Mixing Oil with Water: Framing and Theorizing in Management Research Informed by Design Science
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Developing Theories of and for Practice
2.2. Theory Development in Design Science
3. Review Scope and Approach
4. Main Observations and Patterns in How DS Is Used
4.1. Deliberate Framing of the Problem Serves to Avoid Being Captured
4.2. Connecting Retrospective and Prospective Knowledge
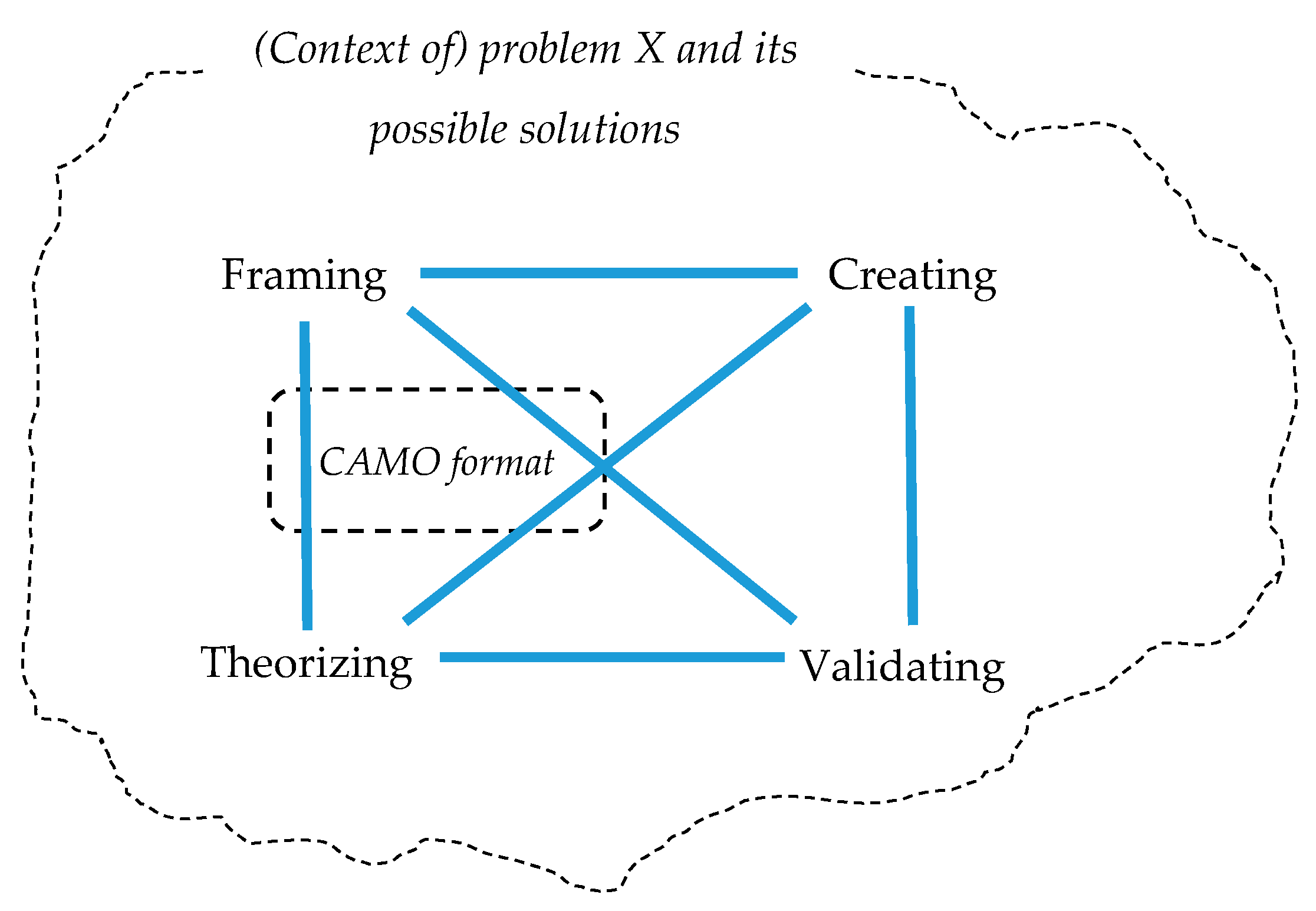
4.3. CAMO-Formatted Knowledge: Codifying Design Science Practice
- final cause—the outcome, for the sake of which it comes into being;
- efficient cause—the agency that initiates the change;
- formal cause—the mechanism that operates as the shaping force; and
- material cause—the context providing the immanent elements [75].
