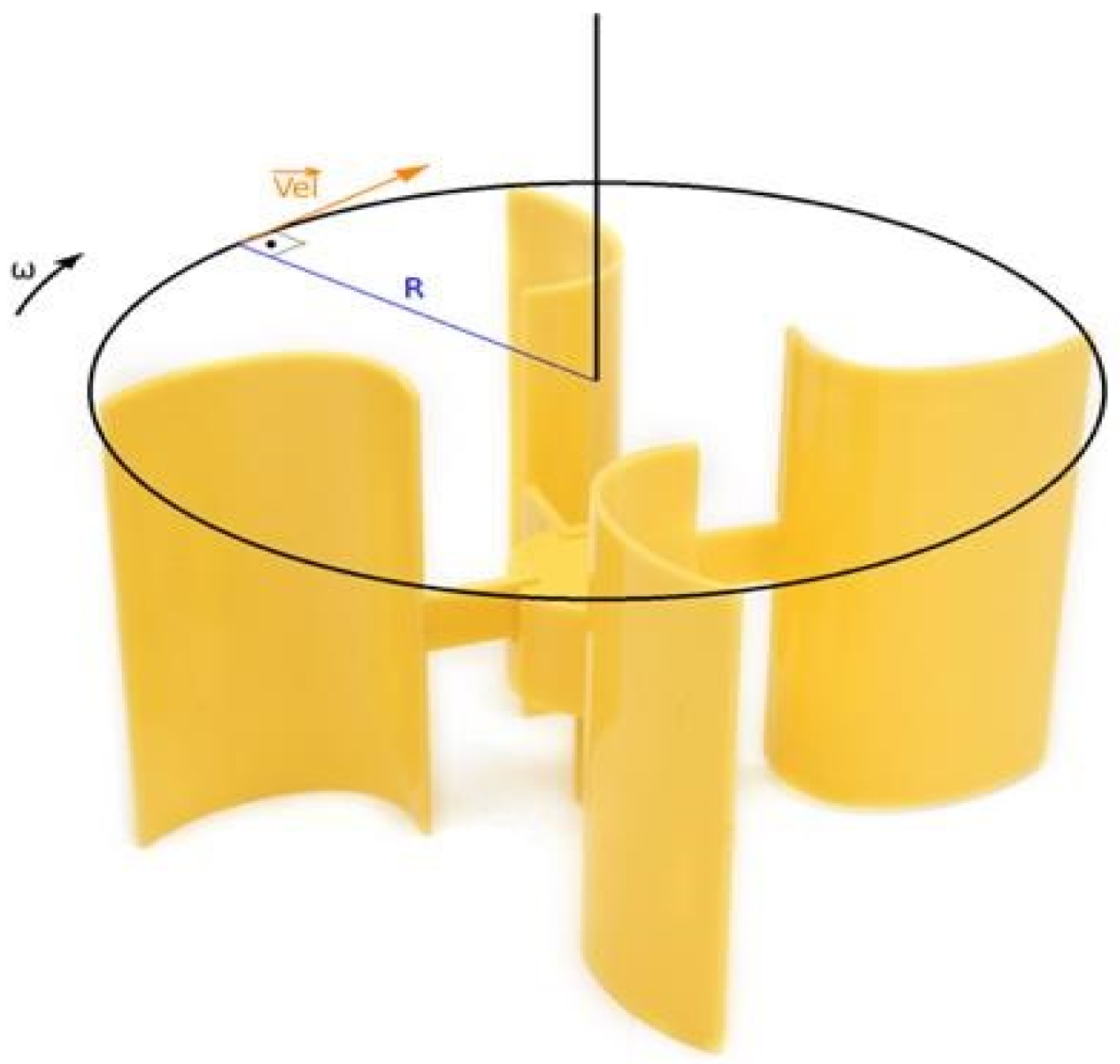
- Kv, is the motor constant, V/RPM;
- V is the voltage applied to the motor (maximum), V;
- ω is the angular velocity, RPM.
- RS is the surface resistance of the sensor at concentrations of various gases.
- RL is the variable resistance.
- VC corresponds to the input voltage (5V).
- VO corresponds to the output voltage.
3.1.3. LoRa Transceivers
- Rb is the nominal bit rate, shown in bits/s.
- SF is the spreading factor from 7 to 12 (based on the environmental conditions between the communication device and the gateway).
- BW is the modulation bandwidth in Hz.
- CR (code rate) is (4/5, 4/6, 4/7 or 4/8).
- is the preamble transmission time.
- is the payload transmission time.
- .
- is the payload size in bytes.
- is the header (0 explicit and 1 implicit).
- is the low data rate optimization (1 for SF11 or SF12 and 0 for the other SFs).
- Lower SF → lower ToA → lower E → less energy consumption.
- Smaller payload → lower ToA → less consumption.
- Fewer retransmissions → lower Ploss → greater energy efficiency.
- Attenuation in free space, obstacles, and vegetation.
- Antenna gain.
3.1.4. Power Supply
3.1.5. Monitoring System
3.2. Hardware Integration
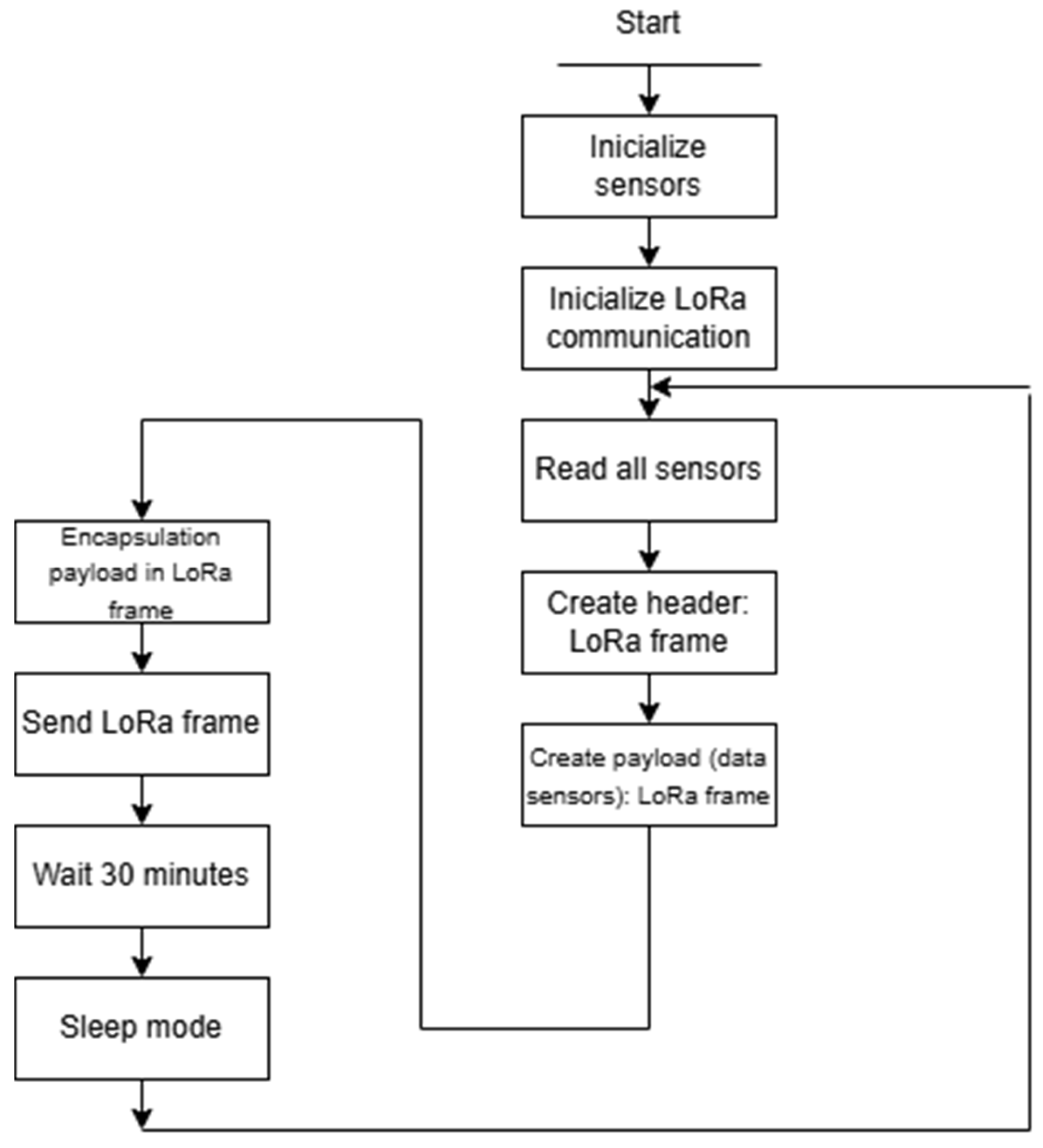
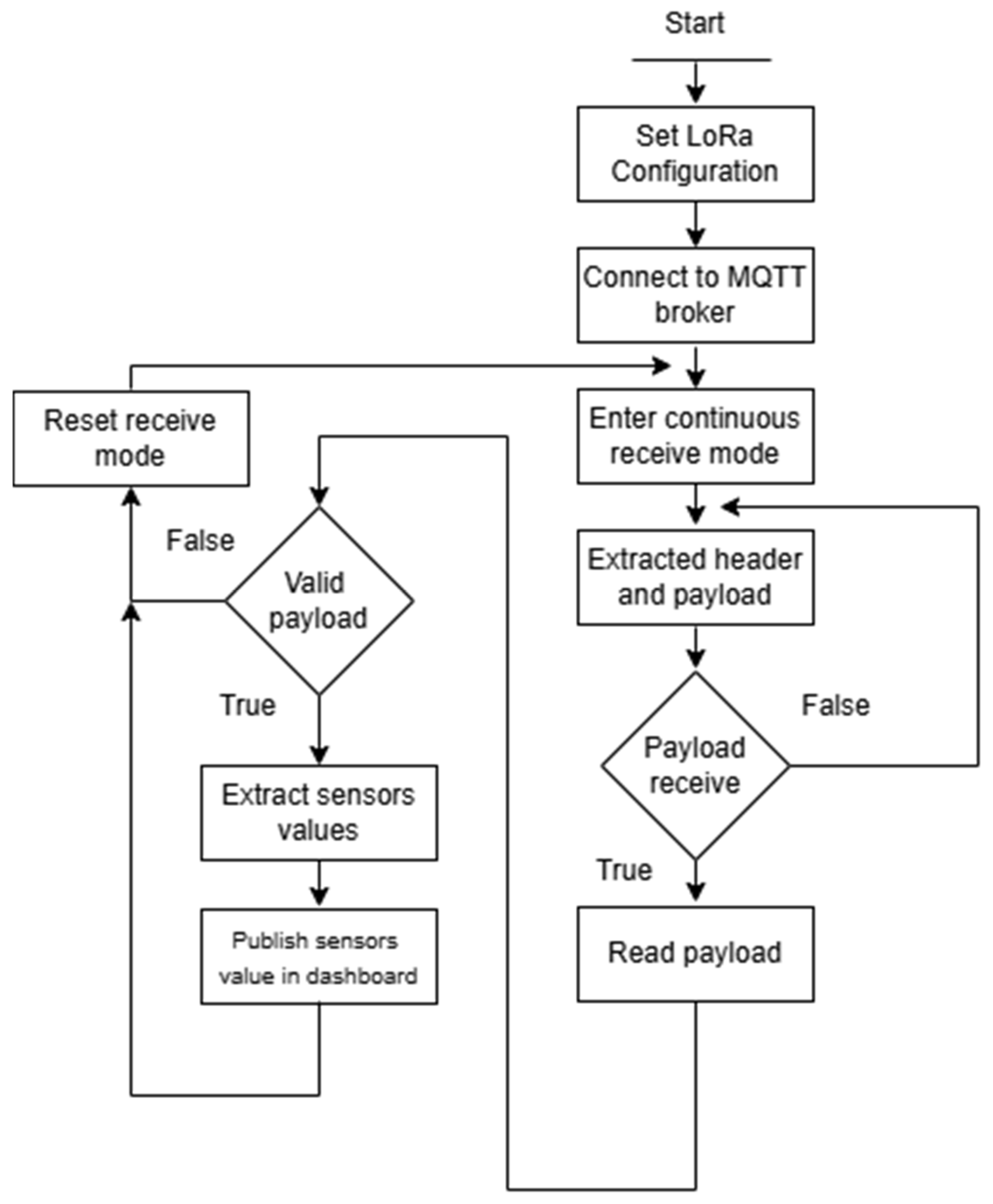
3.3. Algorithms Developed
| Algorithm 1: IoT node |
| FUNCTION Setup Configure I/O pins Initialize Air Quality Sensor Initialize CO sensor Initialize DHT sensor Configure LoRa modem parameters Initialize LoRa Communication END_FUNCTION FUNCTION Loop Get current time in milliseconds IF 30 min have passed since last data transmission THEN REPEAT Read Air Quality Sensor UNTIL data is valid Read analog value from anemometer Convert analog reading to voltage Calculate wind velocity in m/s Read temperature and humidity from DHT sensor IF MQ07 heating cycle not yet executed THEN Turn ON MQ07 sensor (heating) for 60 s Turn OFF MQ07 sensor (cooling) for 90 s Set MQ07 heating cycle flag to TRUE END_IF Read analog value from MQ07 sensor (CO) Reset MQ07 heating cycle flag to FALSE (for next loop) Read PM2.5 and PM10 PM100 values from Air Quality sensor Compose data string: temperature, humidity, wind velocity, MQ07 ppm, PM2.5, PM10 Send data via LoRa module Wait for transmission to complete Update last transmission timestamp END_IF Enter low-power sleep mode (IDLE) END_FUNCTION |
| Algorithm 2: Gateway |
| IMPORT necessary modules: INITIALIZE LoRa board configuration DEFINE class LoRaReceiver (inherits from LoRa): METHOD Constructor: - Call superclass constructor - Set LoRa module to SLEEP mode - Configure digital IO mapping - Set MQTT broker IP address - Set MQTT topic - Create MQTT client instance - Define callback for MQTT connection METHOD on_mqtt_connect: - Subscribe to the predefined MQTT topic METHOD on_rx_done: - Clear IRQ flags for RxDone