Scheimpflug-Derived Corneal Lower and Higher Order Aberrations Post Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments for Keratoconus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Population
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Imaging
2.4. Statistical Analysis
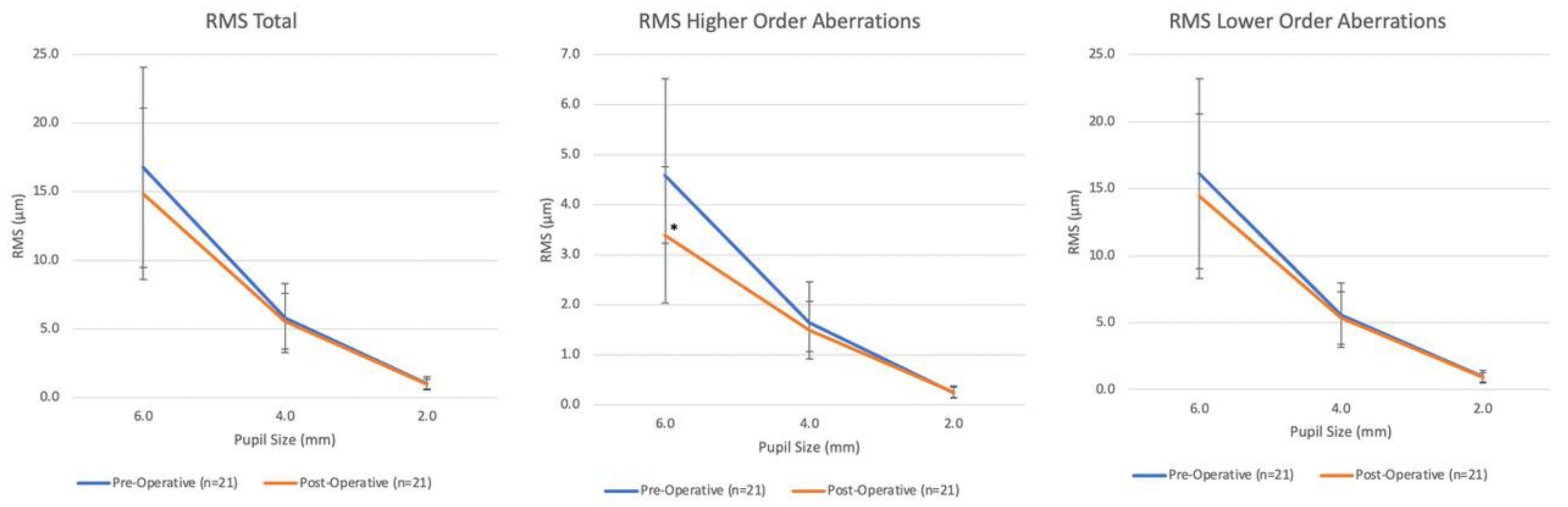
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vega-Estrada, A.; Alio, J.L. The use of intracorneal ring segments in keratoconus. Eye Vis. (Lond.) 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, T.E. Intrastromal corneal ring technology: Results and indications. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 1998, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alio, J.L.; Piñero, D.P.; Daxer, A. Clinical outcomes after complete ring implantation in corneal ectasia using the femtosecond technology: A pilot study. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Vega Cueto, L.; Lisa, C.; Poo-López, A.; Madrid-Costa, D.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Alfonso, J.F. Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segment Implantation in 409 Paracentral Keratoconic Eyes. Cornea 2016, 35, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, J.; Cochener, B.; Savary, G.; Malet, F. Correcting keratoconus with intracorneal rings. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2000, 26, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Estrada, A.; Alio, J.L.; Brenner, L.F.; Javaloy, J.; Plaza Puche, A.B.; Barraquer, R.I.; Teus, M.A.; Murta, J.; Henriques, J.; Uceda-Montanes, A. Outcome analysis of intracorneal ring segments for the treatment of keratoconus based on visual, refractive, and aberrometric impairment. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 575–584.e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, G.R.; Rocha, K.M.; Santhiago, M.R.; Smadja, D.; Krueger, R.R. Applications of wavefront technology. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2012, 38, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S. Keratoconus. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1998, 42, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshika, T.; Tanabe, T.; Tomidokoro, A.; Amano, S. Progression of keratoconus assessed by fourier analysis of videokeratography data. Ophthalmology 2002, 109, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, S.; Velazco, J.; Delgado Pelayo, R.M.; Ruiz-Quintero, N. Correlation of higher order aberrations in the anterior corneal surface and degree of keratoconus measured with a Scheimpflug camera. Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2016, 91, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquetti, L.; Ferrara, G.; Almeida, F.; Cunha, L.; Araujo, L.P.; Machado, A.; Marcelo Lyra, J.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Ferrara, P. Intrastromal corneal ring segments implantation in patients with keratoconus: 10-year follow-up. J. Refract. Surg. 2014, 30, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S. INTACS for keratoconus and ectasia after LASIK. