Development of Ballistic Protection Soft Panels According to Regulatory Documents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Literature Review: Conducting an extensive review of existing standards and BPV soft panel configuration’s designs.
- -
- BPSP Pattern Design: Developing and scaling soft panels patterns using CAD systems, based on the typical measurements of regional soldiers.
- -
- Fitting Evaluation: Assessing the patterns through physical fitting on mannequins and virtual fitting using the Clo3D program.
- -
- Algorithm Development: Formulating an algorithm for design of patterns for soft panels, incorporating necessary improvements and adjustments identified during the fitting process.
- -
2.1. BPV Types and Design Recommendations
2.2. Analysis of Existing BPV Soft Panels
2.3. Data Collection and Adaptation
2.4. Determining Ease Allowances
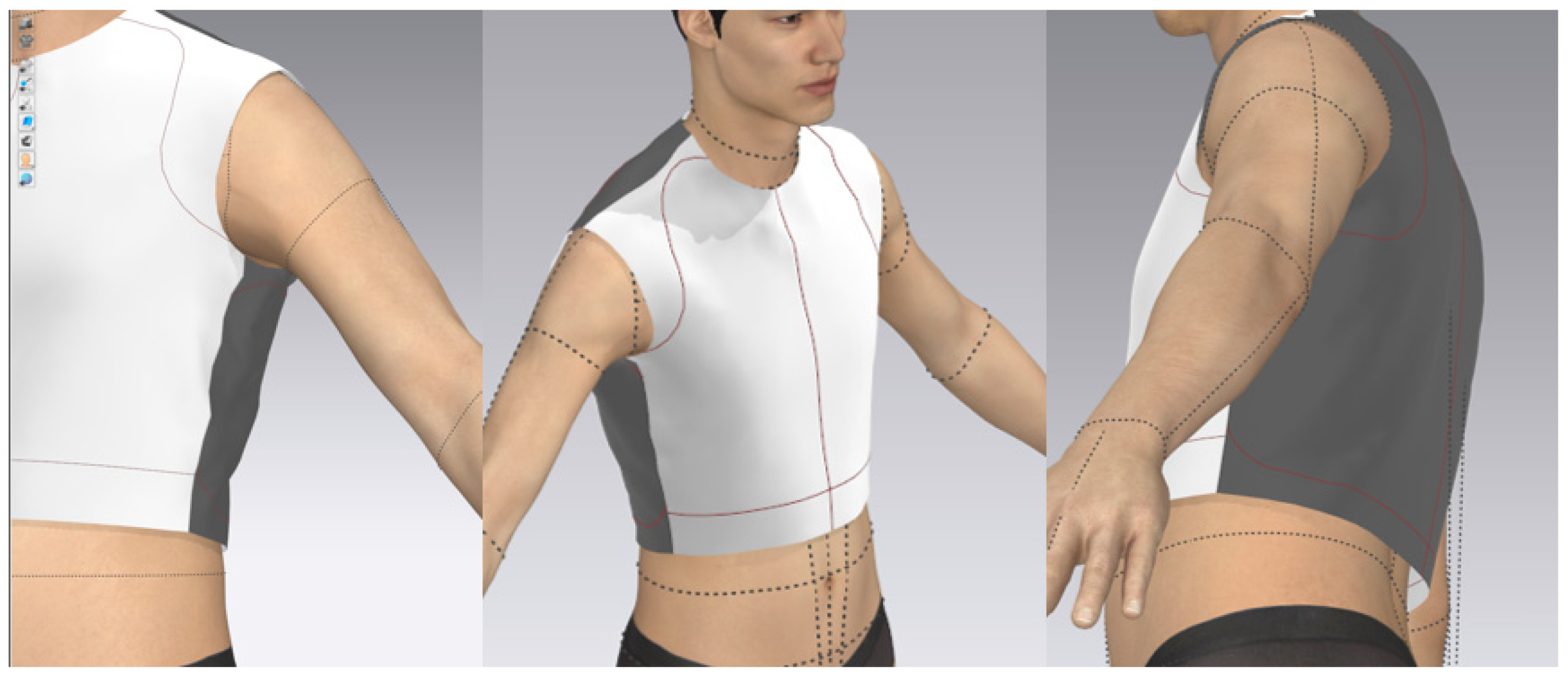
2.5. Design and Fitting Evaluation
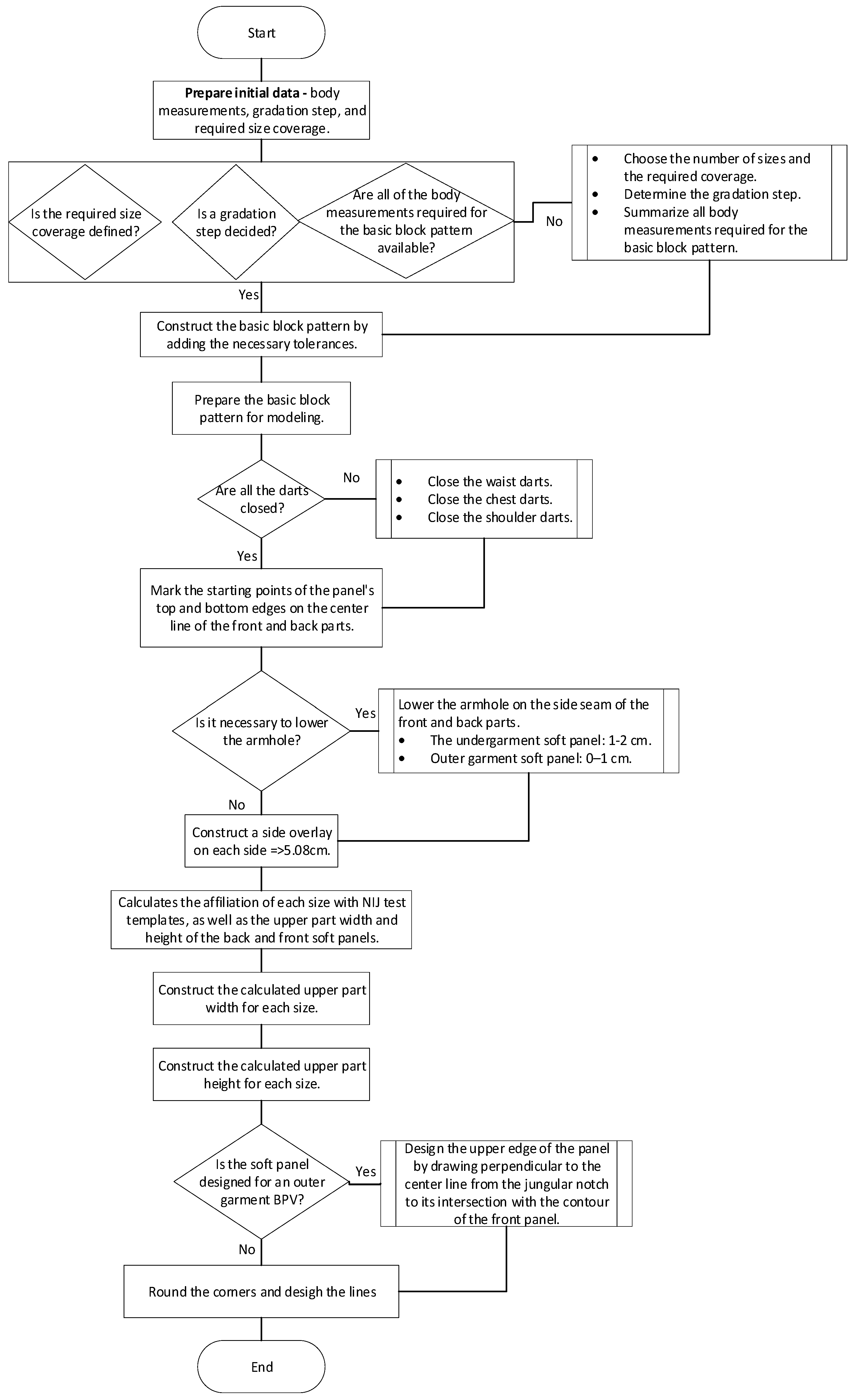
2.6. Development of Design Methodology
3. Discussion
3.1. Determination of Research Data
3.2. Physical Comfort of the BPV
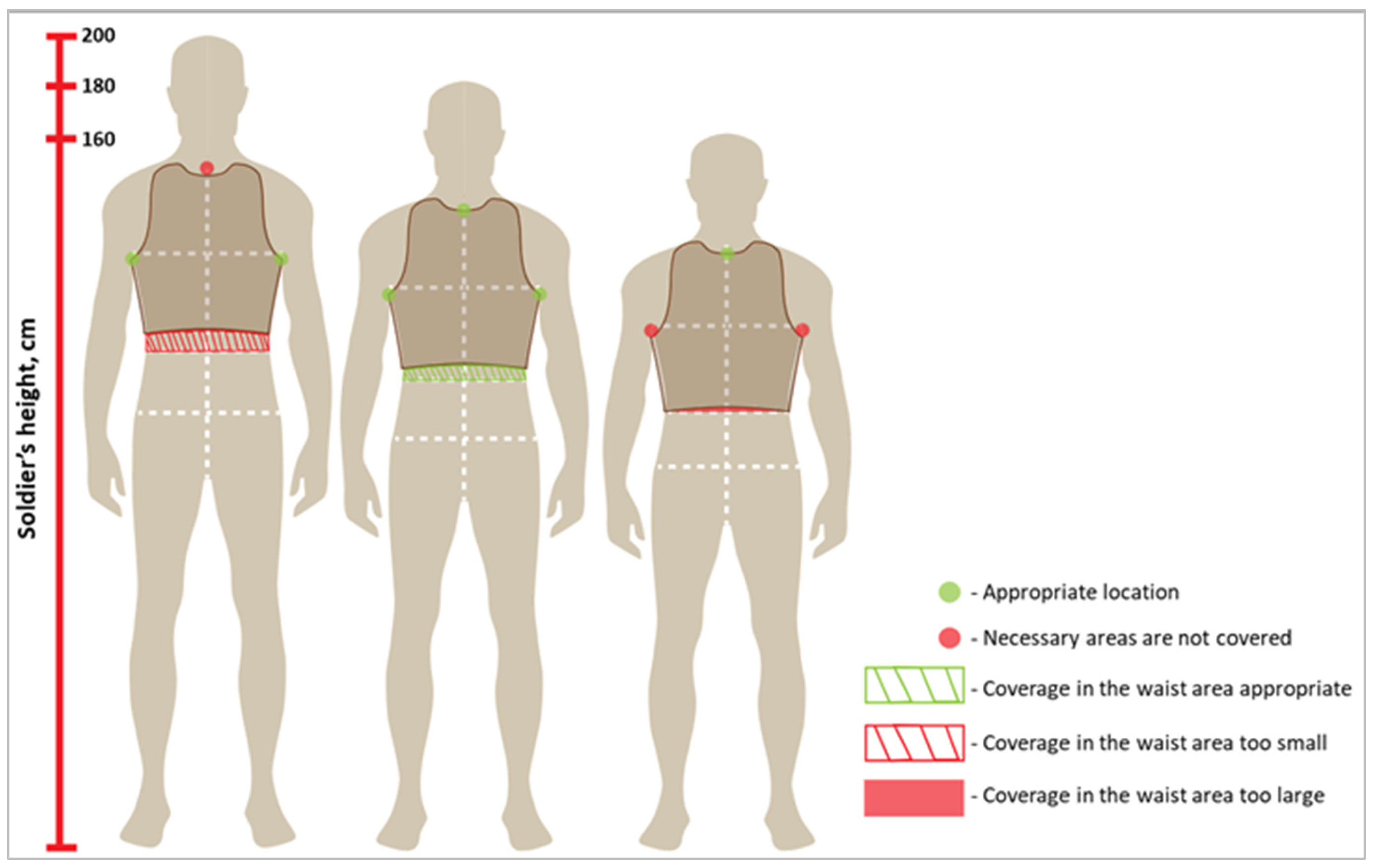
3.3. Dimensions of the BPSP
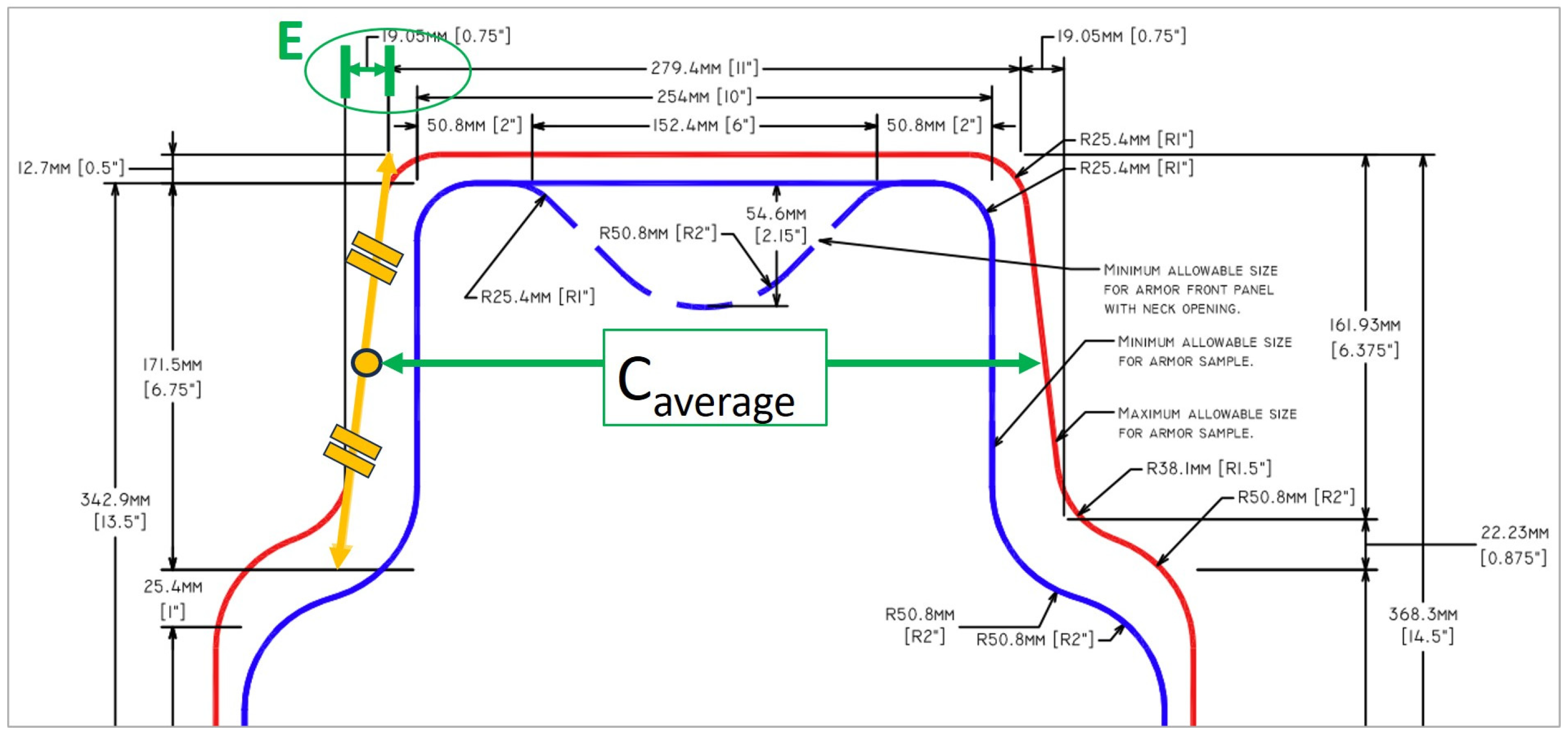
- The first is a ballistic test template surface area with a very accurate configuration, according to which soft panels are prepared for ballistic protection tests;
- The second and third are the maximum and minimum surface areas for production soft panels to be placed in protective vests, specifying only their configuration with specific indications about panel overlapping in the side parts and indications ensuring the ergonomic comfort of the BPV wearer in the neck, waist, and arm areas.