event - Read received payload from LoRa (raw bytes) - Clean payload string (remove non-printable characters) - Split cleaned payload by comma (expect 5 values) IF the payload has at least 6 values: - Extract and clean: - Temperature - Humidity - Wind velocity - CO value - PM10 - PM2.5 ELSE: - Print “Invalid payload” with the raw string - Set LoRa mode to SLEEP - Reset receive pointer - Set LoRa to continuous receive mode (RXCONT) METHOD start: - Connect MQTT client to broker - Start MQTT background loop - Reset LoRa RX pointer - Set LoRa to continuous receive mode LOOP forever: - Sleep for 0.5 s - Get current RSSI value - Get modem status - Flush output buffer Main Program Execution CREATE instance of LoRaReceiver SET LoRa configurations: TRY: CALL start() method on LoRaReceiver instance CATCH KeyboardInterrupt: - Print interruption message FINALLY: - Set LoRa to SLEEP mode |
4. Results
4.1. Experiment Scenarios
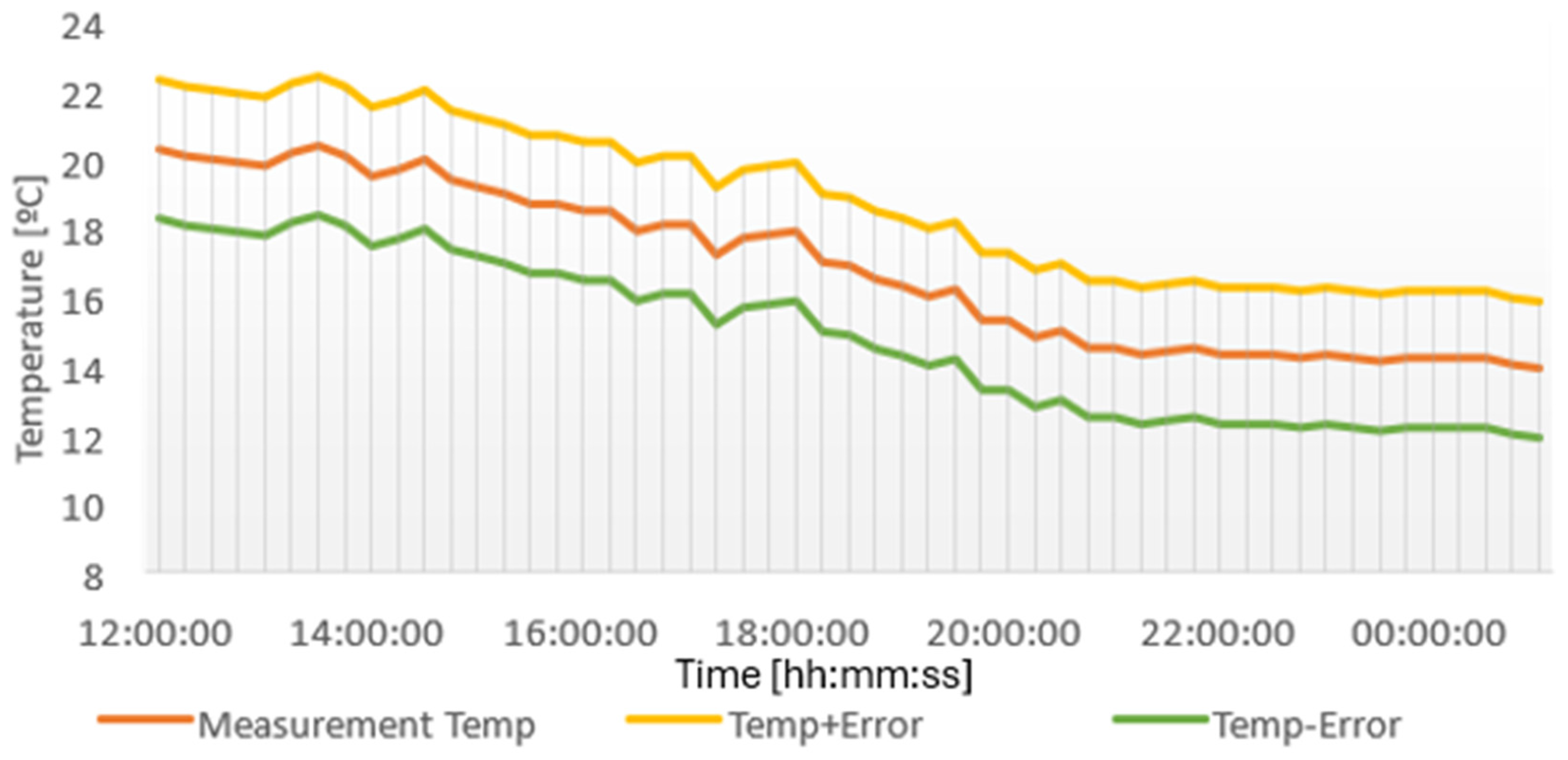
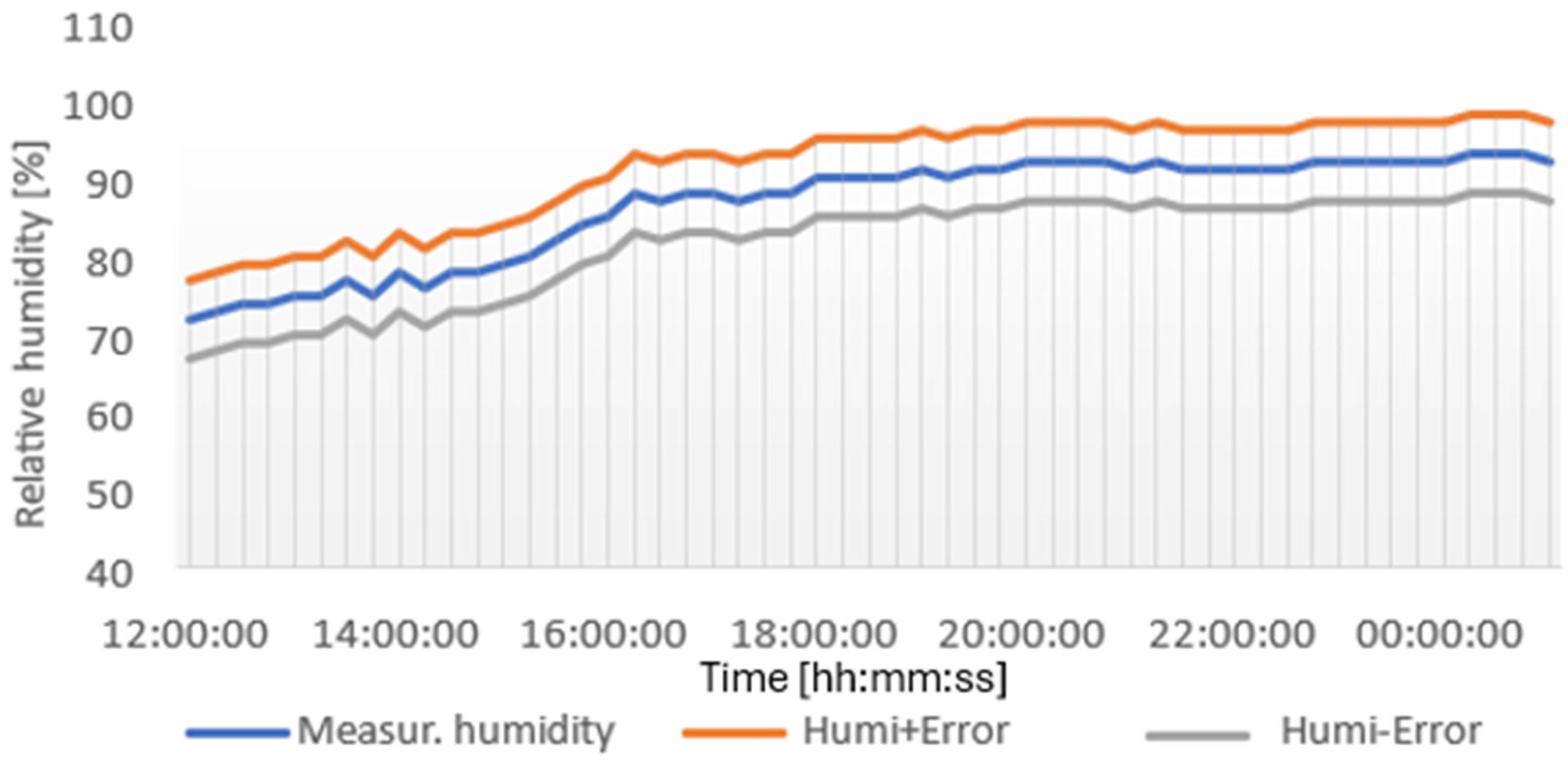
4.1.1. Results from DHT11 Sensor
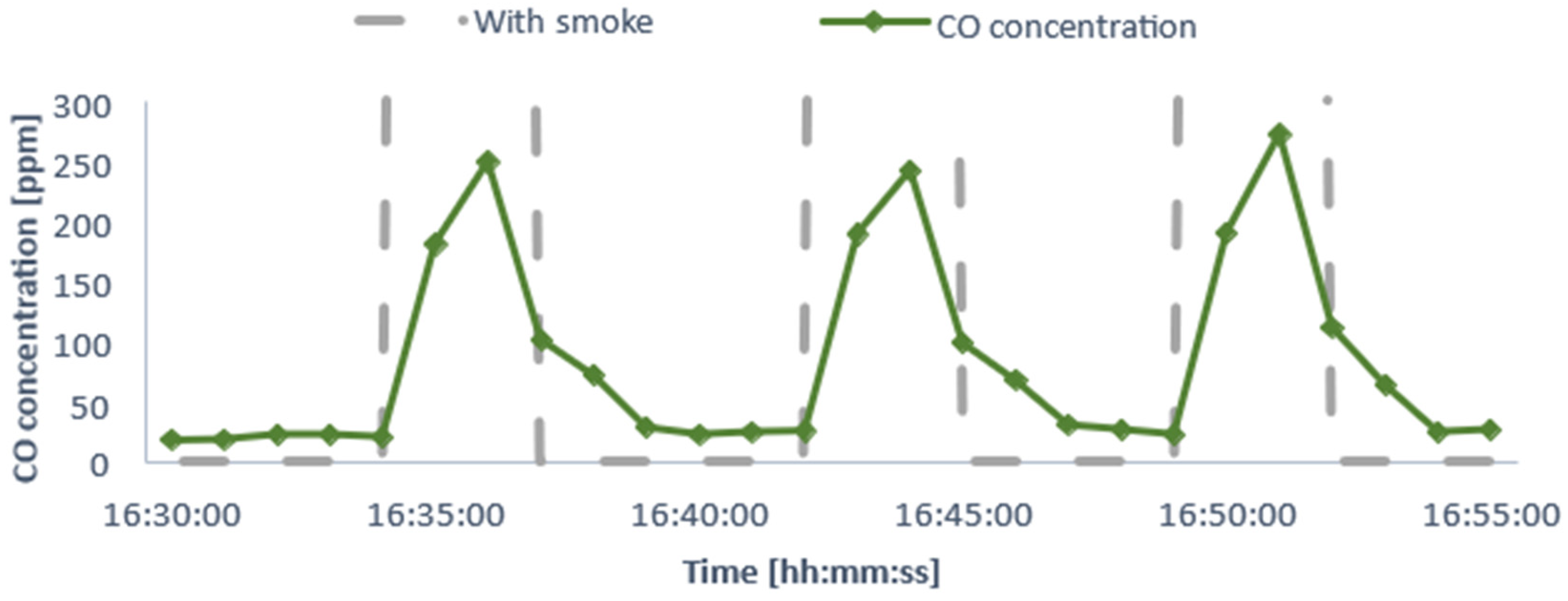
4.1.2. Results from CO (MQ7 Sensor)
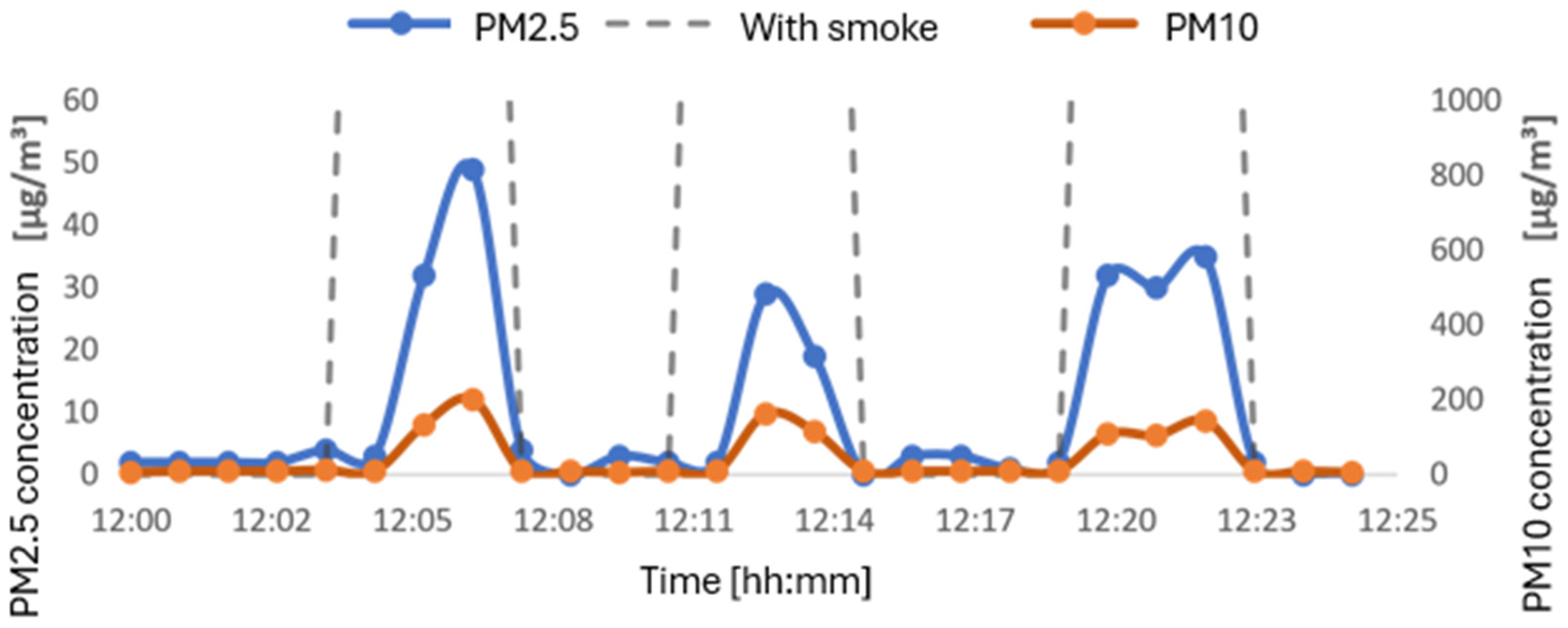
4.1.3. Results from PM2.5 and PM10 Sensors
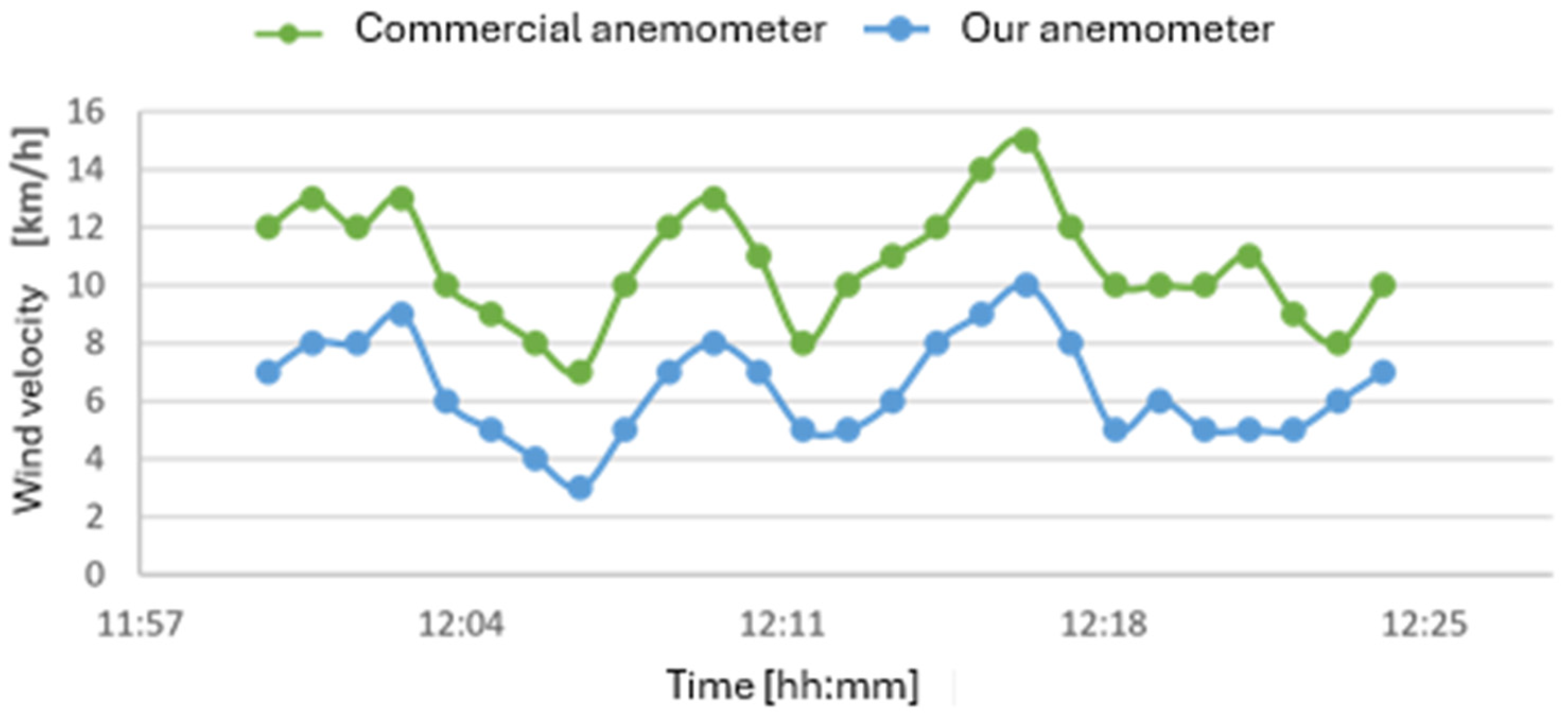
4.1.4. Results from the Anemometer
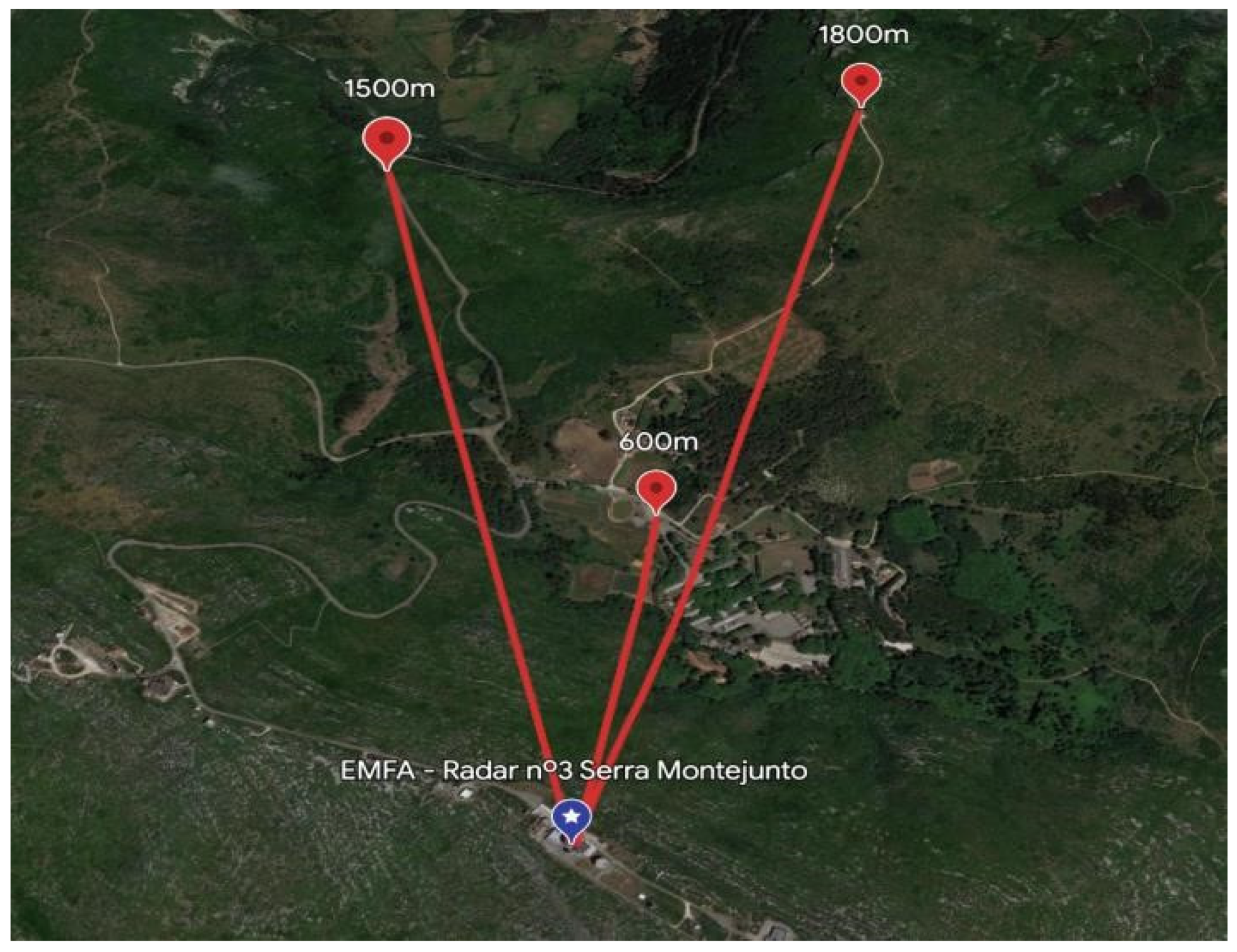
4.1.5. Results from LoRa Coverage
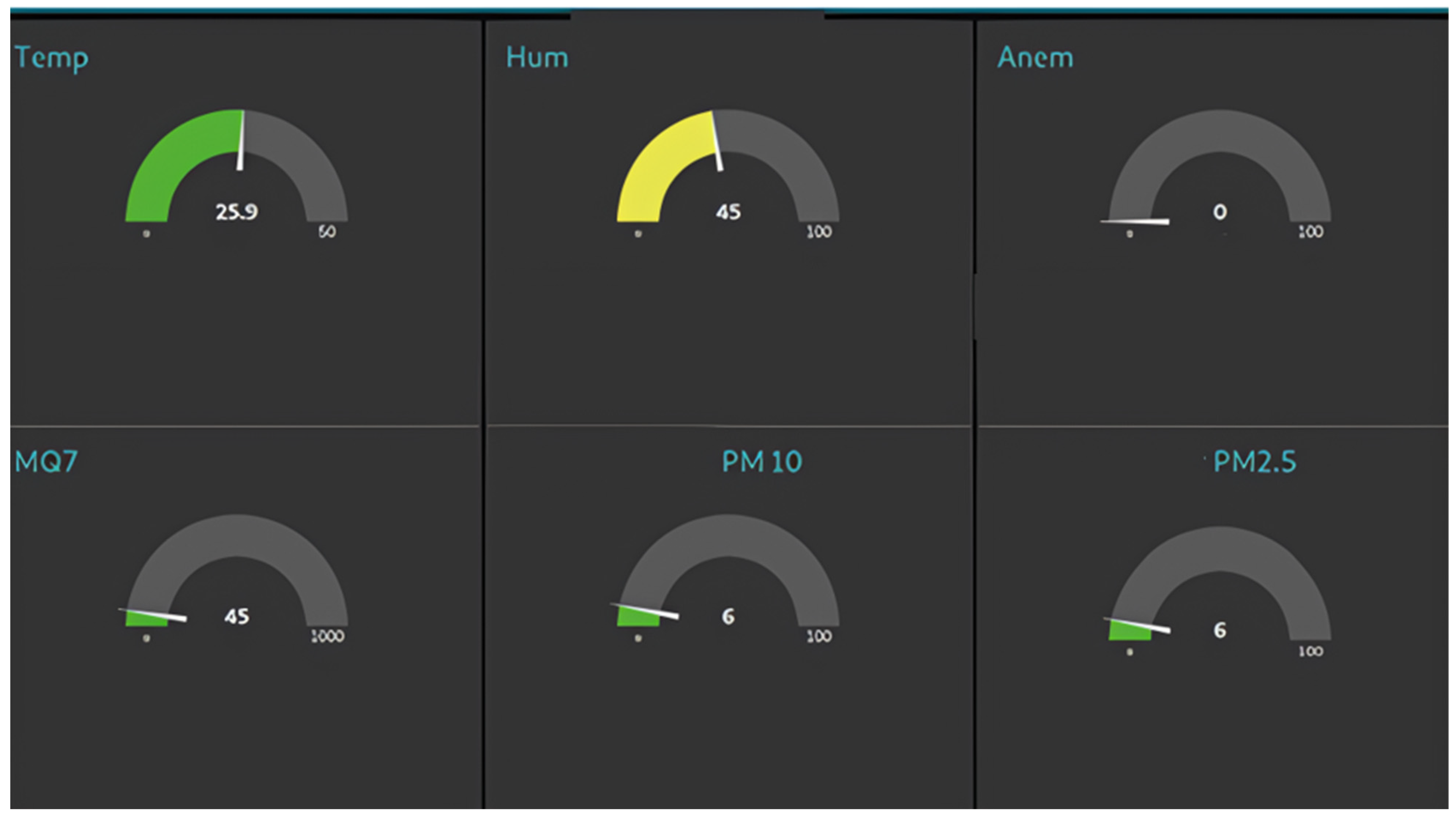
4.1.6. Dashboard Results
4.2. Extended 168-Hour Test
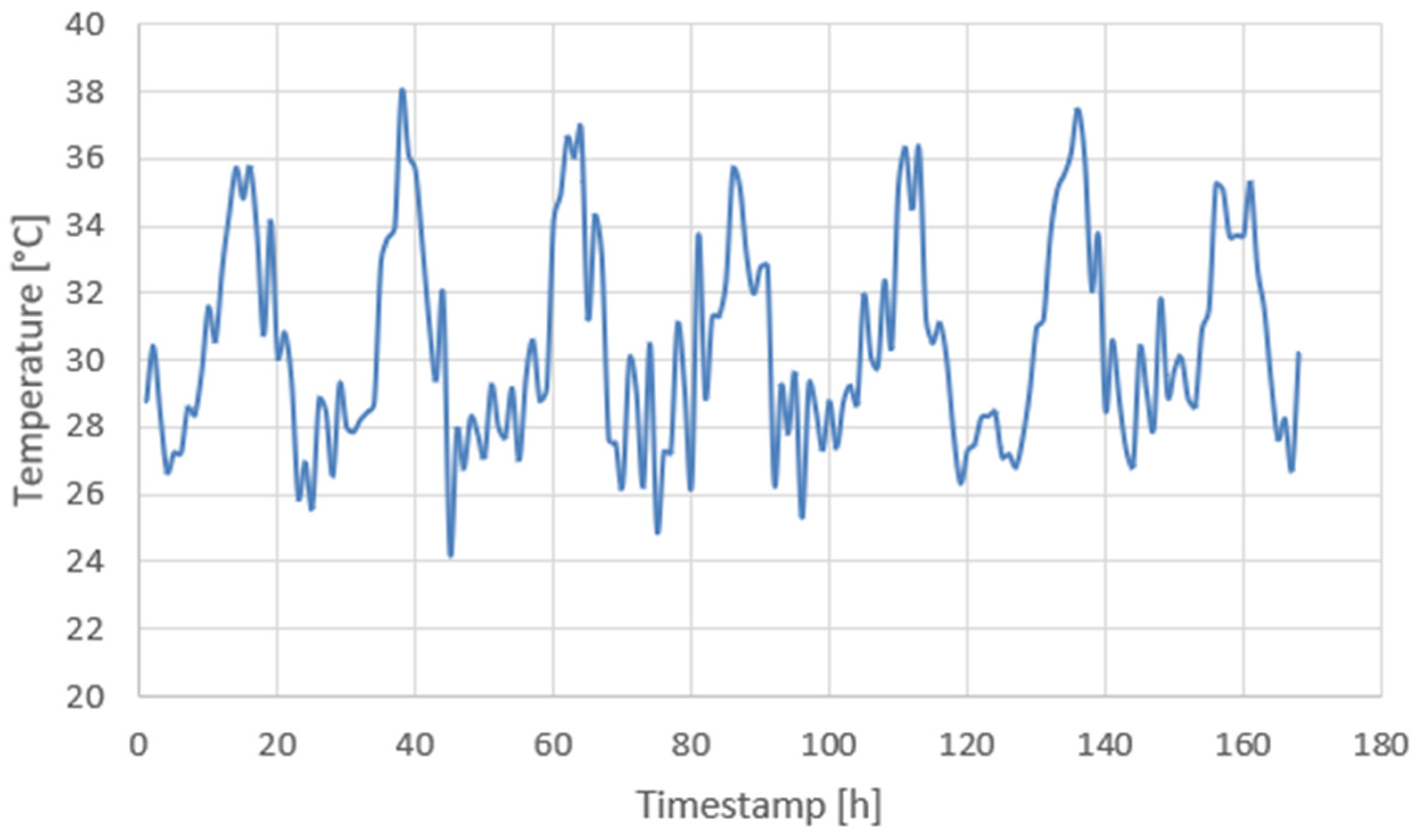

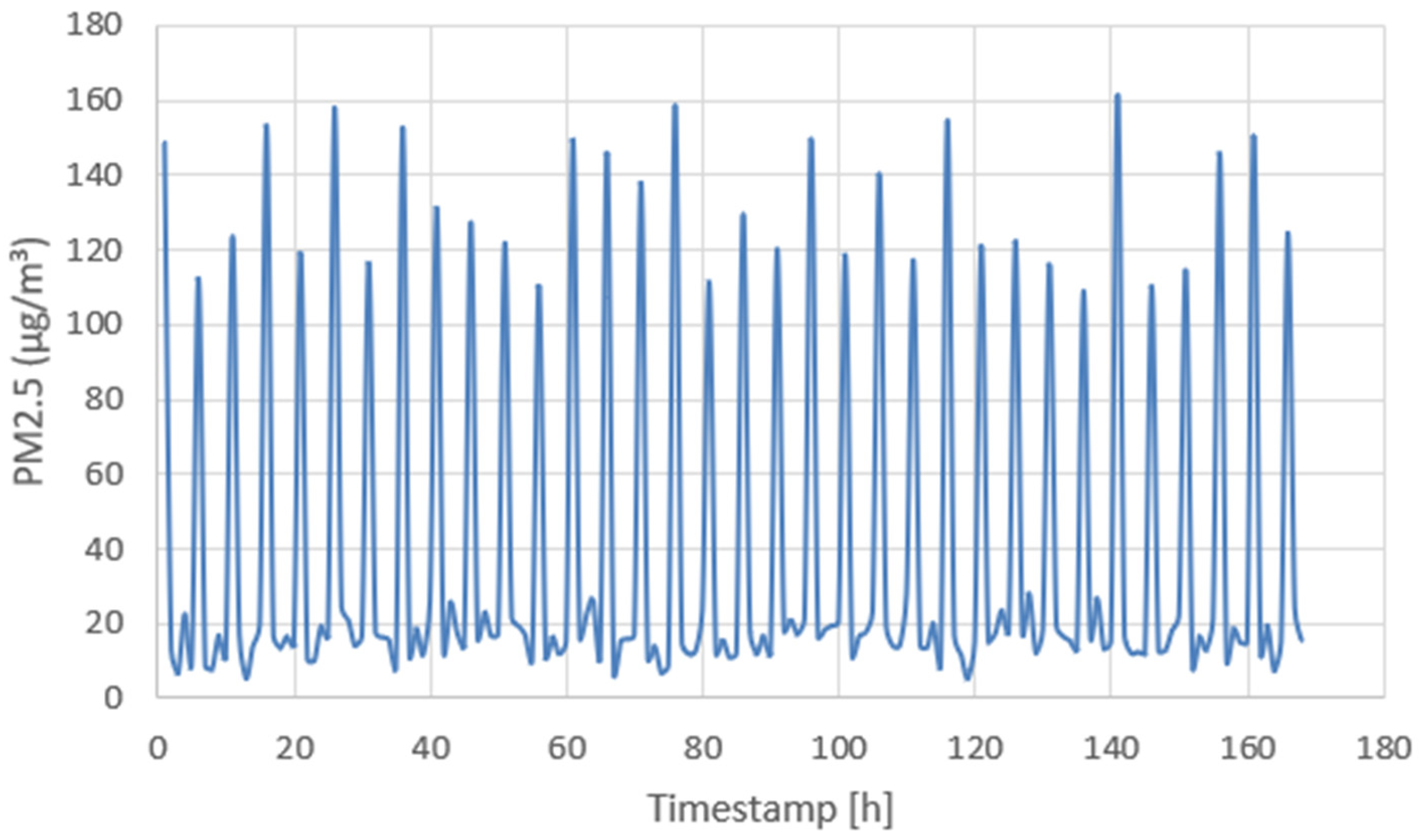
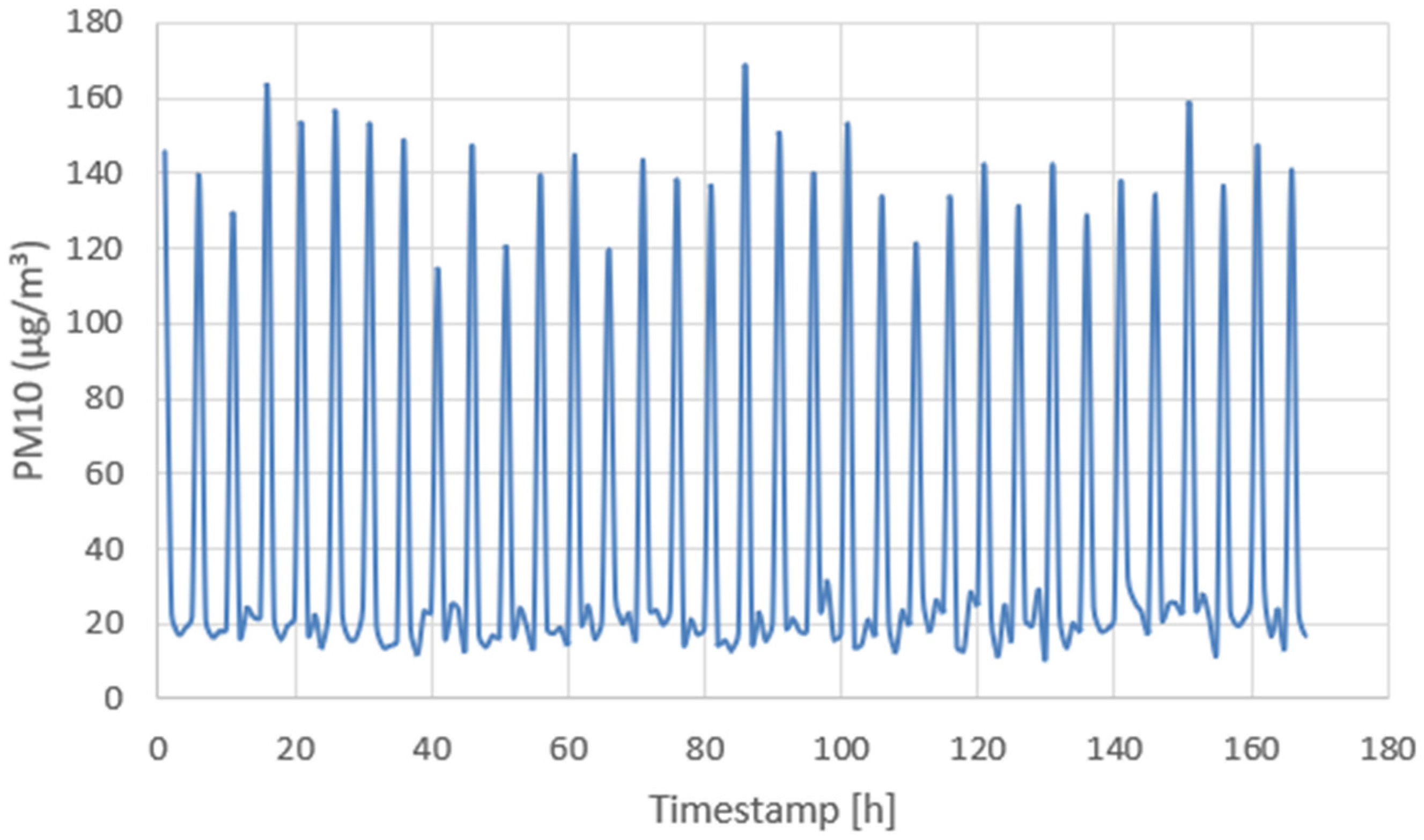
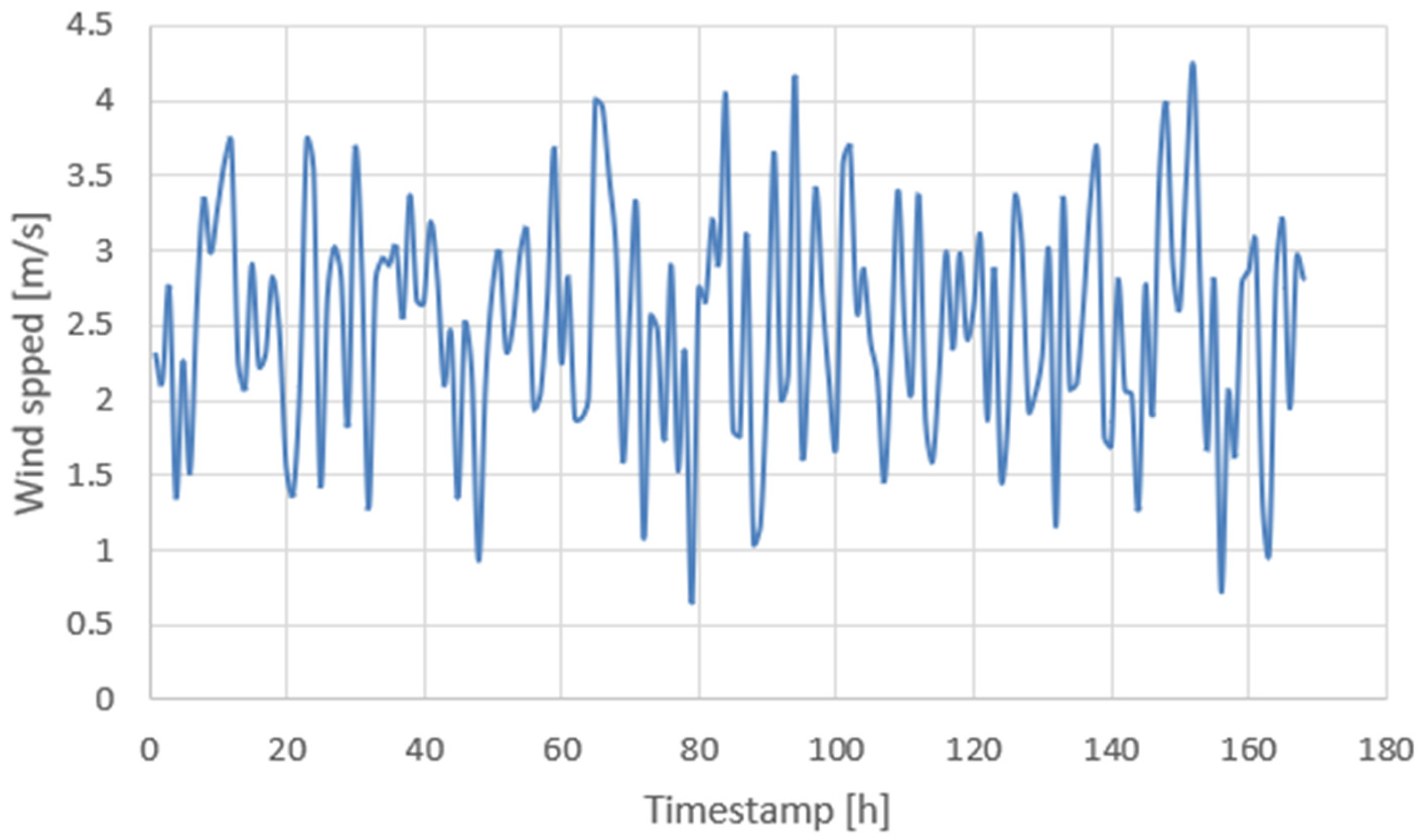
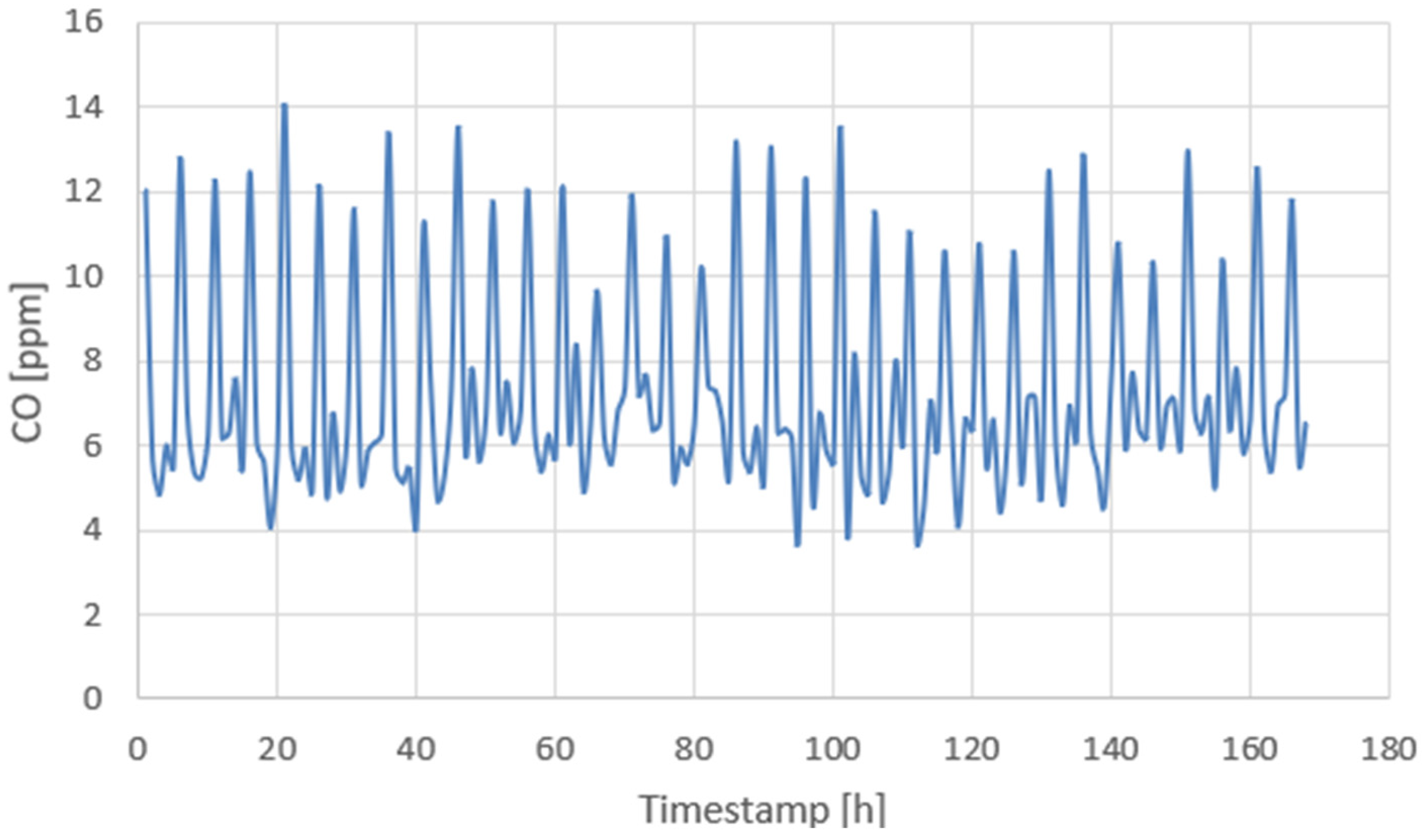
4.3. Energy Consumption
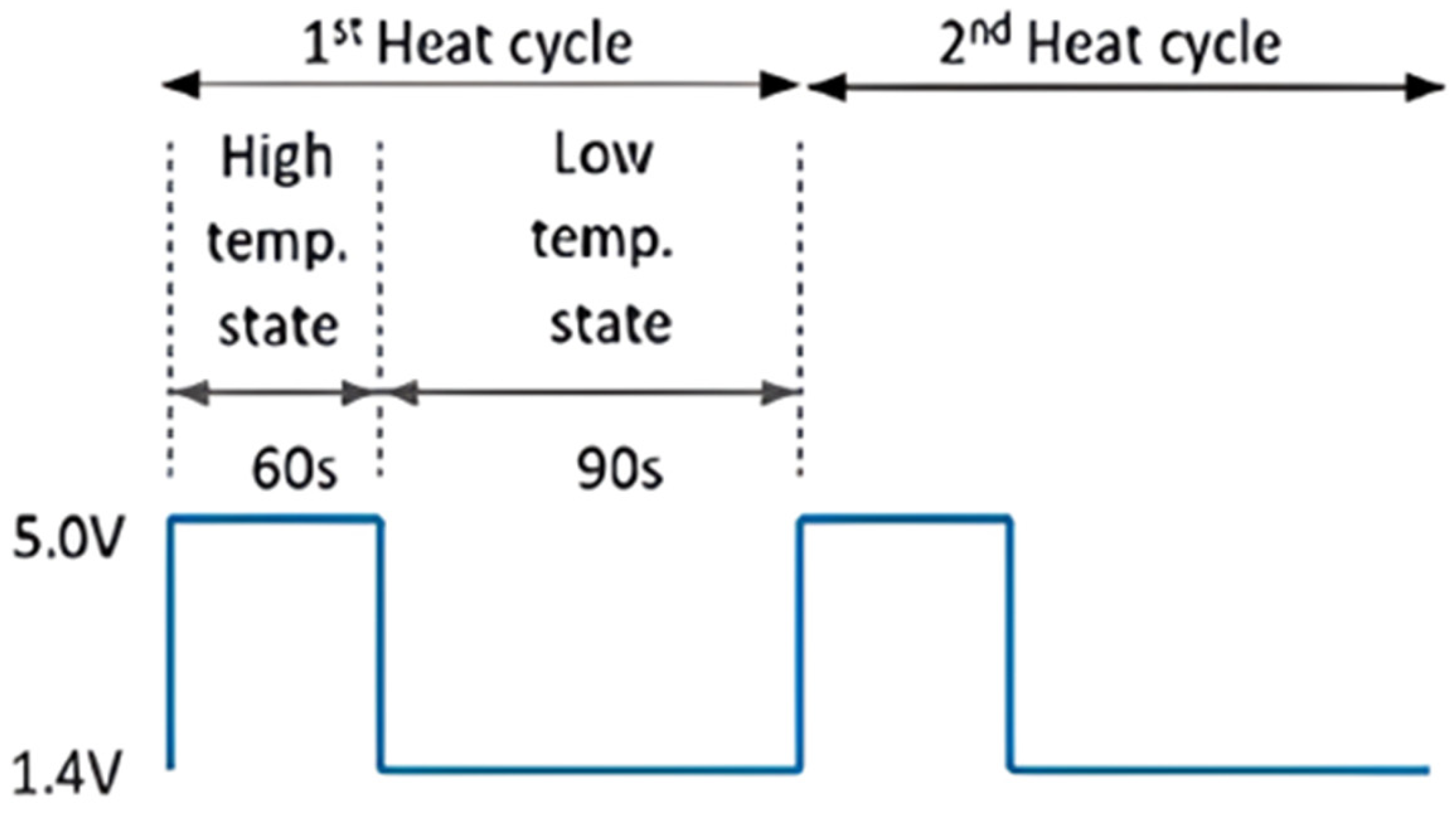
- Stage 0: MQ7 preheating phase. In this mode, the microcontroller is active, and the CO sensor begins its heating cycle. This process takes 60 s.
- Stage 1: Sensor sampling phase. In this mode, the microcontroller is active and activates the sensors to take environmental samples.
- Stage 2: Data transmission phase. Only the microcontroller and transceiver are turned on, and the data is sent at full power.
- Stage 3: Hibernation phase. This is the mode in which the node will spend most of its time. In this phase, all the devices are in hibernation mode.
- Stage 0: 4.17 mAh.
- Stage 1: 0.55 mAh.
- Stage 2: 0.08 mAh.
- Stage 3: 32.43 mAh.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
| BW | Bandwidth |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CNC | Critical Noxious Concentration |
| CR | Code Rate |
| CSS | Chirp Spread Spectrum |
| DHT | Digital Humidity and Temperature |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IoRT | Internet of Robotic Things |
| LoRa | Long Range |
| LOS | Line of Sight |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| M2M | Machine-to-Machine |