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2013, 53, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellopoulos, A.J.; Pe, L.H.; Perry, H.D.; Donnenfeld, E.D. Modified intracorneal ring segment implantations (INTACS) for the management of moderate to advanced keratoconus: Efficacy and complications. Cornea 2006, 25, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alió, J.L.; Shabayek, M.H.; Artola, A. Intracorneal ring segments for keratoconus correction: Long-term follow-up. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, R.; Kurian, M.; Anand, D.; Mhaske, P.; Narayana, K.M.; Shetty, B.K. Intacs in advanced keratoconus. Cornea 2008, 27, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, J.F.; Lisa, C.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Fernández-Vega Cueto, L.; Montés-Micó, R. Intrastromal corneal ring segment implantation in paracentral keratoconus with coincident topographic and coma axis. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2012, 38, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-García, P.; Alió, J.L.; Vega-Estrada, A.; Barraquer, R.I. Internal, corneal, and refractive astigmatism as prognostic factors for intrastromal corneal ringsegment implantation in mild to moderate keratoconus. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2014, 40, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoist d’Azy, C.; Pereira, B.; Chiambaretta, F.; Dutheil, F. Efficacy of Different Procedures of Intra-Corneal Ring Segment Implantation in Keratoconus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabayek, M.H.; Alió, J.L. Intrastromal corneal ring segment implantation by femtosecond laser for keratoconus correction. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Estrada, A.; Alió, J.L.; Brenner, L.F.; Burguera, N. Outcomes of intrastromal corneal ring segments for treatment of keratoconus: Five-year follow-up analysis. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstein, S.A.; Chung, D.; Rosato, L.; Gelles, J.D.; Hersh, P.S. Corneal higher-order aberrations after crosslinking and intrastromal corneal ring segments for keratoconus. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shajari, M.; Mackert, M.J.; Langer, J.; Kreutzer, T.; Wolf, A.; Kohnen, T.; Priglinger, S.; Mayer, W.J. Safety and efficacy of a small-aperture capsular bag-fixated intraocular lens in eyes with severe corneal irregularities. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pre Op (n = 21) | Post Op (n = 21) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manifest Refraction Spherical Equivalent (SE) (D) | −3.56 ± 3.95 | −2.09 ± 5.35 | 0.329 a |
| Cylinder (D) | 3.51 ± 2.48 | 2.65 ± 2.01 | 0.235 b |
| Corrected Distance Visual Acuity (CDVA) (logMAR) | 053 ± 0.31 | 0.44 ± 0.49 | 0.521 b |
| Mean Keratometry (KM) (D) | 54.11 ± 7.78 | 50.21 ± 5.36 | 0.066 b |
| Maximum Keratometry (Kmax) (D) | 66.40 ± 12.48 | 60.91 ± 8.06 | 0.098 b |
| Corneal asphericity (Q value) | −1.23 ± 0.67 | −1.07 ± 0.68 | 0.448 a |
| Pupil Size * | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | 2 mm Pupil (n = 21) | 4 mm Pupil (n = 21) | 6 mm Pupil (n = 21) |
| Defocus (µm) | −0.029 (−0.064, 0.005) p = 0.095 | −0.483 (−1.166, 0.199) p = 0.165 | −1.794 (−4.548, 0.961) p = 0.202 |
| Astigmatism 0° (µm) | −0.007 (−0.165, 0.152) p = 0.933 | −0.352(−0.993, 0.289) p = 0.281 | −1.347 (−2.430, −2.630) p = 0.015 |
