Design and Implementation of Modified INC, Conventional INC, and Fuzzy Logic Controllers Applied to a PV System under Variable Weather Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
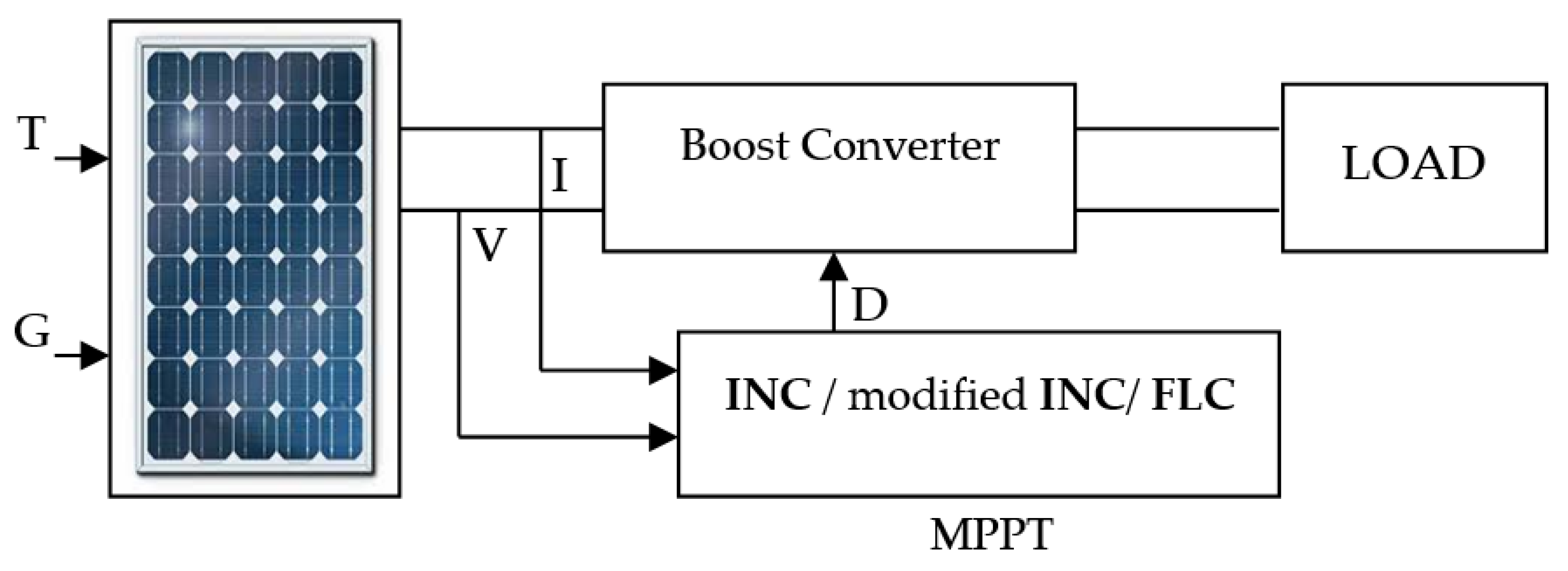
2. Design of Complete PV System
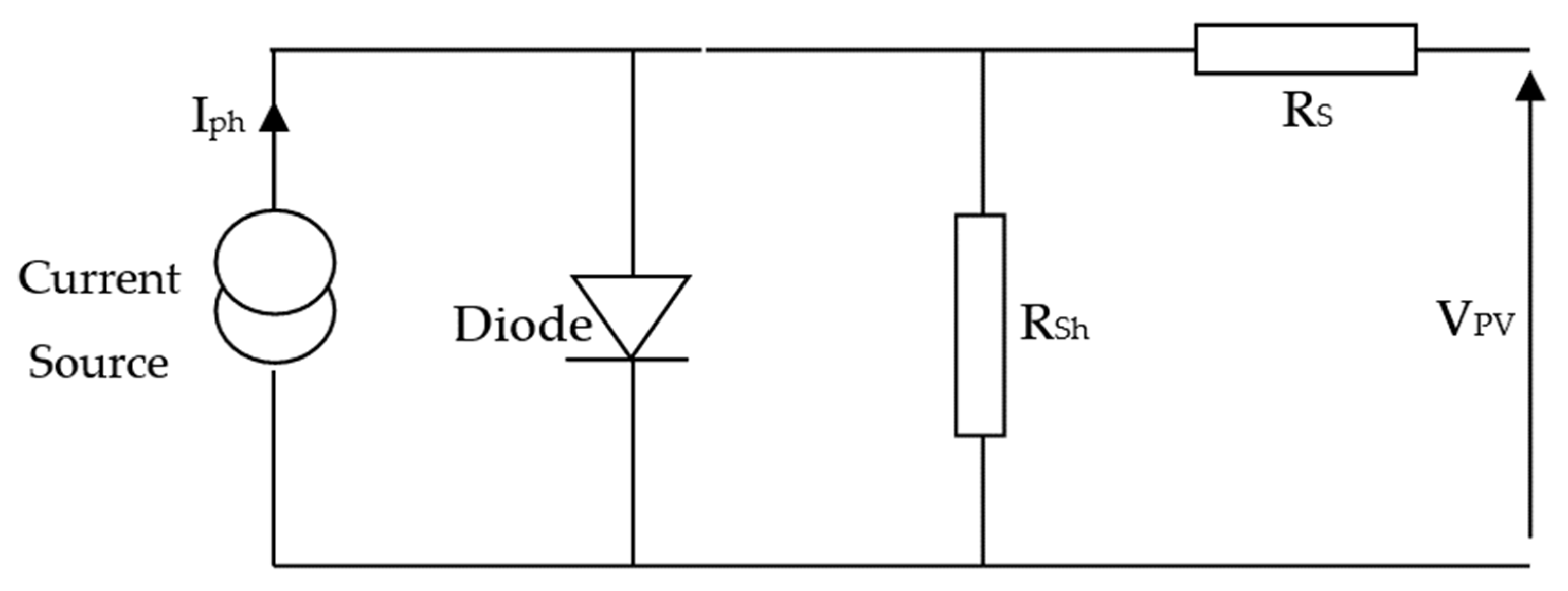
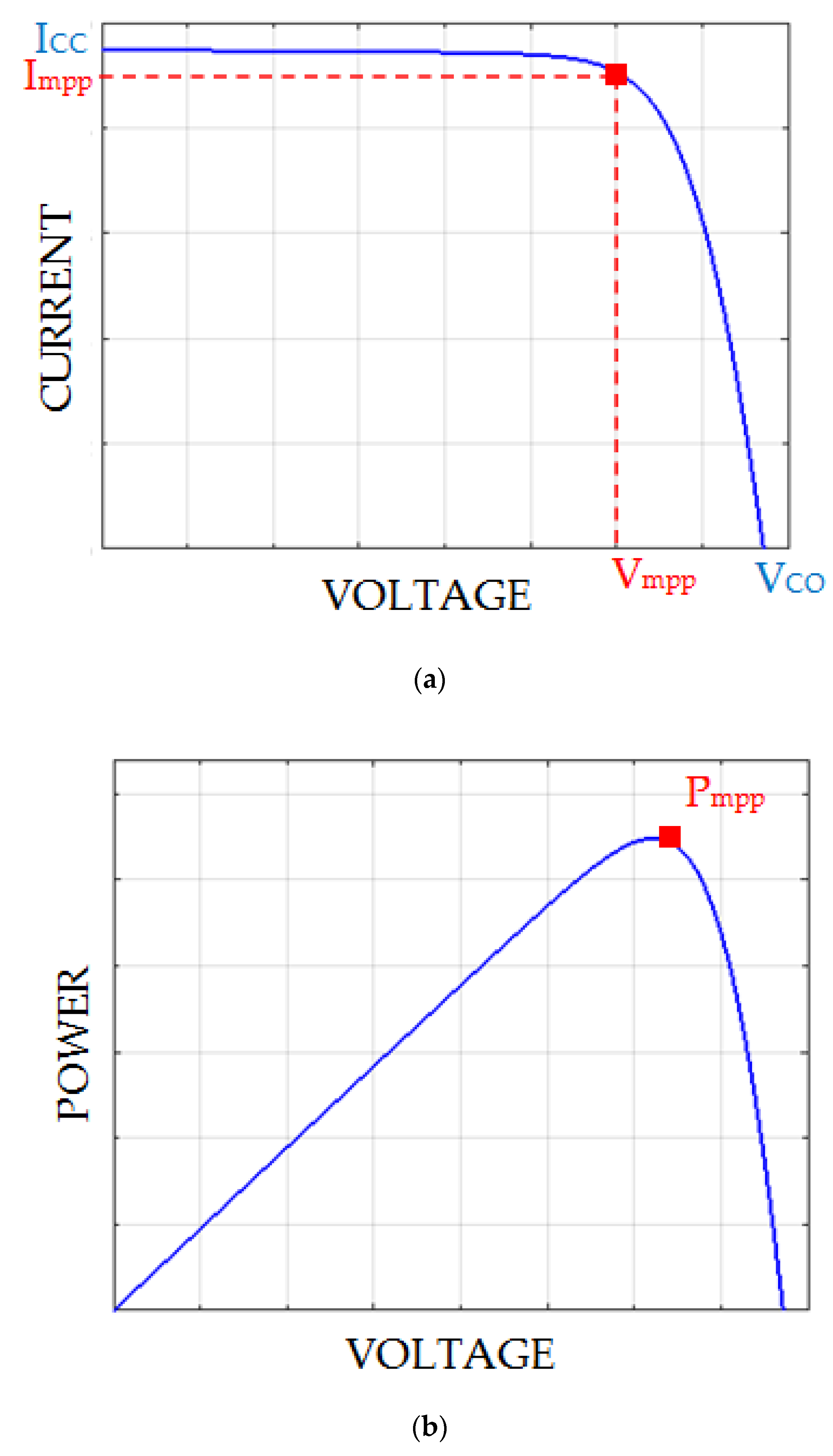
2.1. Design of a PV Panel
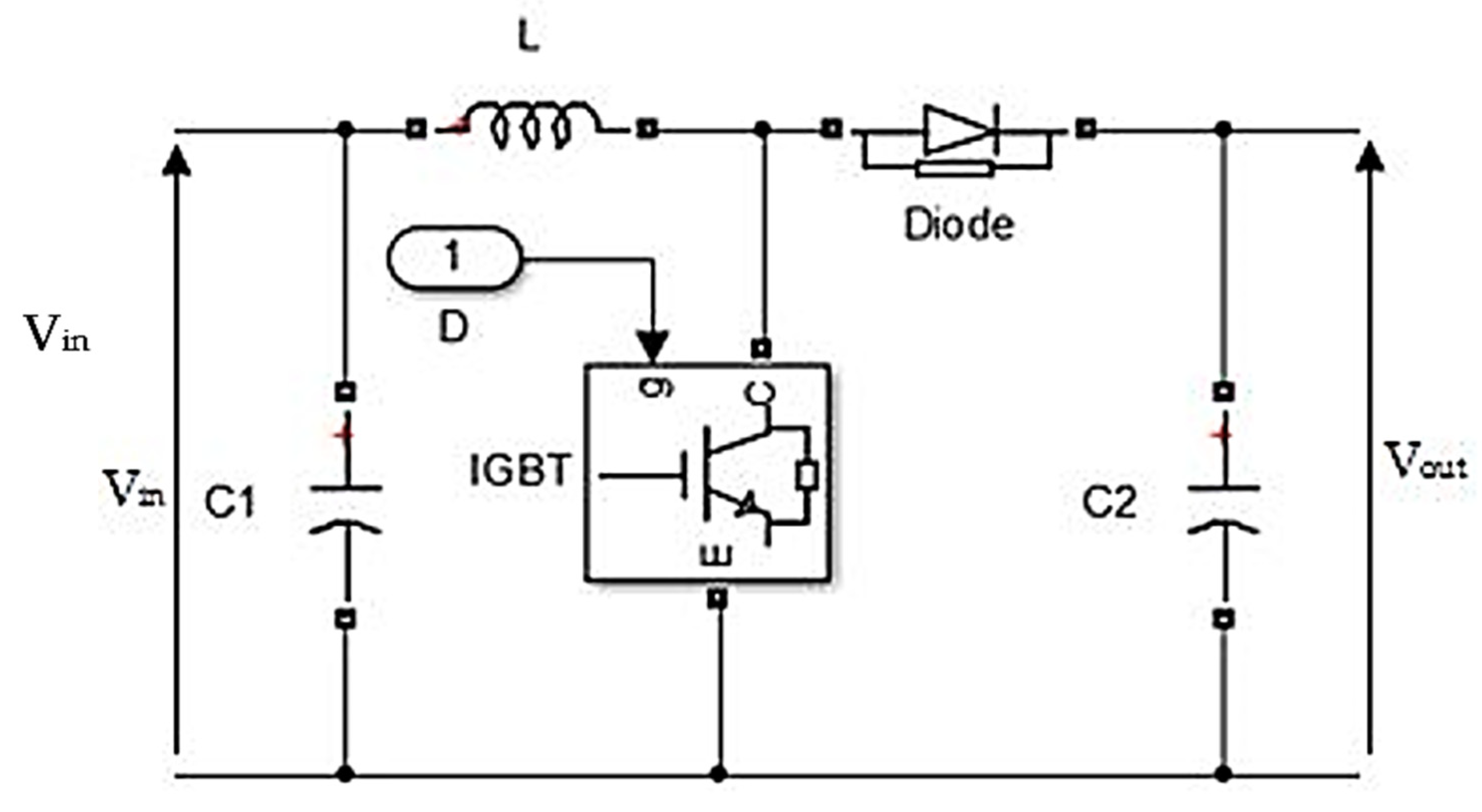
2.2. Modeling of Boost Converter
2.3. MPPT Algorithms
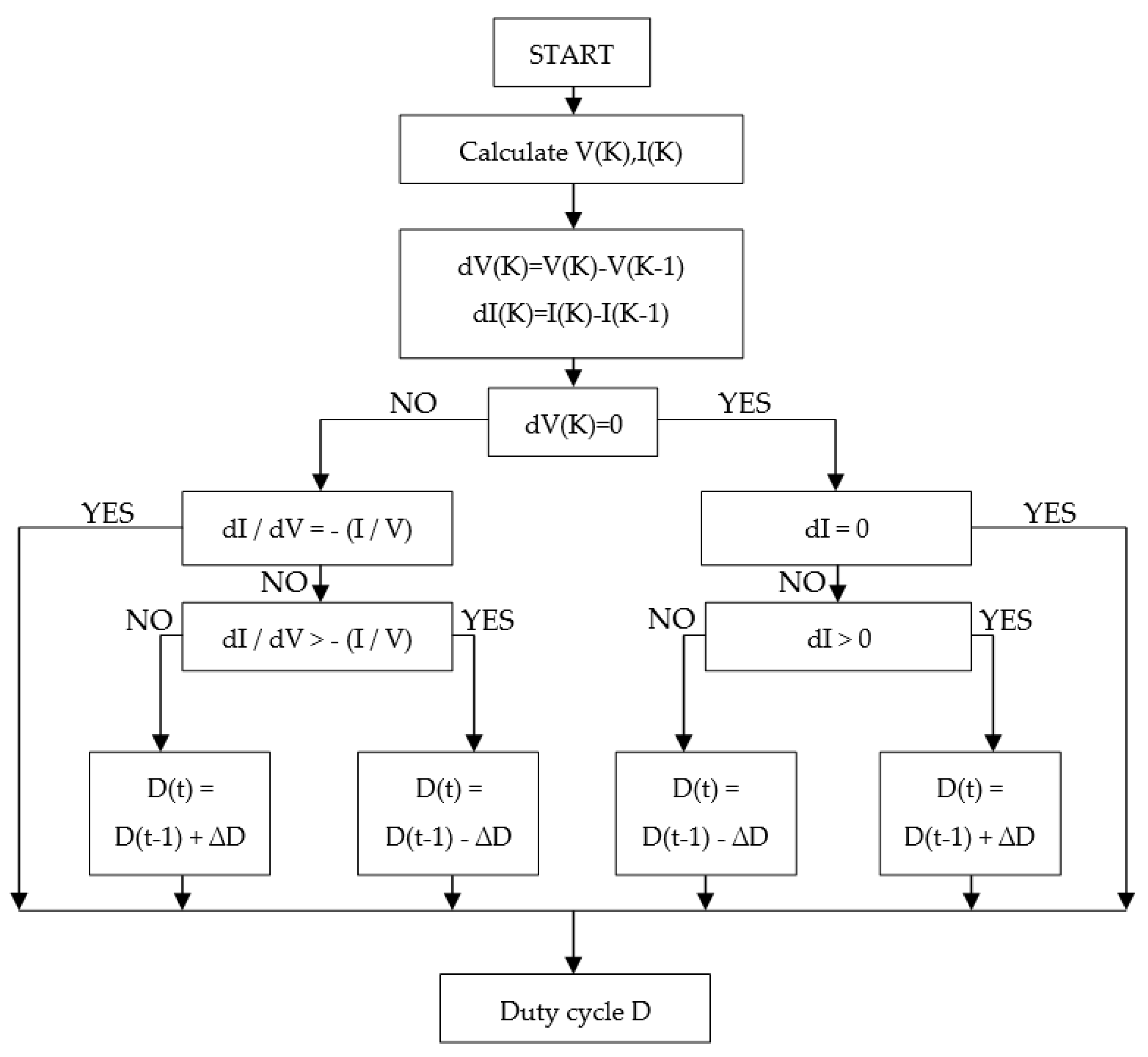
2.3.1. Incremental Conductance Algorithm
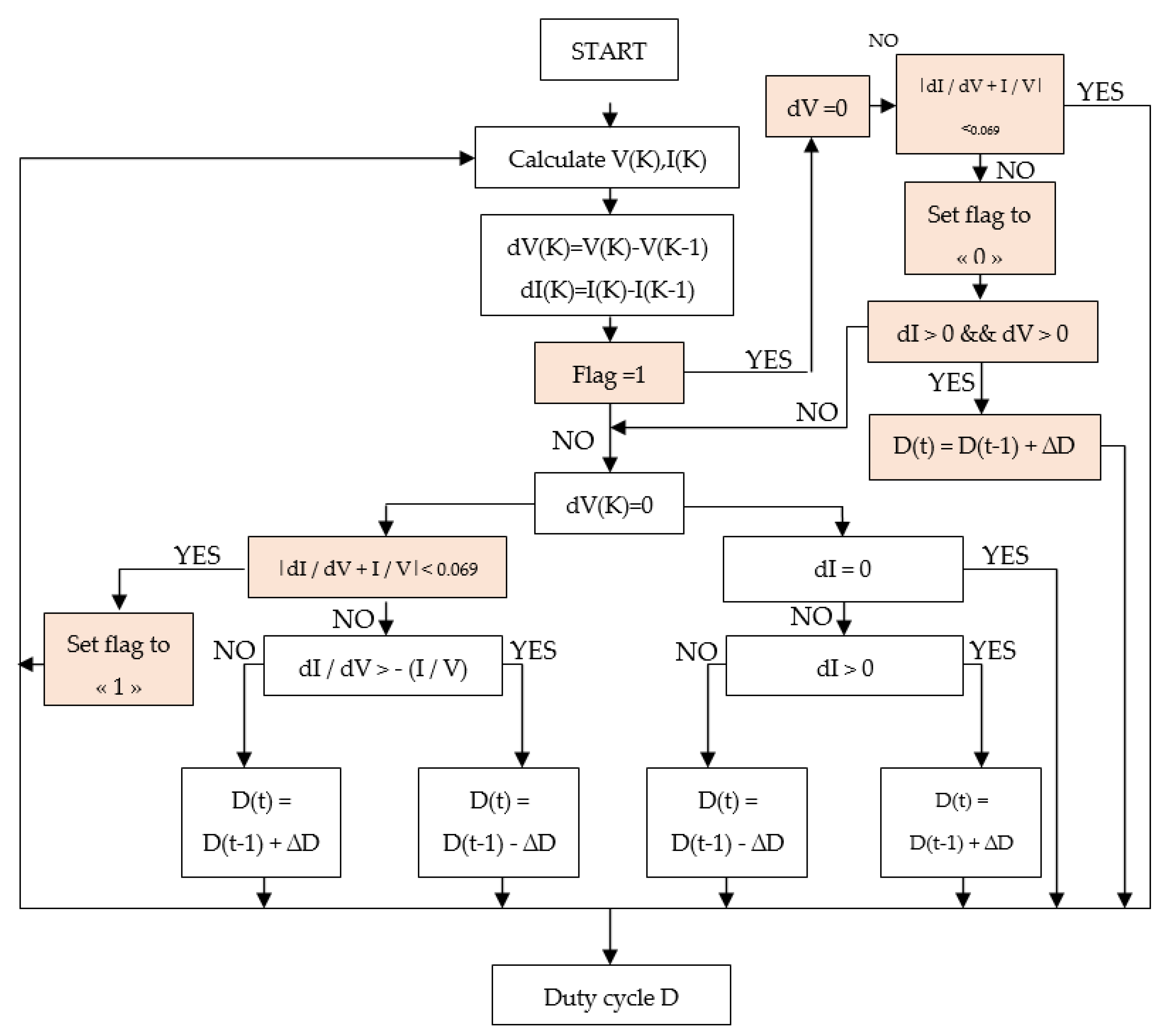
2.3.2. Modified Incremental Conductance Algorithm
2.3.3. Fuzzy Logic Controller
- Fuzzification: Allows the conversion of physical input variables into fuzzy sets. In this paper [36], there aretwo inputs, the error E(K) and the change of error CE(K) defined as follows:E(K) = [Ppv(K) − Ppv(K−1)]/[Vpv(K) − Vpv(K − 1)],CE(K) = E(K) − E(K − 1)
- Defuzzification: Converts the output fuzzy subsets into numerical values.
3. Results and Discussions
- Conventional incremental conductance (INC);
- Modified incremental conductance (modINC);
- Fuzzy logic controller (FLC);
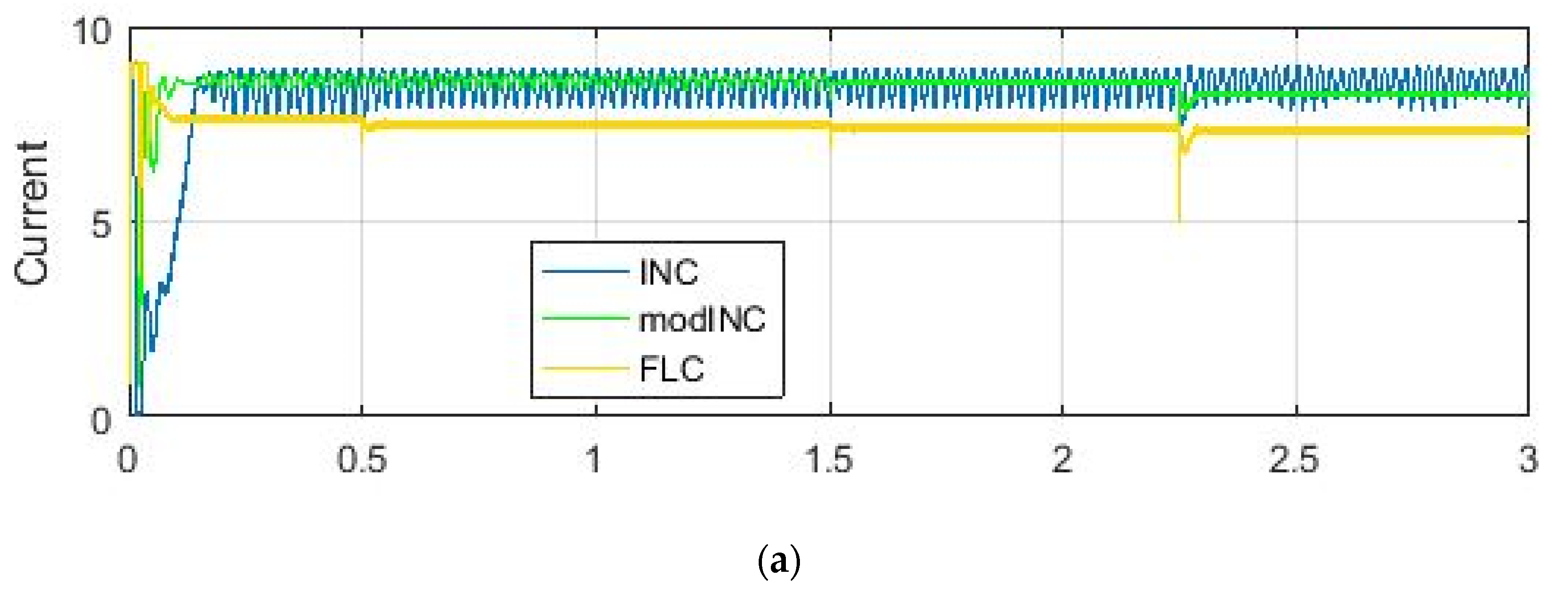
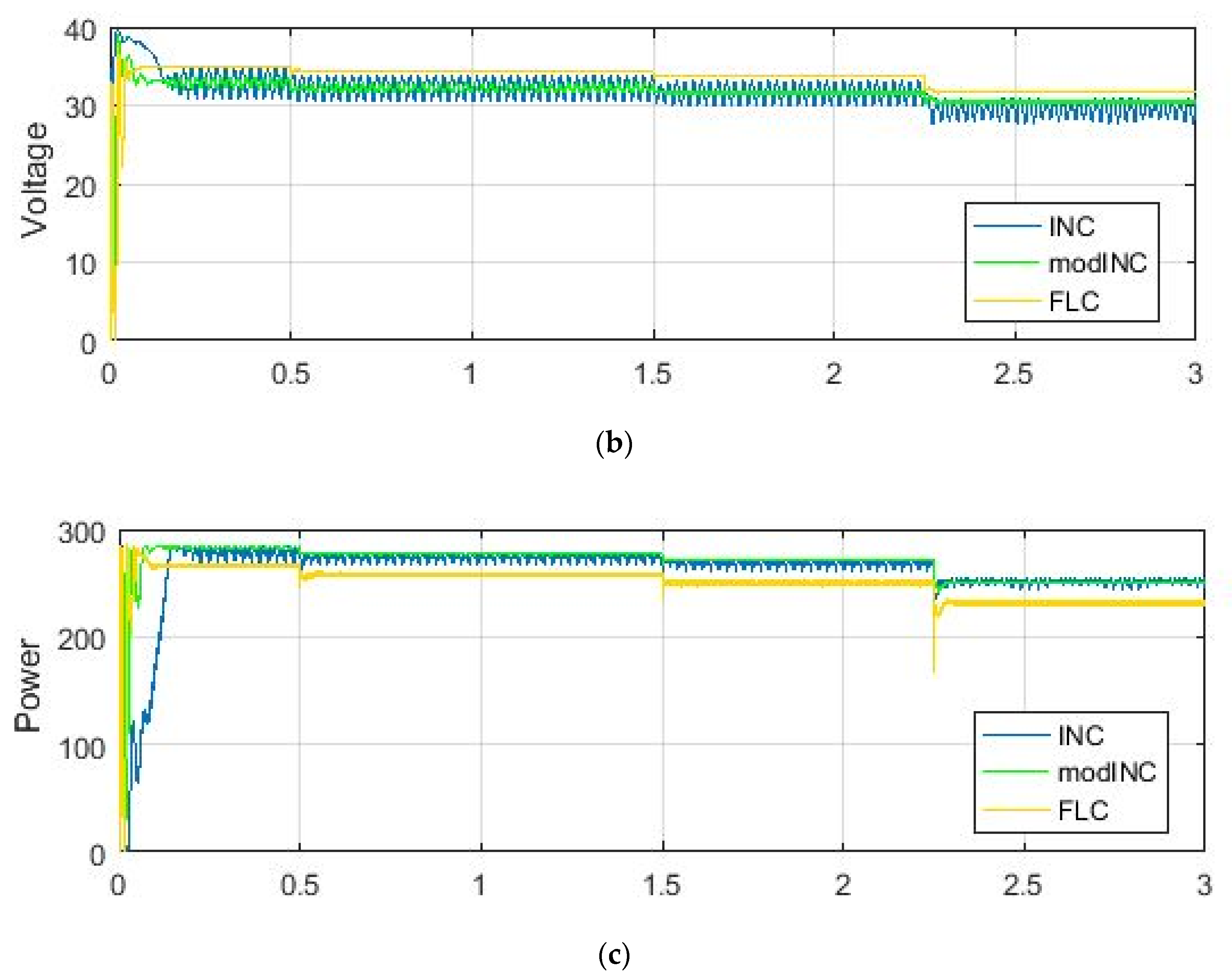
3.1. Simulation Results Using Matlab/Simulink
3.2. Implementation of Three Algorithms on Proteus
| Characteristics | INC | FLC | modINC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | Low | High | Very High |
| Convergence Speed | Varies | Fast | Fast |
| Oscillations around MPP | High | Low | No |
| Complexity | Medium | High | Medium |
