Machine Learning with Applications in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Abstract
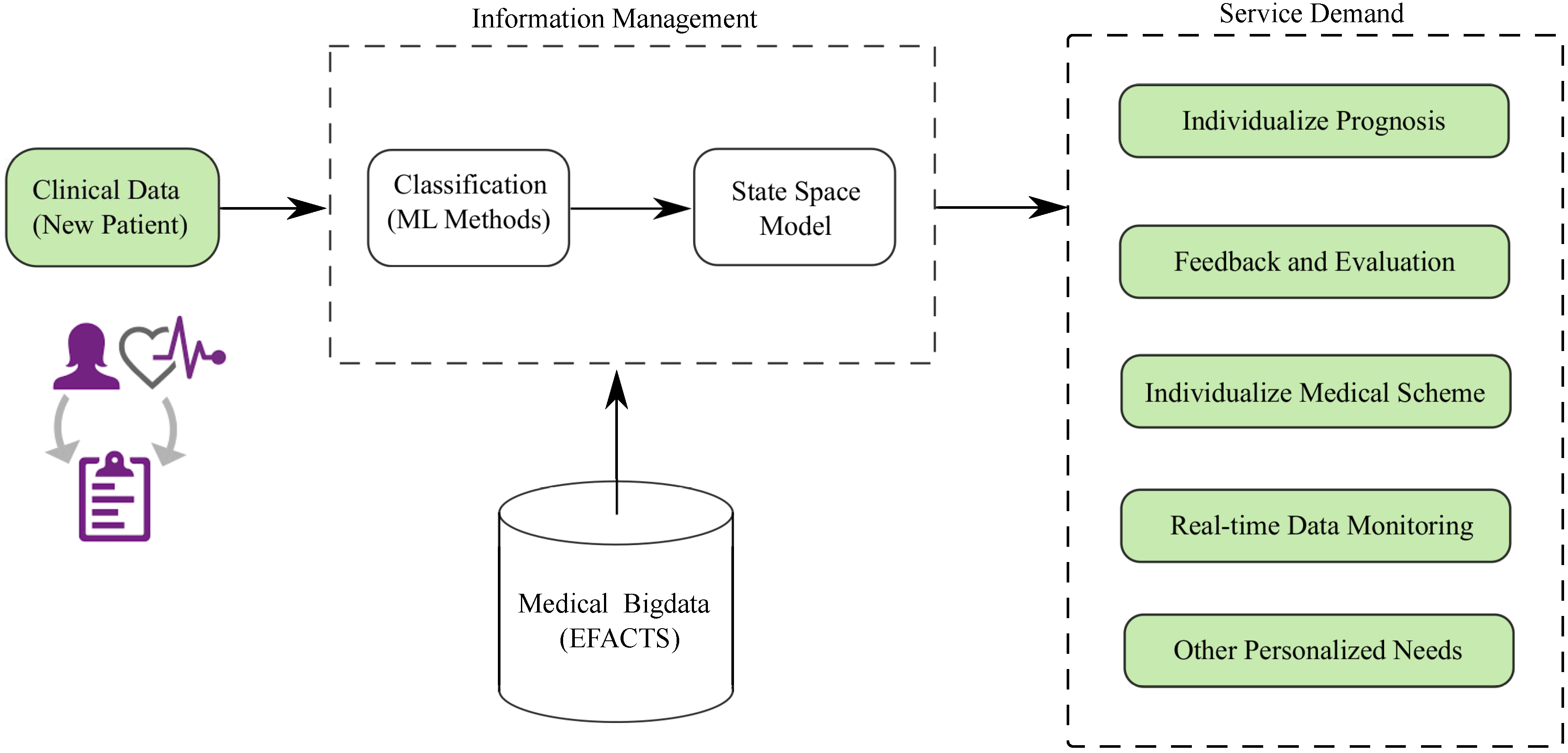
:1. Introduction
2. ML Approaches
3. ML Applications in BC Diagnosis and Prognosis
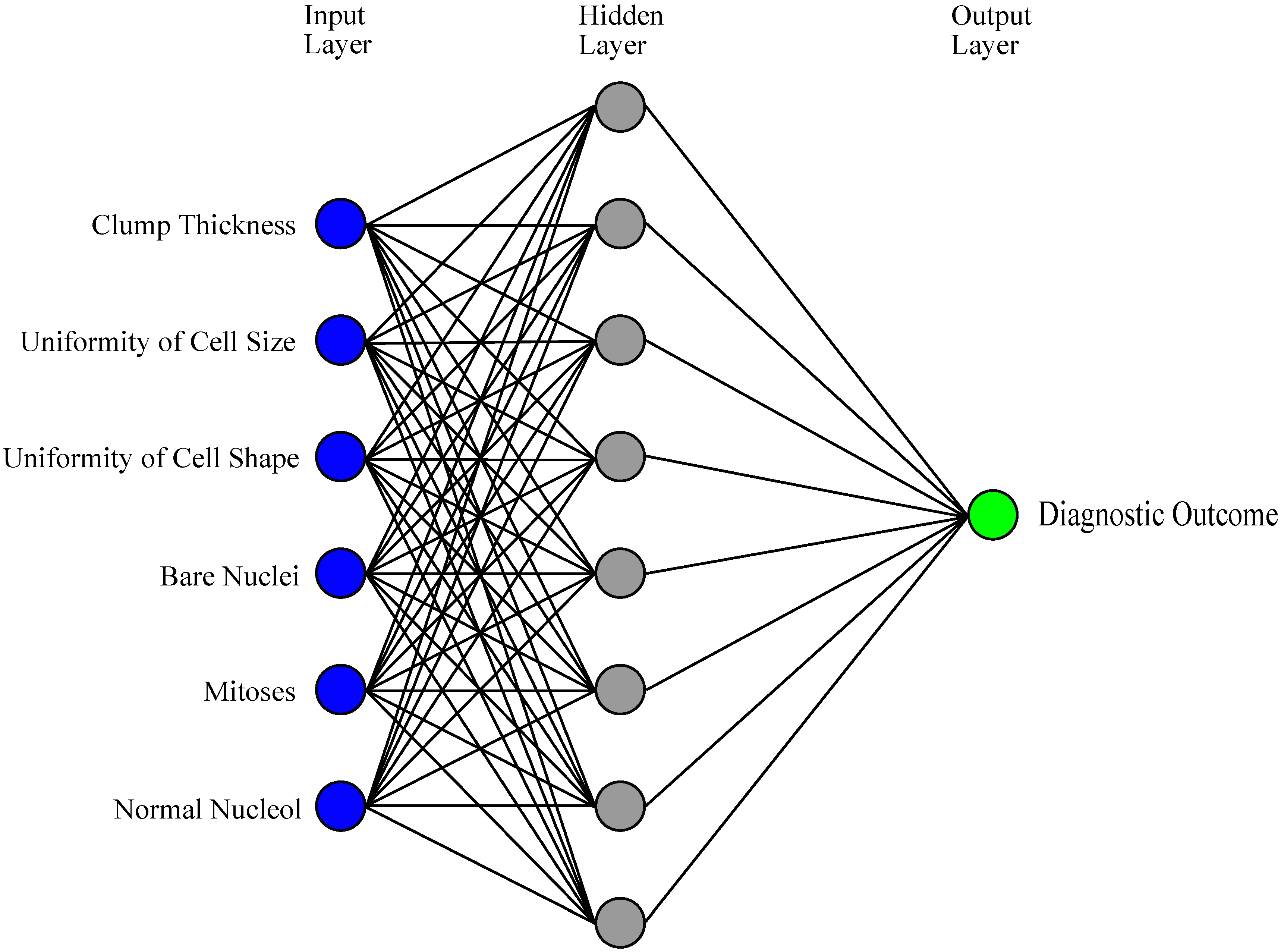
3.1. ANNs
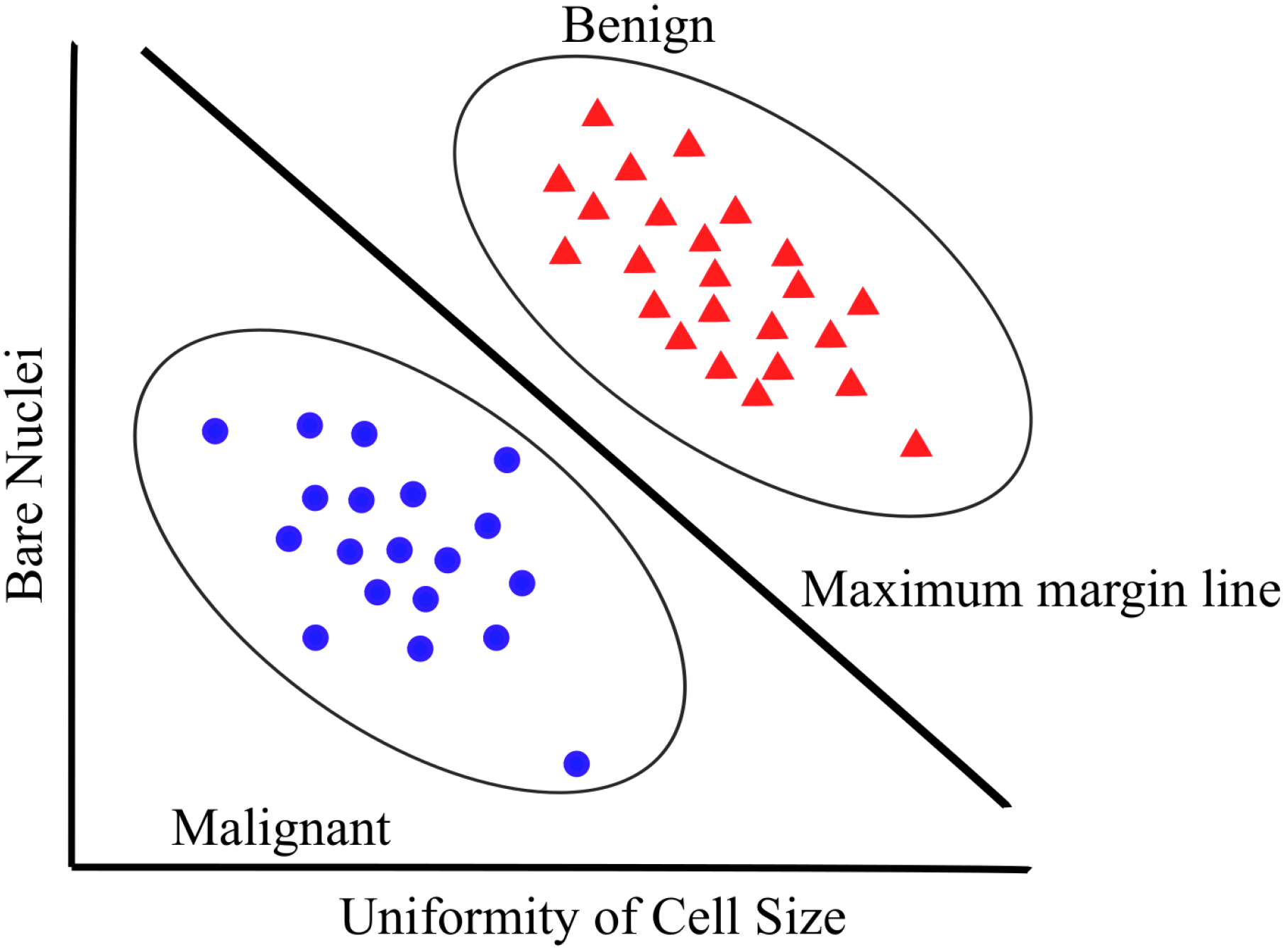
3.2. SVMs
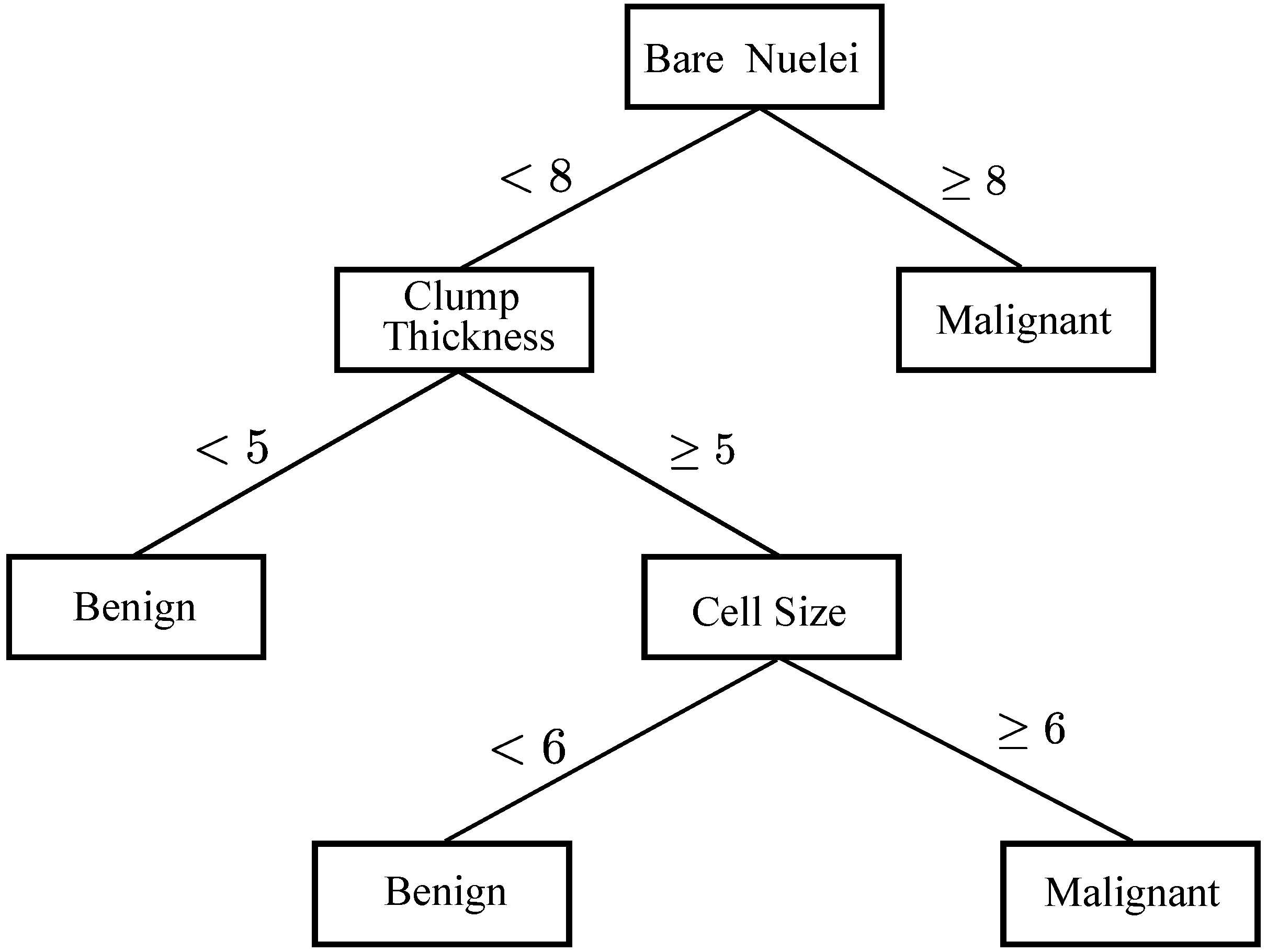
3.3. DTs
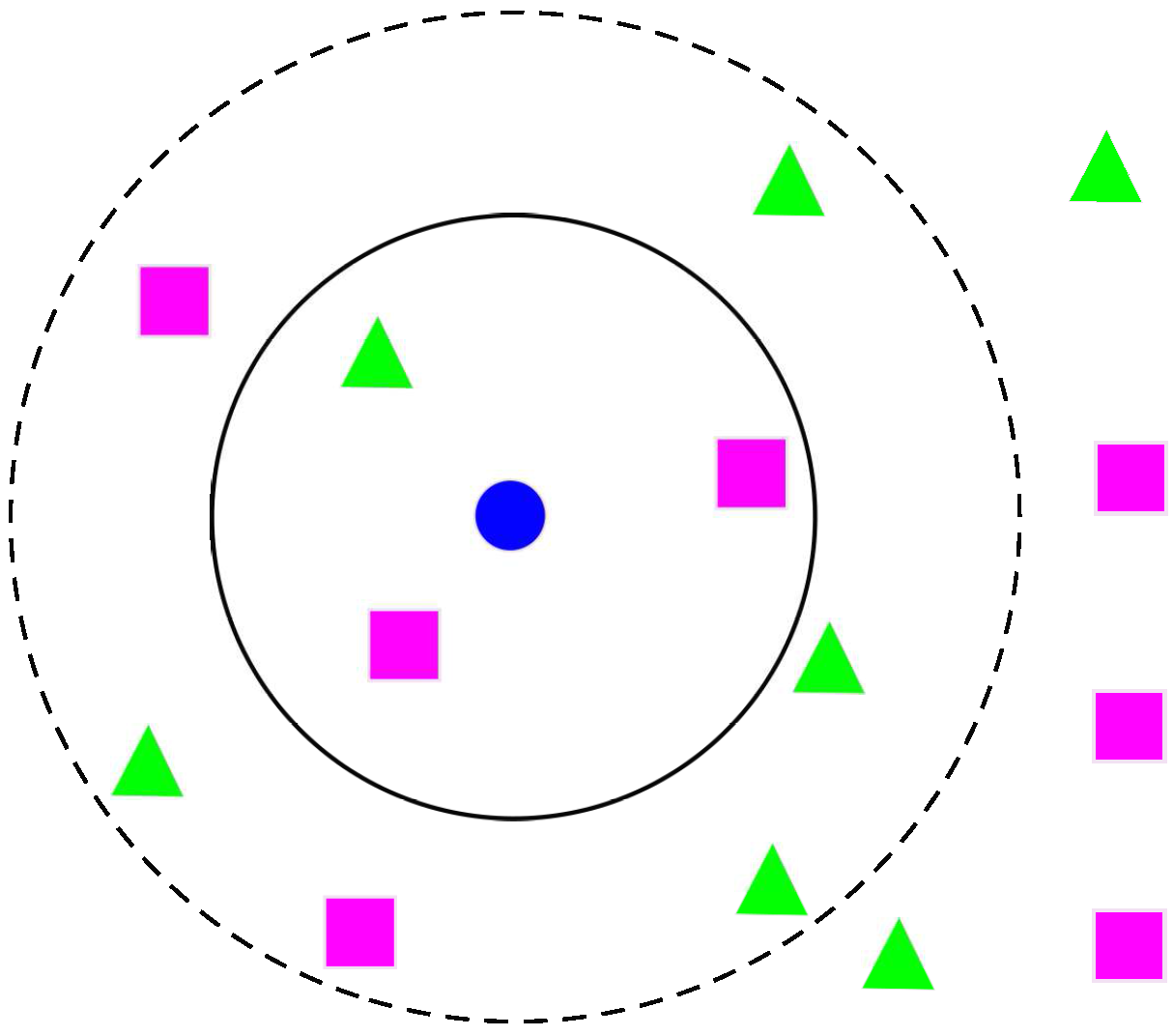
3.4. k-NNs
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meesad, P.; Yen, G.G. Combined numerical and linguistic knowledge representation and its application to medical diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2003, 33, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, S.A.; Delopoulos, A.N. Designing and implementing the transition to a fully digital hospital. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 1999, 3, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reetz, K.; Dogan, I.; Costa, A.S.; Dafotakis, M.; Fedosov, K.; Giunti, P.; Parkinson, M.H.; Sweeney, M.G.; Mariotti, C.; Panzeri, M.; et al. Biological and clinical characteristics of the European Friedreich’s Ataxia Consortium for Translational Studies (EFACTS) cohort: A cross-sectional analysis of baseline data. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barracliffe, L.; Arandjelović, O.; Humphris, G. A pilot study of breast cancer patients: Can machine learning predict healthcare professionals’ responses to patient emotions? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 20–22 March 2017; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Birkett, C.; Arandjelović, O.; Humphris, G. Towards objective and reproducible study of patient-doctor interaction: Automatic text analysis based VR-CoDES annotation of consultation transcripts. In Proceedings of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Conference, Jeju Island, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2638–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangasarian, O.L.; Setiono, R.; Wolberg, W.H. Pattern recognition via linear programming: Theory and application to medical diagnosis. In Large-Scale Numerical Optimization; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg, W.H.; Mangasarian, O.L. Multisurface method of pattern separation for medical diagnosis applied to breast cytology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9193–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Kulshrestha, S.; Daniel, S. Machine learning approaches for breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Soft Computing and Its Engineering Applications, Changa, India, 1–2 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Delen, D.; Walker, G.; Kadam, A. Predicting breast cancer survivability: A comparison of three data mining methods. Artif. Intell. Med. 2005, 34, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funahashi, K.; Nakamura, Y. Approximation of dynamical systems by continuous time recurrent neural networks. Neural Netw. 1993, 6, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, M.A.; Athappilly, K. A comparative predictive analysis of neural networks (NNs), nonlinear regression and classification and regression tree (CART) models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2005, 29, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A.; Ercelebi, E. Classification of EEG signals using neural network and logistic regression. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 2005, 78, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, A.; Cuzick, J.; Baum, M.; Buzdar, A.; Dowsett, M.; Forbes, J.F.; Hoctin-Boes, G.; Houghton, J.; Locker, G.Y.; Tobias, J.S.; et al. Results of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination) trial after completion of 5 years’ adjuvant treatment for breast cancer. Lancet 2004, 365, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M.; Gladstone, I.M.; Ehrenkranz, R.A. A regularity statistic for medical data analysis. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 1991, 7, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, J.H.; Sox, H.C.; Neff, R.K.; Goldman, L. Clinical prediction rules: Application and methodological standards. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, M.; Blanchette, C.; Dressman, H.; Huang, E.; Ishida, S.; Spang, R.; Zuzan, H.; Olson, J.A.; Marks, J.R.; Nevins, J.R.; et al. Predicting the clinical status of human breast cancer by using gene expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11462–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, M.; Kumar, U.A. Neural networks and statistical techniques: A review of applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furundzic, D.; Djordjevic, M.; Bekic, A.J. Neural networks approach to early breast cancer detection. J. Syst. Archit. 1998, 44, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrman, M.; Linder, R.; Assadi, A.H.; Stacey, B.R.; Backonja, M.-M. Classification of patients with pain based on neuropathic pain symptoms: Comparison of an artificial neural network against an established scoring system. Eur. J. Pain 2007, 11, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ture, M.; Kurt, I.; Kurum, A.T.; Ozdamar, K. Comparing classification techniques for predicting essential hypertension. Expert Syst. Appl. 2005, 29, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortiz, M.; Gutiérrez, P.A.; Hervás-Martínez, C.; Yao, X. Graph-Based Approaches for over-Sampling in the context of ordinal regression. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 27, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-Y. Analysis of freeway accident frequencies: Negative binomial regression versus artificial neural network. Saf. Sci. 2005, 43, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.A. Comparison of neural networks and regression analysis: A new insight. Expert Syst. Appl. 2005, 29, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SubbaNarasimha, P.N.; Arinze, B.; Anandarajan, M. The predictive accuracy of artificial neural networks and multiple regression in the case of skewed data: Exploration of some issues. Expert Syst. Appl. 2000, 19, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A. Clustering Algorithms; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, J.A.; Wishart, D.S. Applications of machine learning in cancer prediction and prognosis. Cancer Inform. 