Seasonal Body Composition Changes in Elite Rugby Players: DXA and Anthropometry-Based Comparison of Backs and Forwards
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
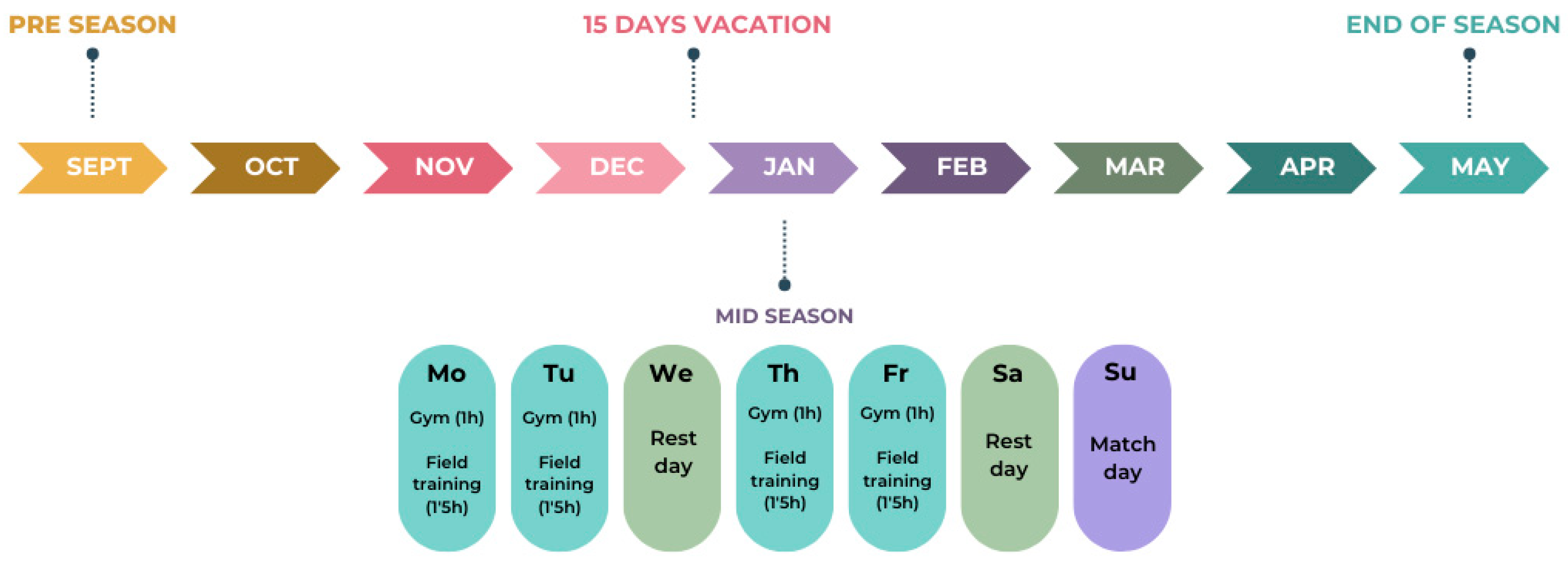
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Anthropometric Assessment
2.2.2. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Rugby. Laws of the game Rugby Union. Dublin: World Rugby; 2024. Available online: https://passport.world.rugby/laws-of-the-game (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Domínguez, R.; López-Tapia, P.; López-Tapia, P.; Tobal, F.M.; Jodra, P.; Montoya, J.J.; Guerra-Hernández, E.J.; Ramos-Álvarez, J.J. A Survey on Dietary Supplement Consumption in Amateur and Professional Rugby Players. Foods 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, R.; Lancaster, S.; Davies, P.; Street, G.; Starling, L.; de Coning, C.; Brown, J. Trends in player body mass at men’s and women’s Rugby World Cups: A plateau in body mass and differences in emerging rugby nations. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, T.; Chew, S.; Godsland, I.; Oliver, N.S.; E Hill, N. A game for all shapes and sizes? Changes in anthropometric and performance measures of elite professional rugby union players 1999–2018. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2022, 8, e001235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeaud, A.; Marc, A.; Schipman, J.; Tafflet, M.; Hager, J.P.; Toussaint, J.F. How they won rugby World Cup through height, mass and collective experience. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holway, F.E.; Garavaglia, R. Kinanthropometry of group I rugby players in Buenos Aires, Argentina. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthumus, L.; Macgregor, C.; Winwood, P.; Darry, K.; Driller, M.; Gill, N. Physical and Fitness Characteristics of Elite Professional Rugby Union Players. Sports 2020, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scantlebury, S.; Costello, N.; Owen, C.; Chantler, S.; Ramirez, C.; Zabaloy, S.; Collins, N.; Allen, H.; Phillips, G.; Alexander, M.; et al. Longitudinal changes in anthropometric, physiological, and physical qualities of international women’s rugby league players. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreyro-Bravo, F.; Rejón-Chan, G.; Mimenza-Concepción, A. Valoración de la composición corporal. In Fisiología del Ejercicio, 4th ed.; López Chicharro, J., Fernández Vaquero, A., Eds.; Editorial Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2023; pp. 431–450. [Google Scholar]
