Changes in Surface Tension of Aqueous Humor in Anterior Segment Ocular Pathologies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographics
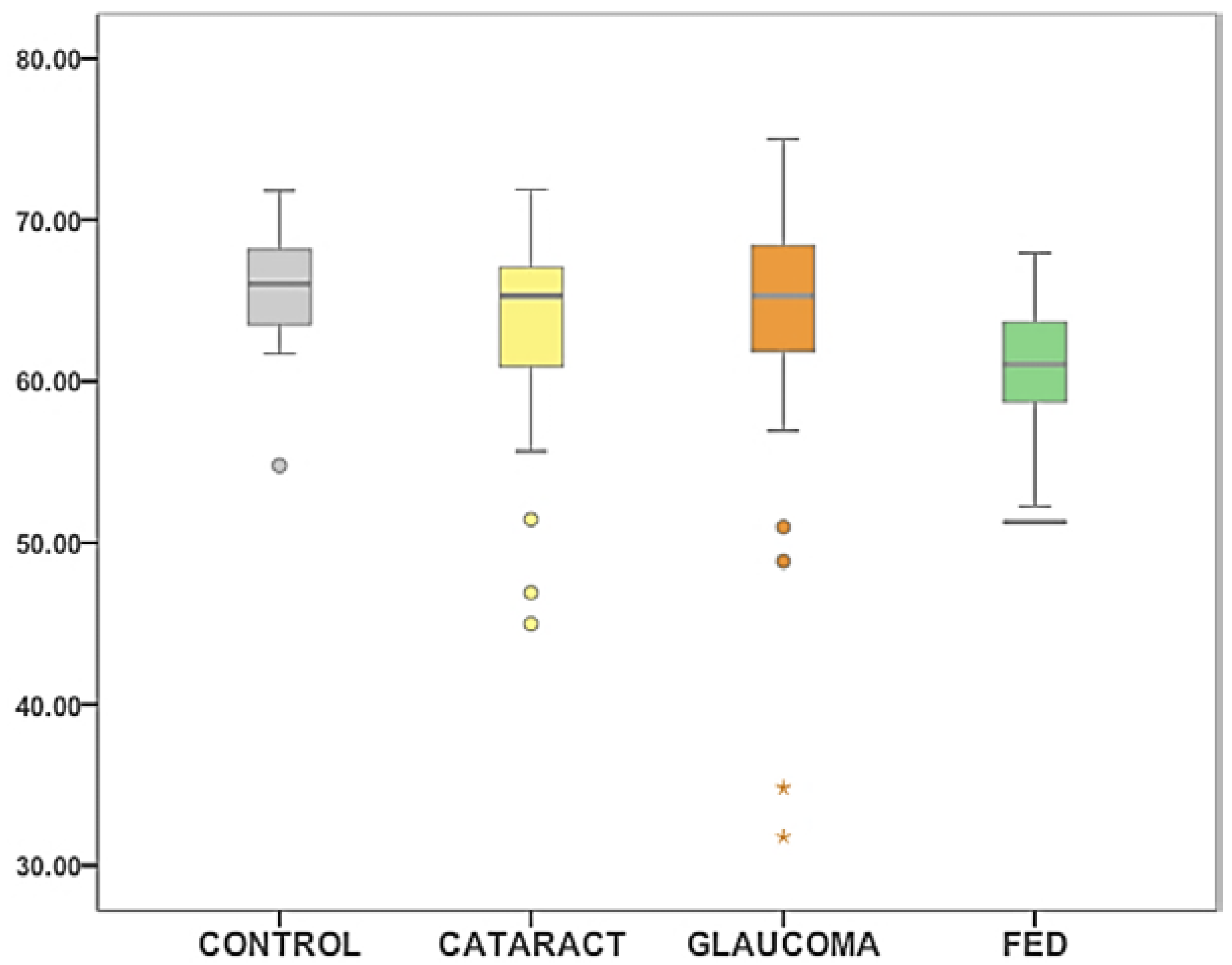
2.2. Surface Tension between Groups
2.3. Age/Gender Distribution
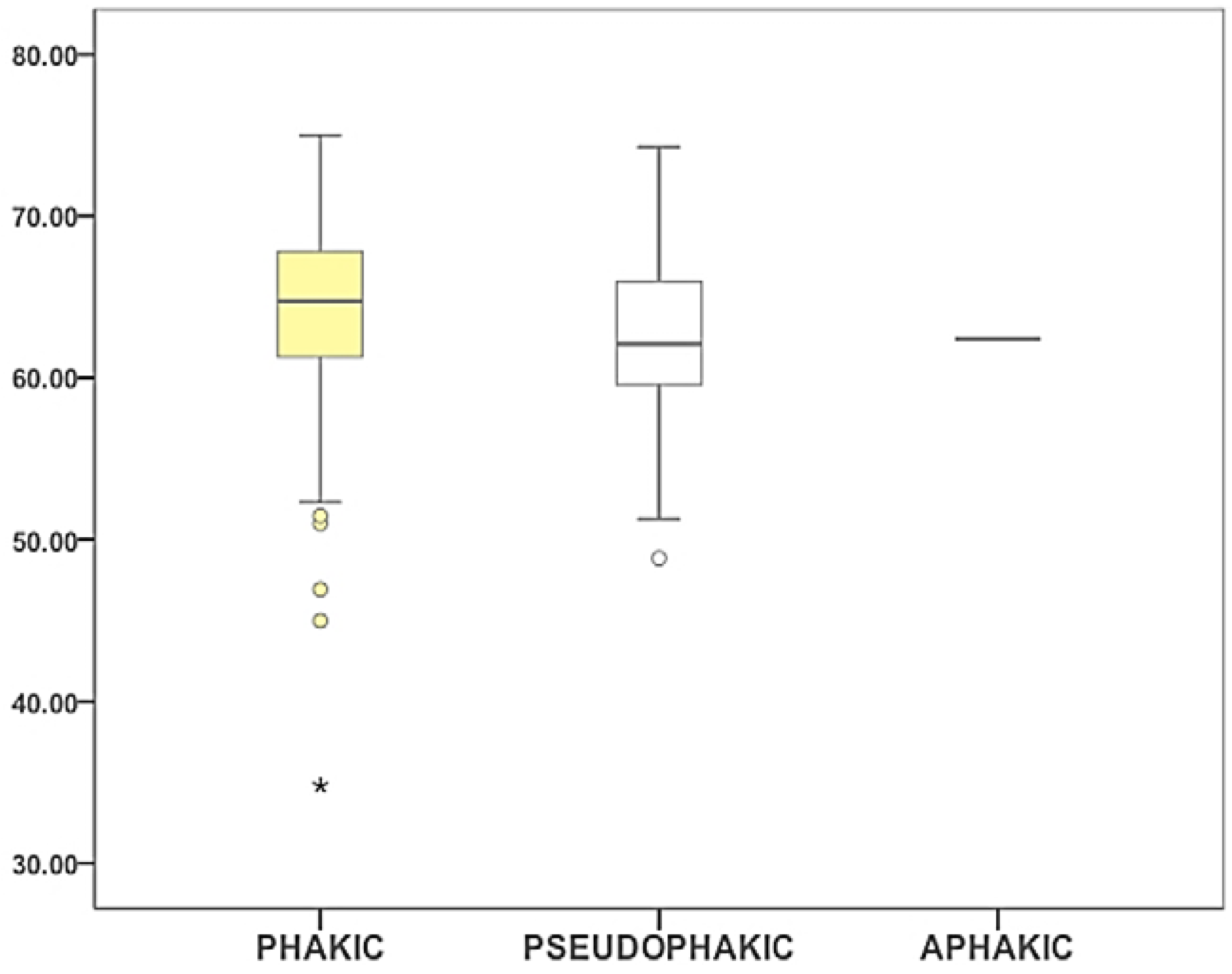
2.4. Lens Condition and Cataract Maturity
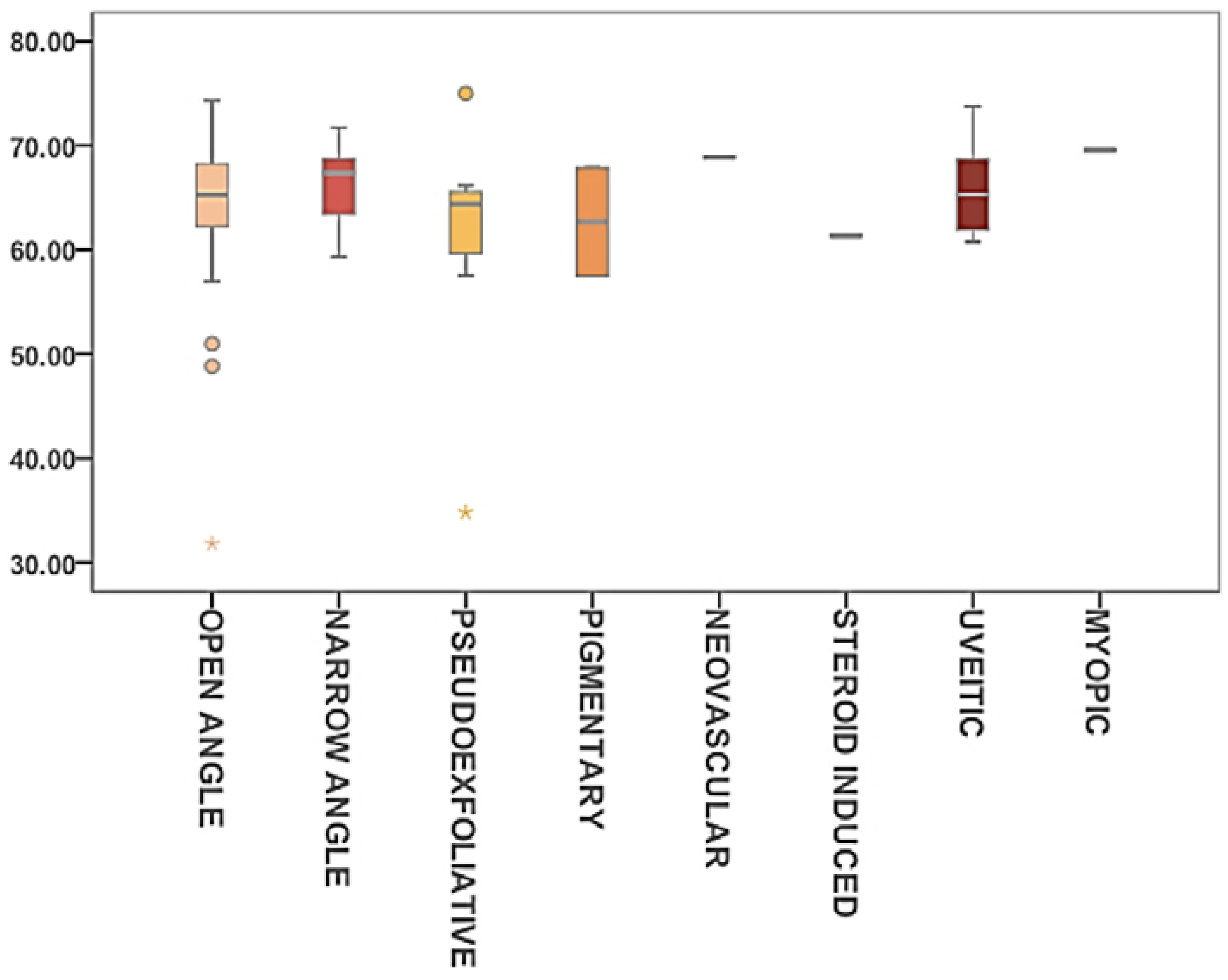
2.5. Glaucoma
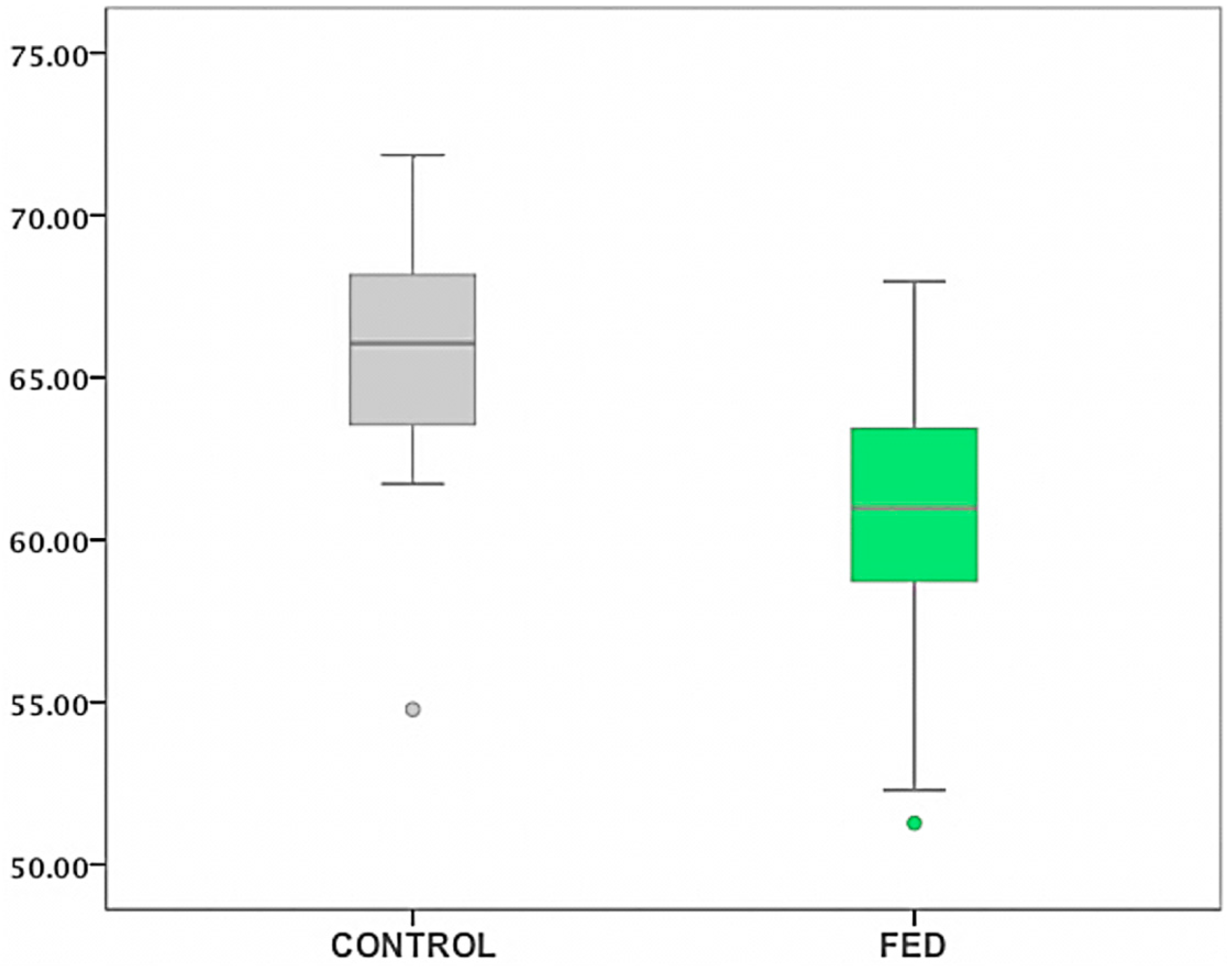
2.6. FED
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Design
4.2. Ethical Statement
4.3. Sampling
4.4. Venue
4.5. Sample Manipulation and Storage
4.6. Surface Tension Analyses
4.7. Data Processing
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, H.E. Modern College Physics; Van Nostrand: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Malijevský, A.; Jackson, G. A perspective on the interfacial properties of nanoscopic liquid drops. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, V.N. Dynamic Surface Tensiometry in Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Available online: http://site.ebrary.com/id/10190301 (accessed on 27 July 2015).
- Ikegami, M.; Weaver, T.E.; Grant, S.N.; Whitsett, J.A. Pulmonary surfactant surface tension influences alveolar capillary shape and oxygenation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 41, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czirok, A.; Little, C.D. Pattern formation during vasculogenesis. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2012, 96, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, V.N.; Vozianov, A.F.; Sinyachenko, O.V.; Trukhin, D.V.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Pison, U. Studies on the application of dynamic surface tensiometry of serum and cerebrospinal liquid for diagnostics and monitoring of treatment in patients who have rheumatic, neurological or oncological diseases. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 86, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.; Santana, M.M.; Aveleira, C.A.; Simões, C.; Maciel, E.; Melo, T.; Santinha, D.; Oliveira, M.M.; Peixoto, F.; Domingues, P.; et al. Alterations in phospholipidomic profile in the brain of mouse model of depression induced by chronic unpredictable stress. Neuroscience 2014, 273, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawai, M.; Kirkness, J.P.; Yamamura, S.; Imaizumi, K.; Yoshimine, H.; Oi, K.; Ayuse, T. Increased phosphatidylcholine concentration in saliva reduces surface tension and improves airway patency in obstructive sleep apnoea. J. Oral Rehabil. 2013, 40, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göbel, K.; Rüfer, F.; Erb, C. Physiology of aqueous humor formation, diurnal fluctuation of intraocular pressure and its significance for glaucoma. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2011, 228, 104–108. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, M. Aqueous Humor Dynamics: A Review. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2010, 4, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudgar, S.M.; Deng, P.; Maddala, R.; Epstein, D.L.; Rao, P.V. Regulation of connective tissue growth factor expression in the aqueous humor outflow pathway. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uda, T.; Suzuki, T.; Mitani, A.; Tasaka, Y.; Kawasaki, S.; Mito, T.; Ohashi, Y. Ocular penetration and efficacy of levofloxacin using different drug-delivery techniques for the prevention of endophthalmitis in rabbit eyes with posterior capsule rupture. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 30, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvenkel, B.; Kopitar, A.N.; Ihan, A. Inflammatory molecules in aqueous humour and on ocular surface and glaucoma surgery outcome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezel, G. A decade of proteomics studies of glaucomatous neurodegeneration. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrerizo, J.; Urcola, J.A.; Saracibar, G.; Vecino, E. Changes in Lipidomic Profile of Aqueous Humor in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. ARVO Annual Meeting Abstract 2015, 56, 1177. [Google Scholar]