| MFB | Mean Fractional Bias |
| MQTT | Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| NLOS | Non-Line of Sight |
| PM2.5 | Particulate Matter less than 2.5 µm |
| PM10 | Particulate Matter less than 10 µm |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
| RSSI | Received Signal Strength Indicator |
| SF | Spreading Factor |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| TFT | Thin-Film Transistor |
| ToA | Time on Air |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
Appendix A. Sensor Specification
- Temperature range: 0–50 °C (accuracy: ±2 °C).
- Relative humidity: 20–95 % (accuracy: ±5 %).
- Single-wire digital output, sampling every 1 s; suitable for trend detection rather than precision measurement.
- Detection range: 20–2000 ppm.
- Analog output based on resistance change.
- Heating cycle: 60 s at 5 V (high), 90 s at 1.4 V (low).
- Requires calibration via RS/R0 ratio based on datasheet curve [31].
- PM2.5 (<2.5 µm) and PM10 (<10 µm) detection.
- UART digital output.
- Internal laser and photodiode configuration.
- Accuracy typically ±10 µg/m3; effective for identifying smoke and pollution concentrations.
- Wind speed, derived from output voltage and known motor constant.
- Radius of propeller: 5 cm.
- Voltage-to-speed conversion obtained using Equation (4).
Appendix B. Algorithm Overview
- Developed in C language.
- Rule-based logic using 30-30-30 wildfire threshold.
- Discards values outside physical limits (e.g., temperature < −10 °C or wind < 0 m/s).
- Integrates the MQ-7 heating/cooling cycle control.
- Implemented in Python on a Raspberry Pi.
- Decodes LoRa payload, publishes to MQTT topics.
- Feeds Node-RED for real-time visualization.
- LoRa: SF7–SF12, BW = 125 kHz, CR = 4/5.
- MQTT: lightweight publish/subscribe protocol.
- Node-RED: dashboard creation and data display.
References
- European Research Executive Agency. The EU-Funded Projects Helping to Fight Forest Fires. Available online: https://rea.ec.europa.eu/news/fighting-flames-eu-funded-projects-protecting-forests-fire-destruction-2024-07-23_en (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- Kobziar, L.N.; Hiers, J.K.; Belcher, C.M.; Bond, W.J.; Enquist, C.A.; Loudermilk, E.L.; Miesel, J.R.; O’bRien, J.J.; Pausas, J.G.; Hood, S.; et al. Principles of Fire Ecology. Fire Ecol. 2024, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divisão de Gestão do Programa de Fogos. 3.º Relatório Provisório de Incêndios Rurais (3.º RPIR/DGPFR/2022). 1 August 2022. Available online: https://www.icnf.pt/api/file/doc/282a0e22f28cc3c7 (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- Lloret, J.; Garcia, M.; Bri, D.; Sendra, S. A Wireless Sensor Network Deployment for Rural and Forest Fire Detection and Verification. Sensors 2009, 9, 8722–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Ortiz, J.; Sendra, S.; Ameigeiras, P.; Lopez-Soler, J.M. Integration of LoRaWAN and 4G/5G for the Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semtech. LoRa Modulation Basics; AN1200.22. 