- Till, K.; Jones, B.; O’Hara, J.; Barlow, M.J.; Hind, K.; Lees, M. Advances in rugby body composition: Comparison between Elite English Academy rugby league and professional Super League. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, S99. [Google Scholar]
- Zemski, A.J.; Slater, G.J.; Broad, E.M. Body composition characteristics of elite Australian rugby union athletes according to playing position and ethnicity. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsborough, J.C.; Greenway, K.; Opar, D.; Livingstone, S.; Cordy, J.; Coutts, A.J. The accuracy and precision of DXA for assessing body composition in team sport athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.; Lindsay, E. The Heath-Carter Anthropometric Somatotype—Instruction Manual. En: Somatotype Instruction Manual San Diego, 2002. pp. 2–26. Available online: https://phentermineclinics.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Heath-CarterManual.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. JAMA 2025, 333, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Ros, F.; Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Marfell-Jones, M. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry (ISAK), Ed.; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Scotland, UK, 2019; ISBN 0620362073. [Google Scholar]
- Nana, A.; Slater, G.J.; Hopkins, W.G.; Burke, L.M. Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Whole-Body Scans to Estimate Body Composition in Tall and/or Broad Subjects. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. 2012, 22, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.E.; Rilstone, S.; Stacey, M.J.; Amiras, D.; Chew, S.; Flatman, D.; Oliver, N.S. Changes in northern hemisphere male international rugby union players’ body mass and height between 1955 and 2015. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2018, 4, e000459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, J.; Bentley, N. The Evolution of Rugby: A Statistical Analysis. Available online: https://www.statsperform.com/resource/revolutionising-rugby-a-statistical-analysis-on-how-the-game-has-evolved/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Georgeson, E.C.; Weeks, B.K.; McLellan, C.; Beck, B.R. Seasonal change in bone, muscle and fat in professional rugby league players and its relationship to injury: A cohort study. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e001400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbett, T.J. Physiological and anthropometric correlates of tackling ability in rugby league players. J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, D.G.; Pyne, D.B.; Anson, J.M.; Dziedzic, C.E.; Slater, G.J. Distribution of fat, non-osseous lean and bone mineral mass in international rugby union and rugby sevens players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, C.; Tobin, D.P.; Tierney, P.; Delahunt, E.; Maher, B. The worst case scenario: Locomotor and collision demands of the longest periods of gameplay in professional rugby union. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Álvarez, J.J.; Montoya, J.J.; Solís-Mencia, C.; Miguel-Tobal, F.; López-Tapia, P.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Domínguez, R.; Martínez-Sanz, J.M. Anthropometric profile assessed by bioimpedance and anthropometry measures of male and female rugby players competing in the spanish national league. Appl Sci. 2021, 11, 11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.R.; Carter, J.E.L.; Patterson, P.; Petti, K.; Orfanos, S.M.; Noffal, G.J. Physique and motor performance characteristics of us national rugby players. J. Sports Sci. 1994, 12, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morehen, J.C.; Routledge, H.E.; Twist, C.; Morton, J.P.; Close, G.L. Position specific differences in the anthropometric characteristics of elite European super league rugby players. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2015, 15, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, F.Y.; Colosio, A.; De Roia, G.F.; Da Lozzo, G.; Pogliaghi, S. Anthropometrics of Italian senior male rugby union players: From elite to second division. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeaud, A.; Saulière, G.; Marquet, L.A.; Del Vecchio, S.; Bar-Hen, A.; Toussaint, J. Collective effectiveness in the XV de France: Selections and time matter. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2017, 17, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulière, G.; Dedecker, J.; Moussa, I.; Schipman, J.; Toussaint, J.-F.; Sedeaud, A. Quantifying Collective Performance in Rugby Union. Front. Sport Act. Living 2019, 1, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 32) | Backs (n = 16) | Forwards (n = 16) | p-Value | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 25.97 (4.51) | 25.19 (5.01) | 26.75 (3.96) | 0.335 a | −0.346 |
| Weight (kg) | 93.00 (15.39) | 80.14 (6.09) | 105.84 (10.00) | <0.001 a | −3.105 |