- Miric, D.J.; Kisic, B.M.; Zoric, L.D.; Miric, B.M.; Mirkovic, M.; Mitic, R. Influence of cataract maturity on aqueous humor lipid peroxidation markers and antioxidant enzymes. Eye 2014, 28, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastner, C.; Löbler, M.; Reske, T.; Sternberg, K.; Guthoff, R.; Schmitz, K.-P. Determination of human anterior lens capsule permeability for fluorescent model substances and after-cataract preventive drugs. Biomed. Eng. Biomed. Tech. 2012, 57, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, C.; Löbler, M.; Sternberg, K.; Reske, T.; Stachs, O.; Guthoff, R.; Schmitz, K.P. Permeability of the anterior lens capsule for large molecules and small drugs. Curr. Eye Res. 2013, 38, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranka, J.A.; Kelley, M.J.; Acott, T.S.; Keller, K.E. Extracellular matrix in the trabecular meshwork: Intraocular pressure regulation and dysregulation in glaucoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 133, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunger, B.M.; Fuchshofer, R.; Tamm, E.R. The aqueous humor outflow pathways in glaucoma: A unifying concept of disease mechanisms and causative treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 95, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knepper, P.A.; Goossens, W.; Hvizd, M.; Palmberg, P.F. Glycosaminoglycans of the human trabecular meshwork in primary open-angle glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Kuleshova, O.N.; Zaidman, A.M.; Korel’, A.V. Glycosaminoglycans of the trabecular meshwork of the eye in primary juvenile glaucoma. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 143, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parc, C.E.; Johnson, D.H.; Brilakis, H.S. Giant vacuoles are found preferentially near collector channels. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, C.; Kelliher, C.; Spitze, A.R.; Speck, C.L.; Eberhart, C.G.; Jun, A.S. Unfolded protein response in fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: A unifying pathogenic pathway? Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, K.; Kaminska, A.; Blasiak, J.; Szaflik, J.; Szaflik, J. Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Keratoconus and Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19294–19308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkunas, U.V.; Bitar, M.S.; Funaki, T.; Azizi, B. Evidence of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentmáry, N.; Szende, B.; Süveges, I. Epithelial cell, keratocyte, and endothelial cell apoptosis in Fuchs’ dystrophy and in pseudophakic bullous keratopathy. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 15, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.J.; Ashraf, M.F.; Shen, D.F.; Green, W.R.; Stark, W.J.; Chan, C.C.; O’Brien, T.P. The role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of Fuchs endothelial dystrophy of the cornea. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2001, 119, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaby, J.M.; Baumann, W.J.; Brockman, H.L. Lipid structure and the behavior of cholesteryl esters in monolayer and bulk phases. J. Lipid Res. 1979, 20, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richardson, M.R.; Segu, Z.M.; Price, M.O.; Lai, X.; Witzmann, F.A.; Mechref, Y.; Yoder, M.C.; Price, F.W. Alterations in the aqueous humor proteome in patients with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 2376–2783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahidullah, M.; Wilson, W.S.; Yap, M.; To, C. Effects of ion transport and channel-blocking drugs on aqueous humor formation in isolated bovine eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, J.W.; Hollingsworth, M.; Rao, R.; Chen, M.; Reitsamer, H.A. Ciliary blood flow and aqueous humor production. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wordinger, R.J.; Clark, A.F. Effects of glucocorticoids on the trabecular meshwork: Towards a better understanding of glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1999, 18, 629–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steely, H.T.; Browder, S.L.; Julian, M.B.; Miggans, S.T.; Wilson, K.L.; Clark, A.F. The effects of dexamethasone on fibronectin expression in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar]