2006, 2, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E. How neural networks learn from experience. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Qiu, S.; Cao, Y.; Ding, X. Improving learning algorithm performance for spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology, Chengdu, China, 27–30 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Alsaadi, F.E. A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications. Neurocomputing 2017, 234, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Alsaadi, F.E. Finite-time state estimation for recurrent delayed neural networks with component-based event-triggering protocol. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Dong, H.; Wang, Z.; Ren, W.; Alsaadi, F.E. A new approach to non-fragile state estimation for continuous neural networks with time-delays. Neurocomputing 2016, 197, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, C.E.; Lo, J.Y.; Yun, A.J.; Sullivan, D.C.; Kornguth, P.J. Prediction of breast cancer malignancy using an artificial neural network. Cancer 1994, 74, 2944–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, D.B.; Wasson, E.C.; Boughton, E.M. Evolving neural networks for detecting breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 1995, 96, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, D.B.; Wasson, E.C.; Boughton, E.M.; Porto, V.W.; Angeline, P.J. Linear and neural models for classifying breast masses. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendharkar, P.C.; Rodger, J.A.; Yaverbaum, G.J.; Herman, N.; Benner, M. Association, statistical, mathematical and neural approaches for mining breast cancer patterns. Expert Syst. Appl. 1999, 17, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiono, R. Extracting rules from pruned neural networks for breast cancer diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 1996, 8, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, P.; Morgan, M.A.; Grygotis, A.E.; Shoffner, M.A.; Rosato, E.F. Application of backpropagation neural networks to diagnosis of breast and ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 1994, 77, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Giger, M.L.; Doi, K.; Vyborny, C.J.; Schmidt, R.A.; Metz, C.E. Artificial neural networks in mammography: Application to decision making in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Radiology 1993, 187, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minsky, M.; Papert, S. Perceptrons; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Mcclellend, J.L. Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V.N. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Schölkopf, B.; Sung, K.; Burges, C.J.C.; Girosi, F.; Niyogi, P.; Poggio, T.; Vapnik, V. Comparing Support vector machines with Gaussian kernels to radial basis function classifiers. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, V.; Campbell, W.M. Support vector machines for speaker verification and identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop on Neural Networks for Signal Processing, Sydney, Australia, 11–13 December 2000; Volume 2, pp. 775–784. [Google Scholar]