| Height (cm) | 181.77 (6.27) | 178.20 (4.98) | 185.33 (5.42) | <0.001 a | −1.370 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.03 (3.62) | 25.21 (0.95) | 30.85 (3.02) | <0.001 b | −2.516 |
| Experience (years) | 5.38 (3.93) | 5.13 (4.30) | 5.63 (3.65) | 0.725 a | −0.125 |
| Body Composition Variables | Moment of the Season | Backs (n = 16) | Forwards (n = 16) | Differences Between Backs and Forwards | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | p-Value (Intra-Group) | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | Mean (SD) | p-Value (Intra-Group) | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | p-Value (Inter-Group) | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | ||
| DXA | |||||||||
| TM (kg) | PS | 80.44 (6.12) | 0.012 a | −0.710 | 106.07 (9.13) | 0.512 a | −0.168 | <0.001 c | −3.296 |
| ES | 81.72 (5.12) | 106.81 (9.92) | <0.001 d | −3.126 | |||||
| LM (kg) | PS | 65.40 (5.32) | 0.005 a | −0.820 | 78.02 (5.90) | 0.344 a | −0.244 | <0.001 c | −2.245 |
| ES | 66.51 (4.92) | 78.38 (6.07) | <0.001 c | −2.150 | |||||
| FFM (kg) | PS | 68.97 (5.58) | 0.004 a | −0.838 | 82.37 (6.29) | 0.306 a | −0.265 | <0.001 c | −2.255 |
| ES | 70.11 (5.16) | 82.77 (6.46) | <0.001 c | −2.165 | |||||
| BF (kg) | PS | 11.47 (1.90) | 0.638 a | −0.120 | 23.70 (7.15) | 0.730 a | −0.088 | <0.001 c | −2.338 |
| ES | 11.60 (1.75) | 24.04 (7.66) | <0.001 c | −2.237 | |||||
| BF (%) | PS | 14.92 (2.28) | 0.872 a | 0.041 | 23.24 (5.67) | 0.852 a | −0.047 | <0.001 c | −1.879 |
| ES | 14.87 (2.10) | 23.17 (5.71) | <0.001 c | −1.930 | |||||
| BM (kg) | PS | 3.57 (0.33) | 0.066 a | −0.495 | 4.36 (0.47) | 0.031 a | −0.594 | <0.001 c | −1.936 |
| ES | 3.60 (0.31) | 4.39 (0.46) | <0.001 c | −2.011 | |||||
| BMD (kg/cm2) | PS | 1.44 (0.09) | 0.273 a | −0.284 | 1.62 (0.11) | 0.535 a | 0.159 | <0.001 c | −1.750 |
| ES | 1.45 (0.08) | 1.61 (0.10) | <0.001 c | −1.759 | |||||
| Anthropometry | |||||||||
| Sum6SF (mm) | PS | 51.64 (8.11) | 0.476 a | −0.183 | 99.16 (32.44) | 0.470 a | −0.185 | <0.001 d | −2.010 |
| ES | 52.68 (9.23) | 103.06 (33.46) | <0.001 d | −2.050 | |||||
| Sum8SF (mm) | PS | 68.16 (11.19) | 0.135 a | −0.395 | 132.56 (44.21) | 0.321 a | −0.257 | <0.001 d | −1.997 |
| ES | 71.42 (12.58) | 141.61 (48.93) | <0.001 d | −1.965 | |||||
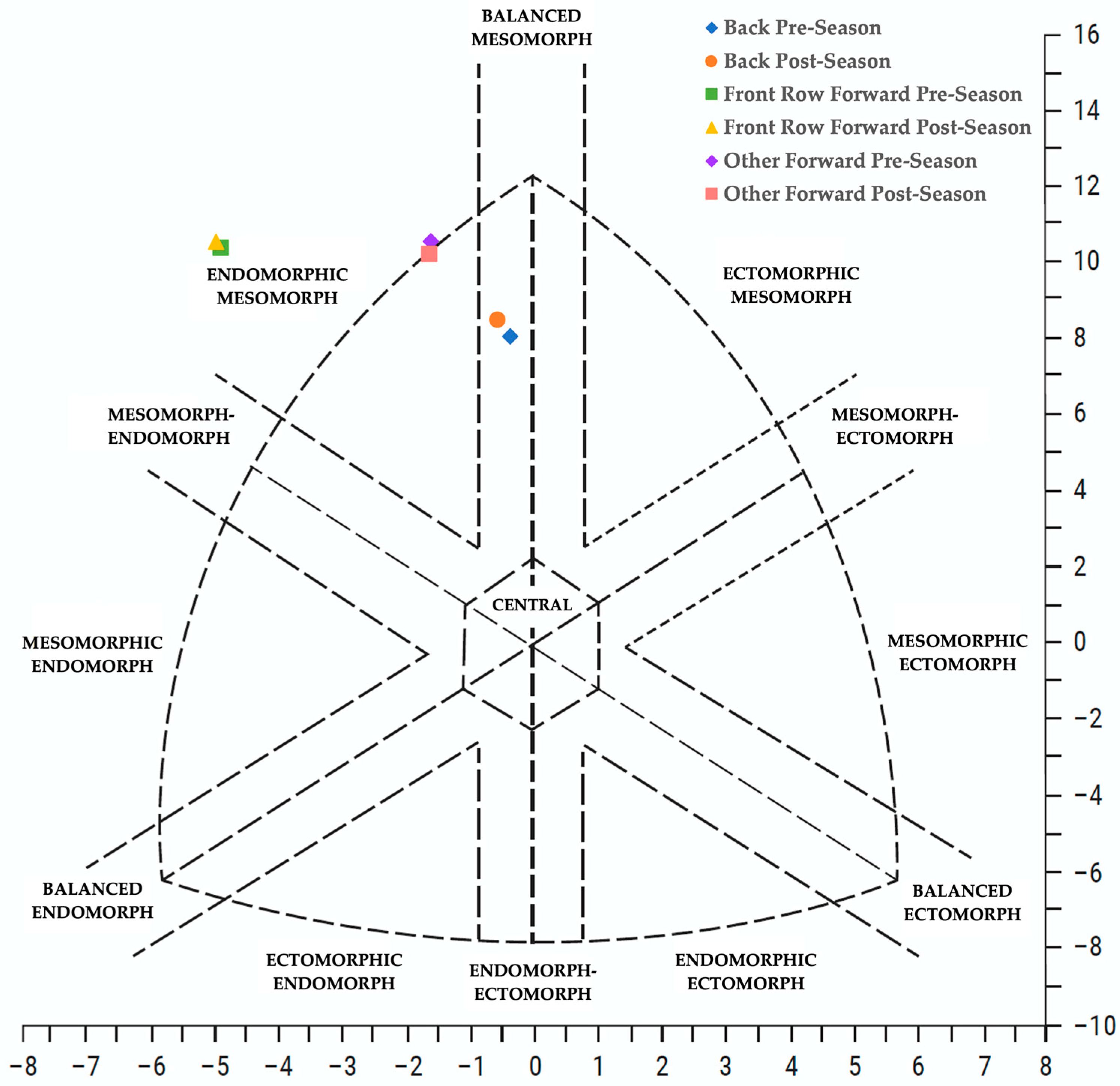
| Endomorphy | PS | 2.06 (0.40) | 0.302 a | −0.267 | 3.89 (1.45) | 0.623 a | −0.125 | <0.001 d | −1.731 |
| ES | 2.12 (0.41) | 3.99 (1.42) | <0.001 d | −1.776 | |||||