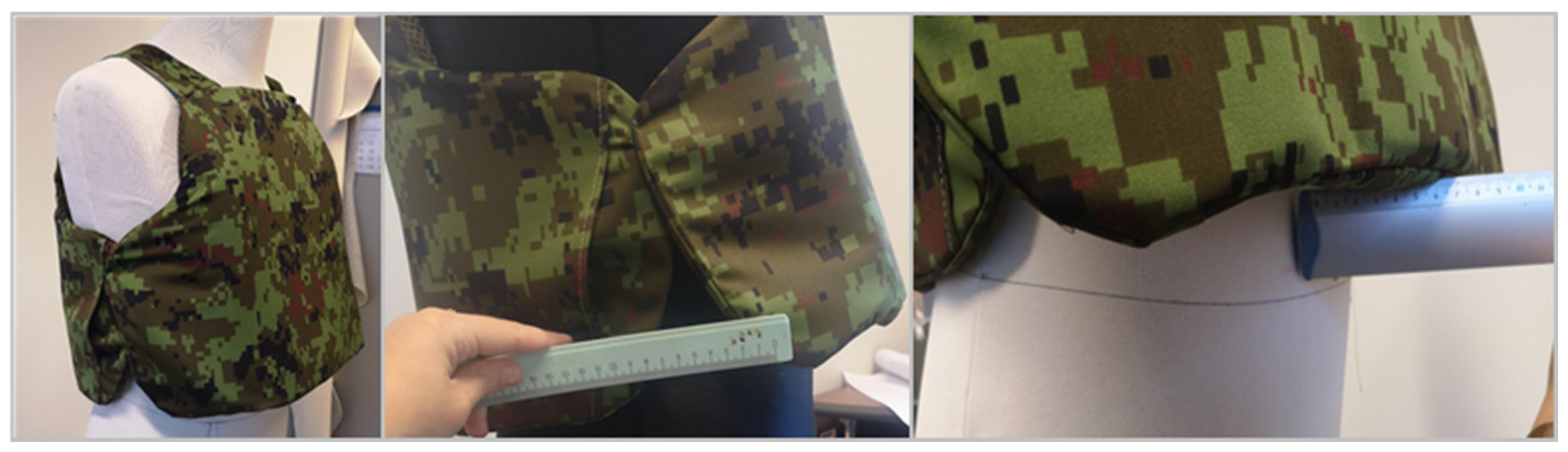
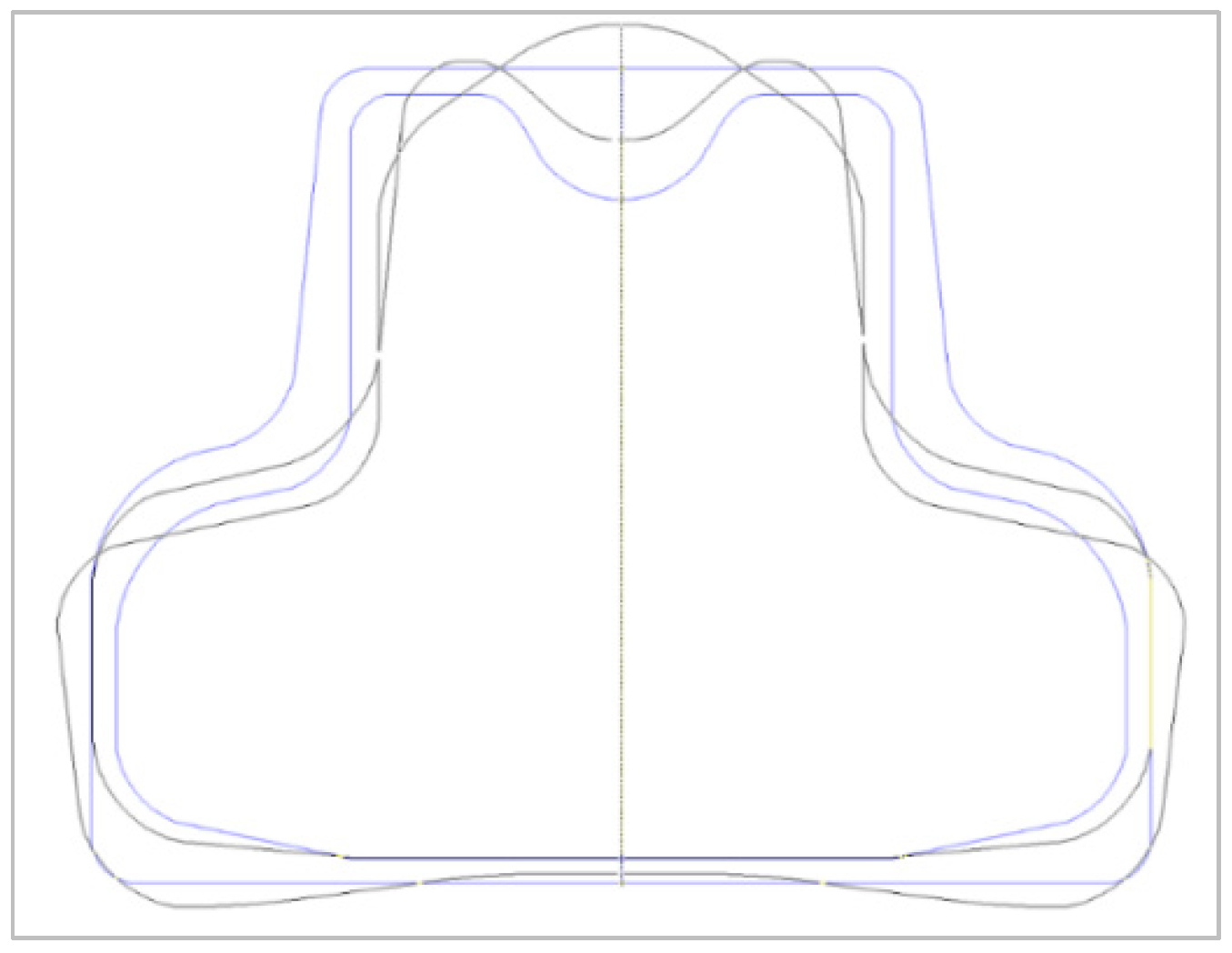
3.4. Configuration Analysis of Ballistic Protection Soft Panel Samples Used in the Military
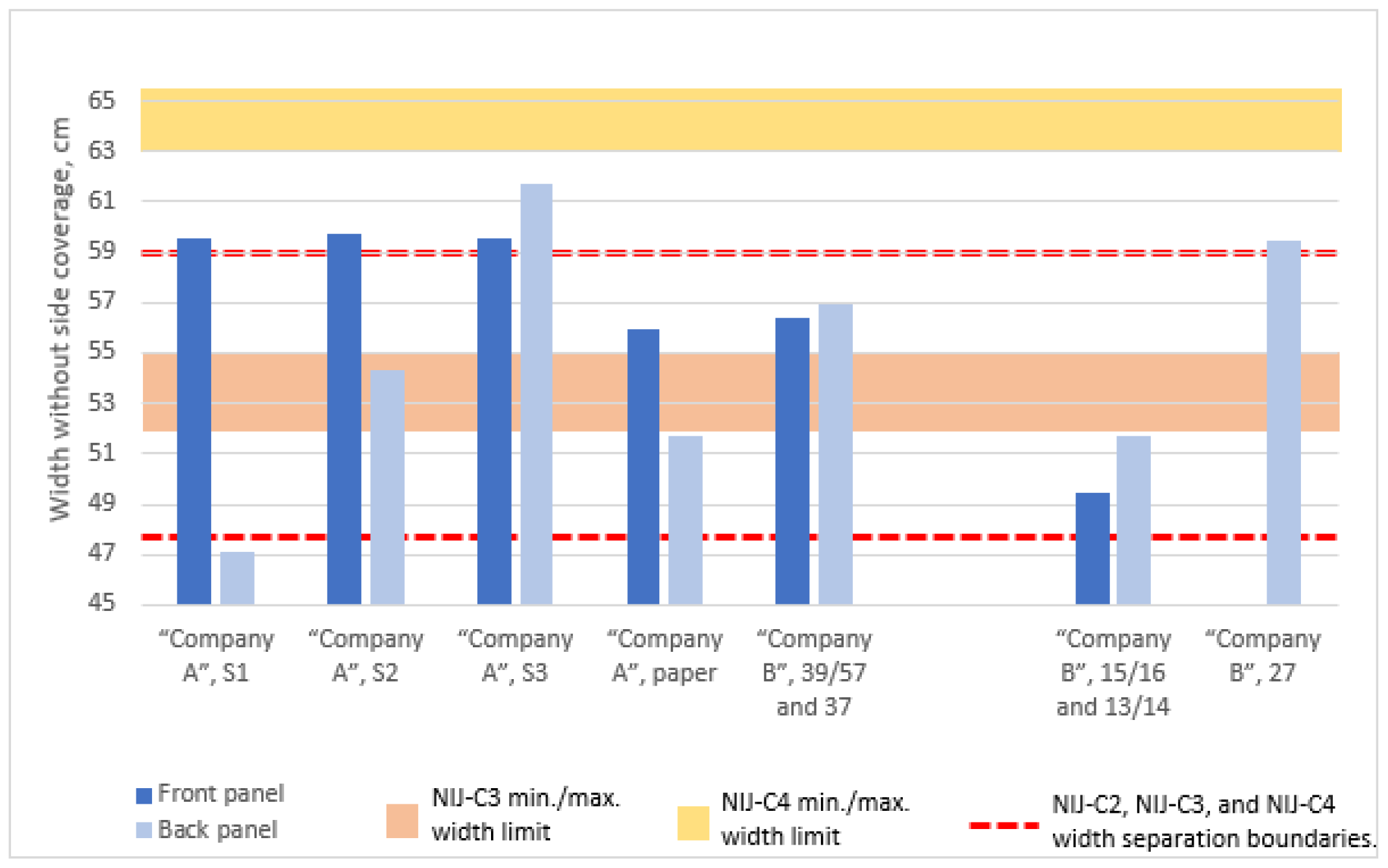
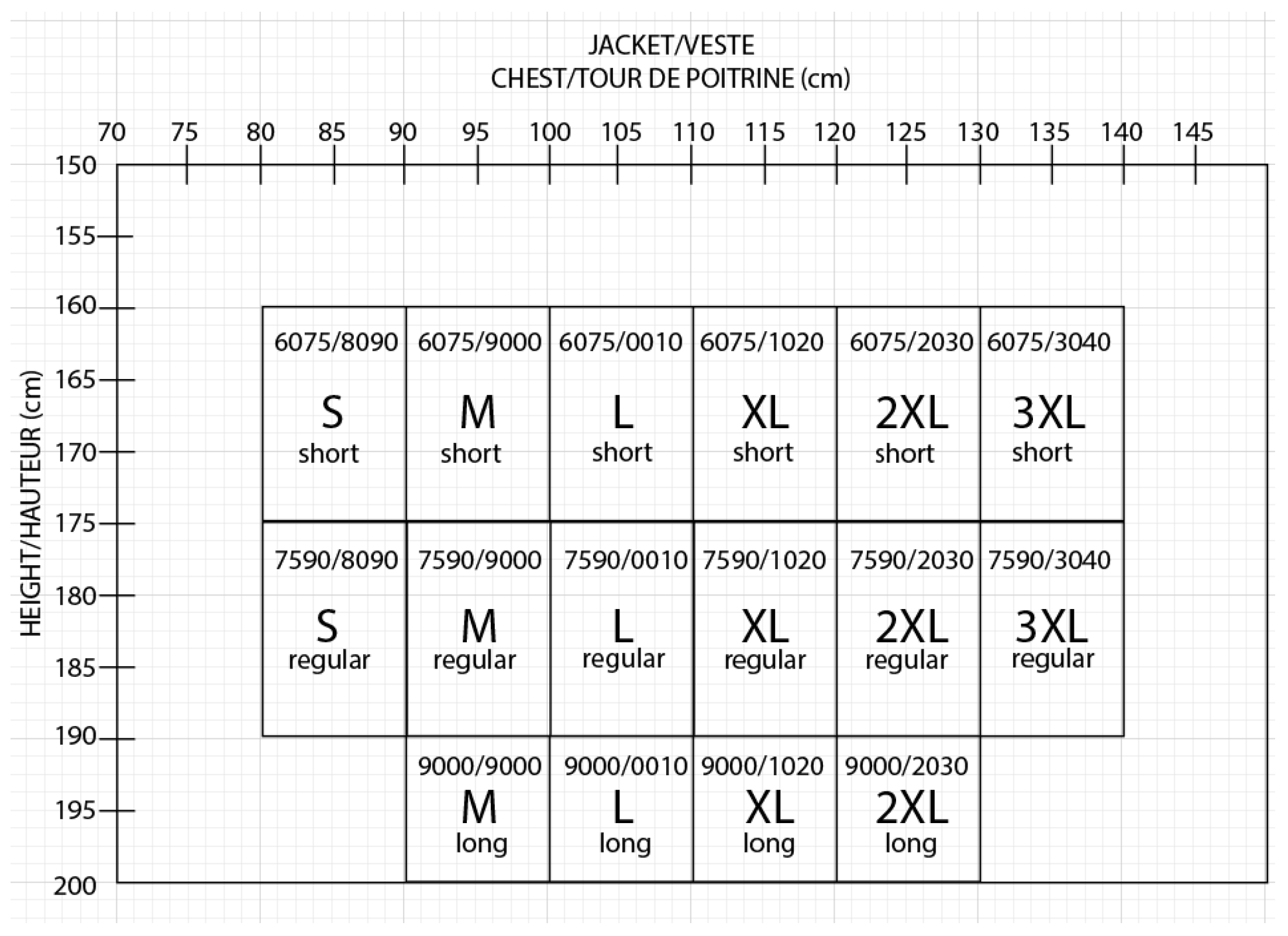
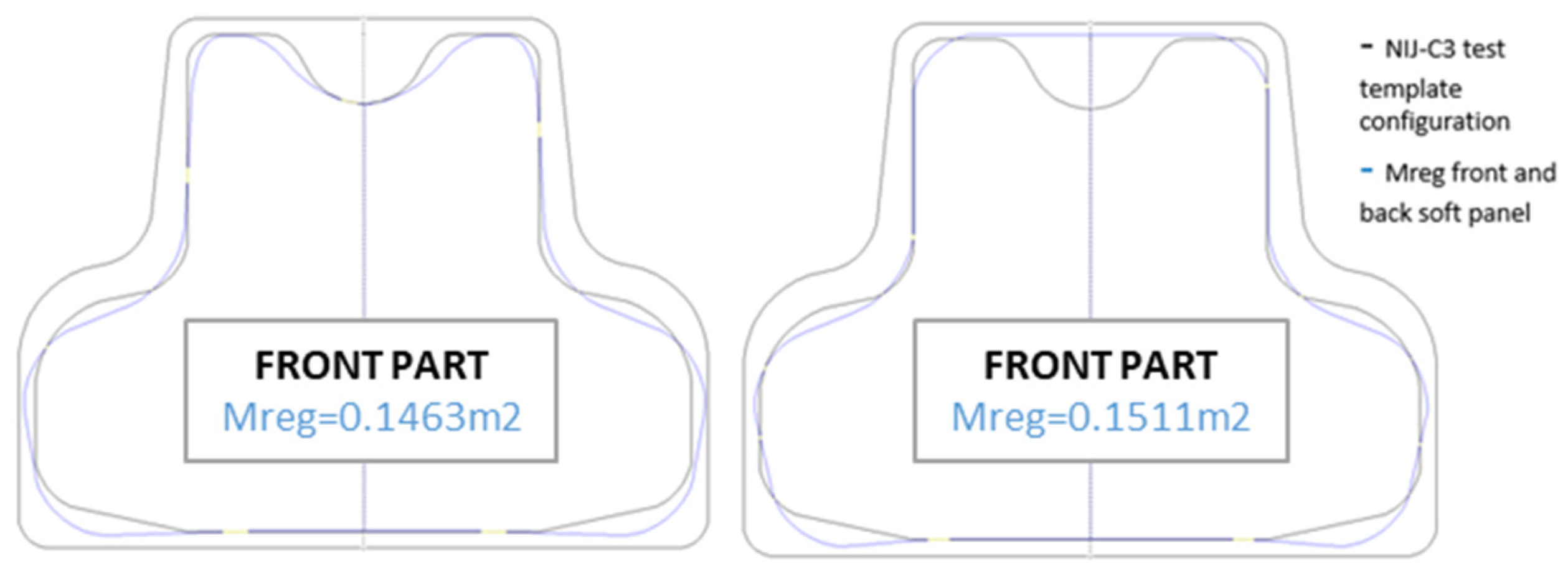
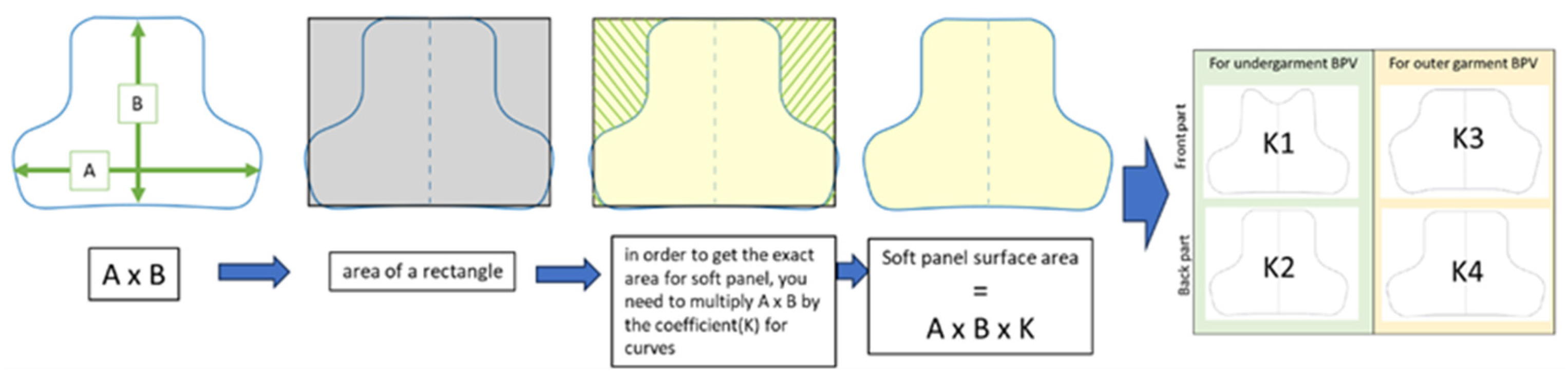
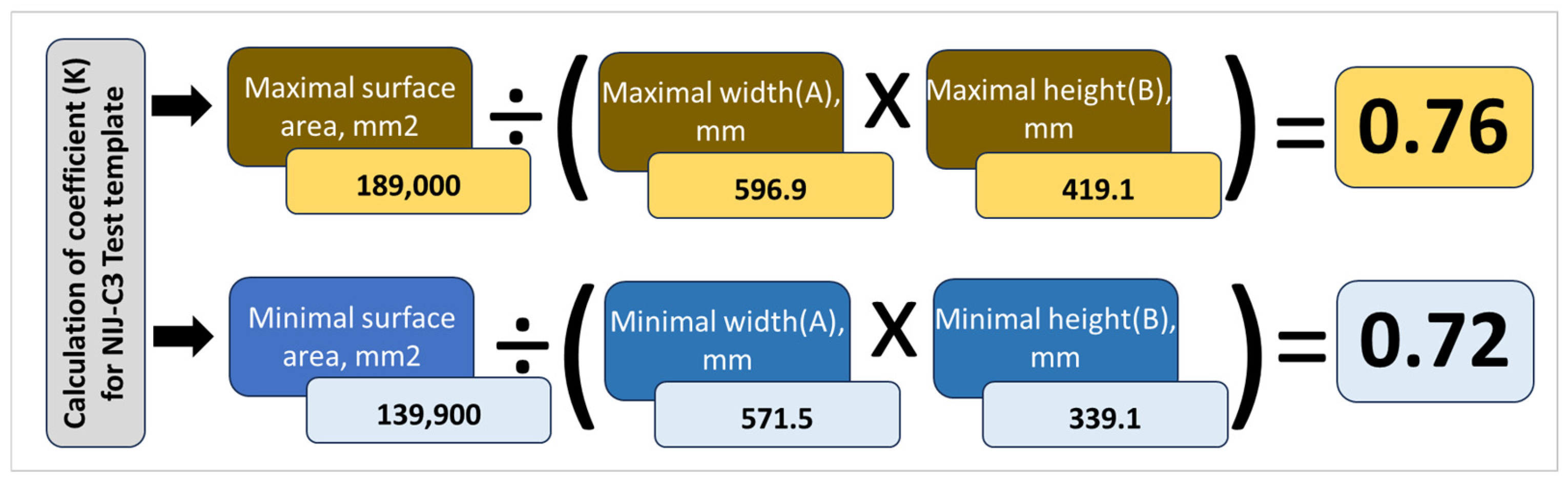
3.5. The First Requirement: Surface Area of BPSPs
3.6. The Second Requirement: Configuration of BPSPs
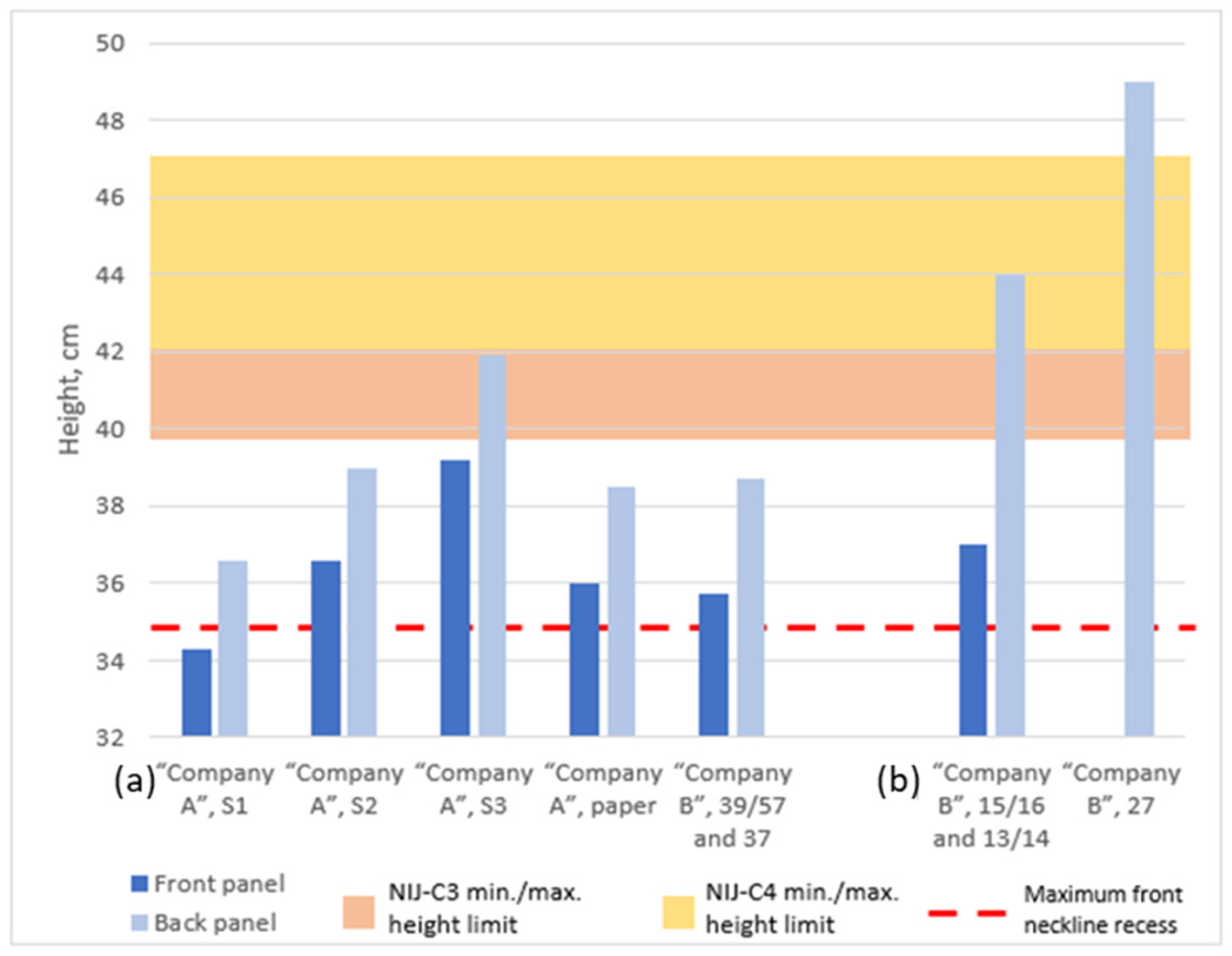
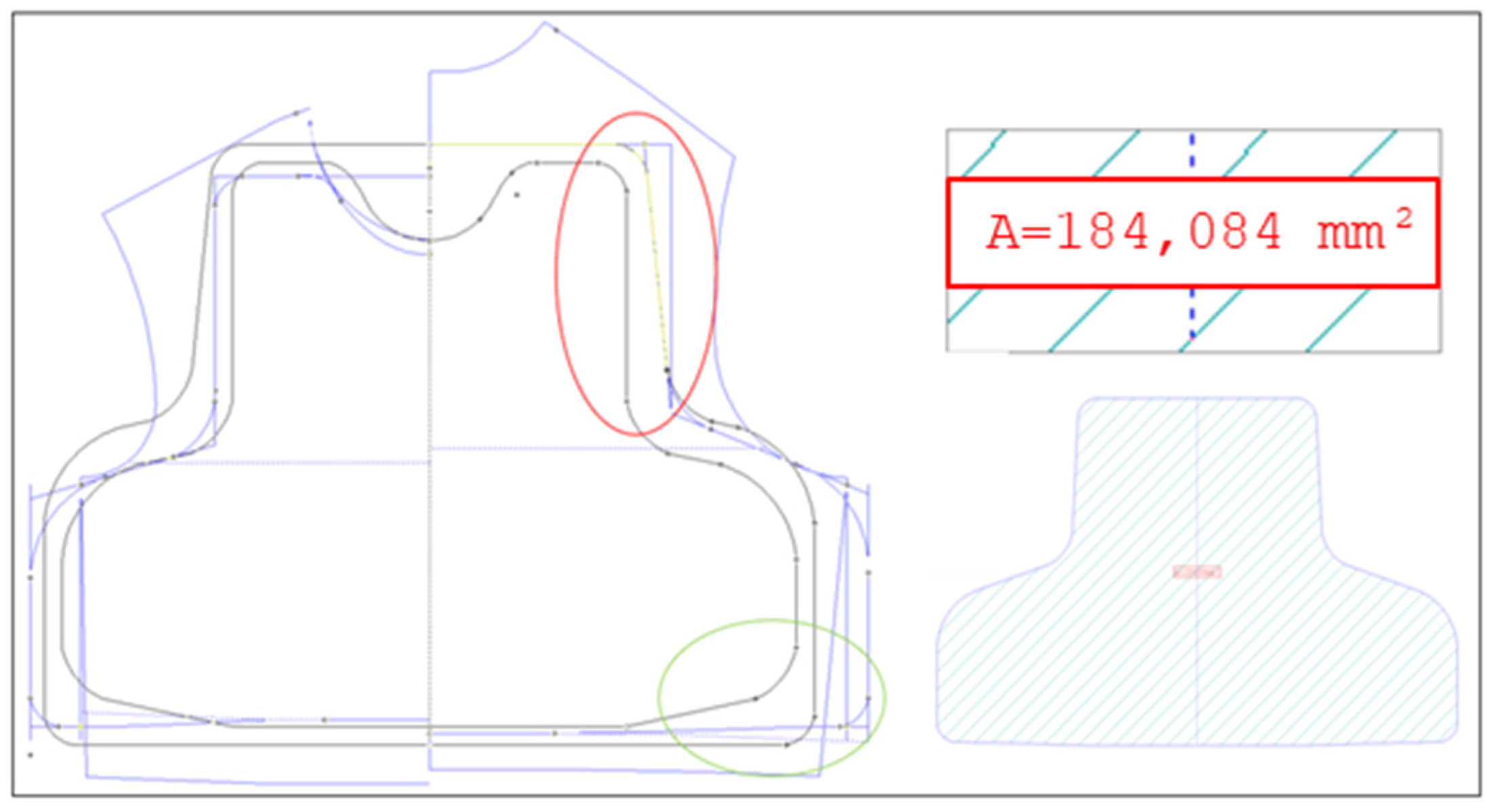
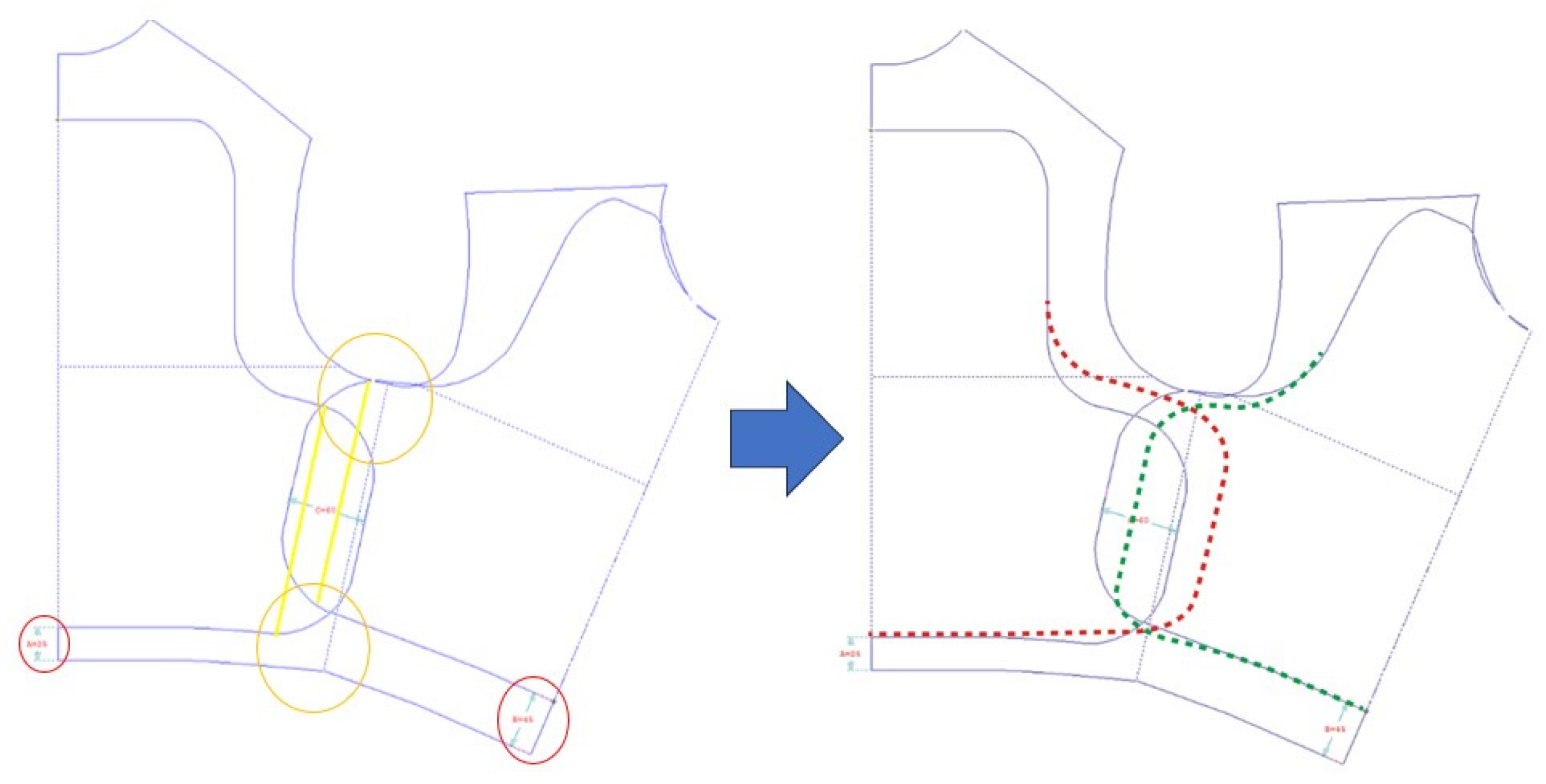
3.7. Determination of the Height B of BPSPs
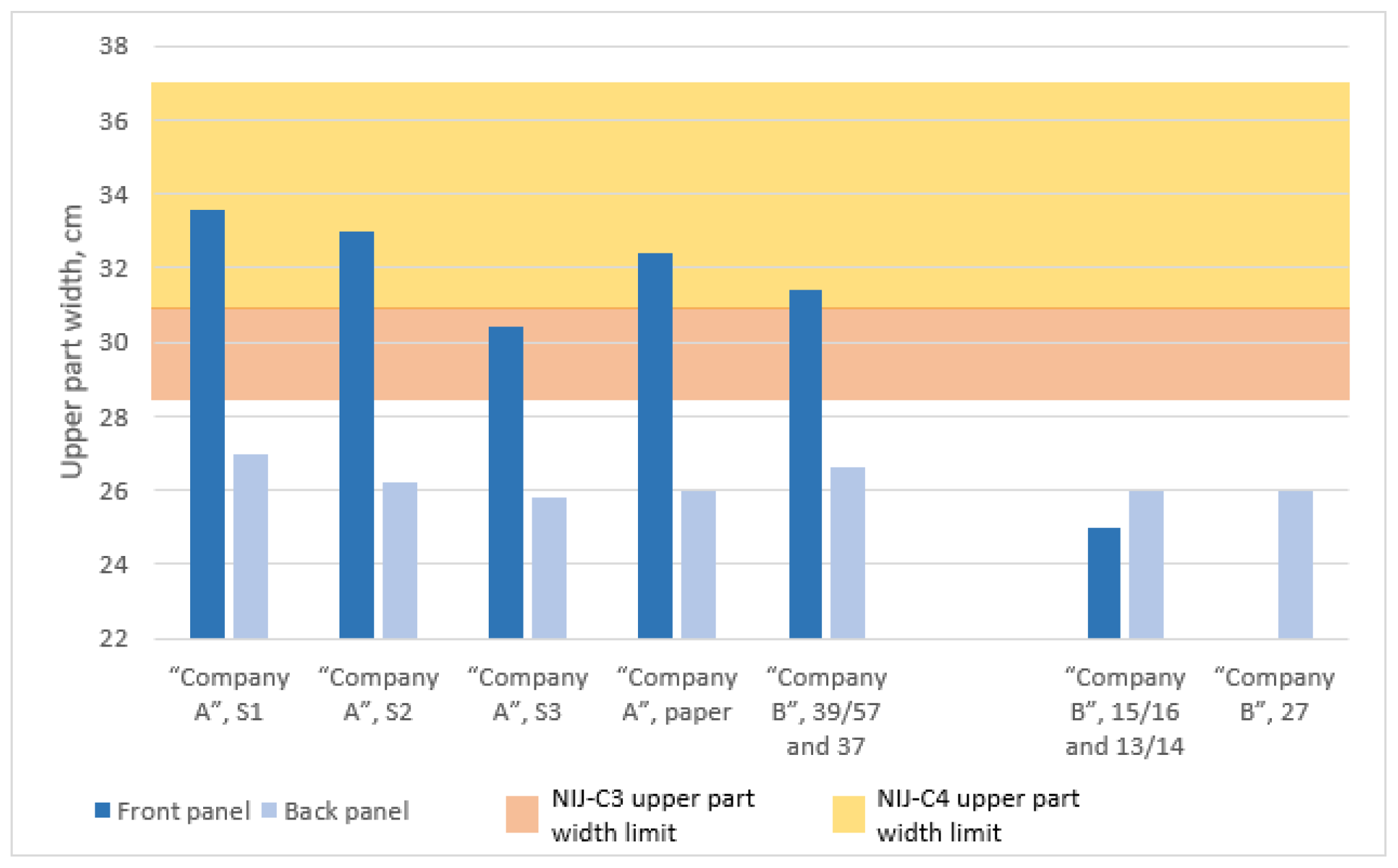
3.8. Determination of the Top Width C of BPSPs
3.9. Determining the Configuration of BPSPs
3.10. Output Parameters for Designing BPSP Patterns
3.11. Designing Patterns for BPSPs
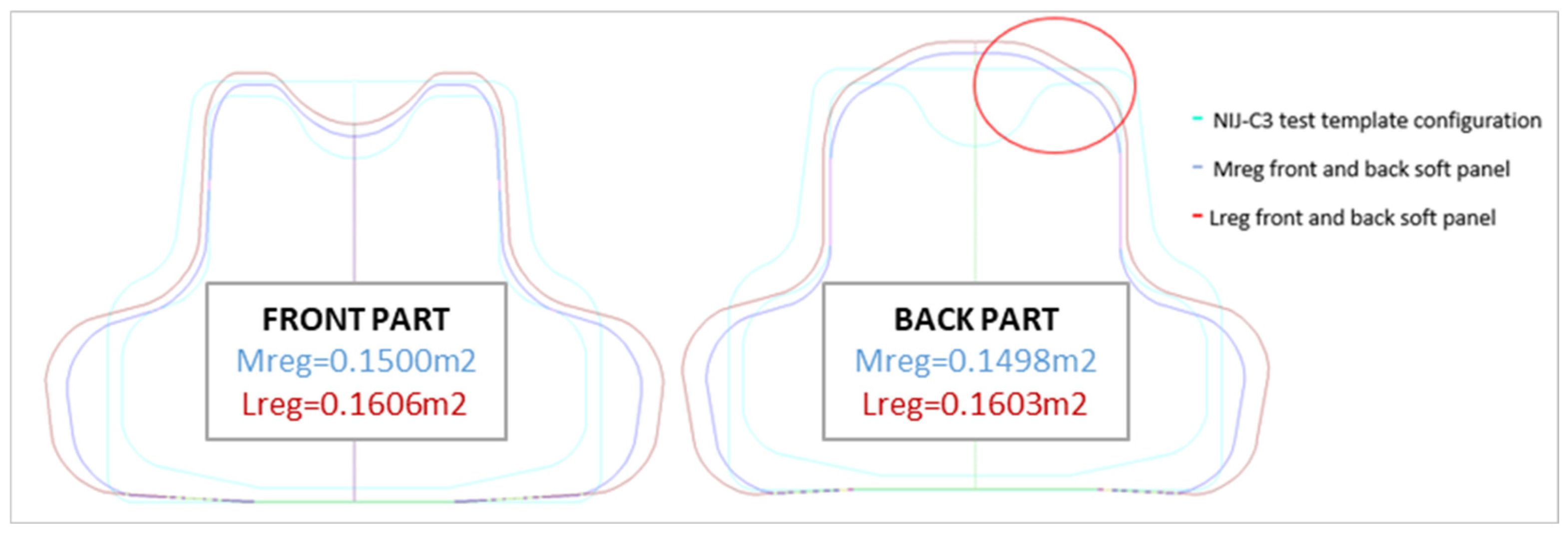
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Precedence Research. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/body-armor-market (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- MarkWide Research Inspiring Growth. Available online: https://markwideresearch.com/ballistic-protection-market/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Hu, Q.; Shen, X.; Qian, X.; Huang, G.; Yuan, M. The personal protective equipment (PPE) based on individual combat: A systematic review and trend analysis. Def. Technol. 2023, 28, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigne, N.L. Ballistic Resistance of Body Armor NIJ Standard 0101.07; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://nij.ojp.gov/ballistic-resistance-body-armor-nij-standard-010107 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Holder, E.H.; Mason, K.V.; Sabol, V.J. National Institute of Justice Guide—Body Armor. In Selection & Application Guide 0101.06 to Ballistic-Resistant Body Armor; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.ojp.gov/pdffiles1/nij/247281.