One-Leg Stance Postural Sway Is Not Benefited by Bicycle Motocross Practice in Elite Riders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis and Reduction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
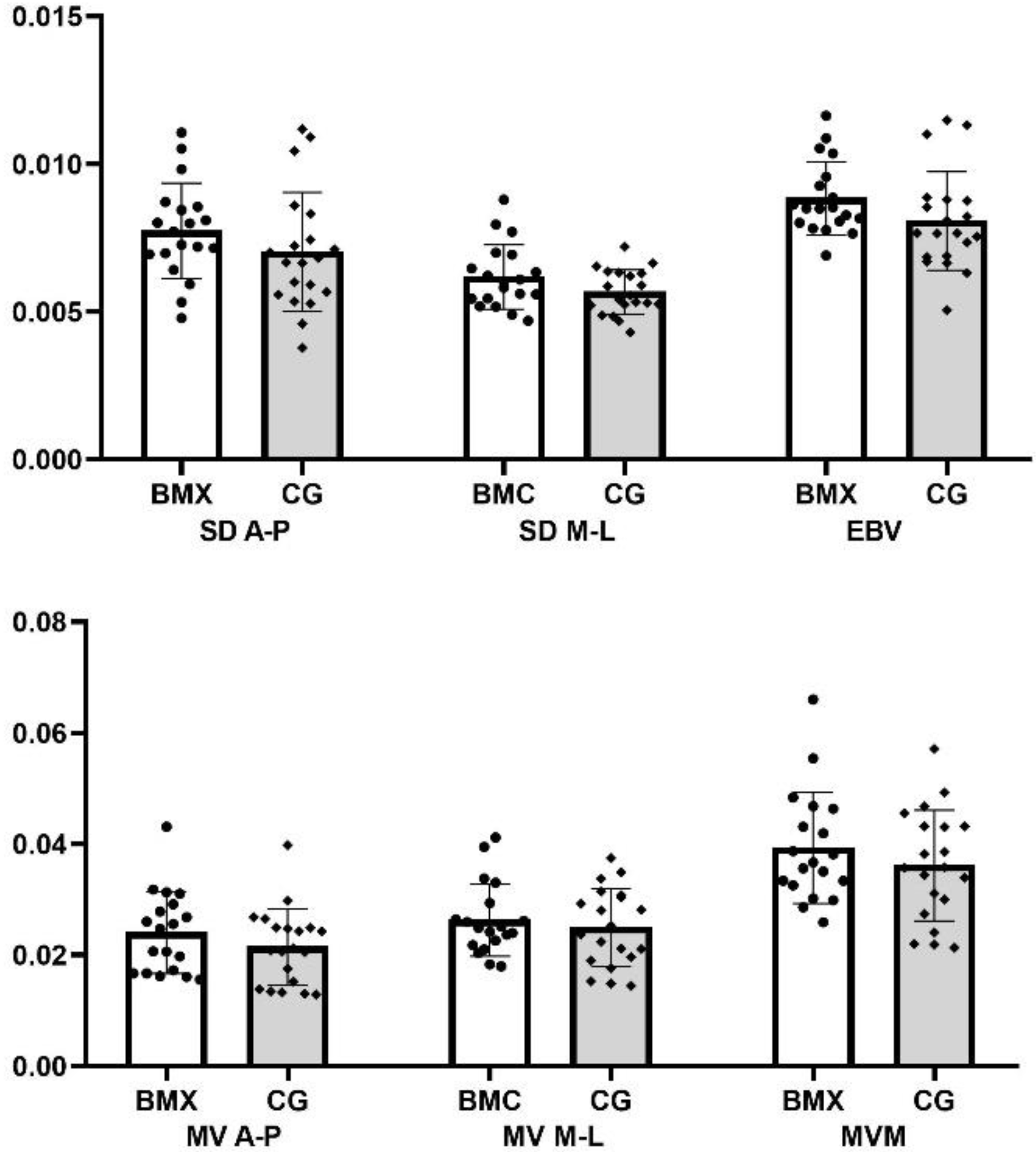
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karadenizli, Z.I.; Erkut, O.; Ramazanoglu, N.; Uzun, S.; Camliguney, A.F.; Bozkurt, S.; Tiryaki, C.; Kucuk, V.; Sirmen, B. Comparision of dynamic and static balance in adolescents handball and soccer players. Turk. J. Sport Exerc. 2014, 16, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Demura, S.; Uchiyama, M. Centre of pressure sway characteristics during static one-legged stance of athletes from different sports. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, R. Soccer players have a better standing balance in nondominant one-legged stance. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2010, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoth, C.J.; van Lummel, R.C.; Beek, P.J. Athletic skill level is reflected in body sway: A test case for accelometry in com-bination with stochastic dynamics. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymakers, J.; Samson, M.; Verhaar, H. The assessment of body sway and the choice of the stability parameter(s). Gait Posture 2005, 21, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quatman-Yates, C.; Bonnette, S.; Gupta, R.; Hugentobler, J.A.; Wade, S.L.; Glauser, T.A.; Ittenbach, R.F.; Paterno, M.V.; Riley, M.A. Spatial and temporal analysis center of pressure displacement during adolescence: Clinical implications of developmental changes. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbado, D.; Sabido, R.; Vera-Garcia, F.J.; Fuertes, N.G.; Moreno, F.J. Effect of increasing difficulty in standing balance tasks with visual feedback on postural sway and EMG: Complexity and performance. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2012, 31, 1224–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, J. 1/f noise and effort on implicit measures of bias. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2008, 94, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilby, M.C.; Slobounov, S.M.; Newell, K.M. Postural Instability Detection: Aging and the Complexity of Spatial-Temporal Distributional Patterns for Virtually Contacting the Stability Boundary in Human Stance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.T.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Stergiou, N. A Nonlinear Dynamic Approach for Evaluating Postural Control. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerdink, M.; De Haart, M.; Daffertshofer, A.; Donker, S.F.; Geurts, A.C.H.; Beek, P.J. Dynamical structure of center-of-pressure trajectories in patients recovering from stroke. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 174, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Yang, W.-H. Using detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA) to analyze whether vibratory insoles enhance balance stability for elderly fallers. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 55, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, C.; Barbado, D.; Hérnandez-Davó, H.; Hernández-Davó, J.L.; Moreno, F.J. Balance dynamics are related to age and levels of expertise. Application in young and adult tennis players. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, C.; Barbado, D.; Urbán, T.; García-Herrero, J.A.; Moreno, F.J. Functional Variability in Team-Handball Players during Balance Is Revealed by Non-Linear Measures and Is Related to Age and Expertise Level. Entropy 2020, 22, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrysomallis, C. Balance Ability and Athletic Performance. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadczak, Ł.; Grygorowicz, M.; Dzudziński, W.; Śliwowski, R. Comparison of Static and Dynamic Balance at Different Levels of Sport Competition in Professional and Junior Elite Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omorczyk, J.; Bujas, P.; Puszczałowska-Lizis, E.; Biskup, L. Balance in handstand and postural stability in standing position in athletes practicing gymnastics. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2018, 20, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T.; Noé, F.; Rivière, T.; Marion, V.; Montoya, R.; Dupui, P. Postural performance and strategy in the unipedal stance of soccer players at different levels of competition. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Paillard, T. Relationship Between Sport Expertise and Postural Skills. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T. Plasticity of the postural function to sport and/or motor experience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 72, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinen, P.; Muehlbauer, T.; Panzer, S. Single-Leg Balance Performance in Sub-Elite Young Soccer Players and Swimmers as a Function of Age and Sports Experience. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2019, 7, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Demura, S.; Demura, T. Examining Differences between Center of Pressure Sway in One-Legged and Two-Legged Stances for Soccer Players and Typical Adults. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2010, 110, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bini, R.R.; Hume, P.A. Assessment of Bilateral Asymmetry in Cycling Using a Commercial Instrumented Crank System and Instrumented Pedals. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebisz, P.; Hebisz, R.; Zatoń, M. Body balance in a free-standing position in road and off-road cyclists. Balt. J. Health Phys. Act. 2014, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, A.; Gauchard, G.C.; Deviterne, D.; Perrin, P.P. Differentiated influence of off-road and on-road cycling practice on balance control and the related-neurosensory organization. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, H.; Rajabi, R.; Minoonejad, H.; Aghaiari, A. Asymmetries in Flexibility, Balance and Power Associated with Preferred and Non-Preferred Leg. World J. Sport Sci. 2009, 2, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Maloney, S.J. The Relationship Between Asymmetry and Athletic Performance: A Critical Review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Chimera, N.J.; Warren, M. Association of Y Balance Test Reach Asymmetry and Injury in Division I Athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.C.; Brech, G.C.; Bourquin, A.M.; Greve, J.M.D. The influence of lower-limb dominance on postural balance. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2011, 129, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, C.; Barbado, D.; Moreno, F.J. Center of pressure preprocessing methods to analyze complexity/performance relation in quiet standing. Rev. Andal. Med. Deporte 2013, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhea, C.K.; Silver, T.A.; Hong, S.L.; Ryu, J.H.; Studenka, B.E.; Hughes, C.M.L.; Haddad, J.M. Noise and Complexity in Human Postural Control: Interpreting the Different Estimations of Entropy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dieën, J.H.; Koppes, L.L.; Twisk, J.W. Postural sway parameters in seated balancing; their reliability and relationship with balancing performance. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Characterization of Surface EMG Signal Based on Fuzzy Entropy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, D.E.; Richman, J.S.; Griffin, M.P.; Moorman, J.R. Sample entropy analysis of neonatal heart rate variability. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 283, R789–R797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Quantification of Scaling Exponents and Crossover Phenomena in Nonstationary Heartbeat Time Series. CHAOS 1995, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.; Newell, K.M. The Structure of Variability in Human Walking and Running is Speed-Dependent. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2008, 36, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K.; Lipsitz, L.A. What is physiologic complexity and how does it change with aging and disease? Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.; Schrader, J.; Applegate, T.; Koceja, D. Unilateral postural control of the functionally dominant and nondominant extremities of healthy subjects. J. Athl. Train. 1998, 33, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- van Melick, N.; Meddeler, B.M.; Hoogeboom, T.J.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W.G.; van Cingel, R.E.H. How to determine leg dominance: The agreement between self-reported and observed performance in healthy adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbado, D.; Sánchez, C.C.; Moreside, J.; Vera-García, F.J.; Moreno, F.J. Can the structure of motor variability predict learning rate? J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2017, 43, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigaki, L.; Rabello, L.M.; Camargo, M.Z.; Santos, V.B.D.C.; Gil, A.W.D.O.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Junior, R.A.D.S.; Macedo, C.D.S.G. Análise comparativa do equilíbrio unipodal de atletas de ginástica rítmica. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2013, 19, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębski, P.; Mielańczyk, J.; Gnat, R. Postural stability in one leg standing on dominant and non-dominant leg in professional soccer players. J. Kinesiol. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 26, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.C.; Wang, Z. Asymmetrical stabilization and mobilization exploited during static single leg stance and goal directed kicking. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2017, 54, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pau, M.; Arippa, F.; Leban, B.; Corona, F.; Ibba, G.; Todde, F.; Scorcu, M. Relationship between static and dynamic balance abilities in Italian professional and youth league soccer players. Phys. Ther. Sport 2015, 16, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bini, R.R.; Hume, P.A. Relationship between pedal force asymmetry and performance in cycling time trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 55, 892–898. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo-Martínez, A.; López-Valenciano, A.; Albaladejo-García, C.; Vallés-González, J.; Elvira, J. Changes in the Trunk and Lower Extremity Kinematics Due to Fatigue Can Predispose to Chronic Injuries in Cycling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouliquen, C.; Nicolas, G.; Bideau, B.; Garo, G.; Megret, A.; Delamarche, P.; Bideau, N. Spatiotemporal analysis of 3D kinematic asymmetry in professional cycling during an incremental test to exhaustion. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| SD | BVE | MV | MVM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-P | M-L | A-P | M-L | ||||
| FuzzyEn | A-P | −0.31 | 0.16 | −0.15 | 0.73 * | 0.61 * | 0.72 * |
| M-L | −0.20 | −0.09 | −0.18 | 0.40 * | 0.77 * | 0.65 * | |
| DFA | A-P | −0.05 | −0.32 * | −0.15 | −0.72 * | −0.50 * | −0.66 * |
| M-L | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.02 | −0.25 | −0.14 | |
| BMX Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kick-Leg Dominance Criteria | BMX-Leg Dominance Criteria | Kick-Leg Dominance Criteria | |||||
| Dom. | No-Dom. | Dom. | No-Dom. | Dom. | No-Dom. | ||
| SD (cm) | A-P | 0.77 ± 0.16 | 0.79 ± 0.25 | 0.80 ± 0.18 | 0.76 ± 0.23 | 0.70 ± 0.20 | 0.67 ± 0.14 |
| M-L | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 0.63 ± 0.13 | 0.60 ± 0.09 | 0.65 ± 0.14 # | 0.57 ± 0.08 * | 0.52 ± 0.08 | |
| MV (cm/s) | A-P | 2.41 ± 0.74 | 2.28 ± 0.65 | 2.29 ± 0.62 | 2.39 ± 0.76 | 2.14 ± 0.69 | 1.82 ± 0.53 |
| M-L | 2.63 ± 0.65 | 2.89 ± 0.91 | 2.62 ± 0.55 | 2.90 ± 0.97 | 2.49 ± 0.70 | 2.29 ± 0.64 | |
| MVM (cm/s) | 3.93 ± 1.01 | 4.03 ± 1.12 | 3.83 ± 0.83 | 4.12 ± 1.24 | 3.61 ± 1.00 | 3.22 ± 0.86 | |
| BVE (cm) | 0.88 ± 0.12 | 0.9 ± 0.23 | 0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.89 ± 0.22 | 0.81 ± 0.17 | 0.75 ± 0.12 | |
| FuzzyEn | A-P | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.51 ± 0.15 | 0.50 ± 0.17 | 0.54 ± 0.14 | 0.54 ± 0.19 | 0.48 ± 0.14 |
| M-L | 0.70 ± 0.12 | 0.74 ± 0.14 | 0.72 ± 0.10 | 0.73 ± 0.16 | 0.72 ± 0.16 | 0.71 ± 0.13 | |
| DFA | A-P | 0.95 ± 0.21 | 1.03 ± 0.21 | 0.99 ± 0.20 | 0.99 ± 0.22 | 1.02 ± 0.17 | 1.12 ± 0.17 |
| M-L | 0.90 ± 0.15 | 0.91 ± 0.12 | 0.90 ± 0.09 | 0.91 ± 0.17 | 0.90 ± 0.14 | 0.86 ± 0.16 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albaladejo-García, C.; Moreno, F.J.; García-Aguilar, F.; Caballero, C. One-Leg Stance Postural Sway Is Not Benefited by Bicycle Motocross Practice in Elite Riders. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010025
Albaladejo-García C, Moreno FJ, García-Aguilar F, Caballero C. One-Leg Stance Postural Sway Is Not Benefited by Bicycle Motocross Practice in Elite Riders. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2023; 8(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbaladejo-García, Carlos, Francisco J. Moreno, Fernando García-Aguilar, and Carla Caballero. 2023. "One-Leg Stance Postural Sway Is Not Benefited by Bicycle Motocross Practice in Elite Riders" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 8, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010025
APA StyleAlbaladejo-García, C., Moreno, F. J., García-Aguilar, F., & Caballero, C. (2023). One-Leg Stance Postural Sway Is Not Benefited by Bicycle Motocross Practice in Elite Riders. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 8(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk8010025