| Efficiency | Medium | High | Very High |
| Cost | Moderate | Expensive | Moderate |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| T | Temperature |
| G | Irradiance |
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking |
| MPP | Maximum power point |
| FLC | Fuzzy logic controller |
| INC | Incremental conductance |
| modINC | Modified incremental conductance |
| PWM | Pulse-width-modulation |
| MOSFET | Metal-oxide-silicon field-effect transistor |
| NB | Negative Big |
| NM | Negative Medium |
| NS | Negative Small |
| ZE | Zero |
| PS | Positive Small |
| PM | Positive Medium |
| PB | Positive Big |
References
- Bouksaim, M.; Acci, Y.; Srifi, M.N. Modeling of Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System Installation in Moroccan Ibn Tofail Uni-versity. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. (ASTESJ) 2019, 4, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-S.; Yun, J.-J. Advanced MPPT Algorithm for Distributed Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2019, 12, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldman, D.; Barbose, G.; Margolis, R.; Bolinger, M.; Chung, D.; Fu, R.; Seel, J.; Davidson, C.; Darghouth, N.; Wiser, R. Pho-tovoltaic System Pricing Trends Historical, Recent, and Near-Term Projections 2015 Edition. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt9pc3x32t/qt9pc3x32t.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Arefifar, S.A.; Paz, F.; Ordonez, M. Improving Solar Power PV Plants Using Multivariate Design Optimization. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, M.A.; Twaha, S.; Ishaque, K.; Al-Turki, Y.A. A review on maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic systems with and without shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagea, I.S.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Grillakis, M. Climate Change Impact on Photovoltaic Energy Output: The Case of Greece. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 264506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Hu, Y. Synchronous buck converter based low-cost and high-efficiency sub-module DMPPT PV system under partial shading conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 126, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Fathy, A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. A comparison of different global MPPT techniques based on meta-heuristic algorithms for photovoltaic system subjected to partial shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilakkat, D.; Kanthalakshmi, S. An improved P&O algorithm integrated with artificial bee colony for photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Sol. Energy 2018, 178, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.-U.; Abbassi, R.; Jerbi, H.; Mehmood, K.; Tahir, M.; Cheema, K.; Elavarasan, R.; Ali, F.; Khan, I. A Novel Algorithm for MPPT of an Isolated PV System Using Push Pull Converter with Fuzzy Logic Controller. Energies 2020, 13, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.A.; Nowak-Ocłon, M. Modified Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm under Time-Varying Solar Irradia-tion. Energies 2020, 13, 6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahhir, S.; Chalh, A.; El Ghzizal, A.; Sebti, S.; Derouich, A. Modeling of Photovoltaic Panel by using Proteus. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 10, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraban, S.; Petreus, D.; Morel, C. A novel MPPT (maximum power point tracking) algorithm based on a modified genetic algorithm specialized on tracking the global maximum power point in photovoltaic systems affected by partial shading. Energy 2014, 74, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouksaim, M.; Krami, N.; Acci, Y.; Srifi, M.N.; Hadjouja, A. Modeling of Photovoltaic Module Using Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Advanced Electrical and Communication Technologies (ISAECT), Rabat, Morocco, 21–23 November 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Tarabsheh, A.; Akmal, M.; Ghazal, M. Series Connected Photovoltaic Cells—Modelling and Analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergura, S. A Complete and Simplified Datasheet-Based Model of PV Cells in Variable Environmental Conditions for Circuit Simulation. Energies 2016, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatimi, H.; Aroudam, E. Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Photovoltaic Power Source using Matlab/Simulink. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2016, 16, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- Abouchabana, N.; Haddadi, M.; Rabhi, A.; Grasso, A.D.; Tina, G.M. Power Efficiency Improvement of a Boost Converter Using a Coupled Inductor with a Fuzzy Logic Controller: Application to a Photovoltaic System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, S.P.; João Pedro, F.T.; Alonso, J.M.; Saraiva, E.S. Large-Signal Characterization of Power Inductors in EV Bidirec-tional DC-DC Converters Focused on Core Size Optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3042–3051. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Sui, H. Maximum Power Point Tracking Technology of Photovoltaic Array under Partial Shading Based on Adaptive Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm. Energies 2020, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, H.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.B.M.; Soon, T.K.; Seyedmahmousian, M.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. Performance Evaluation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Approaches and Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, D.; Nema, S.; Shandilya, A.M.; Dash, S.K. Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) techniques: Recapitulation in so-lar photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquib, M.; Jain, S.; Agarwal, V. A Time-Based Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Technique for PV System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J. A High-Performance Adaptive Incremental Conductance MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2016, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visweswara, K. An Investigation of Incremental Conductance based Maximum Power Point Tracking for Photovoltaic