| Mesomorphy | PS | 5.88 (0.51) | 0.008 a | −0.767 | 7.48 (0.67) | 0.932 b | 0.033 | <0.001 c | −2.686 |
| ES | 6.07 (0.53) | 7.51 (0.78) | <0.001 c | −2.152 | |||||
| Ectomorphy | PS | 1.70 (0.38) | 0.022 a | 0.638 | 0.65 (0.54) | 0.507 b | −0.255 | <0.001 c | 2.252 |
| ES | 1.56 (0.38) | 0.69 (0.57) | <0.001 c | 1.808 | |||||
| Change FR | Change OF | p-Value | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DXA | ||||
| TM (kg) | 3.061 (4.548) | −1.071 (3.482) | 0.344 a | 0.490 |
| LM (kg) | 1.42 (1.42) | −0.46 (0.92) | 0.009 a | 1.507 |
| FFM (kg) | 1.464 (1.402) | −0.437 (0.951) | 0.009 a | 1.514 |
| BF (kg) | 1.597 (4.362) | −0.634 (3.404) | 0.869 a | 0.084 |
| BM (kg) | 0.040 (0.054) | 0.026 (0.060) | 0.651 a | 0.231 |
| BMD (kg/cm2) | −0.003 (0.039) | −0.011 (0.054) | 0.564 a | 0.295 |
| Anthropometry | ||||
| Sum6SF (mm) | 13.157 (21.116) | −3.400 (18.341) | 0.407 a | 0.188 |
| Sum8SF (mm) | 28.543 (36.566) | −6.111 (27.178) | 0.713 a | 0.428 |
| Endomorphy | 0.357 (0.793) | −0.111 (0.685) | 0.975 a | 0.016 |
| Mesomorphy | 0.214 (0.406) | −0.122 (0.239) | 0.222 c | 0.648 |
| Ectomorphy | −0.029 (0.049) | 0.100 (0.212) | 0.828 b | −0.078 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Couce, B.; Recarey-Rodríguez, A.E.; Baos, S.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Martínez-Ferrán, M. Seasonal Body Composition Changes in Elite Rugby Players: DXA and Anthropometry-Based Comparison of Backs and Forwards. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030357
Couce B, Recarey-Rodríguez AE, Baos S, Pareja-Galeano H, Martínez-Ferrán M. Seasonal Body Composition Changes in Elite Rugby Players: DXA and Anthropometry-Based Comparison of Backs and Forwards. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(3):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030357
Chicago/Turabian StyleCouce, Blanca, Anel E. Recarey-Rodríguez, Selene Baos, Helios Pareja-Galeano, and María Martínez-Ferrán. 2025. "Seasonal Body Composition Changes in Elite Rugby Players: DXA and Anthropometry-Based Comparison of Backs and Forwards" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 3: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030357
APA StyleCouce, B., Recarey-Rodríguez, A. E., Baos, S., Pareja-Galeano, H., & Martínez-Ferrán, M. (2025). Seasonal Body Composition Changes in Elite Rugby Players: DXA and Anthropometry-Based Comparison of Backs and Forwards. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(3), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030357








