Acute Blood Pressure Changes Following Resistance Exercise in Adults with Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
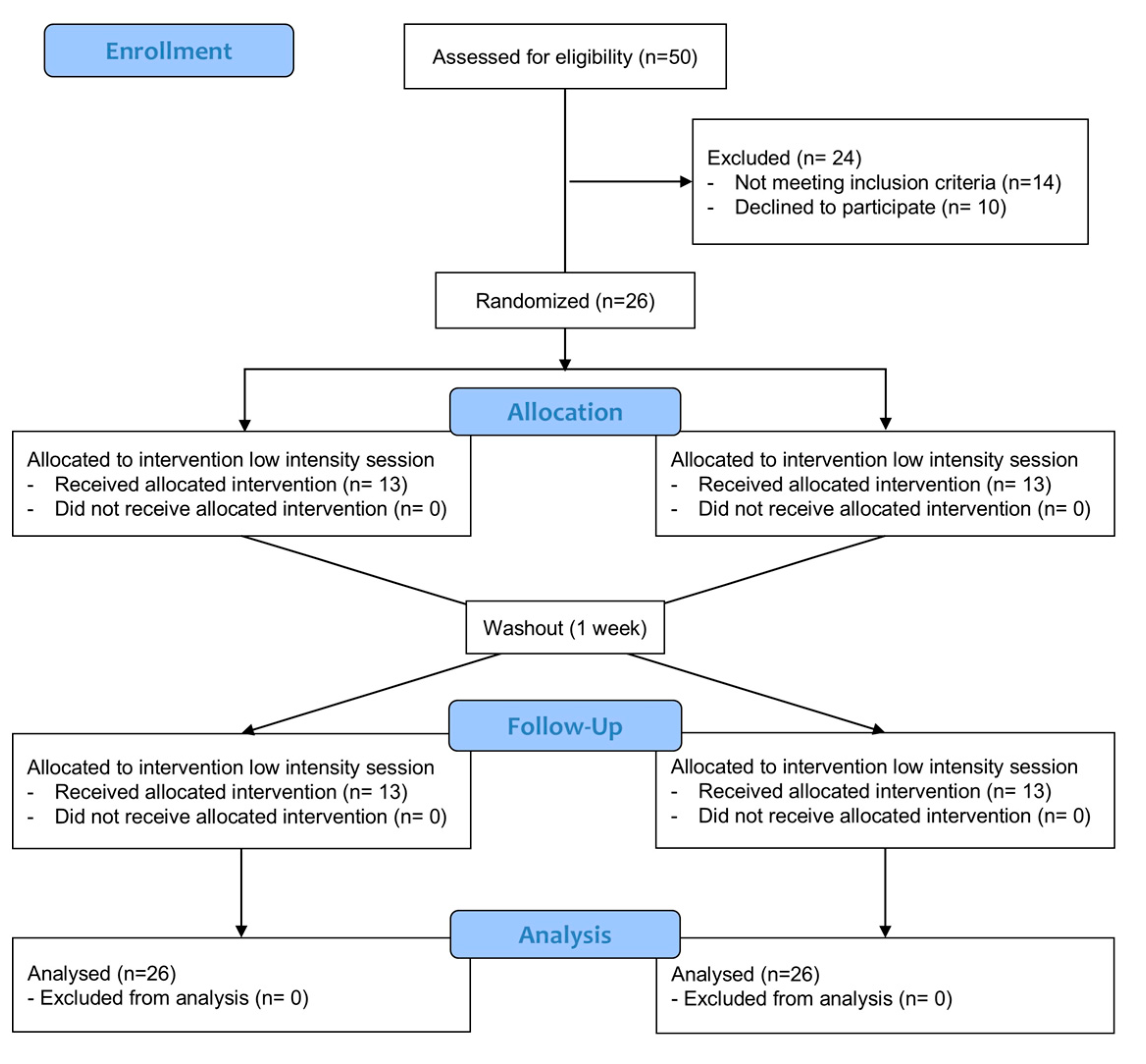
2.2. Participants
| Participants n = 26 | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 47.3 ± 9.6 |
| Male/female | 10/16 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.1 ± 0.1 |
| Medication use (%) | |
| Angiotensin receptor blocker | 65.4% |
| ACE inhibitors | 15.4% |
| Calcium channel blockers | 7.7% |
| Diuretics | 7.7% |
| Beta-blocker | 3.8% |
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Randomization and Blinding
2.5. Resistance Training
2.6. Main Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopes, S.; Mesquita-Bastos, J.; Garcia, C.; Bertoquini, S.; Ribau, V.; Teixeira, M.; Ribeiro, I.P.; Melo, J.B.; Oliveira, J.; Figueiredo, D.; et al. Effect of exercise training on ambulatory blood pressure among patients with resistant hypertension: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, J.S.; Pinto, R.S.; Machado, C.L.; Wilhelm, E.N. Chronic effect of resistance training on blood pressure in older adults with prehypertension and hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 177, 112193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Martinez, P.A.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Martinez-Aranda, L.M.; Martinez-Rodriguez, A.; Rubio-Arias, J.A. Chronic effects and optimal dosage of strength training on SBP and DBP: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.R.; Veras, A.S.C.; Tebar, W.R.; Rufino, J.C.; Batista, V.R.G.; Teixeira, G.R. Strength training for arterial hypertension treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.D.C.; da Silva, C.R.; Valduga, R.; Saraiva, B.; de Sousa Neto, I.V.; Vieira, A.; Funghetto, S.S.; Silva, A.O.; Oliveira, S.D.C.; Pereira, G.B.; et al. Blood pressure response to resistance training in hypertensive and normotensive older women. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, T.; Nakamura, F.; Zempo-Miyaki, A. Nitric oxide and decreases in resistance exercise blood pressure with aerobic exercise training in older individuals. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, V.; Curry, B.H.; Adams, R.G.; Obisesan, T.; Pemminati, S.; Gorantla, V.R.; Kadur, K. Cardiovascular responses to an isometric handgrip exercise in females with prehypertension. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 8, 243. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, R.; Cadore, E.L.; Perico, B.; Kothe, G.B. Acute effects of body-weight resistance exercises on blood pressure and glycemia in middle-aged adults with hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2021, 43, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, P.A.M.; Rica, R.L.; Evangelista, A.L.; Serra, A.J.; Figueira, A., Jr.; Pontes, F.L., Jr.; Kilgore, L.; Baker, J.S.; Bocalini, D.S. Effects of exercise intensity on postexercise hypotension after resistance training session in overweight hypertensive patients. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Ohta, T.; Zhang, J.; Hashimoto, S.; Tanaka, H. Influence of age and gender on exercise training-induced blood pressure reduction in systemic hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 84, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forjaz, C.L.; Ortega, K.C.; Santaella, D.F.; Mion, D., Jr.; Negrão, C.E. Factors affecting post-exercise hypotension in normotensive and hypertensive humans. Blood Press. Monit. 