System. Energy Procedia 2014, 54, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vital Rao, P.; Sudha, K.R.; Prameela Devi, S. Incremental conductance (IncCond) algorithm for Maximum Power Operating Point (MPOP) of Photo-Voltaic (PV) power generation system. Am. J. Eng. Res. (AJER) 2013, 2, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, A.F.; Mansoor, M.; Ling, Q.; Khan, M.I.; Aldossary, O.M. Advanced Variable Step Size Incremental Conductance MPPT for a Standalone PV System Utilizing a GA-Tuned PID Controller. Energies 2020, 13, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tey, K.S.; Mekhilef, S. Modified incremental conductance MPPT algorithm to mitigate inaccurate responses under fast-changing solar irradiation level. Sol. Energy 2014, 101, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahhir, S.; El Ghzizal, A.; Sebti, S.; Derouich, A. Modeling of Photovoltaic System with Modified Incremental Conductance Algorithm for Fast Changes of Irradiance. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 3286479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, M.A.G.; Galotto, L.; Sampaio, P.L.; de Azevedo e Melo, G.; Canesin, C.A. Evaluation of the main MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, R.M.; Rehman, A.U.; Rehman, S.U.; Arshad, J.; Hamid, J.; Sadiq, M.T.; Tahir, S. Design and analysis of robust fuzzy logic maximum power point tracking based isolated photovoltaic energy system. Eng. Rep. 2020, 2, e12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, M.; Aboelhassan, A.; Abdelgeliel, M.; Galea, M. PV Systems Control