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Mukasey, B.M.; Sedgwick, J.L.; Hagy, D.W. Ballistic Resistance of Body Armor NIJ Standard-0101.06; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/oles/ballistic.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- STANAG 2335 (Edtion 3); Interchangeability Combat Clothing Sizes. NATO Standartization Agency: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2012. Available online: https://www.intertekinform.com/en-gb/standards/stanag-2335-2012-736803_saig_nato_nato_1789762/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Hard Shell. Available online: https://www.hardshell.ae/size-chart/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Alvanon. Available online: https://alvanon.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/AF-SPECS_ASD-EU-Men_v4.0__06MAR2015.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Safeguard Armor. Available online: https://www.safeguardarmor.com/pages/size-chart (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Bullet Safe. Available online: https://bulletsafe.com/pages/bulletproof-vest-size-chart (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- BAO, Body Armor Outlet. Available online: https://www.bodyarmoroutlet.com/pages/sizing-charts (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- BAO, Body Armor Outlet. Available online: https://www.bodyarmoroutlet.com/products/baot-cxiiia-xseries-w-iiia-ballistics (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Protection Group Danmark Wholesale ApS. Available online: https://protectiongroupdenmark.com/shop/4-bulletproof-vest/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- GH Armor. Available online: https://www.gharmor.com/sizing (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- National Body Armor, Concealed Experts. Available online: https://nationalbodyarmor.com/pages/sizing-chart-1 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- The Tactical Boutique. Available online: https://www.thetacticalboutique.com/product/bulletsafe-bulletproof-vest (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Safe Life Defence. Available online: https://safelifedefense.com/concealable-multi-threat-vest-level-iiia-hg2 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Šitvjenkins, I. Karavīra individuālās aizsardzības sistēma. In Lietošanas Rokasgrāmata. 2008; Volume 1, 160p. Available online: https://www.mod.gov.lv/sites/mod/files/document/karavira_ias_0.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- NATO Standard AEP-2333; Combat Clothing Performance and Protective Properties and Trial Guidance. NATO: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/14486495/aep-2333 (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- EN 13921:2007; Personal Protective Equipment—Ergonomic Principles. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. Available online: https://www.lvs.lv/lv/products/index?ProductsSearch%5Bproduct_number%5D=EN+13921%3A2007&yt0=&Products%5Bstatus_code%5D%5B%5D=11&page=0 (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Vigne, N.L. Specification for NIJ Ballistic Protection Levels and Associated Test Threats—NIJ Standard 0123.00; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://nij.ojp.gov/specification-nij-ballistic-protection-levels-and-associated-test-threats-nij-standard-012300 (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Dabolina, I.; Lapkovska, E.; Vilumosone, A. Dynamic Anthropometry for Investigation of Body Movement Comfort in Protective Jackets. In Functional Textiles and Technology; Majumdar, A., Gupta, D., Gupta, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 241–259. ISBN 9789811377204. [Google Scholar]