| Astigmatism 45° (µm) | −0.109 (−0.286, 0.069) p = 0.230 | −0.506 (−0.952, −0.600) p = 0.026 | −0.663 (−1.192, −0.135) p = 0.014 |
| Coma 0° (µm) | 0.034 (0.007, 0.062) p = 0.014 | .036 (−0.078, 0.149) p = 0.539 | −0.494 (−0.808, −0.180) p = 0.002 |
| Coma 90° (µm) | 0.005 (−0.031, 0.041) p = 0.802 | −0.230 (−0.417, −0.044) p = 0.0015 | −1.384 (−1.822, −0.945) p < 0.001 |
| Trefoil 0° (µm) | −0.003 (−0.025, 0.019) p = 0.810 | −0.013 (−0.118, 0.091) p = 0.803 | 0.034 (−0.097, 0.165) p = 0.611 |
| Trefoil 30° (µm) | −0.007 (−0.028, 0.015) p = 0.539 | 0.011 (−0.155, 0.178) p = 0.893 | −0.034 (−0.399, 0.330) p = 0.853 |
| Astigmatism 4th order 0° (µm) | 0.007 (−0.004, 0.017) p = 0.221 | 0.042 (−0.019, 0.103) p = 0.174 | 0.098 (−0.118, 0.313) p = 0.374 |
| Astigmatism 4th order 45° (µm) | 0.001 (−0.009, 0.010) p = 0.913 | −0.021 (−0.121, 0.078) p = 0.676 | −0.232 (−0.492, 0.028) p = 0.080 |
| Spherical Aberration (µm) | −0.011 (−0.001, 0.240) p = 0.064 | 0.108 (−0.051, 0.266) p = 0.182 | 0.094 (−0.549, 0.737) p = 0.775 |
| Pentafoil 18° (µm) | 0.002 (0.001, 0.002) p < 0.001 | 0.037 (0.017, 0.057) p < 0.001 | 0.156 (0.073, 0.239) p < 0.001 |
| Coma 5th order 0° (µm) | 0.001 (0.000, 0.002) p = 0.025 | 0.041 (0.018, 0.065) p = 0.001 | 0.184 (0.100, 0.268) p < 0.001 |
| Spherical Aberration 6th order (µm) | <0.001 (0.000, 0.001) p = 0.379 | 0.010 (−0.004, 0.024) p = 0.180 | 0.123 (0.048, 0.199) p = 0.001 |
| RMS LOA (µm) | −0.041 (−0.205, 0.124) p = 0.626 | −0.210 (−0.982, 0.562) p = 0.593 | −1.679 (−4.013, 0.655) p = 0.159 |
| RMS HOA (µm) | 0.011 (−0.037, 0.059) p = 0.645 | −0.153 (−0.387, 0.081) p = 0.199 | −1.189 (−1.775, −0.603) p < 0.001 |
| RMS Total (µm) | −0.039 (−0.208, 0.130) p = 0.650 | −0.246 (−1.048, 0.556) p = 0.547 | −1.925 (−4.309, 0.459) p = 0.113 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
M. van den Berg, R.; B. van den Berg, A.; Dodhia, M.; Shahid, M.; Jammal, A.A.; de Freitas, D.; Rocha, K.M. Scheimpflug-Derived Corneal Lower and Higher Order Aberrations Post Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments for Keratoconus. Vision 2022, 6, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040076
M. van den Berg R, B. van den Berg A, Dodhia M, Shahid M, Jammal AA, de Freitas D, Rocha KM. Scheimpflug-Derived Corneal Lower and Higher Order Aberrations Post Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments for Keratoconus. Vision. 2022; 6(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleM. van den Berg, Roberta, Arthur B. van den Berg, Maya Dodhia, Michel Shahid, Alessandro A. Jammal, Denise de Freitas, and Karolinne M. Rocha. 2022. "Scheimpflug-Derived Corneal Lower and Higher Order Aberrations Post Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments for Keratoconus" Vision 6, no. 4: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040076
APA StyleM. van den Berg, R., B. van den Berg, A., Dodhia, M., Shahid, M., Jammal, A. A., de Freitas, D., & Rocha, K. M. (2022). Scheimpflug-Derived Corneal Lower and Higher Order Aberrations Post Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments for Keratoconus. Vision, 6(4), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision6040076