Using Fuzzy Logic Controller Employing Dynamic Safety Margin under Normal and Partial Shading Conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livinti, P. Comparative Study of a Photovoltaic System Connected to a Three-Phase Grid by Using PI or Fuzzy Logic Controllers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napole, C.; Derbeli, M.; Barambones, O. Fuzzy Logic Approach for Maximum Power Point Tracking Implemented in a Real Time Photovoltaic System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majidi, S.D.; Abbod, M.F.; Al-Raweshidy, H.S. A novel maximum power point tracking technique based on fuzzy logic for photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 14158–14171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechiche, O.B.H.B.; Barkaoui, B.; Hamza, M.; Sammouda, H. Simulation and comparison of P&O and fuzzy logic MPPT techniques at different irradiation conditions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Green Energy Conversion Systems (GECS), Hammamet, Tunisia, 23–25 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Algarín, C.R.; Giraldo, J.T.; Álvarez, O.R. Fuzzy Logic Based MPPT Controller for a PV System. Energies 2017, 10, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasmin, E.R.; James, J. Implementation of fuzzy logic based maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Communication and Power Engineering 2014—CCPE 2014, Chennai, India, 21–22 February 2014; pp. 547–556. [Google Scholar]




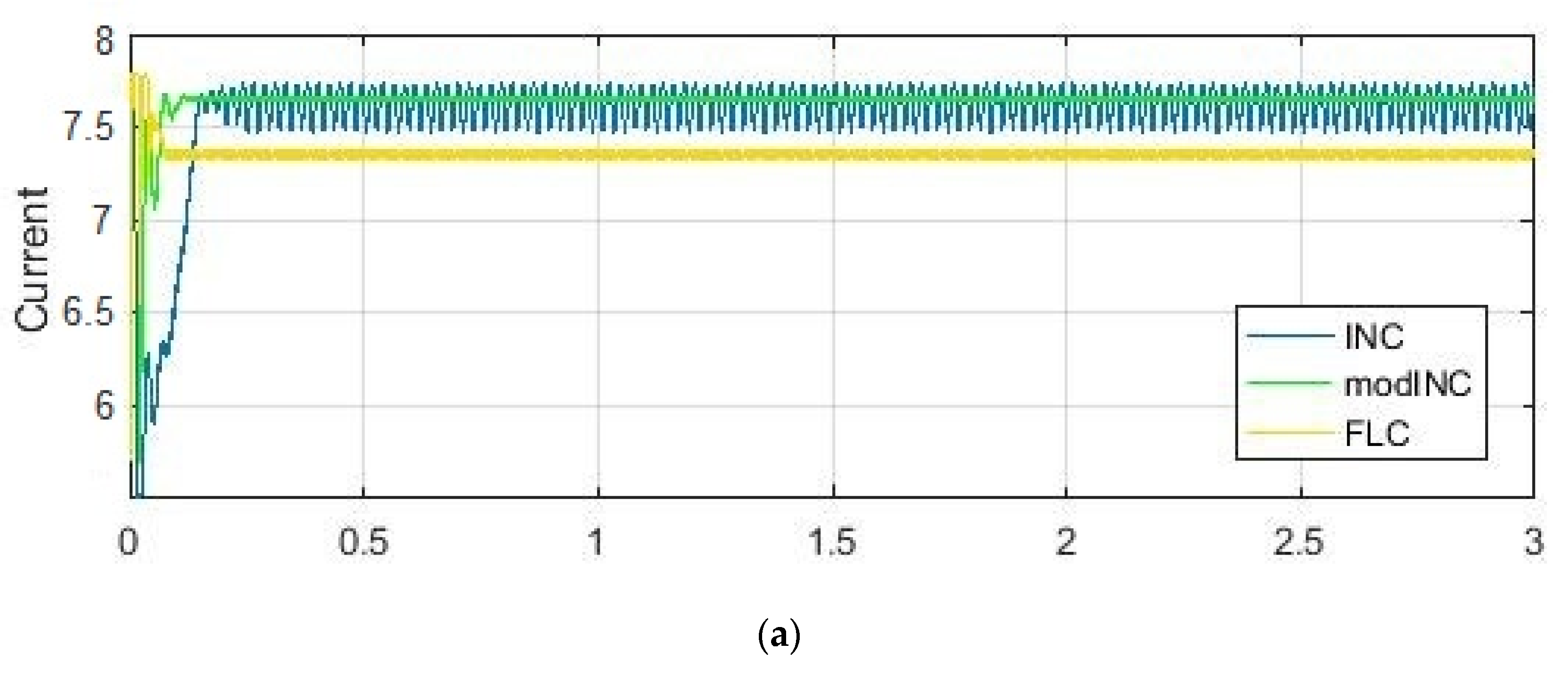
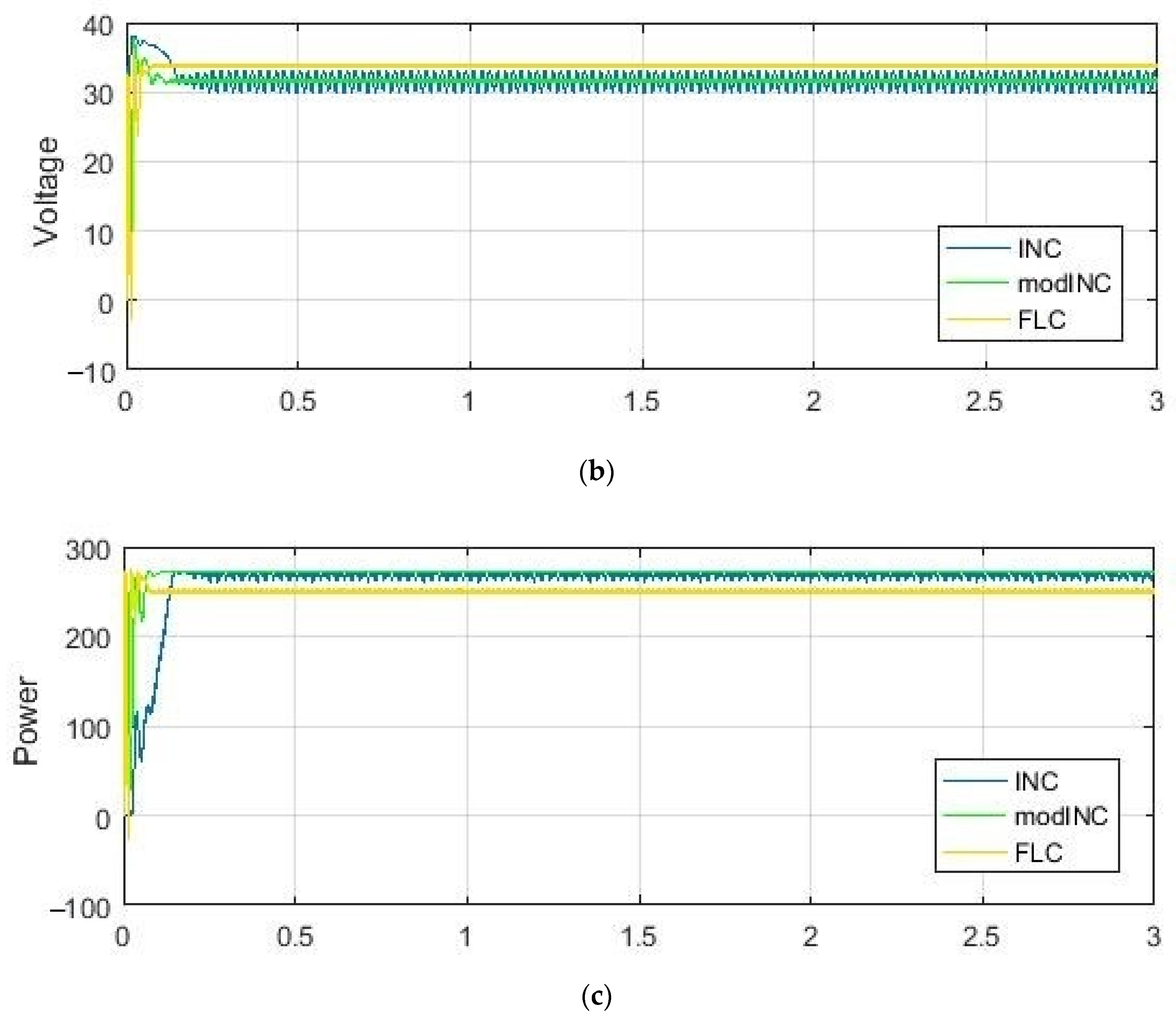