| Surface Area, mm2 | Width (A), mm | Height (B), mm | Upper Part Width (C), mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Amin | Amax | Bmin (Front/Back) | Bmax | Cmin | Cmax | |
| NIJ-C1 | <98,000 | 98,000 | 292.2 | 317.5 | 262.9/292.1 | 317.5 | 228.6 | 254 |
| NIJ-C2 | 98,000 | 139,900 | 406.4 | 431.8 | 313.7/342.9 | 368.3 | 254 | 279.4 |
| NIJ-C3 | 139,900 | 189,000 | 520.7 | 546.1 | 364.5/393.7 | 419.1 | 279.4 | 304.8 |
| NIJ-C4 | 189,000 | 245,500 | 635 | 660.4 | 415.3/444.5 | 469.9 | 304.8 | 330.2 |
| NIJ-C5 | 245,500 | >245,500 | 749.3 | 774.7 | 466.1/495.3 | 520.7 | 330.2 | 355.6 |
| No. | Requirement | Front Panel | Back Panel | Instructions for Outer Garment BPVs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Side coverage | Front and back panels overlap at least 5.08 cm on each side. | - | ||
| 2. | Height | It should extend from just below the jugular notch to two to three finger-widths above the top of the belt when the individual is in the standing position. | Should extend from approximately 5.08 cm below the collar to approximately 2.54 cm above the belt. | They can be slightly longer without impeding movement or comfort. | |
| 3. | Armpit area coverage | Ballistic coverage under the arms should be as high as possible without compromising the ability to reach a shooting position. | They may afford slightly greater protection in this area. | ||
| 4. | Surface area | The minimum and maximum specified in the NIJ standard must be maintained. | A larger area of the body should be covered, and more protection should be provided. | ||