4.4. Benefits of CAMO-Formatted Knowledge
5. Connecting Design and Science
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simon, H.A. The Sciences of the Artificial, 3rd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hatchuel, A.; Weil, B. CK design theory: An advanced formulation. Res. Eng. Des. 2009, 19, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, S.T.; Smith, G.F. Design and natural science research on information technology. Deci. Support Syst. 1995, 15, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venable, J.; Pries-Heje, J.; Baskerville, R. A comprehensive framework for evaluation in design science research. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2012, 7286, 423–438. [Google Scholar]
- Romme, A.G.L. Making a difference: Organization as design. Organ. Sci. 2003, 14, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, J.E. Management research based on the paradigm of the design sciences: The quest for field-tested and grounded technological rules. J. Manag. Stud. 2004, 41, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, D. Toward a design science of entrepreneurship. In Models of Start-up Thinking and Action: Theoretical, Empirical, and Pedagogical Approaches; Corbett, A.C., Katz, J.A., Eds.; Emerald Group: Bingley, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Plsek, P.; Bibby, J.; Whitby, E. Practical methods for extracting explicit design rules grounded in the experience of organizational managers. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 2007, 43, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, A.; Thomas, C.; Romme, A.G.L. Developing a human-centred and science-based approach to design: The knowledge management platform project. Br. J. Manag. 2013, 24, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulman, F.; Reymen, I.M.M.J.; Podoynitsyna, K.; Romme, A.G.L. Searching for partners in open innovation settings: How to overcome the constraints of local search. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2018, 60, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Masson, P.; Hatchuel, A.; Le Glatin, M.; Weil, B. Designing decisions in the unknown: A generative model. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2019, 16, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdenakker, R.; Cuypers, C. Effective Virtual Project Teams: A Design Science Approach to Building a Strategic Momentum; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Konda, S.; Monarch, I.; Sargent, P.; Subrahmanian, E. Shared memory in design: A unifying theme for research and practice. Res. Eng. Des. 1992, 4, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchuel, A. Towards design theory and expandable rationality: The unfinished program of Herbert Simon. J. Manag. Gov. 2002, 5, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorff, K. The Semantic Turn: A New Foundation for Design; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanian, E.; Reich, Y.; Krishnan, S. We Are not Users: Dialogues, Diversity, and Design; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, N. Science and design methodology: A review. Res. Eng. Des. 1993, 5, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. Models of My Life; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, C.Y.; Clark, K.B. Design Rules, Volume 1: The Power of Modularity; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Khurana, R. From Higher Aims to Hired Hands: The Social Transformation of American Business Schools and the Unfulfilled Promise of Management as a Profession; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, R. Tent poles, tribalism, and boundary spanning: The rigor-relevance debate in management research. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.; Spender, J.C.; Herbert, A. Simon on what ails business schools: More than a problem in organizational design. J. Manag. Stud. 2012, 49, 619–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmandad, H.; Vakili, K. Explaining heterogeneity in the organization of scientific work. Organ. Sci. 2019, 30, 1125–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. The business school: A problem in organizational design. J. Manag. Stud. 1967, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzybski, A. Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics, 5th ed.; Institute of General Semantics: New York, NY, USA, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, N. Fact, Fiction, and Forecast, 4th ed.; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Suddaby, R. Editor’s comments: Why theory? Acad. Manag. Rev. 2014, 39, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentland, B.T. Building process theory with narrative: From description to explanation. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1999, 24, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, Z. I’ve got a theory paper―Do you? Conceptual, empirical, and theoretical contributions to knowledge in the organizational sciences. Organ. Sci. 2011, 22, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, I. Beyond constraining and enabling: Toward new microfoundations for institutional theory. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2018, 43, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, K.; Golden-Biddle, K. Constructing opportunities for contribution: Structuring intertextual coherence and problematizing in organizational studies. Acad. Manag. J. 1997, 40, 1023–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Weick, K.E. Theory construction as disciplined imagination. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasvathy, S.D.; Venkataraman, S. Entrepreneurship as method: Open questions for an entrepreneurial future. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2011, 35, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchuel, A.; Le Masson, P.; Reich, Y.; Subrahmanian, E. Design theory: A foundation of a new paradigm for design science and engineering. Res. Eng. Des. 2018, 29, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romme, A.G.L.; Putzel, R. Designing management education: Practice what you teach. Simul. Gaming 2003, 34, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, Y. The principle of reflexive practice. Des. Sci. 2017, 3, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfield, J.N. A Science of Generic Design, 2nd ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Romme, A.G.L.; Avenier, M.-J.; Denyer, D.; Hodgkinson, G.P.; Pandza, K.; Starkey, K.; Worren, N. Towards common ground and trading zones in management research and practice. Brit. J. Manag. 2015, 26, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, G. Steps to an Ecology of Mind; Ballantine Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Niiniluoto, I. The aim and structure of applied research. Erkenntnis 1993, 38, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Masson, P.; Hatchuel, A.; Weil, B. Design theory at Bauhaus: Teaching splitting knowledge. Res. Eng. Des. 2016, 27, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, Y.; Subrahmanian, E. The PSI framework and theory of design. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, J.; Ketokivi, M.; Hameri, A. Bridging practice and theory: A design science approach. Decis. Sci. 2009, 40, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.M. Designing a better business school: Channelling Herbert Simon, addressing the critics, and developing actionable knowledge for professionalizing managers. J. Manag. Stud. 2012, 49, 600–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudovskiy, J. The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies; University of Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson, G.P.; Healey, M.P. Toward a (pragmatic) science of strategic intervention: Design propositions for scenario planning. Organ. Stud. 2008, 29, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilbeam, C.; Denyer, D.; Doherty, N.; Davidson, R. Designing safer working interventions through a literature review using a mechanisms-based approach. Safety Sci. 2019, 120, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriessen, D. Designing and testing an OD intervention: Reporting intellectual capital to develop organizations. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 2007, 43, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, J.-L.; Brusset, X.; Chabot, M. Protecting franchise chains against weather risk: A design science approach. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 125, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, H.; Robert, G.; Bate, P.; Maher, L.; Wells, J. Using a design approach to assist largescale organizational change: 10 high impact changes to improve the National Health Service in England. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 2007, 43, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgoyne, J.; James, K.T. Towards best or better practice in corporate leadership development: Operational issues in mode 2 and design science research. Br. J. Manag. 2006, 17, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, D.J. Bridging social constraint and social action to design organizations for innovation. Organ. Stud. 2008, 29, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmquist, M.; Le Masson, P. The value of a failed R&D project: An emerging evaluation framework for building innovative capabilities. R D Manag. 2009, 39, 136–152. [Google Scholar]
- Healey, M.P.; Hodgkinson, G.P.; Whittington, R.; Johnson, G. Off to plan or out to lunch? Relationships between design characteristics and outcomes of strategy workshops. Br. J. Manag. 2015, 26, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, S.S.; Van Eijnatten, F.M.; Romme, A.G.L.; Demerouti, E. Developing actionable knowledge on value crafting: A design science approach. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooge, S.; Kokshagina, O.; Le Masson, P.; Levillain, K.; Weil, B.; Fabreguettes, V.; Popiolek, N. Gambling versus designing: Organizing for the design of the probability space in the energy sector. Create Innov. Manag. 2016, 25, 464–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y. Designing business models and similar strategic objects: The contribution of IS. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2012, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romme, A.G.L.; Damen, I. Toward science-based design in organization development: Codifying the process. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 2007, 43, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romme, A.G.L.; Endenburg, G. Construction principles and design rules in the case of circular design. Organ. Sci. 2006, 17, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagath, D.; Van Burg, E.; Cornelissen, J.P.; Giannopapa, C. Identifying design principles for business incubation in the European space sector. J. Bus. Ventur. Insights 2019, 11, e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, T.; Chow, T.E. Developing a digital marketing tool for ethnic ventures’ mixed business model and market-shaping: A design scientific approach of web demographics. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2021, 93, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanskanen, K.; Ahola, T.; Aminoff, A.; Bragge, J.; Kaipia, R. Towards evidence-based management of external resources: Developing design propositions and future research avenues through research synthesis. Res. Policy 2017, 46, 1087–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.G.; Patrício, L.; Tuunanen, T. Advancing service design research with design science research. J. Serv. Manag. 2019, 30, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Burg, E.; Jager, S.; Reymen, I.M.M.J.; Cloodt, M. Design principles for corporate venture transition processes in established technology firms. R D Manag. 2012, 42, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Burg, E.; Romme, A.G.L. Creating the future together: Toward a framework for research synthesis in entrepreneurship. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2014, 38, 369–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Burg, E.; Romme, A.G.L.; Gilsing, V.A.; Reymen, I.M.M.J. Creating university spin-offs: A science-based design perspective. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2008, 25, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Borgh, M.; Xu, J.; Sikkenk, M. Identifying, analyzing, and finding solutions to the sales lead black hole: A design science approach. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 88, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, B.; Konietzko, J.; Brown, P.; Calabretta, G.; Bocken, N.; Karpen, I.O.; Hultink, E.J. Addressing the design-implementation gap of sustainable business models by prototyping: A tool for planning and executing small-scale pilots. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthe, C.I.; Uppvall, L.; Engwall, M.; Dahlén, L. Dealing with the devil of deviation: Managing uncertainty during product development execution. R D Manag. 2014, 44, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlgren, L.; Elmquist, M.; Rauth, I. The challenges of using design thinking in industry: Experiences from five large firms. Creat. Innov. Manag. 2016, 25, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romme, A.G.L. Domination, self-determination and circular organizing. Organ. Stud. 1999, 20, 801–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, B.J. Holacracy: The New Management System for a Rapidly Changing World; Henry Holt: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Denyer, D.; Tranfield, D.; Van Aken, J.E. Developing design propositions through research synthesis. Organ. Stud. 2008, 29, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville, R.; Pries-Heje, J. Design logic and the ambiguity operator. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2010, 6105, 180–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, W.D. Aristotle’s Metaphysics; Oxford University: Oxford, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, N. A pragmatist theory of social mechanisms. Am. Soc. Rev. 2009, 74, 358–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuorikoski, J.; Pöyhönen, S. Looping kinds and social mechanisms. Soc. Theory 2012, 30, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddens, A. The Constitution of Society; Polity: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Battilana, J.; Leca, B.; Boxenbaum, E. How actors change institutions: Towards a theory of institutional entrepreneurship. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2009, 3, 65–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emirbayer, M.; Mische, A. What is agency? Am. J. Soc. 1998, 103, 962–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyris, C.; Putnam, R.; McLain Smith, D. Action Science: Concepts, Methods, and Skills for Research and Intervention; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Janssens, M.; Steyaert, C. A practice-based theory of diversity: Respecifying in equality in organizations. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2019, 44, 518–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, J.; Willmott, H. Embedded agency in institutional theory: Problem or paradox? Acad. Manag. Rev. 2019, 44, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedström, P.; Ylikoski, P. Causal mechanisms in the social sciences. Annu. Rev. Soc. 2010, 36, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, R.; Vaara, E. Causation, counterfactuals, and competitive advantage. Strateg. Manag. J. 2009, 30, 1245–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, S.H.; Baker, T.; Markham, S.K.; Kingon, A.I. Bridging the valley of death: Lessons learned from 14 years of commercialization of technology education. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2009, 8, 370–388. [Google Scholar]