- Akingbehin, A.O. Comparative study of the intraocular pressure effects of fluorometholone 0.1% versus dexamethasone 0.1%. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1983, 67, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louttit, M.D.; Kopplin, L.J.; Igo, R.P.; Fondran, J.R.; Tagliaferri, A.; Bardenstein, D.; Aldave, A.J.; Croasdale, C.R.; Price, M.O.; Rosenwasser, G.O.; et al. A multicenter study to map genes for Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: Baseline characteristics and heritability. Cornea 2012, 31, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Vesco, C.; Fleming, J.; Choh, V. Density of ocular components of the bovine eye. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2009, 86, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.; Blake, R.C.; Ayyala, R.S. Surface tension of aqueous humor. J. Glaucoma 2010, 19, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.D.; Neeson, M.J.; Dagastine, R.R.; Chan, D.Y.C.; Tabor, R.F. Measurement of surface and interfacial tension using pendant drop tensiometry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Hung, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-Y. Accurate surface tension measurement of glass melts by the pendant drop method. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, S.M.I.; Neumann, A.W. Laplacian drop shapes and effect of random perturbations on accuracy of surface tension measurement for different drop constellations. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 222, 622–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Demographic Data | Control | Cataract | Glaucoma | FED | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Average (Range) | 52.09 | 74.4 | 70.81 | 70.42 | 69.69 |
| (28–80) | (53–102) | (18–92) | (53–87) | (18–102) | |
| Gender Male/Female | 8/14 | 13/43 | 43/38 | 21/21 | 85/116 |