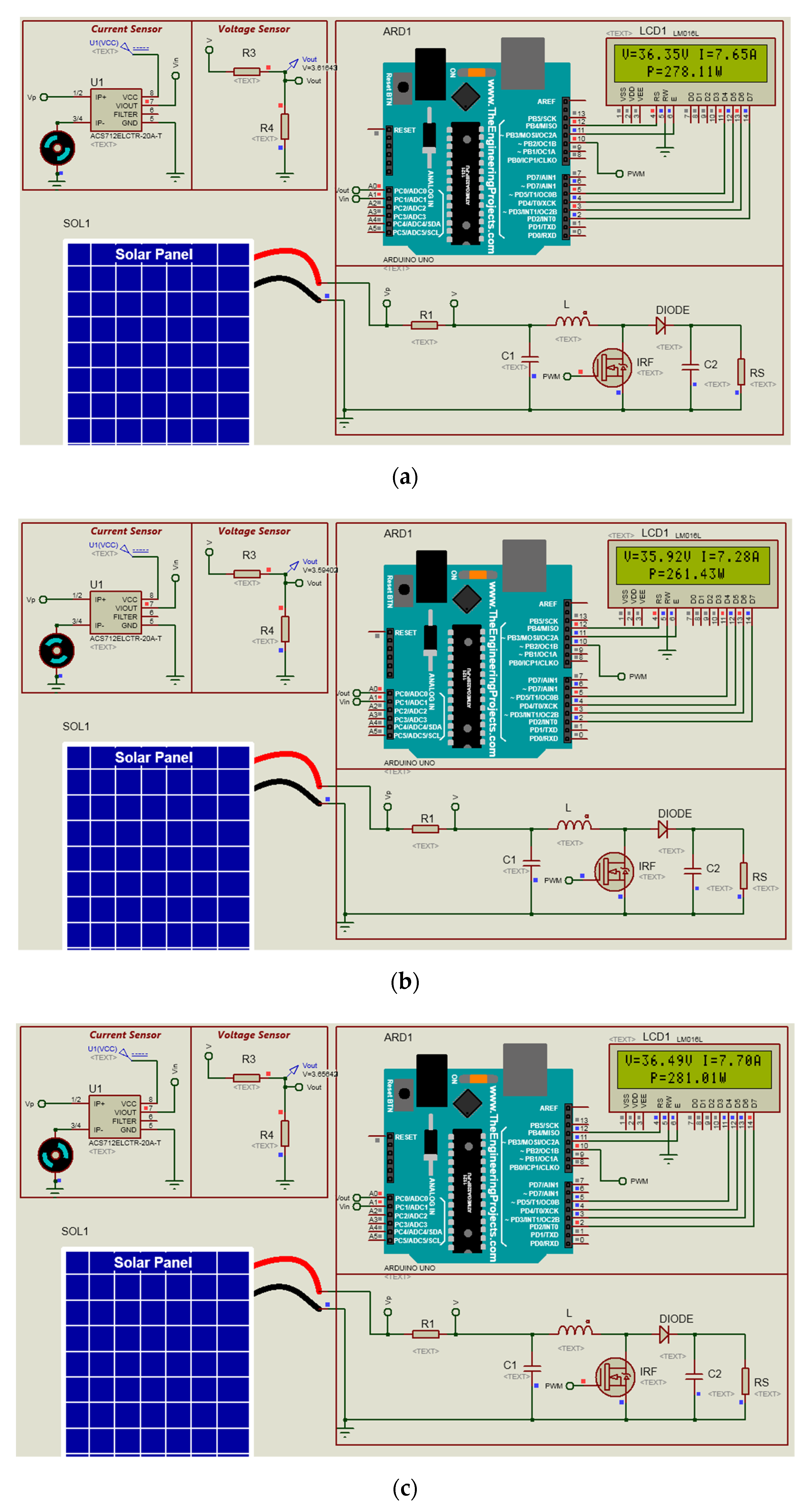
| Electrical Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Maximum Power | 281.05 W |
| Number of cells | 72 |
| Imp | 7.7 A |
| Vmp | 36.5 V |
| ISC | 8.3 A |
| VOC | 44.4 V |
| E/CE | NB | NS | ZE | PS | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | ZE | ZE | PB | PB | PB |
| NS | ZE | ZE | PS | PS | PS |
| ZE | PS | ZE | ZE | ZE | NS |
| PS | NS | NS | NS | ZE | ZE |
| PB | NB | NB | NB | ZE | ZE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouksaim, M.; Mekhfioui, M.; Srifi, M.N. Design and Implementation of Modified INC, Conventional INC, and Fuzzy Logic Controllers Applied to a PV System under Variable Weather Conditions. Designs 2021, 5, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5040071
Bouksaim M, Mekhfioui M, Srifi MN. Design and Implementation of Modified INC, Conventional INC, and Fuzzy Logic Controllers Applied to a PV System under Variable Weather Conditions. Designs. 2021; 5(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouksaim, Maroua, Mohcin Mekhfioui, and Mohamed Nabil Srifi. 2021. "Design and Implementation of Modified INC, Conventional INC, and Fuzzy Logic Controllers Applied to a PV System under Variable Weather Conditions" Designs 5, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5040071
APA StyleBouksaim, M., Mekhfioui, M., & Srifi, M. N. (2021). Design and Implementation of Modified INC, Conventional INC, and Fuzzy Logic Controllers Applied to a PV System under Variable Weather Conditions. Designs, 5(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5040071