- Joachims, T. Transductive inference for text classification using support vector machines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Bled, Slovenia, 27–30 June 1999; Volume 99, pp. 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Mangasarian, O.L.; Wolberg, W.H. Breast cancer survival and chemotherapy: A support vector machine analysis. DIMACS Ser. Discret. Math. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2000, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- De Mántaras, R.L. A distance-based attribute selection measure for decision tree induction. Mach. Learn. 1991, 6, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingers, J. An empirical comparison of selection measures for decision-tree induction. Mach. Learn. 1989, 3, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apté, C.; Weiss, S. Data mining with decision trees and decision rules. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 1997, 13, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Seco, F.; Micó, L.; Oncina, J. A modification of the LAESA algorithm for approximated k-NN classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk, Z.K.; Kara, R. Breast cancer diagnosis via data mining: Performance analysis of seven different algorithms. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2014, 4, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabár, L.; Dean, P.B. Teaching Atlas of Mammography; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Setiono, R.; Liu, H. Understanding neural networks via rule extraction. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Setiono, R. Generating concise and accurate classification rules for breast cancer diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2000, 18, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbass, H.A. An evolutionary artificial neural networks approach for breast cancer diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2002, 25, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cowan, C.F.N.; Grant, P.M. Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Brabanter, J.D.; Huffel, S.V.; Vergote, I.; Timmerman, D. Using artificial neural networks to predict malignancy of ovarian tumors. In Proceedings of the 23th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Istanbul, Turkey, 25–28 October 2001; pp. 1637–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyan, T.; Yildirim, T. Breast cancer diagnosis using statistical neural networks. IU-J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2004, 4, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Karabatak, M.; Ince, M.C. An expert system for detection of breast cancer based on association rules and neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3465–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano-Cedeño, A.; Quintanilla-Domłnguez, J.; Andina, D. WBCD breast cancer database classification applying artificial metaplasticity neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 9573–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.C.; Bear, M.F. Metaplasticity: The plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2001, 5, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, H.; Ceylan, R. Artificial neural network based on rotation forest for biomedical pattern classification. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing, Rome, Italy, 2–4 July 2013; pp. 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.; Cuncheva, L.; Alonso, C.J. Rotation forest: A new classifier ensemble method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsopoulos, K.E.; Vrahatis, M.N. Particle swarm optimization method for constrained optimization problems. Intell. Technol. Theory Appl. New Trends Intell. Technol. 2002, 76, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Koza, J.R.; Rice, J.P. Genetic generation of both the weights and architecture for a neural network. In Proceedings of the IJCNN-91-Seattle International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 July 1991; Volume 2, pp. 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Tiwari, A. Breast cancer diagnosis using genetically optimized neural network model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 4611–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahato, K.B.; Harichandran, K.N.; Arputharaj, K. Knowledge mining from clinical datasets using rough sets and backpropagation neural network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 460189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Zaher, A.M.; Eldeib, A.M. Breast cancer classification using deep belief networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 46, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.P.; Blue, J.A. A support vector machine approach to decision trees. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998; Volume 3, pp. 2396–2401. [Google Scholar]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Vandewalle, J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Proccess. Lett. 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, K.; Güneş, S. Breast cancer diagnosis using least square support vector machine. Digit. Signal Process. 2007, 17, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, M.F. Support vector machines combined with feature selection for breast cancer diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3240–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.-Y. A support vector machine classifier with rough set-based feature selection for breast cancer diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 9014–9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G. H.; Kohavi, R.; Pfleger, K. Irrelevant features and the subset selection problem. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Machine Learning, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 10–13 July 1994; pp. 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-L.; Yang, B.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.-J.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.-Y. Support vector machine based diagnostic system for breast cancer using swarm intelligence. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 2505–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, A.T.; El-Said, S.A. Performance analysis of support vector machines classifiers in breast cancer mammography recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchoumi, T.P.; Parthiban, L. Abnormality detection using weighed particle swarm optimization and smooth support vector machine. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, 4749–4751. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, A.H. An enhanced breast cancer diagnosis scheme based on two-step-SVM technique. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.R. Improved use of continuous attributes in C4.5. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1996, 4, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, A.B.; Boggess, L.C. A resource limited artificial immune classifier. In Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; pp. 926–931. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, K.; Sahan, S.; Kodaz, H.; Gnes, S. A new classification method for breast cancer diagnosis: Feature selection artificial immune recognition system (FS-AIRS). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Computation, Changsha, China, 27–29 August 2005; Volume 3611, pp. 830–838. [Google Scholar]
- Pach, F.P.; Abonyi, J. Association rule and decision tree based methods for fuzzy rule base generation. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2006, 13, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.-Y.; Chang, P.-C.; Lin, J.-J.; Hsieh, J.C. A hybrid model combining case-based reasoning and fuzzy decision tree for medical data classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Trigg, L.E.; Hall, M.A.; Holmes, G.; Cunningham, S.J. Weka: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques with Java Implementations. Available online: https://researchcommons.waikato.ac.nz/handle/10289/1040 (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Sumbaly, R.; Vishnusri, N.; Jeyalatha, S. Diagnosis of breast cancer using decision tree data mining technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 98, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, R.D.H.; Devi, M.I. Outlier detection algorithm combined with decision tree classifier for early diagnosis of breast cancer. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2016, 12, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Seera, M.; Lim, C.P. A hybrid intelligent system for medical data classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayman, Y.; Wang, L. Data mining using dynamically constructed recurrent fuzzy neural networks. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Melbourne, Australia, 15–17 April 1998; pp. 122–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chu, F.; Xie, W. Accurate cancer classification using expressions of very few genes. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2007, 4, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zulkernine, M.; Haque, A. Random-forests-based network intrusion detection systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2008, 38, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.K.; Nikhil, M.B.S.; Sumangali, K. Prediction of breast cancer using voting classifier technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Smart Technologies and Management for Computing, Communication, Controls, Energy and Materials, Chennai, India, 2–4 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, M.; Leong, T.Y. Application of k-nearest neighbors algorithm on breast cancer diagnosis problem. In Proceedings of the AMIA Symposium, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4–8 November 2000; pp. 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Bagui, S.C.; Bagui, S.; Pal, K.; Pal, N.R. Breast cancer detection using rank nearest neighbor classification rules. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjahed, S.A.; Ait Saadi, T.; Benyettou, A. Breast cancer diagnosis by using k-nearest neighbor with different distances and classification rules. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 62, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, M.; Liu, X. A hybrid EKF and switching PSO algorithm for joint state and parameter estimation of lateral flow immunoassay models. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2012, 9, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Alsaadi, F.E. A novel switching delayed PSO algorithm for estimating unknown parameters of lateral flow immunoassay. Cogn. Comput. 2016, 8, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J. Parameters identification of unknown delayed genetic regulatory networks by a switching particle swarm optimization algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2523–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J. Feedback learning particle swarm optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 4713–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, K.; Dogan, I.; Hilgers, R.D.; Giunti, P.; Mariotti, C.; Durr, A.; Boesch, S.; Klopstock, T.; de Rivera, F.J.R.; Schöls, P.L.; et al. Progression characteristics of the European Friedreich’s Ataxia Consortium for Translational Studies (EFACTS): A 2 year cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Ghinea, G.; Alsaadi, F.E. A resilient approach to distributed filter design for time-varying systems under stochastic nonlinearities and sensor degradation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Attribute | Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Sample code number | id number |
| 1 | Clump Thickness | 1–10 |
| 2 | Uniformity of Cell Size | 1–10 |
| 3 | Uniformity of Cell Shape | 1–10 |
| 4 | Marginal Adhesion | 1–10 |
| 5 | Single Epithelial Cell Size | 1–10 |
| 6 | Bare Nuclei | 1–10 |
| 7 | Bland Chromatin | 1–10 |
| 8 | Normal Nucleoli | 1–10 |
| 9 | Mitoses | 1–10 |
| 10 | Class | 2 for benign |
| 4 for malignant |
| References | Algorithms | Sampling Strategies | Classification Accuracies (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quinlan 1996 [91] | C DT | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Setiono 1996 [45] | Pruned ANN | 50–50 training-testing | |
| Bennett & Blue 1998 [81] | SVM | 5–fold cross validation | |