| Lens Condition Phakic/Pseudophakic | 22/0 | 56/0 | 57/24 | 11/32 | 146/56 |
| Number of Cases | 22 | 56 | 81 | 43 | 202 |
| Descriptives of ST Data | Mean | Median | Variance | Standard Deviation | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 65.74 mN/m | 66.05 mN/m | 14.26 | 3.78 | 17.07 |
| Cataract | 63.59 mN/m | 65.29 mN/m | 30.28 | 5.50 | 26.92 |
| Glaucoma | 64.35 mN/m | 65.29 mN/m | 48.88 | 6.99 | 43.21 |
| FED | 60.89 mN/m | 61.16 mN/m | 13.89 | 3.72 | 16.69 |
| All | 63.55 mN/m | 64.21 mN/m | 34.44 | 5.87 | 43.21 |
| ST in Different Types of Glaucoma | N | Mean (mN/m) | SD | Mean Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Angle | 55 | 64.35 | 6.8 | 41.0 |
| Narrow Angle | 7 | 66.1 | 4.4 | 46.4 |
| Pseudoexfoliative | 8 | 61.13 | 11.7 | 33.5 |
| Pigmentary | 2 | 62.7 | 7.4 | 31.5 |
| Neovascular | 1 | 68.89 | - | 65.0 |
| Steroid induced | 1 | 61.31 | - | 18.0 |
| Uveitic | 6 | 66.38 | 4.9 | 43.4 |
| Myopic | 1 | 66.56 | - | 69.0 |
| Total | 81 | 81 | 7.0 | - |
| ST in FED vs. Controls | N | Mean Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Controls | 22 | 47.45 |
| FED | 43 | 25.60 |
| Phakic FED | 11 | 19.45 |
| Pseudophakic FED | 32 | 22.88 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabrerizo, J.; Urcola, J.H.; Vecino, E. Changes in Surface Tension of Aqueous Humor in Anterior Segment Ocular Pathologies. Vision 2017, 1, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision1010006
Cabrerizo J, Urcola JH, Vecino E. Changes in Surface Tension of Aqueous Humor in Anterior Segment Ocular Pathologies. Vision. 2017; 1(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabrerizo, Javier, J. Haritz Urcola, and Elena Vecino. 2017. "Changes in Surface Tension of Aqueous Humor in Anterior Segment Ocular Pathologies" Vision 1, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision1010006
APA StyleCabrerizo, J., Urcola, J. H., & Vecino, E. (2017). Changes in Surface Tension of Aqueous Humor in Anterior Segment Ocular Pathologies. Vision, 1(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision1010006