| 5. | Fit | It should fit snugly but not so tightly that it may affect breathing (including deep breathing, such as that which may occur during an on-foot chase). The armor should slide slightly on the body as the torso is rotated back and forth. | Less tight/looser | ||
| 6. | BPV and soft panel’s physical comfort check | When trying on the soft panels and the BPV itself, soldiers must conduct various daily movements, such as rotating their upper bodies or sitting down, to ensure that the soft panels are not “sitting” on the belt and the upper edge is not pressing against their neck. | |||
| Title 1 | Allowable Surface Areas for Production BPV, Min–Max, m2 | Manufacturer, Name of the Analyzed Soft Panel | Size | Type of Wear | Surface Area, m2 | Height B, cm | Width A, cm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front Panel | Back Panel | Front Panel | Back Panel | Front Panel | Back Panel | |||||
| NIJ-C3 | 0.1399–0.1890 | “Company A”, S1 | S1 | Outer garment | 0.1710 | 0.1436 | 34.3 | 36.6 | 64.6 | 52.2 |
| “Company A”, S2 | S2 | 0.1770 | 0.1635 | 36.6 | 39 | 64.8 | 59.4 | |||
| “Company A”, S3 | S3 | 0.1832 | 0.1838 | 39.2 | 41.9 | 64.6 | 66.8 | |||
| “Company A”, paper | S1/S2 | 0.1635 | 0.1505 | 36 | 38.5 | 61 | 56.8 | |||
| “Company B”, No. 39/57, No. 37 | S2 | 0.1675 | 0.1651 | 35.7 | 38.7 | 61.5 | 62 | |||
| “Company B”, No. 15/16, No. 13/14 | LL | Undergarment | 0.1523 | 0.1639 | 37 | 44 | 54.5 | 56.8 | ||
| NIJ-C4 | 0.1890–0.2455 | “Company B”, No. 27 | 2XLL | Undergarment | - | 0.1999 | - | 49 | - | 64.5 |
| Designation | Name | Tolerance Value for Undergarment BPV, cm | Tolerance Value for Outer Garment BPV, cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vkra | Tolerance in chest circumference | 4 | 7 |
| Vva | Tolerance in waist circumference | 2 | 4 |