2015. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/uploads/technology/LoRa/lora-and-lorawan.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Soderholm, B. How the 30-30-30 Rule Is Essential for Wildfire Safety; The Weather Network: Oakville, ON, Canada, 2024; Available online: https://www.theweathernetwork.com/en/news/weather/severe/how-the-30-30-30-rule-is-essential-for-wildfire-safety (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Gokhale, P.; Bhat, O.; Bhat, S. Introduction to IoT. Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2018, 5, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, M.U.; Waseem, M.; Mazhar, S.; Khairi, A.; Kamal, T. A Review on Internet of Things (IoT). Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 113, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitan, N.C.; Hojbota, P. Forest Fire Detection System Using LoRa Technology. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. IoT Connected Devices Worldwide 2019–2030. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1183457/iot-connected-devices-worldwide/ (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Mohammadi, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Sorour, S.; Guizani, M. Deep Learning for IoT Big Data and Streaming Analytics: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2923–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiroglu, S.; Sinanc, D. Big Data: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–24 May 2013; pp. 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Seker, D.Z.; Hameed, S.; Draheim, D. The Rising Role of Big Data Analytics and IoT in Disaster Management: Recent Advances, Taxonomy and Prospects. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54595–54614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasteh, H.; Hosseinnezhad, V.; Loia, V.; Tommasetti, A.; Troisi, O.; Shafie-khah, M.; Siano, P. IoT-Based Smart Cities: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Riazul Islam, S.M.; Kwak, D.; Kabir, M.H.; Hossain, M.; Kwak, K.-S. The Internet of Things for Health Care: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 678–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinni, E.; Saifullah, A.; Han, S.; Jennehag, U.; Gidlund, M. Industrial Internet of Things: Challenges, Opportunities, and Directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, K.; Ritts, M. Smart Earth: A Meta-Review and Implications for Environmental Governance. Glob. Environ. Change 2018, 52, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González García, C.; Meana-Llorián, D.; Pelayo G-Bustelo, B.C.; Cueva Lovelle, J.M.; Garcia-Fernandez, N. Midgar: Detection of People through Computer Vision in the Internet of Things Scenarios to Improve the Security in Smart Cities, Smart Towns, and Smart Homes. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, A.A.A. A Review on Forest Fire Detection Techniques. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 597368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashini, M.J.; Sudarmani, R.; Gobika, S.; Varshini, R. Development of Smart Flood Monitoring and Early Warning System Using Weather Forecasting Data and Wireless Sensor Networks—A Review. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), Tirunelveli, India, 4–6 February 2021; pp. 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nawafleh, A.; Al-Sarayreh, K.; Al-Rababah, A.; Al-Tarawneh, M.; Alshraideh, H. EFFSIP: Efficient Forest Fire System Using IoT and Parallel Computing. Egypt. Inform. J. 2025, 29, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C.; Alvi, S.A.; Zhou, X.; Durrani, S.; Wilson, N.; Yebra, M. A Survey on IoT Ground Sensing Systems for Early Wildfire Detection: Technologies, Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 172785–172819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistoni, P.; Cantone, A.A.; Martino, G.; Passamano, V.; Romano, M.; Sebillo, M.; Vitiello, G. A Cyber-Physical System for Wildfire Detection and Firefighting. Future Internet 2023, 15, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üremek, İ.; Leahy, P.; Popovici, E. A System for Efficient Detection of Forest Fires through Low Power Environmental Data Monitoring and AI. Eng. Proc. 2024, 68, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rango, A.; Furnari, L.; Cortale, F.; Senatore, A.; Mendicino, G. Wildfire Early Warning System Based on a Smart CO2 Sensors Network. Sensors 2025, 25, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduino. Arduino Mega ADK Rev3. Available online: https://docs.arduino.cc/retired/boards/arduino-mega-adk-rev3/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- RFM95. RFM95 LoRa Module. Available online: https://www.botnroll.com/pt/lora-868/2600-rfm95-m-dulo-lora-868mhz.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- DHT11. DHT11 Sensor. Available online: https://www.botnroll.com/pt/temperatura/471-sensor-de-temperatura-e-humidade-dht11.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Air Quality. Air Quality Sensor SDS011. Available online: https://botland.store/air-quality-sensors/8332-laser-dustair-sensor-pm25-pm10-sds011-5v-uartpwm-5904422375829.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- CO. CO MQ7 Sensor. Available online: https://elcereza.com/mq7/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Anemometer. Anemometer Manufacturer TopHomer. Available online: https://www.walmart.com/ip/Vertical-Wind-Turbines-Small-Motor-Blades-Generator-for-DIY-Teaching/8760510557?classType=REGULAR (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Raspberry Pi. Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.com/products/raspberry-pi-3-model-b-plus/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- TFT Display. 7 Inch HDMI LCD (C). Available online: https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/7inch_HDMI_LCD_%28C%29 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- NASA Earth Observatory. Carbon Monoxide & Fire. 31 August 2022. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/global-maps/MOP_CO_M/MOD14A1_M_FIRE (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Semtech Semiconductor. IoT Systems and Cloud Connectivity. Available online: https://www.semtech.com (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Semtech. Understanding LoRa Adaptive Data Rate. Available online: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/uploads/documents/files/Understanding_LoRa_Adaptive_Data_Rate_Downloadable.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Rabaça, A.F.B. Aplicação de Tecnologia LoRaWAN à Monitorização de Redes de Distribuição de Energia. 2018. Available online: https://fenix.tecnico.ulisboa.pt/cursos/meec/dissertacoes (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- The Things Network. Spreading Factors | The Things Network. Available online: https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/docs/lorawan/spreading-factors/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Etiabi, Y.; Jouhari, M.; Amhoud, E.M. Spreading Factor and RSSI for Localization in LoRa Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrow Electronics. Solar Panel. Available online: https://www.arrow.com/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Seeedstudio. LiPo Rider Pro. Available online: https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Lipo_Rider_Pro/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Seeedstudio. Lithium-Ion Polymer Battery Pack 6A. Available online: https://www.seeedstudio.com/Lithium-Ion-polymer-Battery-pack-6A-p-602.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- OASIS Standard. MQTT Version 5.0. Available online: https://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v5.0/mqtt-v5.0.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Autodesk. Autodesk AutoCAD 2024. Available online: https://www.autodesk.pt/products/autocad/overview (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Wambebe, N.; Duan, X. Air Quality Levels and Health Risk Assessment of Particulate Matters in Abuja Municipal Area, Nigeria. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google. Google Maps. Available online: https://maps.google.com (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- OpenJS Foundation. Node-RED. Available online: https://nodered.org/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).




