CLARA: Building a Socially Assistive Robot to Interact with Elderly People
Abstract
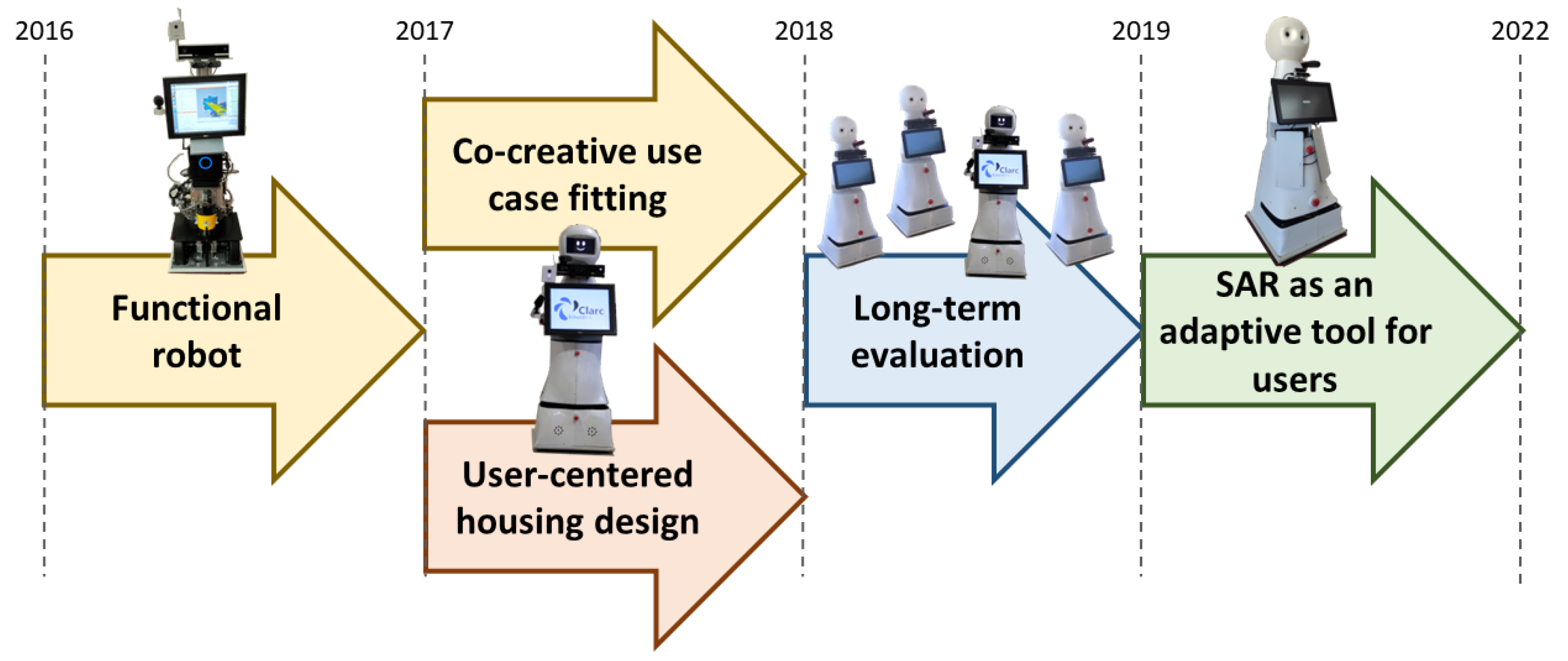
:1. Introduction
2. Designing a Robot for Automatizing the CGA
2.1. Choosing a Robotic Platform
- Robust base and navigation skill—The SCITOS G3 is comparable to the MiR100, RB-1, or TIAGO bases.
- Flexibility—The SCITOS G3 is a complete and modular platform that can be adapted to our specific requirements. This was considered a relevant feature, as the external appearance of the robot (and also other behavioral aspects) had to be adapted to our scenario and use cases.
- Feasibility analysis—Designed to deal with HRI scenarios, Metralabs provided all low-level, fundamental functionalities to enable fast prototyping and testing of the scenario. This aspect can also be provided by the improved MobiNa platform (Fraunhofer IPA), the RB-1 from Robotnik, or the TIAGO IRON from PAL Robotics. Other companies focused mainly on the base platform and the ability to navigate.
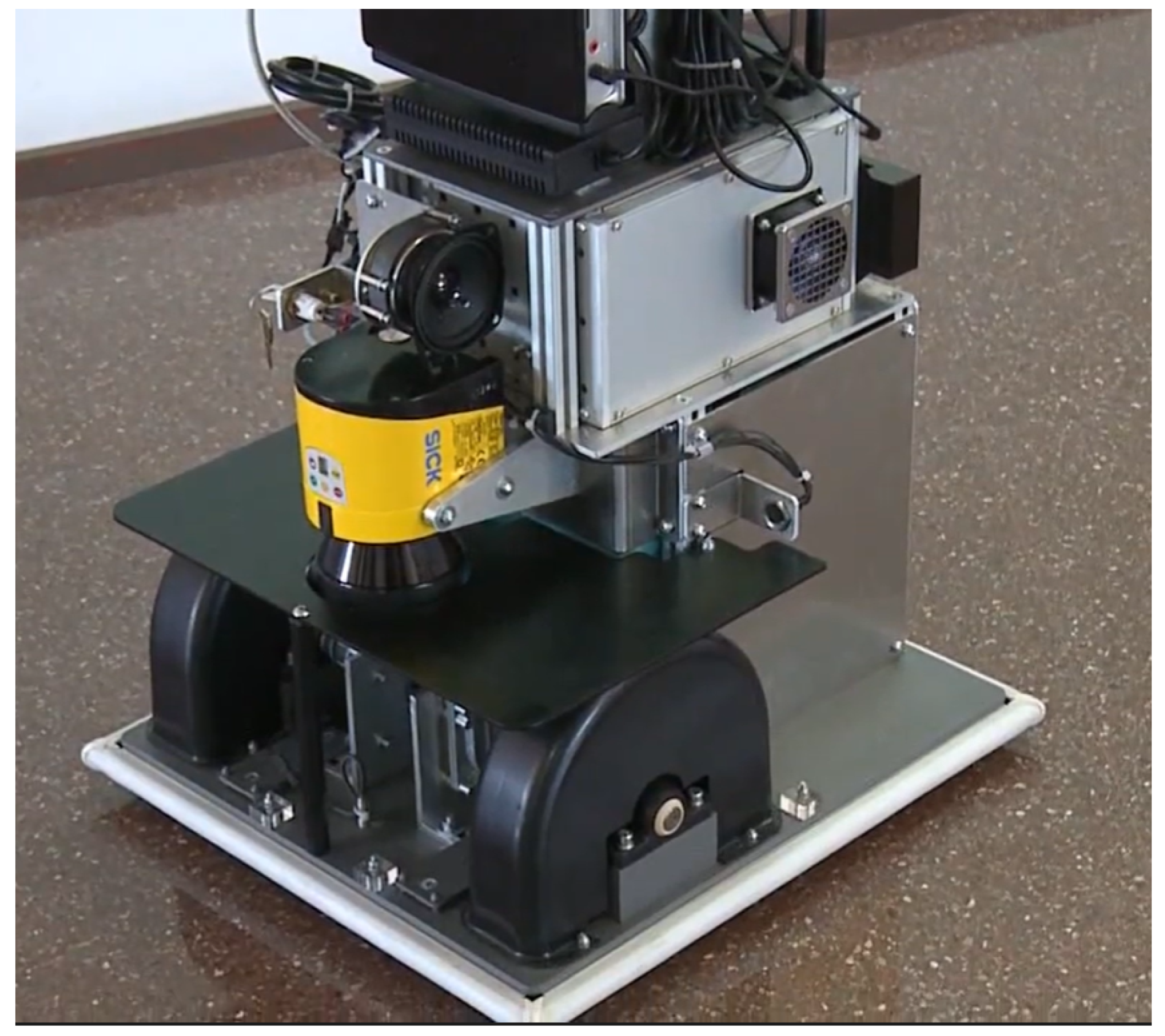
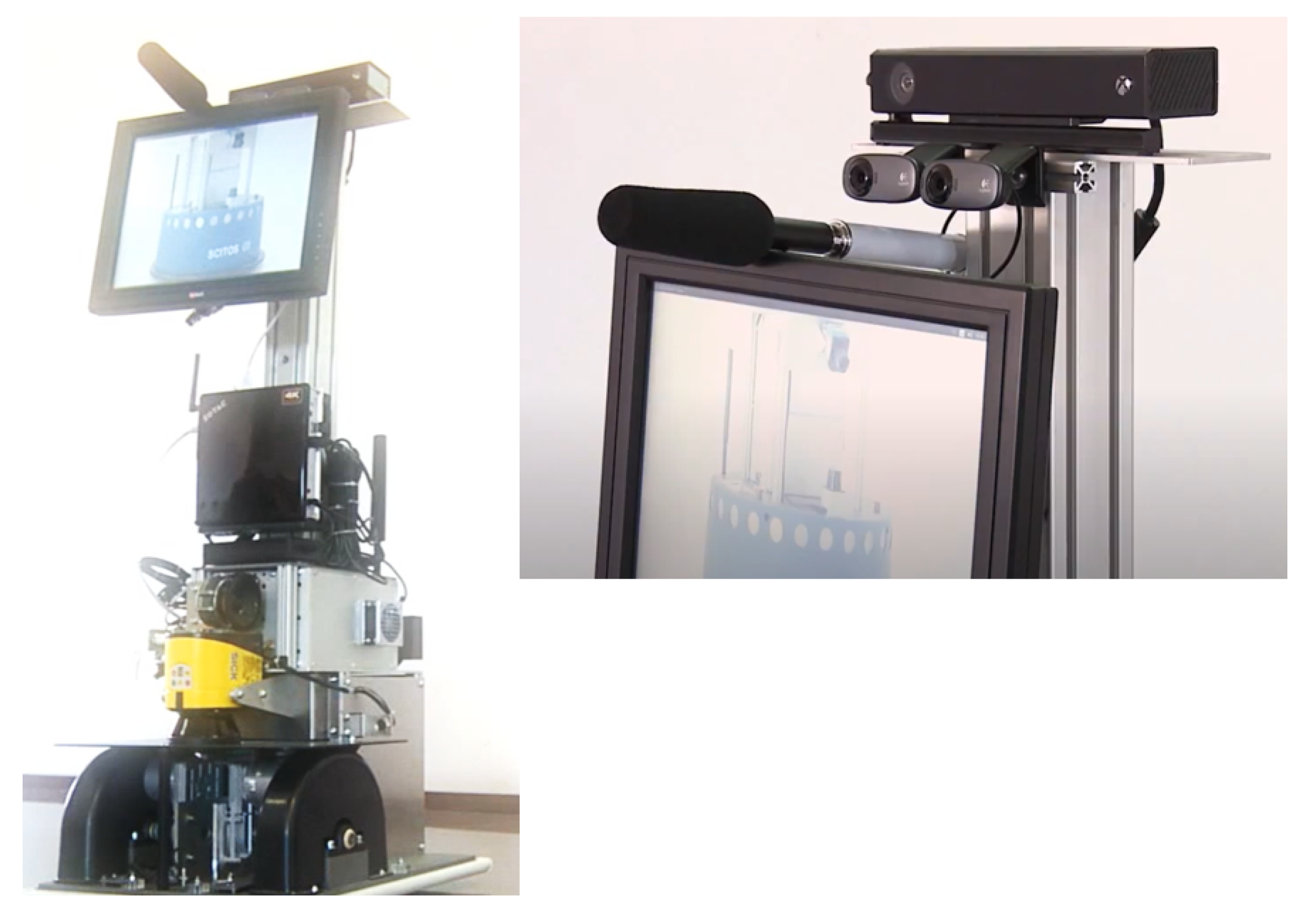
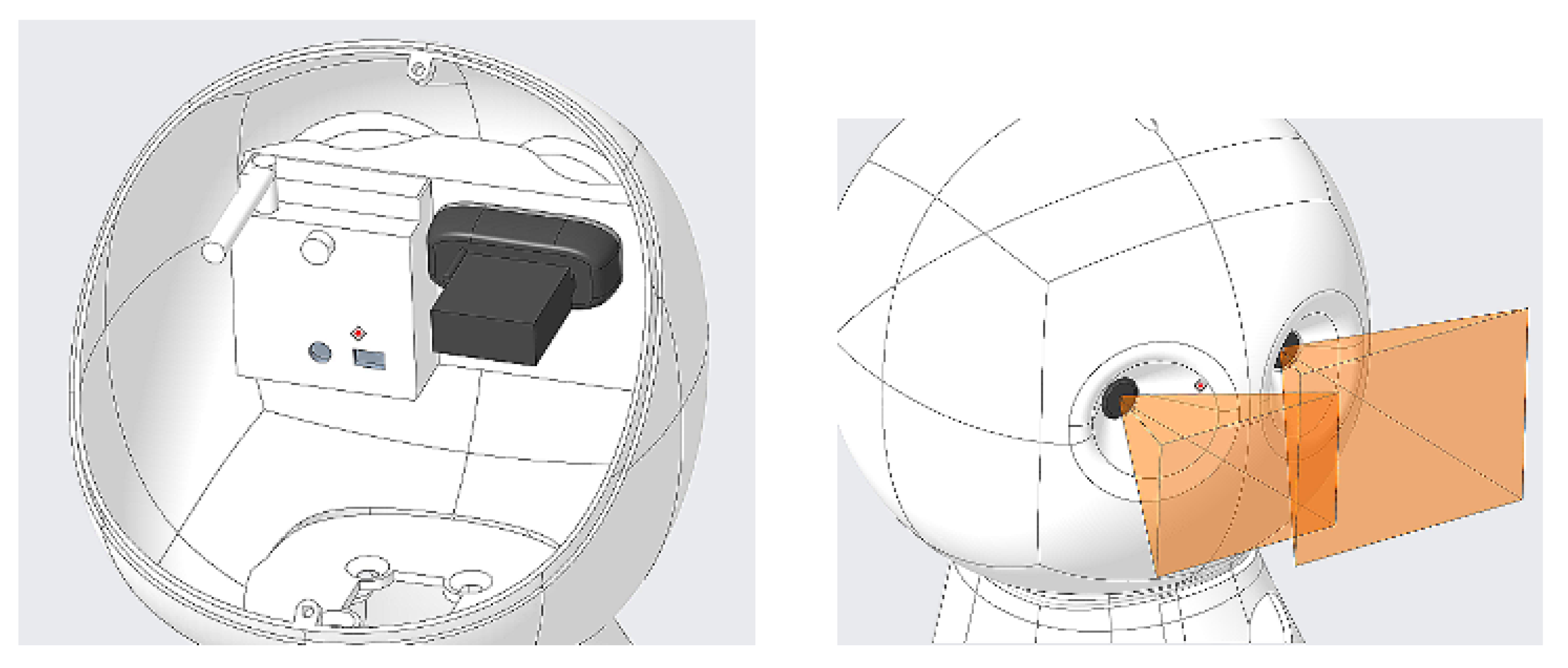
2.2. Sensors
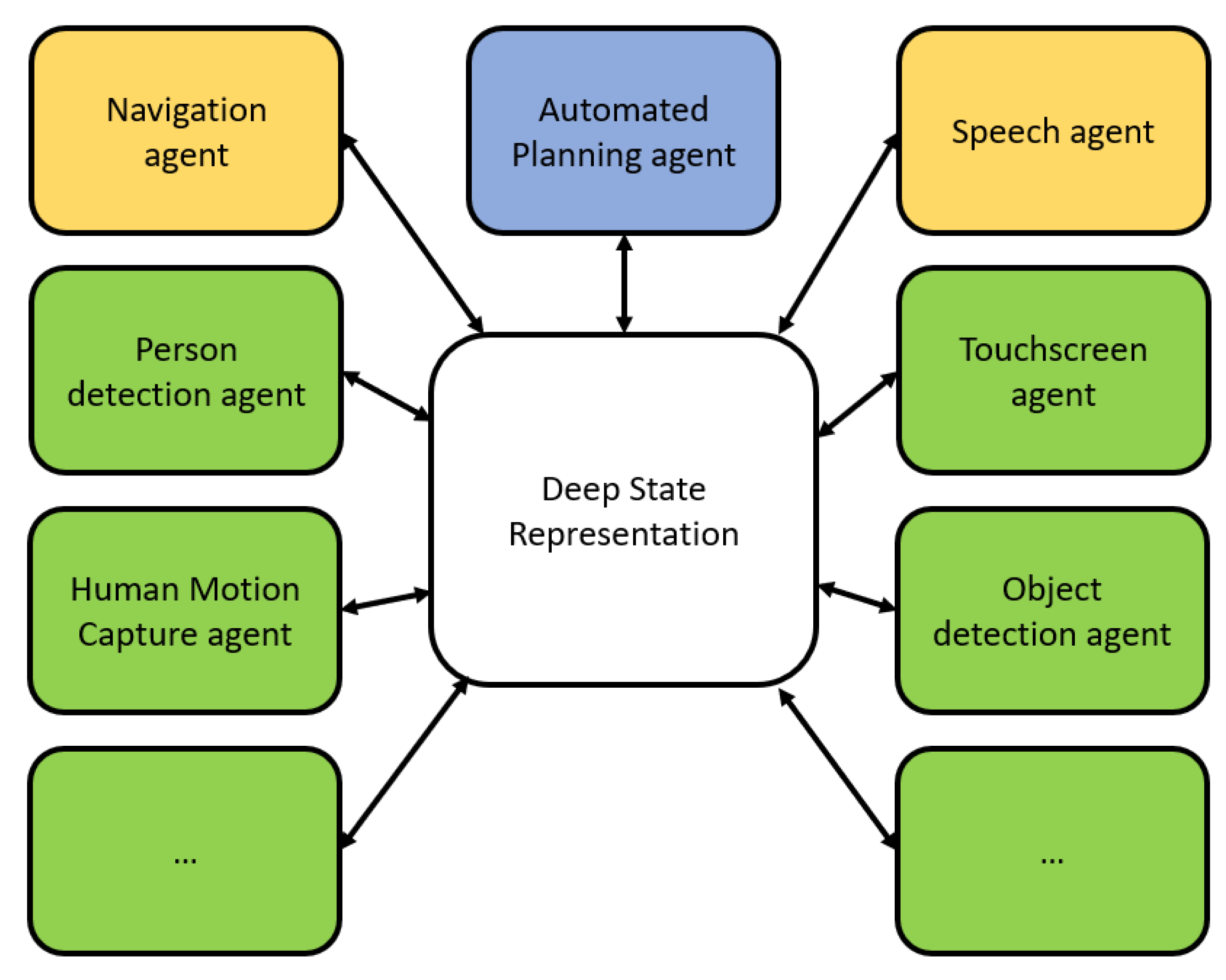
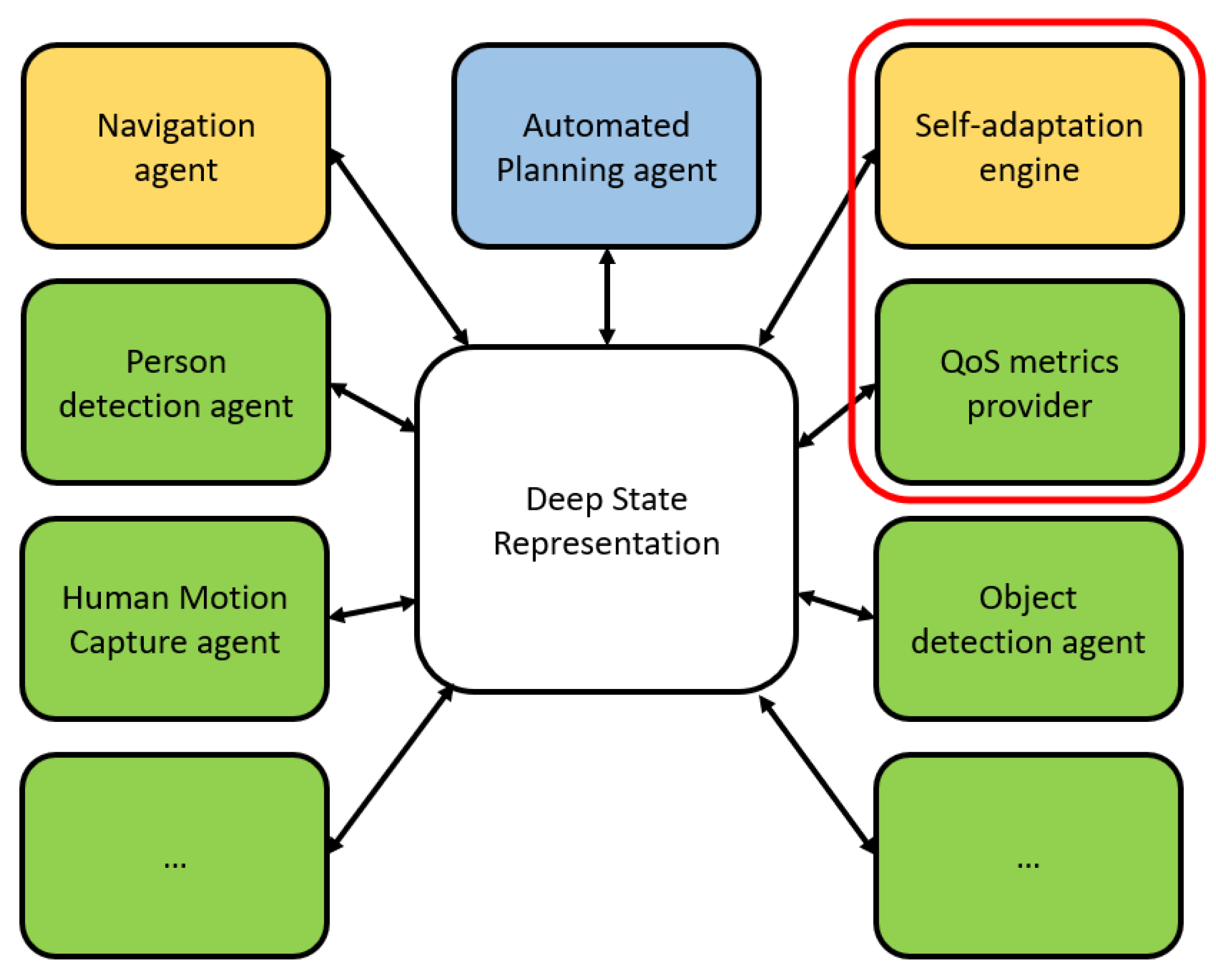
2.3. The Software Architecture CORTEX
2.4. Encoding the Use Cases in CORTEX
3. User-Centered Design
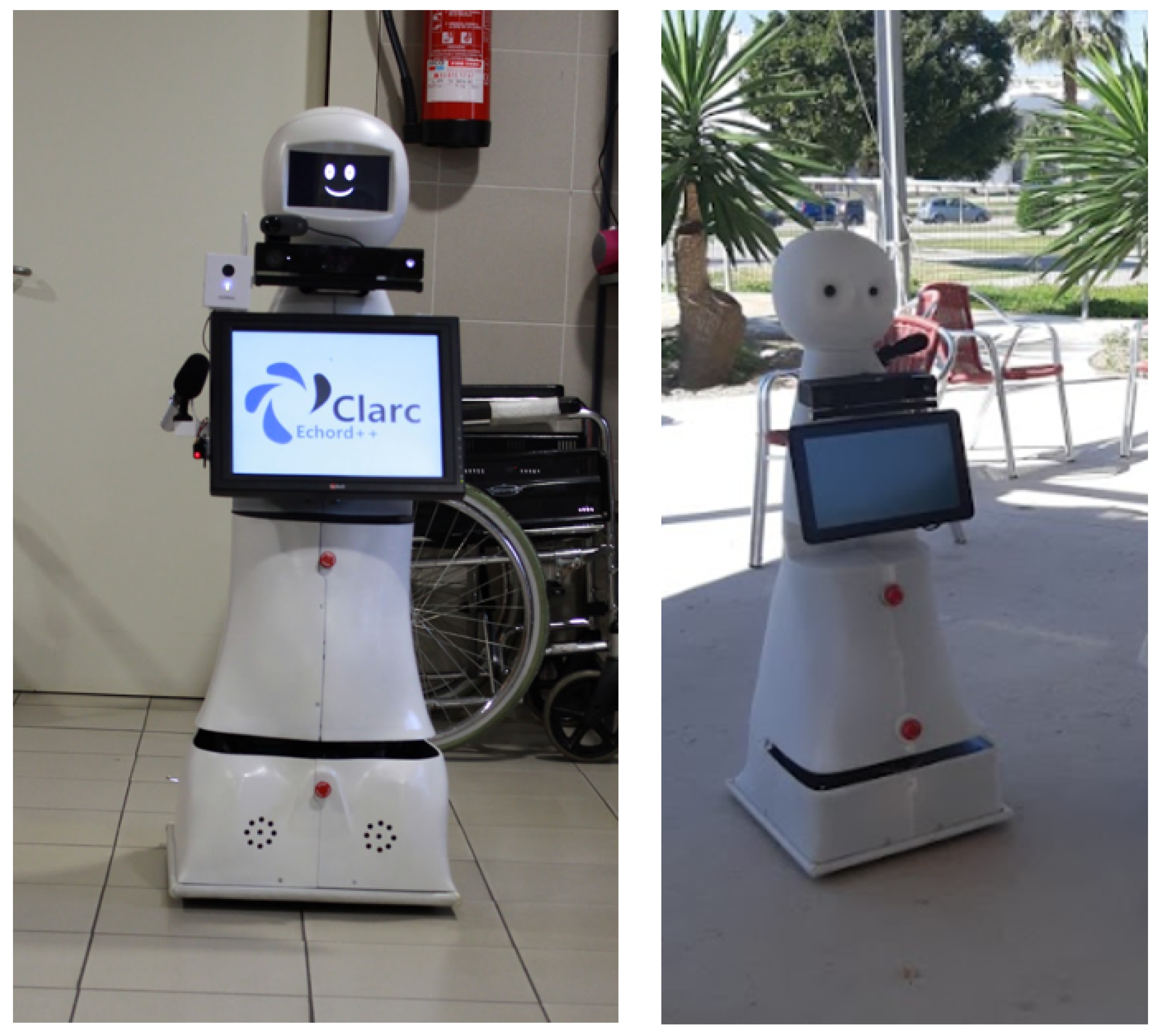
3.1. Design of the Robot Housing
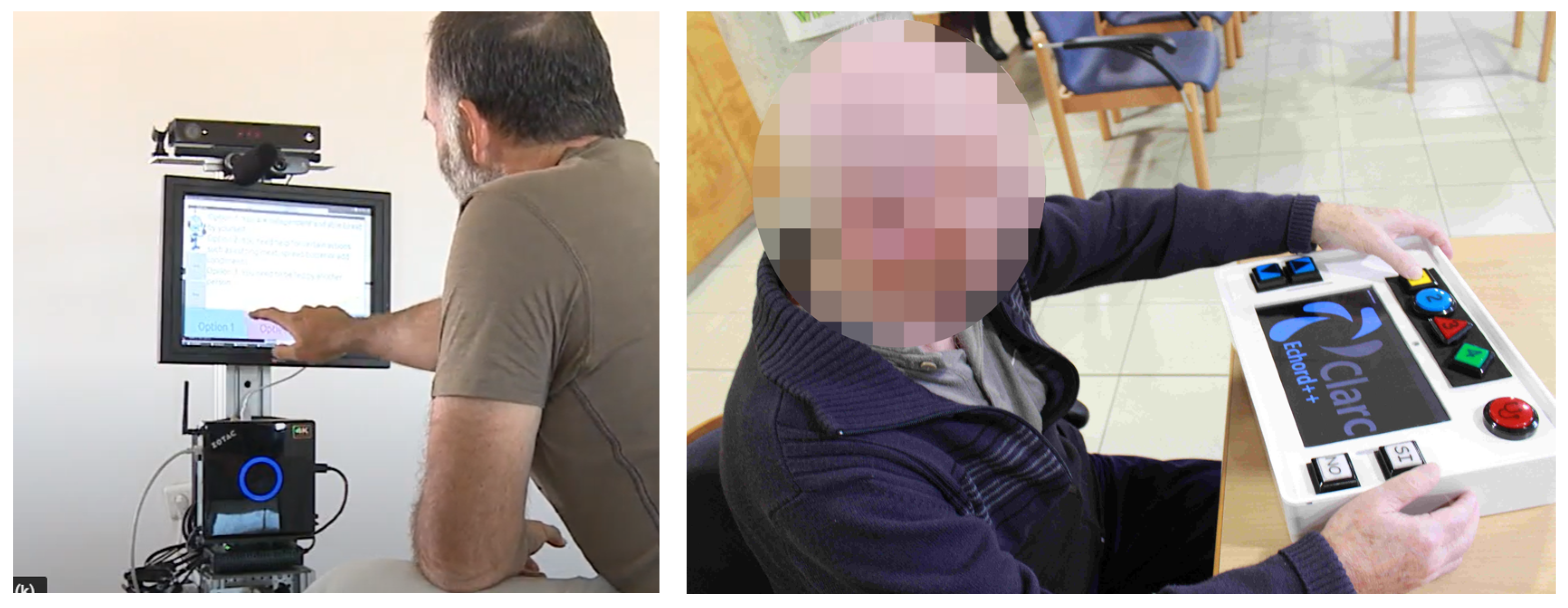
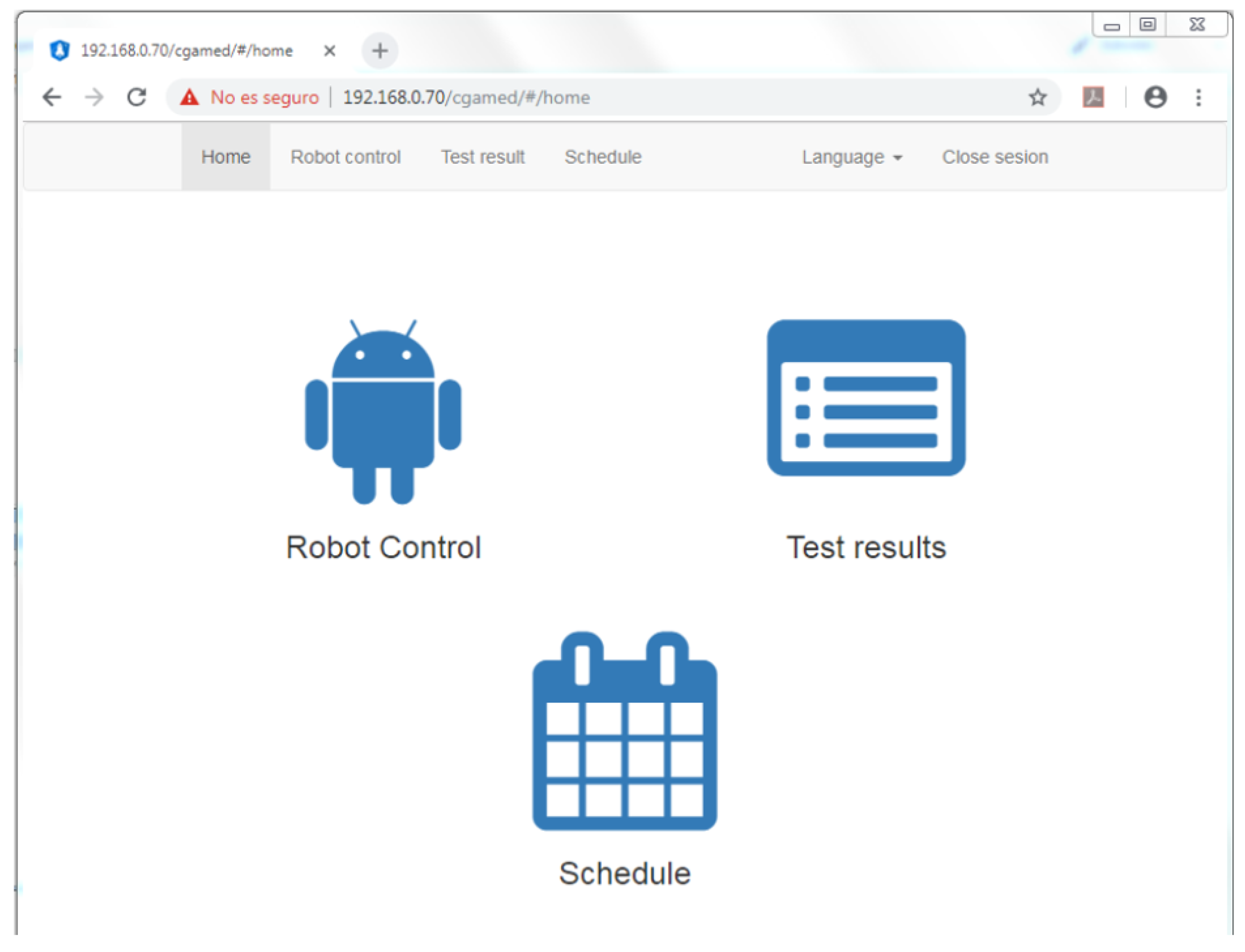
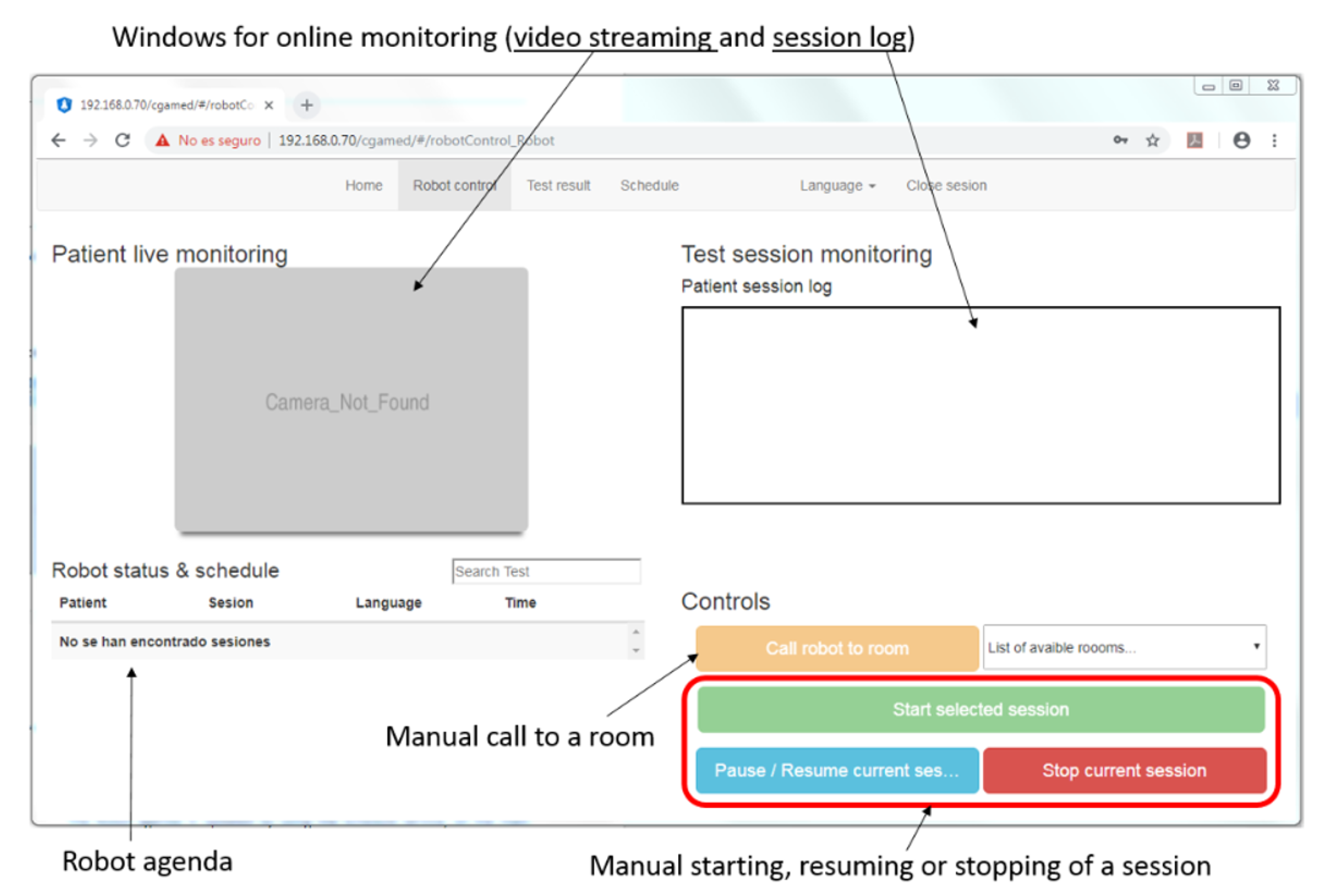
3.2. Connecting CLARA to End Users
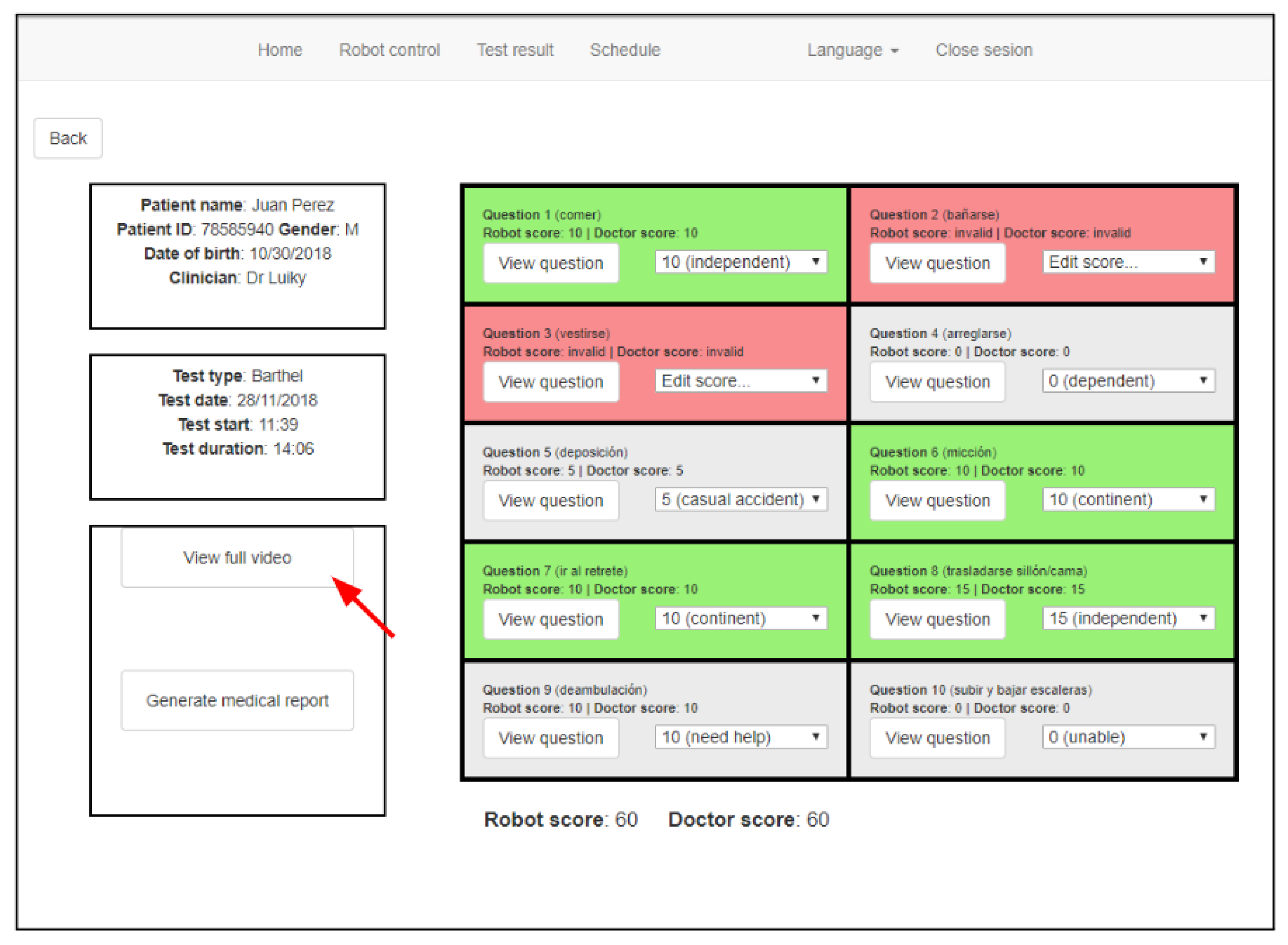
4. Large-Scale Evaluation in Care Centers
4.1. Redesign of the Housing
4.2. Evaluation Results
5. A Tool for Caregivers in a Retirement Home
5.1. User-Driven Definition of the Use Cases
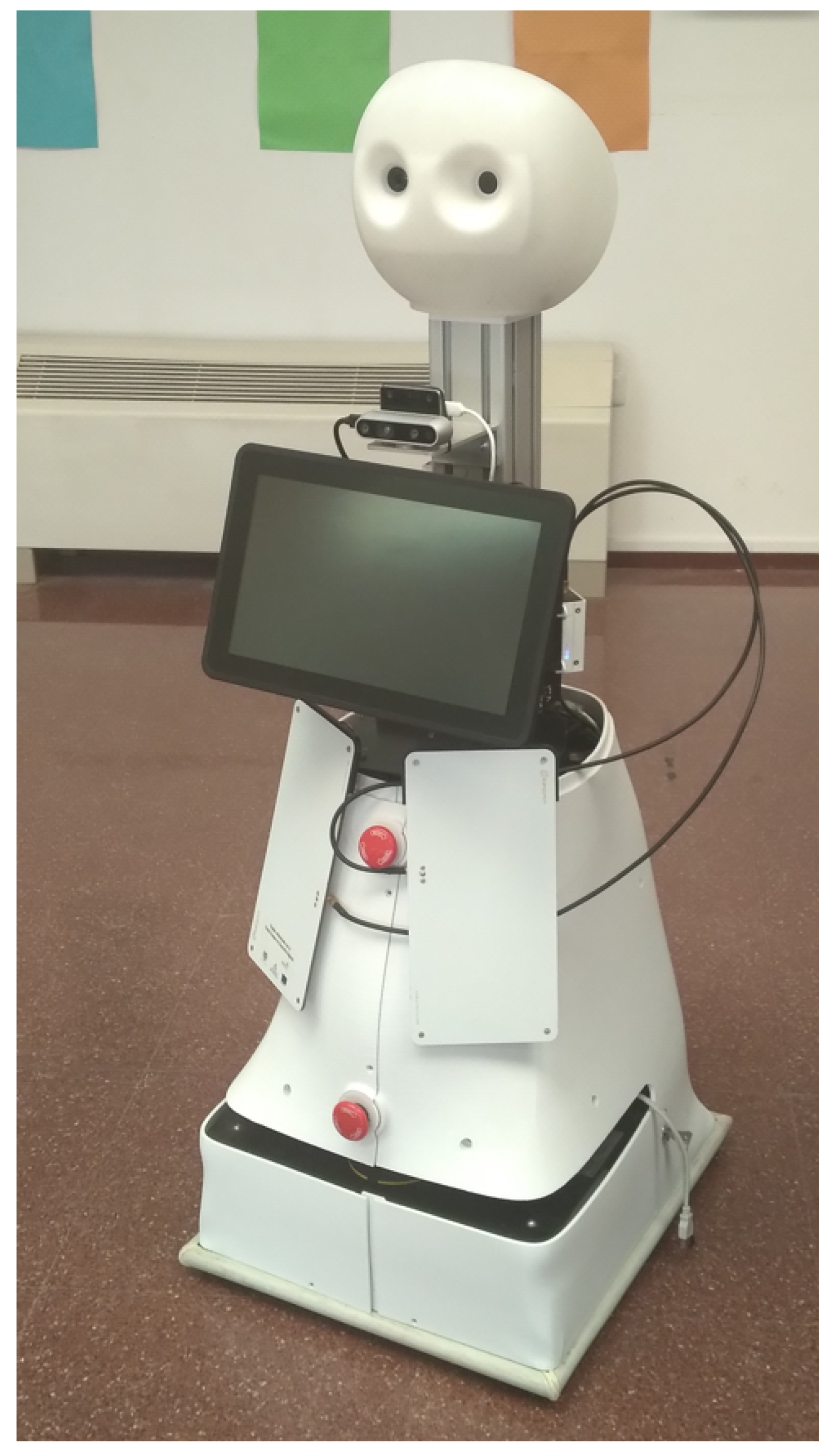
5.2. Redesigning the Sensor Configuration
5.3. Software Updates
5.4. Evaluation Results