- Lackéus, M.; Williams Middleton, K. Venture creation programs: Bridging entrepreneurship education and technology transfer. Educ. Train. 2015, 57, 48–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y.; Tucci, C.L. Clarifying business models: Origins, present, and future of the concept. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2005, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscio, A.; Quaglione, D.; Ramaciotti, L. The effects of university rules on spinoff creation: The case of academia in Italy. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Monsen, E.W.; MacKenzie, N.G. Follow the leader or the pack? Regulatory focus and academic entrepreneurial intentions. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2017, 34, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Burg, E.; Gilsing, V.A.; Reymen, I.M.M.J.; Romme, A.G.L. The formation of fairness perceptions in the cooperation between entrepreneurs and universities. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2013, 30, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, K. Frame Innovation: Create New Thinking by Design; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goffman, E. Frame Analysis: An Essay on the Organization of Experience; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Locke, K.; Golden-Biddle, K.; Feldman, M.S. Making doubt generative: Rethinking the role of doubt in the research process. Organ. Sci. 2008, 19, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, K. Field Theory in Social Science: Selected Theoretical Papers; Cartwright, D., Ed.; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Starbuck, W.H. The Production of Knowledge: The Challenge of Social Science Research; Oxford University: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Suddaby, R.; Hardy, C.; Huy, Q.N. Introduction to special topic forum: Where are the new theories of organization? Acad. Manag. Rev. 2011, 36, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, D.A. The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in Action; Temple Smith: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.J. Should social science be more solution-oriented? Nat. Hum. Behav. 2017, 1, 0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Giambalvo, J.; Vance, J.; Faludi, J.; Hoffenson, S. A product development approach advisor for navigating common design methods, processes, and environments. Designs 2020, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Context | Agency | Mechanism | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definitions | Conditions that can enable or constrain (e.g., managerial) behavior and choices (cf., Aristotle’s material cause). While many actors have discretion in making choices, these conditions tend to direct and/or restrict these choices. | The capacity of a specific (group of) actor(s) to act in a given context (cf., Aristotle’s efficient cause). Agency, here, therefore, refers to both the actor(s) and its/their actions. | Driver, or Aristotle’s formal cause, gives rise to a particular kind of outcome. Mechanisms can often not be directly observed; further conceptual and analytical work is then required to identify them. | The intended or unintended results of the combined agency–context–mechanism; the agent’s intended result reflects Aristotle’s final cause. |
| CAMO Synthesis | General structure of a CAMO proposition: If in context C agency A activates mechanism M, this is likely to generate outcome pattern O. This proposition thus explains the O from a specific CAM combination, with M being the key causal driver, A the activator of this cause, and C the boundary condition. The various component-relations of any CAMO proposition (e.g., A–M or M–O) are descriptive and/or explanatory in nature. However, the synthesized (set of) CAMO proposition(s) is descriptive-explanatory as well as prescriptive-normative in nature. Thus, the CAMO proposition above can be rewritten as a design principle as follows: To generate outcome pattern O in context C, do something like A to activate mechanism M. | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romme, A.G.L.; Dimov, D. Mixing Oil with Water: Framing and Theorizing in Management Research Informed by Design Science. Designs 2021, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5010013
Romme AGL, Dimov D. Mixing Oil with Water: Framing and Theorizing in Management Research Informed by Design Science. Designs. 2021; 5(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomme, A. Georges L., and Dimo Dimov. 2021. "Mixing Oil with Water: Framing and Theorizing in Management Research Informed by Design Science" Designs 5, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5010013
APA StyleRomme, A. G. L., & Dimov, D. (2021). Mixing Oil with Water: Framing and Theorizing in Management Research Informed by Design Science. Designs, 5(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5010013