| Article | Technologies Used | Focus | Sensor Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | Wi-Fi and Cloud | Flood monitoring and early warning system | Rain, ultrasonic, temperature, and level |
| [22] | LoRa transceivers and Gateway with multiple interfaces: Wi-Fi, LoRa, 3G/GPRS, and Bluetooth | Early fire detection, prediction of fire spread and behavior, energy efficiency, and testing and validation in a real environment | Temperature and humidity |
| [23] | LoRa/LoRaWAN and IoT Camaras | Early detection of forest fires, with emphasis on the latency, accuracy, and energy efficiency of IoT devices | This article is a survey identifying multiple types of sensors: pressure, wind speed, soil moisture, gas, smoke, and flame detectors. |
| [24] | IoT UAVs and autonomous UGVs with ROS M2M communication (MQTT) and Node-Red | Early detection and automatic response to fires, integration between sensors and collaborative robotics, and autonomous operation and remote monitoring in real time | Temperature, humidity RGB and infrared camera, CO sensor, and UAV equipped with location and extinguishing sensors |
| [25] | LoRa node equipped with BME280, Gateway, and MQTT for data transmission | Early detection of fires based on environmental anomalies, optimizing communication and energy with LoRa/MQTT, with predictive models | BME280 |
| [26] | LoRaWAN and Cloud | Early detection of forest fires through changes in CO2 levels, increasing sensitivity, and temporal coverage with the use of AI. | Smart CO2 sensors |
| This work | LoRa, Gateway, M2M, based on MQTT, Node-RED dashboard | Smart detection of wildfire prevention Fire risk conditions Firmware implementation of wildfire safety rule: 30-30-30 | Temperature, wind, humidity, CO, air quality (PM2.5 and PM10) |
| Max. Temperature [°C] | Min. Temperature [°C] | Max. Relative Humidity [%] | Min. Relative Humidity [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23.7 | 14.3 | 95 | 55 |
| IQA | PM2.5 (µg/m3) | PM10 (µg/m3) | Level of Health Concern |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–50 | 0–12 | 0–54 | Good |
| 51–100 | 12.1–35.4 | 55–154 | Moderate |
| 101–150 | 35.5–55.4 | 155–254 | Dangerous for sensitive groups |
| 151–200 | 55.5–150.4 | 255–354 | Dangerous |
| 201–300 | 150.5–250.4 | 355–424 | Very dangerous |
| 301 e -high | 250.5–high | 425–high | Toxic |
| Local | Distance (m) | SF | Received Packet | Average RSSI (dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 100 | 7, 10 and 12 | For SF7: 10/10 For SF10: 10/10 For SF12: 10/10 | For SF7 10/10: −59 For SF10 10/10: −60 For SF12 10/10: −57 |
| P2 | 300 | 7, 10 and 12 | For SF7: 8/10 For SF10: 7/10 For SF12: 10/10 | For SF7 10/10: −83 For SF10 10/10: −85 For SF12 10/10: −79 |