2000, 5, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsano, V.S.M.; de Moraes, W.M.A.M.; de Sousa, N.M.F.; de Moura, F.C.; Tibana, R.A.; Silva, A.O.; Schwerz Funghetto, S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Prestes, J. Comparison of the acute effects of traditional versus high velocity resistance training on metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychophysiological responses in elderly hypertensive women. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia-Chairperson, G.; Brunström, M.; Burnier, M.; Grassi, G.; Januszewicz, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tsioufis, K.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Algharably, E.A.E.; Azizi, M.; et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension Endorsed by the European Renal Association (ERA) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH). J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 1874–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Lopez, C.; Alcazar, J.; Sánchez-Martín, C.; Ara, I.; Csapo, R.; Alegre, L.M. Mechanical characteristics of heavy vs. light load ballistic resistance training in older adults. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Belmonte, A.; Buendía-Romero, Á.; Pallares, J.G.; Martínez-Cava, A. Velocity-based method in free-weight and machine-based training modalities: The degree of freedom matters. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2023, 37, e500–e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Ubric, A.; Díez-Fernández, D.M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.A.; Ortega-Becerra, M.; Pareja-Blanco, F. Analysis of the load-velocity relationship in deadlift exercise. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2020, 19, 452. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Torres, O.; Fernandez-Elias, V.E.; Li, J.; Gomez-Ruano, M.A.; Guadalupe-Grau, A. Validity and reliability of a new low-cost linear position transducer to measure mean propulsive velocity: The ADR device. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2022, 239, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, G.F.; Ades, P.A.; Kligfield, P.; Arena, R.; Balady, G.J.; Bittner, V.A.; Coke, L.A.; Fleg, J.L.; Forman, D.E.; Gerber, T.C.; et al. Exercise Standards for Testing and Training. Circulation. 2013, 128, 873–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Q.; Zhang, L. Oxidative regulation of vascular Cav1.2 channels triggers vascular dysfunction in hypertension-related disorders. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescatello, L.S. (Ed.) ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, C.P.; Bruno, R.M.; McEvoy, J.W.; Touyz, R.M. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension: What is new in pharmacotherapy? Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2024, 11, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, L.; Póvoa, T.I.R.; Jardim, P.C.V.; Lima, A.L.; Barroso, W.K.S.; Seguro, C.S.; Gentil, P.; Jardim, T.V. Acute effects of high-intensity resistance training on central blood pressure parameters of elderly hypertensive women: A crossover clinical trial. J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescatello, L.S.; Buchner, D.M.; Jakicic, J.M.; Powell, K.E.; Kraus, W.E.; Bloodgood, B.; Campbell, W.W.; Dietz, S.; Dipietro, L.; George, S.M.; et al. Physical Activity to Prevent and Treat Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, A.F.; Carneiro, J.A.; Jardim, P.C.; Jardim, T.V.; Steele, J.; Fisher, J.P.; Gentil, P. Acute effects of different resistance training loads on cardiac autonomic modulation in hypertensive postmenopausal women. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, G.O.; Myklestad, D.; Raastad, T. The influence of volume of exercise on early adaptations to strength training. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2003, 17, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, F.S.; Costa, B.D.D.V.; Ferreira, M.E.C.; Paes, S.; de Lima-Junior, D.; Kassiano, W.; Cyrino, E.S.; Gantois, P.; Fortes, L.S. Acute effects of equated volume-load resistance training leading to muscular failure versus non-failure on neuromuscular performance. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2020, 18, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguro, C.S.; Rebelo, A.C.S.; Silva, A.G.; Dos Santos, M.M.A.; Cardoso, J.S.; Apolinário, V.; Jardim, P.C.V.; Gentil, P. Use of low volume, high effort resistance training to manage blood pressure in hypertensive patients inside a public hospital: A proof of concept study. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2021, 31, 9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radaelli, R.; Botton, C.E.; Wilhelm, E.N.; Bottaro, M.; Lacerda, F.; Gaya, A.; Moraes, K.; Peruzzolo, A.; Brown, L.E.; Pinto, R.S. Low-and high-volume strength training induces similar neuromuscular improvements in muscle quality in elderly women. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Masuhara, M.; Ikuta, K. Effects of eccentric and concentric resistance training on arterial stiffness. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2006, 20, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, E. Effect of eccentric resistance exercise velocity on blood pressure in collegiate females. Gazz. Med. Ital.—Arch. Sci. Med. 2023, 182, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöhr, E.J.; Stembridge, M.; Shave, R.; Samuel, T.J.; Stone, K.J.; Esformes, J.I. Systolic and diastolic LV mechanics during and following resistance exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, D.L.; Neiva, H.P.; Fail, L.B.; Gil, M.H.; Marques, M.C. Acute effects of low and high-volume resistance training on hemodynamic, metabolic and neuromuscular parameters in older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 125, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, R.A.L.; Hagenbeck, K.F.; Arsa, G.; Pardono, E. Moderate/high resistance exercise is better to reduce blood glucose and blood pressure in middle-aged diabetic subjects. Rev. Bras. Educ. Fis. Esporte 2020, 34, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushma, T.; Sangeeta, G.; Tiwari, S.K.; Girish, S. Effect of isotonic exercise (walking) on various physiological parameters in hypertension. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 7, 122–131. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza Nery, S.; Gomides, R.S.; da Silva, G.V.; de Moraes Forjaz, C.L.; Mion, D., Jr.; Tinucci, T. Intra-arterial blood pressure response in hypertensive subjects during low-and high-intensity resistance exercise. Clinics 2010, 65, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.J.; Kravitz, L.E.N. A review of the acute cardiovascular responses to resistance exercise of healthy young and older adults. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 1999, 13, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwuemeka, U.M.; Benjamin, C.P.; Uchenwoke, C.I.; Okonkwo, U.P.; Anakor, A.C.; Ede, S.S.; Fabunmi, A.A.; Amaechi, I.A.; Akobundu, U.N. Impact of squatting on selected cardiovascular parameters among college students. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayor, M.; Gajjar, P.; Murthy, V.L.; Miller, P.E.; Velagaleti, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Lewis, G.D.; Mitchell, G.F.; Shah, R.V. Blood Pressure Responses During Exercise: Physiological Correlates and Clinical Implications. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apkarian, M.R. Blood Pressure Characteristics and Responses During Resistance Exercise. Strength Cond. J. 2020, 43, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haennel, R.G.; Snydmiller, G.D.; Teo, K.K.; Greenwood, P.V.; A Quinney, H.; Kappagoda, C.T. Changes in blood pressure and cardiac output during maximal isokinetic exercise. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1992, 73, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Niebauer, J.; Boerjesson, M.; Carre, F.; Caselli, S.; Palatini, P.; Quattrini, F.; Serratosa, L.; Adami, P.E.; Biffi, A.; Pressler, A.; et al. Recommendations for participation in competitive sports of athletes with arterial hypertension: A position statement from the sports cardiology section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| High Intensity | Low Intensity | Intensity | Exercise Type | Interaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | ||||||
| SBP (mmHg) | Baseline | 121 ± 12 | 124 ± 10 | 0.60 | <0.0001 | 0.25 |
| Squat *,α | 134 ± 18 | 138 ± 15 | ||||
| Rows *,†,α | 132 ± 14 | 132 ± 12 | ||||
| Deadlift * | 138 ± 15 | 137 ± 11 | ||||
| Bench Press † | 126 ± 15 | 127 ± 10 | ||||
| DBP (mmHg) | Baseline | 81 ± 8 | 83 ± 9 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | 0.12 |
| Squat α,# | 83 ± 9 | 86 ± 9 | ||||
| Rows | 77 ± 10 | 83 ± 8 | ||||
| Deadlift α,# | 83 ± 8 | 86 ± 7 | ||||
| Bench Press | 78 ± 8 | 79 ± 6 | ||||
| SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise | Delta Change (Δ) | Cohen’s d | Delta Change (Δ) | Cohen’s d | |
| High Intensity | Squat | 13.2 ± 13.9 | 0.86 | 2.5 ± 6.8 | 0.24 |
| Rows | 11.6 ± 10.4 | 0.84 | −3.5 ± 6.5 | −0.46 | |
| Deadlift | 17.7 ± 10.7 | 1.20 | 2.3 ± 6.2 | 0.25 | |
| Bench Press | 30.0 ± 5.6 | 0.30 | −2.3 ± 6.2 | −0.39 | |
| Low Intensity | Squat | 14.8 ± 11.2 | 1.10 | 3.3 ± 7.8 | 0.34 |
| Rows | 8.5 ± 8.5 | 0.70 | −0.3 ± 7.4 | 0.05 | |
| Deadlift | 13.7 ± 11.6 | 1.20 | 3.2 ± 9.7 | 0.38 | |
| Bench Press | 2.9 ± 10 | 0.30 | −4.0 ± 6.9 | −0.50 | |
| Condition | Exercise | Dependent Variables | Independent Variables Medication Use | r2 | B | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Intensity | Deadlift | ΔSBP | Diuretic | 0.17 | 17.63 | 0.04 |
| ΔDBP | ARB | 0.23 | −9.78 | 0.01 | ||
| ΔDBP | ACE inhibitors | 0.17 | 10.91 | 0.04 | ||
| High Intensity | Bench Press | ΔDBP | ARB | 0.19 | −6.75 | 0.02 |
| ΔDBP | ACE inhibitors | 0.16 | 7.48 | 0.05 | ||
| ΔDBP | Diuretic | 0.17 | 9.54 | 0.04 | ||
| ΔDBP | CCB | 0.17 | 9.54 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benavides-Roca, L.A.; Parra, G.; Zamunér, A.R. Acute Blood Pressure Changes Following Resistance Exercise in Adults with Hypertension. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030349
Benavides-Roca LA, Parra G, Zamunér AR. Acute Blood Pressure Changes Following Resistance Exercise in Adults with Hypertension. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(3):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030349
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenavides-Roca, Luis A., Germán Parra, and Antonio R. Zamunér. 2025. "Acute Blood Pressure Changes Following Resistance Exercise in Adults with Hypertension" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 3: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030349
APA StyleBenavides-Roca, L. A., Parra, G., & Zamunér, A. R. (2025). Acute Blood Pressure Changes Following Resistance Exercise in Adults with Hypertension. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(3), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030349