| Vmgpl | Tolerance for back width | 1 | 1.75 |
| Vkrpl | Tolerance for front width | 0.5 | 8.8 |
| Vrocei | Tolerance in armpit area | 2.5 | 4.37 |
| Main Characteristics of the NIJ Standard [4,6] Test Templates | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width (A), mm | Height (B), mm | Upper Part Width (C), mm | Back Upper Part Height (D), mm | Front Upper Part Height (D), mm | ||||
| Template | Amin | Amax | Bmin | Bmax | Cmin | Cmax | Dback | Dfront |
| NIJ-C1 | 292.2 | 317.5 | 292.1 | 317.5 | 228.6 | 254 | 146.1 | 136.5 |
| NIJ-C2 | 406.4 | 431.8 | 342.9 | 368.3 | 254 | 279.4 | 171.5 | 161.9 |
| NIJ-C3 | 520.7 | 546.1 | 393.7 | 419.1 | 279.4 | 304.8 | 196.9 | 187.3 |
| NIJ-C4 | 635 | 660.4 | 444.5 | 469.9 | 304.8 | 330.2 | 222.3 | 212.7 |
| NIJ-C5 | 749.3 | 774.7 | 495.3 | 520.7 | 330.2 | 355.6 | 247.7 | 238.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barkane, D.; Grecka, M.; Almli, D.; Mecnika, V.; Ziemele, I. Development of Ballistic Protection Soft Panels According to Regulatory Documents. Designs 2024, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8040076
Barkane D, Grecka M, Almli D, Mecnika V, Ziemele I. Development of Ballistic Protection Soft Panels According to Regulatory Documents. Designs. 2024; 8(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarkane, Dana, Marianna Grecka, Dana Almli, Viktorija Mecnika, and Inese Ziemele. 2024. "Development of Ballistic Protection Soft Panels According to Regulatory Documents" Designs 8, no. 4: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8040076
APA StyleBarkane, D., Grecka, M., Almli, D., Mecnika, V., & Ziemele, I. (2024). Development of Ballistic Protection Soft Panels According to Regulatory Documents. Designs, 8(4), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8040076