| P3 | 350 | 7, 10 and 12 | For SF7: 8/10 For SF10: 10/10 For SF12: 10/10 | For SF7 10/10: −77 For SF10 10/10: −73 For SF12 10/10: −93 |
| P4 | 500 | 7, 10 and 12 | For SF7: 3/10 For SF10: 4/10 For SF12: 7/10 | For SF7 10/10: −93 For SF10 10/10: −93 For SF12 10/10: −94 |
| P5 | 850 | 7, 10 and 12 | For SF7: 0/10 For SF10: 0/10 For SF12: 3/10 | For SF7 10/10: no RSSI For SF10 10/10: no RSSI For SF12 10/10: −99 |
| Local | Distance (m) | SF | Received Packet | Average RSSI (dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 600 | 7, 10, and 12 | For SF7: 10/10 For SF10: 10/10 For SF12: 10/10 | For SF7 10/10: −74 For SF10 10/10: −73 For SF12 10/10: −73 |
| P2 | 1500 | 7, 10, and 12 | For SF7: 10/10 For SF10: 10/10 For SF12: 10/10 | For SF7 10/10: −86 For SF10 10/10: −84 For SF12 10/10: −83 |
| P3 | 1800 | 7, 10, and 12 | For SF7: 10/10 For SF10: 10/10 For SF12: 7/10 | For SF7 10/10: −77 For SF10 10/10: −77 For SF12 10/10: −77 |
| Stage | MCU | Sensors | LoRA Module RX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preheating MQ7 | ON | Only MQ7 | OFF |
| Sampling | ON | ON | OFF |
| Data transmission | ON | OFF | ON |
| Sleep mode | OFF | OFF | OFF |
| Device | Consumption ON State [mA] | Consumption Idle State [mA] |
|---|---|---|
| Arduino Mega 2560 R3 | 45 | 24 |
| RFM95 | 24 | 10 |
| DHT11 | 0.3 | 0.06 |
| MQ7 | 70 | - |
| PM2.5 | 120 | 0.2 |
| Stage | Arduino Mega [mA] | Sensors [mA] | LoRa Module Tx [mA] | Total [mA] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preheating MQ7 | 45 | 70 | 10 | 125 |
| Sampling | 45 | 190.3 | 10 | 245.3 |
| Data transmission | 45 | 0.26 | 24 | 69.26 |
| Sleep mode | 24 | 0.26 | 10 | 34.26 |
| Stage 0 | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-time [ms] | 60,000 | 4000 | 1975 | 1,704,025 |
| Consumption [mA] | 125 | 245.3 | 69.26 | 34.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pires, L.M.; Fialho, V.; Pécurto, T.; Madeira, A. Towards Smart Wildfire Prevention: Development of a LoRa-Based IoT Node for Environmental Hazard Detection. Designs 2025, 9, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9040091
Pires LM, Fialho V, Pécurto T, Madeira A. Towards Smart Wildfire Prevention: Development of a LoRa-Based IoT Node for Environmental Hazard Detection. Designs. 2025; 9(4):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9040091
Chicago/Turabian StylePires, Luis Miguel, Vitor Fialho, Tiago Pécurto, and André Madeira. 2025. "Towards Smart Wildfire Prevention: Development of a LoRa-Based IoT Node for Environmental Hazard Detection" Designs 9, no. 4: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9040091
APA StylePires, L. M., Fialho, V., Pécurto, T., & Madeira, A. (2025). Towards Smart Wildfire Prevention: Development of a LoRa-Based IoT Node for Environmental Hazard Detection. Designs, 9(4), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9040091