| Setiono 2000 [64] | Neuro-rule ANN | 10-fold cross validation | |
| Sarkar & Leong 2000 [104] | k-NN | 50–50 training-testing | |
| Fuzzy k-NN | 50–50 training-testing | ||
| Abbass 2002 [65] | EANN | 80–20 training-testing | |
| Bagui et al., 2003 [105] | k-RNN | 10-fold cross validation | |
| Kiyan & Yildirim 2004 [69] | RBN | 50–50 training-testing | |
| GRNN | 50–50 training-testing | ||
| PNN | 50–50 training-testing | ||
| MLP | 50–50 training-testing | ||
| Polat et al., 2005 [93] | C + FS-AIRS | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Pach & Abonyi 2006 [94] | F-DT | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Polat & Gne 2007 [83] | LS-SVM | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Akay 2009 [84] | F-score-SVM | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Karabatak & Ince 2009 [70] | AR-ANN | 3–fold cross validation | |
| Marcano-Cedeño et al., 2011 [71] | AMMLP | 60–40 training-testing | |
| Chen et al., 2011 [85] | RS-SVM | 80–20 training-testing | |
| Fan et al., 2011 [95] | CBFDT | 75–25 training-testing | |
| Chen et al., 2012 [87] | PSO-SVM | 10-fold cross validation | |
| Koyuncu & Ceylan 2013 [74] | RF-ANN | 50–50 training-testing | |
| PSO-ANN | 50–50 training-testing | ||
| Medjahed & Saadi 2013 [106] | k-NN (Euclidean) | Holdout method | |
| Azar & El-Said 2014 [88] | PSVM | 4–fold cross validation | |
| NSVM | 4–fold cross validation | ||
| LPSVM | 4–fold cross validation | ||
| LSVM | 4–fold cross validation | ||
| SSVM | 4–fold cross validation | ||
| Sumbaly et al., 2014 [97] | J48 | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Seera & Lim 2014 [99] | FMM-CART-RF | 50–50 training-testing | |
| Bhardwaj & Tiwari 2015 [78] | GOANN | 10-fold cross validation | |
| Nahato et al., 2015 [79] | RS-BPANN | 80–20 training-testing | |
| Abdel-Zaher & Eldeib 2016 [80] | DBN-ANN | – training-testing | |
| Devi & Devi 2016 [98] | FFC + OD + J48 | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Kumar et al., 2017 [103] | SVM-Naive Bayes-J48 | 10–fold cross validation | |
| Latchoumi & Parthiban 2017 [89] | WPSO-SSVM | 5–fold cross validation | |
| Osman 2017 [90] | Two-Step-SVM | 10–fold cross validaiton |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Payne, A.; Liu, X. Machine Learning with Applications in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Designs 2018, 2, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs2020013
Yue W, Wang Z, Chen H, Payne A, Liu X. Machine Learning with Applications in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Designs. 2018; 2(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs2020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Wenbin, Zidong Wang, Hongwei Chen, Annette Payne, and Xiaohui Liu. 2018. "Machine Learning with Applications in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis" Designs 2, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs2020013
APA StyleYue, W., Wang, Z., Chen, H., Payne, A., & Liu, X. (2018). Machine Learning with Applications in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Designs, 2(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs2020013