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro, O.; Araújo, L.; Figueiredo, D.; Paúl, C.; Teixeira, L. The Caregiver Support Ratio in Europe: Estimating the Future of Potentially (Un)Available Caregivers. Healthcare 2022, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlbacher, F.; Herstatt, C. The Silver Market Phenomenon: Business Opportunities in an Era of Demographic Change; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Christoforou, E.G.; Avgousti, S.; Ramdani, N.; Novales, C.; Panayides, A.S. The Upcoming Role for Nursing and Assistive Robotics: Opportunities and Challenges Ahead. Front. Digit. Health 2020, 2, 585656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, Y.-K.; Jung, H.-T.; Baird, J.; Grupen, R.A. Multidisciplinary stroke rehabilitation delivered by a humanoid robot: Interaction between speech and physical therapies. Aphasiology 2013, 27, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasola, J.; Mataric, M. Robot exercise instructor: A socially assistive robot system to monitor and encourage physical exercise for the elderly. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium in Robot and Human Interactive Communication RO-MAN, 2010 IEEE, Viareggio, Italy, 13–15 September 2010; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Kitt, E.R.; Crossman, M.K.; Matijczak, A.; Burns, G.B.; Kazdin, A.E. Evaluating the Role of a Socially Assistive Robot in Children’s Mental Health Care. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2021, 30, 1722–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez Mejas, C.; Echevarria, C.; Nuñez, P.; Manso, L.; Bustos, P.; Leal, S.; Parra, C. Ursus: A robotic assistant for training of children with motor impairments. In Biosystems & Biorobotics. Converging Clinical and Engineering Research on Neurorehabilitation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Feil-Seifer, D.; Mataric, M.J. Defining socially assistive robotics. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), IEEE, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005; pp. 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- SPARC: The Partnership for Robotics in Europe. Robotics 2020 Multi-Annual Roadmap for Robotics in Europe; The EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Report; euRobotics Aisbl: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Payr, S. Towards Human–Robot Interaction Ethics. In A Construction Manual for Robots’ Ethical Systems. Cognitive Technologies; Trappl, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccanfuso, L.; O’Kane, J.M. Charlie: An adaptive robot design with hand and face tracking for use in autism therapy. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2011, 3, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, P.S.; Moradi, H.; Mahmoudi, M.; Pouretemad, H.R. The design, development, and deployment of roboparrot for screening autistic children. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2015, 7, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozima, H.; Michalowski, M.P.; Nakagawa, C. Keepon. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2008, 1, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataric, M.; Eriksson, J.; Feil-Seifer, D.; Winstein, C. Socially assistive robotics for post-stroke rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2007, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainer, J.; Dautenhahn, K.; Robins, B.; Amirabdollahian, F. A pilot study with a novel setup for collaborative play of the humanoid robot kaspar with children with autism. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2013, 6, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-L.; Šabanovic, S. Interaction expands function: Social shaping of the therapeutic robot PARO in a nursing home. In Proceedings of the Tenth Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, HRI ’15, Portland, OR, USA, 2–5 March 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Mehmood, F.; Ayaz, Y.; Sajid, M.; Sadia, H.; Nawaz, R. An Experimental Trial: Multi-Robot Therapy for Categorization of Autism Level Using Hidden Markov Model. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2022, 60, 722–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, J.C.; González, J.C.; Suárez-Mejías, C.; Bandera, A.; Bustos, P.; Fernández, F. Evaluating the Child–Robot interaction of the NAOTherapist platform in pediatric rehabilitation. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2017, 9, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wainer, J.; Robins, B.; Amirabdollahian, F.; Dautenhahn, K. Using the humanoid robot KASPAR to autonomously play triadic games and facilitate collaborative play among children with autism. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2014, 6, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, A.M.; Sarmadi, A.; Pirastehzad, A.; Moradi, H.; Soleiman, P. RoboParrot 2.0: A multi-purpose social robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics, ICROM, IEEE, Tehran, Iran, 26–28 October 2016; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Granata, C.; Pino, M.; Legouverneur, G.; Vidal, J.S.; Bidaud, P.; Rigaud, A.S. Robot services for elderly with cognitive impairment: Testing usability of graphical user interfaces. Technol. Health Care 2013, 21, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.M.; Sheng, W.; Harrington, E.E.; Bishop, A.J. Clinical screening interview using a social robot for geriatric care. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, J.; Gruendel, L.; Seßner, J.; Meiners, M.; Lieret, M.; Lechler, T.; Konrad, C.; Franke, J. Camera-based fall detection system with the service robot sanbot ELF. In Smart Public Building 2018 Conference Proceedings; University of Applied Sciences Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2018; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jauhri, S.; Peters, J.; Chalvatzaki, G. Robot Learning of Mobile Manipulation With Reachability Behavior Priors. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 8399–8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miseikis, J.; Caroni, P.; Duchamp, P.; Gasser, A.; Marko, R.; Miseikiene, N.; Zwilling, F.; de Castelbajac, C.; Eicher, L.; Fruh, M.; et al. Lio-A Personal Robot Assistant for Human-Robot Interaction and Care Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5339–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, T.; Virk, G.S. ISO 13482—The new safety standard for personal care robots. In Proceedings of the ISR/Robotik 2014; 41st International Symposium on Robotics, Munich, Germany, 2–3 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pareto-Boada, J.; Román-Maestre, B.; Torras Genís, C. The ethical issues of social assistive robotics: A critical literature review. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandemeulebroucke, T.; Casterle, B.D.; Gastmans, C. Ethics of socially assistive robots in aged-care settings: A socio-historical contextualisation. J. Med. Ethics 2020, 46, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibt, J.; Damholdt, M.F.; Vestergaard, C. Integrative social robotics, value-driven design, and transdisciplinarity. Interact. Stud. 2020, 21, 111–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voilmy, D.; Suárez, C.; Romero-Garcés, A.; Reuther, C.; Pulido, J.C.; Marfil, R.; Manso, L.J.; Lan Hing Ting, K.; Iglesias, A.; González, J.C.; et al. CLARC: A cognitive robot for helping geriatric doctors in real scenarios. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Proceedings of the ROBOT 2017: Third Iberian Robotics Conference, Sevilla, Spain, 22–24 November 2017; Ollero, A., Sanfeliu, A., Montano, L., Lau, N., Cardeira, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandera, J.P.; Marfil, R.; Romero-Garcés, A.; Voilmy, D. A new paradigm for autonomous human motion description and evaluation: Application to the Get Up & Go test use case. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 118, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lan Hing Ting, K.; Voilmy, D.; Iglesias, A.; Pulido, J.C.; García, J.; Romero-Garcés, A.; Bandera, J.P.; Marfil, R.; Dueñas, A. Integrating the users in the design of a robot for making Comprehensive Geriatric Assessments (CGA) to elderly people in care centers. In Proceedings of the 2017 26th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Lisbon, Portugal, 28 August–1 September 2017; pp. 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, P.; Manso, L.; Bandera, A.; Bandera, J.; García-Varea, I.; Martínez-Gómez, J. The CORTEX cognitive robotics architecture: Use cases. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 55, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marfil, R.; Romero-Garces, A.; Bandera, J.; Manso, L.; Calderita, L.; Bustos, P.; Bandera, A.; Garcia-Polo, J.; Fernandez, F.; Voilmy, D. Perceptions or Actions? Grounding How Agents Interact Within a Software Architecture for Cognitive Robotics. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 12, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, I.-L. Health Professionals’ Perceptions of the Robot ’Giraff’ in Brain Injury Rehabilitation; Assistive Technology Research Series 33; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.M.; Debes, K.; Einhorn, E.; Mueller, S.; Scheidig, A.; Weinrich, C.; Bley, A.; Martin, C. Mobile Robotic Rehabilitation Assistant for walking and orientation training of Stroke Patients: A report on work in progress. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; pp. 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Garcés, A.; Hidalgo-Paniagua, A.; González-García, M.; Bandera, A. On Managing Knowledge for MAPE-K Loops in Self-Adaptive Robotics Using a Graph-Based Runtime Model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, V.; Madrid, I.; Guzmán, C.; Prior, D.; Borrajo, D.; Castillo, L.; Onaindía, E. PELEA: Planning, learning and execution architecture. In Proceedings of the 28th Workshop of the UK Planning and Scheduling Special Interest Group (PlanSIG’10), Brescia, Italy, 1 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kurth, A.E.; Martin, D.P.; Golden, M.R.; Weiss, N.S.; Heagerty, P.J.; Spielberg, F.; Handsfield, H.H.; Holmes, K.K. A comparison between audio computer-assisted self-interviews and clinician interviews for obtaining the sexual history. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2004, 31, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan Hing Ting, K.; Voilmy, D.; De Roll, Q.; Iglesias, A.; Marfil, R. Fieldwork and Field Trials in Hospitals: Co-Designing A Robotic Solution to Support Data Collection in Geriatric Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Garcés, A.; Martínez-Cruz, J.; Inglés-Romero, J.; Vicente-Chicote, C.; Marfil, R.; Bandera, A. Measuring Quality of Service in a Robotized Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment Scenario. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Viciana, R.; Pérez-Lorenzo, J.M.; Ting, K.L.H.; Tudela, A.; Marfil, R.; Dueñas, A.; Bandera, J.P. Towards long term acceptance of socially assistive robots in retirement houses: Use case definition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions (ICARSC), Ponta Delgada, Portugal, 15–17 April 2020; pp. 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Cruces, A.; Tudela, A.; Romero-Garcés, A.; Bandera, J.P. Multimodal object recognition module for social robots. In Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Proceedings of the ROBOT2022: Fifth Iberian Robotics Conference Zaragoza, Spain, 23–25 November 2022; Tardioli, D., Matellán, V., Heredia, G., Silva, M.F., Marques, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Romero-Garcés, A.; Suarez-Mejias, C.; Marfil, R.; Lan Hing Ting, K.; Iglesias, A.; García, J.; Fernández, F.; Dueñas-Ruiz, A.; Calderita, L.V.; et al. Towards a robust robotic assistant for Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment procedures: Updating the CLARC system. In Proceedings of the 2018 27th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Nanjing, China, 27–31 August 2018; pp. 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; García, J.; García-Olaya, A.; Fuentetaja, R.; Fernández, F.; Romero-Garcés, A.; Marfil, R.; Bandera, A.; Lan Hing Ting, K.; Voilmy, D.; et al. Extending the Evaluation of Social Assistive Robots With Accessibility Indicators: The AUSUS Evaluation Framework. IEEE Trans.-Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2021, 51, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





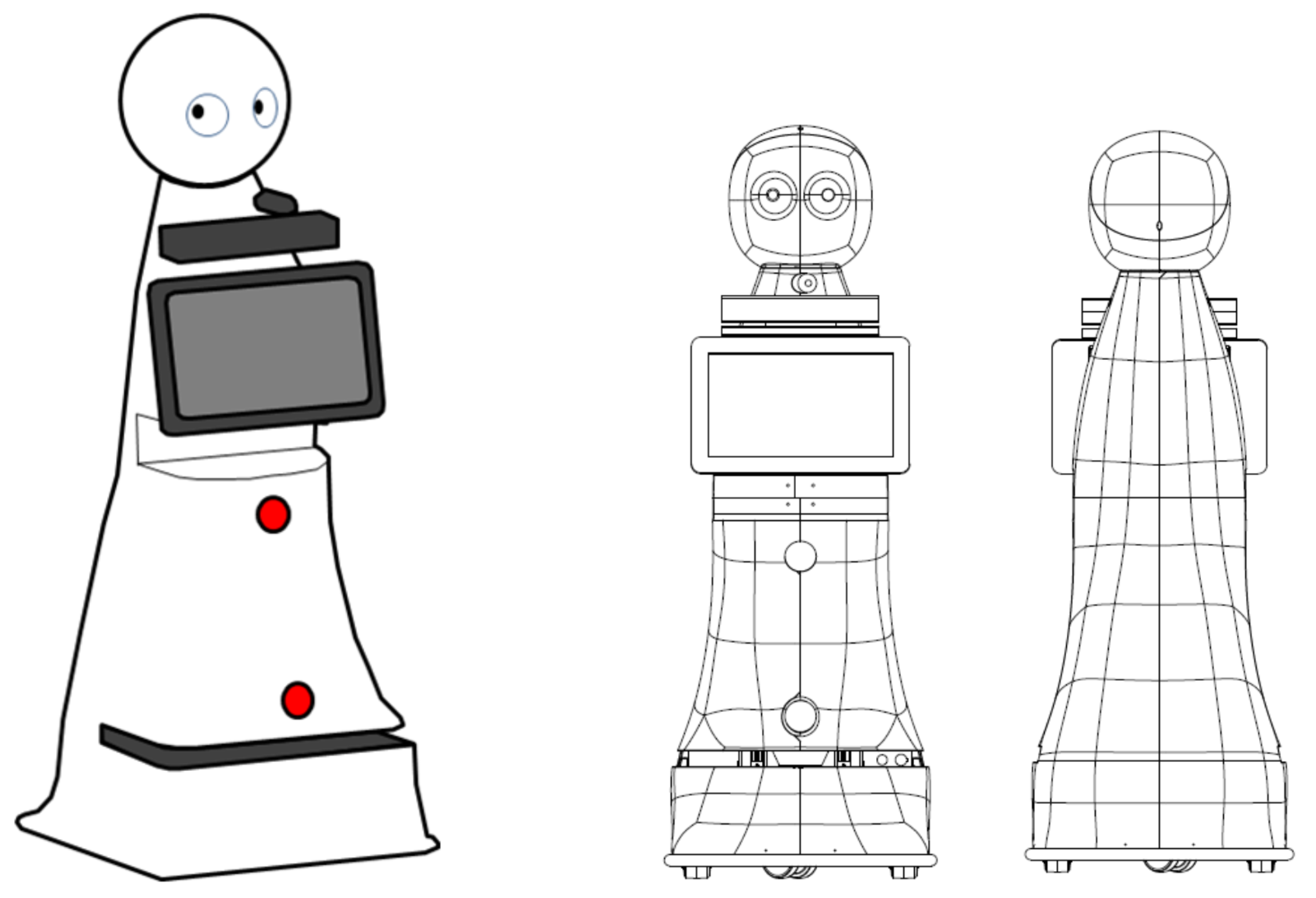


| Criterium | GIRAFF | SCITOS G5 | RB-1 Base | TIAGO | MiR100 | Mobina |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maintenance | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Relevant customers in healthcare | Yes | Yes | Yes | SACRO project | Yes | Yes |
| Relevant expertise | Extensive experience in real human–robot interaction use cases (TERESA, ExCITE, or GiraffPlus projects) | Experience in real healthcare scenarios focusing on HRI applications (ROREAS, ALIAS, ROBOT-ERA, HOBBIT, CompanionAble projects) | Experience in providing robotic platforms for use in real use cases (ROBO-SPECT, RUBICON, RADIO projects) | Expertise in robots designed to interact with people. Social HRI (e.g., socSMCs FET project) and European projects (Factory in a Day FP7) | Experience in deployment in real scenarios (healthcare systems) | Experience in providing robotic platforms for use in real use cases (WiMi-Care, EFFIROB, Elevon, SeRoDi projects) |
| Sales channels | Direct sales | Direct sales | Direct sales | Direct sales | Direct sales/EU distributors | R & D services |
| Price | EUR 9500 | Ca. EUR 25,000 | Ca. EUR 15,000 | EUR 29,750 | Ca. EUR 22,200 (w VAT) | Ca. EUR 10,000 |
| Payload | 5 kg | 50 kg | 50 kg | 30 kg | 100 kg | 10 kg |
| Optional sensors | No | Customizable | Customizable | Force/torque sensor. Laser 10 m upgrade. Rear sonars. Additional RGBD camera in the base. Additional speaker | No | Customizable |
| Interface with the patient | Monitor and microphone/speakers | Needs to be added | Needs to be added | Mobile head with RGBD camera, microphones. Multilanguage text-to-speech, speakers. | Needs to be added | RGBD camera, microphones, and a touchscreen |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Garcés, A.; Bandera, J.P.; Marfil, R.; González-García, M.; Bandera, A. CLARA: Building a Socially Assistive Robot to Interact with Elderly People. Designs 2022, 6, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6060125
Romero-Garcés A, Bandera JP, Marfil R, González-García M, Bandera A. CLARA: Building a Socially Assistive Robot to Interact with Elderly People. Designs. 2022; 6(6):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6060125
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Garcés, Adrián, Juan Pedro Bandera, Rebeca Marfil, Martín González-García, and Antonio Bandera. 2022. "CLARA: Building a Socially Assistive Robot to Interact with Elderly People" Designs 6, no. 6: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6060125
APA StyleRomero-Garcés, A., Bandera, J. P., Marfil, R., González-García, M., & Bandera, A. (2022). CLARA: Building a Socially Assistive Robot to Interact with Elderly People. Designs, 6(6), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6060125







